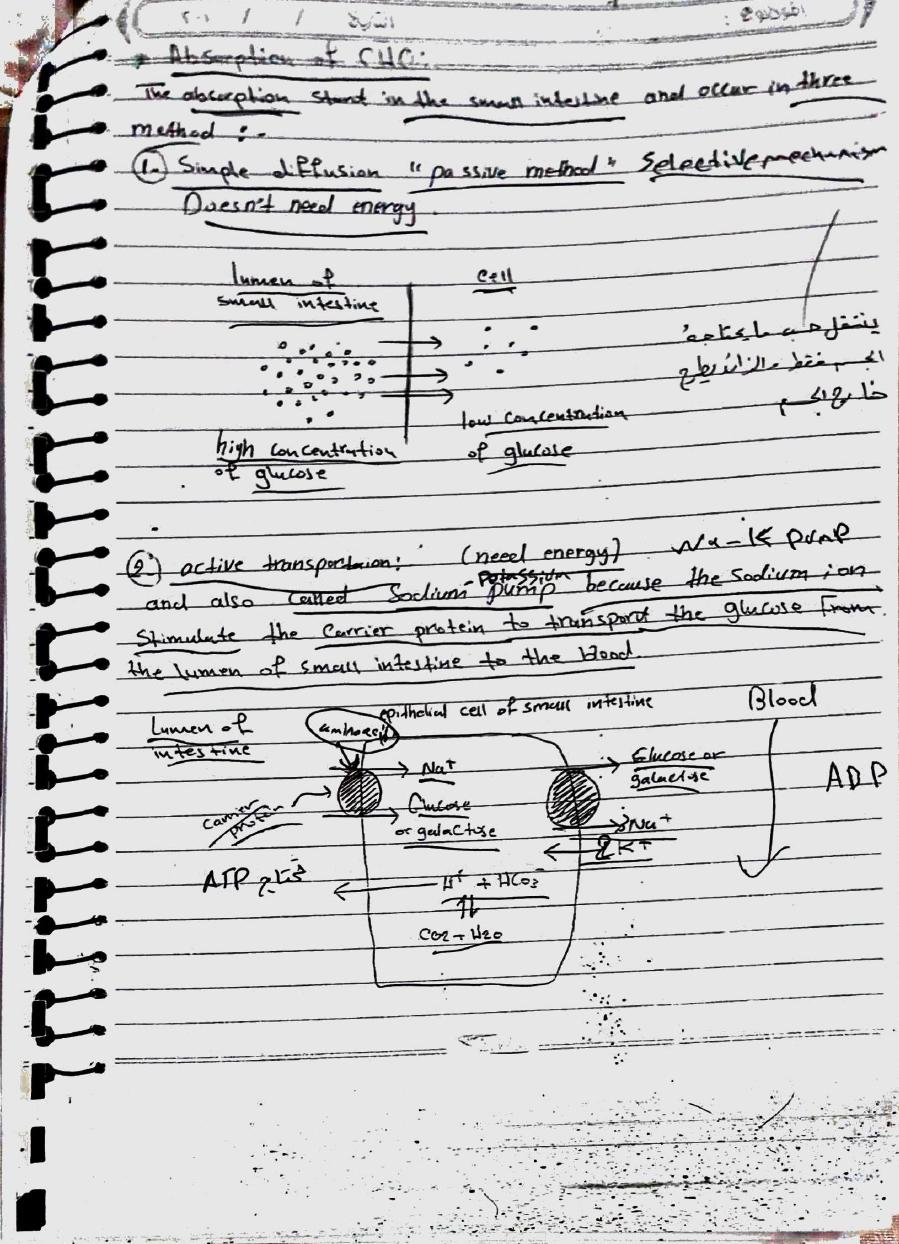
Lecl :
Jntrodoetioo•
Biochemistry
Definition of BIOCHEMISTRY
1: chemistry that deals with the chemical compounds and
processes occurring in organisms.
2 the chemical characteristics and reactions of a particular living
system or biological substance.
Studying Structures and functions of enzymes, proteins,
carbohydrates, fats, process of metabolism and the molecular
basis of the action of genes also form a part of biochemistry.
Advances made in biochemistry have made significant
contributions towards elucidation and understanding of the DNA.
Carhobvdcates
Carbohydrates (or saccharides) consist of only carbon,
hydrogen and oxygen
Carbohydrates come primarily from plants, however animals
n
can also biosynthesize them
• The "Carbon Cycle" describes the processes By which carbo•n is
recycled oh our planet
n
- Energy from the sun is stored in plants, which use photosynthesis
n
to convert
the reverse
carbon
process,
dioxide
energy
and water
is produced
to glucose
when
and
animals
oxygen
oxidize
- In
glucose during respiration
Carbohydrates a major source of energy in animal diets.
n
6C02 +•6H20 +Energy
Photosynthesis
C6H1206 + 602
Respiration
They also serve as structural components, such as cellulose
in plants and chitin in some animals. Their derivatives play an
essential role in the working process of the immune system,
fertilization, .and pathogenesis.

Cvcte
Sim plified Carbon
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Carbohydrate functions as storage food of Carbohydrate
stored in living organism as storage food.
Polysaccharide starch acts as storage food for plants.
Glycogen stored in liver and muscles acts as storage food fdr
animals:
Inulin acts as storage food of dahlias, onion and garlic.
functions as framework In _>Qdv
Different Carbohydrates especially Polysaccharides act as
framework in living organism.
Cellulose forms cell wail of plant cell along with hernicelluloses and
Pectin.
Chitin
forms cell Wall of fungal cell and exoskeleton of
Arthropods.
Peptidoglycan forms cell wäll of bacteria.
Thus carbohydrates fuhction as contributing material,to the cellular
structure.
Cr
dr
fun •oh s Antico ul
Heparin is a polysåccharide (carbohydrate) which acts as
'l
anticoagulant and prevents* intravascular clotting,
Cr
h dr e fn
i %
•Many antigens are gly±protein (which contains oligosaccharide)
in nature and give immunqlogieal properties to the blood.

Carb
fun
Many Hormones like FSH
(Follicular Stimulating Hormone which
takes part in ovulation in
females) and LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
are glycoprotein and help in
reproductive processes.
Carb h drates rovi e raw materi I fo • du
Carbohydrates are an important component of many industries like
textile, paper.
Other nc ions
Agar is polysaccharide used in culture media, laxative and food.
Cellulose acts as roughage of food. It stimulates peristalsis
movement and secretion of digestive enzymes.
Hyaluronic acid found in between joints acts as synovial fluid and
provides frictionless movement.
3
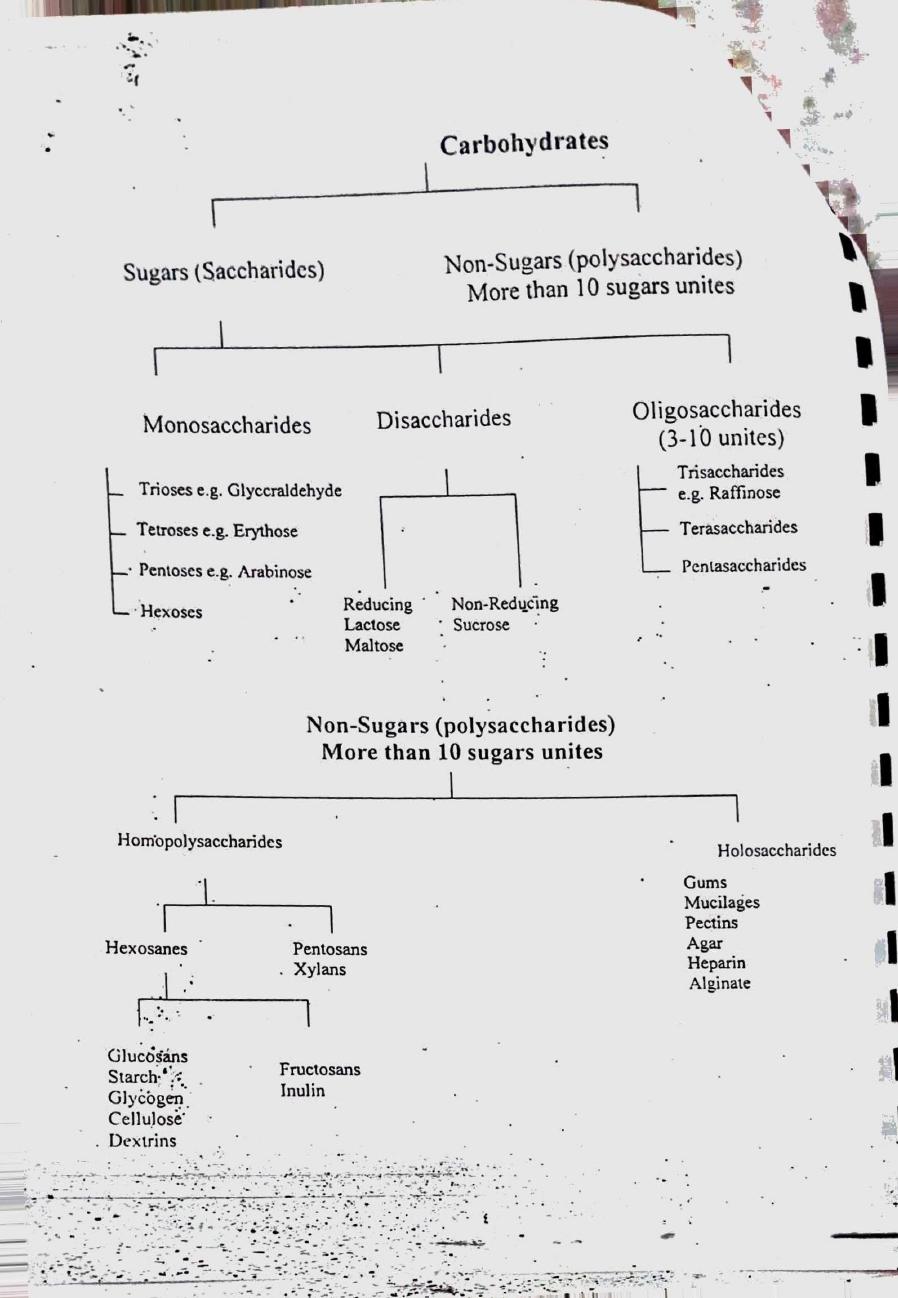
Carbohydrates
Sugars (Saccharides)
Non-Sugars (polysaccharides)
More than 10 sugars unites
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides
Trioses e.g. Glyccraldehyde
Tetroses e.g. Erythose
• Pentoses e.g. Arabinose
Hexoses
Reducing
Non-Reducing
Lactose
Sucrose
Maltose
Non-Sugars (polysaccharides)
More than 10 sugars unites
Hom•opojysaccharides
Hexosanes
GlucÖSåns
Starch"
Glyéögen
Pentosans
Xylans
Fructosans
Inulin
Oligosaccharides
(3-10 unites)
Trisaccharides
e.g. Raffinose
Terasaccharides
Pentasaccharides
1
Holosaccharidcs
Gums
Mucilaées
Pectins
Agar
Heparin
Alginate
Cellulose
Dextrins

each ,2!!
-3