To list the muscles of the flexor compartment of the thigh
To describe the course of sciatic nerve in the thigh
To define the popliteal fossa, boundaries & contents
To find the popliteal pulse
To describe the lumbosacral plexus
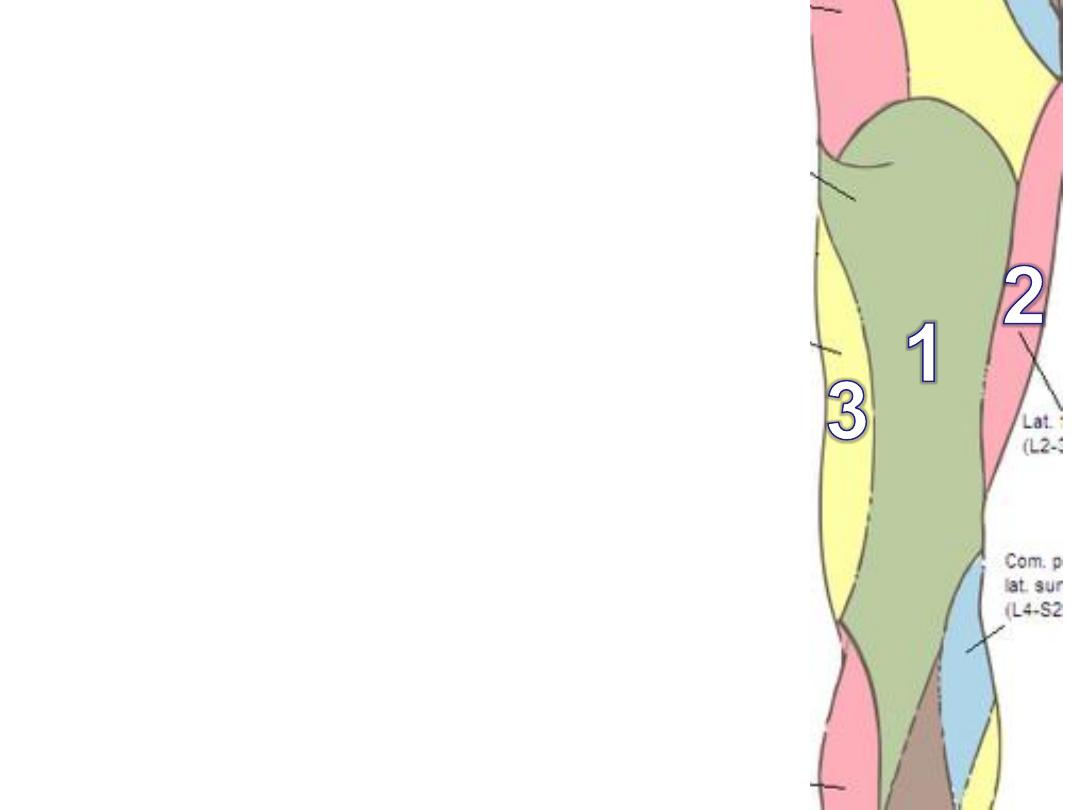
The flexor (hamstring) compartment):
Cutaneous innervation:
1- Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh
2- LCNT
3- Obturator nerve
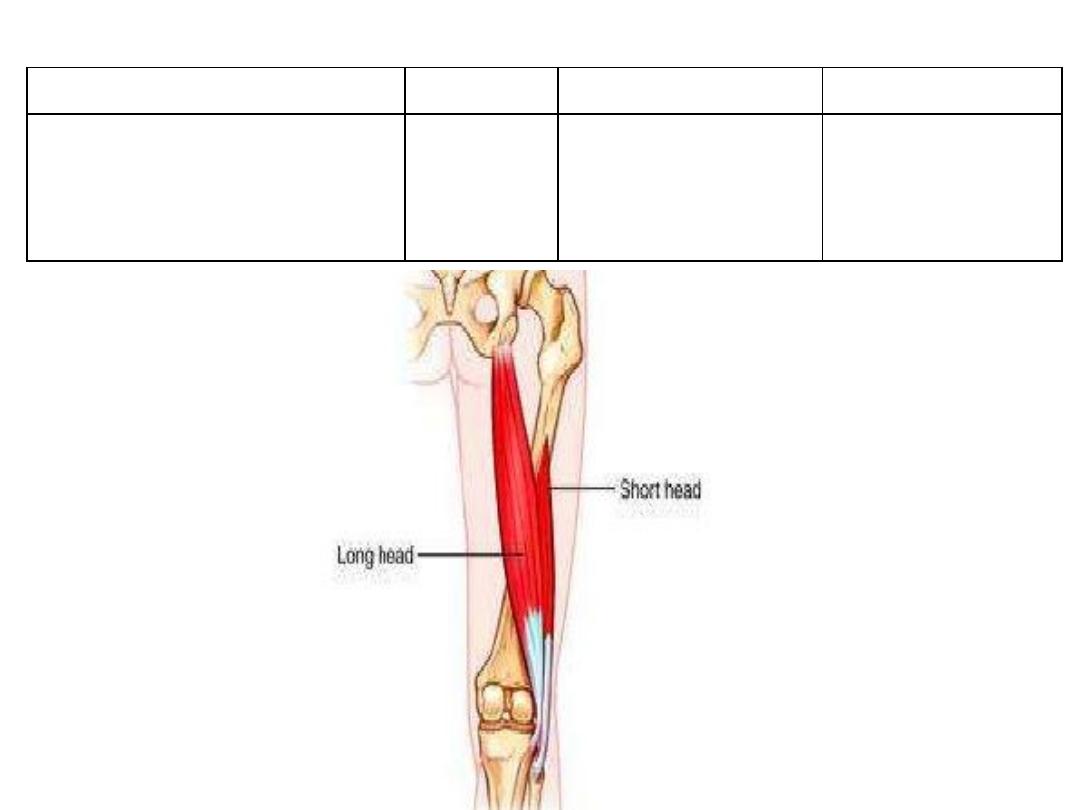
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
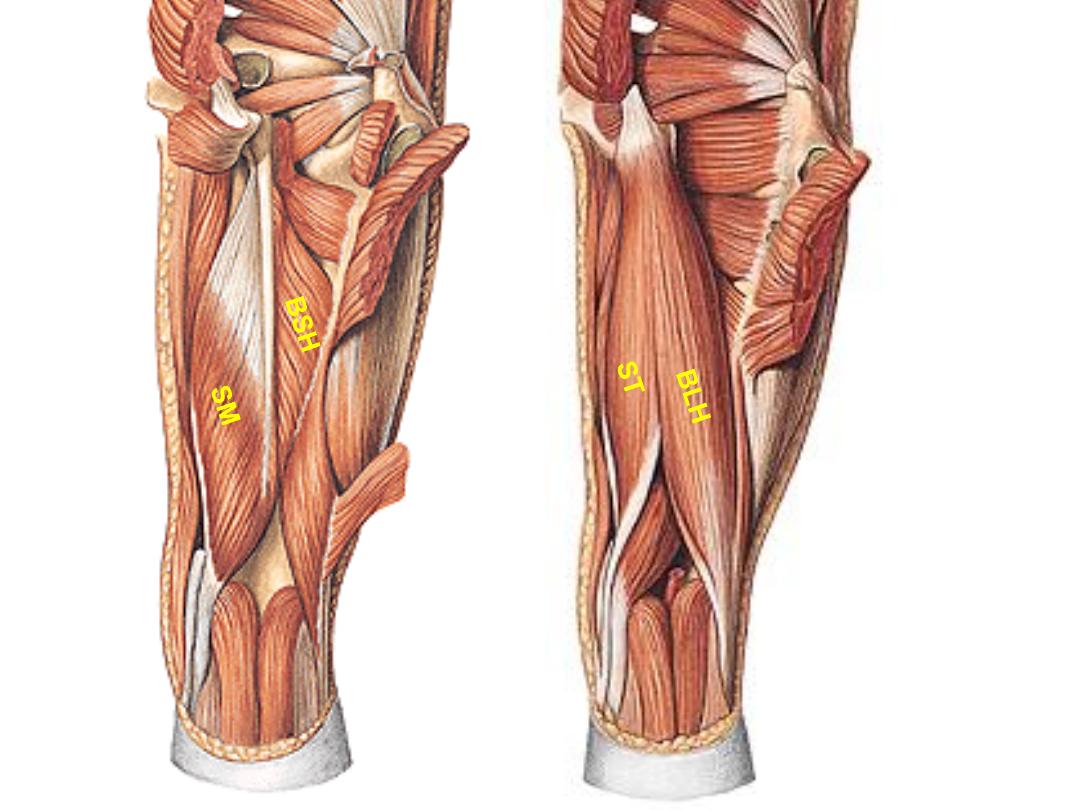
-LH; inferomedial part of ischial
tuberosity
-SH; lateral lip of LA
Head of
fibula
- LH; sciatic n (tibial)
- SH: sciatic n (CP)
- Hip extensor & LR
- Knee flexor & LR
Biceps femoris:
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
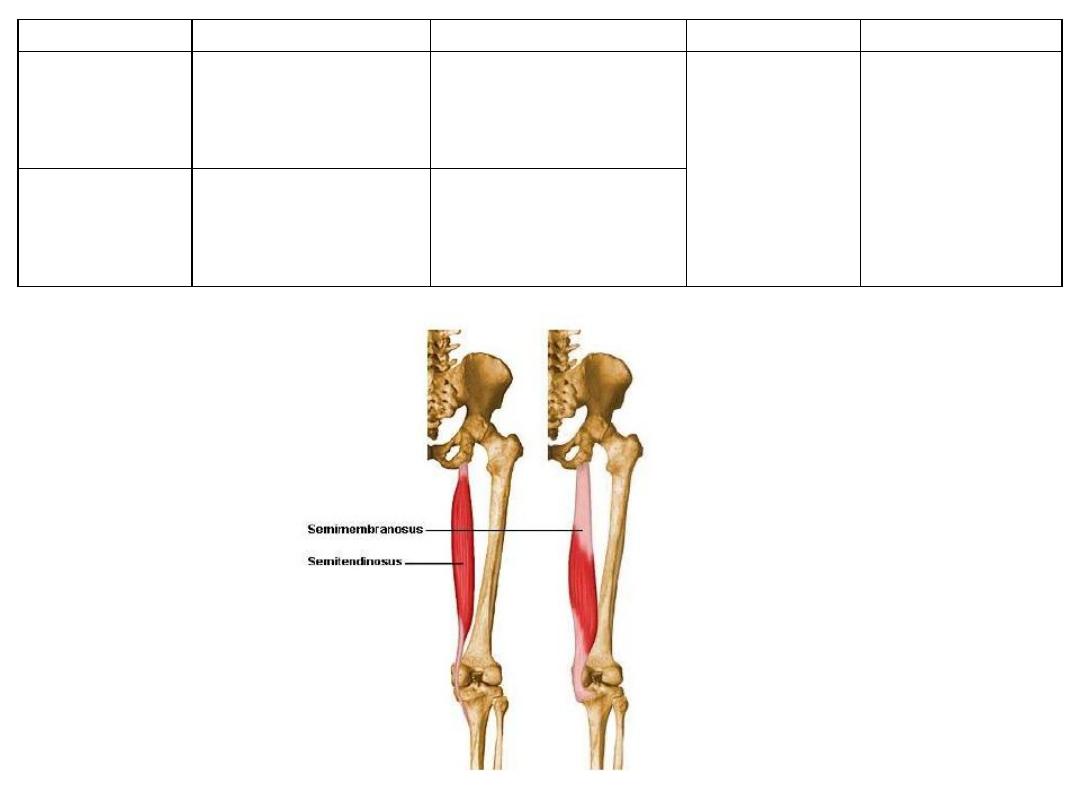
Semi-
tendinosus
With biceps LH
Medial surface of
proximal tibia
Sciatic nerve
L5 - S2
(TIibial)
- Hip extensor &
MR
- Knee flexor &
MR
Semi-
membranosus
Superolateral part of
ischial tuberosity
Posterior surface of
medial tibial condyle
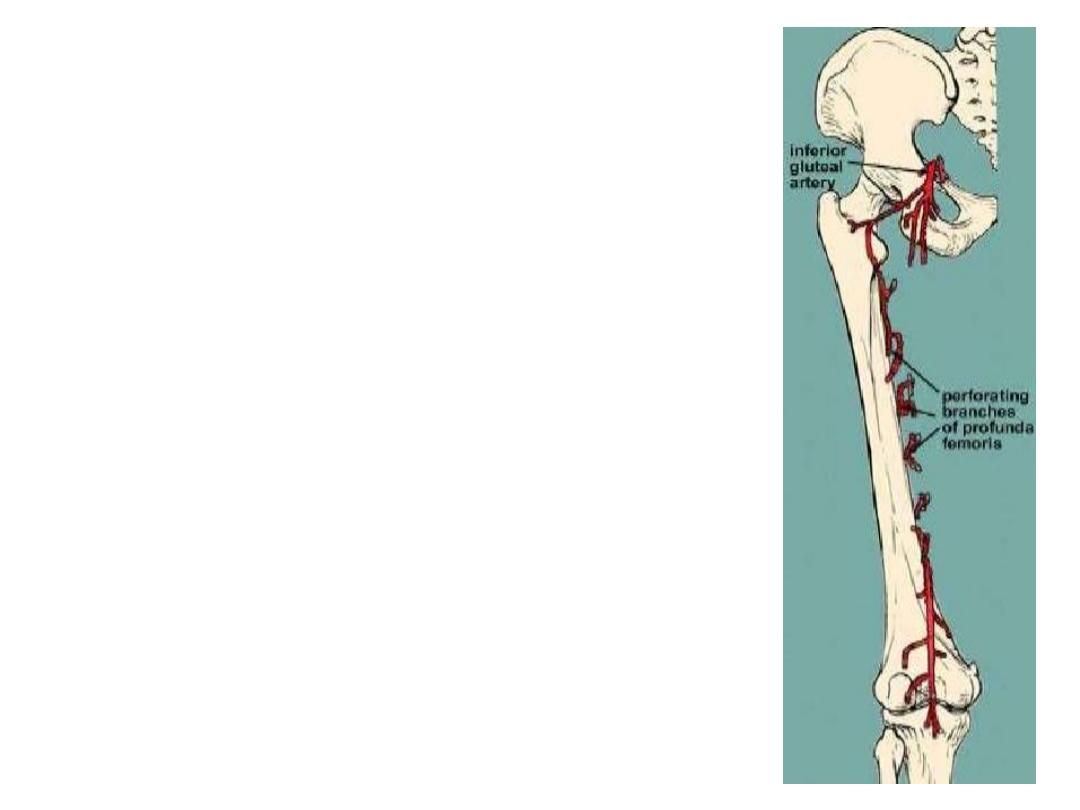
The perforating arteries:
-Four branches of the profunda femoris, the 4
th
is
the continuation of the artery
-So named because they perforate adductor
magnus to reach the hamstring compartment
-They have circular course around the shaft of
femur
-They anastomose with each other
-P1 shares in the cruciate anastomosis
-P4 shares in the knee anastomosis
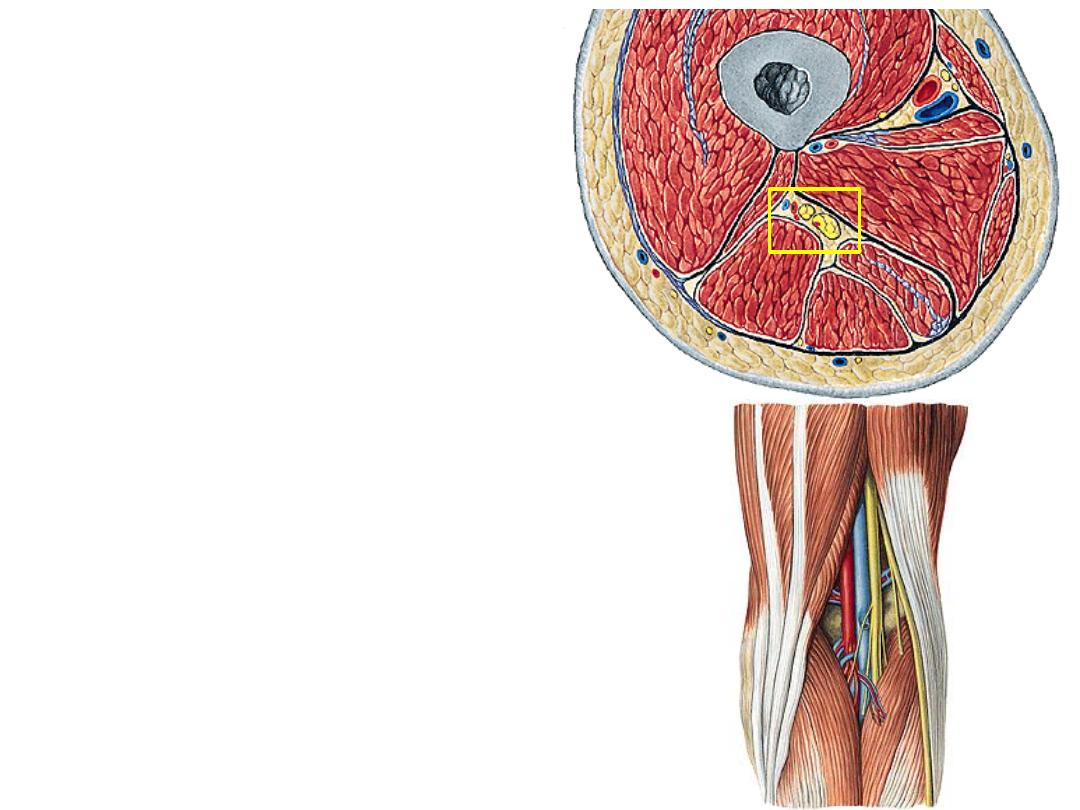
The sciatic nerve:
-Descends in the flexor compartment
deep to BF, posterior to adductor
magnus
-The tibial component lies medial in
the nerve & supplies all flexor
muscles except the short head of
biceps (by the common peroneal part)
-At the popliteal fossa the nerve
divides into its main components
again
-Tibial nerve descends vertically while
CPN winds around the neck of fibula
BF
AM
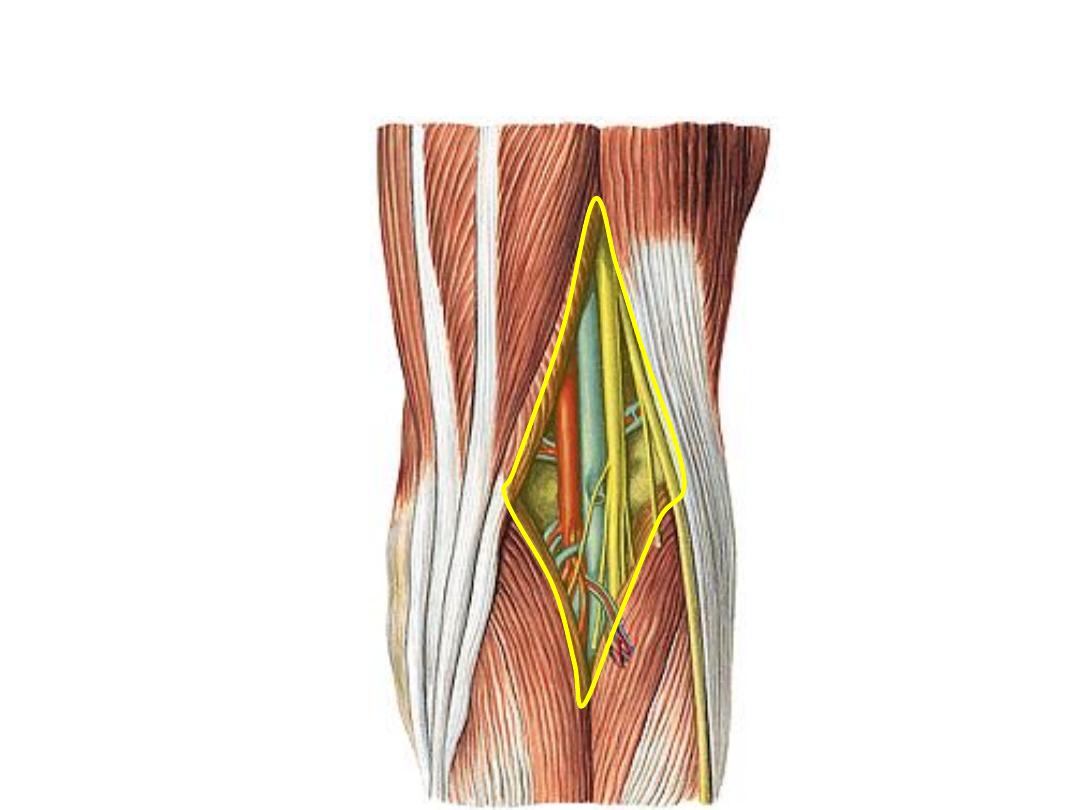
The popliteal fossa:
A diamond-shaped, fat-filled space which lies behind the knee joint
Boundaries:
Upper medial
Semi- muscles
Upper lateral
Biceps F
Lower medial
Gastrocnemius
MH
Lower lateral
Gastrocnemius
LH
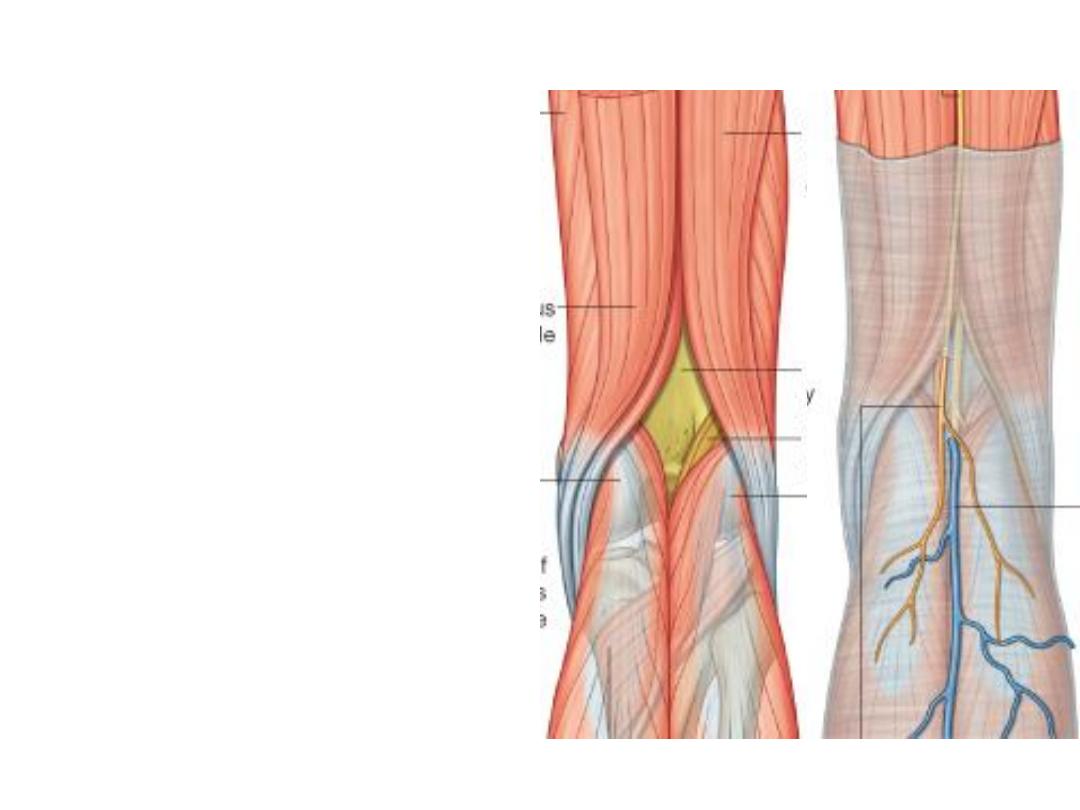
The roof:
The roof of the fascia is formed by
fascia lata pierced here by the
small saphenous vein & the PFCN
The floor:
Formed by the back of the capsule
of the knee joint, oblique popliteal
ligament & popliteus muscle
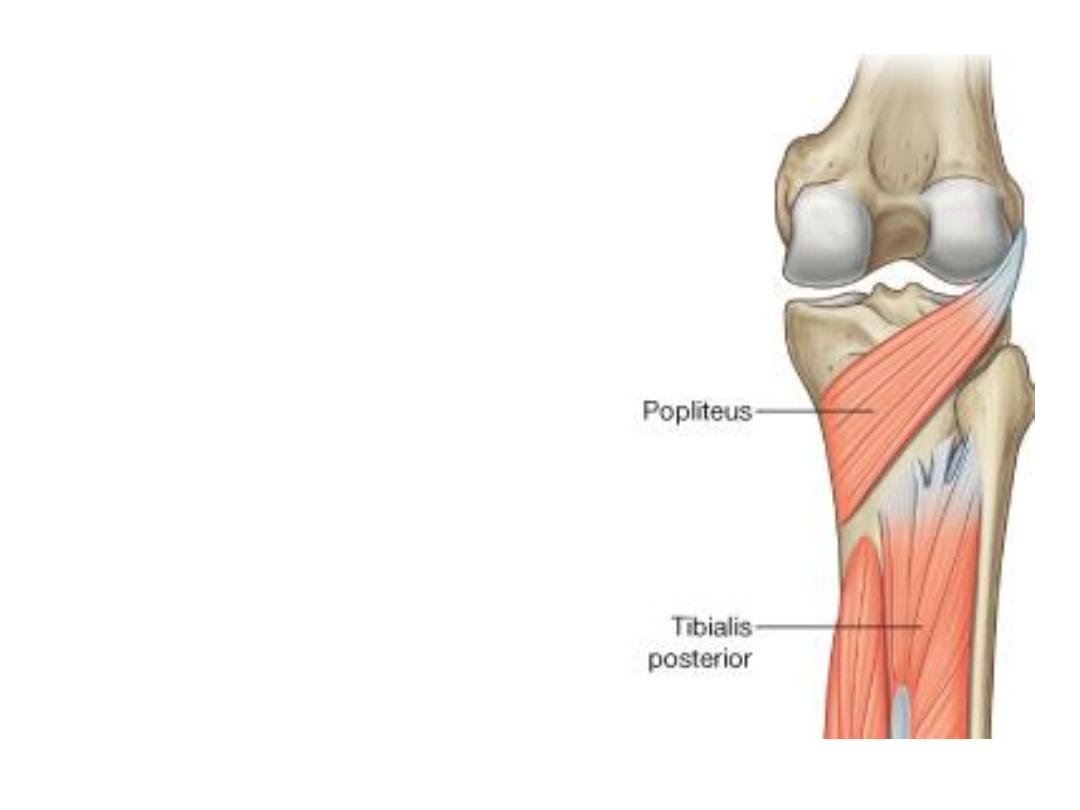
Popliteus muscle:
-This small muscle arises from the back
of tibia above the soleal line
-Fibers pass supero-laterally giving a
tendon which passes through the knee
joint to be inserted into the lateral
femoral
condyle,
some
fibers
are
inserted into the back of lateral meniscus
-Supplied by the tibial nerve (L4-S1)
-The muscle unlocks the extended knee
(laterally rotates the femur on a fixed
tibia), & pulls the lateral meniscus away
from the harm during knee movements
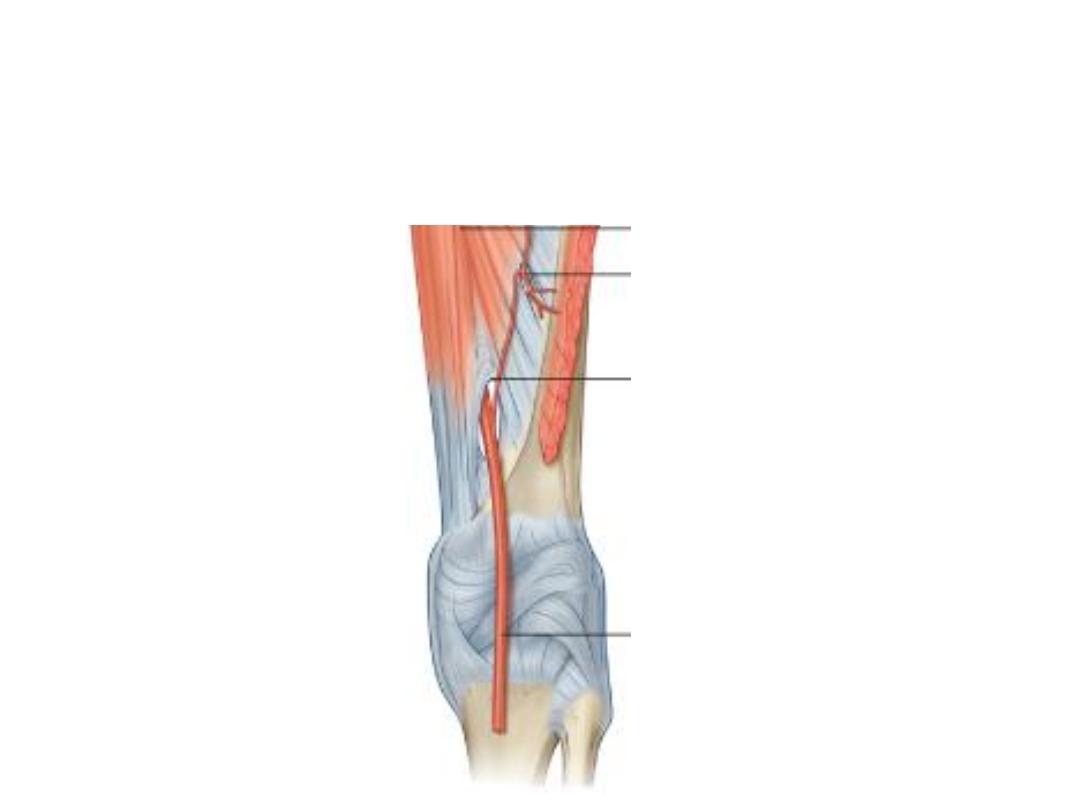
The popliteal artery:
-Is the continuation of the femoral artery at the adductor hiatus
-Descends in the fossa, being the deepest structure with medio-lateral
inclination
-Ends at the lower border of popliteus by dividing into the tibial arteries
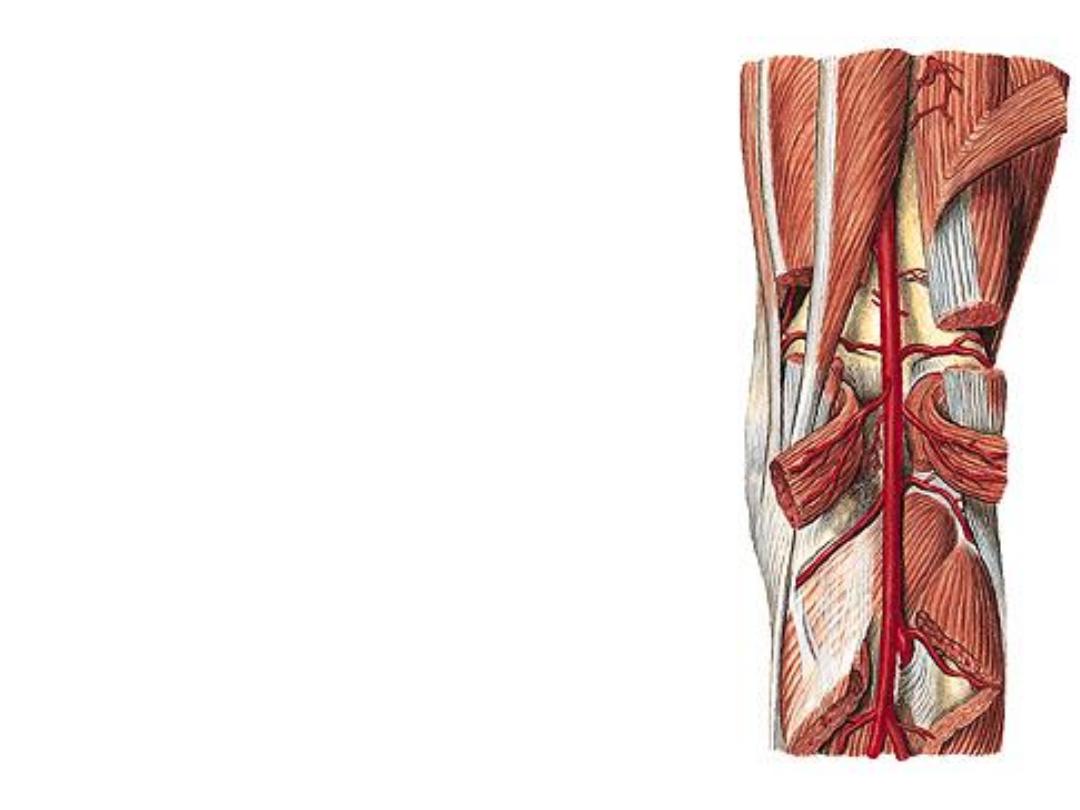
Branches:
1- Muscular branches to both heads of Gn
2- The genicular branches: to the knee joint:
a) Lateral superior GA:
-Lies deep to biceps tendon
-Anastomoses with the descending branch of
LCFA & LIGA
b) Medial superior GA:
-Lies deep to semi tendons
-Anastomoses with the MIGA
a
b
d
d
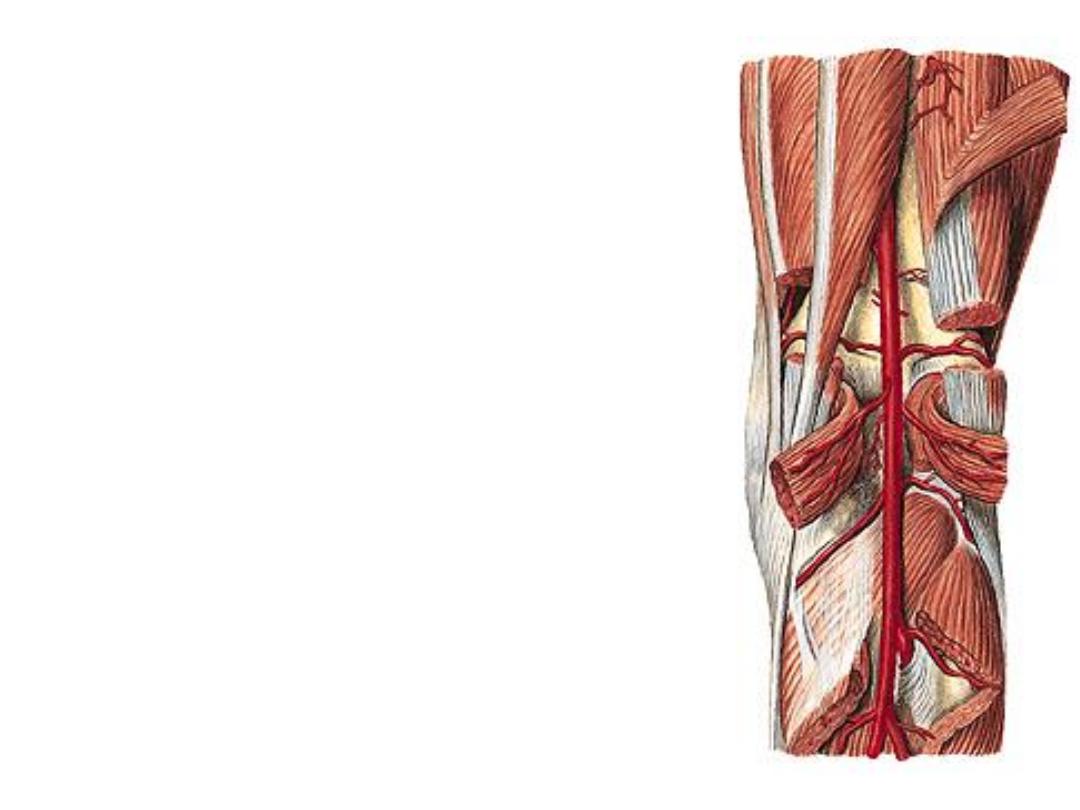
c) Lateral inferior GA:
-Lies across popliteus, deep to the lateral head of
Gn, on the fibular collateral ligament
-Anastomoses with the LSGA, MIGA & anterior
tibial recurrent arteries
d) Medial inferior GA:
-Lies along the upper border of popliteus, deep to
the medial head of Gn, on the tibial collateral
ligament
-Anastomoses with the MSGA, LIGA & anterior
tibial recurrent arteries
e) Middle GA:
pierces the oblique popliteal
ligament & enters the knee joint to supply the
cruciate ligaments
a
b
d
d
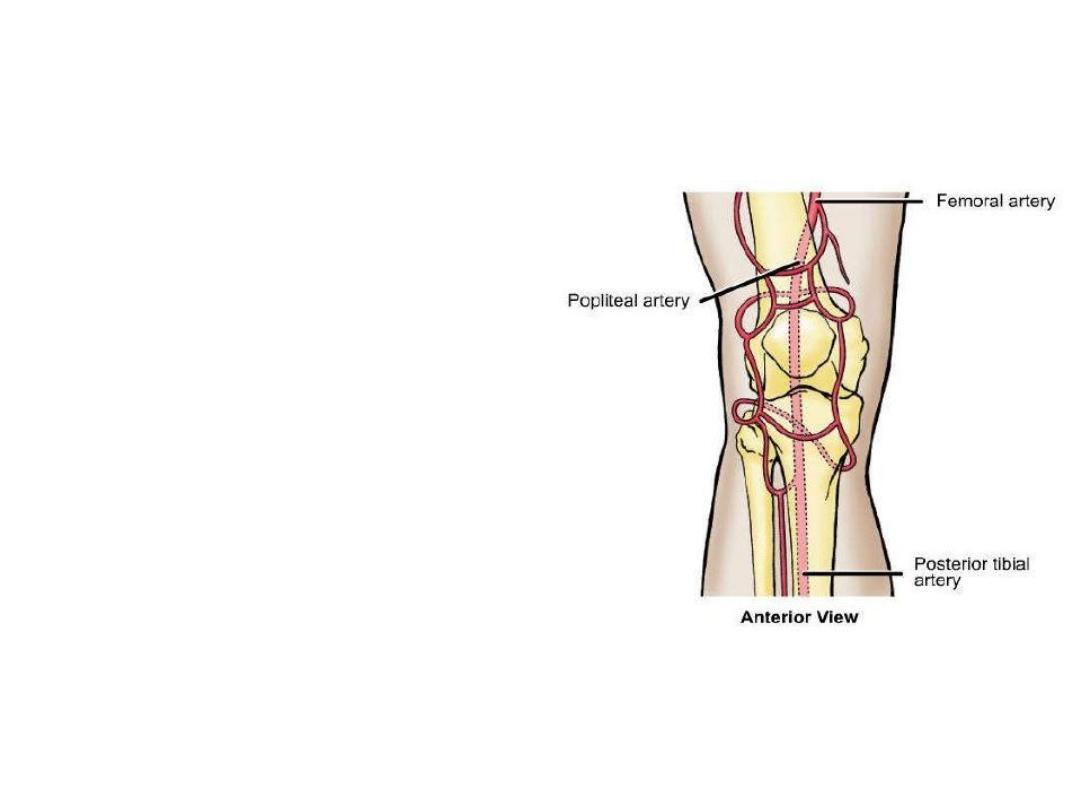
The patellar network (anastomosis around
the knee):
-A rich arterial arcade distributed around the
patella & adjacent ends of the tibia & femur
-They provide collateral pathway when the
knee is fully flexed or when the popliteal
artery is diseased
-Members:
1) The genicular arteries (except the
middle)
2) Descending branch of LFCA
3) Descending genicular artery
4) Fourth perforator artery
5) Anterior & posterior tibial recurrents
6) Circumflex fibular artery
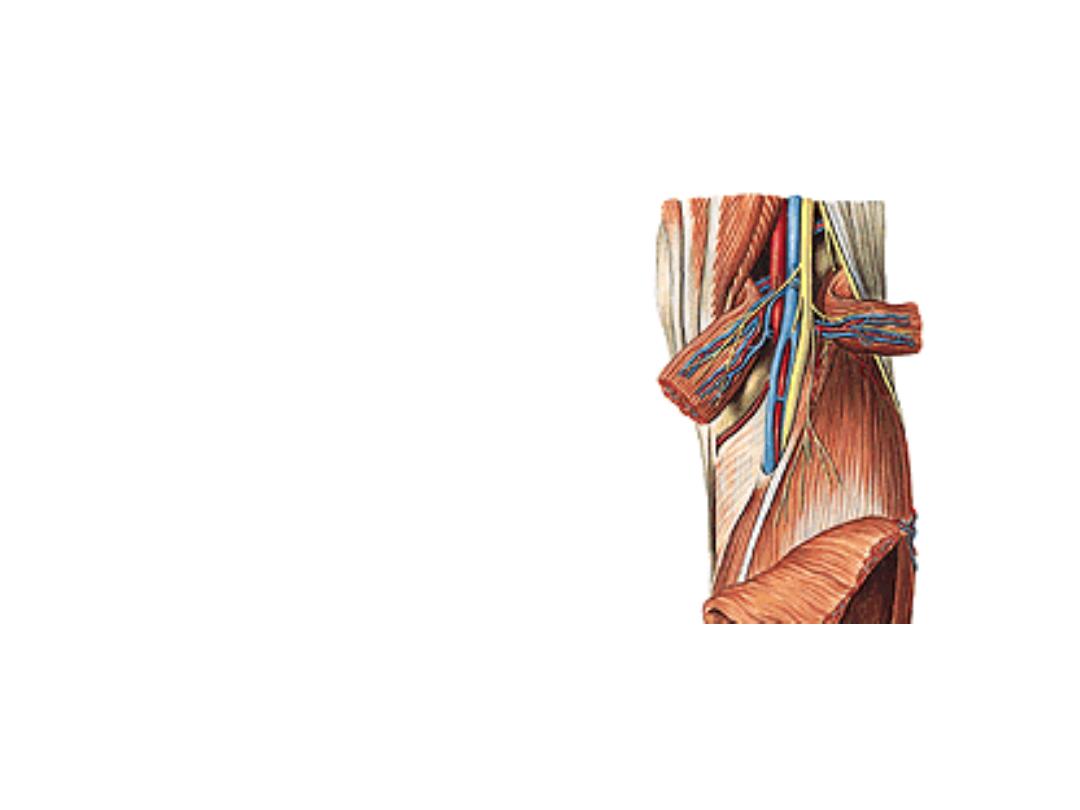
The popliteal vein:
-Formed by union of the anterior &
posterior tibial veins
-Lies superficial to the artery in
the fossa
-Ends by becoming the femoral
vein at the adductor hiatus
-Receives
corresponding
tributaries to the branches of the
popliteal artery
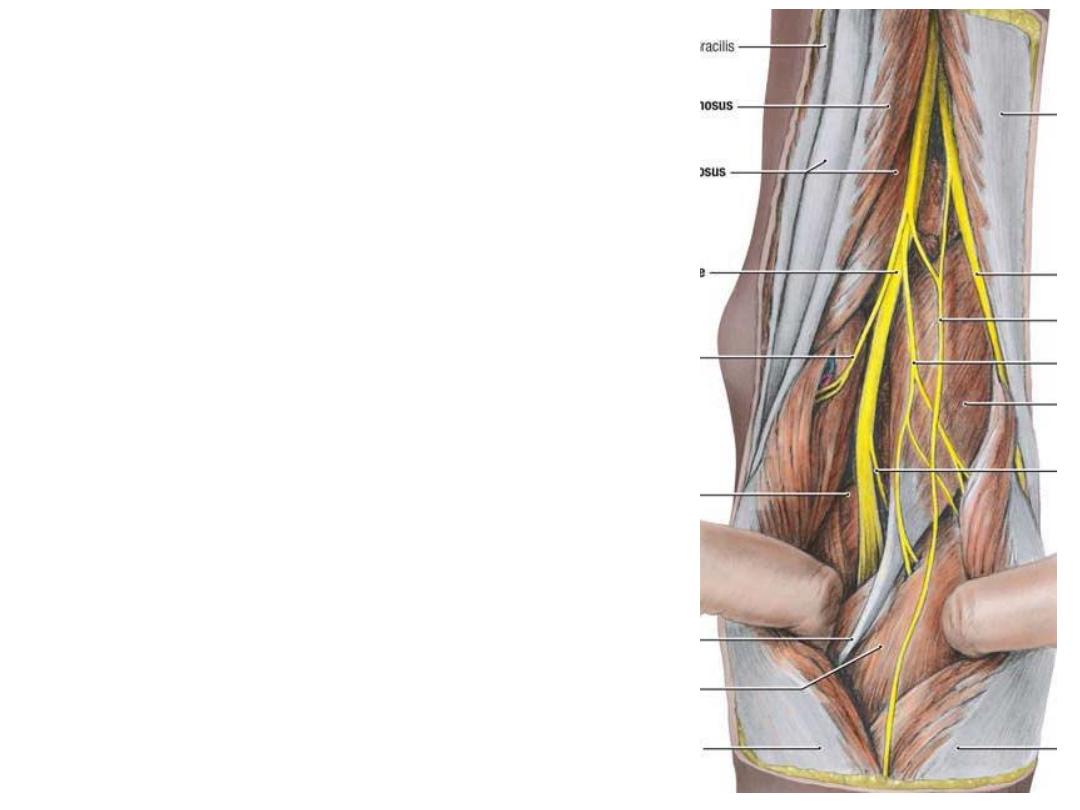
Nerves of the popliteal fossa:
-Tibial nerve descends in the fossa
lying superficial to the vein, just deep to
the roof
-Common peroneal nerve along the
superolateral border to reach the neck
of fibula & goes to the peroneal
compartment
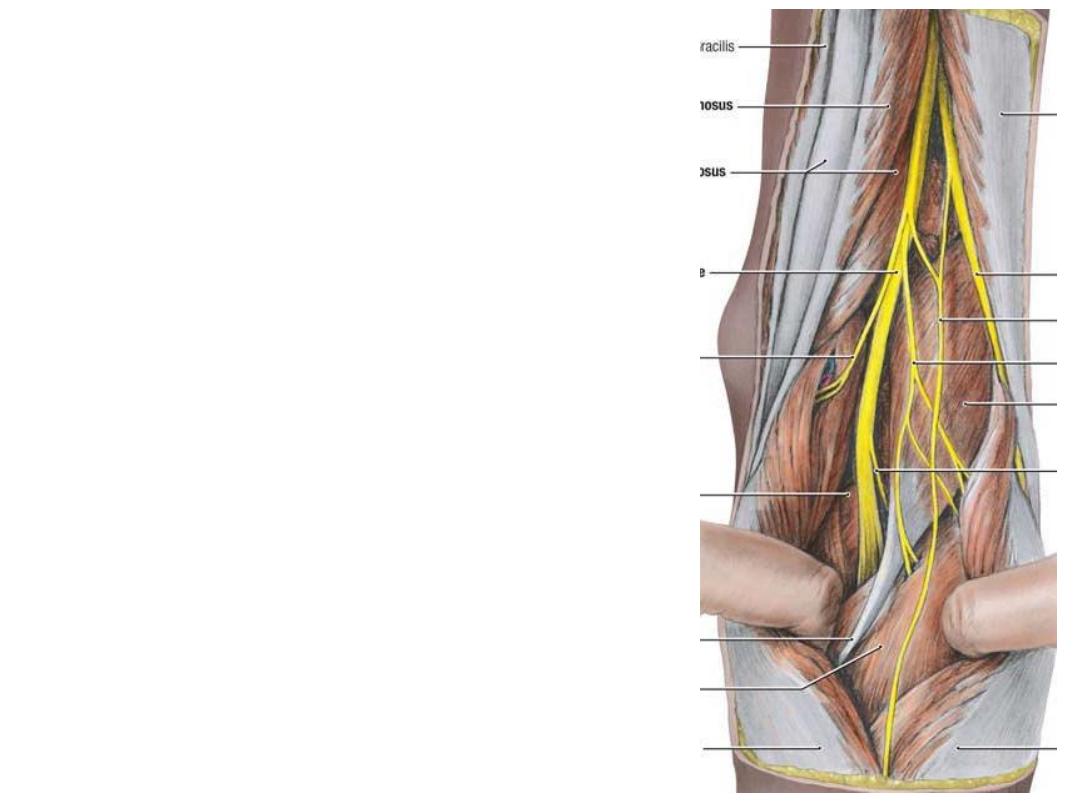
Branches of tibial nerve:
1-
Articular
branches;
correspond
&
accompany he medial genicular arteries
2- Muscular branches to calf muscles
3- Cutaneous, the medial sural nerve; in the
middle 1/3 of the leg it pierces the deep
fascia to join the sural communicating
branch of the common peroneal nerve
forming the sural nerve
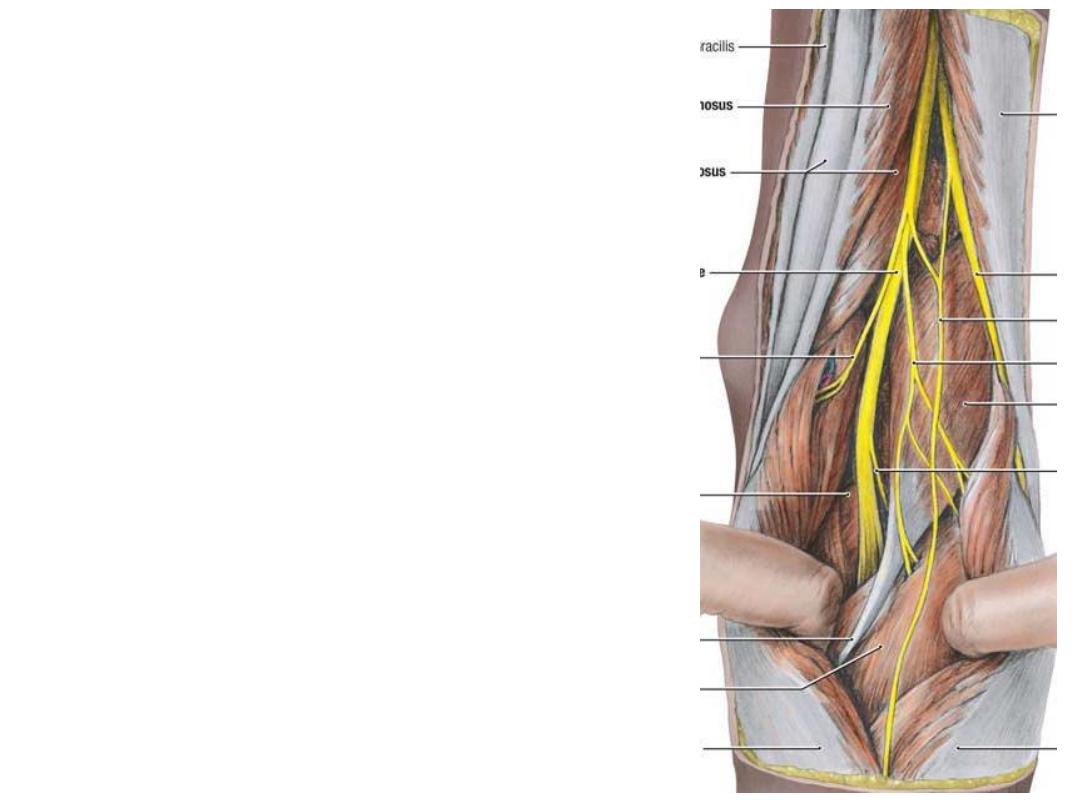
Branches of common peroneal nerve:
1-
Articular
branches;
correspond
&
accompany the lateral genicular arteries
2- Muscular branch to short head of biceps
3- Cutaneous:
a) Sural communicating; joins the medial
sural branch to form the sural nerve
b) The lateral sural nerve; to the skin of the
lateral aspect of the leg
The sural n. accompanies the small
saphenous nerve, supplies the skin of the
distal part of the back of leg & lateral aspect
of the foot
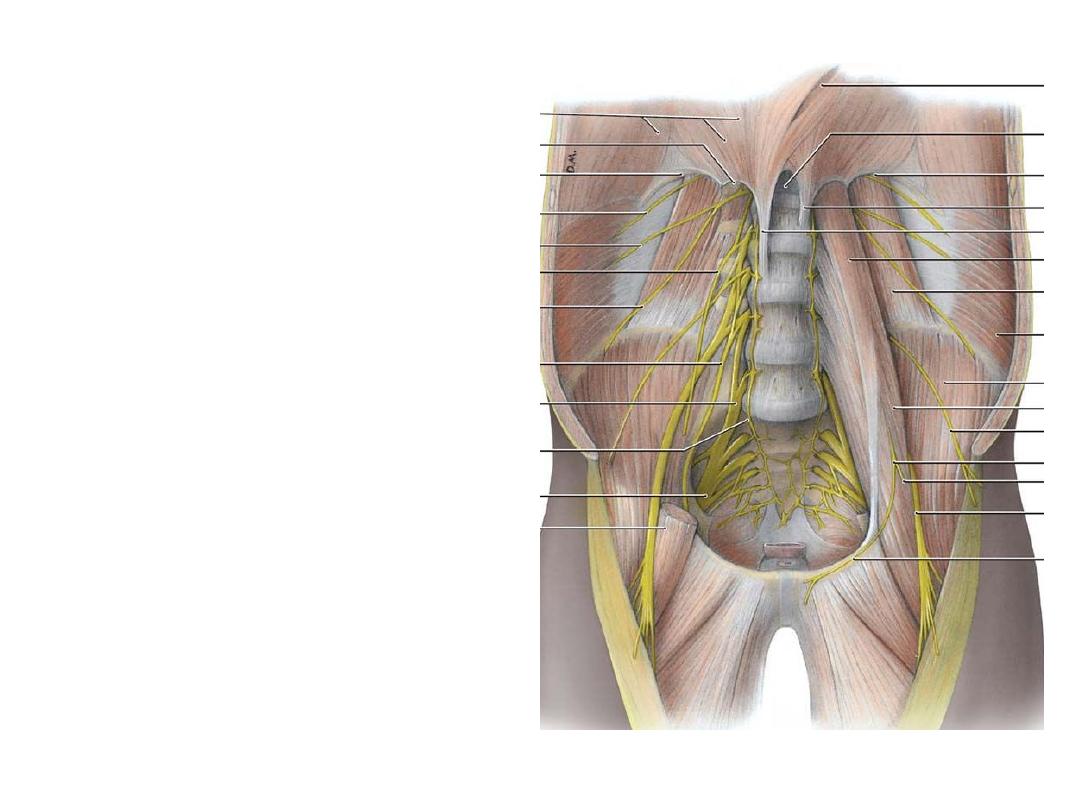
Lumbar plexus:
-The anterior primary rami of L1-L5
once leave the vertebral canal lie
within psoas major substance
-They
supply
it
&
quadratus
lumborum segmentally
-They divide into anterior & posterior
divisions then re-unite within the
muscle to give the branches
-All branches leave through psoas
major in the posterior abdominal wall
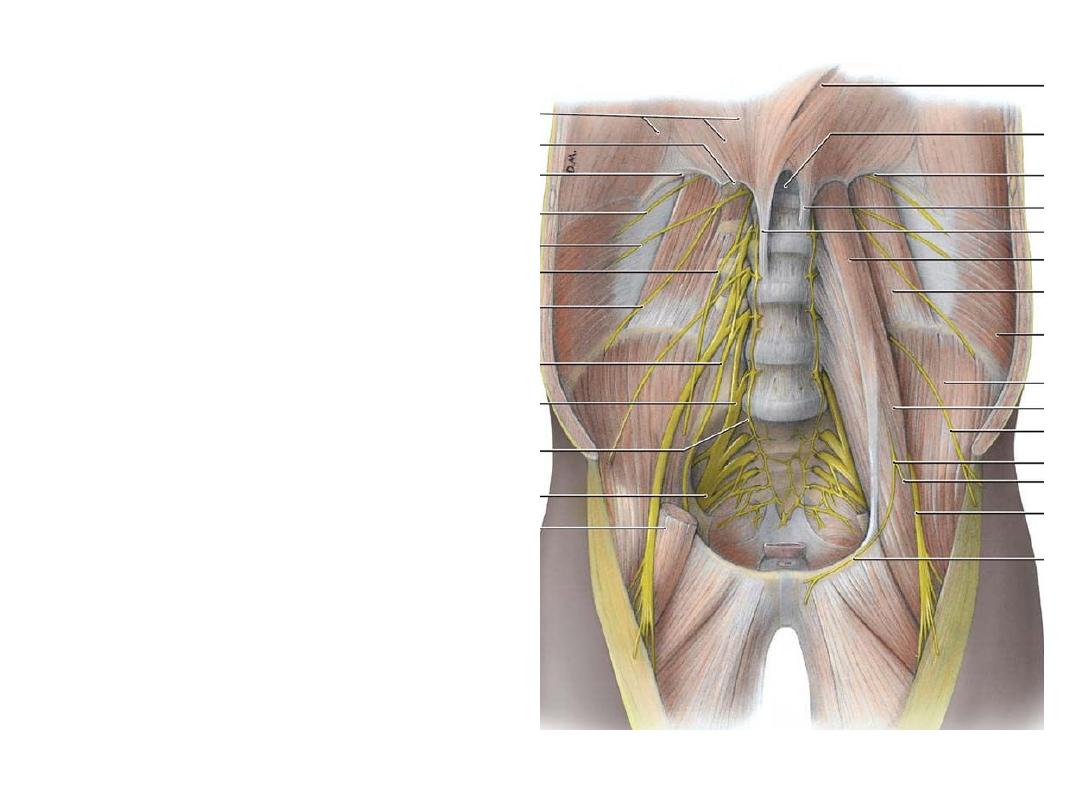
-L1 goes to the abdomen & external
genitalia
-L2-4 give the thigh nerves
-The reminder of L4 + L5 enter the
pelvis as the lumbosacral trunk
-LS trunk shares with the sacral
nerves in the formation of sacral
plexus which will supply the rest of
the lower limb & the pelvis
Branches:
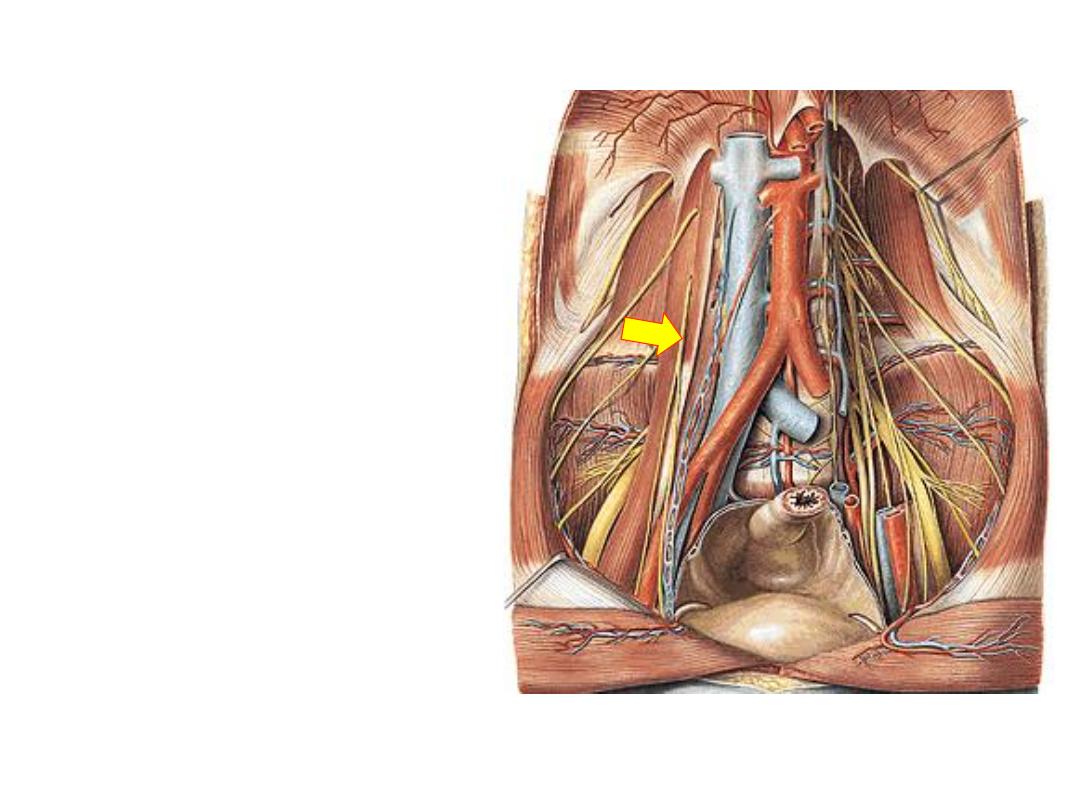
1- Genitofemoral nerve (L1,2):
-Leaves the anterior surface of
psoas
-Descends in the PAW
-Behind the inguinal ligament it
divides into:
a) Femoral branch (L1);
to the
skin overlying the femoral
triangle
b) Genital (L2);
to cremasteric
muscle
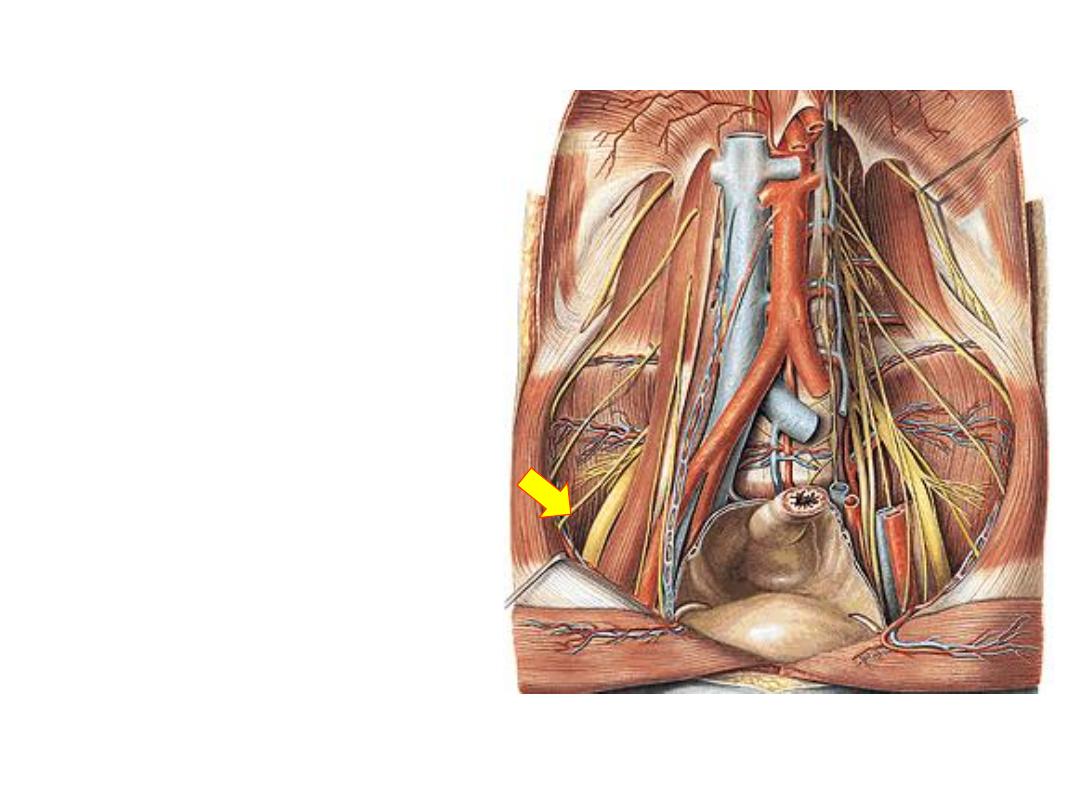
2- Lateral femoral cutaneous
nerve (L2,3 posterior):
-Leaves the lateral border of
psoas
-Passes in the iliac fossa
-Pierces the lateral part of
inguinal ligament
-Distributed to the skin of the
lateral thigh via anterior &
posterior branches
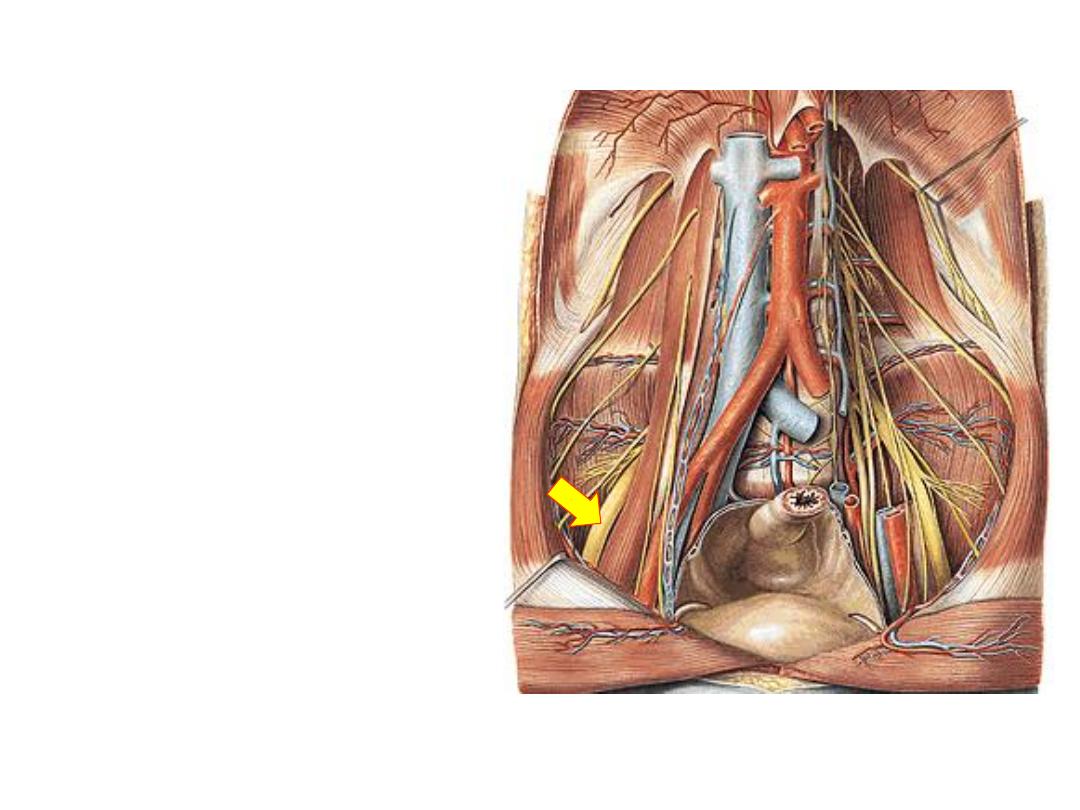
3- Femoral nerve (L2-4 posterior):
-Appears in the groove between
iliacus & psoas in the iliac fossa
-Passes underneath the inguinal
ligament
outside
the
femoral
sheath
-Distributed as mentioned
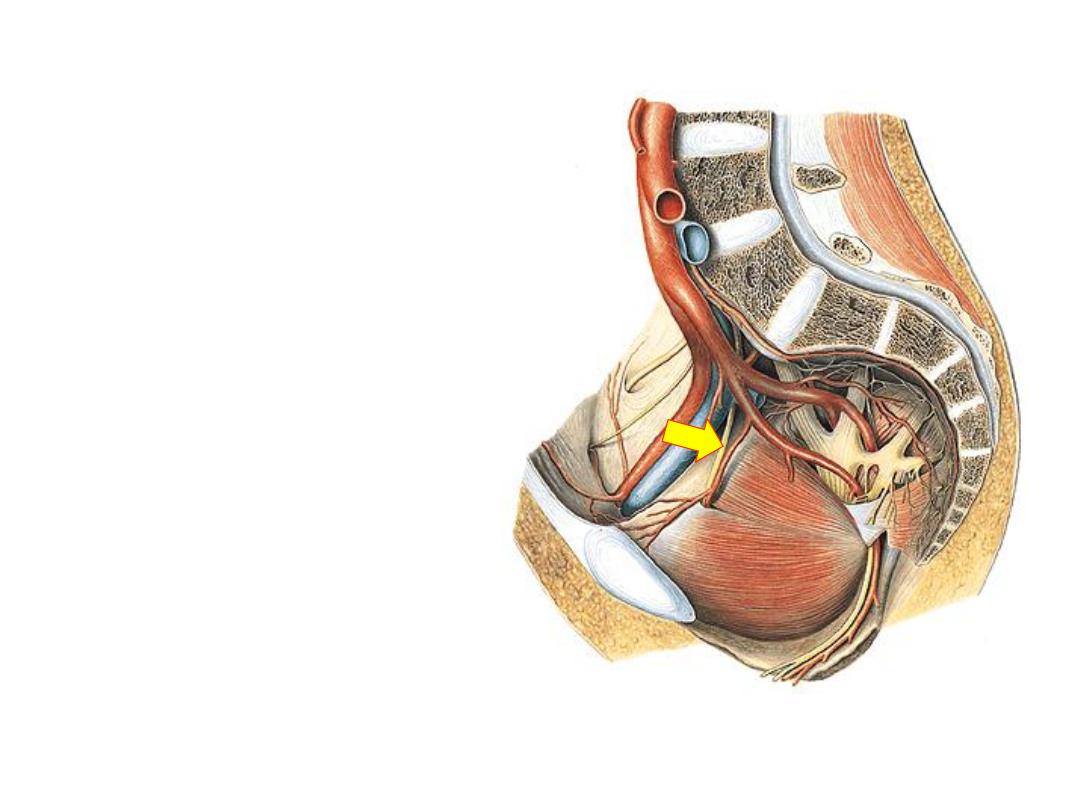
4- Obturator nerve (L2-4 anterior):
-Appears in the pelvis on the
medial border of psoas
-Passes on the lateral pelvic wall
in relation to the female ovary
-Passes
with
the
obturator
vessels in the obturator canal &
distribyed
to
the
adductor
compartment of the thigh
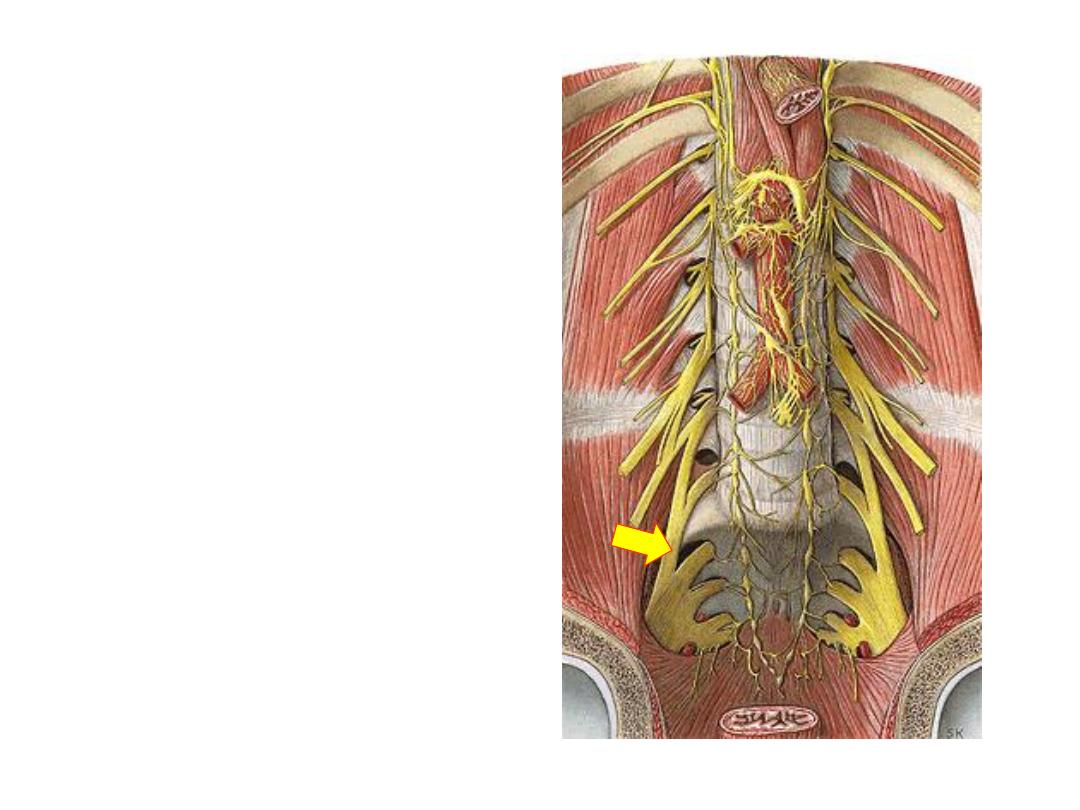
5- Lumbosacral trunk (L4,5 mixed):
-Giant trunk leaves the medial
border of psoas
-Passes on the sacral ala
-Joins S1-3 roots of the sacral
plexus to form the sciatic nerve
Sacral plexus:
-Formed on the anterior surface of
piriformis by the anterior primary
rami of L4,5 & sacral nerves
-Supply
pelvic
&
lower
limb
structures

Root branches:
1- To piriformis
2- Perforating cutaneous
3- Pelvic splanchnics
4- Perineal branch of S4
5- Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve (S2,3 posterior)
6- Pudendal nerve (S2-4 anterior)
To pelvis
To LL
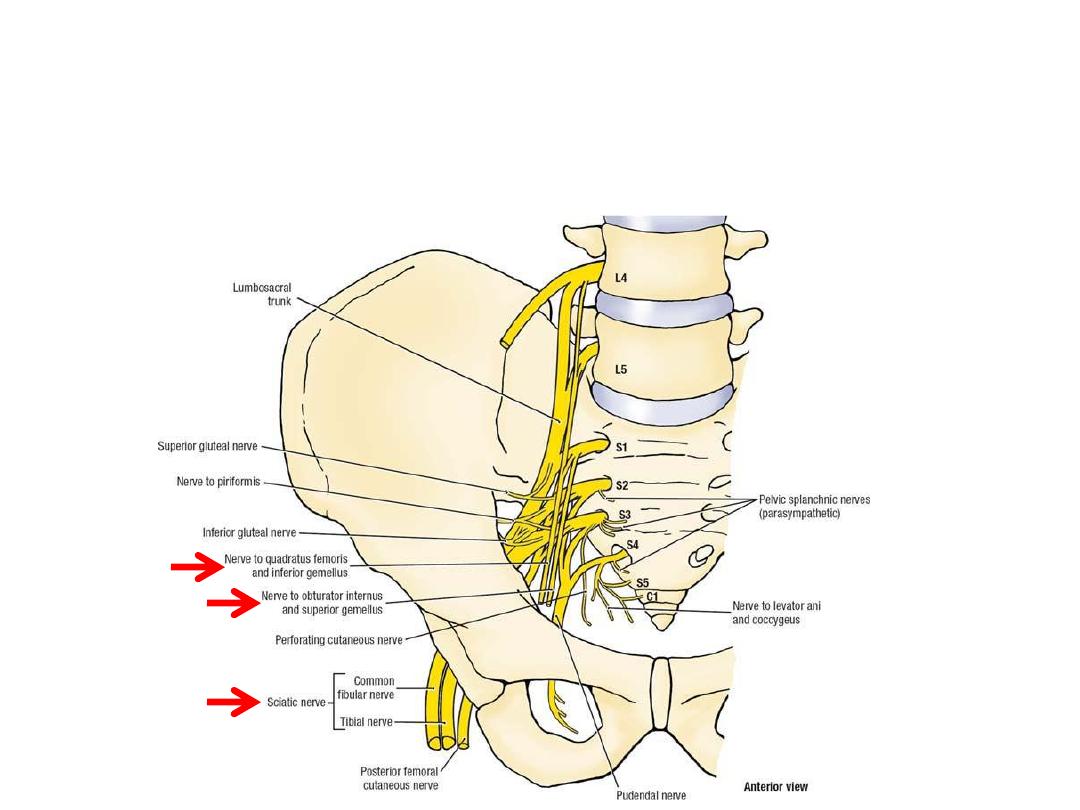
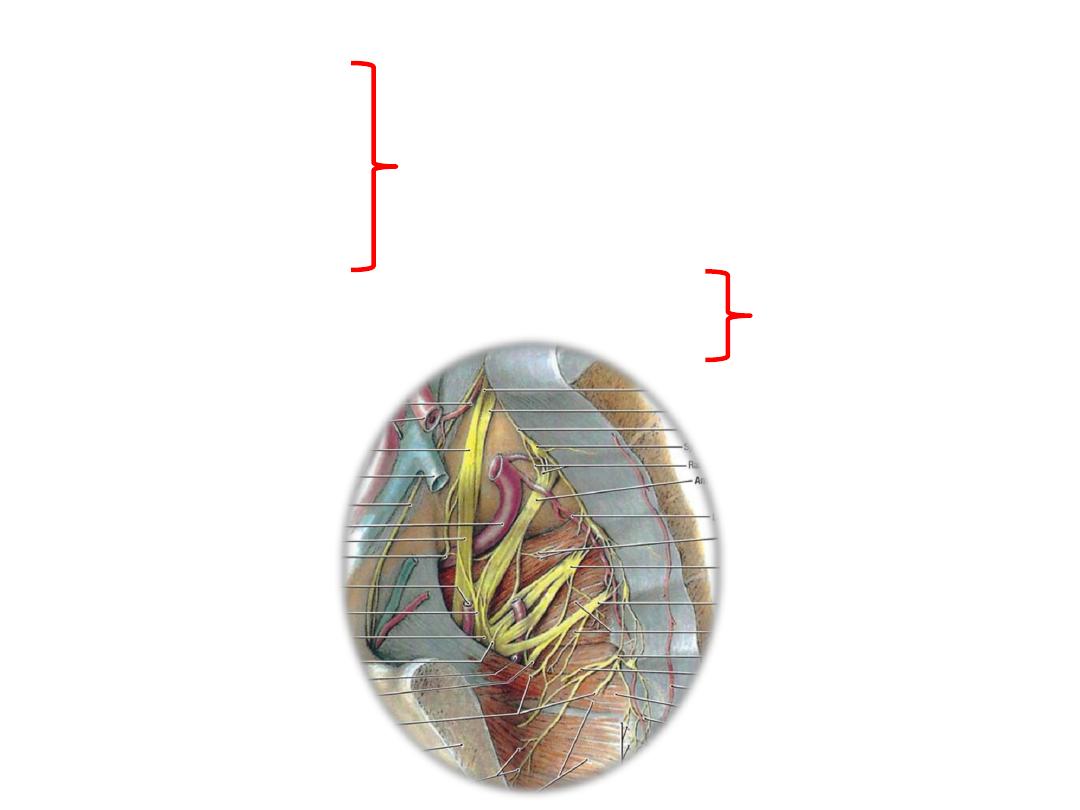
Anterior division branches:
1- Tibial component of sciatic (L4-S3)
2- Nerve to obturator internus (L5,S1)
3- Nerve to quadratus femoris (L5,S1)
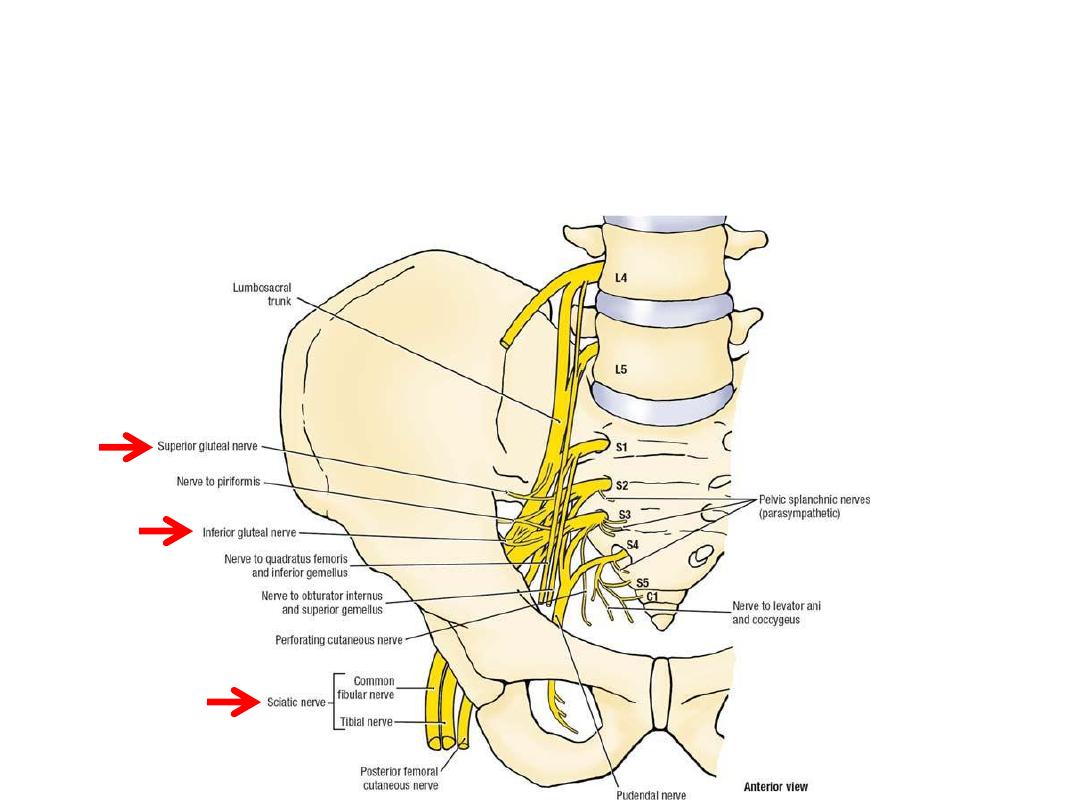
Posterior division branches:
1- Common peroneal component of sciatic (L4-S2)
5- Superior gluteal n. (L4,5,S1)
6- Inferior gluteal n. (L5,S1,2)
