
1
Fifth stage
mv
Pediatrics
mv
kl
Lec
Dr.Athal
مااتذكرm/10/2015
Lower Airway Diseases
Foreign Body Aspiration
Epidemiology
• Aspiration of foreign bodies into the trachea and bronchi is relatively common. The
majority of children who aspirate foreign bodies are under 4 years of age.
• Because the right mainstem bronchus takes off at a less acute angle than the left mainstem
bronchus, foreign bodies tend to lodge in right-sided airways.
• Some foreign bodies, especially nuts, can also lodge more proximally in the larynx or
subglottic space totally occluding the airway.
• Many foreign bodies are not radiopaque, which makes them difficult to detect
radiographically.
• The most common foreign bodies aspirated by young children are food (especially nuts)
and small toys. Coins more often lodge in the esophagus than in the airways. Older
children have been known to aspirate rubber balloons, which can be life-threatening.
Clinical Manifestations
• Many children who aspirate foreign bodies have clear histories of choking, witnessed
aspiration, or physical or radiographic evidence of foreign body aspiration.
• However, a small percentage of patients have a negative history because the aspiration
went unrecognized.
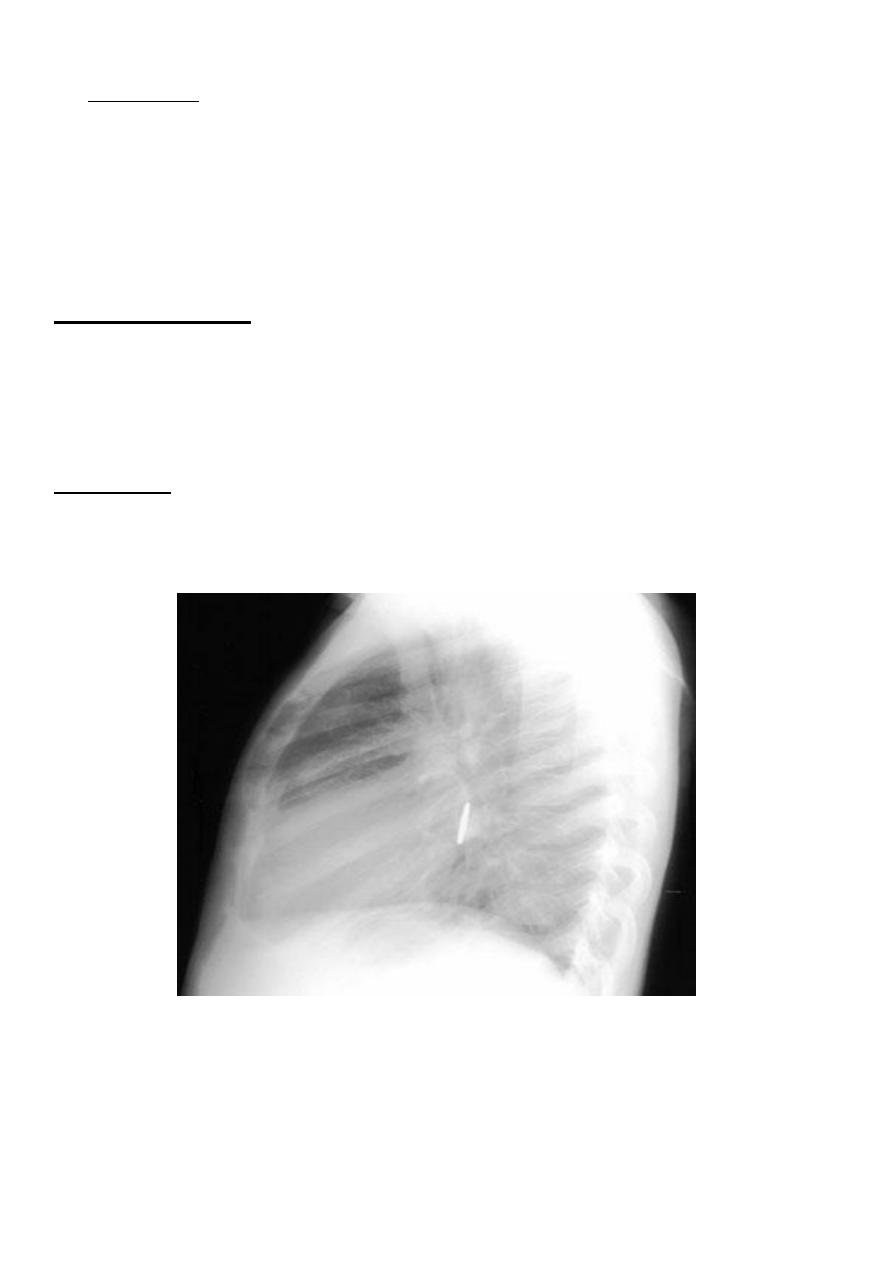
• Physical findings observed with acute foreign body aspiration include:
o Cough
o Localized wheezing
o Unilateral absence of breath sounds
o Stridor
o Rarely, bloody sputum.
2
• Most foreign bodies are small and quickly expelled, but some may remain in the lung for
long periods of time and presented as:
o persistent cough with sputum production
o persistent wheezing unresponsive to bronchodilator therapy
o recurrent or persistent unilateral pneumonia.
o persistent atelectasis
Diagnostic Studies:
• CXR : expiratory or lateral decubitus , reveal the presence of radiopaque objects and
can also identify focal air trapping.
• Bronchoscopy.
Treatment:
• Foreign body removal via rigid bronchoscopy.
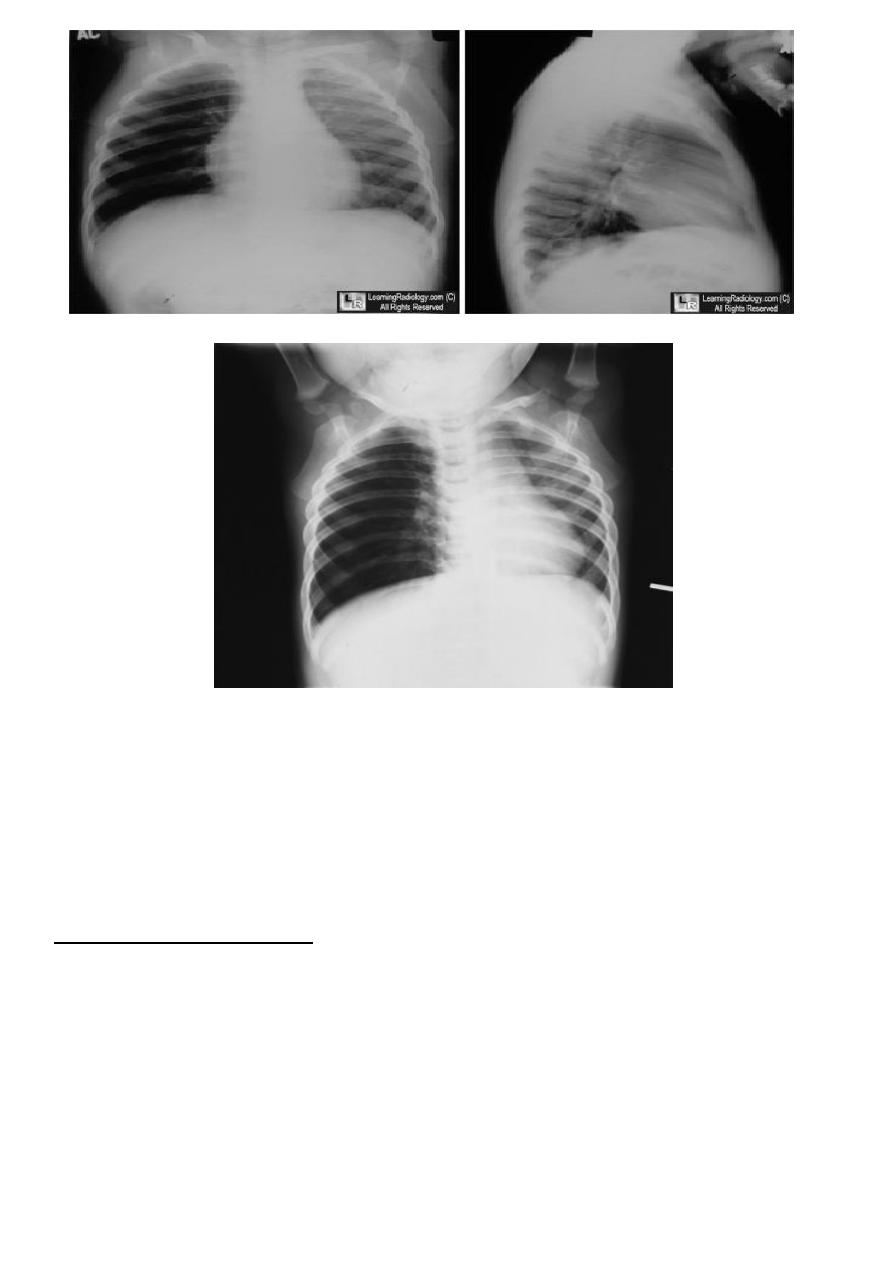
3
Expiratory chest radiograph in a 12-month-old boy with a 2-month history of wheezing demonstrates
continued hyperlucency and hyperexpansion of the right hemithorax.
-----------------------------------------------
BRONCHIOLITIS
Etiology & Epidemiology
• Bronchiolitis is a disease of small bronchioles with increased mucous production &
occasional bronchospasm, some time leading to air way obstruction.
• Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the primary cause of bronchiolitis, followed in
frequency by human metapneumovirus, parainfluenza viruses, influenza viruses,
adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, and, infrequently, Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
• Bronchiolitis is the leading cause of hospitalization of infants.
• Bronchiolitis occurs almost exclusively during 1
st
2 year of life, with a peak age at 2-6
months.

4
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
• Bronchiolitis caused by RSV has an incubation period of 4 to 6 days.
• Bronchiolitis classically presents as a progressive respiratory illness that is similar to
the common cold in its early phase with cough, coryza, and rhinorrhea.
• It progresses over 3 to 7 days to noisy, raspy breathing and audible wheezing. There is
usually a low-grade fever accompanied by irritability, which may reflect the increased
work of breathing.
• In contrast to the classic progression of disease, young infants infected with RSV may
not have a prodrome and may have apnea as the first sign of infection.
Physical signs:
• Dyspnea, intercostal & suprasternal retractions.
• Hyperexpansion of the lungs.
• Hyperresonance percussion.
• Auscultation reveals prolongation of the expiratory phase of breathing, diffuse
wheezes and crackles throughout the breathing cycle.
• With more severe disease, grunting and cyanosis may be present.
LABORATORY AND IMAGING STUDIES
• Routine laboratory tests are not required to confirm the diagnosis.
• Pulse oximetry: it is important to assess oxygenation in severe cases.
• CXR: shows signs of hyperexpansion of the lungs, including increased lung
radiolucency and flattened or depressed diaphragms. Areas of increased density may
represent either viral pneumonia or localized atelectasis.
• Frequent, regular assessments and cardiorespiratory monitoring of tired infants are
necessary because RF may developed.
• Viral detection (PCR, ELISA or culture) is not indicated in uncomplicated
bronchiolitis.

5
TREATMENT
• Indications for hospitalization include:
1. Moderate to marked respiratory distress, extreme tachypnea, hypoxemia (Po
2
< 60
mm Hg or oxygen saturation <92% on room air).
2. Apnea.
3. Inability to tolerate oral feeding.
4. Lack of appropriate care available at home.
5. Presence of risk factors for severe disease as:
o age <12 wk.
o preterm birth.
o underlying comorbidity such as cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurologic, or
immunologic disease.
• The mainstay of treatment is supportive
o Cool humidified oxygen if hypoxemic.
o Upper airway suctioning
o Sitting with head and chest elevated at a 30-degree angle with neck extended.
o Control of fever.
o Good hydration.
• Bronchodilators may produce short-term improvement in clinical features in severe
cases.
• Corticosteroids???, are not recommended in previously healthy infants with RSV.
Combined therapy with nebulized epinephrine and dexamethasone has been used with
some success, but additional studies are needed to confirm its efficacy.
• Nebulized hypertonic saline on demand has been reported to have some benefit.
• Heliox delivered by tight fitting mask or by continuous positive airway pressure has been
of some benefit in moderate to severe cases.
• Ribavirin, an antiviral agent administered by aerosol, has been used for infants with RSV
who have congenital heart disease or chronic lung disease.
• Intubation and ventilatory assistance for respiratory failure or apnea.

6
COMPLICATIONS AND PROGNOSIS
• Most hospitalized children show marked improvement in 2 to 5 days with supportive
treatment alone & resolve completely.
• Apnea especially in very young infant.
• Respiratory failure.
• Minor abnormalities of pulmonary function and bronchial hyperreactivity may persist
for several years. The incidence of asthma seems to be higher for children hospitalized
for bronchiolitis as infants.
• Recurrence is common but tends to be mild and should be assessed and treated
similarly to the first episode.
• The case fatality rate is 1%, highest among infants with preexisting cardiopulmonary
or immunologic impairment.
Vi
R
