1
Ambiguous genitalia
(
Disorders of sex development
); is any case in which the external
genitalia do not appear completely
male or completely female.
Disorders of sex development (DSD);
• True hermaphrodite; presence of both ovarian and testicular tissue in same individual.
• Male pseudohermophrodite; the genotype is 46,XY but the external genitalia are undervirilized.
• Female pseudohermophrodite; the genotype is 46,XX. the gonads are ovaries, but the external
genitalia are virilized.
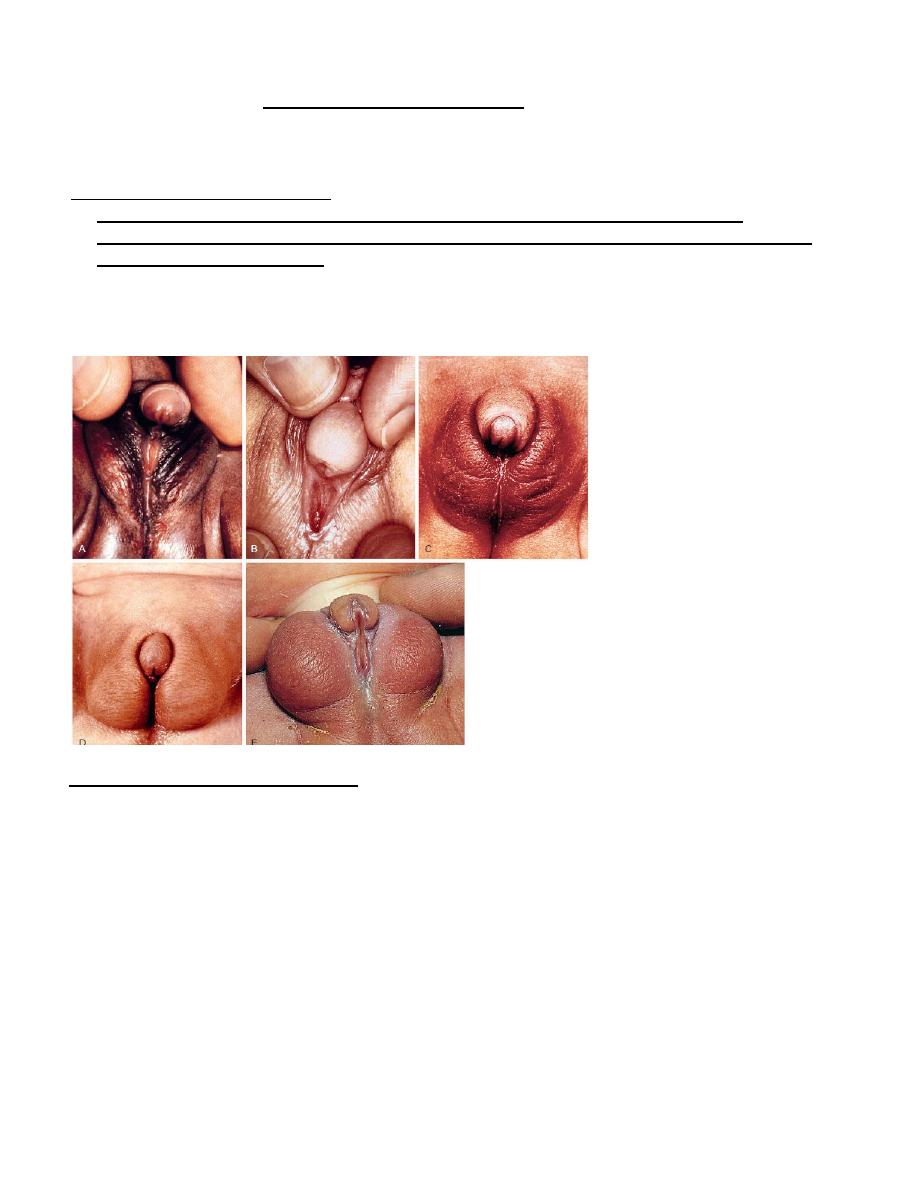
Examples of atypical genitalia. These cases include ovotesticular disorder of sexual development (A) and
congenital virilizing adrenal hyperplasia (B-E) Examples of atypical genitalia.
Causes of disorders of sex development (DSD);
1. Undervirilized male (46,XY karyotype)
– Defect of androgen synthesis.
– Androgen resistance, receptor defects.
2. Virilized female (46,XX karyotype)
– Excess androgen; congenital adrenal hyperplasia CAH
– Maternal androgen exposure; medication, virilizing adrenal or ovarian tumor.
– Disorder of ovarian development
3. Intersex (mosaic karyotypes e.g. XO/XX)
4. Structural abnormalities
2
A child with ambiguous genitalia may have a male karyotype (46,XY) or a female karyotype (46.XX), and
appearance of the external genitalia is rarely diagnostic of a particular disorder of DSD. The most
common forms of 46,XX DSD are virilizing forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, while in 46,XY DSD,
the specific diagnosis is not found in up to 50% of cases; partial androgen insensitivity syndrome and
pure gonadal dysgenesis are common identifiable etiologies.
The major goal is a rapid identification of any life-threatening disorders (salt loss and shock caused by the
salt-losing form of CAH).
Diagnosis of disorders of sex development (DSD);
The first step toward diagnosis is to determine if the disorder represents virilization of a genetic female
(androgen excess) or under-development of a genetic male (androgen deficiency)
Statistically, most virilized females have congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), and 90% of these
females have 21-hydroxylase deficiency. The diagnosis is established by measuring the plasma
concentration of 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP).
Evaluation of disorders of sex development (DSD);
• S. electrolytes
• Ultrasonography: helpful for identifying internal structures ,particularly the uterus & the ovaries.
• Chromosomal analysis.
• Measurement of adrenal steroids, steroids precursor (17-hydroxyprogesterone and progesterone)
• Measurement of testesterone and dihydrotestosterone.
• Pelvic CT or MRI
Treatment:
• Replacing deficient hormones (cortisol in adrenal hyperplasia or testosterone to increase phallic size)
• Surgical restoration to make the individual look more appropriate for the sex of rearing. Gonads and
internal organs discordant for the sex of rearing are removed because gonadoblastomas or
dysgerminomas subsequently may develop.
• Psychological support of the whole family.
21-HYDROXYLASE DEFICIENCY
• Autosomal recessive disorder, affects both sexes equally.
• The gene for 21-hydroxylase lies on the short arm of chromosome 6
• Approximately 70% of affected infants have the salt-losing form, whereas 30% have the simple
virilizing form of the disorder.
• The classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency (salt-losing form) occurs in approximately 1 in 15,000-20,000
births in most populations.
• Pathophysiology; both cortisol and aldosterone require 21-hydroxylase for their synthesis, both
hormones are deficient in the most severe, salt wasting form. The decreased production of cortisol
causes hypersecretion of ACTH, and leads to adrenocortical hyperplasia which stimulates the
synthesis of steroids precursor immediately proximal to the block and causes overproduction of
androgens.
• The signs and symptoms of cortisol and aldosterone deficiency include progressive weight loss,
anorexia, vomiting, dehydration, weakness, hypotension, hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, and
hyperkalemia. These problems typically first develop at 10-14 days of age. Without treatment, shock,
3
cardiac arrhythmias, and death may occur within days or weeks. CAH causes high ACTH levels, and
high levels of steroids precursor (17-hydroxyprogesterone and progesterone), which are shunted into
the pathway for androgen biosynthesis.
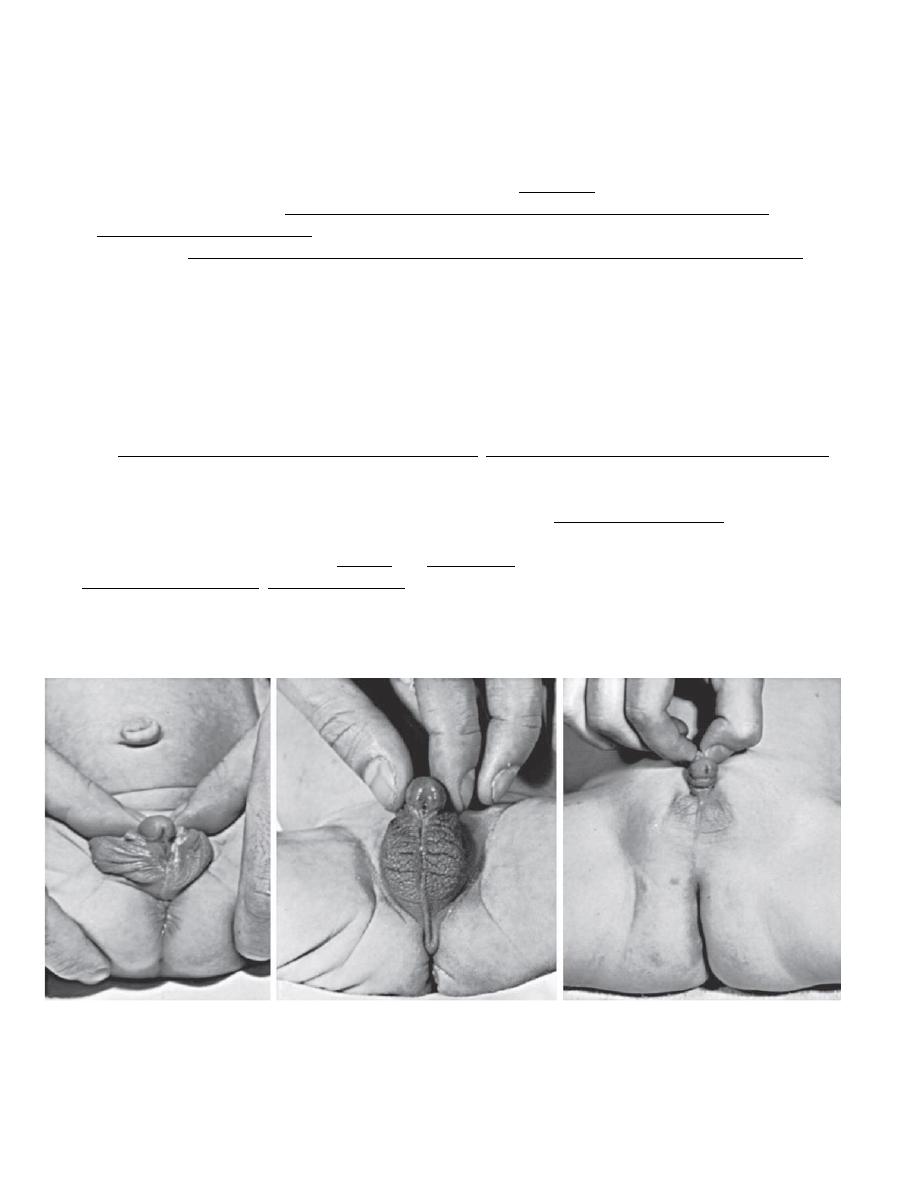
• Affected female; The primary clinical manifestation is the virilization of the external genitalia of
female fetus in whom the development of the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes remains
unaffected by the androgens. The severity of virilization is usually greatest in females with the salt-
losing form. Virilization ranges from mild clitoromegaly to complete fusion of labioscrotal folds.
Clitoris may be so enlarged that it resembles a penis; because the urethra opens below this organ, so
it may be mistaken be a male with hypospadias and cryptorchidism. Later on, girls may demonstrate
aggressive play behavior, tend to be interested in masculine toys rather than playing with dolls.
Women may have decreased interest in maternal roles.
• Affected male; appears normal at birth, and diagnosis may not be made until signs of adrenal
insufficiency develop. Aldosterone deficiency (in 75% of patients) causes salt wasting, shock and
dehydration unless diagnosis is established and treatment is given.
• So infant boys are more likely to die than infant girls, and thus CAH is included in newborn screening.
Later on, signs of excess androgen include rapid somatic growth, excessive height gain, advanced
bone age and early epiphyseal fusion leading to short adult. Early appearance of pubic hair and acne
may develop, with enlarging penis and prostate, however, the testes are usually small.
In nonclassic 21-hydroxylase deficiency, cortisol and aldosterone levels are normal, and affected females
have normal genitalia at birth. Males and females may present with early development of pubic and axillary
hair. Hirsutism, acne, menstrual disorders, and infertility may develop later in life, but many females and
males are completely asymptomatic.
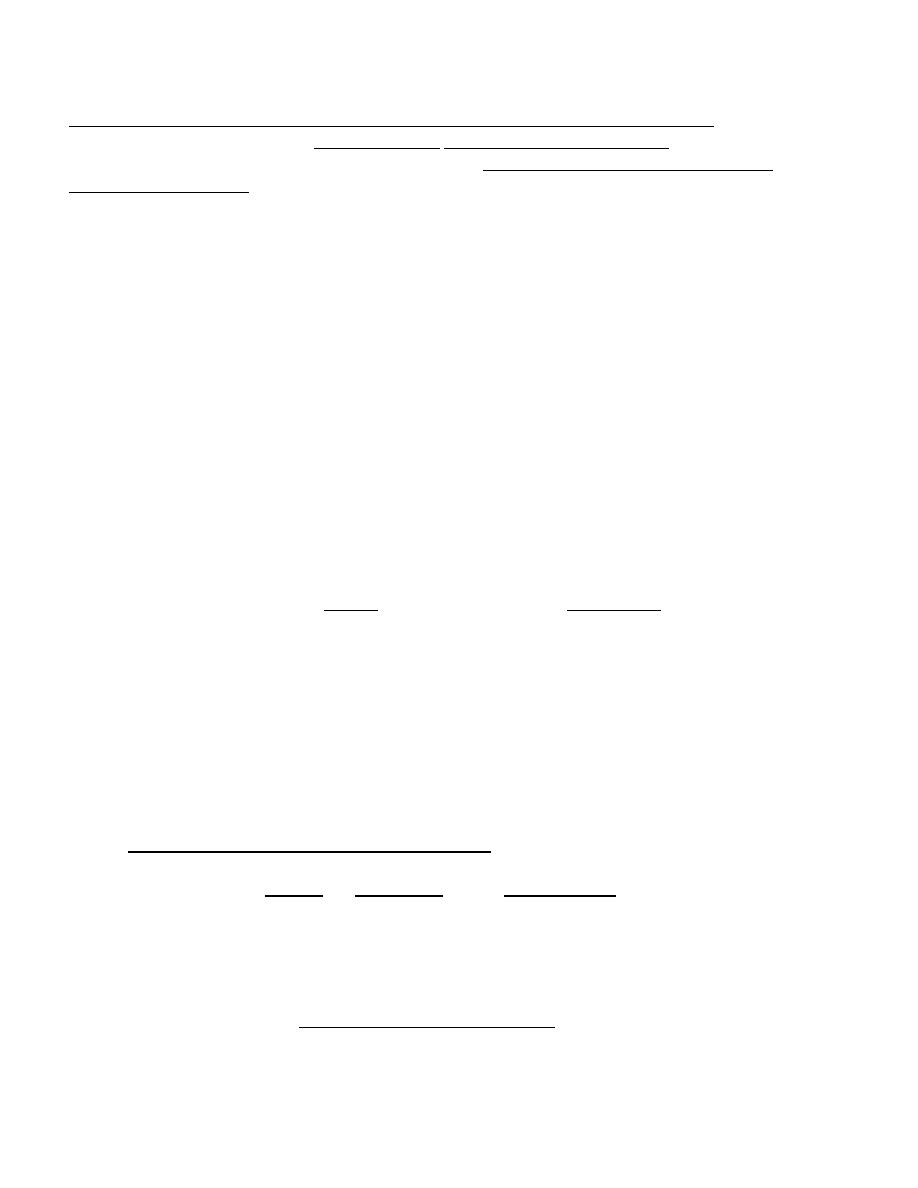
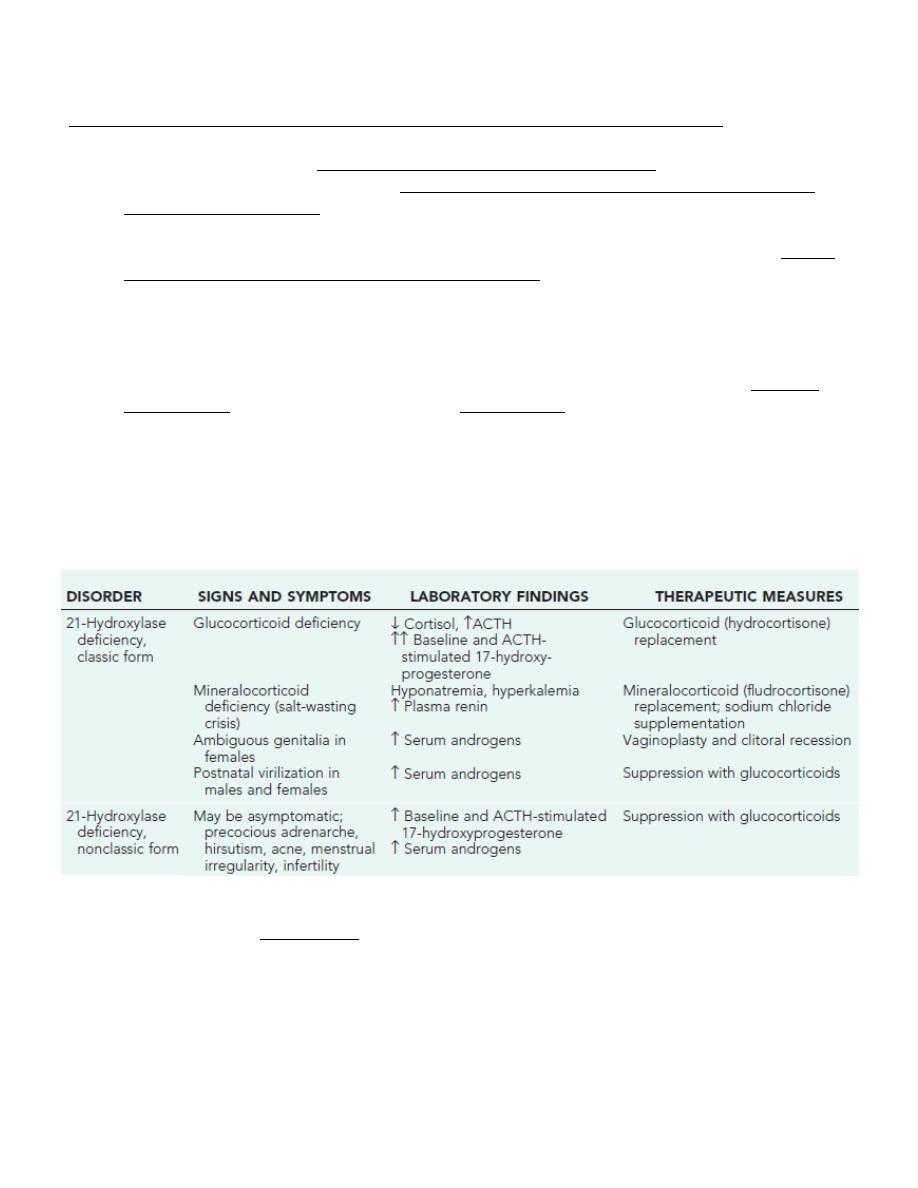
Three virilized females with untreated congenital adrenal hyperplasia. All were wrongly assigned male sex at birth,
and each had a normal female sex-chromosome complement(46,XX). Infants A and B had the salt-wasting form and
received the diagnosis early in infancy. Infant C was referred at 1 yr of age because of bilateral cryptorchidism.
4
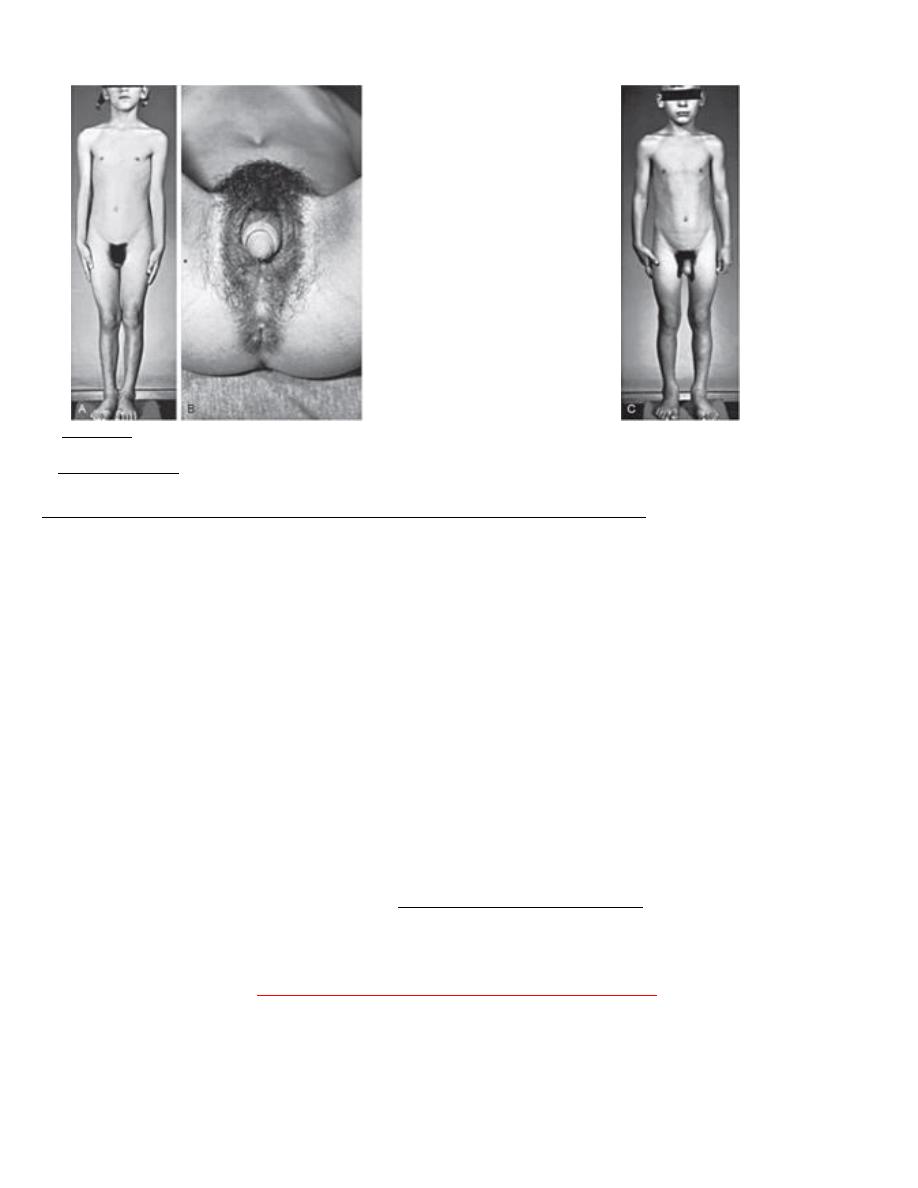
A, 6-yr-old girl with congenital virilizing adrenal hyperplasia. The height age was 8.5 yr, and the bone age was 13 yr.
B, Notice the clitoral enlargement and labial fusion.
C, Her 5 yr old brother was not considered to be abnormal by the parents. The height age was 8 yr, and the bone age was 12.5 yr.
Clinical manifestations of the classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency (salt-losing form):
Cortisol deficiency
• Hypoglycemia
• Inability to withstand stress
• Vasomotor collapse
• Hyperpigmentation
• Muscle weakness, fatigue
Aldosterone deficiency
•
Hyponatremia
• Hyperkalemia
• Vomiting
• Urinary sodium wasting
• Failure to thrive
• Acidosis
• Volume depletion
• Hypotension
• Dehydration
• Shock
• Serum electrolyte; measurement reveals hyponatremia and hyperkalemia usually developing by 5 to
7 days after birth but not usually immediately after birth. Vomiting, dehydration, and acidosis soon
follow, as do shock and death.
• In all infants, the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency may be confused with pyloric stenosis.
Pyloric
stenosis manifests by hypochloremia, normal or hypokalemia, and alkalosis
. This distinction may be
lifesaving in preventing unnecessary investigations or inappropriate therapy.
• Elevated levels of serum 17-OHP (17-hydroxyprogesterone).
• Serum cortisol and aldosterone levels are low (in salt losers), whereas the testosterone level is
elevated because it is derived from 17-OHP.
5
The goals of treatment are to achieve normal linear growth and bone age advancement. Long-term
therapy consists of providing;
• Glucocorticoids; (cortisol) suppresses excessive production of androgens by the adrenal cortex
and thus minimizes problems such as excessive growth and skeletal maturation and virilization,
and continued indefinitely in classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency, but may not be necessary in
nonclassic disease unless signs of androgen excess are present.
• Mineralocorticoid therapy; for salt losers consists of fludrocortisone (Florinef),often with sodium
chloride supplementation in infancy and early childhood.
• Surgery; Significantly virilized females with severe clitoromegaly, the clitoris is reduced in size
with partial excision between 2-6 months to permit normal development of gender identity.
Prenatal diagnosis and Newborn screening
• Prenatal diagnosis; is possible late in the 1
st
trimester by analysis of DNA obtained by chorionic
villus sampling or during the 2nd trimester by amniocentesis.
• Newborn screening; analyze of 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels in blood obtained by heel stick
and absorbed on filter paper cards; the same cards are screened in parallel for other congenital
conditions, such as hypothyroidism and phenylketonuria. Potentially affected infants are quickly
recalled for additional testing (electrolytes and repeat 17-hydroxyprogesterone) at approximately
2 wk of age.
Summary of diagnosis and treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia CAH
Umbilical hernias
• Often associated with diastasis recti and consists of omentum or portions of the small intestine,
appears as a soft swelling covered by skin that protrudes during crying, coughing and can be reduced
easily. Predisposing factors include black race and low birthweight.
• The size of the defect varies from < 1 cm in diameter to as much as 5 cm, but large defects are rare.
• Most umbilical hernias that appear before the age of 6 mo disappear spontaneously by 1 yr of age.
Even large hernias (5-6 cm in all dimensions) have been known to disappear spontaneously by 5-6 yr
of age.
6
• Strangulation is extremely rare.
• Treatment; It is generally agreed that “strapping” is ineffective. Surgery is not advised unless the
hernia persists to the age of 4-5 yr, or becomes strangulated.
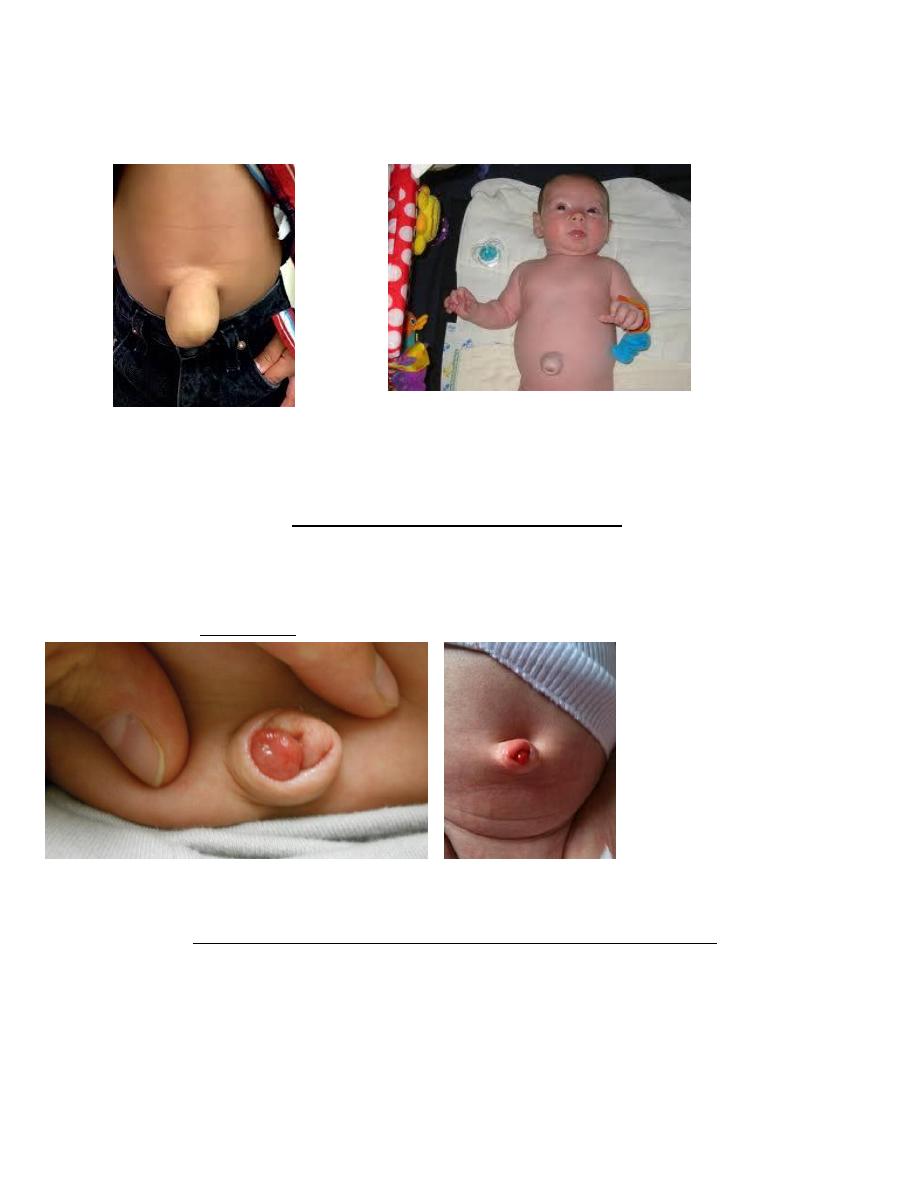
Umbilical granuloma
• The umbilical cord usually dries and separates within 6-8 days after birth.
• The raw surface becomes covered by a thin layer of skin; scar tissue forms, and the wound is usually
healed within 12-15 days. Mild infection or incomplete epithelialization may result in a moist
granulating area at the base of the cord with a slight mucoid or mucopurulent discharge.
• Good results are usually obtained by cleansing with alcohol several times daily. Persistence of
granulation tissue at the base of the umbilicus is common. The tissue is soft, 3-10 mm in size, vascular
and granular, and dull red or pink, and it may have a seropurulent secretion.
• Treatment; is cauterization with silver nitrate, repeated at intervals of several days.
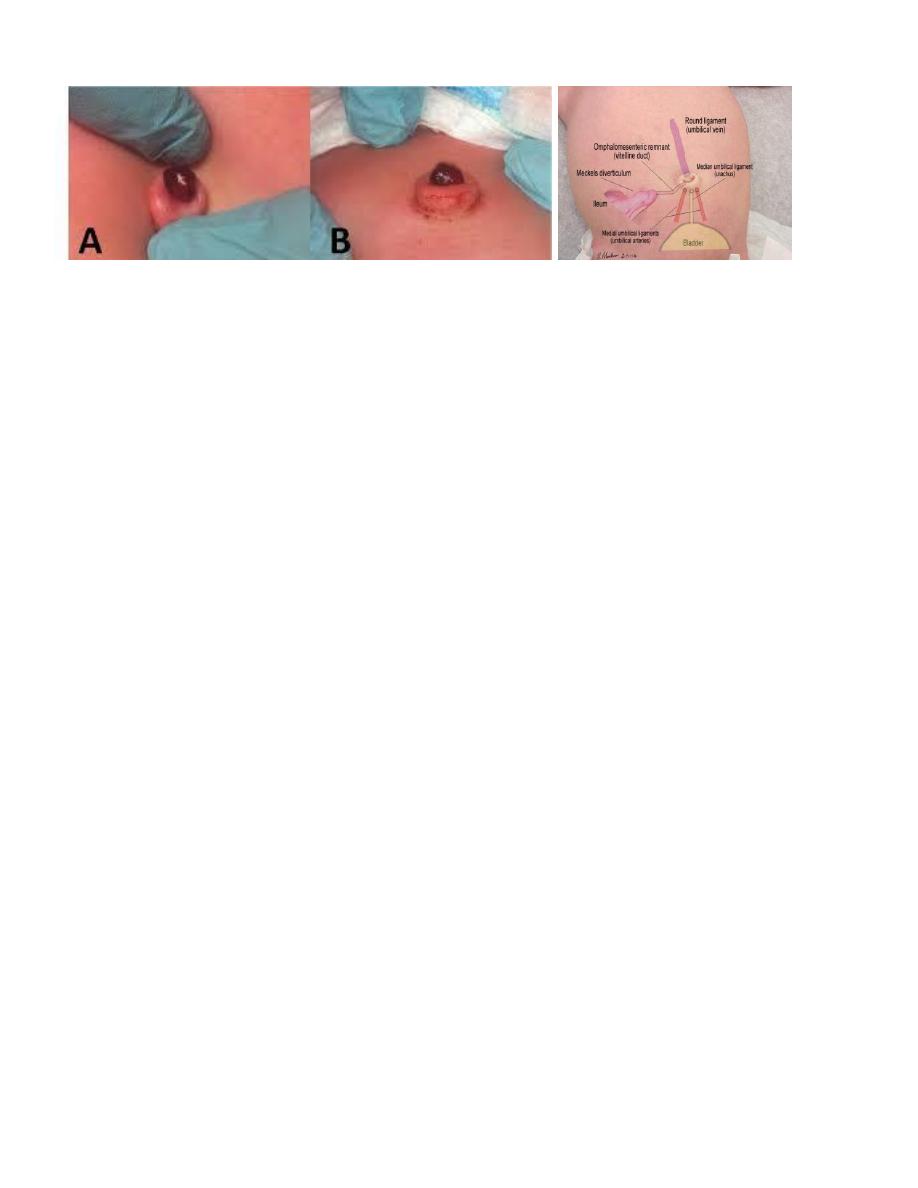
Umbilical polyp
• Results from persistence of all or part of the omphalomesenteric duct or the urachus.
• The tissue of the polyp is firm and resistant, is bright red, and has a mucoid secretion.
• If the polyp is communicating with the ileum or bladder, small amounts of fecal material or urine may
be discharged intermittently.
• Histologically; the polyp consists of intestinal or urinary tract mucosa.
• Treatment; is surgical excision of the entire omphalomesenteric or urachal remnant.
7
