Bone disease
Osteomylitis :Osteomyelitis is most often caused by staphylococcus aureus & usually affects infants & children.
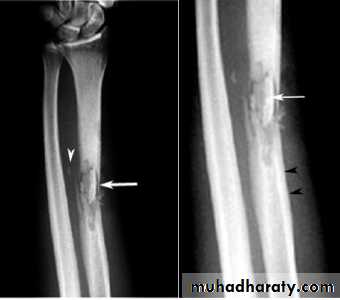
The initial radiographs are normal as bone changes are not visible until 10 -14 days after the onset of the infection.
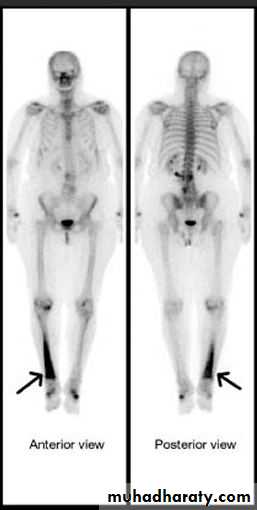
The TC 99m radionuclide bone scan and MRI show changes much earlier.
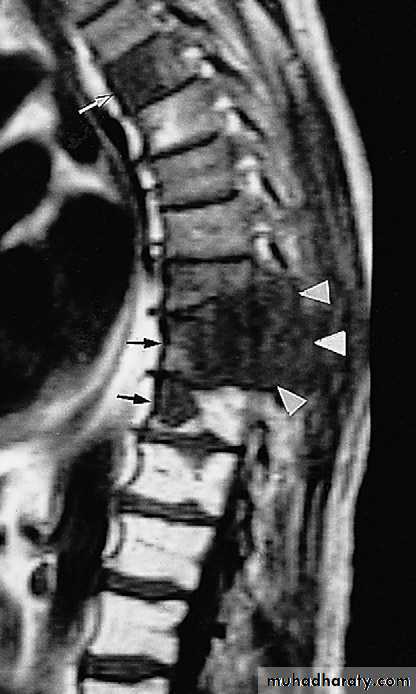
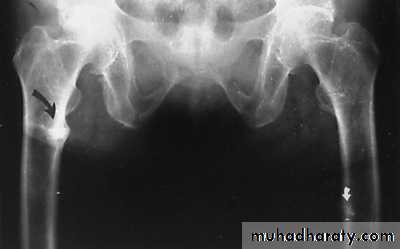
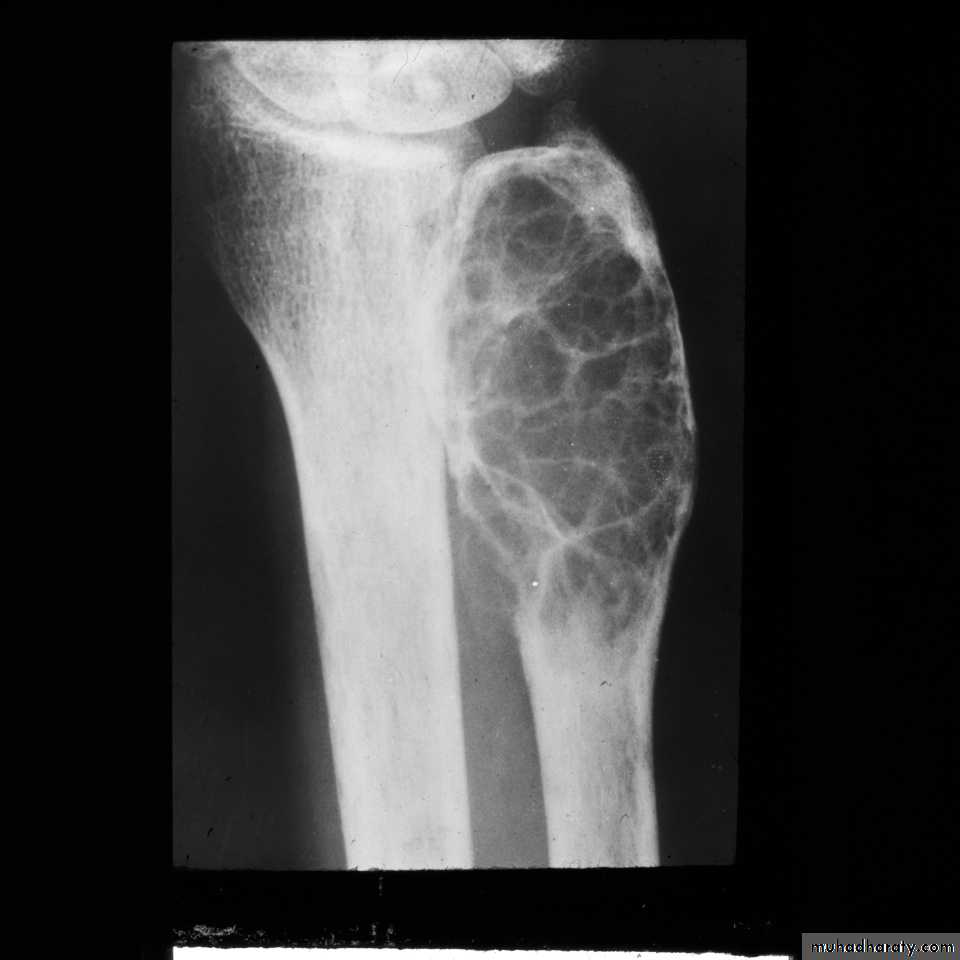
the earliest sings on plain radiographs are soft tissue swelling , and bone destruction in the metaphysis with a periosteal reaction that eventually may become very extensive and surround the bone to form an involucrumpart of the original bone may die and form a separate dense fragment known as a sequestrum
a radionuclide bone scan will show increased activity both on the early ( blood pool ) images reflecting hyperaemia and on the delayed bone phase images.
U/S can demonstrate sub periosteal collections of pus .
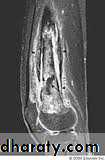
MRI is the imaging modality of choice & shows evidence of bone odema and pus accumulation in the bone & soft tissue .distinction of neoplasm from osteomyelitis :
With malignant bone tumor the radiographs are usually abnormalwhen the patient first presents , whereas with osteomyelitis the initial film are often normal .
The presence of fever & some times of discharging sinuses usually help to diagnose of infective lesion.
CT & MRI more informative.
Bone scanning is positive in both osteomyelitis & malignant tumour and can not be used in differentiation .
bone infarction :
Occurs most often in the intra –articular portions of the bonesCan occur in the shaft of a bone in several disease including caisson disease , sickle cell disease or following radiation therapy. . once healed , they appear as irregular calcification in the medulla of along bone.
Multiple focal lesions
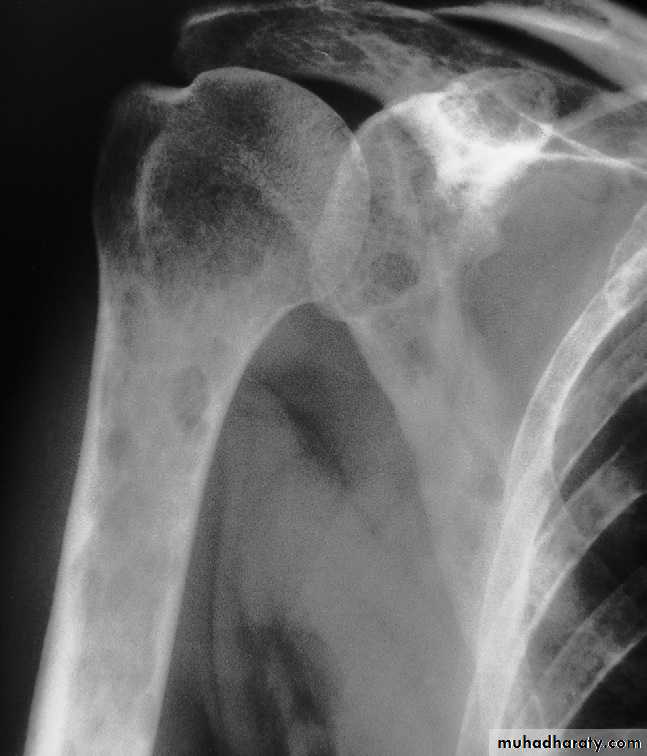
Metastases :Metastases are by far the commonest malignant bone tumor.
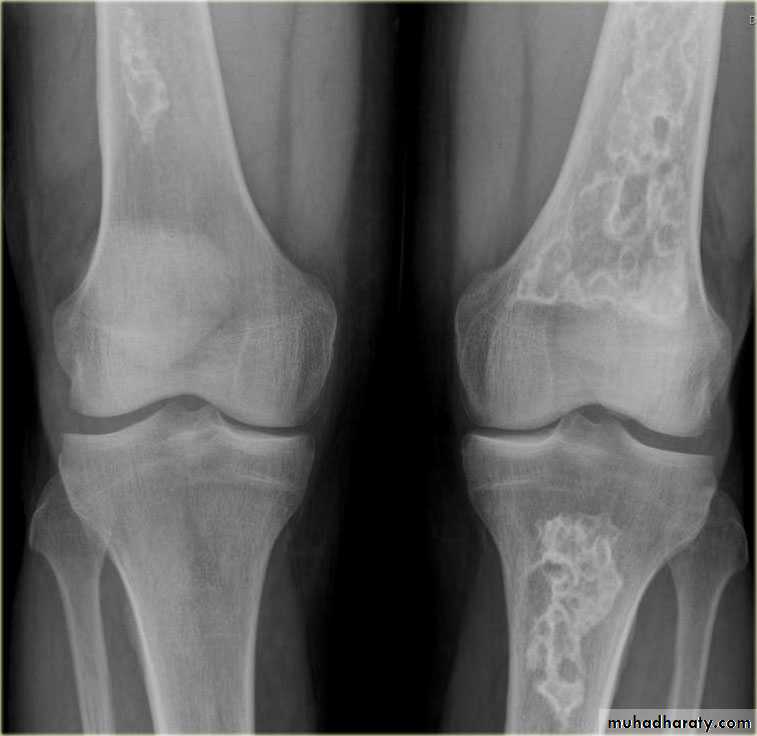
Metastases may be sclerotic , lytic or a mixture of lysis& sclerosis
Lytic metastases.
1- in adults most commonly arise from a carcinoma of the breast and bronchus , less commonly from carcinoma of the thyroid , kidney or colon .
2- in children from neuroblastoma or leukaemia .
Lytic metastases give rise to well defined or ill defined areas of bone destruction with out a sclerotic rim .the lesions vary from small holes to large areas of bone destruction.
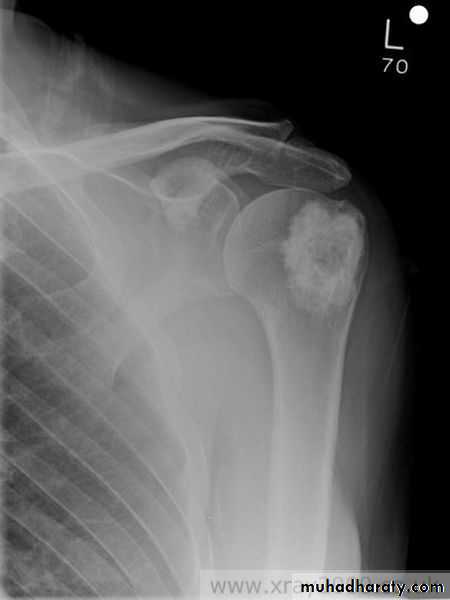
Sclerotic metastases appear as ill-defined areas of increased density of varying size with ill-defined margins .
1-in men they are most commonly due to metastases from carcinoma of the prostate .
2-in women from carcinoma of breast , metastases with bone expansion occurs in primary tumour of the kidney & thyroid .
Mixed lytic & sclerotic metastases are not uncommon , they are often seen with carcinoma of beast .
A radionuclide bone scan is much more sensitive for detecting metastases than plain film .
MRI is better than radionuclide scanning for the detection of metastases, but it is more difficult to survey the whole skeleton .Multiple myeloma :
frequently seen in bones with active haemopoiesislesions .may resemble lytic metastases in every way but are often better defined- diffuse marrow involvement may give rise to generalized loss of bone density
MRI has good role in detecting multiple myloma lesions .
\
Generalized decrease bone density ( osteopenia ):
Osteoporosis :Is the consequence of a deficiency of protein matrix ( osteoid ) . the remaining bone is normally mineralized and appears normal histologically .
The most common causes of osteoporosis are :
idiopathic .cushing disease& steroid therapy .
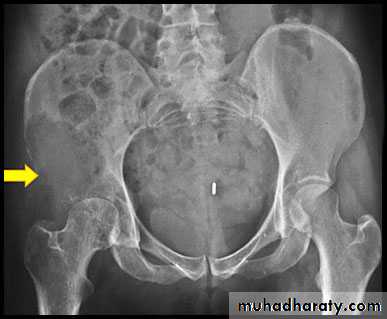
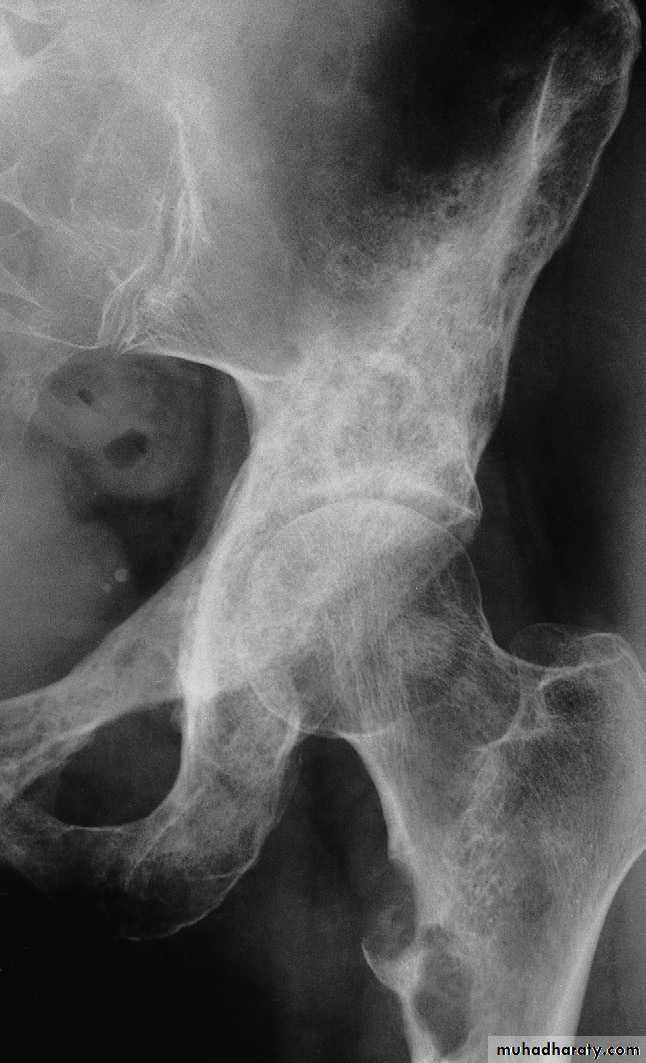
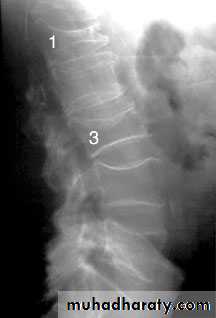
.disuse .Changes of osteoporosis are best seen in the spine , decrease in bone density, compression fractures , vertebral bodies appearing wedged or biconcave , secondary widening of disc spaces .
Long bones have thin cortices .
Screening by measuring of bone mass using DEXA .Rickets and osteomalacia :
In these condition there are poor mineralization of osteoid .if this occur before epiphyseal closure the condition is known as rickets , in adult the condition is known as osteomalacia .The main causes of both above conditions :.
1- Dietary deficiency of vitamin D , or lack of exposure to sunlight.
2- malabsorption.
3-Renal disease.In osteomalacia the features are
. loss of bone density.Thinning of the trabeculae and the cortex
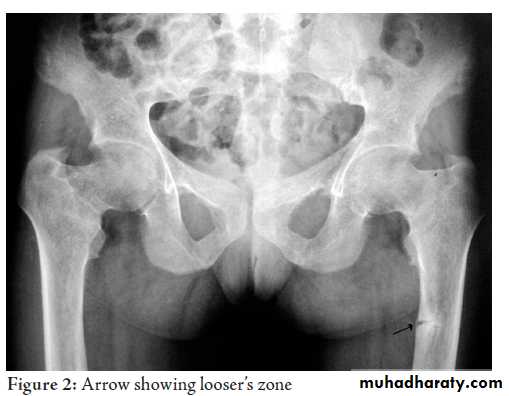
.looser zones
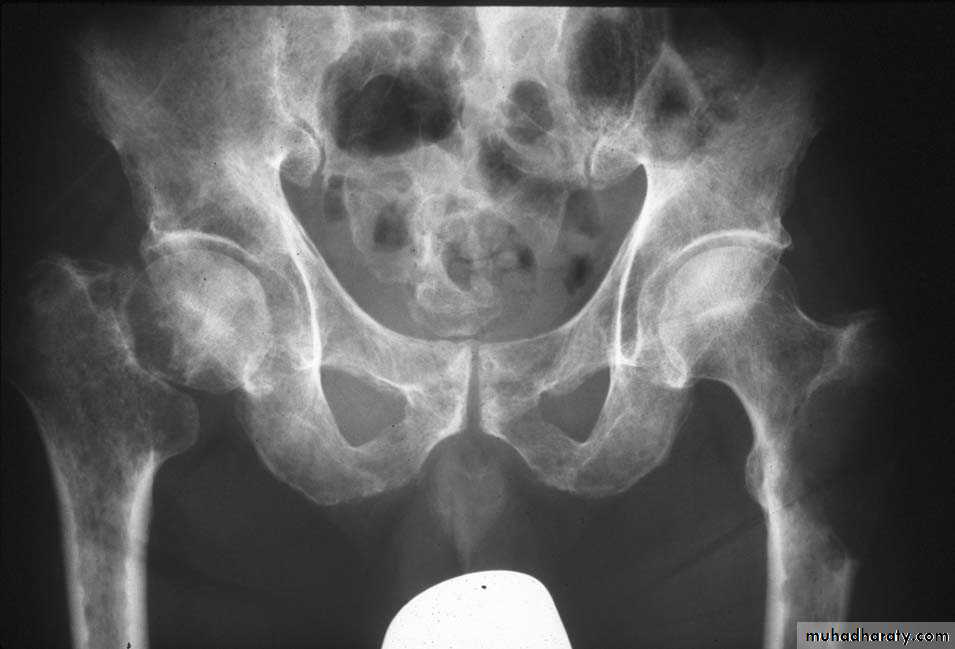
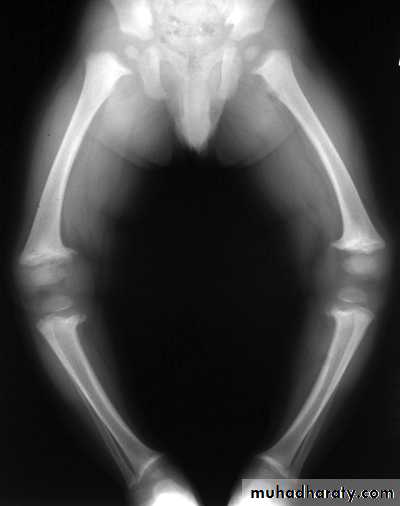
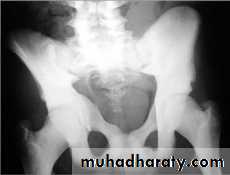
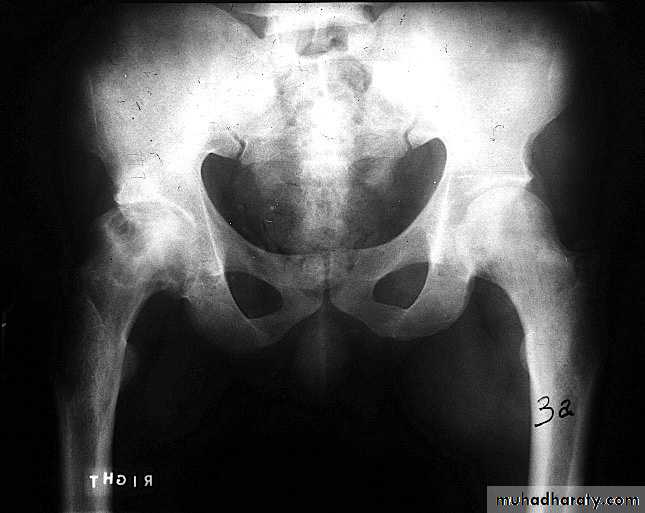
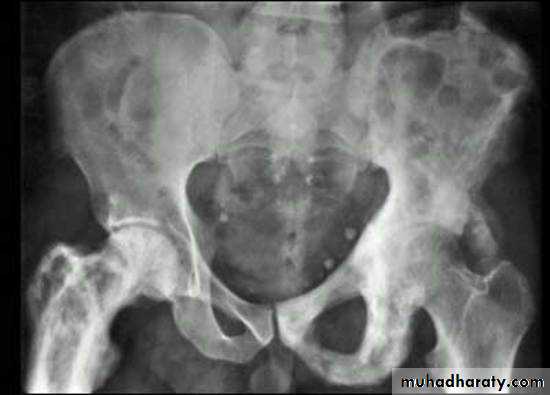
.bone deformity vertebral bodies are biconcave , the femora may be bowed & in severe cases the side walls of the pelvis may bend inwards , giving to the so called triradiate pelvis .
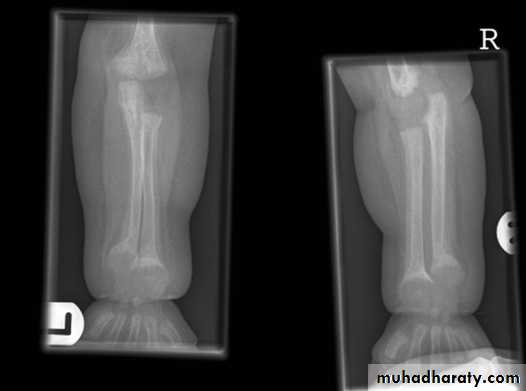
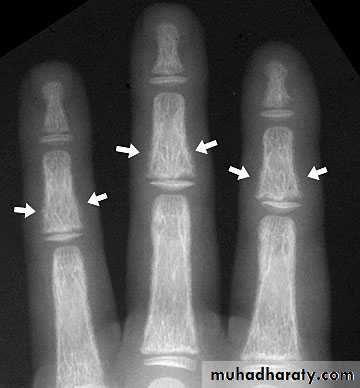
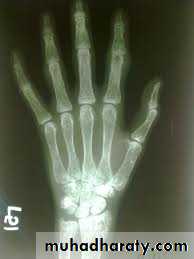
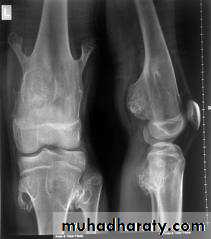
In rickets the changes are maximal where bone growth is occurring , so they are best seen at the knee, wrist and ankle .seen as
. Deficient the zone of provisional calcification .
.widening with irregularly mineralized metaphyses with cupping
.increase distance between the visible epiphysis & the calcified portion of the metaphysis .
.generalized decrease in bone density .
. Deformities of the bones occur because the under mineralized bone is soft , green stick fractures are common .
Hyperparathyroidism:
Excess parathyroid hormone secretion mobilizes calcium from the bones , resulting in a decrease in bone density , it may be primary from hyperplasia or tumour of the parathyroid glands or secondary to chronic renal failure. generalized loss of bone density.
. subperiosteal bone resorption.
. soft tissue calcification.
.brown tumour.
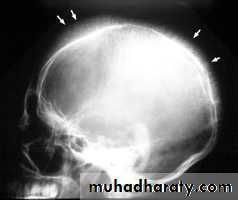
Generalized increase in bone density :
1. sclerotic metastases.2.osteopetrosis . 3 .myelosclerosis.