Ph.D. Lecturer Msc. Teacher AssistantZubiada Najat Noor Mahmood Shakoor
PracticalMedical Bacteriology
• Lab.1:- Sterilization & Disinfection
Definitions
Sterilization:-The processes that removing or killing all the microbial life and viruses on an object or any material.
Disinfection:-
The processes that result in the destruction of only the vegetative forms of microbial life (pathogenic organisms) but not spores.
They should possess the following properties-
1. Chemical stability.
2. Economical.
3. Non-staining with acceptable color and odour.
4. Bactericidal, not only static but capable of destroying spores as well.
5. Wider spectrum of action.
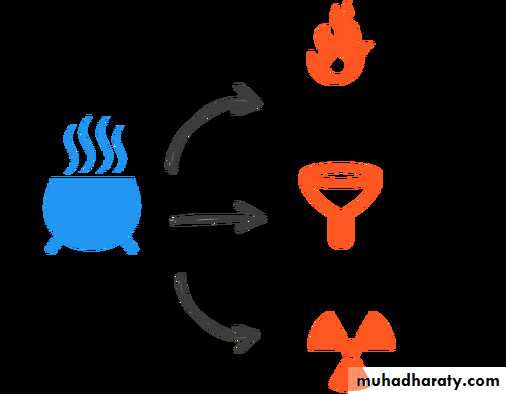
Classification of Sterilization Methods
Physical SterilizationChemical Sterilization
Heat
Filtration
Radiation
Dry Heat
Moist Heat
Flaming
Red heat
Hot air oven
Sterilization at a temp. Below 100Co
Sterilization at 100Co
Sterilization at temp. Above 100Co
Direct Sun Light
Non Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing Radiation
Infrared Radiation
Physical Sterilization:-
Heat:-
Is most practical and dependable method of sterilization, Sterilization by heat depend on :- Time, Temperature, Number of M.O., species of M.O. and Nature of material containing bacteria.Flaming
Dry heat :- Red heat
Hot air oven
Sterilization at a temp. Below 100Co
Moist heat :- Sterilization at 100CoSterilization at temp. Above 100Co
Heat:-
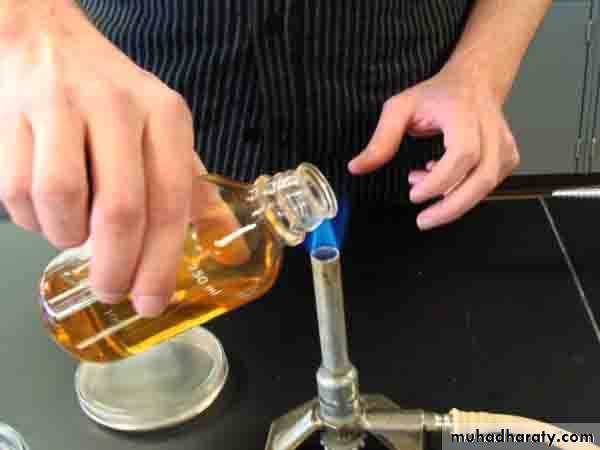
Dry heat :-Flaming: This method is used for sterilization, the mouth of culture tube, needle, spatula, glass slide and cover. This method in valuing passing of materials, through the flame of benzene burner without allowing to become red
Heat:-
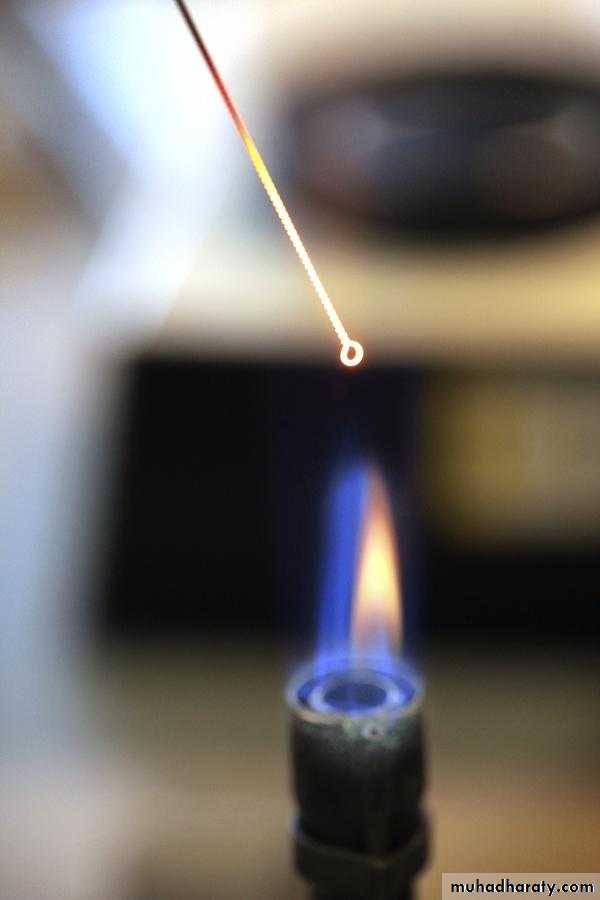
Dry heat :-Red heat: It mean holding the instrument in the flam of bunsen burner until they become red. ex. Loops and needle transfer.
Heat:- Dry heat
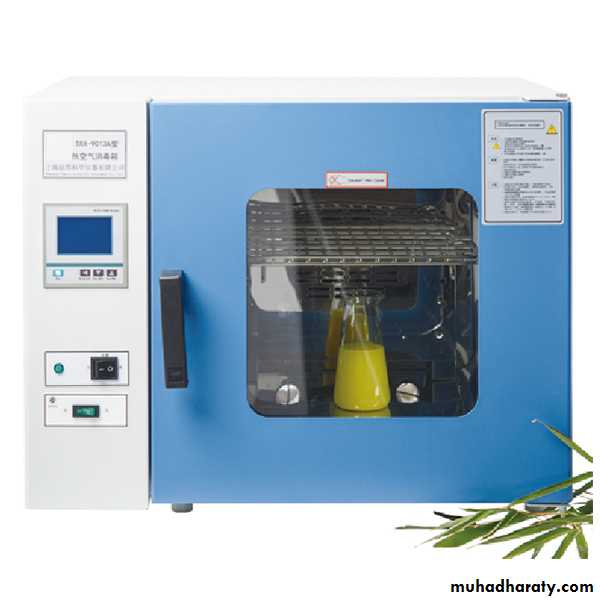
Hot air oven: this type requires longer exposure times(1.5-3 Hours) and the temperature is higher than moist heat (160-180 Co), Hot air oven is the best method for sterilizing dry glass wares and also for preparation powders extract under septic conditions.The oven should be set to:-
• Temperature
• Time• 160Co
• for 2 hours
• 170Co
• for 1hour
• 180Co
• for 30 Min
Heat:-
Moist heat :-At a temp. below 100 Co:- For example pasteurization of milk, This will kill ALL non-spore forming pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Brucella abortus and various Salmonellae, so that this method can be used to kill food pathogen.
the temp. should be :-
• 63-65 Co
• for 30 min. (slow pasteurization).• 71Co
• for at least 15 seconds (fast Pasteurization ).
Heat:-
At a temperature of 100 Co:-a) Boiling at 100Co for 5-10 min. :-
This is sufficient to kill ALL vegetative organisms & many but NOT all spore-forming microorganisms, used to sterile water.
b) Steaming at 100Co .for 30 min. :-
Tyndallization which involves steaming for 30 min. on each 3 successive days.
After heating, the medium is incubated to allow spores to germinate and vegetative organisms to grow which will be killed by the second steaming; the 3rd heating is a safety precaution .used for culture media containing sugar or gelatin.
Heat:-
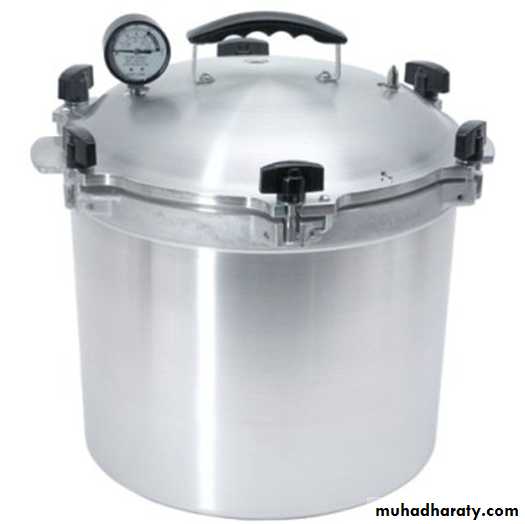
At a temperature above 100CoSteam under increased pressure, this is called (autoclaving) Under autoclave conditions, pressurize steam KILLS bacterial spore, vegetative cells and other microbial forms. This is the usual method of sterilization bacteriological media ,surgical instruments ,…ect.
The 2 common sterilization temp. :-
• 121Co for 15 min for sterilizing items such as media, liquid and medical instruments.• sterilized at 132Co for 30-60 Min. Infectious waste such as unused portion of patients’ specimens, patients’ culture, sharp disposable, sharp instruments such as scalpels, needles.
Sterilization control :-
Chemical test : By using browns tube, with each load changing the color from green to brown as indicator for sterilization.Bacteriological control : of proper autoclave function are essential to ensure that sterilization is being achieved with each run of steam-pressure sterilizer, Bacillus sterothermophilus is used as the test.
Physical Sterilization:-
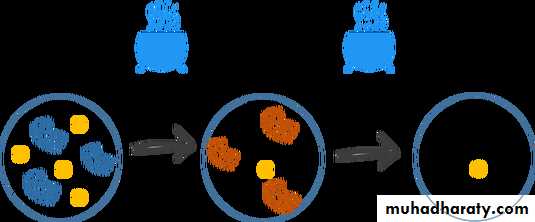
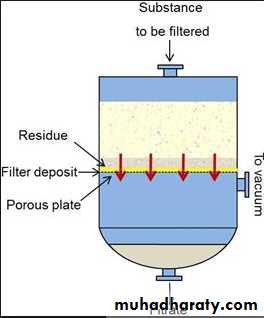
FiltrationTo render fluids, including bacterial culture, free from bacteria by passing them through special filters e.g. seitz filter, Berkefield filters. This method is used in sterilizing liquids that would be damaged by heat such as serum, vaccines, antibiotic solutions, sugars, toxins …etc.
Physical Sterilization:-
Radiationused in commercial purpose to sterile high quantity of pre packed material
a) Direct sun light kills vegetative organisms rapidly, but spores are much more resistant.
b) Non ionizing radiation (Ultra violet light)is commonly used to sterilize the air in the surfaces (used in Bacteriological hood).
c) Ionizing radiation includes Gama rays, X-rays. It has effect on under surfaces. This method is used for sterilizing disposal such as gloves catheter, plastic syringe and Petri dishes.
d) Infrared radiation: by electrically heat element at temp180 C can be attained. used for glass ware.
Physical Sterilization:-
Mode of action :Protein coagulation.
Disruption of cell membrane.
Removal of sit groups ( oxidizing agent )
Damage of DNA.
Inhibit of DNA replication.