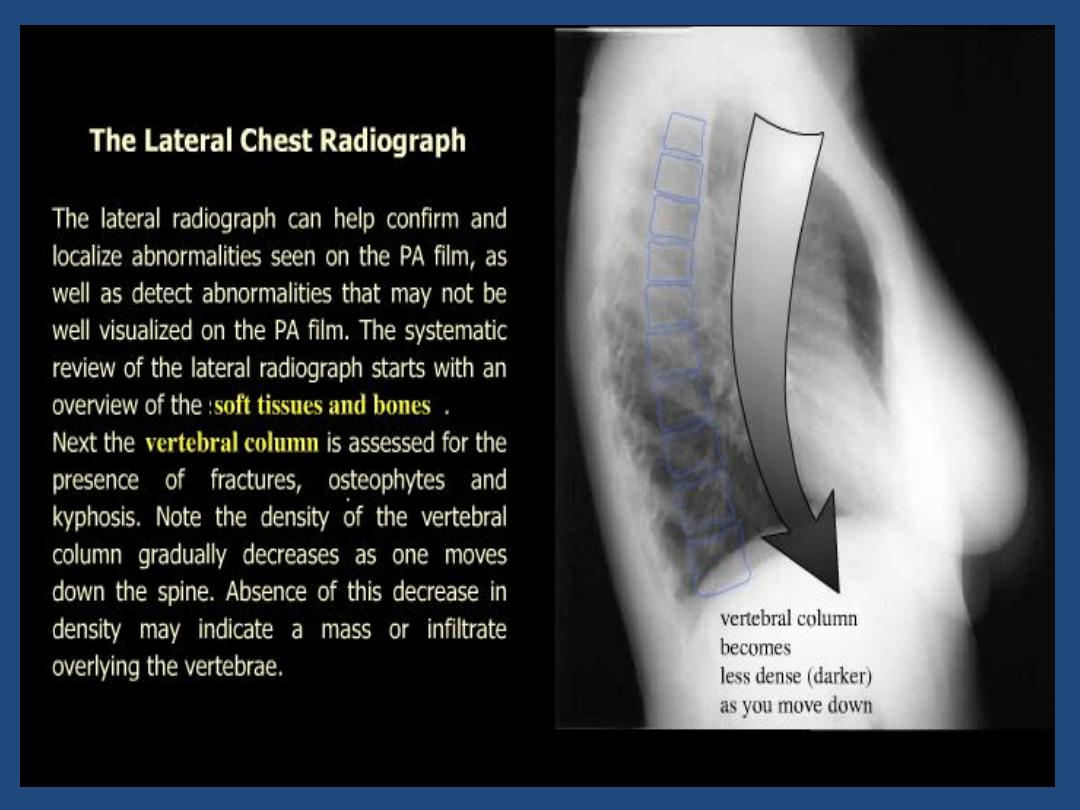
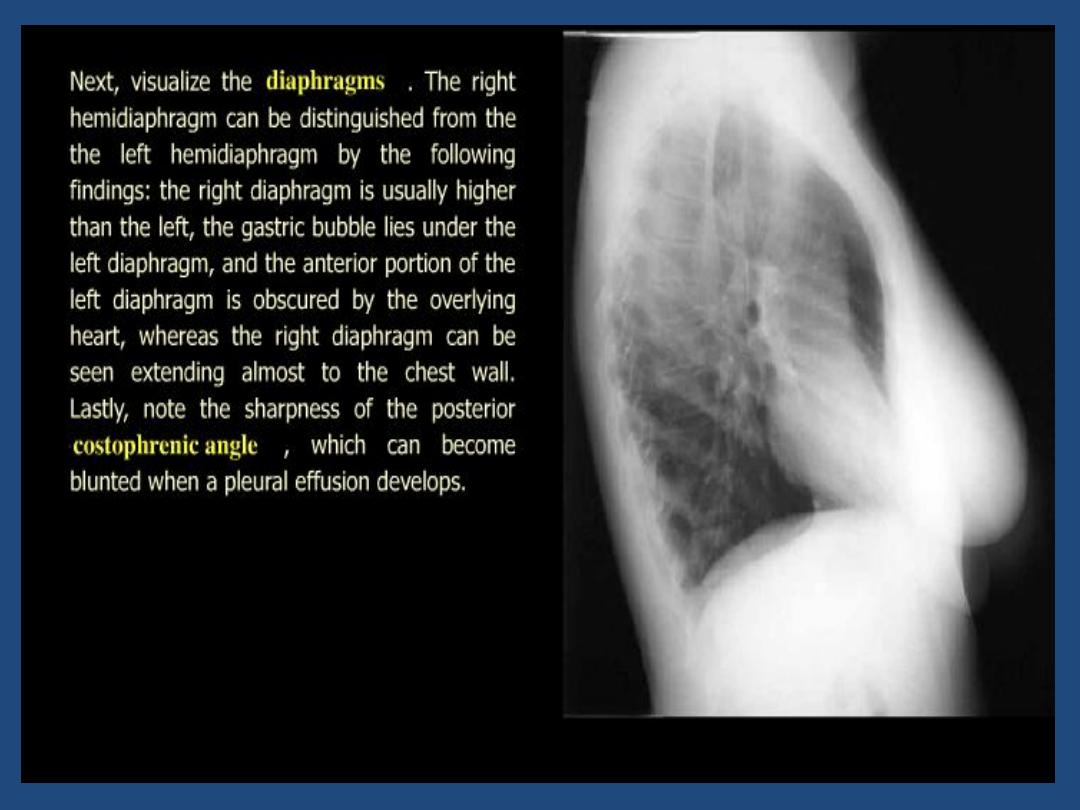
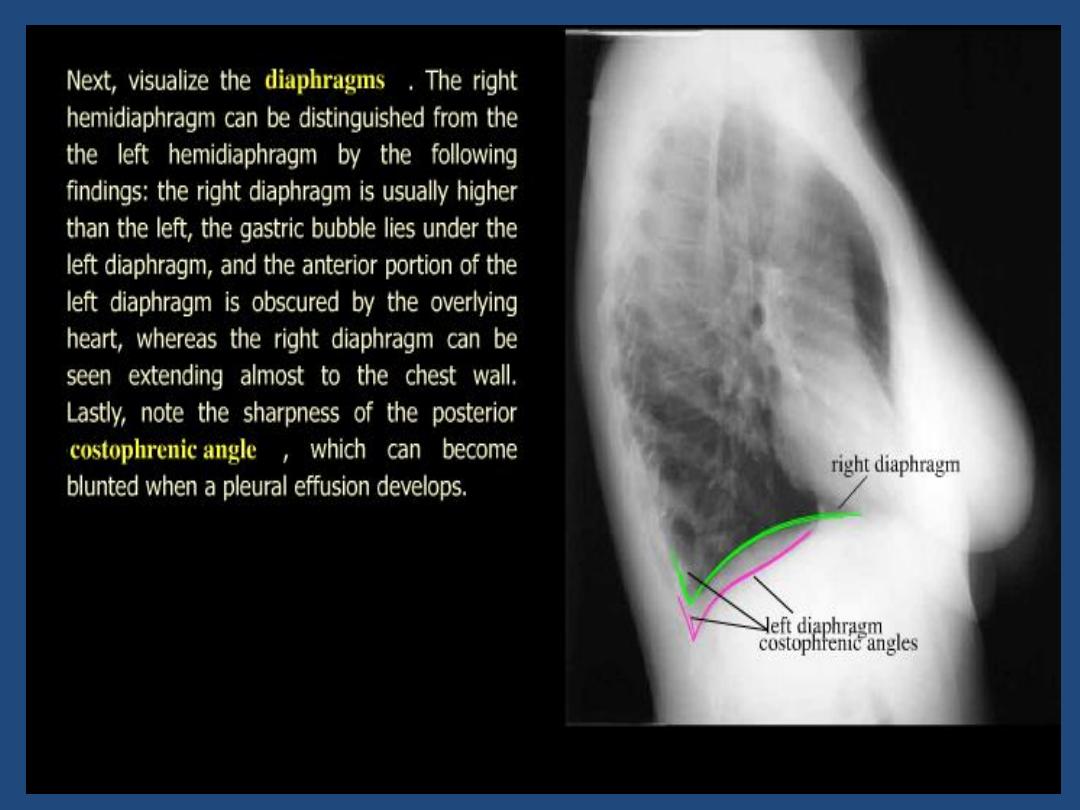
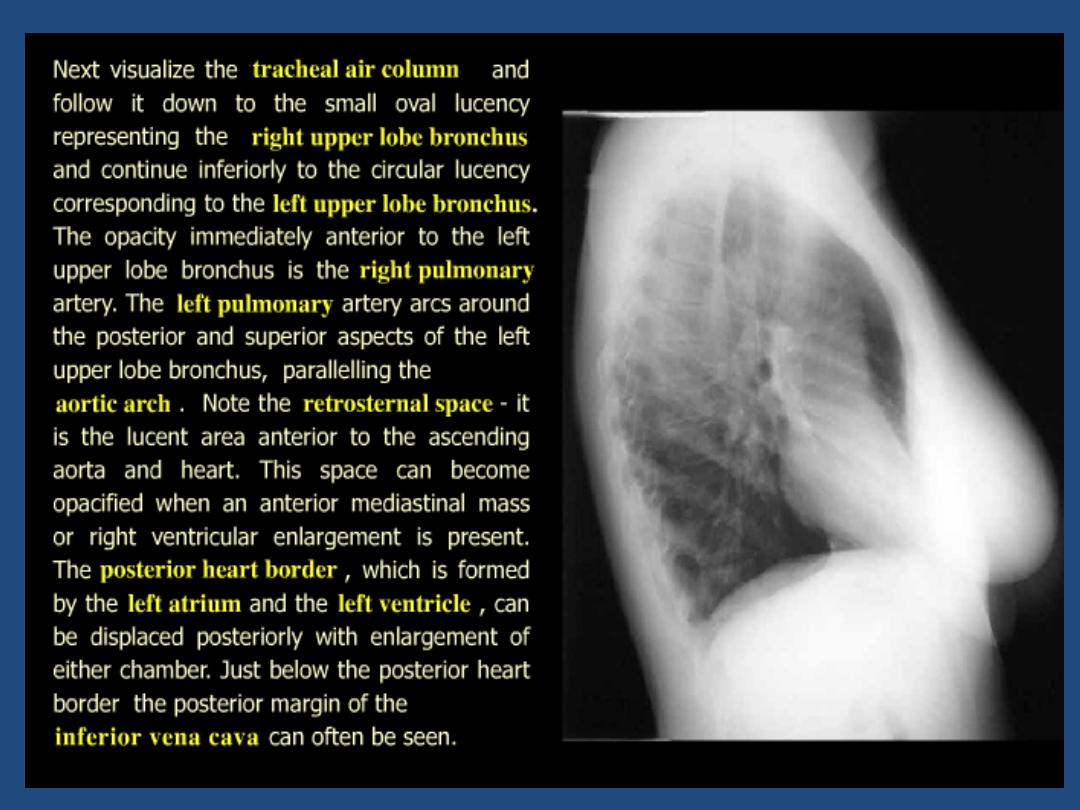
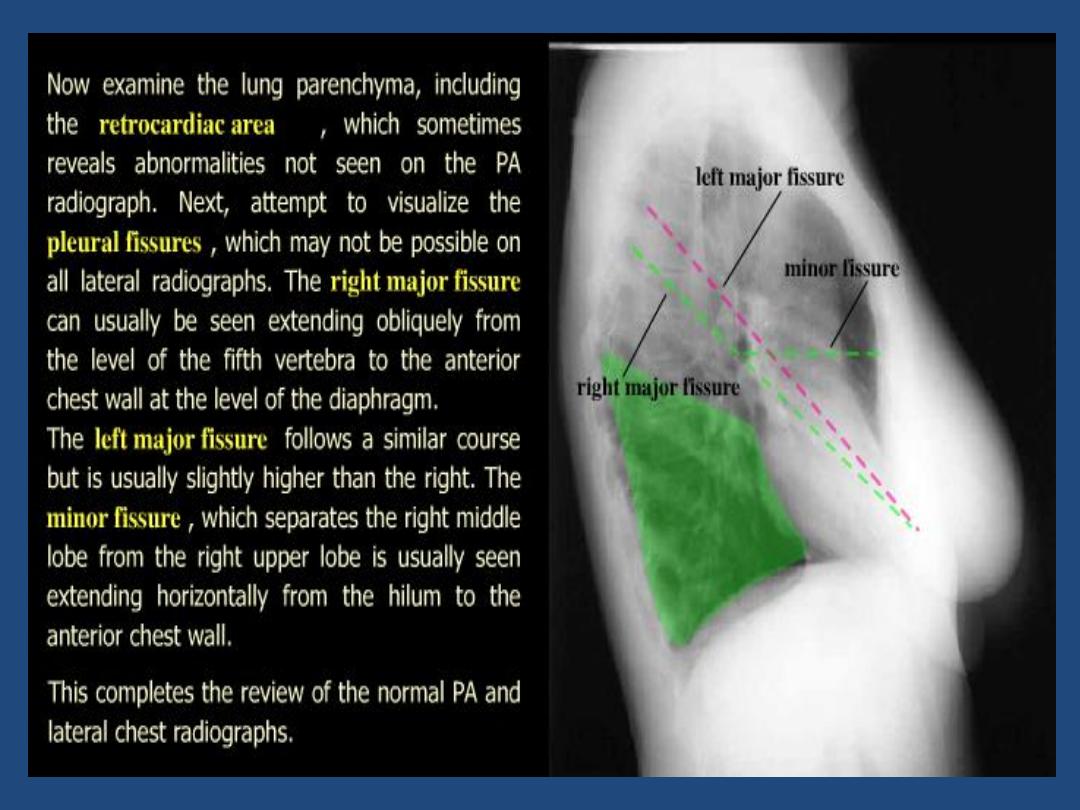
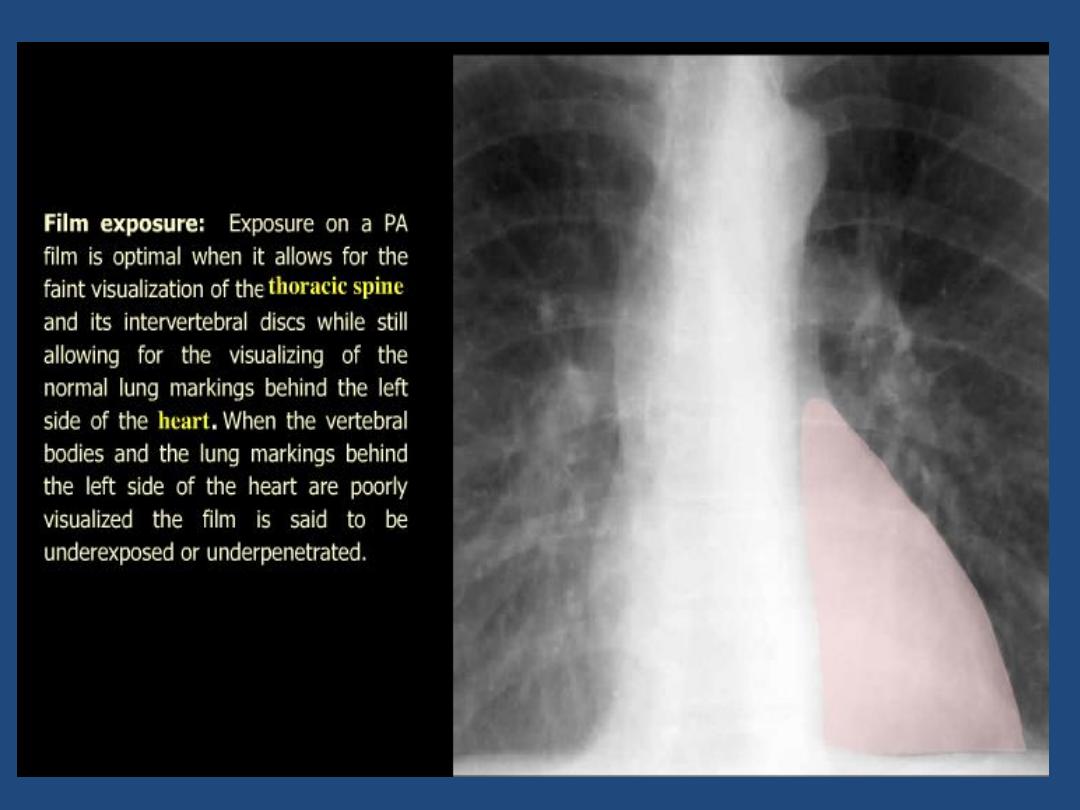
CHEST X-RAY
METHODS OF
INVESTIGATION

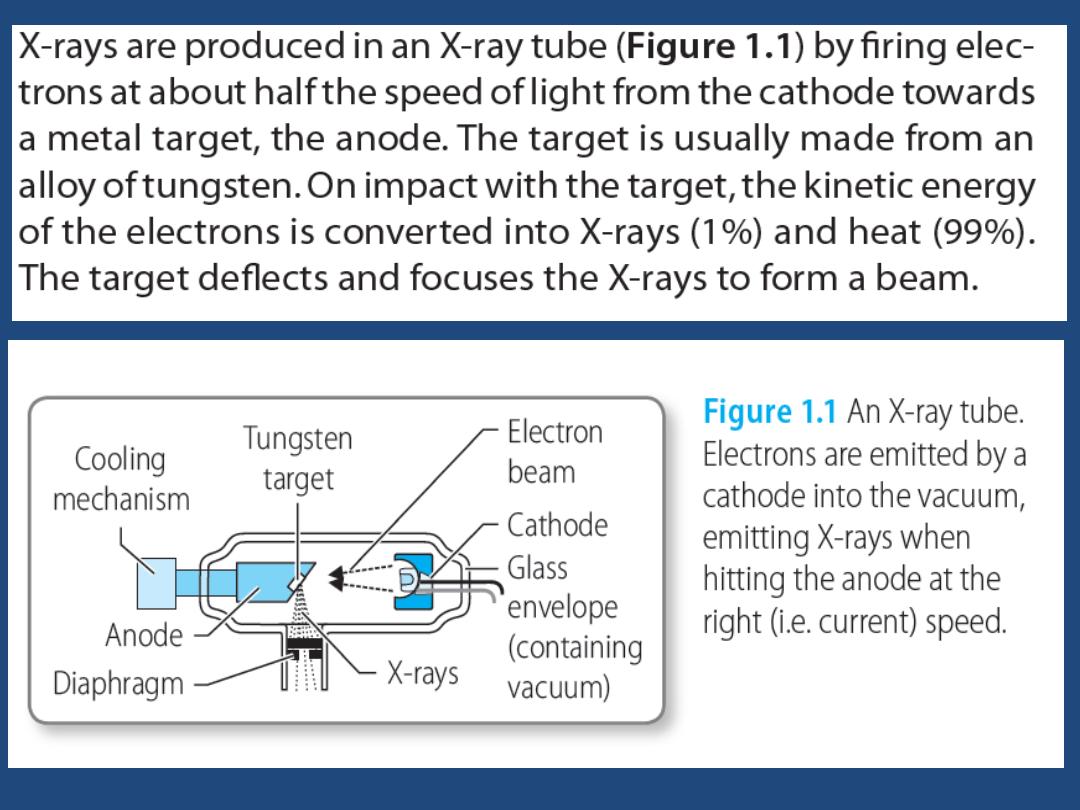

The X-ray beam is directed at the patient in
a short pulse and is absorbed (attenuated) by
the tissues of the body. Materials with high
electron density, such as bone, attenuate the
beam to a greater extent than soft tissue,
water or air. Therefore the beam that emerges
from the patient carries a pattern of intensity
that reflects the physical anatomy through
which it has passed.

METHODS OF INVESTIGATION
• PA ( postero-anterior ) ,Lateral
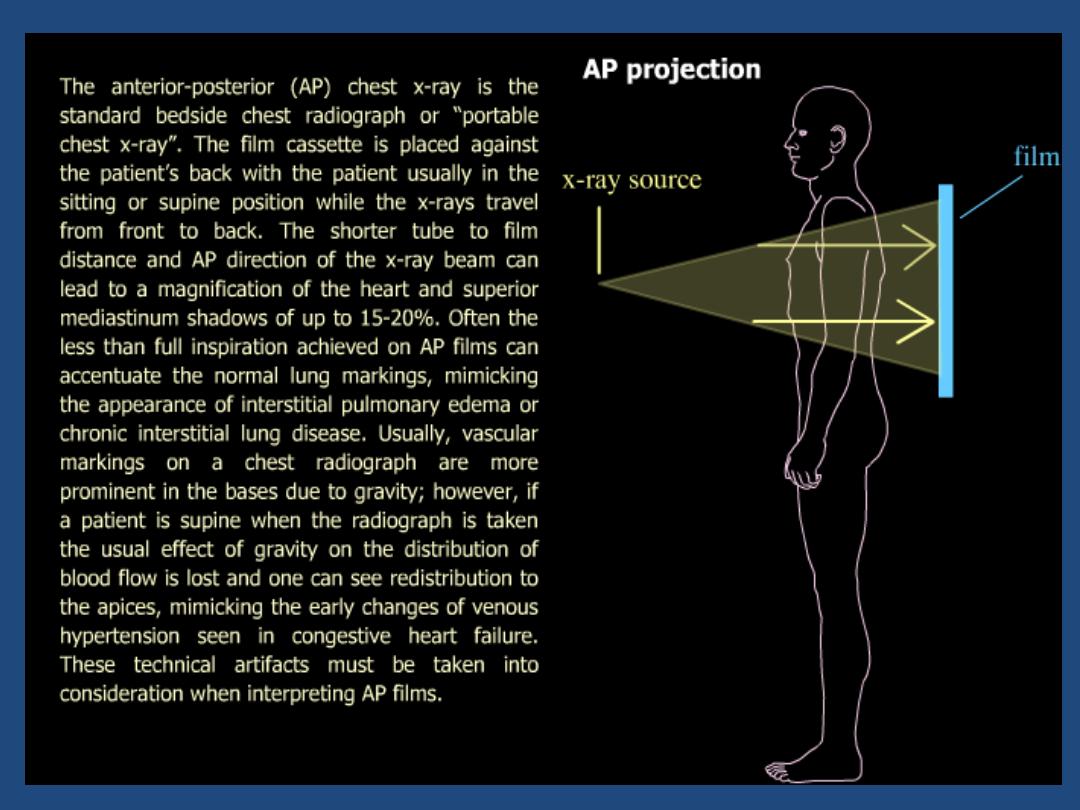
• AP (antero-posterior ) , decubitus , supine
,oblique
• Inspiratory , Expiratory
• Lordotic , apical , penetrated
• Portable / mobile radiographs

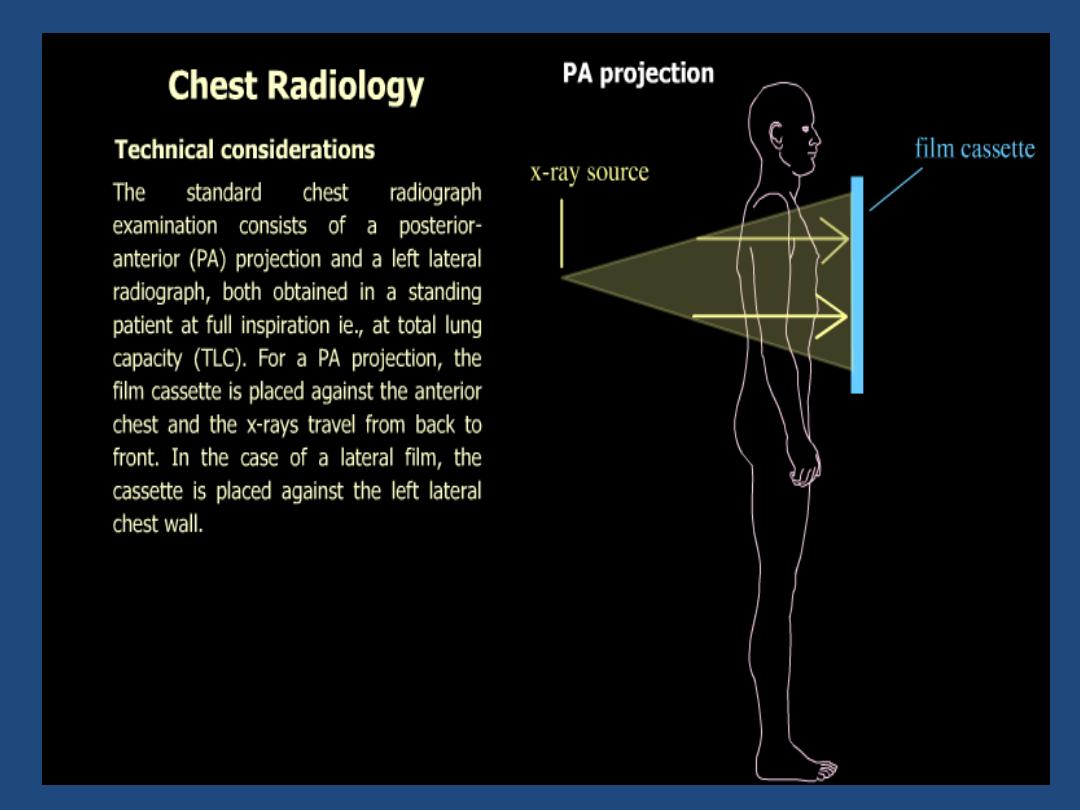
PA VIEW
The patient faces the film chin up with
shoulders rotated forwards to displace the
scapulae from the lung fields .Exposure is
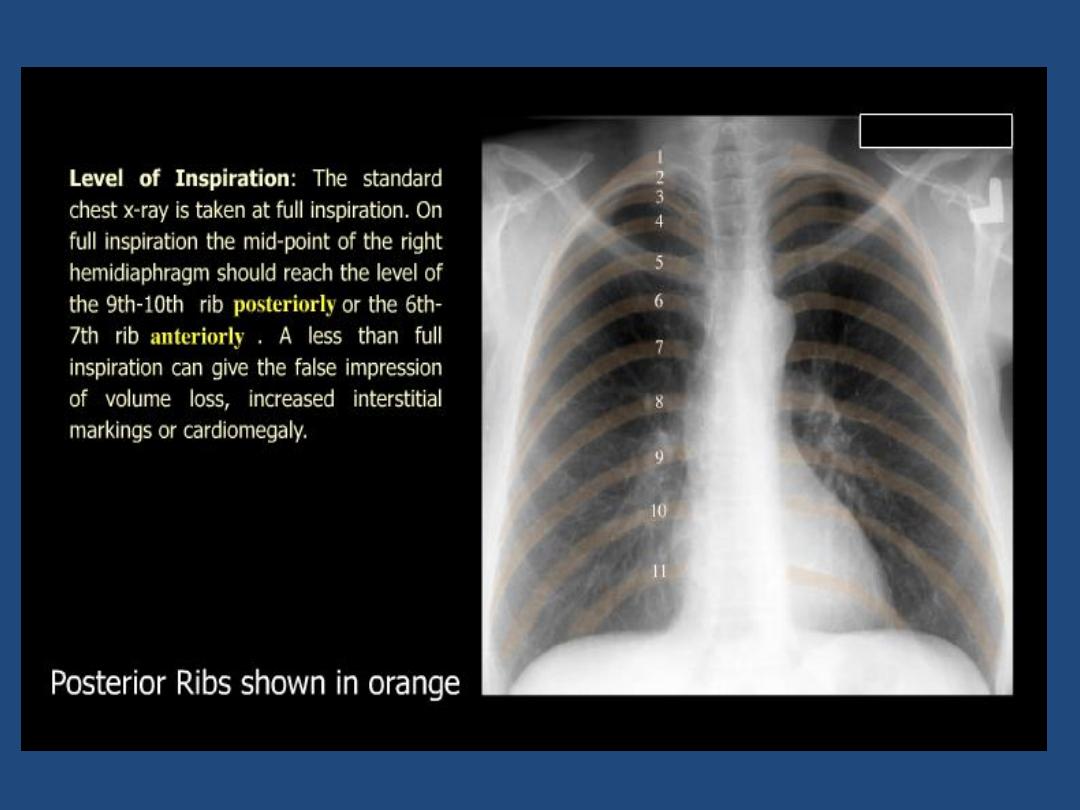
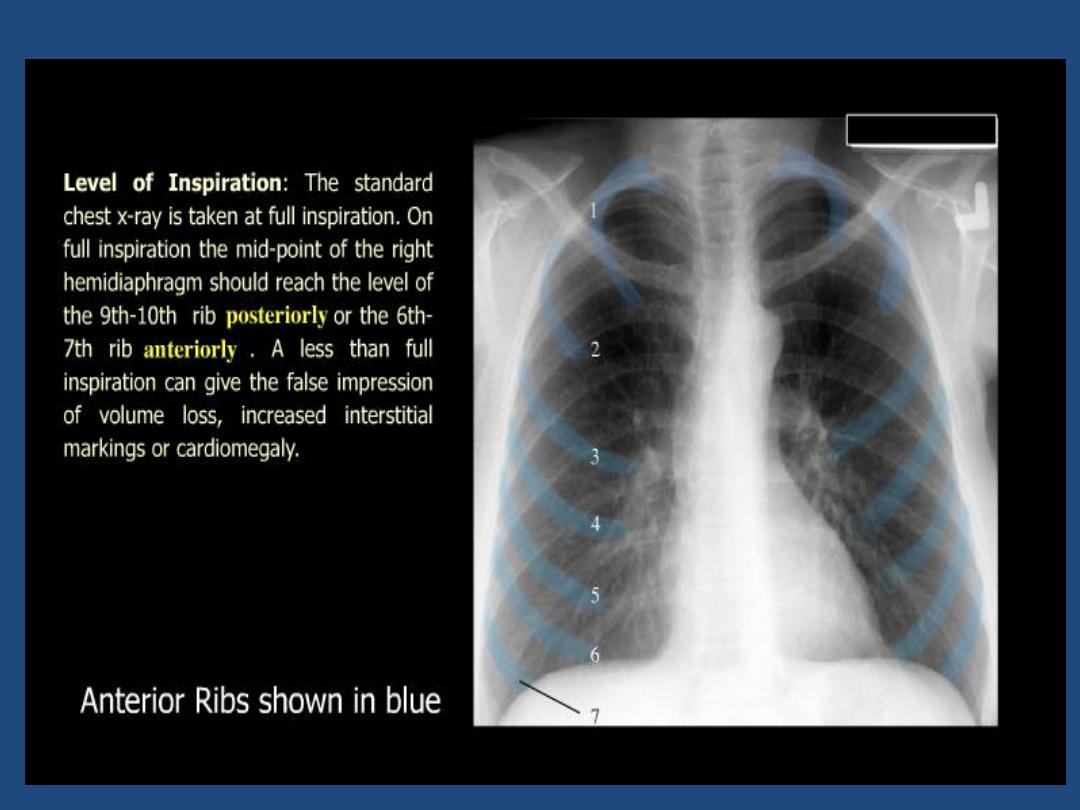
made on full inspiration for optimum
visualization of the bases , centering at T5.
The breasts should be compressed against
the film to prevent them obscuring the lung
bases

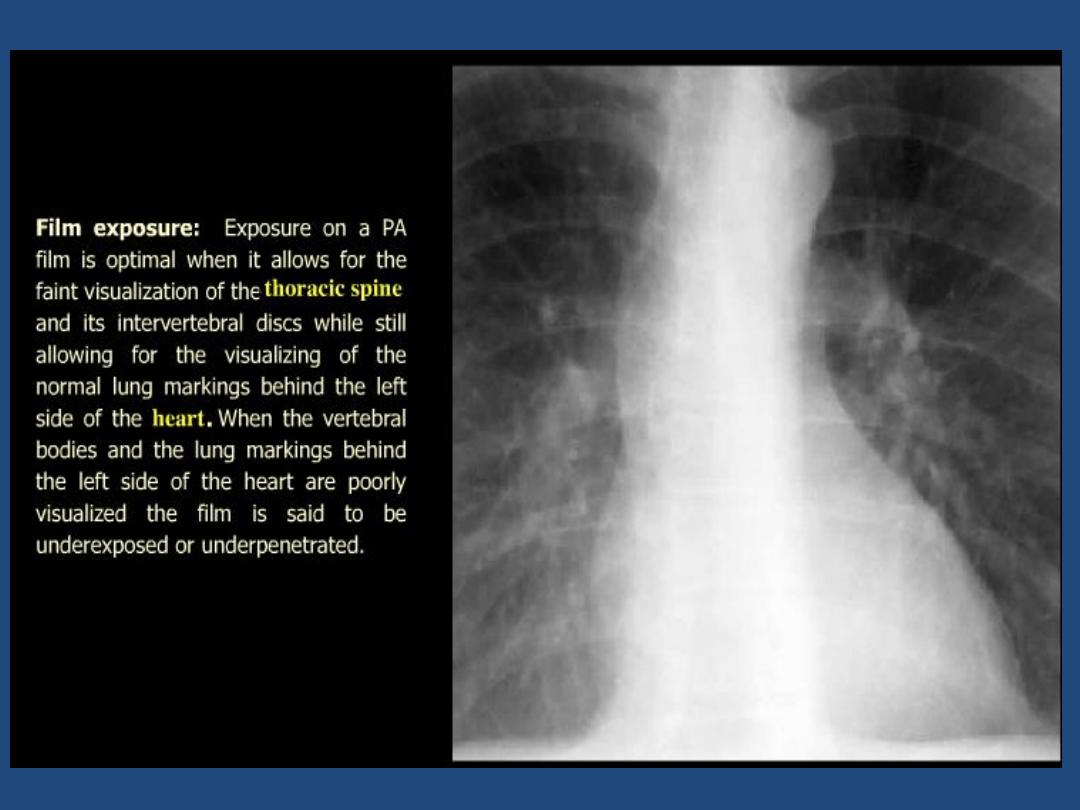
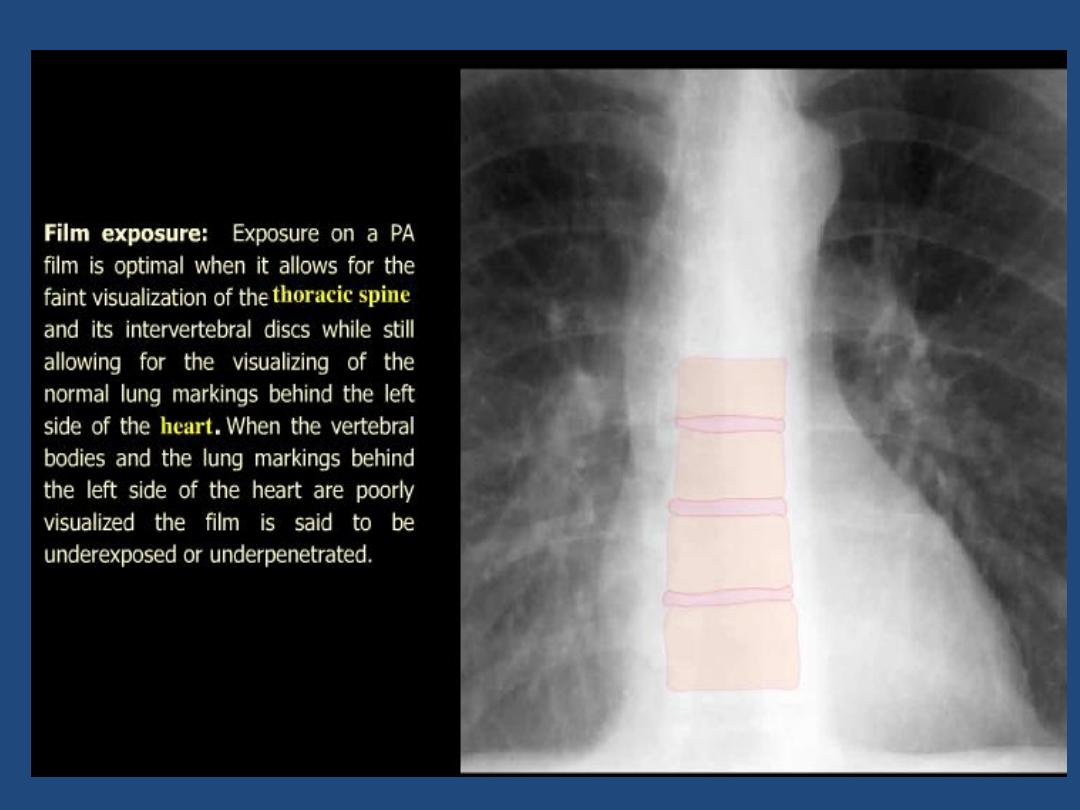
Low kVp ( 60-80 kV ) :
produces a high-contrast
film , with miliary shadowing and calcification
being more clearly seen than on a high kV film
High kVp ( 120-170 kV):
these use for large
patient with grid reduces scattering and FFD
is of 1.85 cm ( 6 feet ) reduces magnification
and produces sharper image .The film with
high kV are of lower contrast and with increase
visualization of the hidden of the lung due to
better penetration of overlying structure, the
bones and pulmonary calcification are less
well seen.
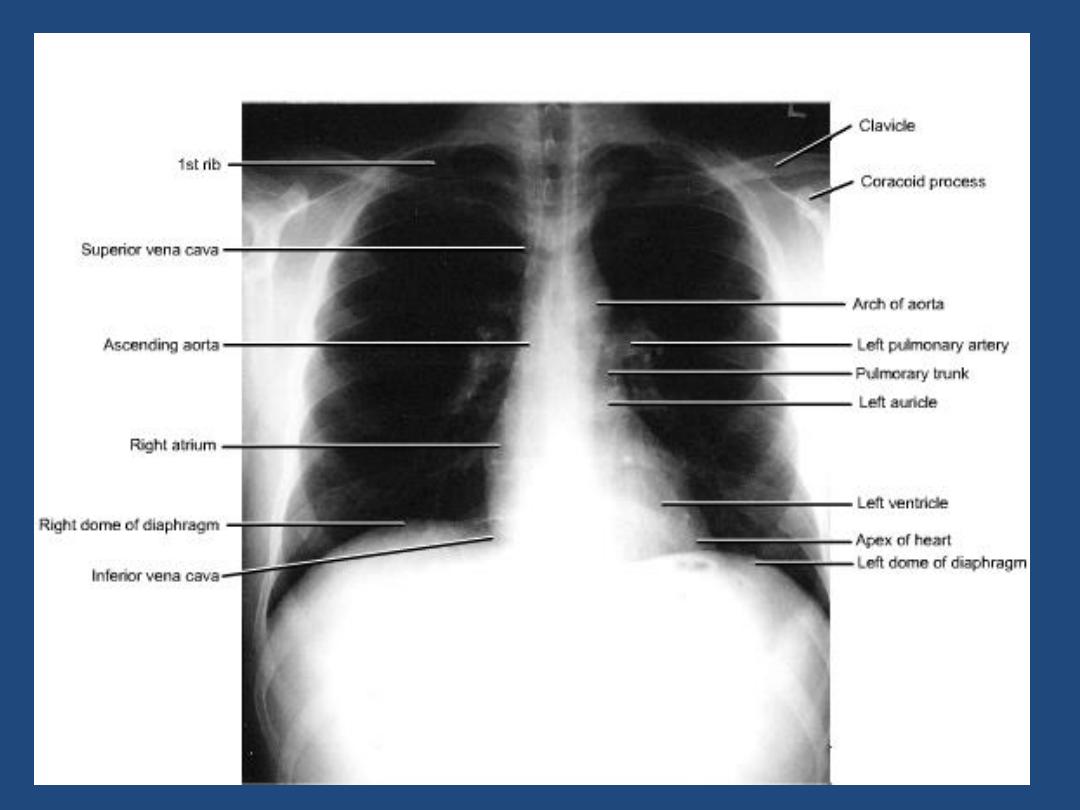
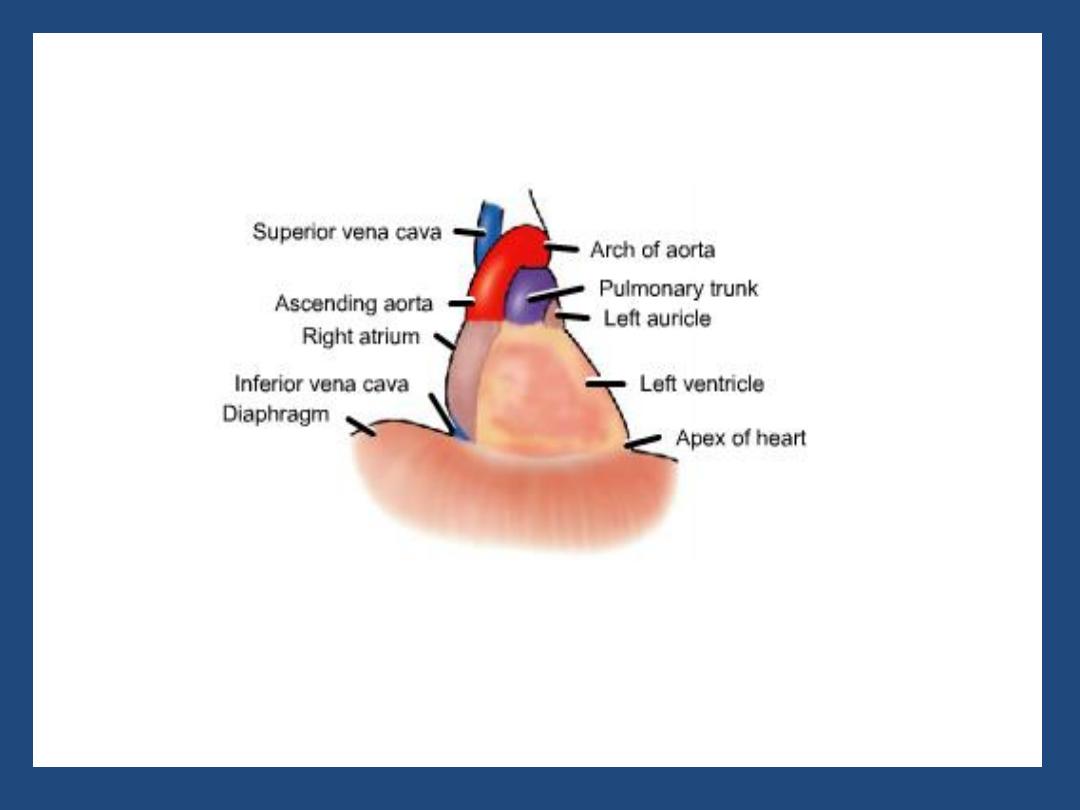
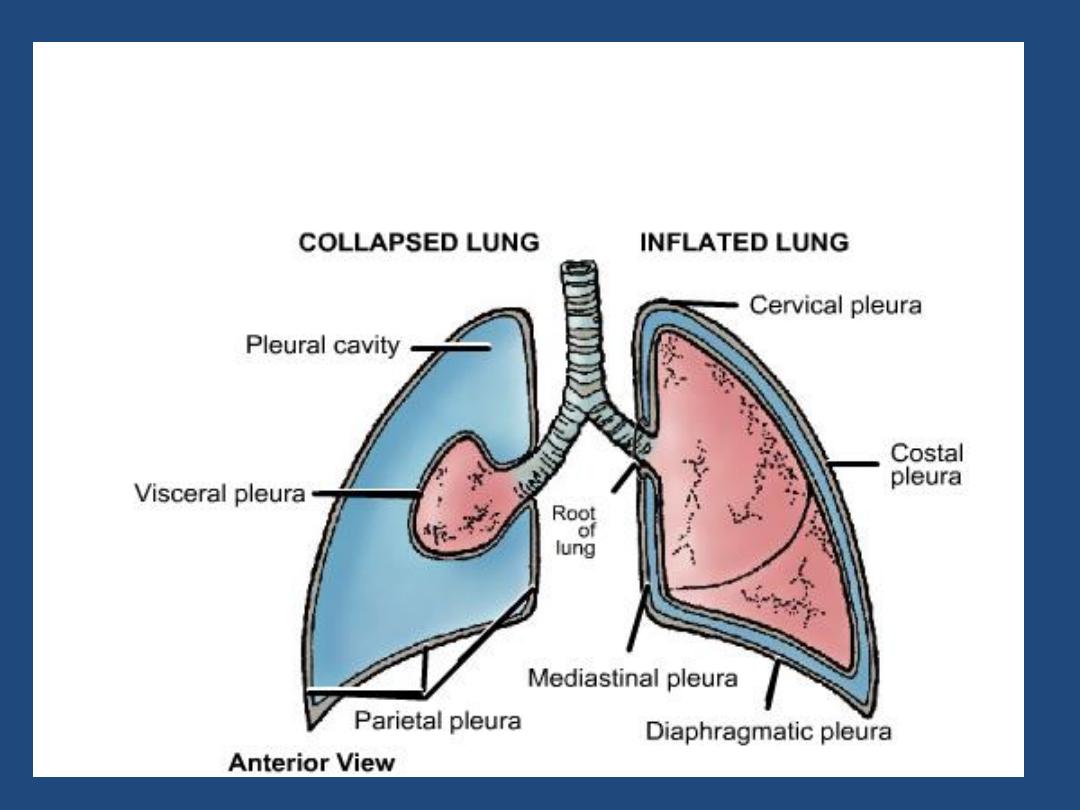
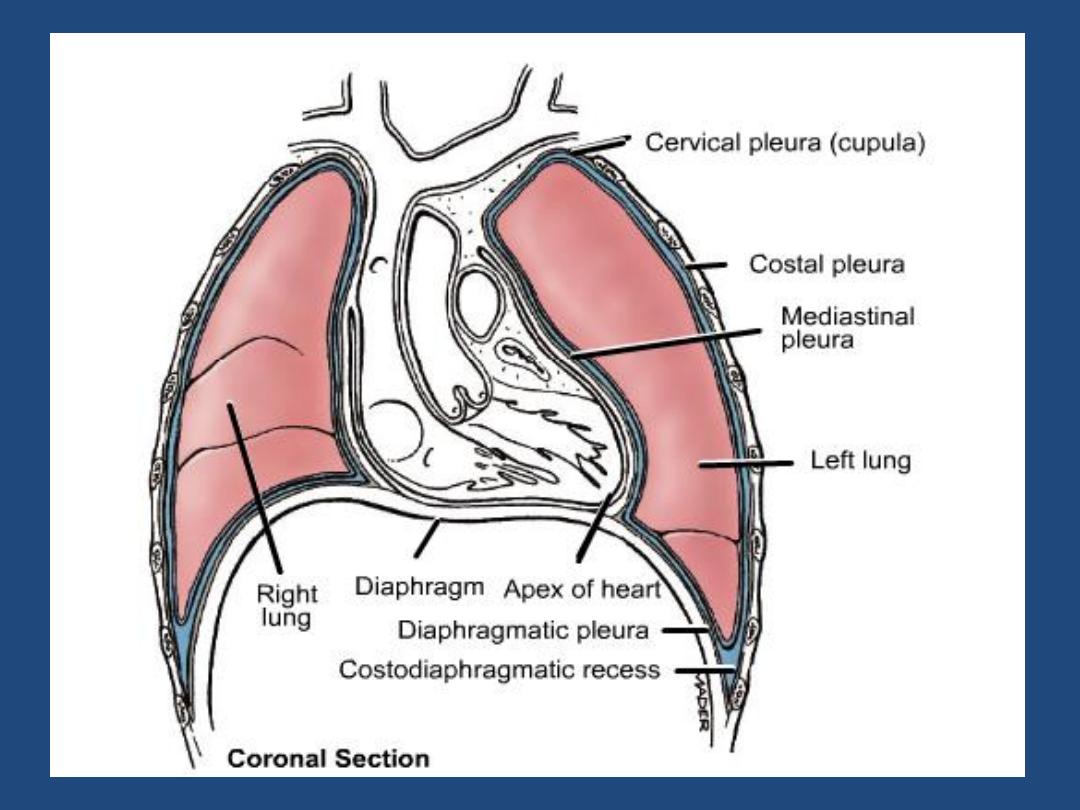

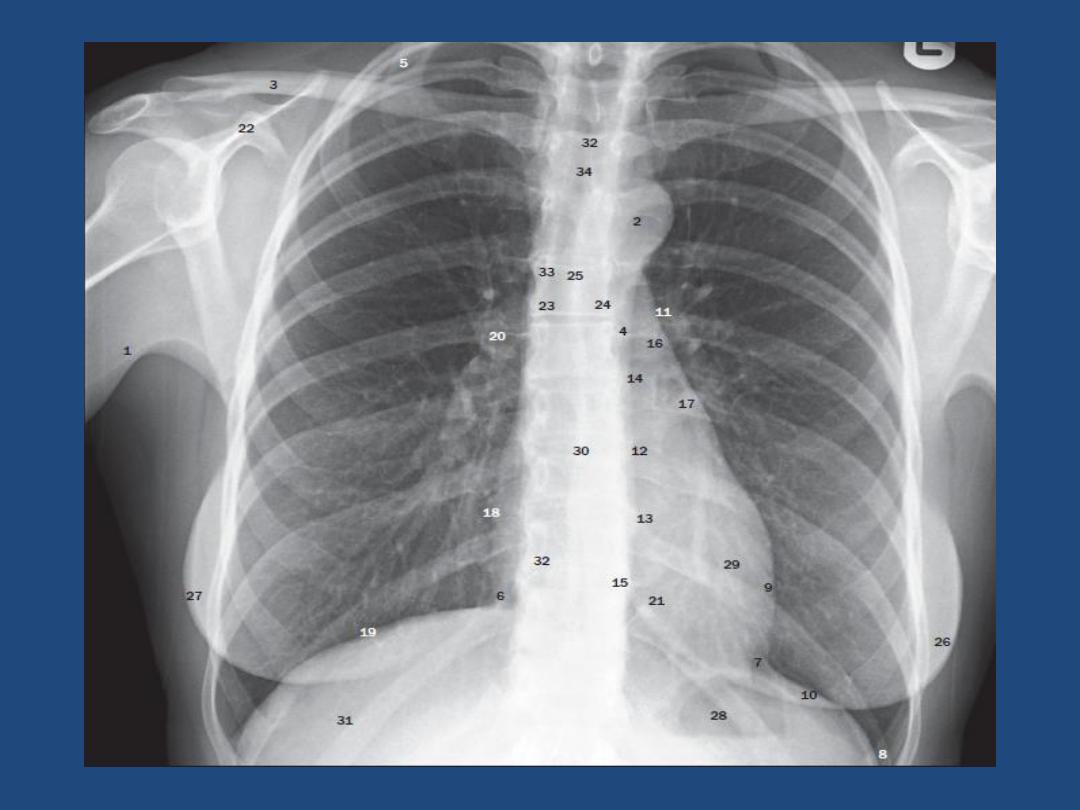
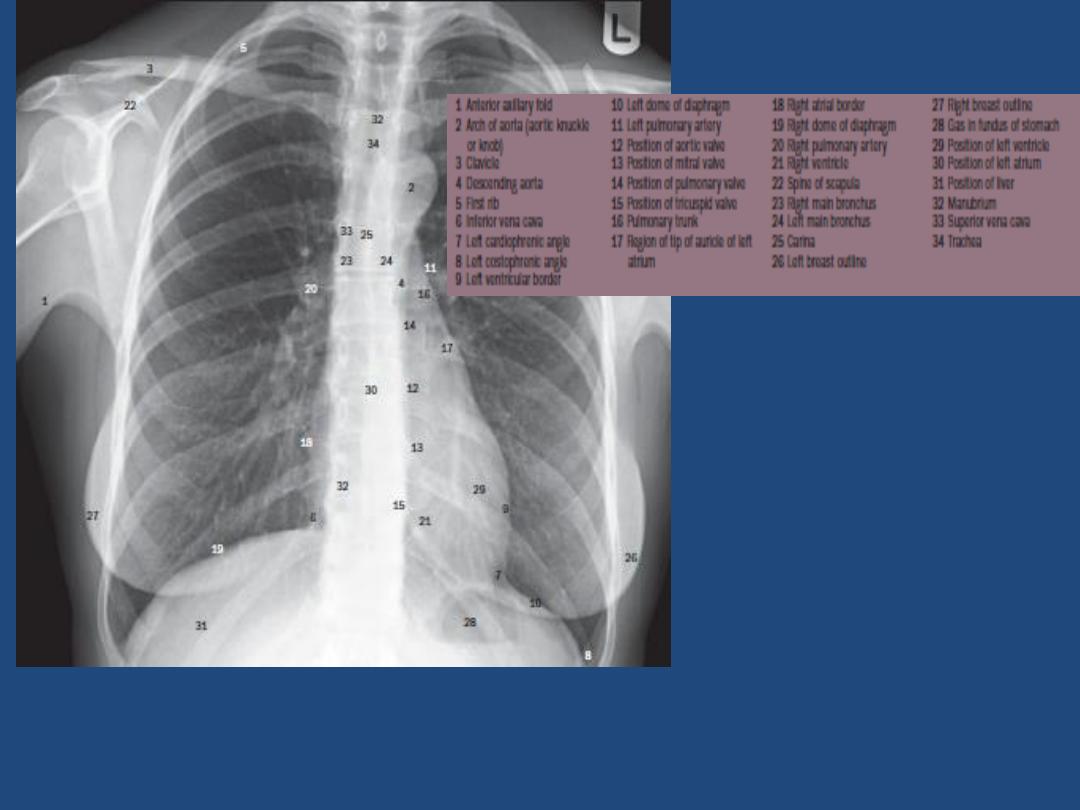
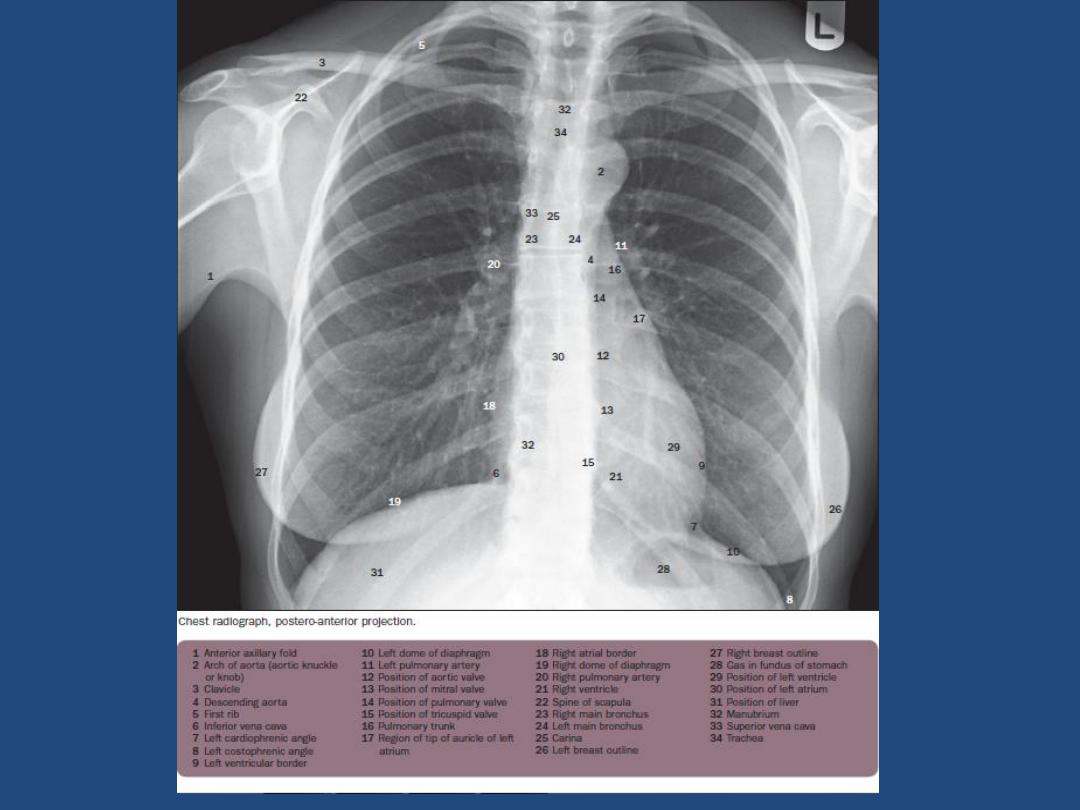
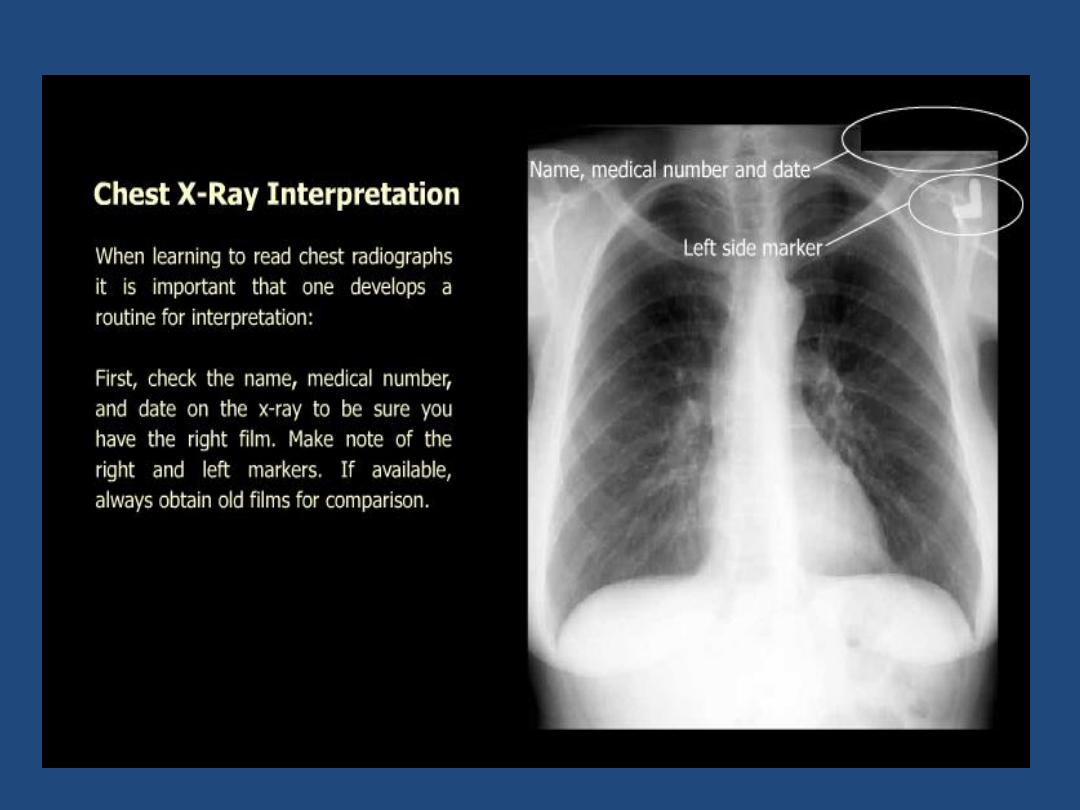
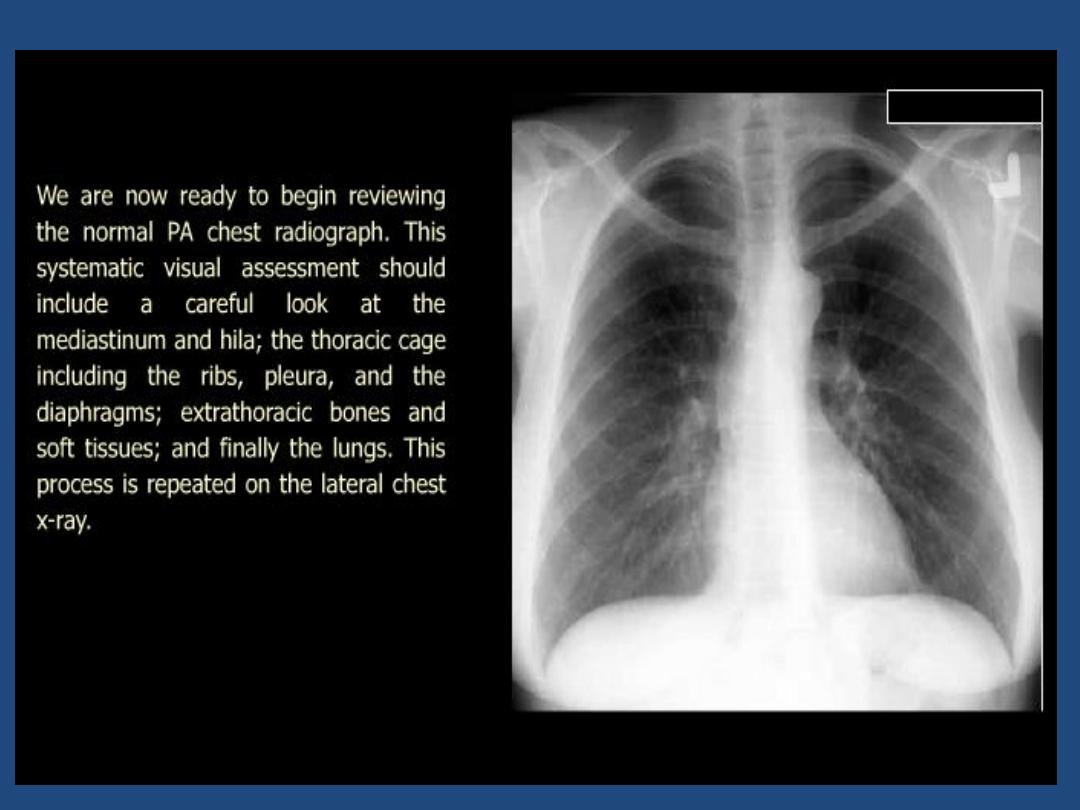
HOW TO VIEW THE PA- FILM
A suggested scheme is as follow, examining each
point in turn
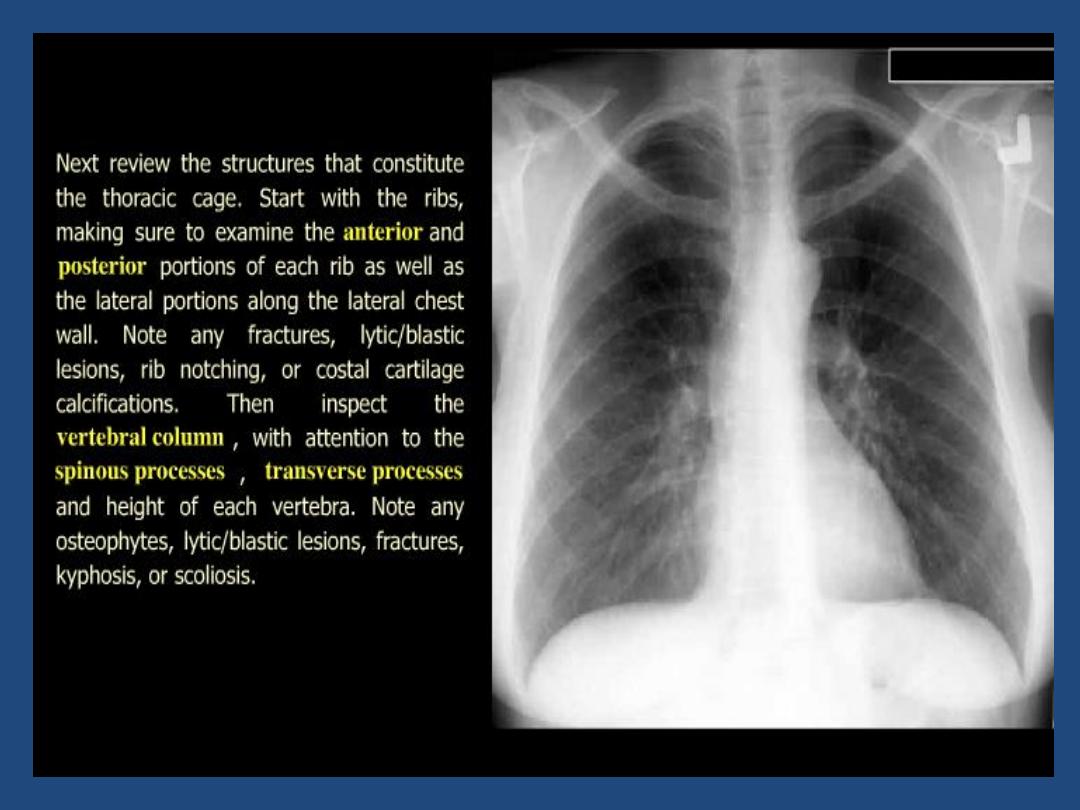
•
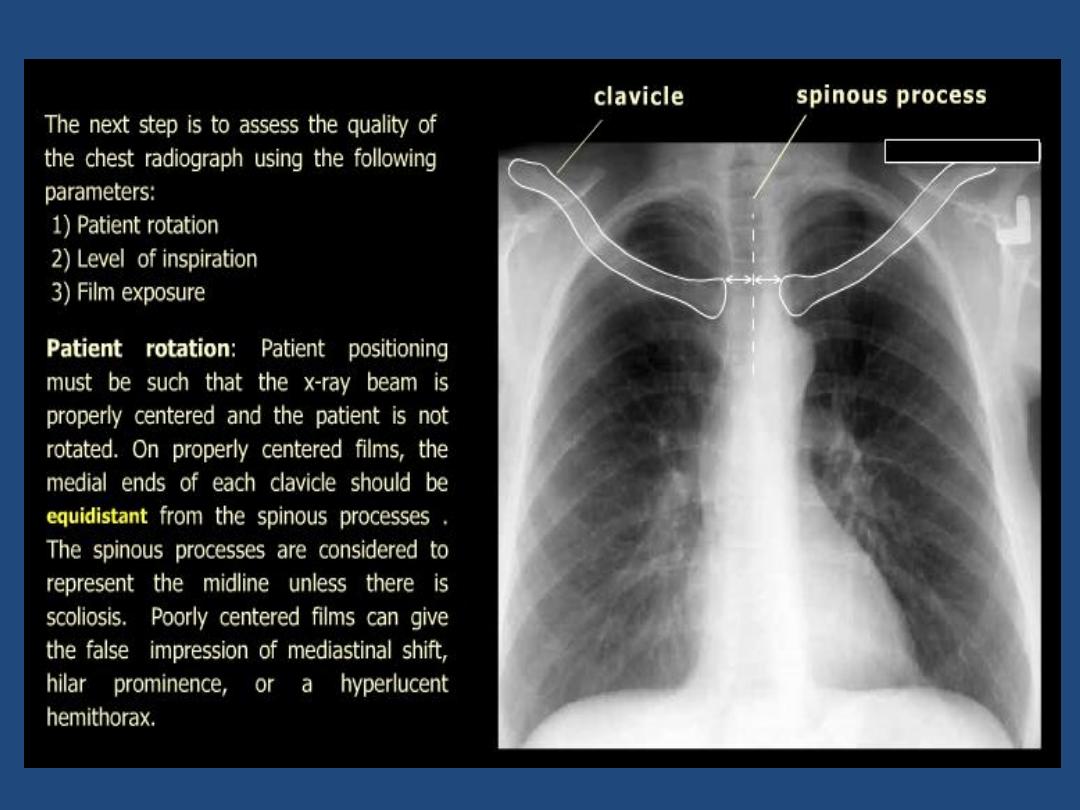
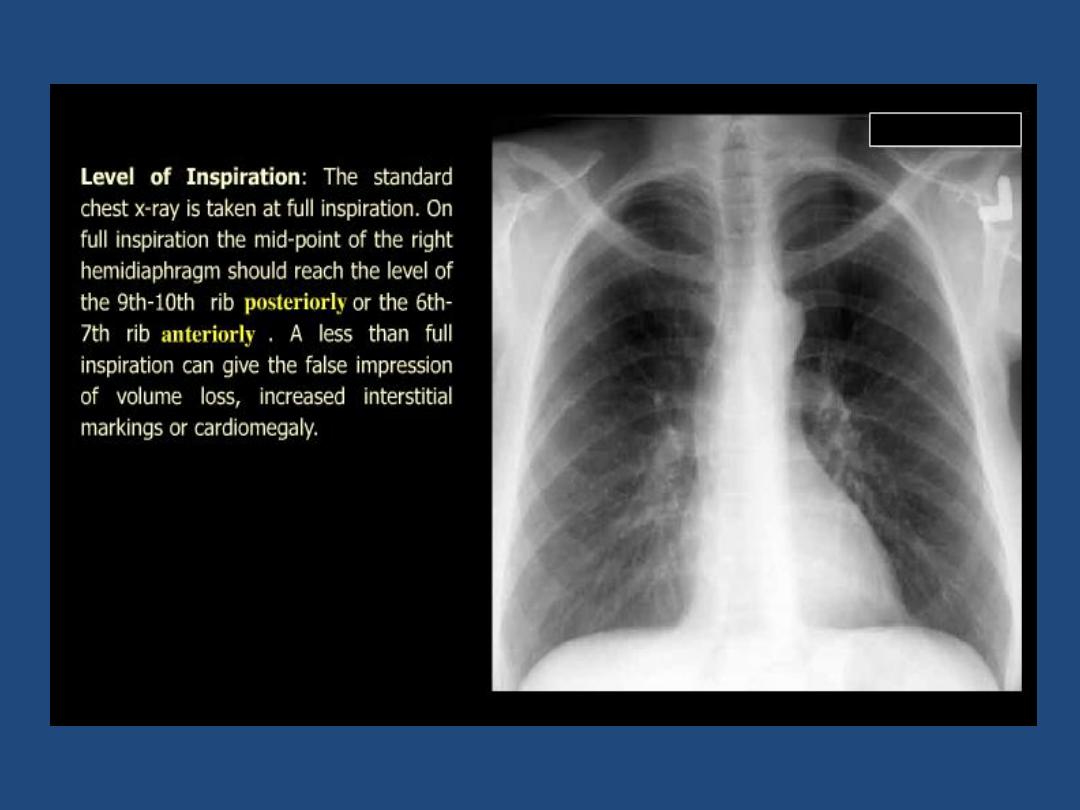
Technical : centering , position , markers , degree of
inspiration
•
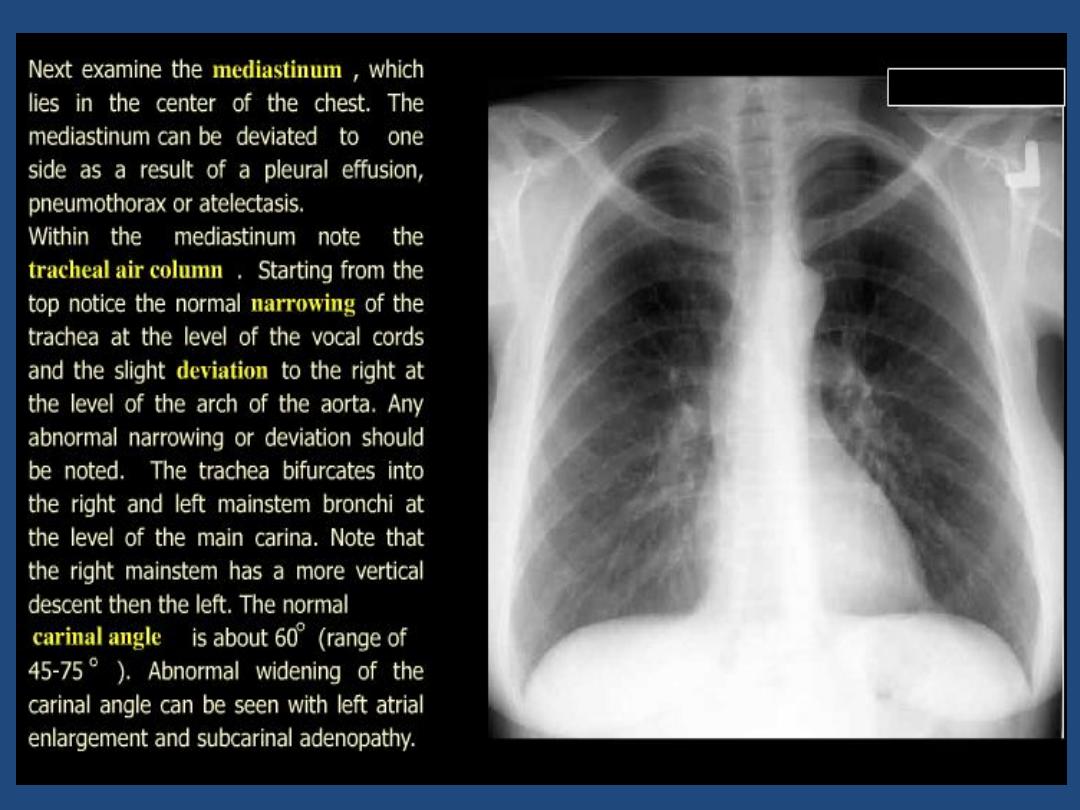
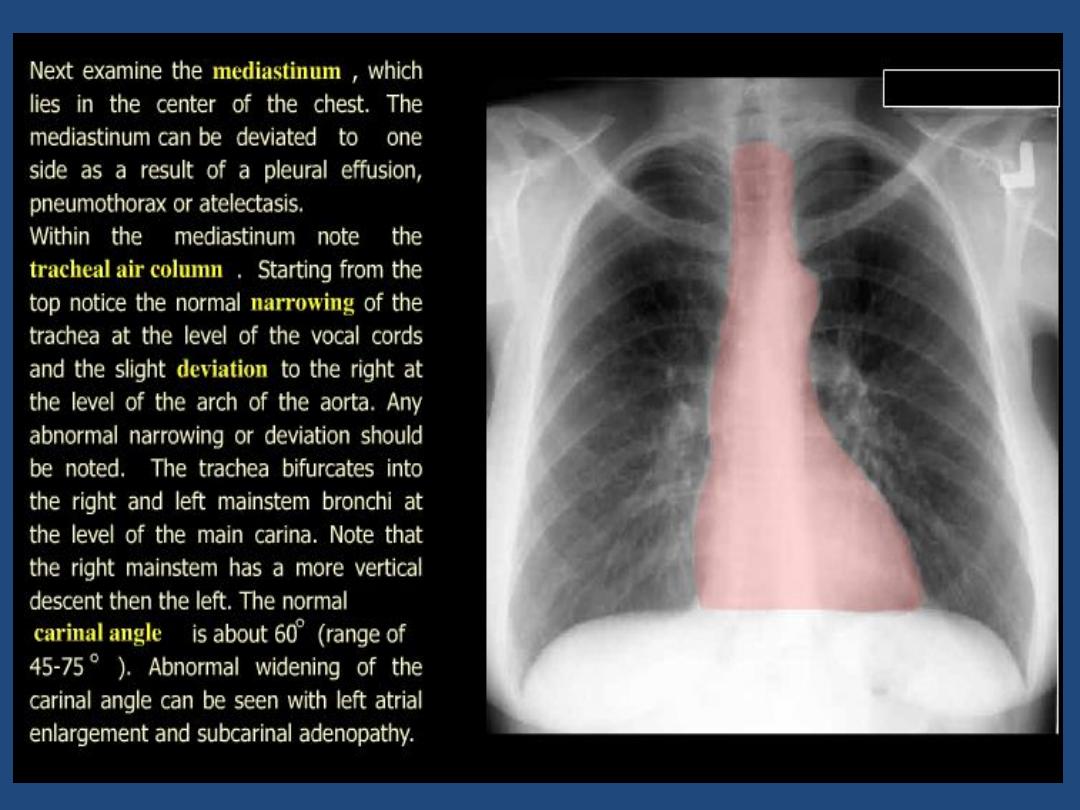
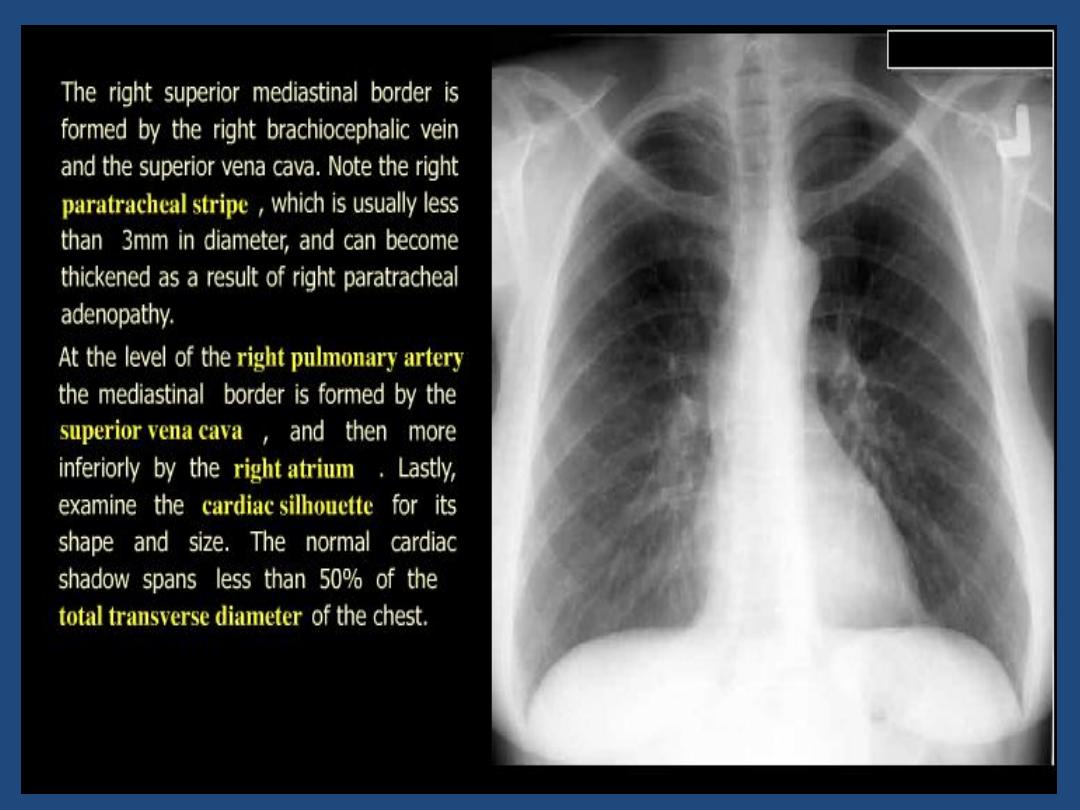
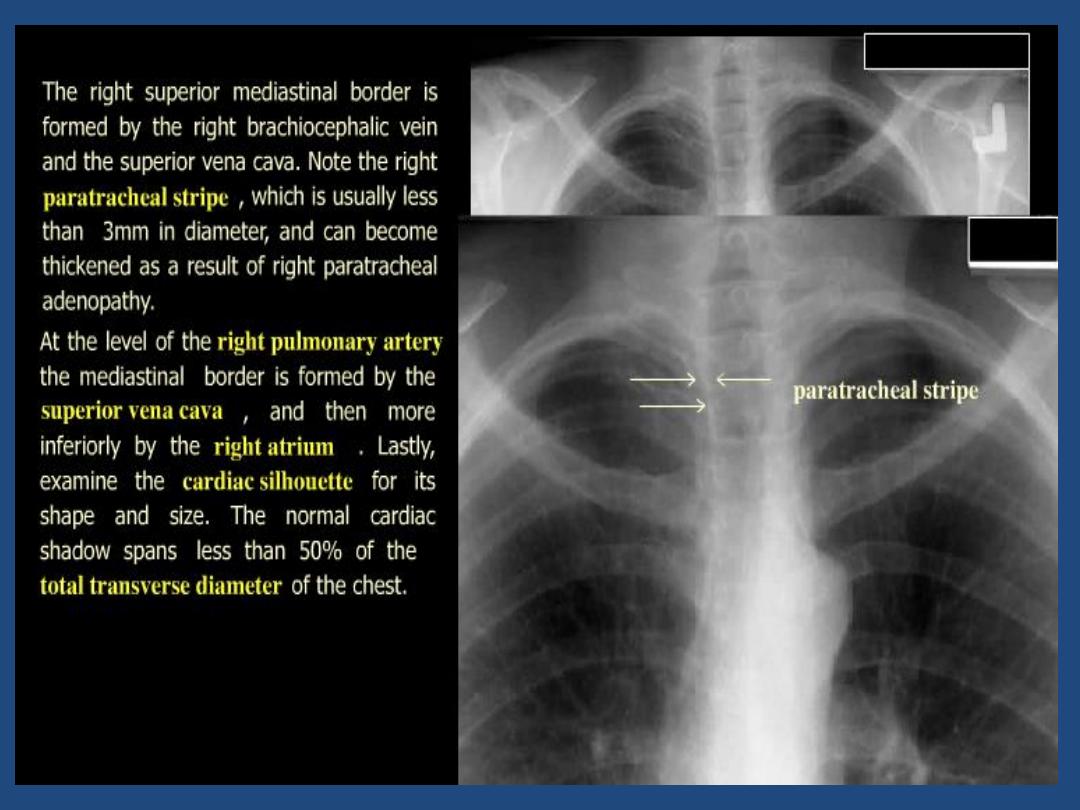
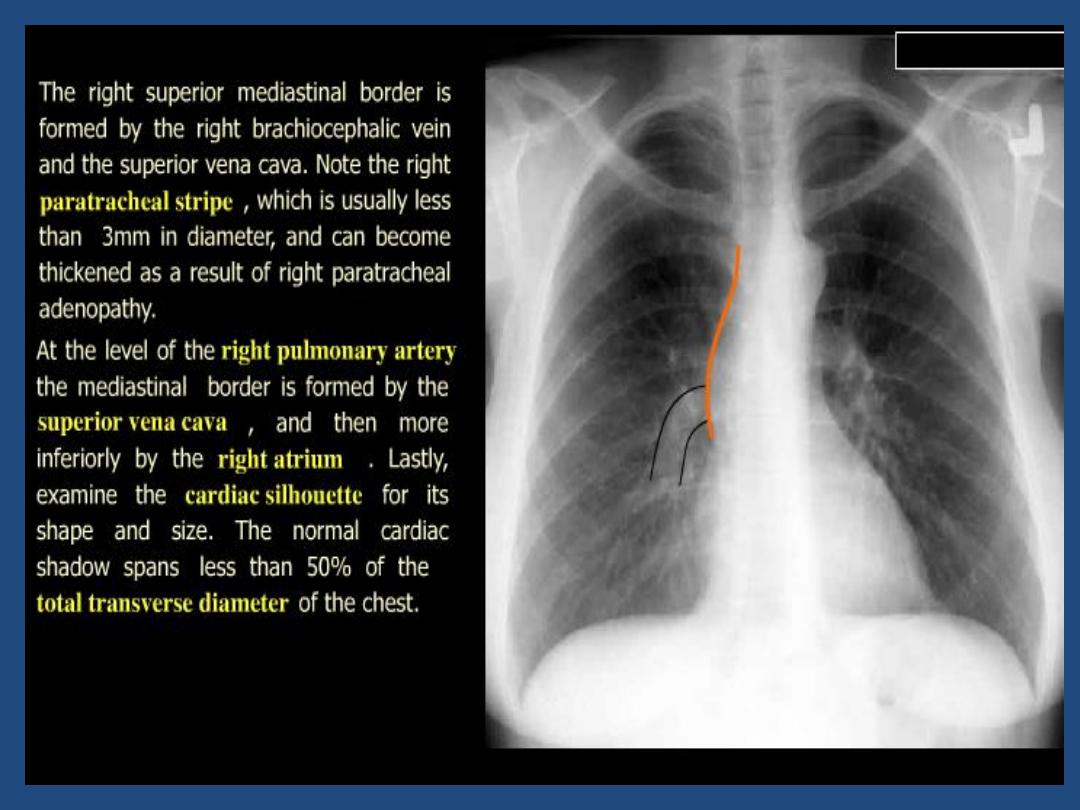
Trachea : position and outline
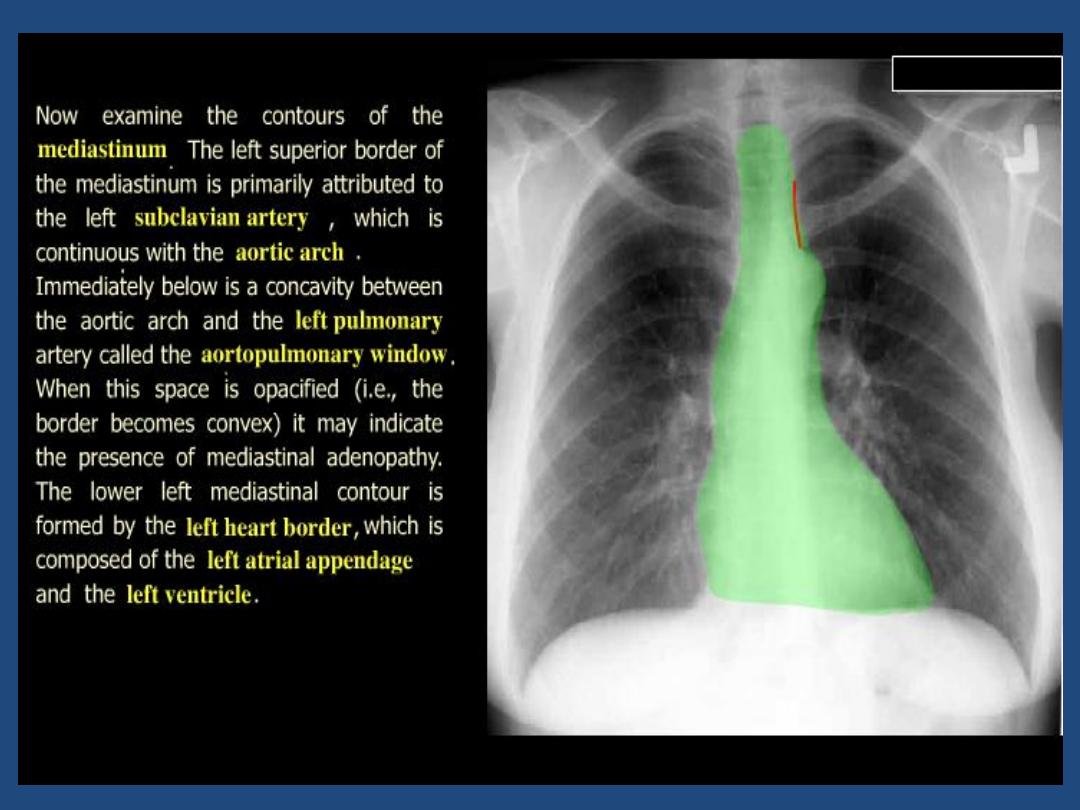
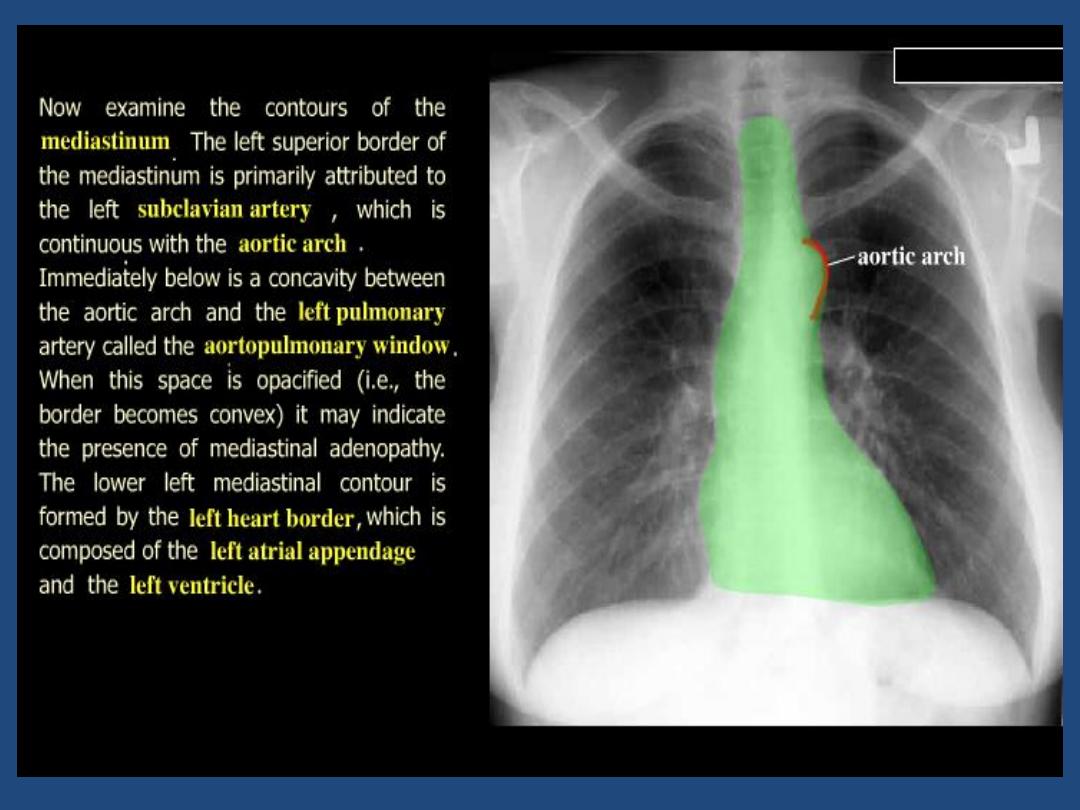
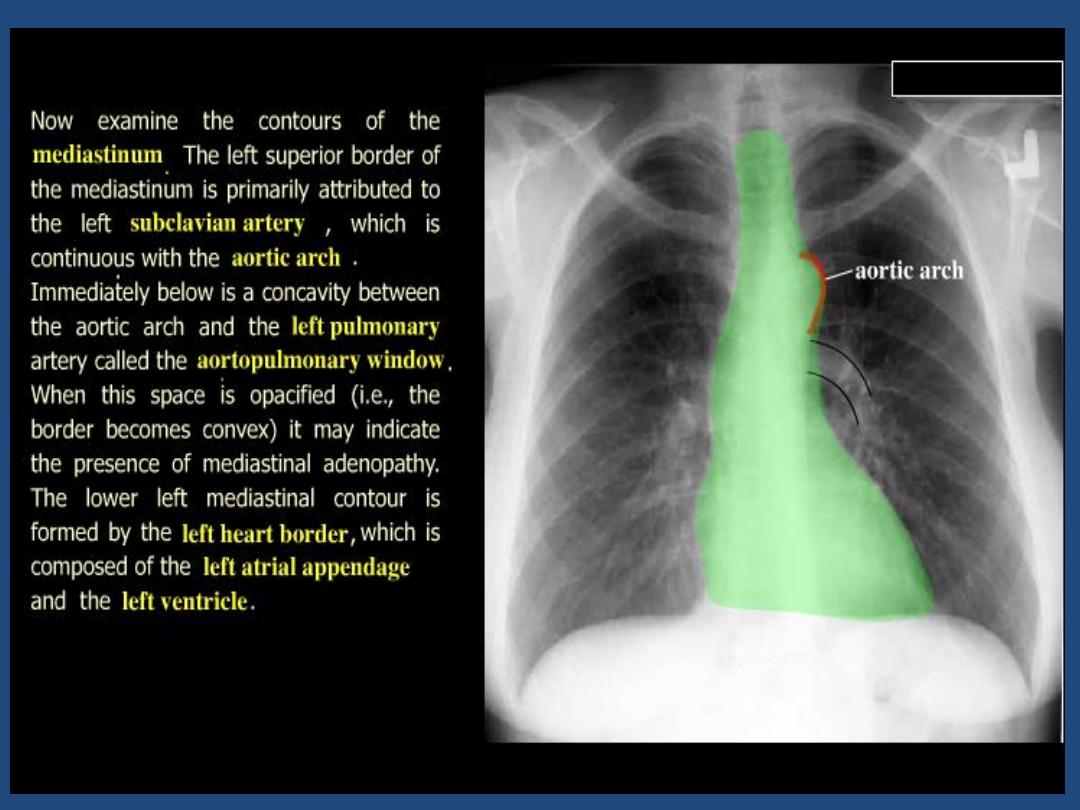
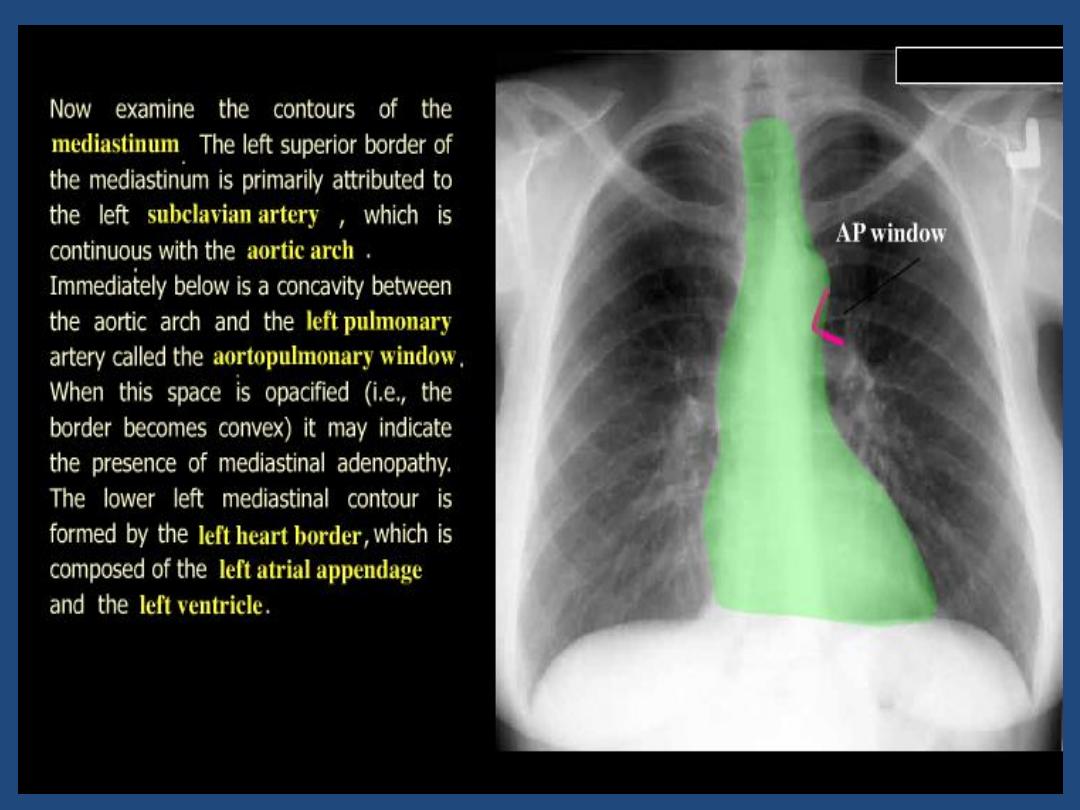
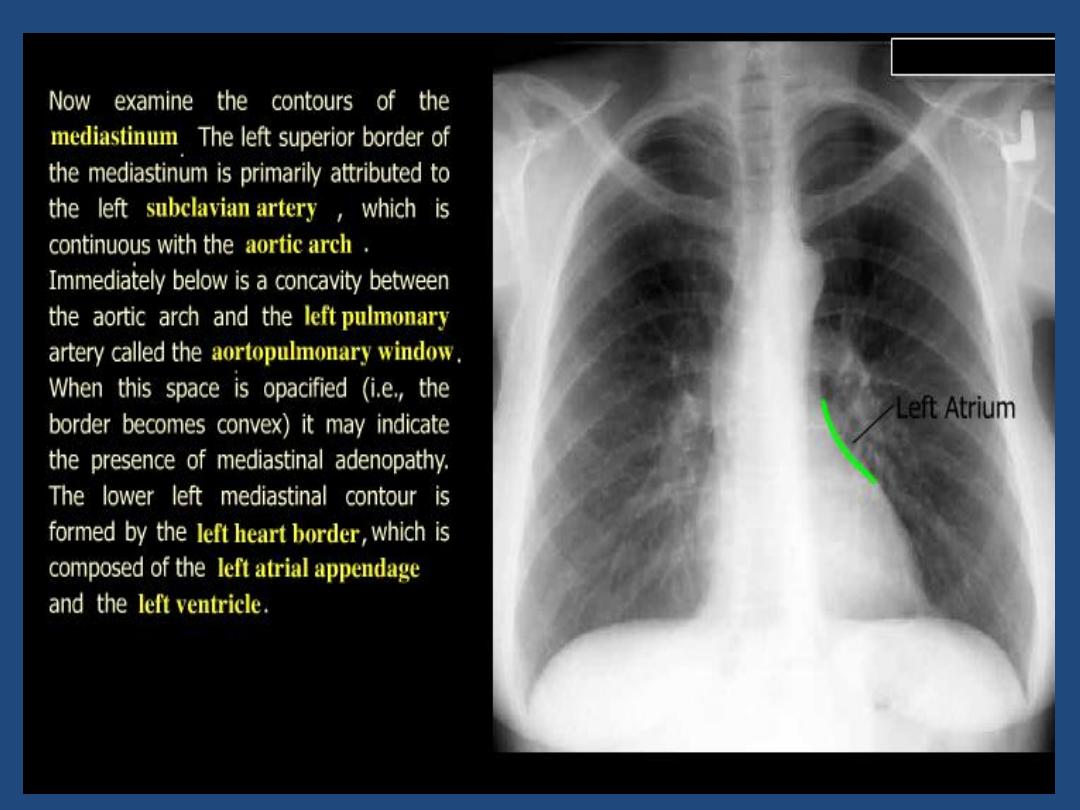
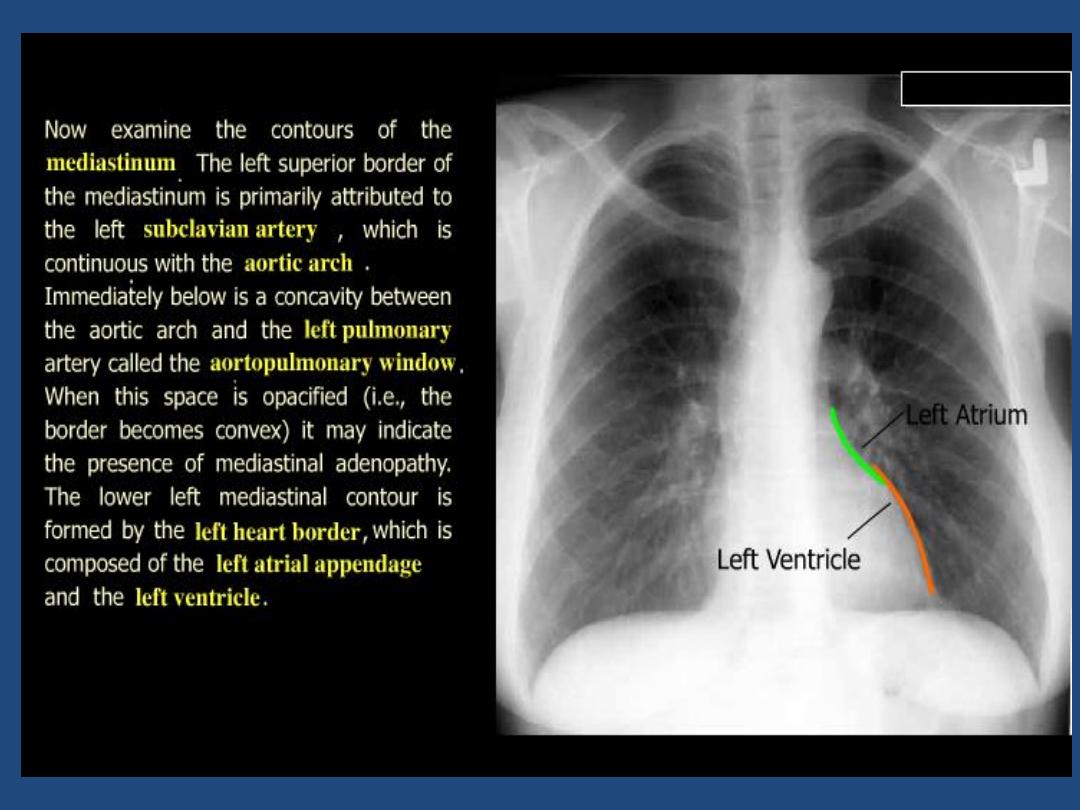
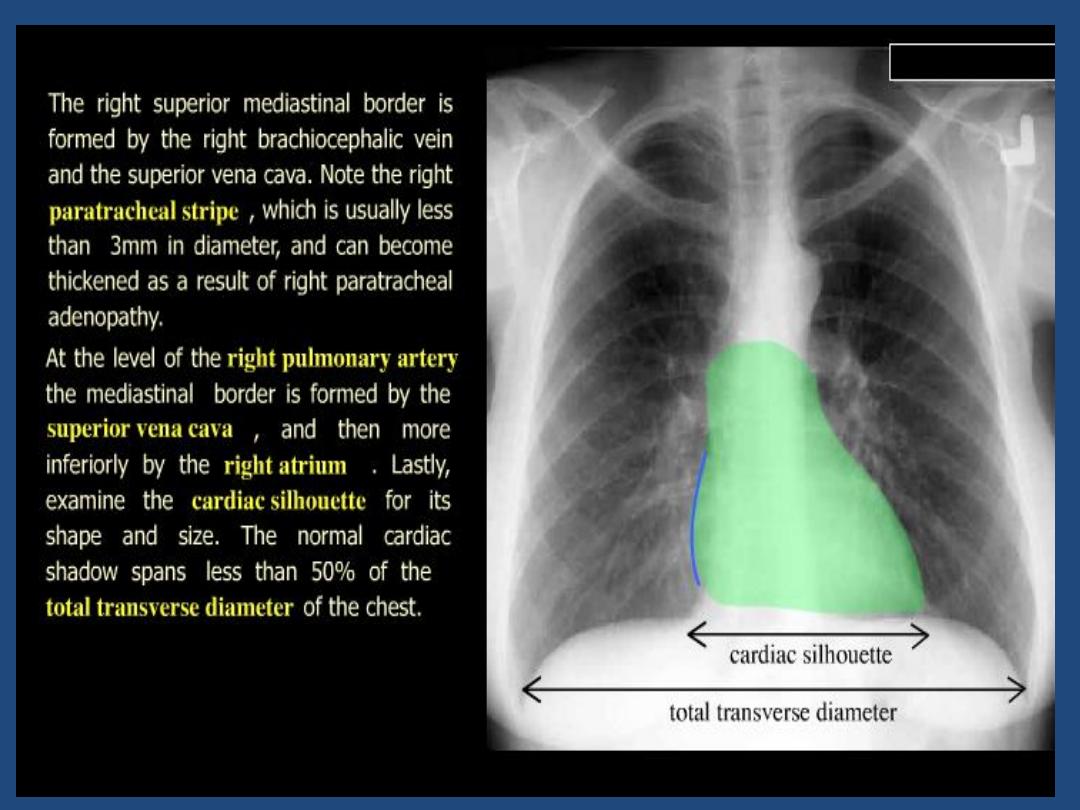
•
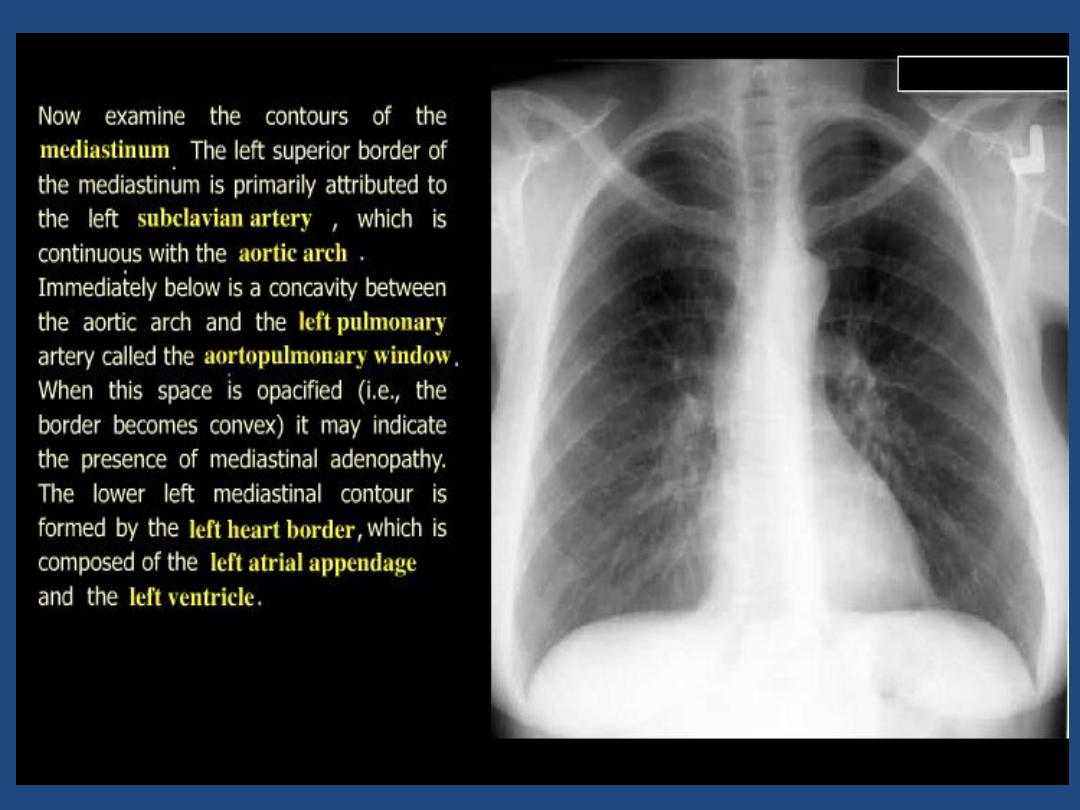
Heart and mediastinum :size , shape , displacement
•
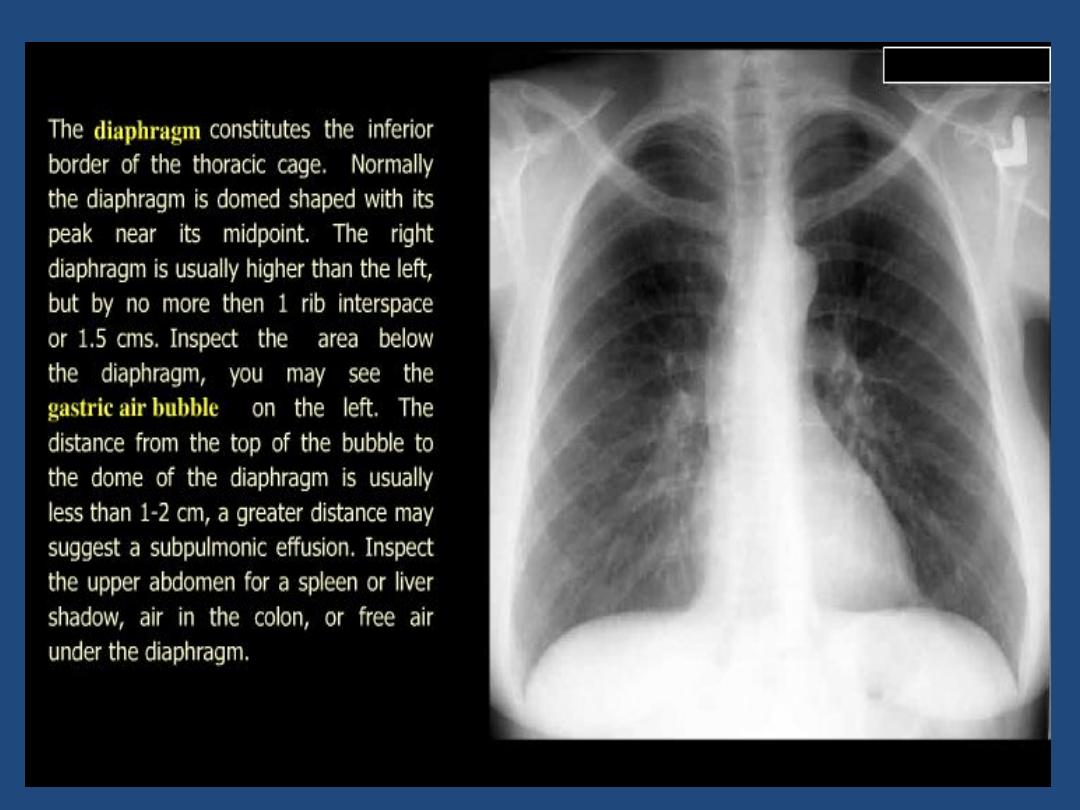
Diaphragm : outline , shape ,relative position
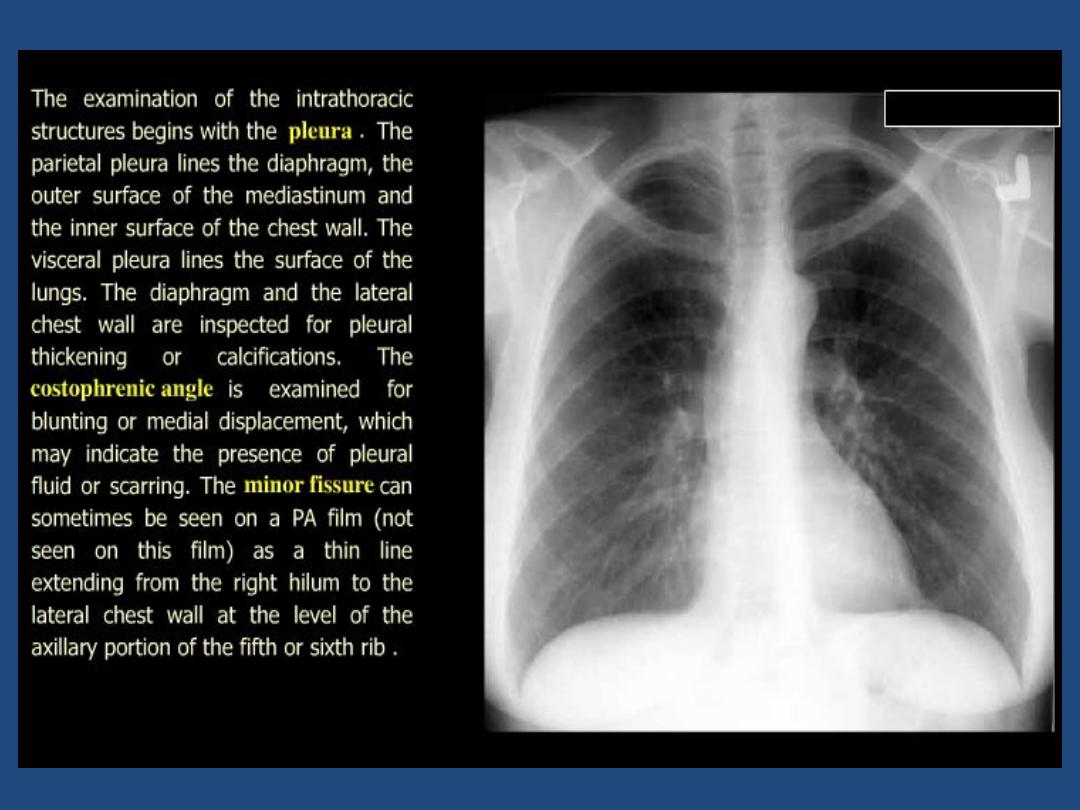
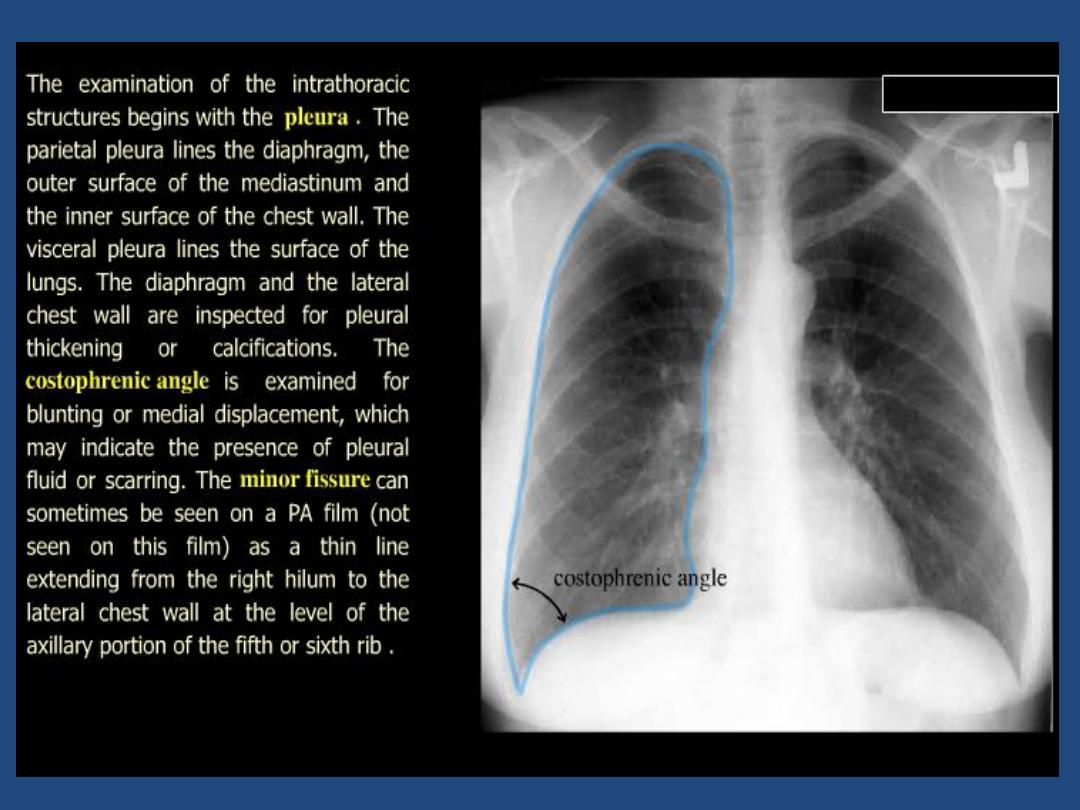
•
Pleura : position of horizontal fissure ,costophrenic and
cardiophrenic angles
•
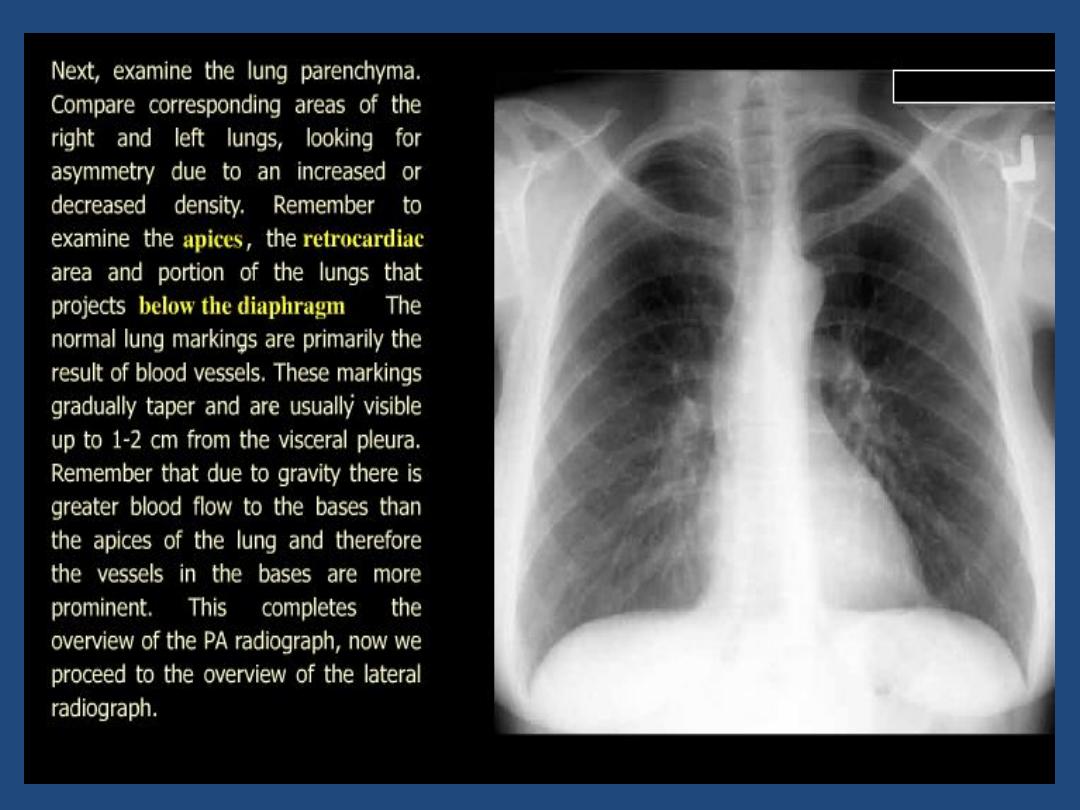
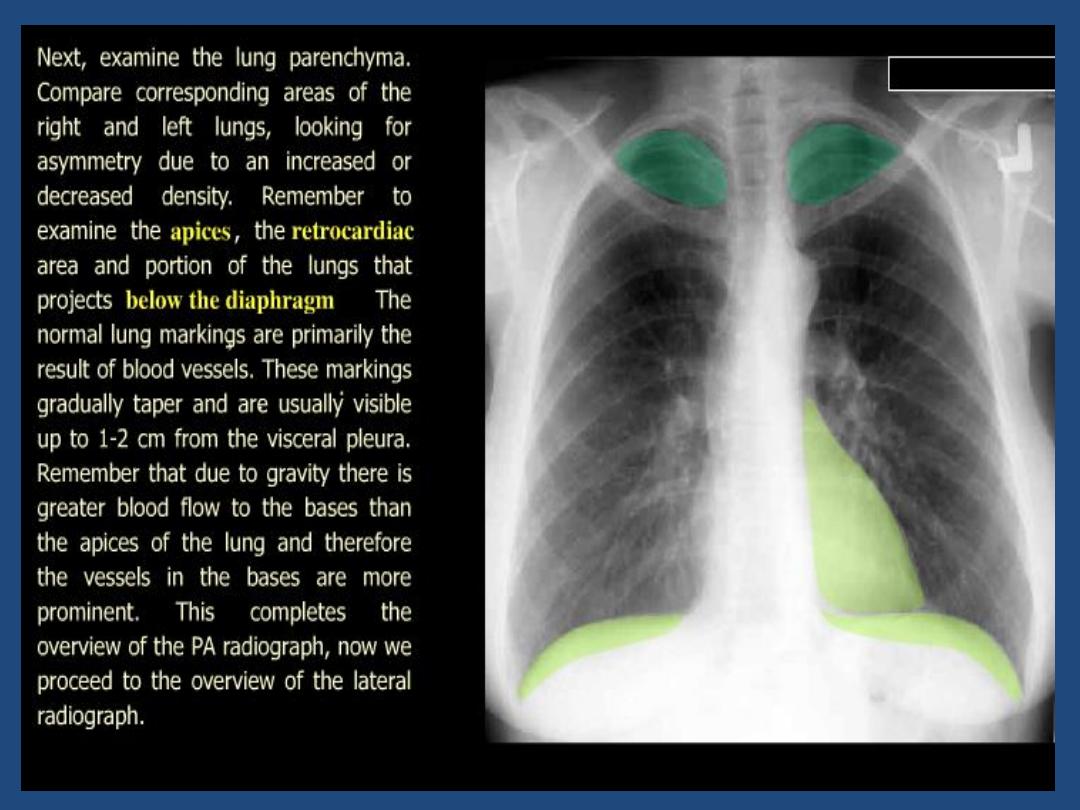
Lung fields : local or generalized abnormality , compare
the two sides for lung markings and translucency

•
Hidden areas : - Apices
- Diaphragm
- Mediastinum , hila
- Bones
•
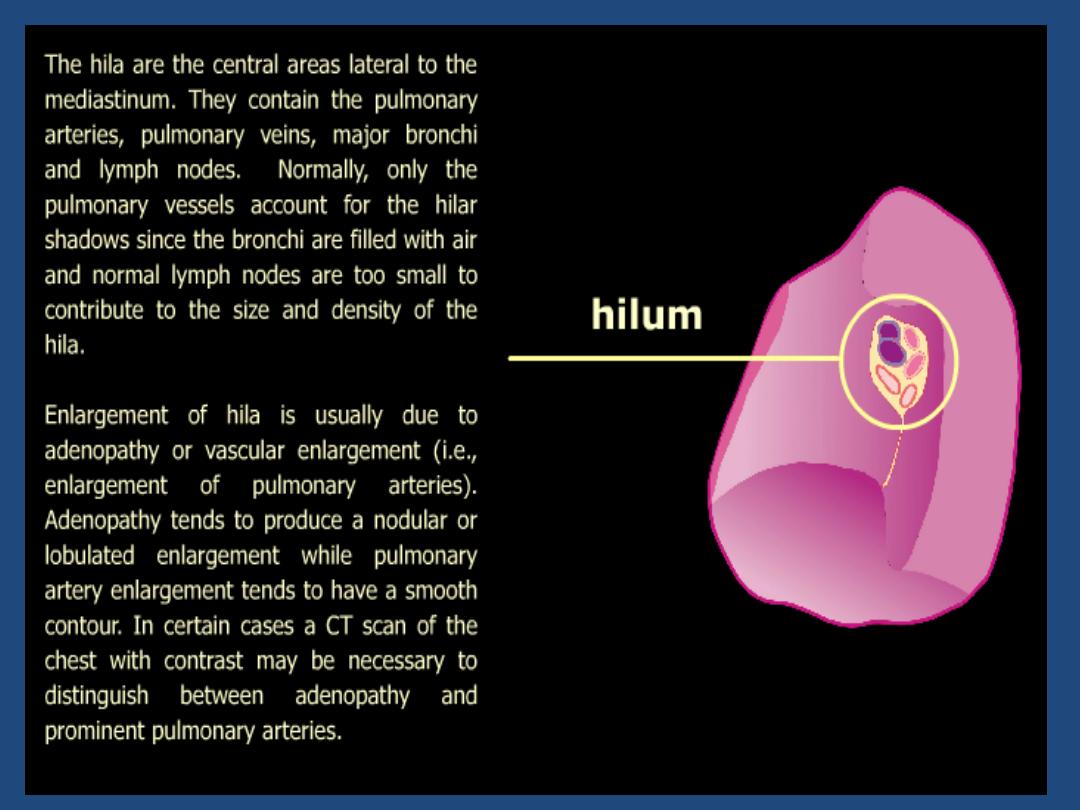
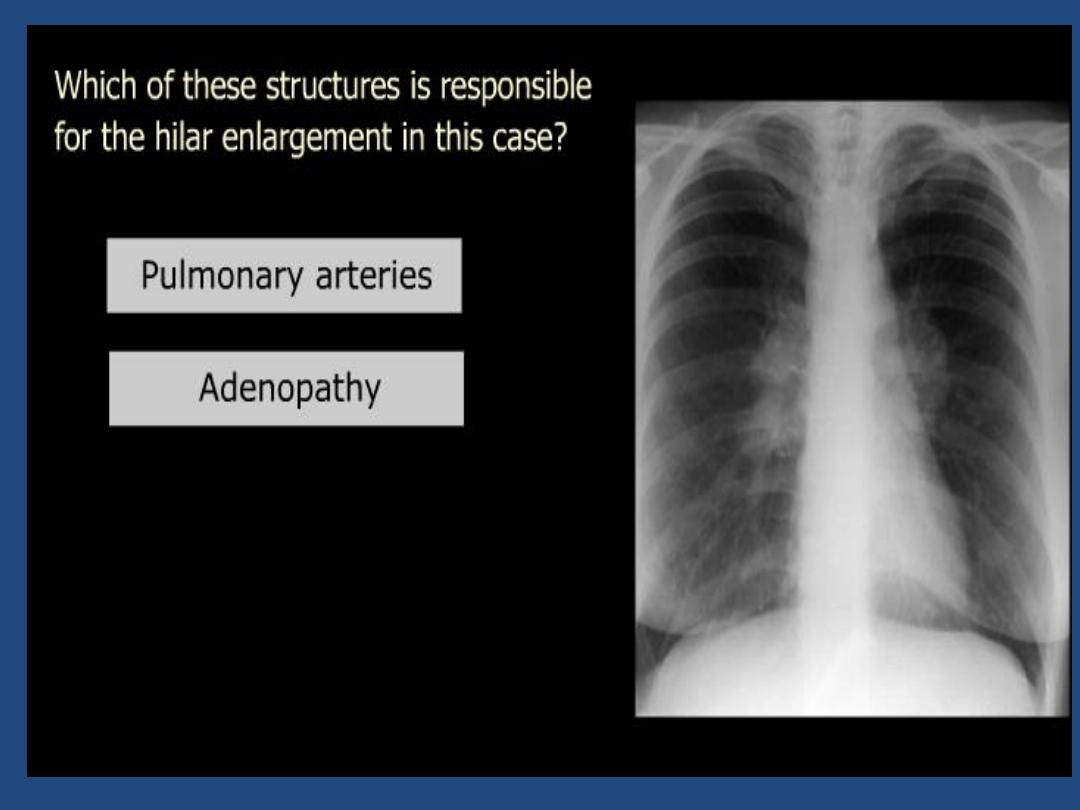
Hila : Density , position , shape
•
Below diaphragm : Gas shadow , calcification
•
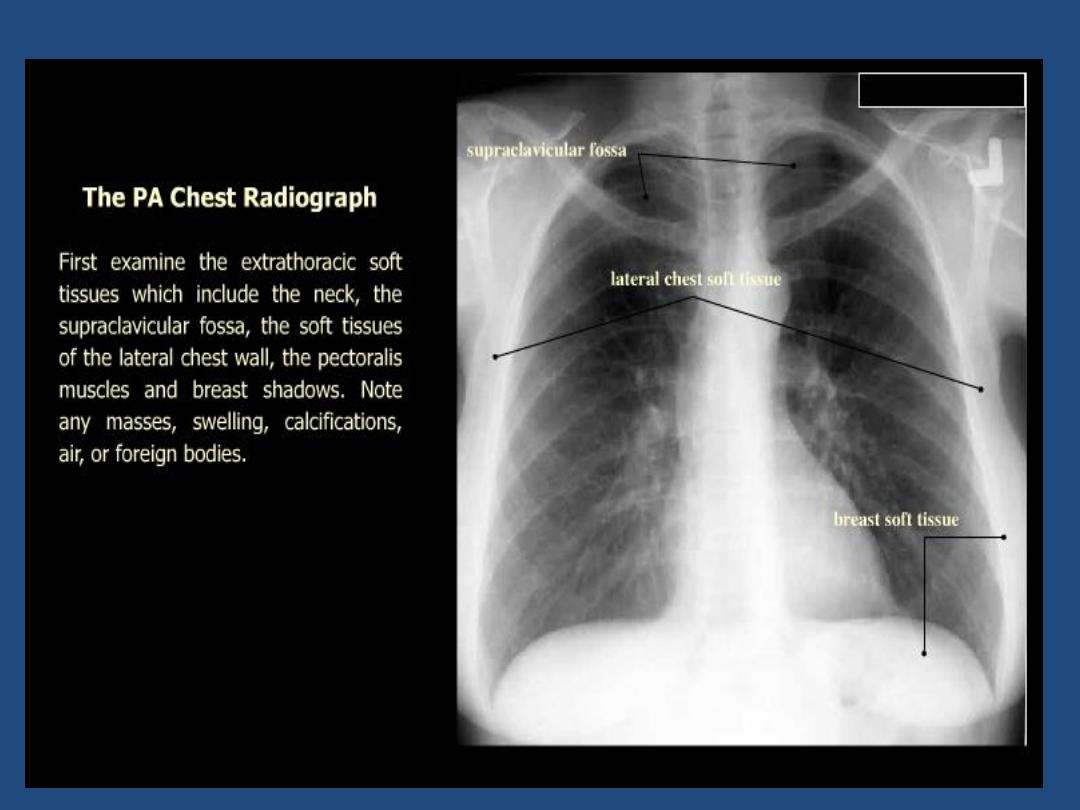
Soft tissues : Mastectomy , densities
•
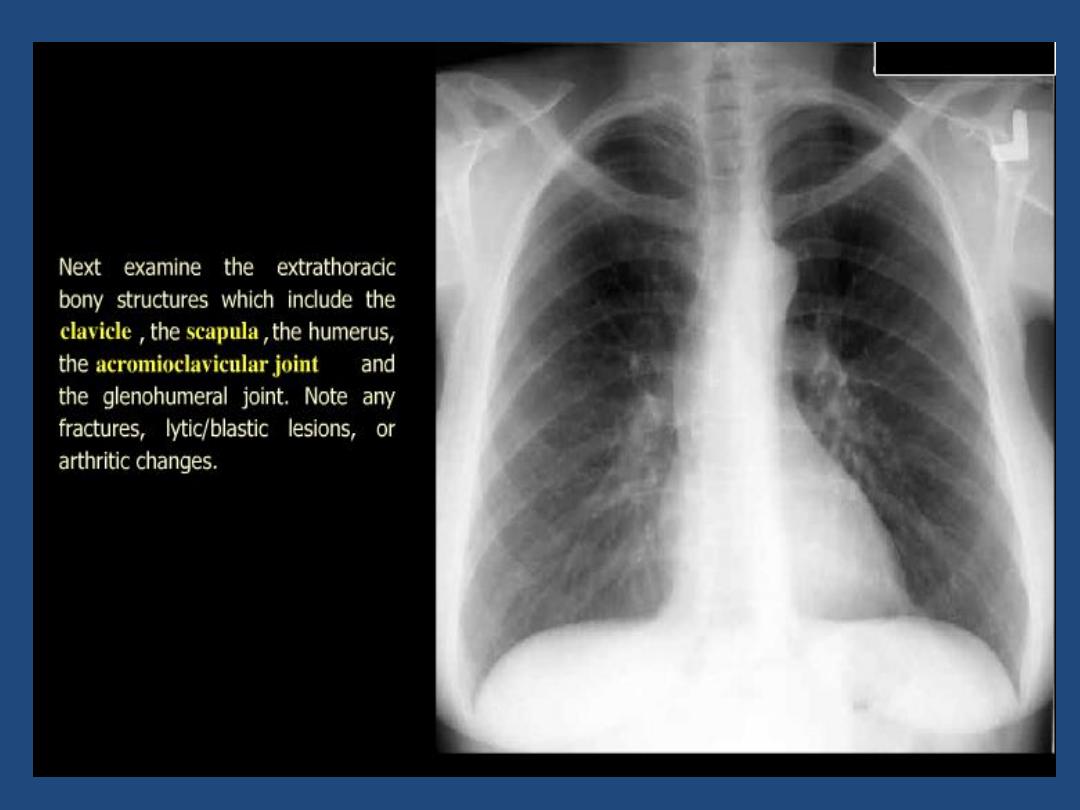
Bones : Destruction , etc
• Note
:Comparison with previous chest radiographs is
essential .
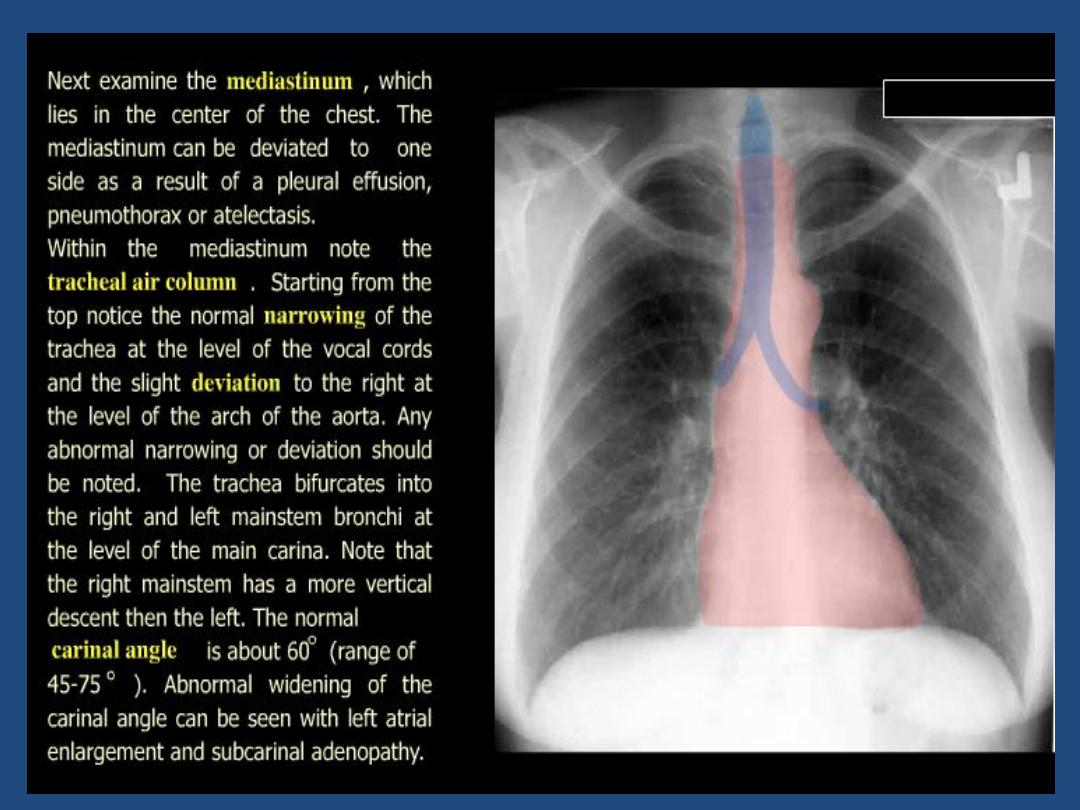
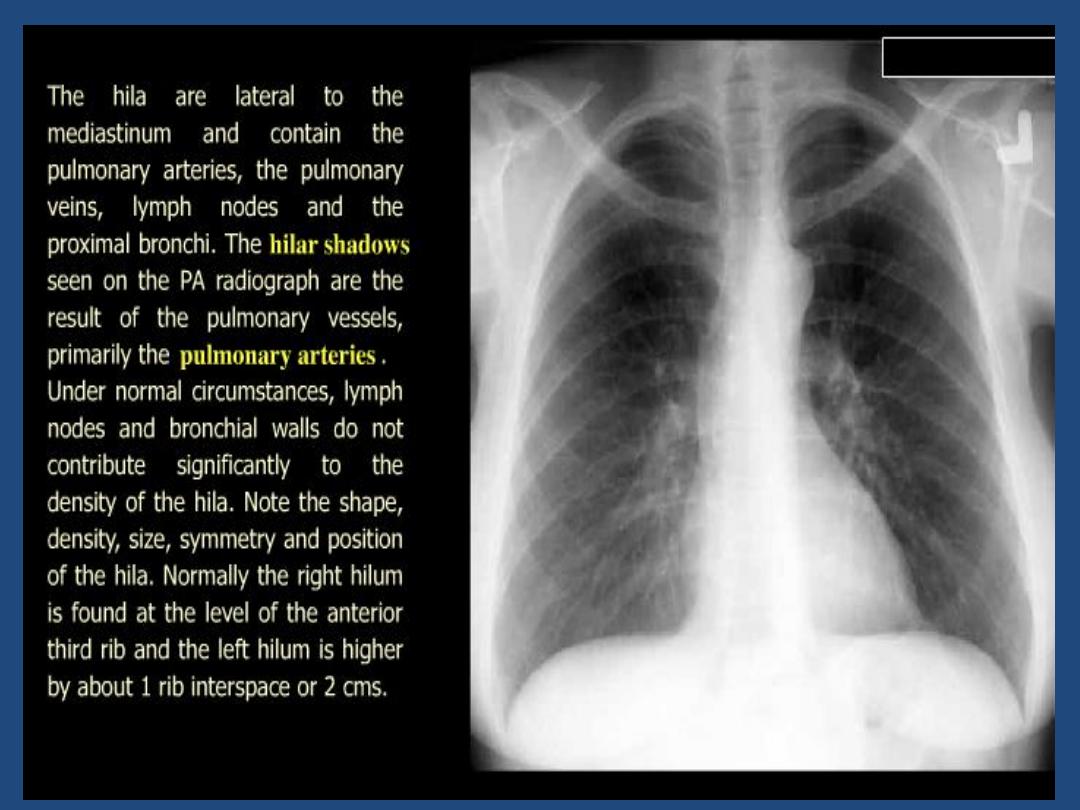
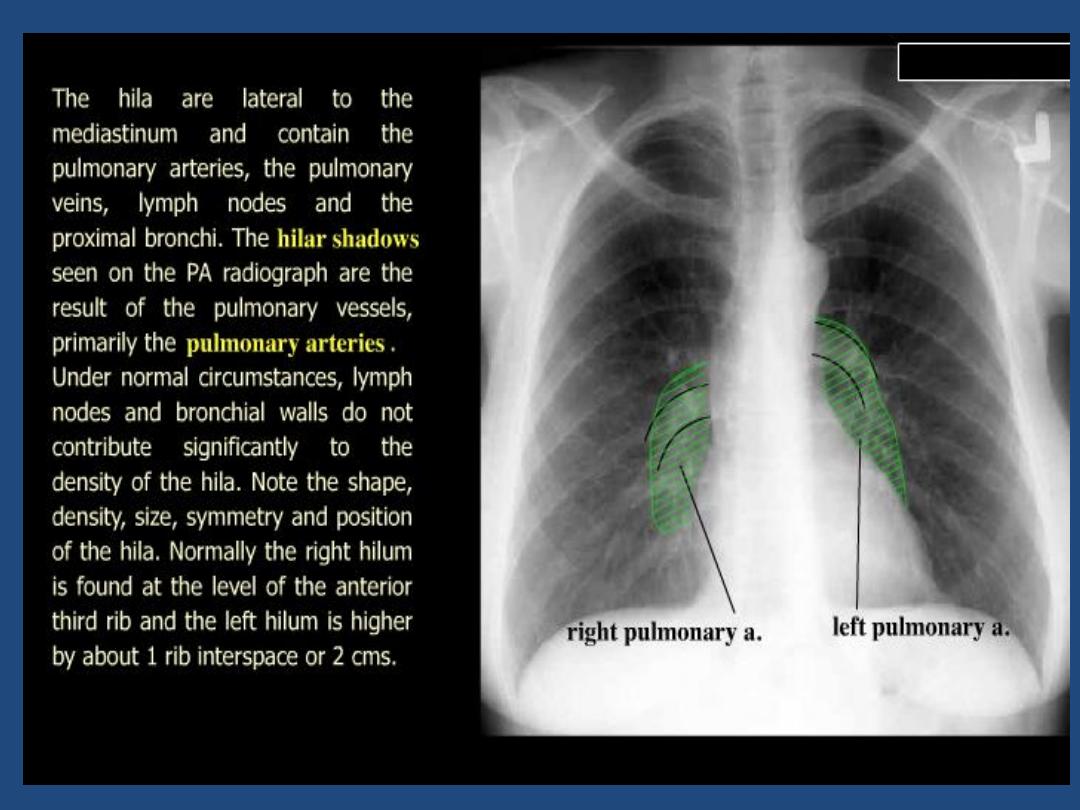
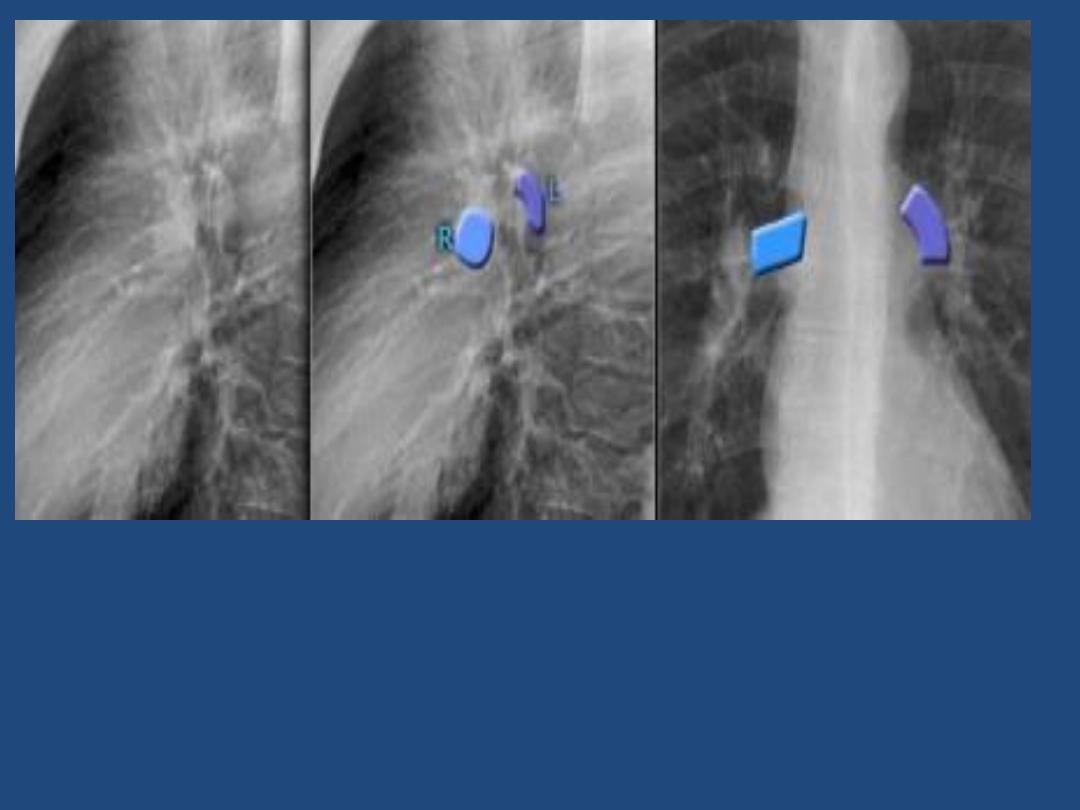
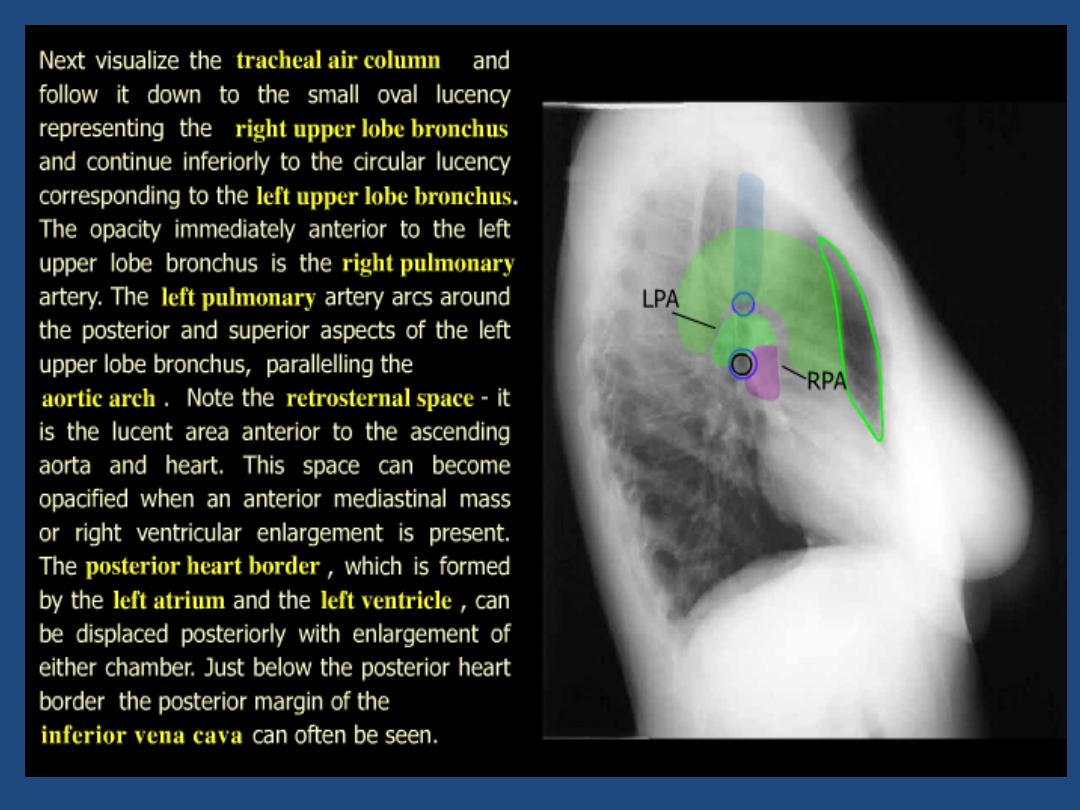
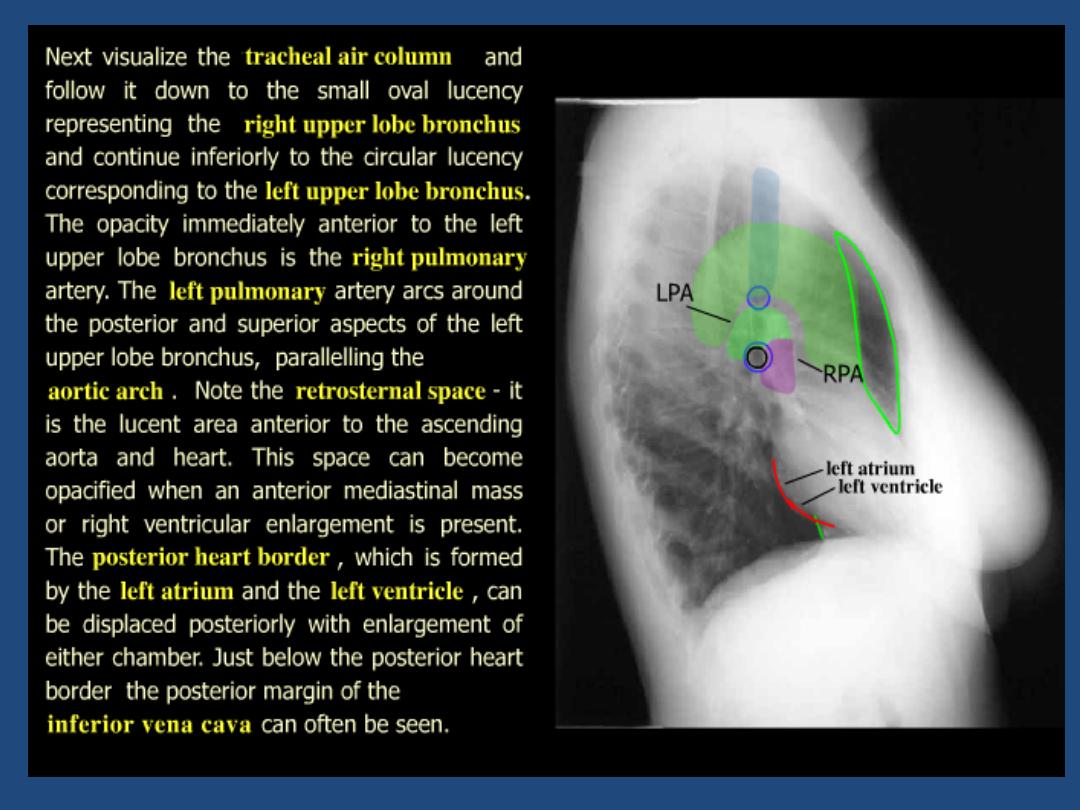
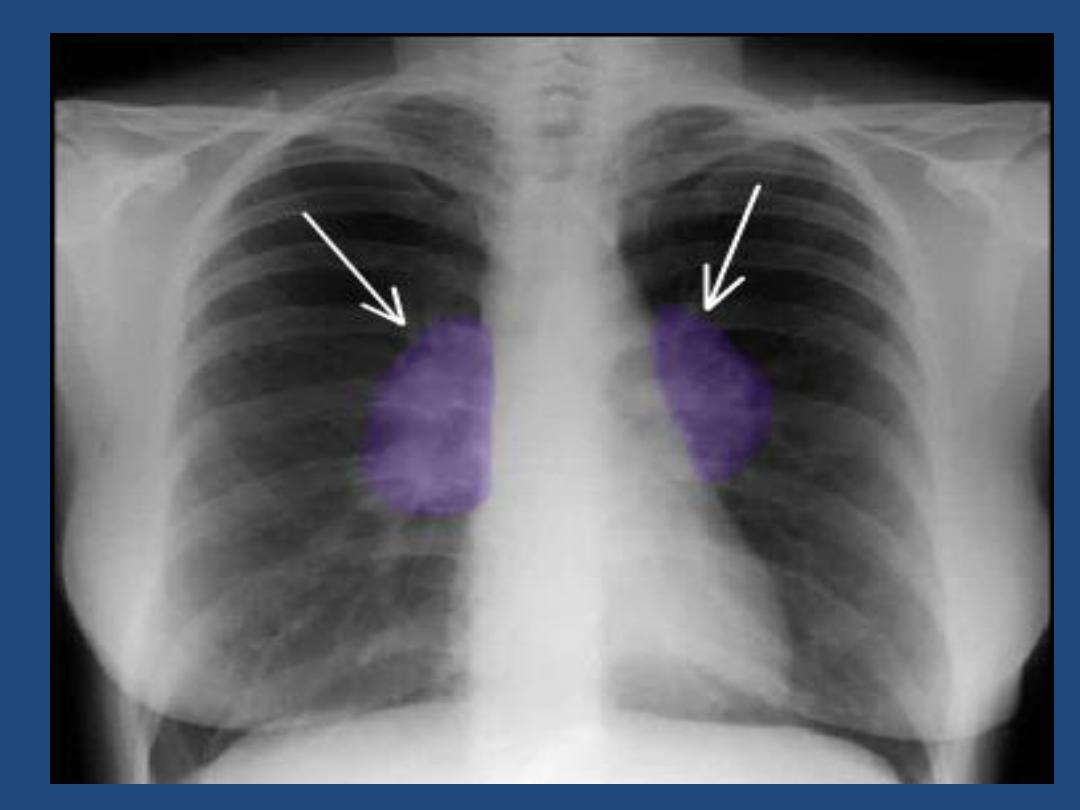
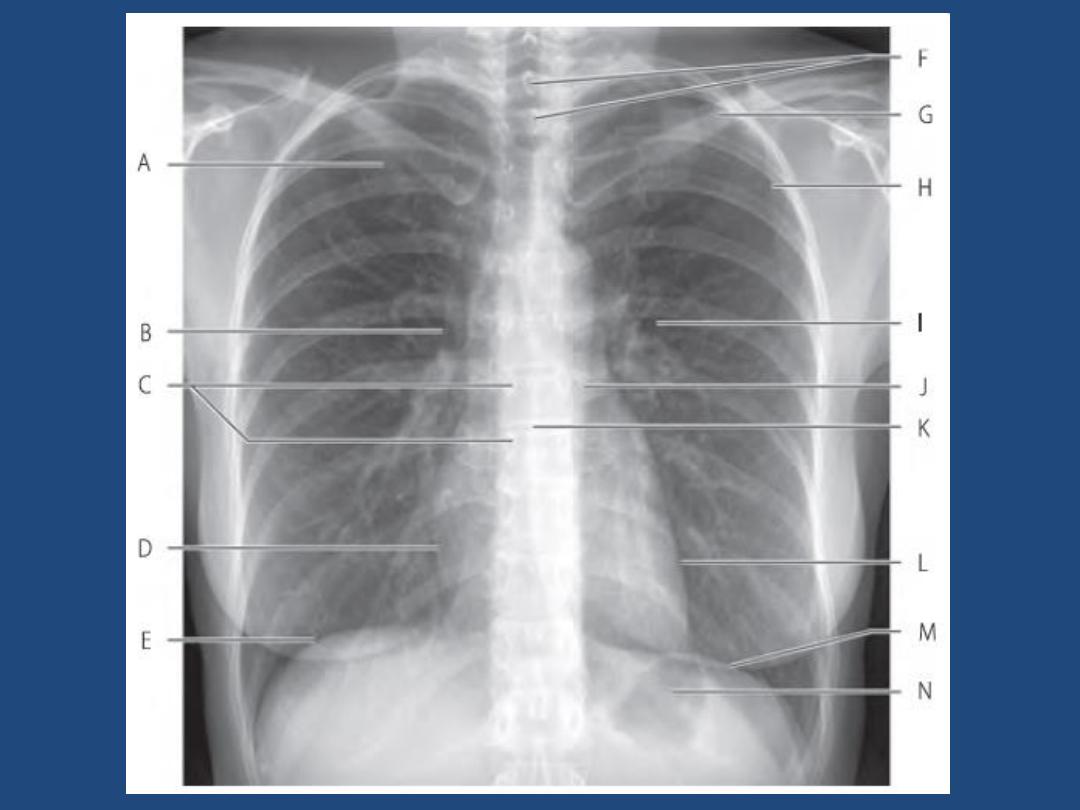
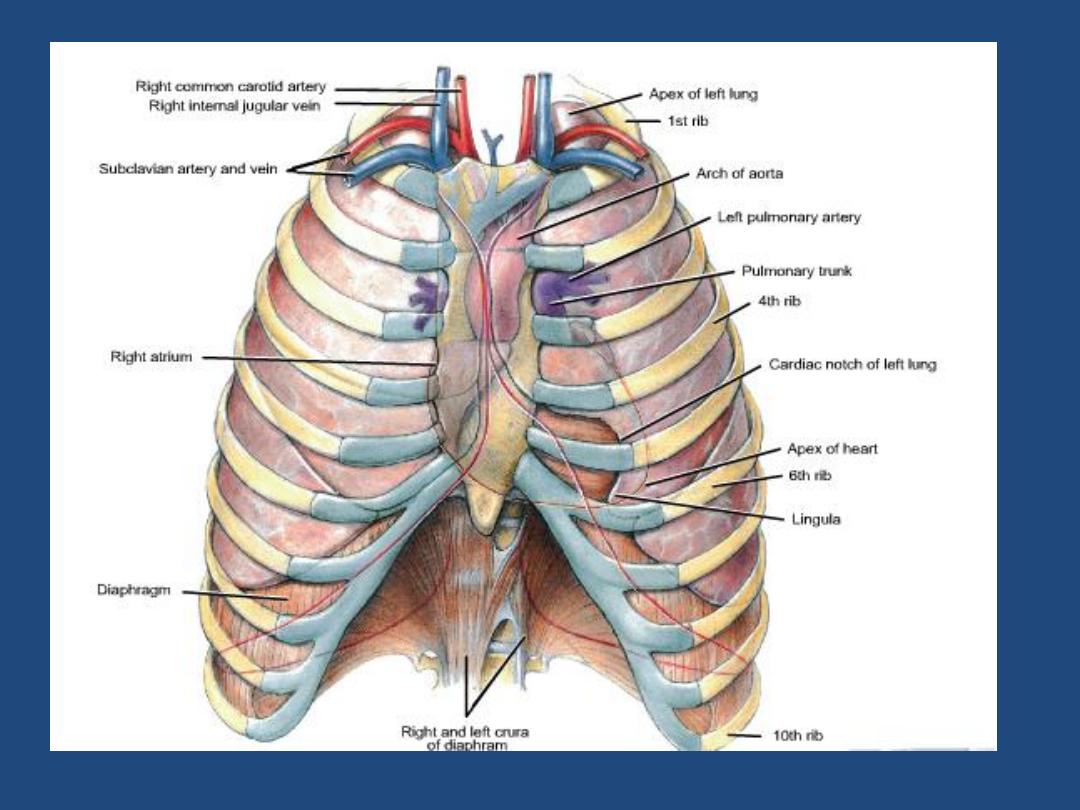
The left main pulmonary artery (in purple) passes over the
left main bronchus and is higher than the right pulmonary
artery (in blue) which passes in front of the right main
bronchus.