1
8086 Microprocessor and Interfacing: reference questions.
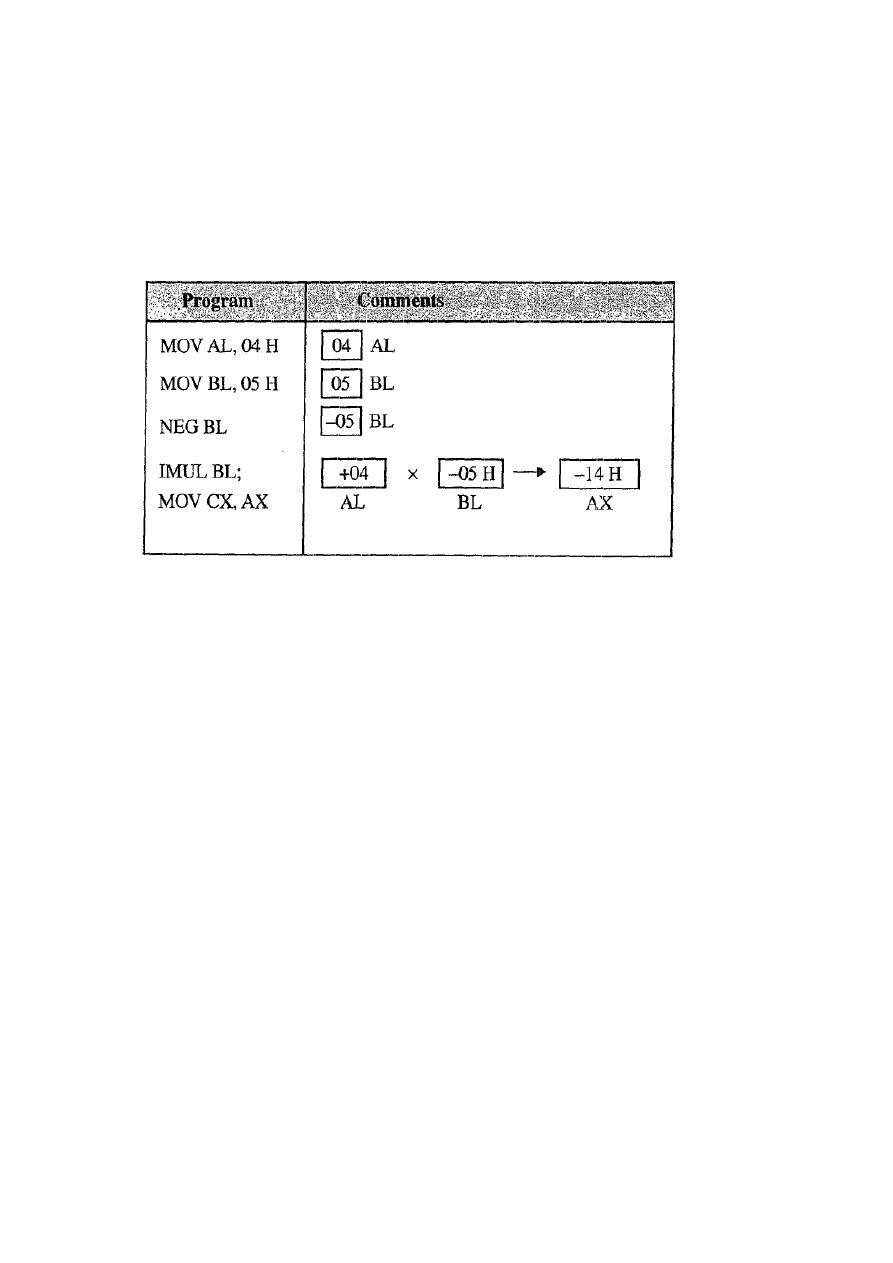
Q1) Write an ALP to perform multiplication of + 4 H and - 5 H. Store
the result in register CX.
Solution:
The result -20D = -14 H will be signed binary number in 2's Complement form.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q2) Perform the Division 1726 H/39 H and store the result in memory
location at an offset of 4000 H in data memory segment.
Solution:
MOV AX,1726H
MOV BH,39H
DIV BH
MOV [4000H],AX
HLT
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q3) Write an ALP to perform the Division F163 H/1023 H. Store the
result in memory at an offset of 9500 H in extra memory segment.
HLT
2
Solution:
MOV AX, 0F163H
MOV DX, 0000H
MOV BX, 1023H
DIV BX
MOV ES:[9500H], AX
MOV ES:[9502H], DX
HLT
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q4) Transfer 16 bit number of memory location having offset 9000 H in
Extra memory segment into output port 8160 H and 8161 H.
Solution:
MOV AX, ES : [9000H]
MOV DX, 8160H
OUT DX,AX
HLT
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
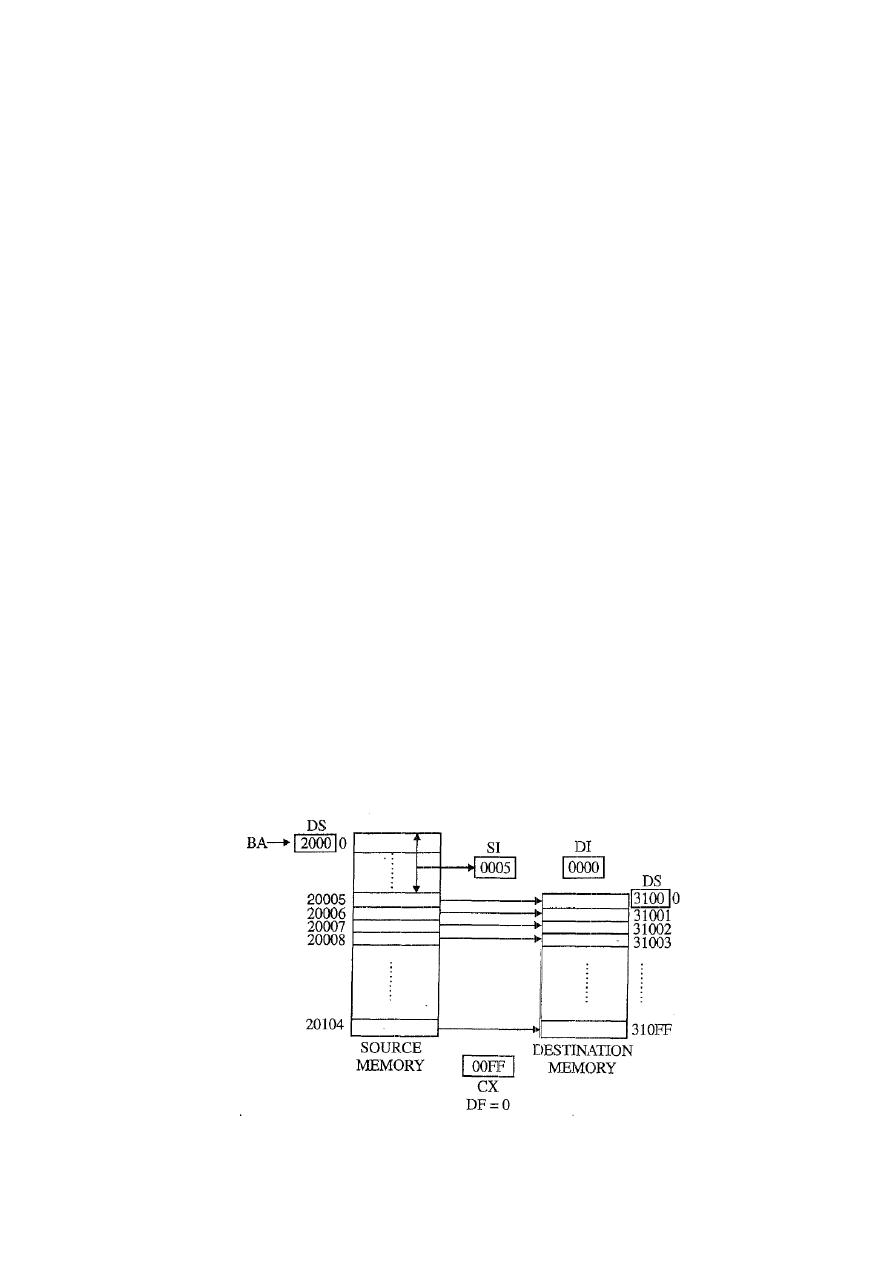
Q5) Write an ALP to transfer a block of 256 byte from starting source address 20005H
to starting destination address 31000H.
Solution:
3
Program:
MOV AX, 2000H
MOV DS,AX
MOV AX, 3100H
MOV ES,AX
MOV SI, 0005H
MOV DI, 0000H
MOV CX, 00FFH
CLD
REP MOVSB
HLT
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
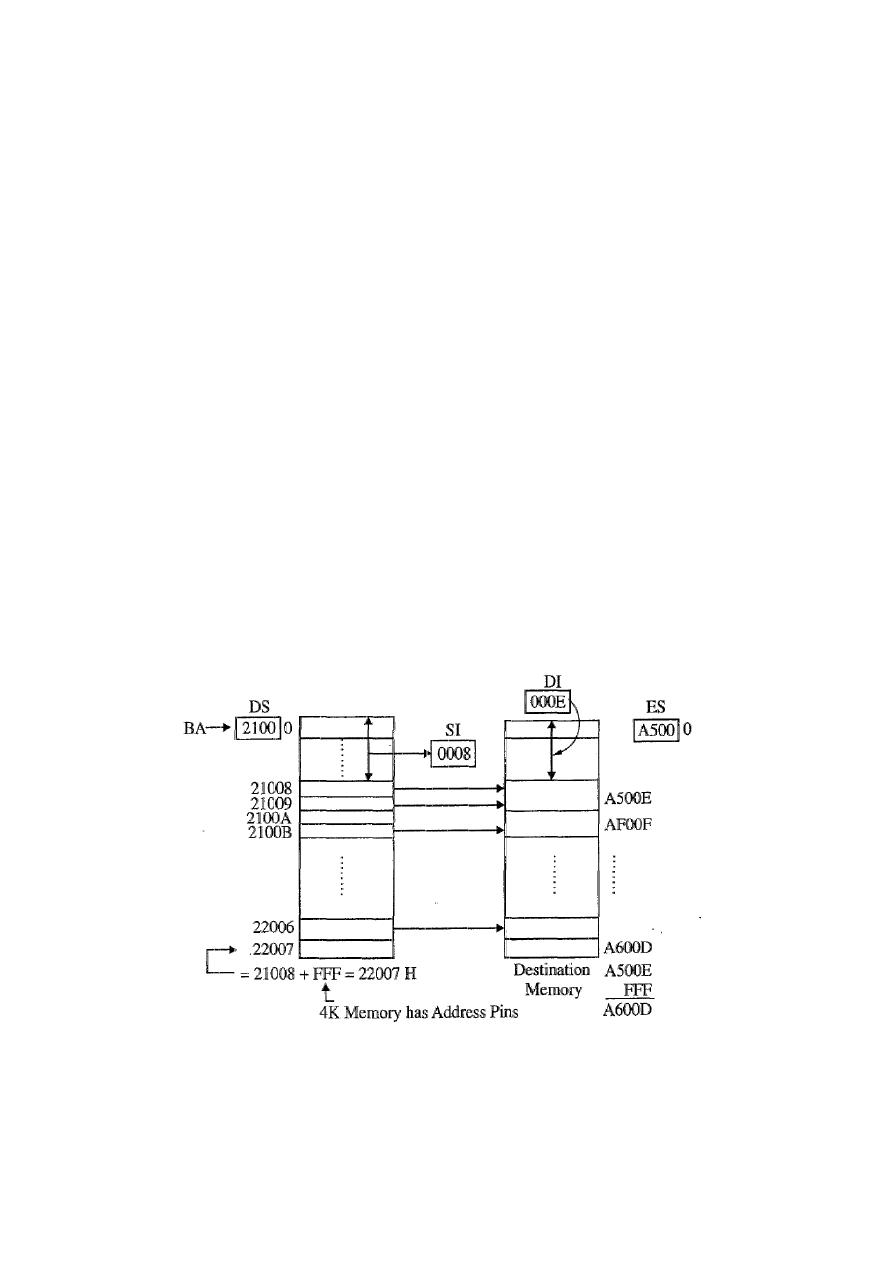
Q6) write a Program to transfer .2K words of data from starting source
address 21008 H to starting destination address A500E H.
Solution:

4
Program:
MOV AX, 2100H
MOV DS, AX
MOV AX, 0A500H
MOV ES, AX
MOV SI, 0008H
MOV DI, 000EH
MOV CX, 07FFH
CLD
REP : MOVSW
HLT
Note: 2K Word is equal to 4K byte so for last location we have to add 4K to
starting address (4K memory has address 12 pins so 1111 1111 1111 = FFF H is
address which will be added in 21008 H.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
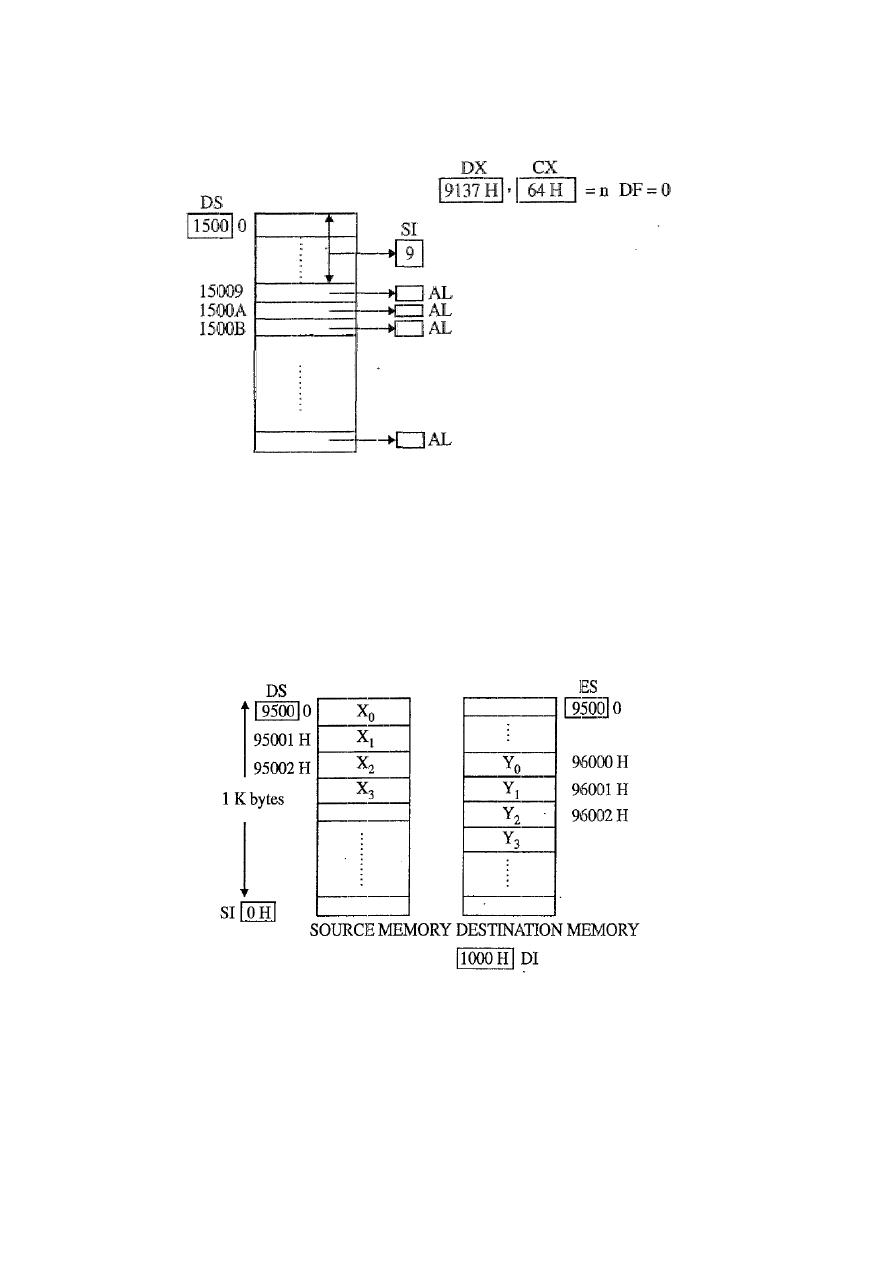
Q7) Write an ALP to transfer 100 bytes· from the starting source memory address
15009 H to Output Port 9137 H.
Solution:
MOV AX, 1500H
MOV DS, AX
MOV SI, 9H
MOV CX, 64 H
MOV DX, 9137H
CLD
L1: LODSB
OUT DX, AL
LOOP L1
HLT
5
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q8) Two blocks of data are present in memory from location 95000 H and 96000 H,
compare the corresponding bytes of the two blocks and when the comparison is
over or mismatching is found, then stop the program. Each block has 1K bytes.
All the segment register .used should contain the same base address.
Solution:
Count (n - 1) for 1K bytes = 01111111111 = 3FF H

6
Program:
MOV AX,
9500H
MOV DS,AX
MOV SI, 0H
MOV AX,
9500H
MOV ES, AX
MOV DI, 1000H
MOV CX, 3FFH
CLD
REPZ: CMPSB
HLT
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q9) Determine the effect of each one of the following 8086 instructions:
(i) PUSH [BX] (ii) DIV DH
(iii) CWD (iv) MOV SB
(v) MOV START [BX], AL
Assume the following data prior to execution of each one of the instructions
independently :
[DS] = 3000H [AX] ==00A9H [ES] = 5000H [SI] ==0400 H
[DX] = 0400H [D1] = 0500H [SP] = 5000H DF ==0
[SS] = 6000H [BX] =6000H [36000H] = 02H [ 3600 H] = 03H
[50500 H] = 05H [30400 H] =02H [30401 H] = 03 H.
Solution:
(i)
20-bit Physical address by taking Base address from DS and Effective
address from BX register = 36000 H. 20 bit Physical location pointed
by SP and SS = 65000 H.
PUSH [BX] pushes the contents of memory locations [36001H] and [36000H]
in to stack locations 64FFFH and 64FFEH respectively. The SP is then

7
decremented by two to contain the 20 bit Physical address 64FFEH (SS=6000H,
SP = 4FFE H). Therefore, [64FFFH] = 03 H and [64FFE H] = 02 H.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q10) Write an assembly language program to reverse the given digits.
Solution:
MOV AX, VARIABLE
MOV cx, 0000H
MOV BX, 0010H
BACK: MOV DX, 0000H
DIV BX
PUSH AX
PUSH DX
MOV AX, CX
MUL BX
POP DX
ADD AX, DX

8
MOV CX,AX
POP AX
OR AX, AX
JNZ BACK
HLT
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q11) the 8088 and 8086 microprocessors by walter A. Triebel :
From Page 503 to page 505 examples (10.14,10.15,10.16)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q12) ) the 8088 and 8086 microprocessors by walter A. Triebel :
Page 573 section 10.6(Q)30, 31,32,33)
