To describe layers of the sole
To define the main nerves & vessels in the sole
To list some important ligaments & tendons in the region
To define foot arches
-The skin of the sole is variable in
thickness being thickest over the weight-
bearing areas
-The subcutaneous fat is intermingled
with fibrous tissue septa providing a
good shock-absorbing & weight bearing
cushion
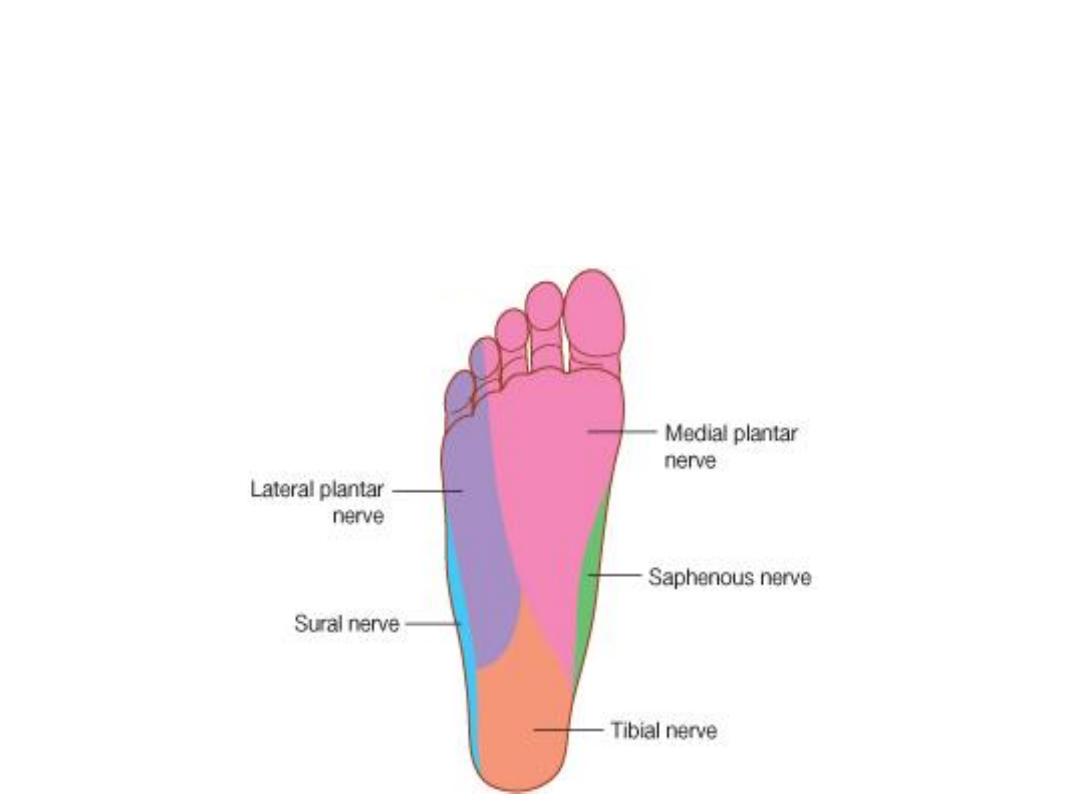
Cutaneous nerves:
Medial calcaneal branch of tibial nerve supplies the heel
Medial aspect of the foot skin is supplied by the saphenous nerve
The sural nerve does the same thing laterally
The major area is supplied by the medial & lateral plantar nerves
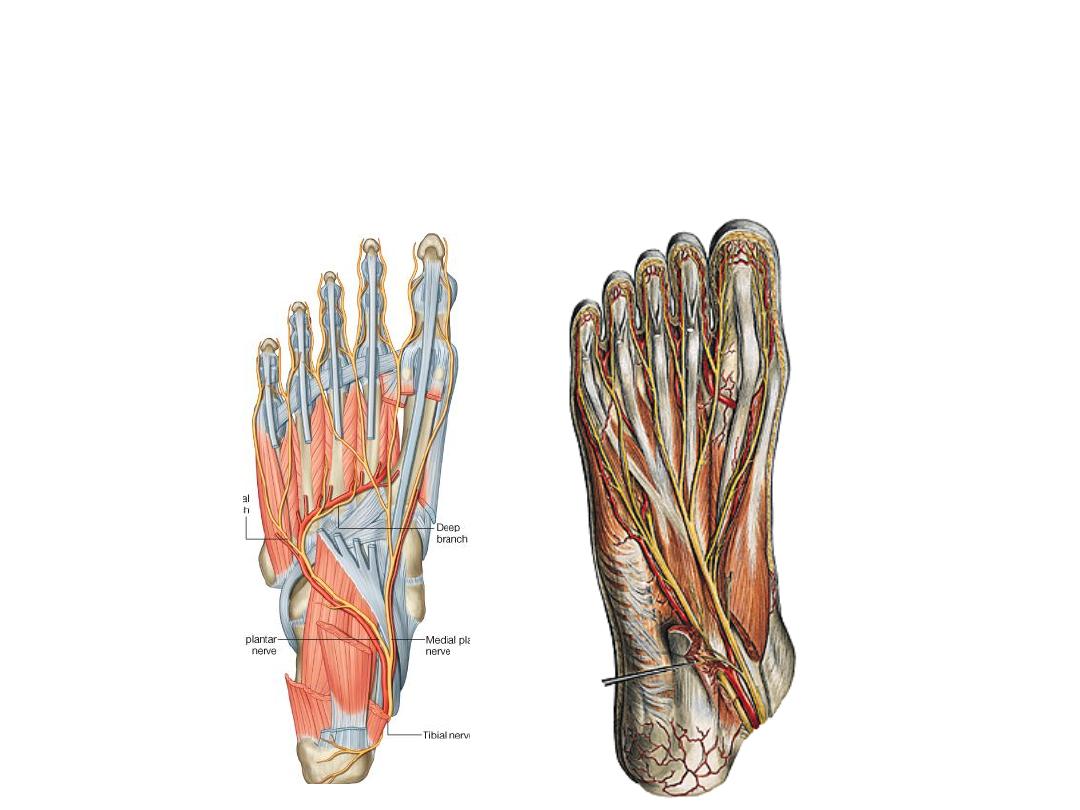
The medial plantar n. gives 1 proper & 3 common digital nerves for the medial
3.5 toes
The lateral plantar n. gives 1 common & I proper digital nerves for the lateral
1.5 toes
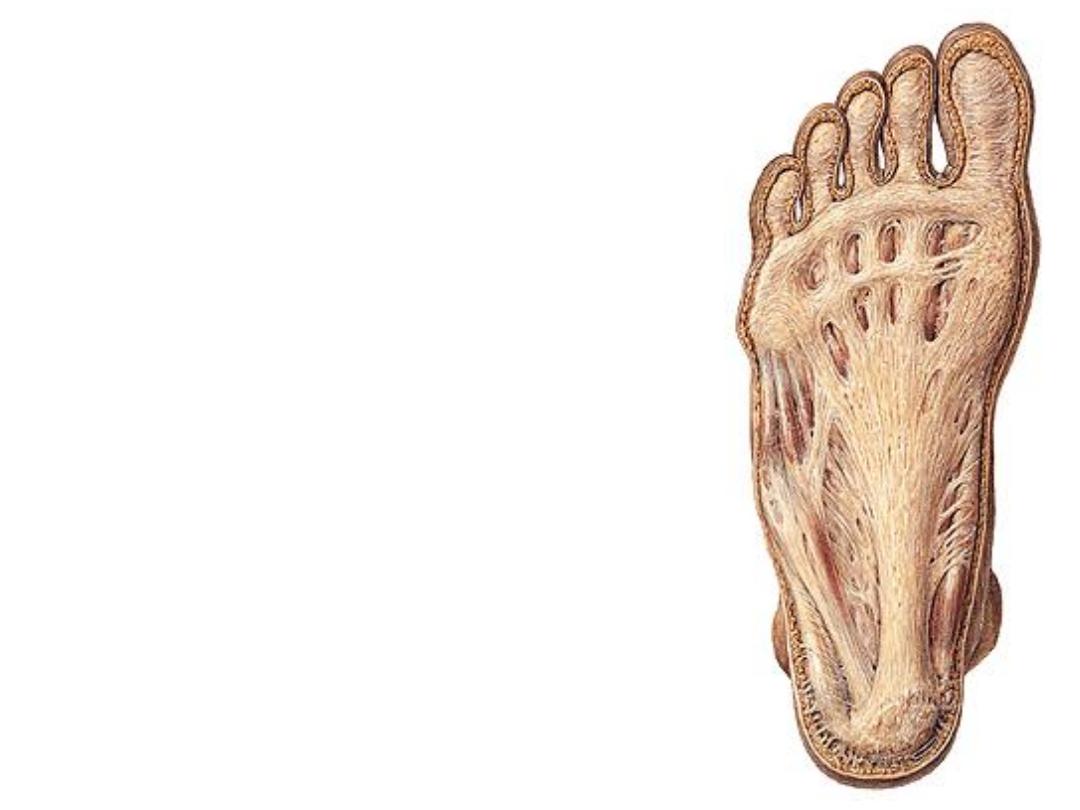
The plantar aponeurosis:
-A fibrous sheet that arises from the medial
process of calcaneal tuberosity & directed to
the toes
-The middle 3 bands of digital slips are the
broadest
-Slips are connected to each other by the
superficial transverse metatarsal ligaments at
the level of metatarsal heads
-From each side of the PA, a strong fibrous
partition (intermuscular septa) dips into the
sole to reach the 2
nd
& 4
th
metatarsals dividing
it
into
a
central,
medial
&
lateral
compartments
-Medial & lateral plantar fascia are the thin
extensions of the PA over the medial & lateral
compartments
Functions:
1- Anchoring skin.
2- Enhancing the grip.
3- Promoting foot arches.
4- Protection.
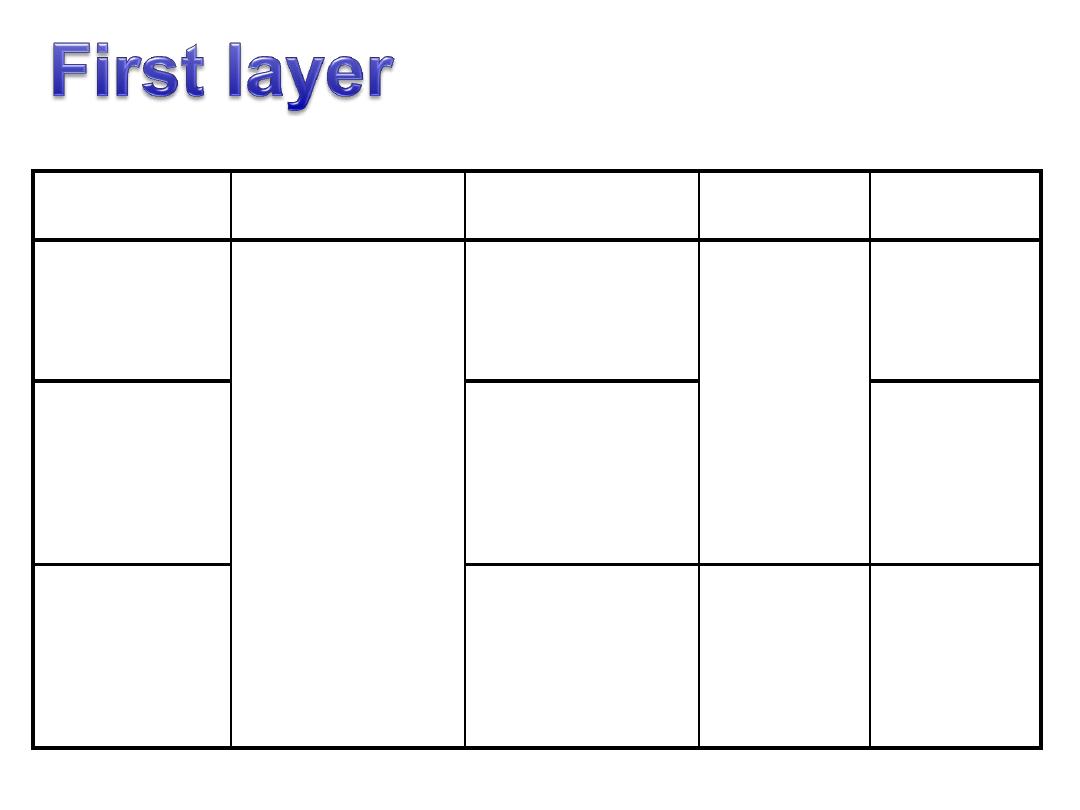
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Action
Flexor
digitorum
brevis
calcaneal
tuberosity
Sides of middle
phalanges of
lateral four toes
Medial
plantar nerve
S2,3
Flexes lateral
four toes at
PIPJ
Abductor
hallucis
Medial side of
base of proximal
phalanx of great
toe
Abducts and
flexes MTPJ
Abductor digiti
minimi
Base of proximal
phalanx of little
toe
Lateral
plantar
nerve from
S2,3
Abducts
little toe at
the MTPJ
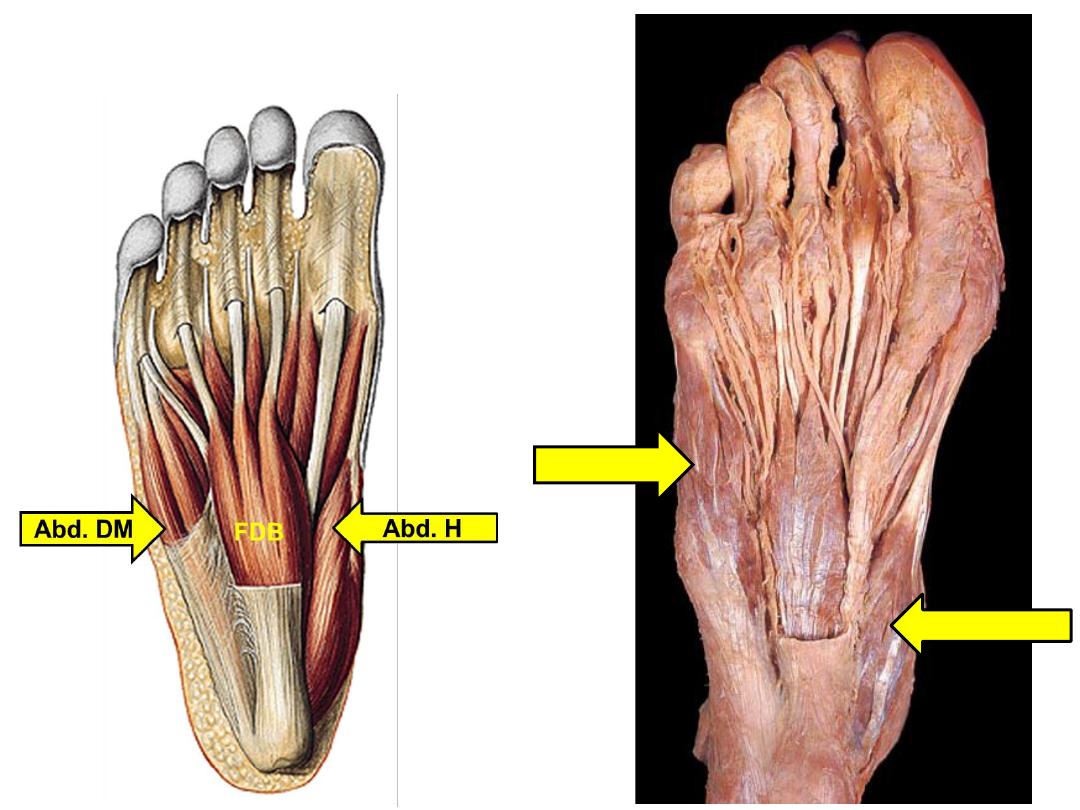
FDB
Abd. H
Abd. DM
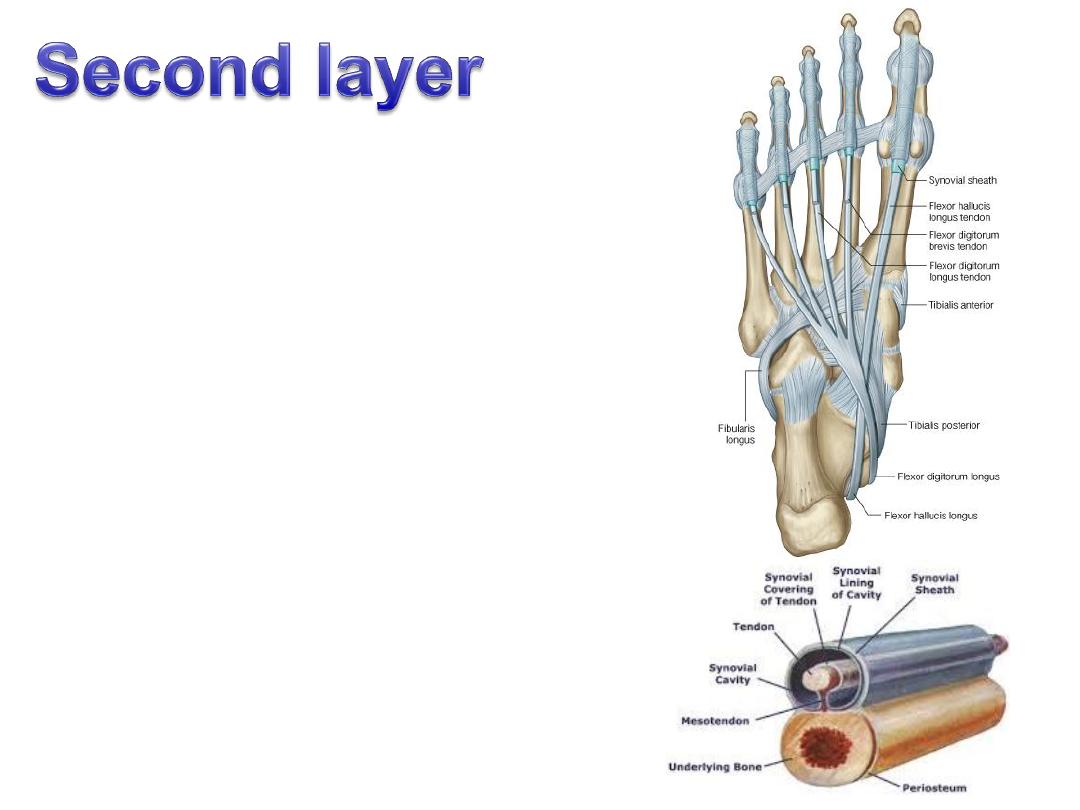
The long flexor tendons:
-Crossing takes place between the tendons
of FDL & FHL, the latter being deeper
-Fibrous flexor sheaths extend on the
undersurface
of
each
toe
from
the
metatarsal head to the base of the proximal
phalanx
-Synovial sheaths start proximal to the
fibrous ones & enclosed inside them
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Action
The
lumbricals
Medial sides
of tendons of
FDL
Medial side
of extensor
hoods 2-4
- 1&2: medial
plantar
- 3&4: lateral
plantar S2,3
- Flexion of MTPJ
- Extension of IPJ
Flexor
accessorius
(quadratus
plantae)
Calcaneal
tuberosity
Lateral side
of tendon of
FDL
Lateral plantar
nerve S1-3
Assists FDL by
offsetting its
direction
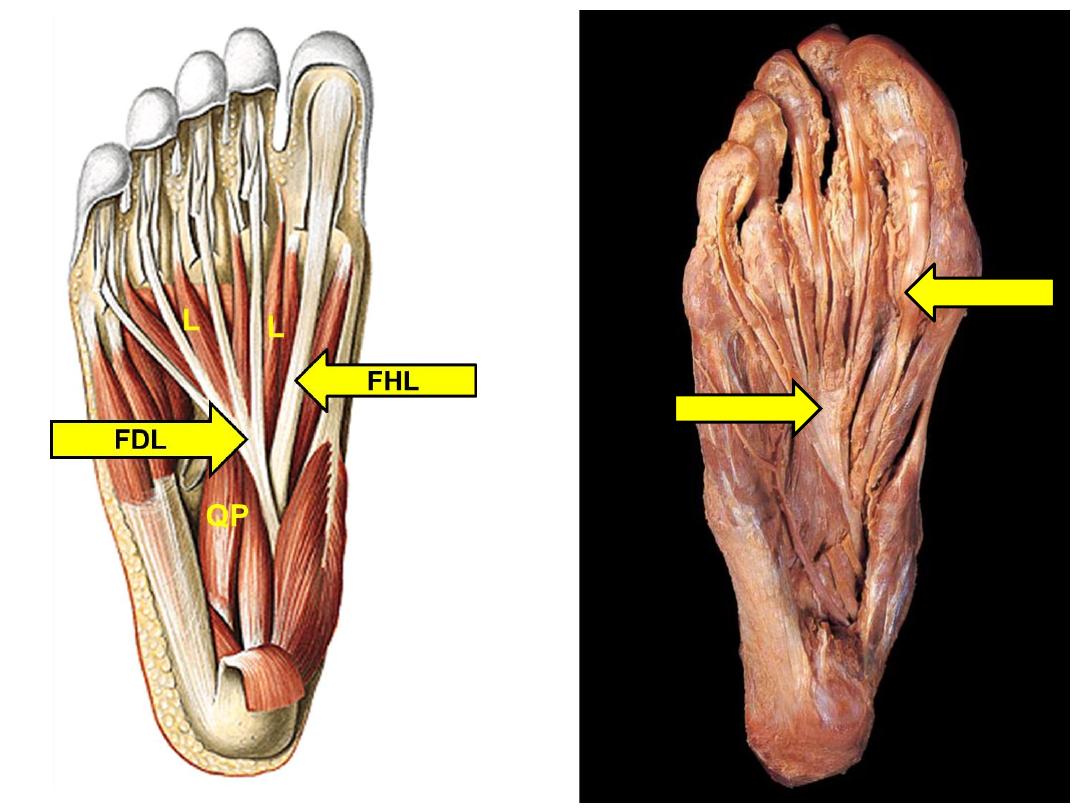
FHL
FDL
QP
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Action
Flexor hallucis
brevis
Cuboid and lateral
cuneiform
Base of proximal
phalanx of the
great toe
Medial
plantar n.
Flexes MTPJ
Flexor digiti
minimi brevis
Base of 5th
metatarsal
Lateral aspect of
the proximal
phalanx of little
toe
Lateral
plantar
nerve S1-3
Flexes little
toe at the
MTPJ
Adductor
hallucis
-
Transverse
head; MTPJ 3-5
-
Oblique head;
bases of
metatarsals 2-4
Lateral side of
base of proximal
phalanx of great
toe
Adducts
great toe at
MTPJ
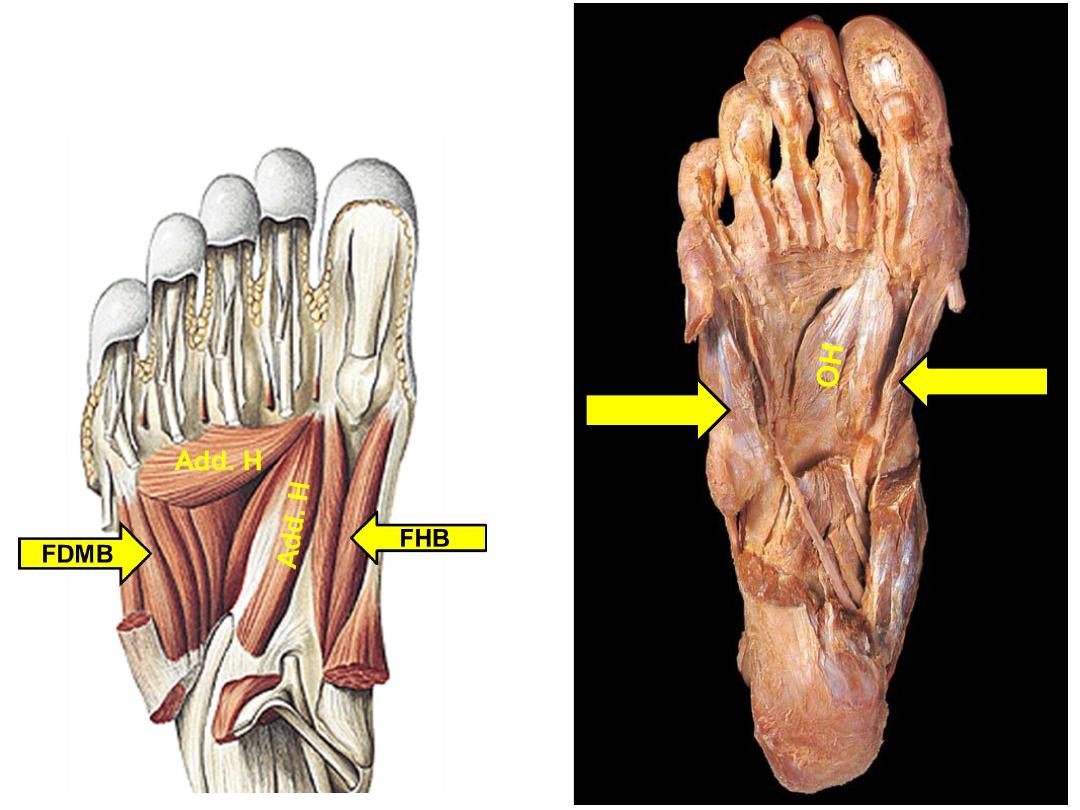
TH
FDMB
FHB
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Action
Dorsal
interossei
Sides of
adjacent
metatarsals
- Dorsal expansions
- Bases of proximal
phalanges of toes
2-4
Lateral plantar
nerve S2,3
(First 2 DI
receive from
deep
peroneal)
Abduction
away from
foot axis
Plantar
interossei
Medial
sides of
metatarsals
3-5
- Dorsal expansions
- Bases of proximal
phalanges of toes
3-5
Adduction
towards foot
axis
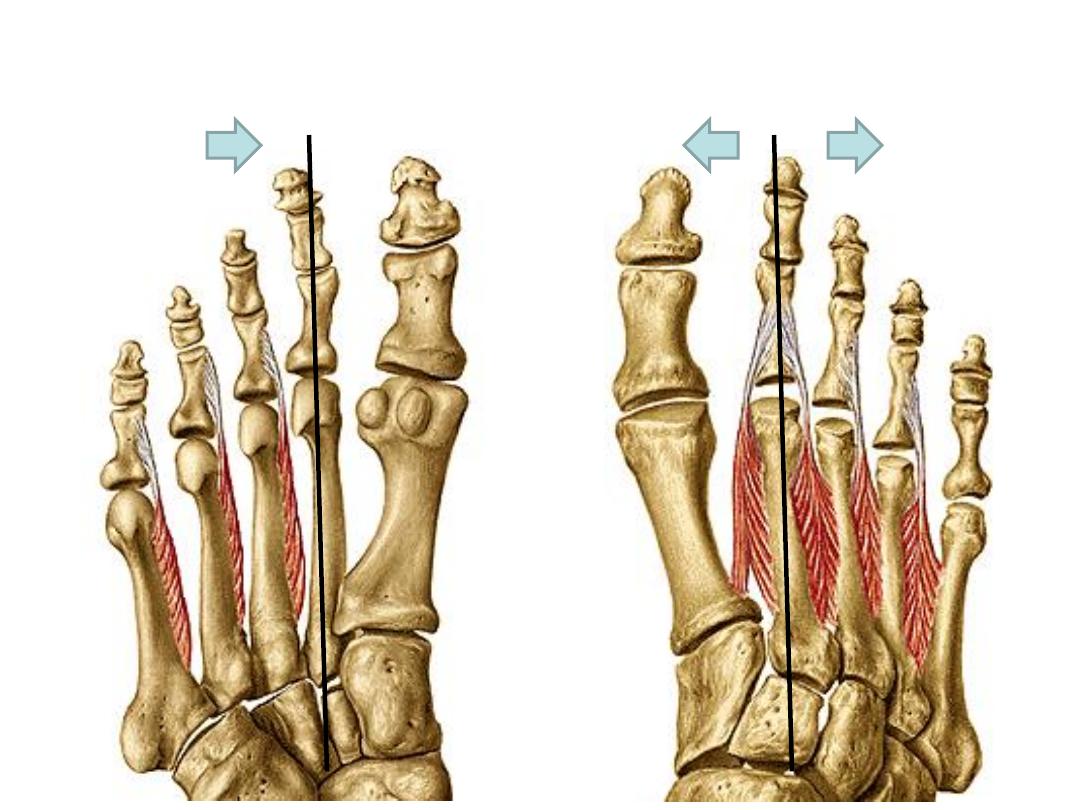
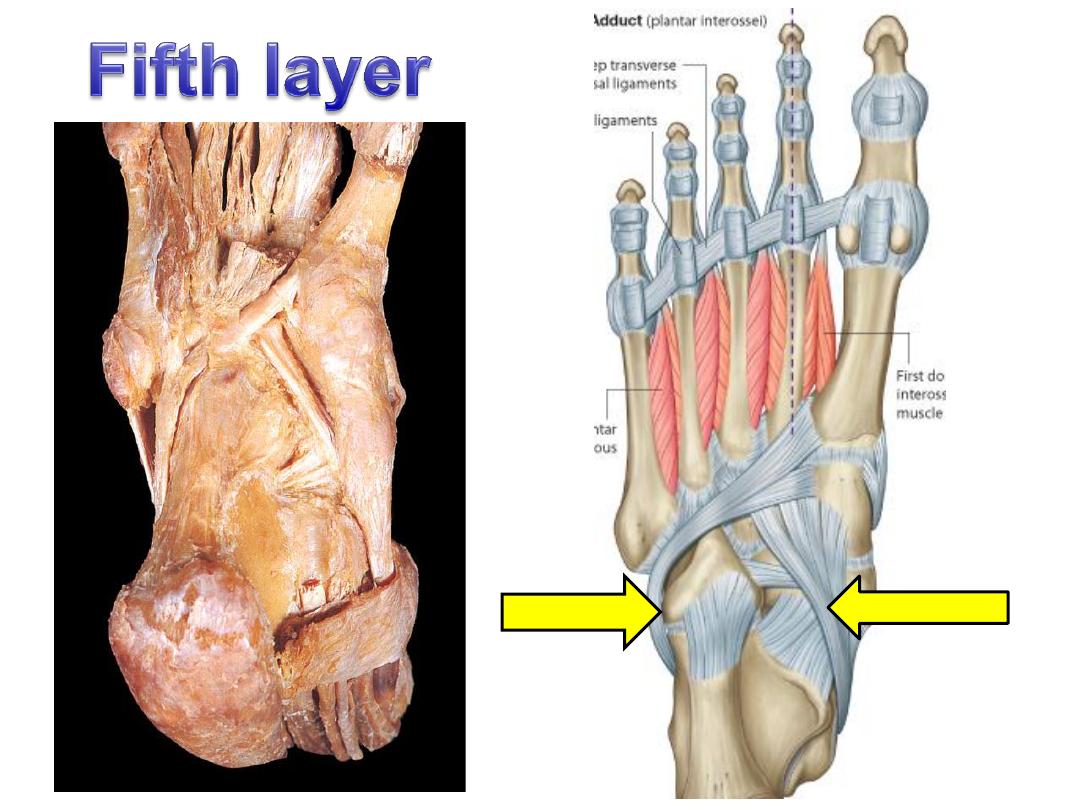
Plantar interossei
(Adductors)
Dorsal interossei
(Abductors)
PL
TP
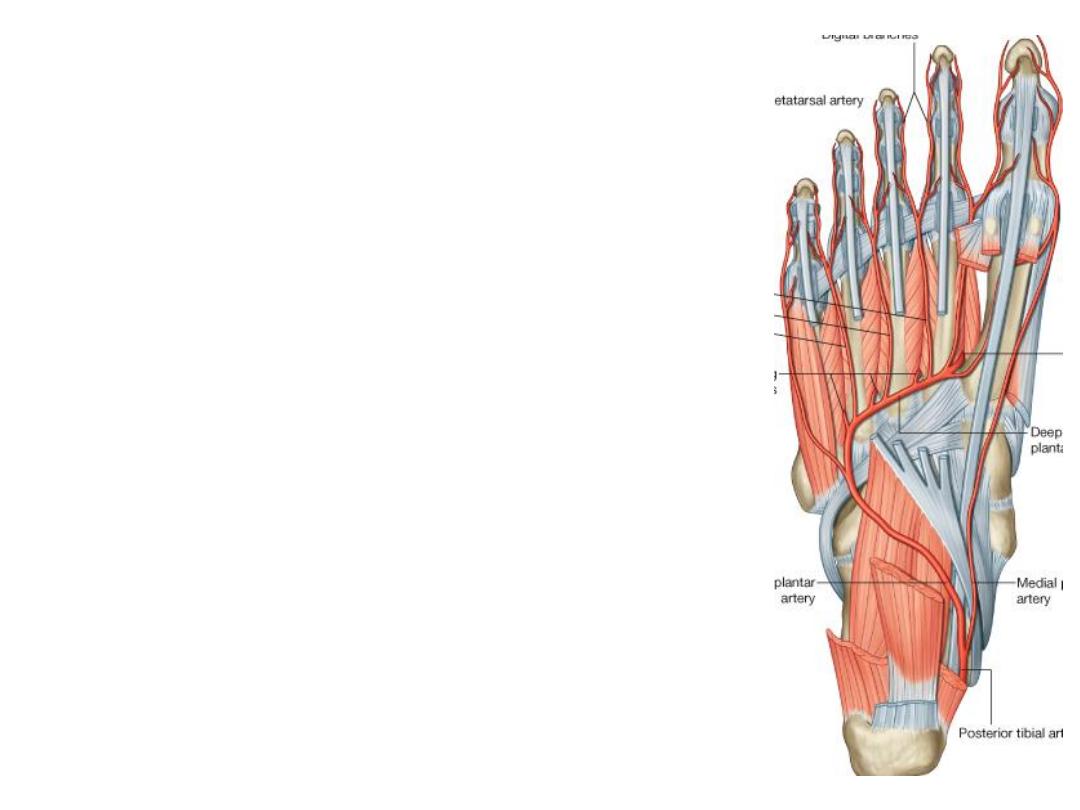
Arteries of the foot:
The medial plantar artery:
-A small artery that accompanies the medial
plantar nerve lying between ABH & FDB supplying
muscles & joints in the region
-At the base of the 1
st
metatarsal it anastomoses
with the 1
st
dorsal
metatarsal a.
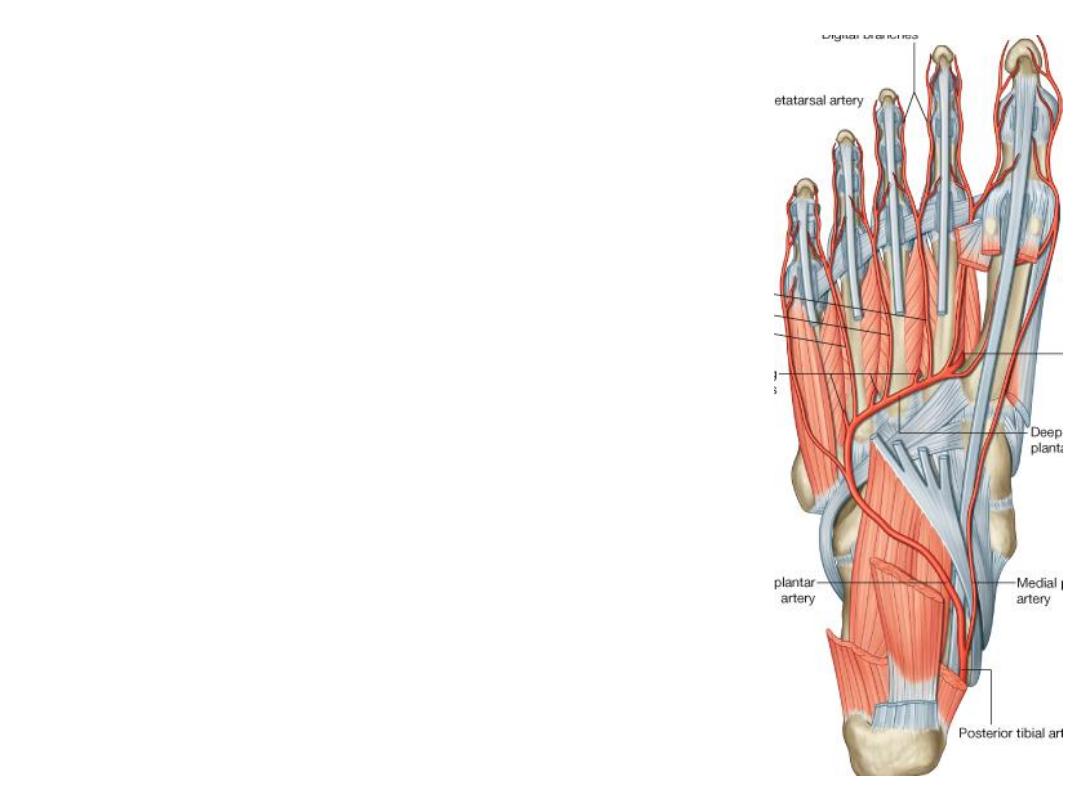
The lateral plantar artery:
-This artery simulates the ulnar artery in
the hand
-It passes diagonally accompanied by the
lateral plantar nerve between FDB & QP
muscles
-At the base of the 5
th
metatarsal, the
artery dips into the interosseous plane &
returns medially forming the plantar
arterial arch
-It ends by anastomosing with the deep
plantar branch of dorsalis pedis
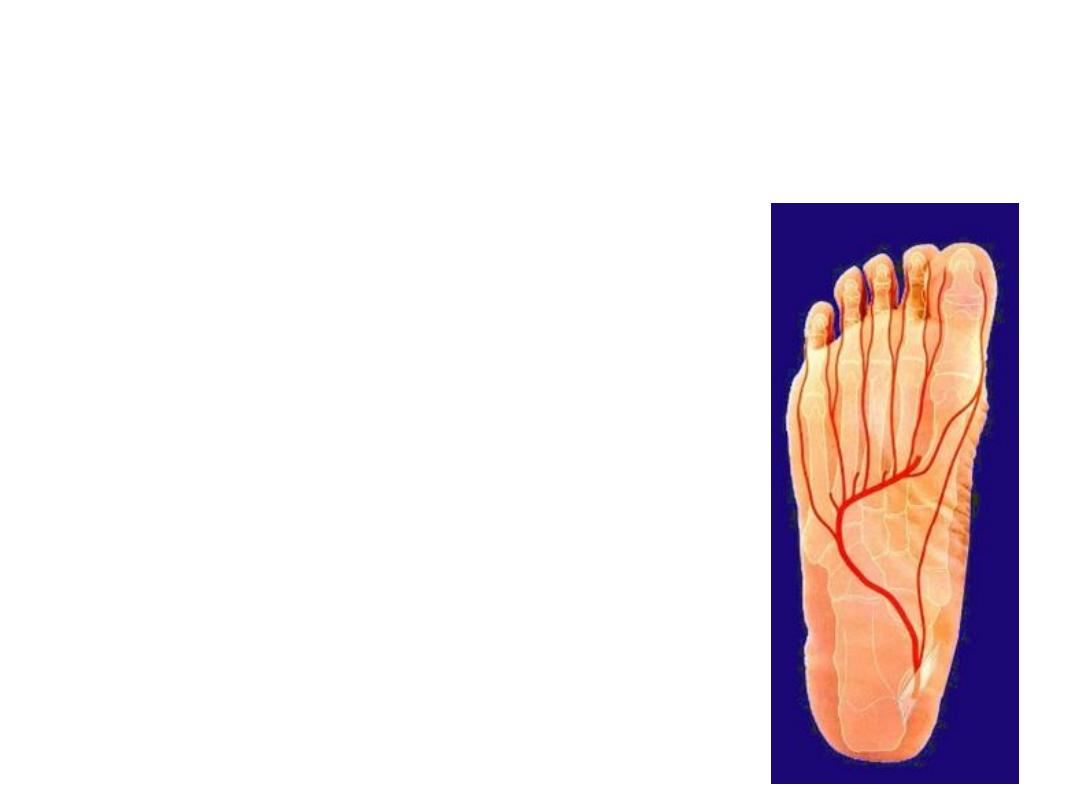
Branches
:
1- Four plantar metatarsal to the 4 clefts to divide into plantar digital arteries
2- Perforating branches; ascend in the lateral 3 spaces between the interossei to
anastomose with branches of dorsalis pedis a.
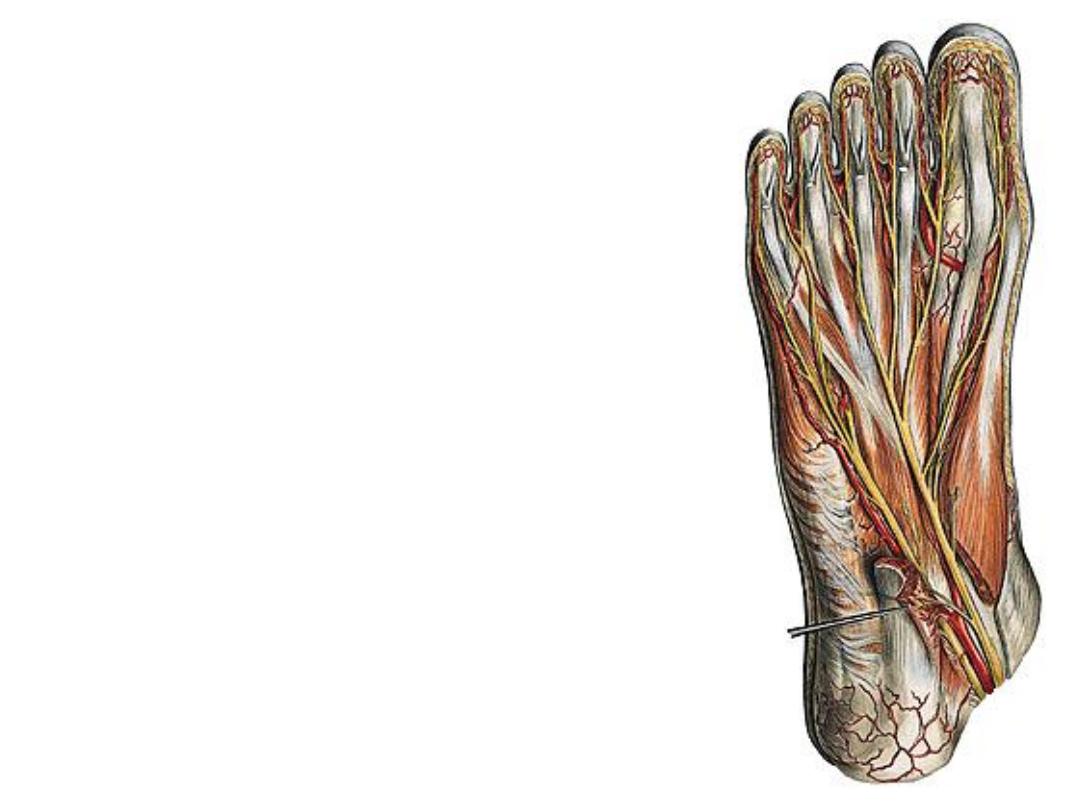
Nerves of the foot:
The medial plantar nerve:
-Accompanies the artery in the same plane
& gives:
1- Muscular; FHB, ABH, FDB & 1
st
2
lumbricals
2- Articular to tarsal joints
3- Plantar cutaneous branches for the
medial side of the sole
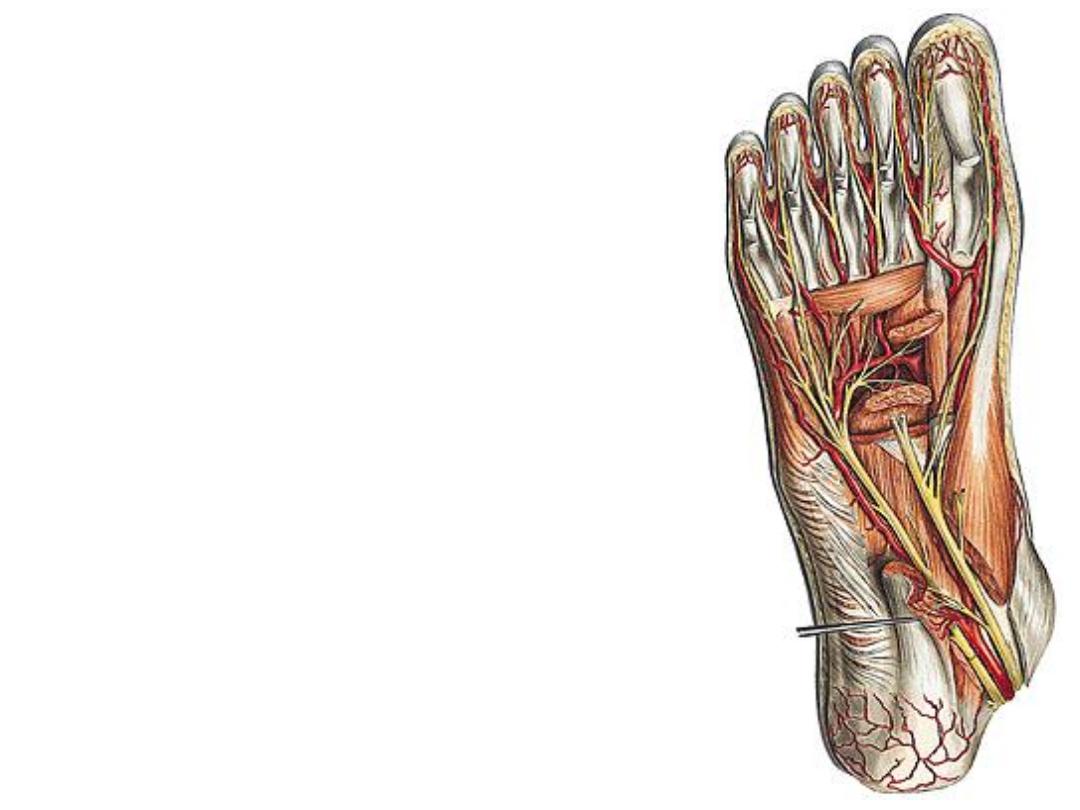
The lateral plantar nerve:
-This is the smaller of the 2 terminal
branches of the tibial nerve, it divides into:
1- Superficial branch; this supplies:
a) Cutaneous
b) Muscular; to flexor digiti minimi brevis &
the two interossei of the 4
th
space
2- Deep branch; accompanies the artery &
supplies:
a)All remaining muscles of the foot
b)Articular branches
Foot arches:
Rigid feet transmit shock to the axial
skeleton
Flexible feet are shock absorbers
Our feet are composed of numerous
bones connected by ligaments, it has
considerable flexibility that allows it to
deform with each ground contact, thereby
absorbing much of the shock.
Additional shock absorbing system is
the longitudinal and transverse arches
that add to the weight-bearing capabilities
and resiliency of the foot.
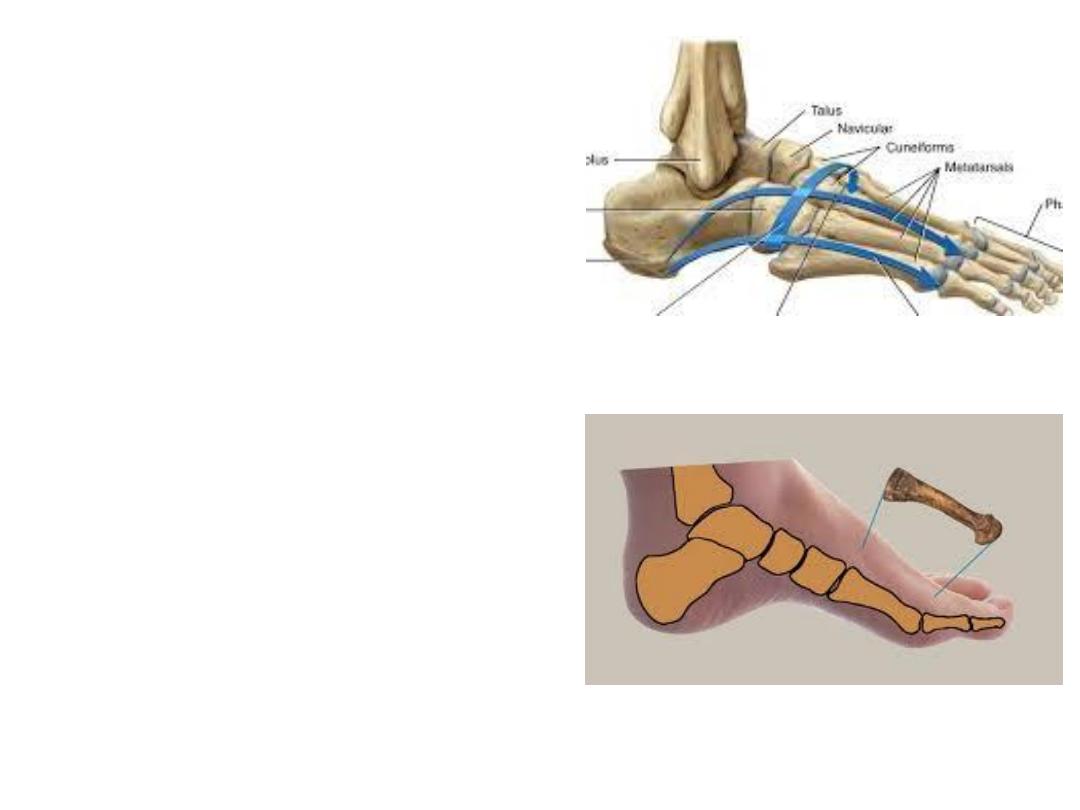
Longitudinal arches:
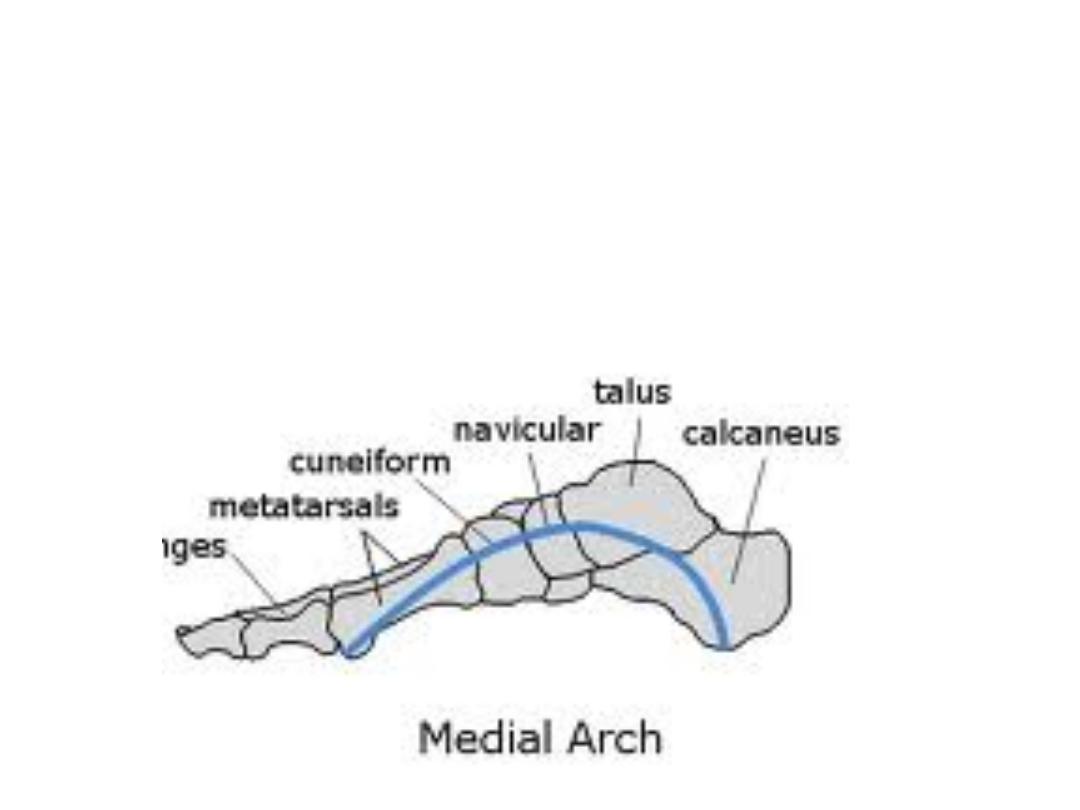
Medial LA:
The medial longitudinal arch is higher and more important.
The medial longitudinal arch is composed of the calcaneus, talus, navicular,
three cuneiforms, and three metatarsals.
Tibialis anterior & peroneus longus tendons predispose & support this arch.
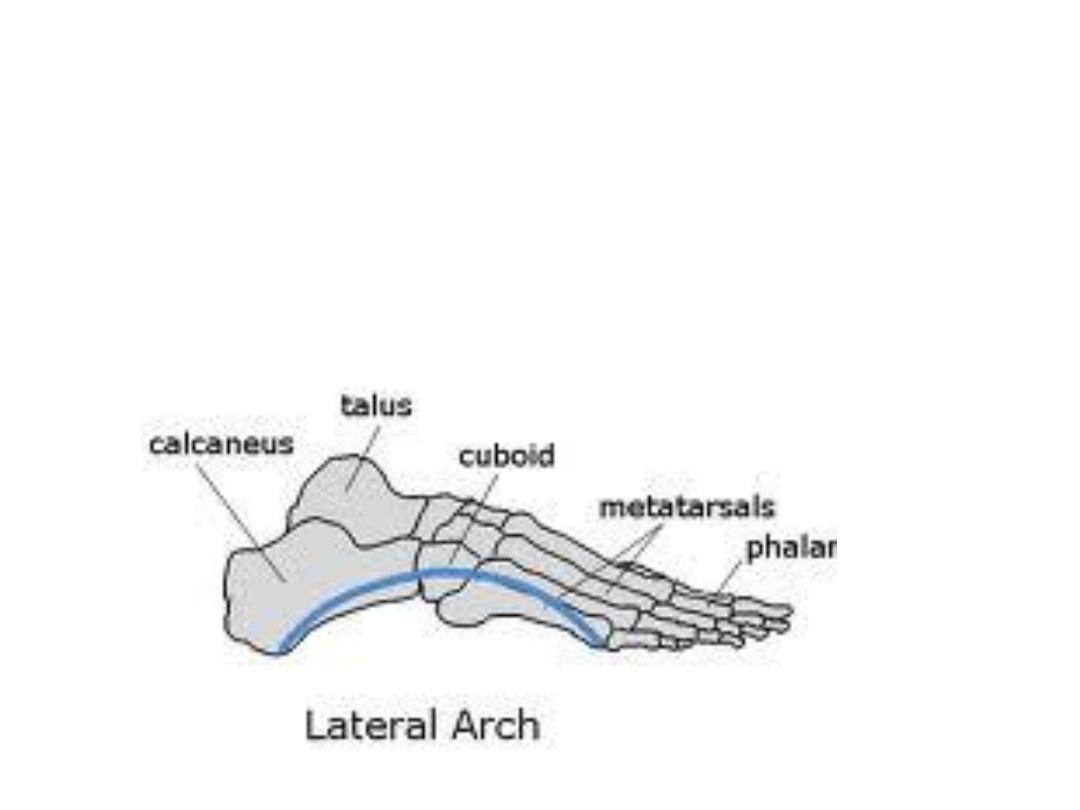
Lateral LA:
Is much flatter than the medial & rests on the ground during standing
It is made up of the calcaneus, cuboid, and lateral two metatarsals.
Plantar aponeurosis with the long & short plantar ligaments support both
arches
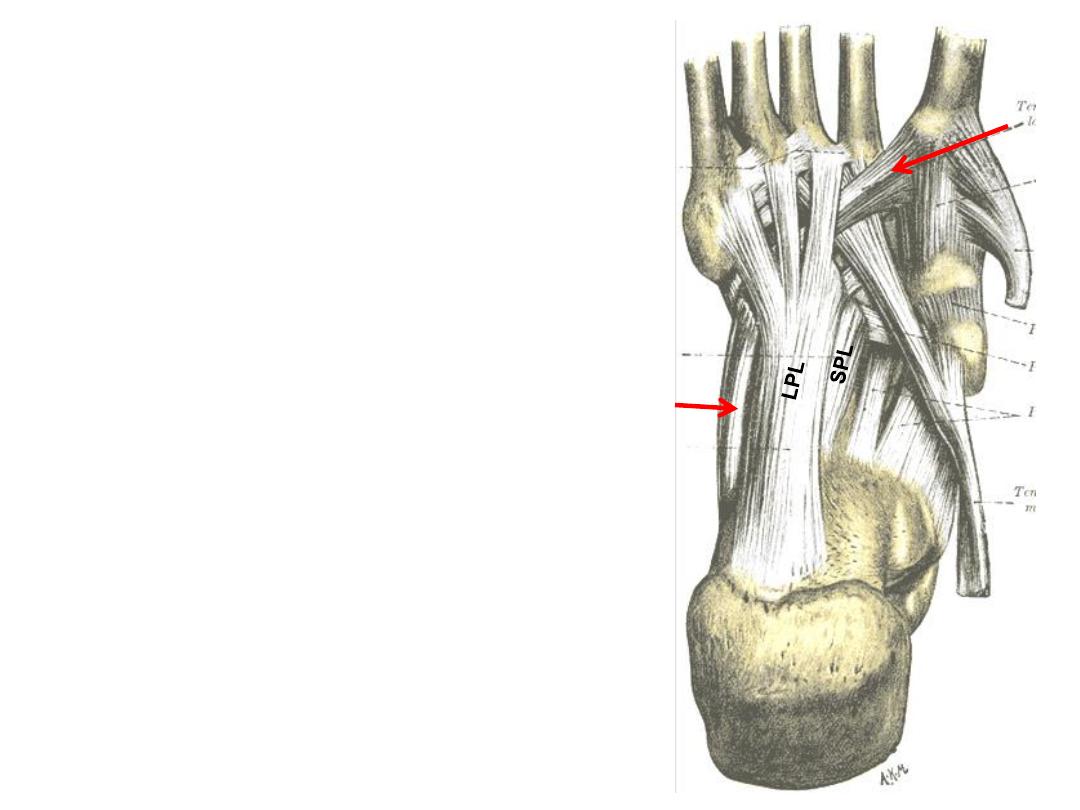
The calcaneo-cuboid ligaments:
1- The long plantar ligament:
-Longest ligament in the foot
-Connects the calcaneus to cuboid
-Passes superficial to the tendon of PL
2- The short plantar ligament:
-Deeper that LPL
-Connects the same bones
-Lies posterior to the tendon of PL
PL
PL
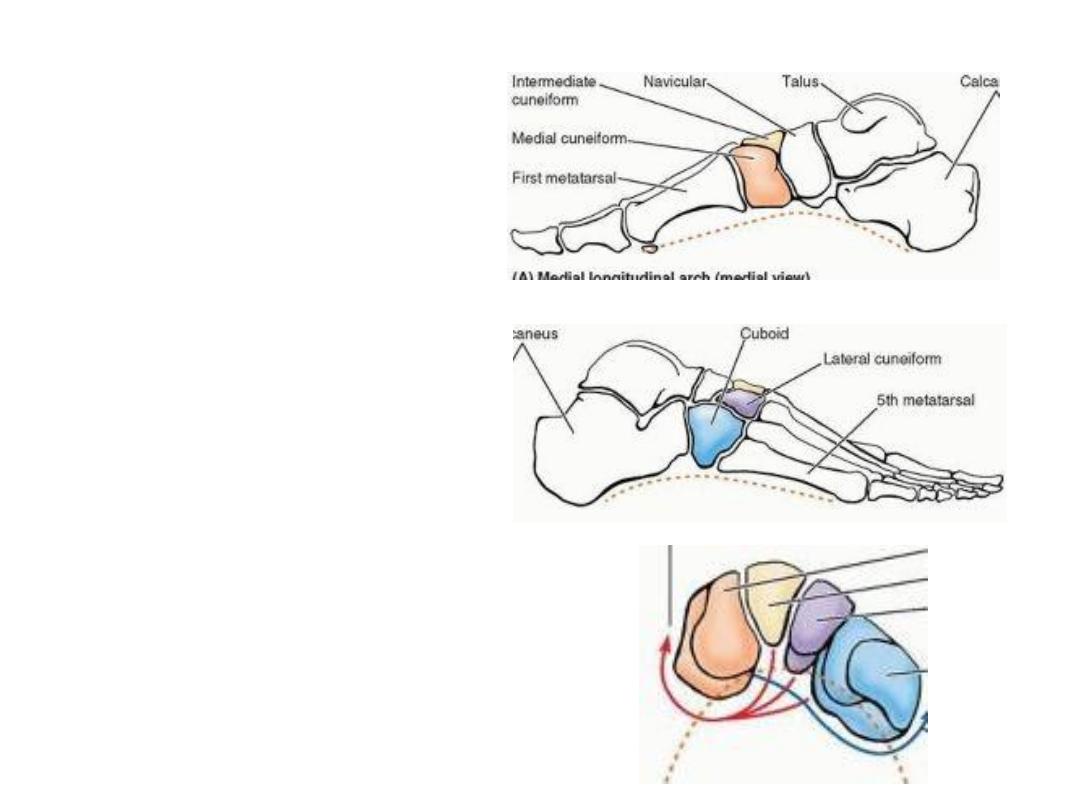
The transverse arch:
Runs from side to side
It is formed by the cuboid,
cuneiforms, and bases of the
metatarsals.
The medial and lateral parts of
the longitudinal arch serve as
pillars for the transverse arch.
The tendons of the fibularis
longus and tibialis posterior help
maintaining the curvature of the
transverse arch.
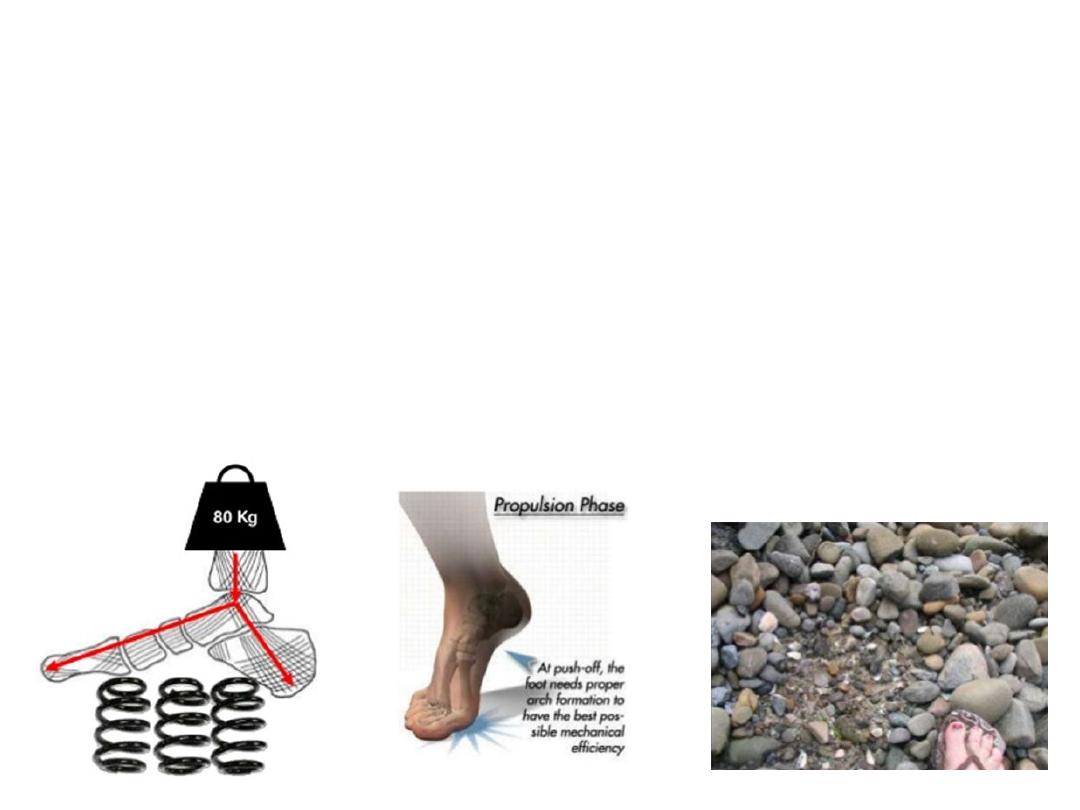
Functions:
1- Divides body weight equally on pressure areas of the sole
2- Propulsion during walking & running
3- Shock absorption
4- Surface adaptation
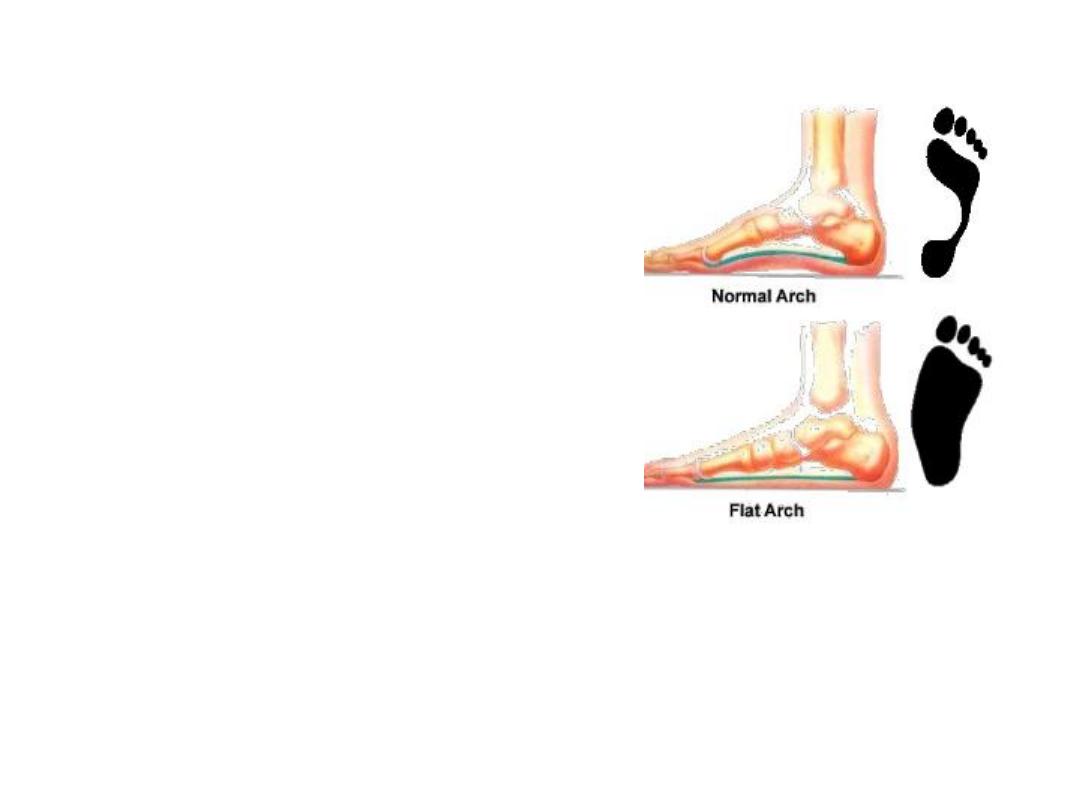
Pes planus (flat foot):
-
Arch collapse (especially MLA)
-
The whole foot area touches the
ground
-
Jumping prevented!
