بسم الله الرحمن الرحيمUrology Investigations
د.أشرف إبراهيم العدول
دكتوراه بورد عربي جراحه الكلى
مدرس ـ فرع الجراحة
M.B.Ch.B., CABMS(Uro).
Investigations
I- URINALYSIS (General urine examination: GUE)complete urinalysis includes physical, chemical, and microscopic analyses.
Physical: color, pH, & Specific Gravity
Color : yellowish
Turbidity :phosphaturia , Pyuria
Specific Gravity and Osmolality :
Specific Gravity usually varies from 1.003 to 1.030.
Osmolality is a measure of the amount of material dissolved in the urine and usually varies between 50 and 1200 mOsm/L.
pH the average pH varies between 4.5 and 8.0. Persistently alkaline urine (pH > 8.0) suggest infection with urea-splitting organism such as Proteus mirabilis
Biochemical Examination of Urine "Dipstick" = a strip coated with chemicals for measuring the urine pH and for detecting the presence of glucose, protein or blood; bilirubin, urobilinogen, ketones and nitrites can also be detected.
Protein
The amount of protein in the urine is normally less than 100 mg/24 hr. Dipstick will only detect levels greater than 300 mg/lTransient proteinuria (e.g. UTI)
persistent (glomerulopathia)
Glycosuria
Usually diabetes mellitus, rarely renal glycosuria
Microscopic analysesCells (RBC , Leukocytes , Epithelial cells , Renal tubular cells) Casts : cast is a protein coagulum that is formed in the renal tubule (The presence of protein casts suggests disease affecting the renal parenchyma)
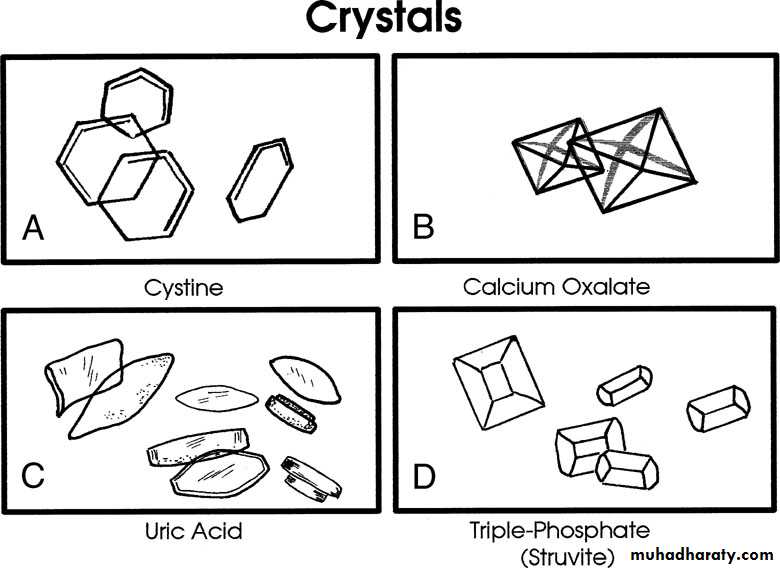
Crystal
Bacteria
Five bacteria/HPF reflects colony counts of about 100,000 bacteria/mLThe finding of any bacteria in a properly collected midstream specimen from a male should be further evaluated with a urine culture
Mid stream urine for c&s.
Early morning sample for AFB
Cytology: poorly differentiated transitional cell tumours anywhere in the urinary tract.
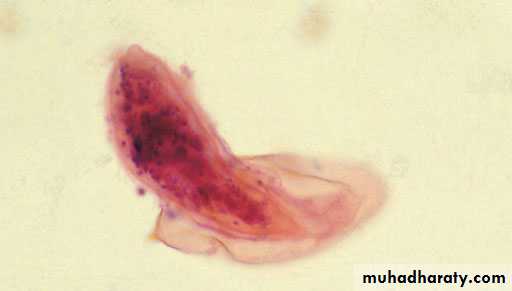
YeastParasites : Schistosoma ovum
Bacteriological culture
Culture & sensitivity (C&S) of a clean-catch midstream specimenThe specimen should be plated out promptly or refrigerated until processing to prevent multiplication of bacteria after voiding.
Significant infection is present if there are more than 100 000 (= 10 5 ) organism/ml , whilst counts less than 10 000 (=10 3 )/ml suggest contamination.
If there are pus cells in the urine but there is no growth on the routine culture media (sterile pyuria), it is worth testing for more fastidious organisms.
Multiple early-morning urine specimens must be cultured on L0wenstein–Jensen medium to detect urinary tract tuberculosis.
Chlamydia
Analysis of a 24-hour specimen of urine
Quantify the rate of loss, and is especially useful in the investigation of calculus disease caused by abnormal excretion of calcium, oxalate, uric acid and other products of metabolismII- Renal function tests:
More than 70% of kidney function must be lost before renal failure becomes evident (Because of large renal reserve, considerable structural damage can occur before functional damage become apparent).1- Blood urea (Blood Urea Nitrogen)normally (15-40 mg/dl) (2.5-6.5 mmol/l)
It increases in dehydration, fasting, fever & after protein meal. Also in renal failure
2- Serum creatinine: (0.6-1.2 mg/dl) ( 62-124 µmol/l)
More accurate than urea and less affected by dehydration.
3- Creatinine clearance: (85-120 ml/min)
Creatinine clearance test will give an approximate value for glomerular filtration rate Needs 24h urine collection and a sample of blood. Cr. CL.=UV/PU : Cr. in urine (mg/dl)
V: ml of urine excreted (per minute or 24hour)
P: Cr. in plasma (mg/dl)
Haematology
Anaemia - tumours, renal impairmentWhite blood cell count - may raised in infections
ESR - elevated in certain disorders, tumors, retroperitoneal fibrosis
Other tests
PSA : prostatic specific antigen.URINARY TRACT IMAGING
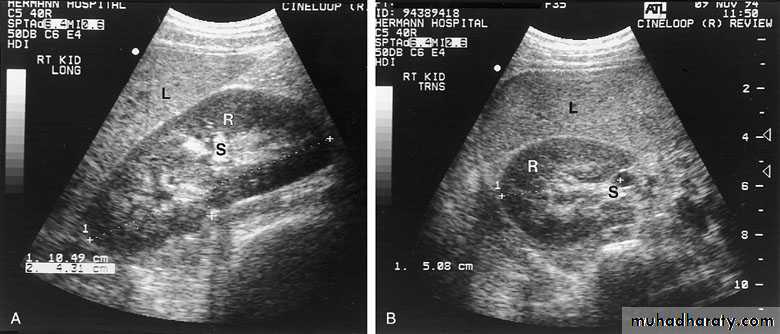
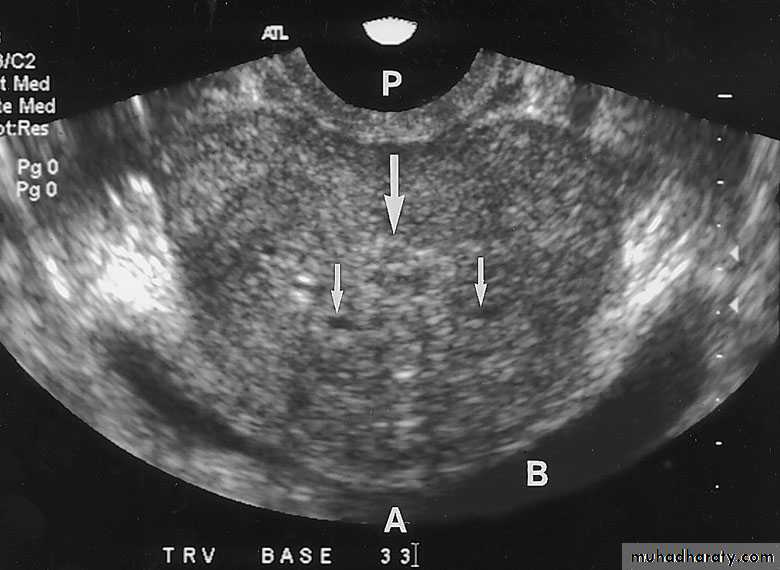
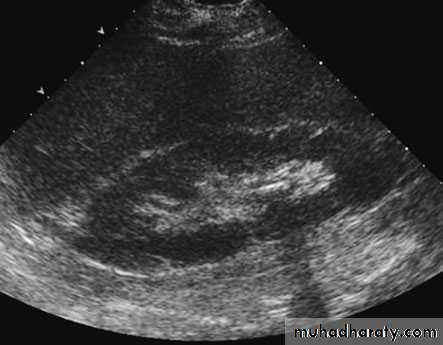
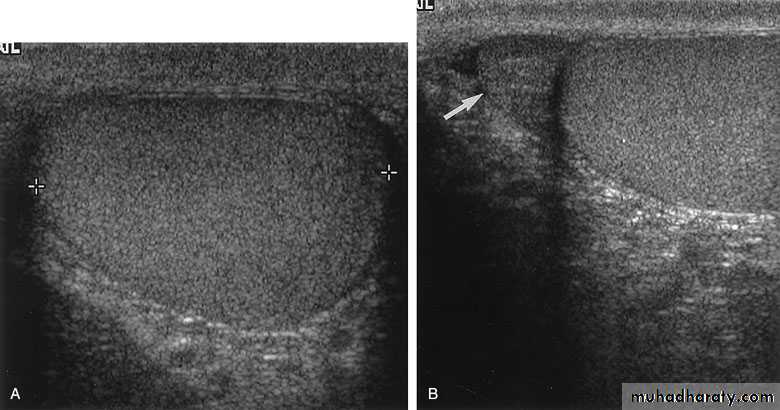
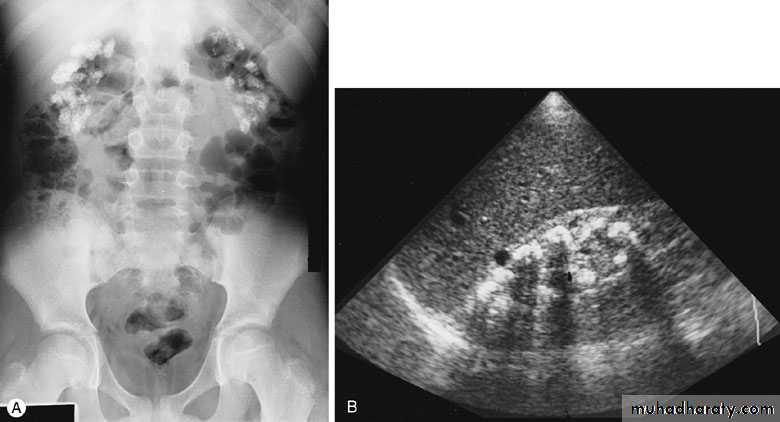
ULTRASONOGRAPHY (U/S )Structural study to differentiate cystic or solid masses, hydronephrosis, renal size, renal cortical thickness, and stones.
The volume of urine in the bladder before and after micturition (post void residue) can be calculated, and even tiny filling defects within it detected.
The prostate
Scrotal contents can be displayed in great detail.
TRUS (transrectal U/S): for prostate evaluation and U/S guided prostate biopsy.
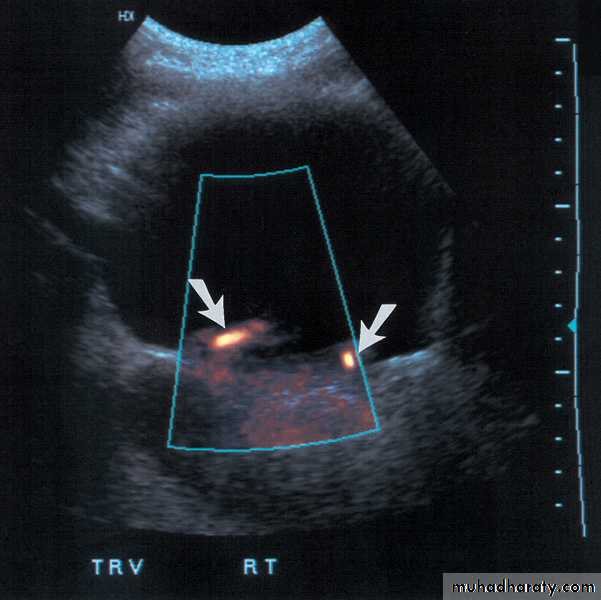
Color-flow Doppler techniques - measuring blood flow
U/S is Non invasive, available, cheap, painless, fast, portable, and almost no contraindications
A brief pulse of high-frequency sound energy produced by a transducer is transmitted into the patient. The sound waves interact with the tissue and are either reflected, refracted, or absorbed, depending on the type of tissue involved
A calculus in the kidney casts an acoustic shadow
Urinary bladderTestis
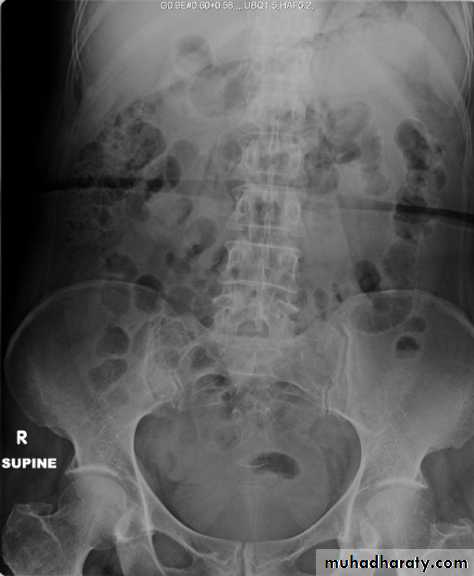
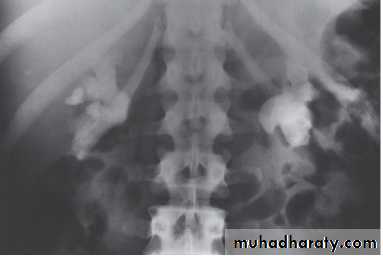
X-Ray: KUB (kidneys, ureters, bladder)
A plain radiograph of the abdomen and pelvis includes the area above both adrenal glands (lower chest) and extends to 2 cm below the symphysis pubis(includes the external genitalia)site, sex, stones, psoas shadow, skeleton, and soft tissue shadow.
Indications
1) as a primary study
2) as a scout film before contrast material injection
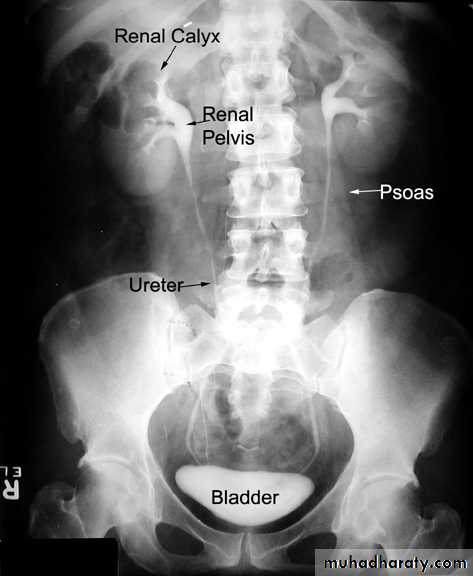
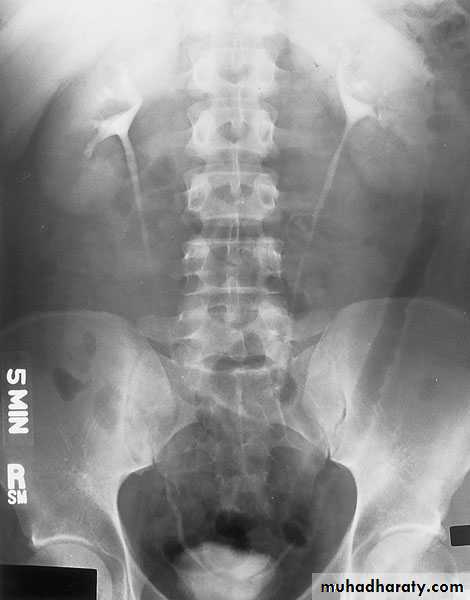
EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY (IVU , IVP, EXU )
These are organic chemicals to which iodine atoms are attached to absorb X-rays.Allows visualization of the entire urinary tract. The study provides demarcation of the renal parenchyma, the pelvicalyceal system, ureters, and bladder, providing both anatomic and functional information.
Number, size, site, function of the kidneys, anatomy of the collecting system, hydronephrosis, and filling defects, stones.
The hypertonicity of the contrast media may have ill effects on the cardiovascular system, the coagulation cascade, the blood-brain barrier, and the kidneys.
Intravenous urography (IVU)
- After a plain film, iodine-containing contrast medium is injected intravenously and serial films are taken to follow its excretion by the kidneysThe nephrogram phase - on the initial film 1-3 minutes after injection, contrast medium is in the glomeruli and proximal tubules so that a clear image of the renal outline is obtained
The pyelogram phase - subsequent excretion of contrast medium outlines the collecting systems, renal pelvis, ureter and bladder, showing any structural abnormalities or filling defects
Adverse Effects of Contrast Media
- Idiopathic or anaphylactoid reactions. Allergic reaction to the contrast medium, range in severity from a mild urticarial rash to anaphylactic shock .- Contrast media may induce an acute impairment of renal function
- Diabetics managed with metformin (Glucophage)
should have the drug withheld for 48 hours after receiving contrast material.
C.I.: allergy, pregnancy, and renal impairment
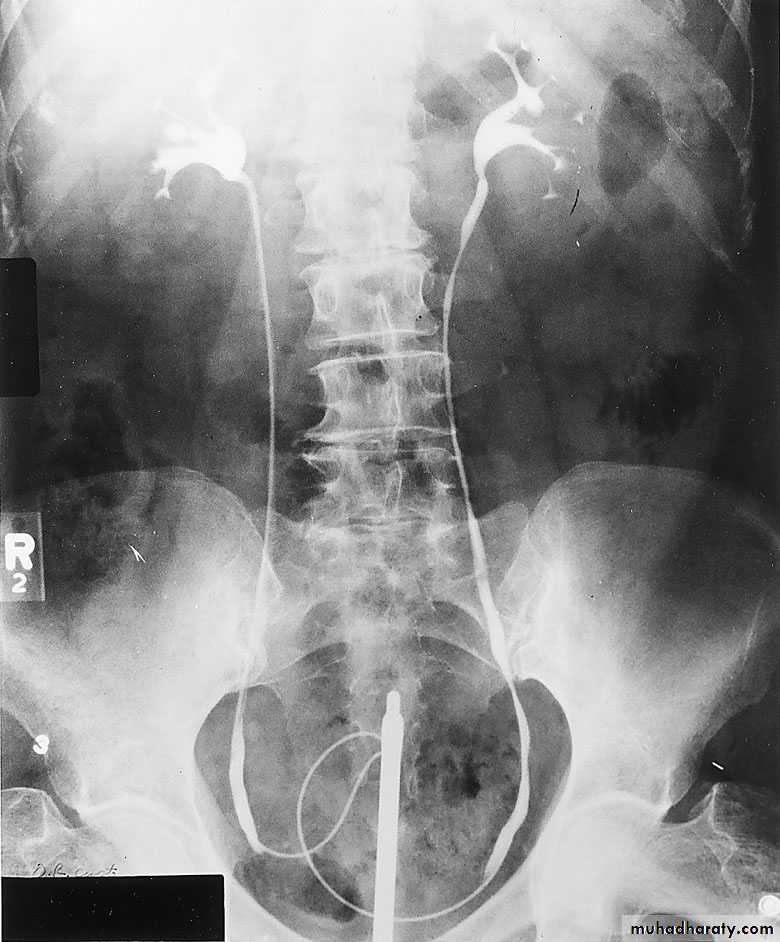
IVU needs Patient PreparationRETROGRADE PYELOGRAPHY
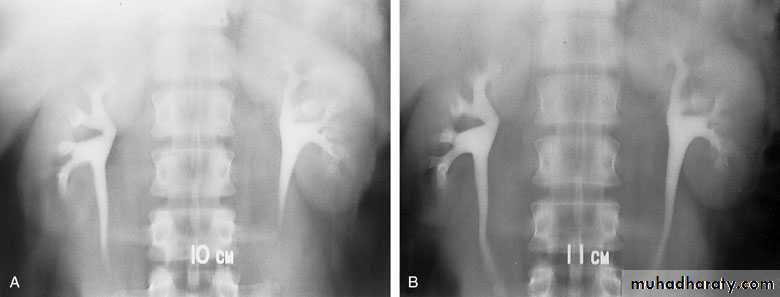
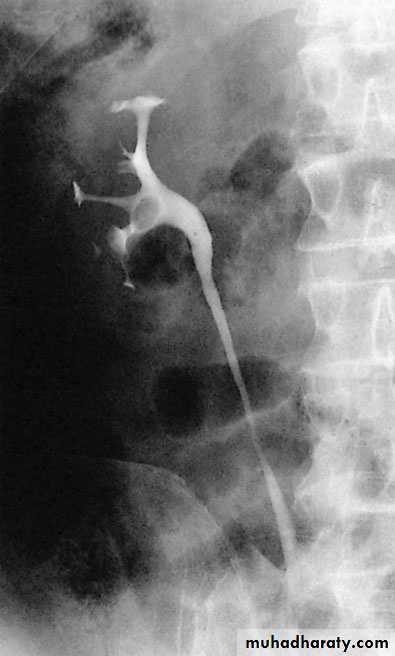
Opacification of the ureter and pelvicalyceal system by the retrograde injection of contrast media using ureteric catheter.Indications
Employed after an excretory urogram that inadequately visualized the anatomy of the upper tract.when there are contraindications to do IVU
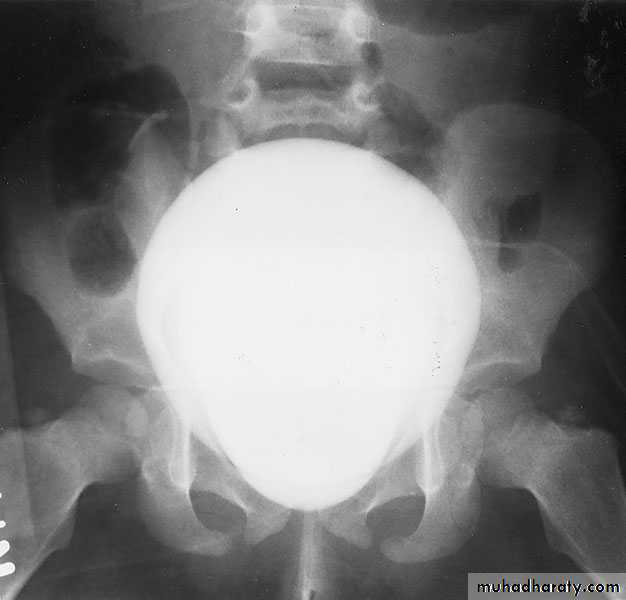
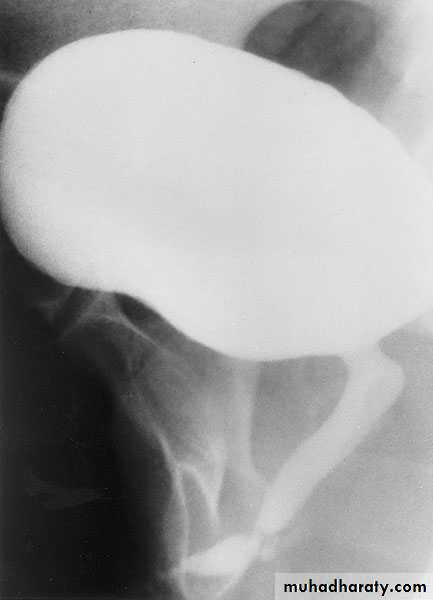
Retrograde ureterogram demonstrating the collectingsystem with radiolucent filling defect in the renal pelvis.
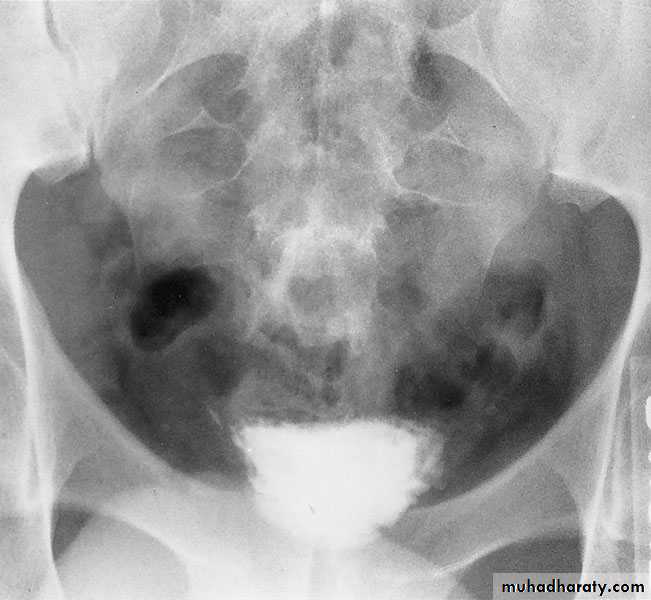
CYSTOURETHROGRAPHY
Contrast-enhanced imaging of the lower urinary tract provides valuable information on the function and anatomy of the bladder and urethraVoiding ( micturating) Cystourethrography (MCUG): looking for vesicoreteric reflux
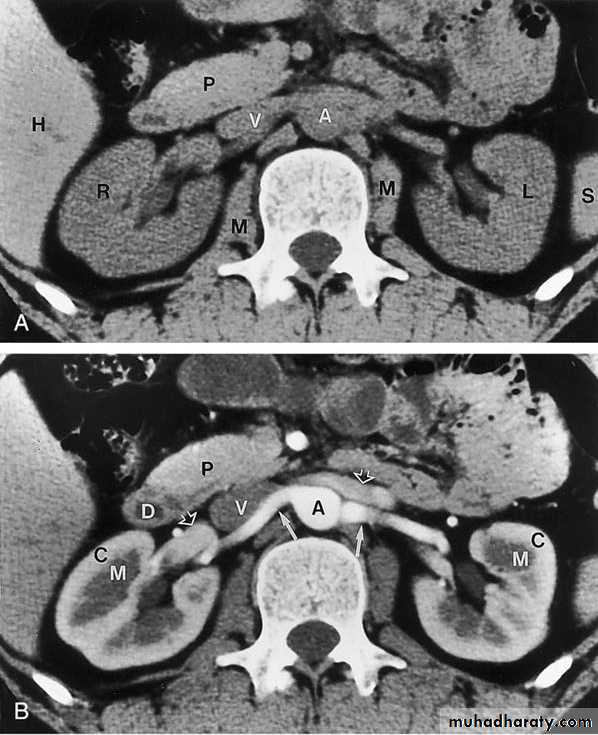
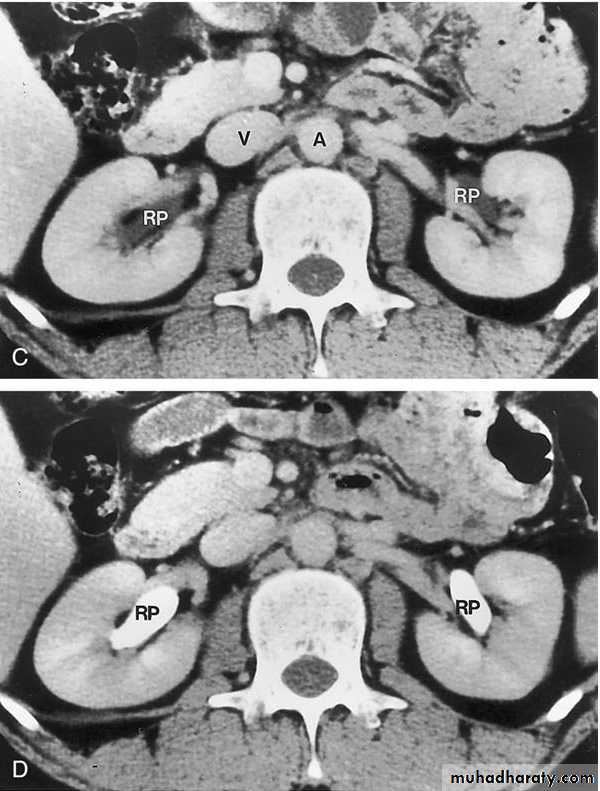
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY ( CT scan)
Non Contrasted (Native, non enhanced)Contrasted: Oral Contrast Agents
Intravenous Contrast Agents
CT scan accurately characterize the nature of tissue in the lesion.
CT is useful in the preoperative evaluation and staging of tumors.CT has replaced IV urography as the primary modality for the assessment of suspected renal injuries and their complications
For the evaluation of patients with acute flank pain, unenhanced spiral CT is more sensitive in detecting calculi than EXU. (except indinaver no radiolucent stones).
Drawbacks: Expensive, more radiation, not always available, need experience, contrast contraindications, pregnancy
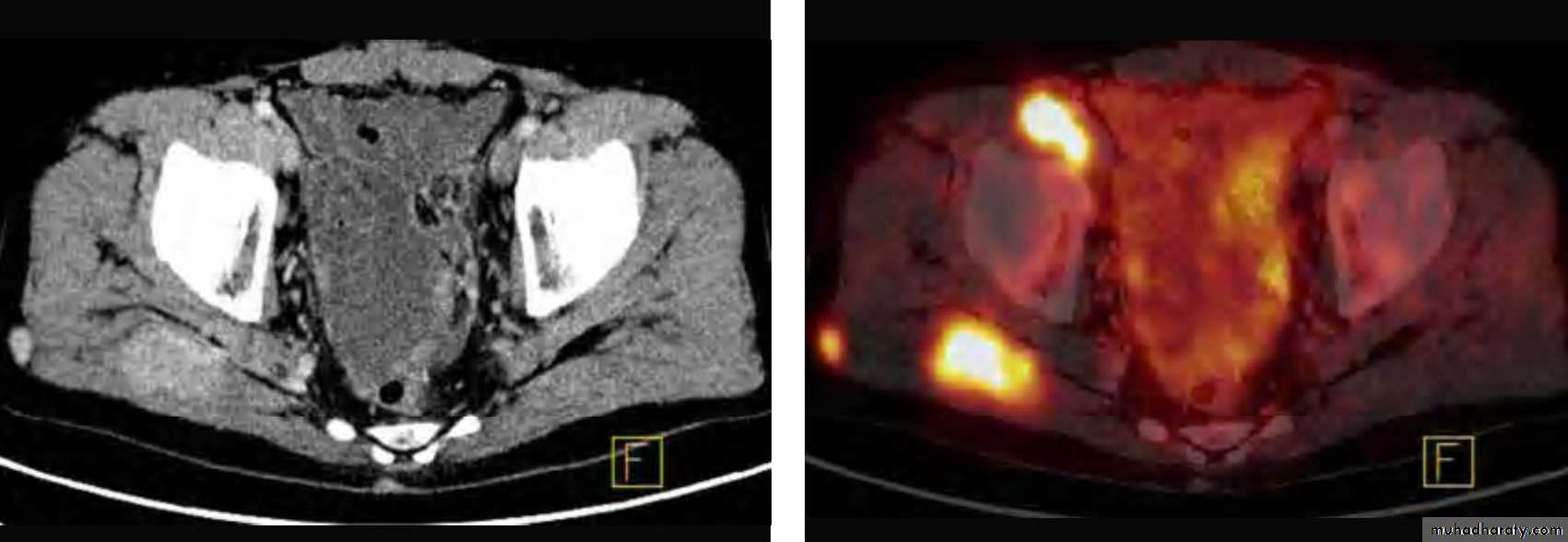
PET/CT
- Combination of positive emission tomography and CT.- It allows precise localization of tumours.
PET/CT with metastases of kidney cancer to the soft tissue around the right hip joint
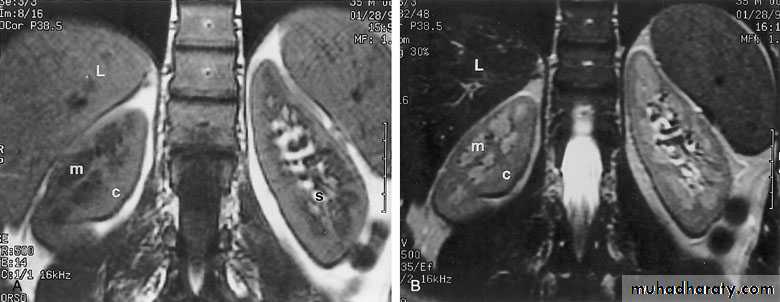
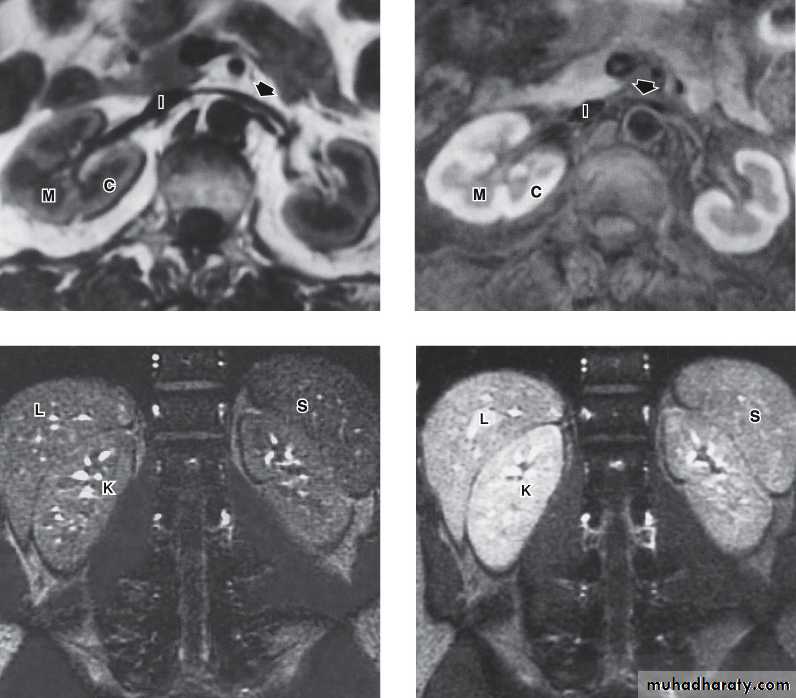
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI)Protons within the body can be thought of as small, spinning bar magnets. Hydrogen has a single proton. When a patient is placed in a large magnetic field, the hydrogen protons within the body align, and this alignment leads to the formation of a net magnetic vector within the patient.
Contrast: Gadolinium
No
radiation
NUCLEAR IMAGING
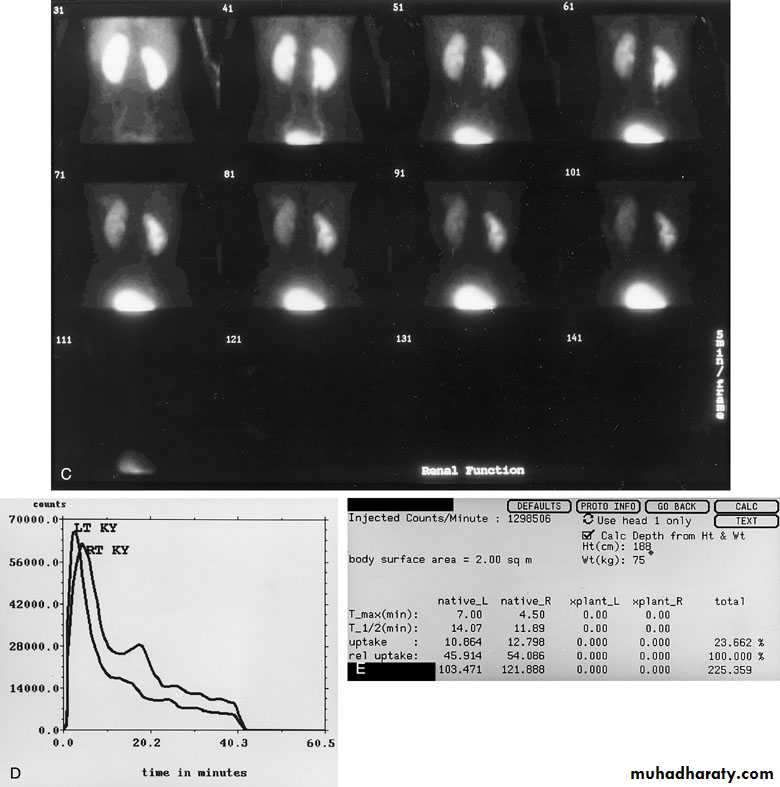
Renal scintigraphyThe radionuclides studies can measure perfusion, functional morphology (glomerular filtration and tubular secretion), excretion, and cortical morphology, upper urinary tract obstruction.
Technetium Tc 99m Diethylenetriaminepenta-acetic Acid 99mTc-DTPA Technetium Tc 99m Mercaptoacetyltriglycine 99mTc-MAG3
Technetium Tc 99m Dimercaptosuccinic Acid 99mTc-DMSA
It gives the split function of each kidney
Bones scintigraphy
It is most widely used in the detection of bony metastases from prostatic, bladder and renal carcinoma.
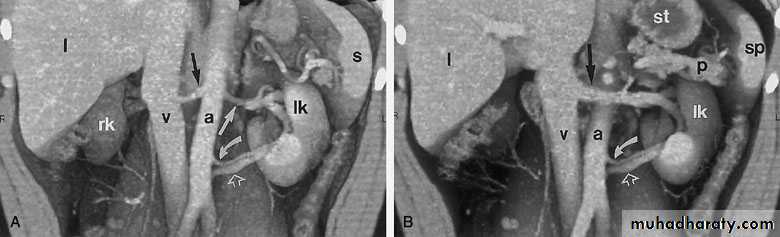
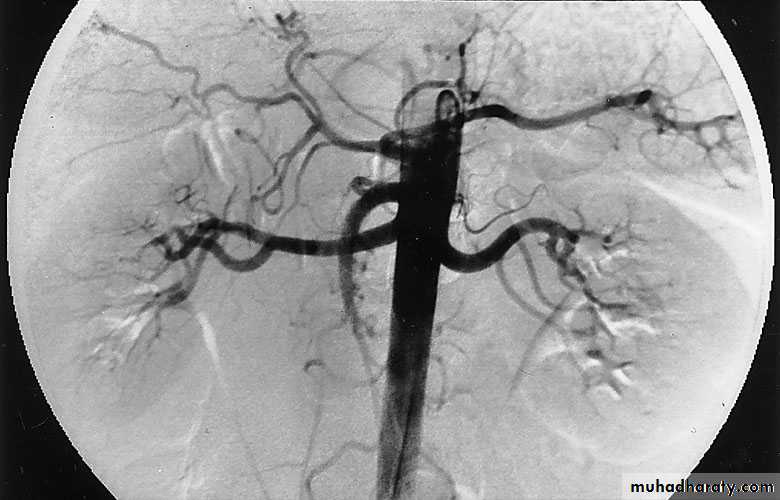
ANGIOGRAPHY
Currently, CT, MRI, and ultrasonography have supplanted angiography for most diagnostic indications, providing equivalent and at times greater information with markedly decreased morbidity and risk.It is used in diagnosis of renal vascular disorders, renal tumours and renal trauma; therapeutic embolization of the renal artery can be performed at the same time to control bleeding from the kidney.
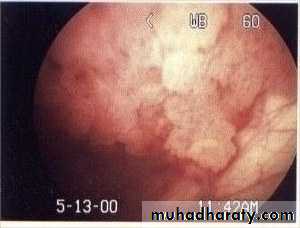
Endoscopy:
Direct visualization of the internal parts of the organ. Urethroscope, Cystoscope, Ureteroscope and Renoscope.Urodynamic studies:
To study the function of the lower urinary tract( vesico-urethral unit).Include cystometry, flow rate, urethral pressure profile, video urodynamic studies, and EMG of pelvic floor