History and examination in Gynecology
Simply it is the art that should be mastered by every practicing doctor so he can pinpoint the disease his patient’s has through the minimum number of test and timeThe initial ID
NameAge
Residence
Occupation or job
Blood group
Last menstrual period date
Name
It is very important to call the patient individual with name that seems most appropriateMisunderstanding this point may lead to a rapid breakdown of the relation between the doctor and his patient
Age and parity
Due to the fact that in general the number of gynecological and obstetrical disordersAge rapidly put a large number of diorders either in the highly or unlikely or even tp presents
Exmples
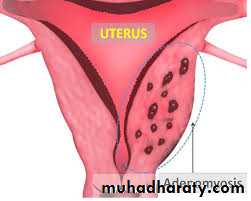
Adenomyosis
Appears almost always in women above 40 years with high parity
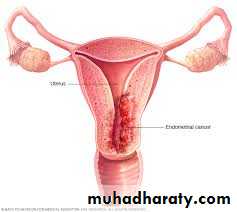
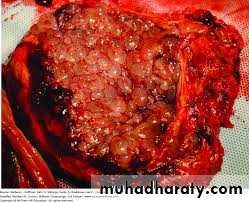
Endometrial carcinoma
Almost always appear among women after 40 years but with few or nulli parityOtherwise all causes of unovulation like PCO predispose to endometria carrcinoma
Menorrhacyclegia at the early
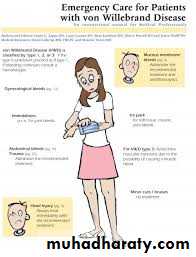
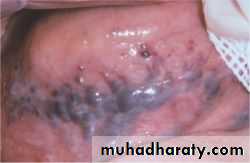
Menorrhagia since early cycles raise strongly the suspicion of von will brand disease or hemophilia BResidence
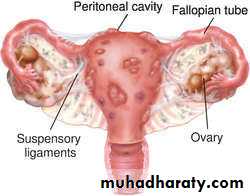
Endometriosis has the highest incidence in JapanResidence
Breast cancer has the highest incidence in USA and west EouropeResidence
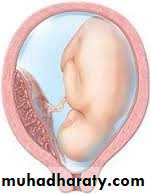
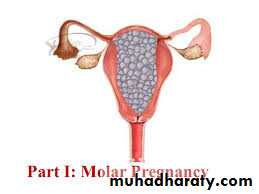
Hydatiform mole has the highest incidence in Malaysia 1/23Has the lowest incidence in Africa
Local residence
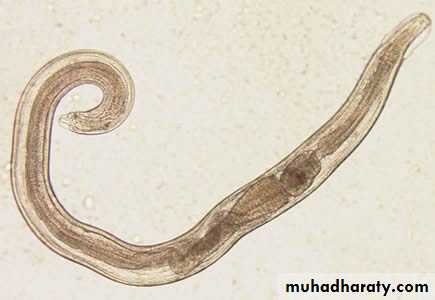
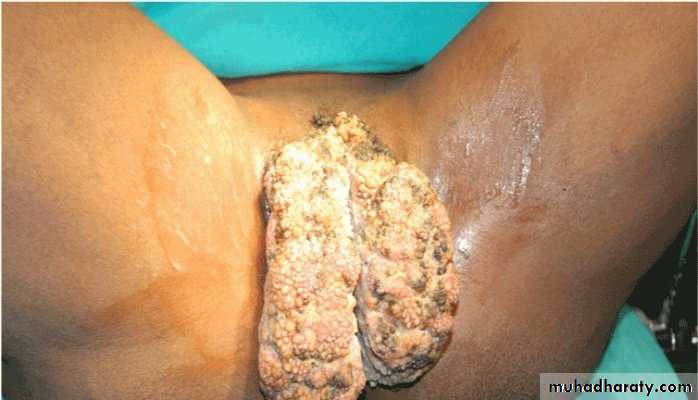
Entrobius Vermicularis is endmic in places of low social classCervical carcinoma is most common in areas with low social class
occupation
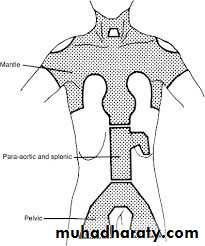
In general occupation has little impact on the gynecological disorderRadiation cause immediate damage and premature ovarian failure
In Hodgkin disease an inverted Y shaped shield to protect against to the ovary to protect them
LMP
It is not uncommon to confuse threatened abortion or low lying placenta with menstrual abnormalitiesExact knowing of the last menstrual date doesn’t only important to exclude pregnancy but to diagnose the type of menstrual abnormality your patient has
Frequent cycle every 14 day is called polymenorrhea and commonly associated with unovulatory cycles
While cycles which have frequency more than 35 days are called oligomenorrhea and commonly associated with PCO
Blood group
Apart from knowing the blood groupBlood group has non understandable correlation to molar pregnancy
The best prognosis among women with O Rh+ve
Has the worst among B and AB blood groups
Chief complain and history of the present illness
History of the present illness is the detailed and comprehensive story extracted from the patient which has brought her from house to the hospital including the first symptom or signs – the doctor she has consulted- the investigations she has done and any therapy she has taken. At last why the doctor in charge has decided to admit her to the hospitalChief complain is simply the first sign felt by the patient and its duration and mentioned before Hx of the present illnes
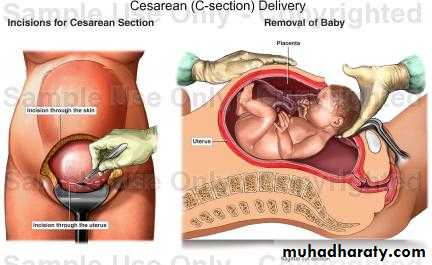
In case the patient has done operation the first thing to mention the name of the operation, the time and date, the indication for it- and the course of the operation and in which post operative day now the history of the present illness is mentioned
It absolutely fatal mistake to mention the name of the doctor she has consulted or meet in the hospital rather the level of their specialty may be mentioned in stead [DON”T MENTION ANY NAME]
Past obstetrical history
In principle the past obstetrical history record the date of marriage- the date of every pregnancy and the course of first, second and third trimester and then the mode of delivery and any significant problem in the puerperium .as a matter of fact many problems in the past obstetrical history may explain the chief complain now presenting inexamples
Asherman’s syndrome
Curretage for post partum hemorrhage may explain the failure of the menstruation return after completion breast feedingCurettage in the post partum period may shed altogether the normal enometrium and mis interpretted as (placental pieces)!?
Shehan syndrome
Women who wish to breast feed their babies may fail as no milk secretion from the very start of puerperiumUsually induced by massive post partum hemorrhage which was inadequately treated due to lack of blood stores or rare type of blood group like B-ve
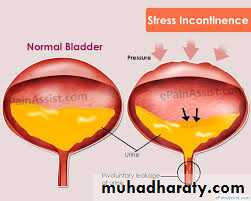
Stress incontinence
Stress incontinence is involuntary loss of urine following any maneuver which increase intra abdominal pressureSI is usually felt by all pregnant women late in pregnancy and gradually disappear by the 6 week post partum
If the condition persist a positive history of use of forceps or ventuse may be extracted from the patient which partially damage the cardinal ligament of the uterus
Uterine prolapse
Uterine descent through the vagina and ultimately remains outside without treatmentThe obstetrical history of those women frequently shows the use of aggressive forceps which damage the cardinal ligament totally which ultimately causes the descent of the uterus
Uterine descent is usually treated by vaginal hysterectomy which is more difficult than abdominal
On the other hand if the patient has previous C/S this may make vaginal hysterectomy a failure which has no clear end unless the surgeon is very competent as C/S makes adhesion between the uterine wall and the bladder base. Trying to separate this adhesion may open the bladder and mis ligation may close both ureters with catastrophic results
Gynecological history
Gynecological historyUnfortunately this part of the gynecological history is the most mistaken part though its importance in any woman life and include the following
• Menarche
• Sexual appearance in primary amenorrhea;
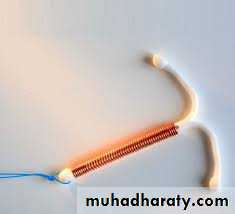
• History of contraception
• Urinary gynecology
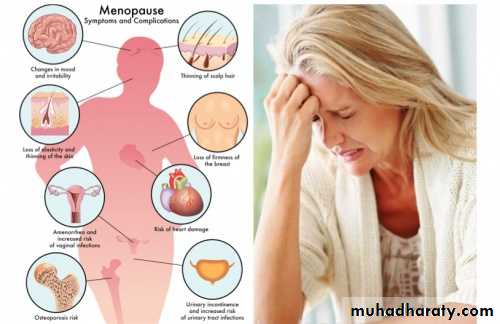
• Menopause and its associated
Menstruation
Menarche is defined as monthly shedding of the endometrium which is usually a mixture of blood, macrophage and dead endometrial tissue which heralds failure to achieve pregnancy
Menstruation is assessed by 3 points
• Cycle which is the period between first day of one menstrual cycle and the first day of the next. Normal range is 21- 35 days
• Period which is the time spent in menstruation. The normal range is 3 to 7 days
• The loss which defined as how much total blood is lost per one cycle. Unfortunately measurement of the loss is a research work done by sensitive weighing machine which measure the pre and post use by a woman. From the difference the loss is calculated however it can be roughly estimated by the number of tampons the patient change per day and her Hb level. Normal range is 30- 70
• From those 3 criteria a 5 pattern may be characterized which
• menorrhagia, heavy cycle
• hypomenorrhia, few blood per cycles drops
• polymenorrhea, cycle < 21 days usually 14 days
• oligomenorrhia > 35 days
• metrorrhagia no correlation between date and pattern exist on calendar
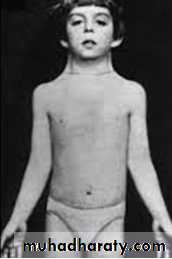
Sexual appearance in primary amenorrhea infantile, feminine or masculine
History of contraception
Menopause and its associated
Medical and surgical history
General examination
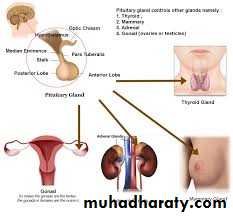
Examination of thyroid
NVB and NDR
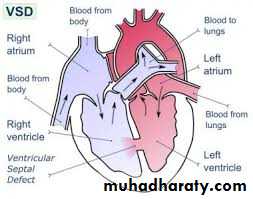
ventricular septal difficultAbdomenial examination
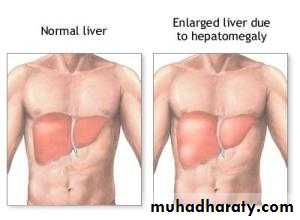
Hepatomegally
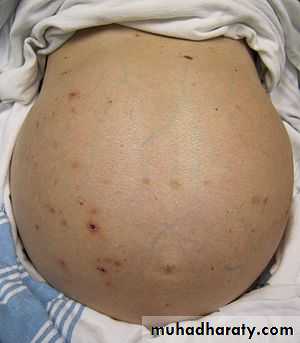
Ascietes