To list surface anatomical landmarks
To follow deep fascia of lower limb
To define the femoral triangle, boundaries, floor & contents
To describe the femoral canal
To outline the passage of femoral hernia
Surface Anatomy:
Anterior thigh & femoral triangle:
1- Iliac crest
2- ASIS; anterior end of the crest
3- Pubic tubercle
4- Inguinal ligament
5- Greater trochanter of femur; 14 cm
below the tubercle of iliac crest
6- Patella
7- Medial & lateral femoral condyles
8- Femoral triangle
1
2
3
5
4
6
7
7
8
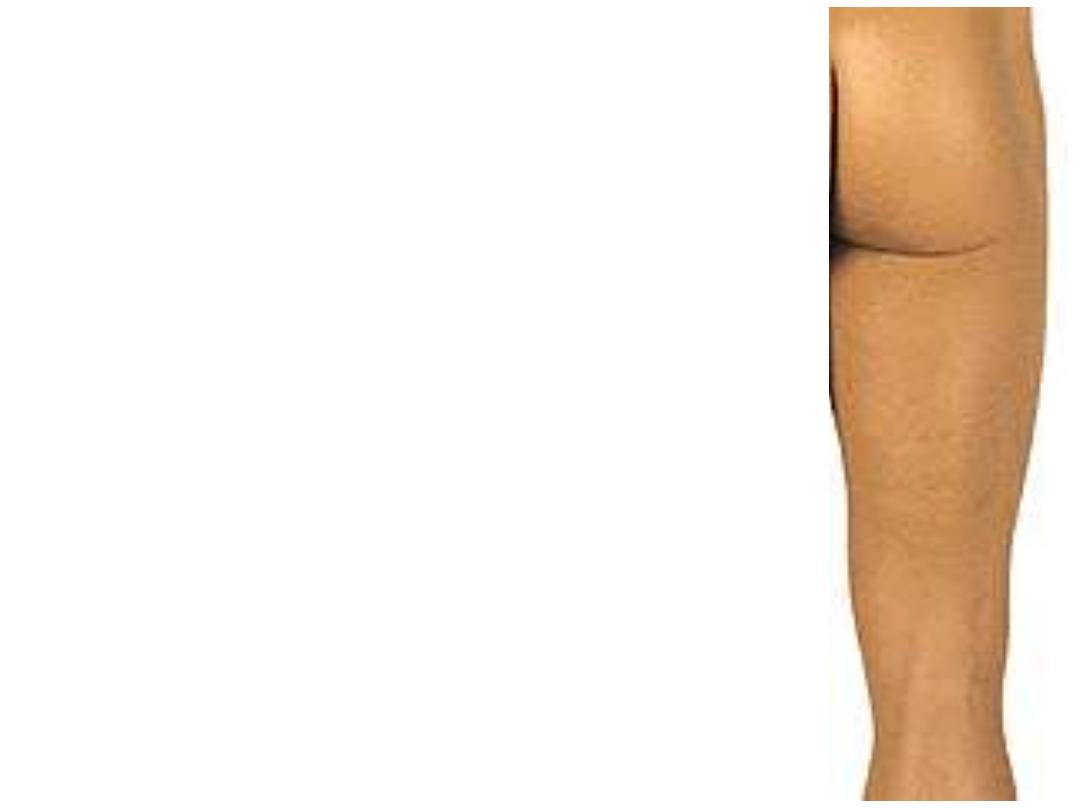

Posterior thigh & gluteal region:
1- Iliac crest
2- Natal cleft
3- Gluteal folds
4- Ischial tuberosity
5- Popliteal fossa
1
2
3
5
4
1
2
3
5
4
6
7
2
4
The leg & foot:
1- Patella
2- Tibial condyles
3- Tibial tuberosity
4- Malleoli (tibial & fibular)
5- Popliteal fossa
6- Achilles tendon
7- The calcaneus
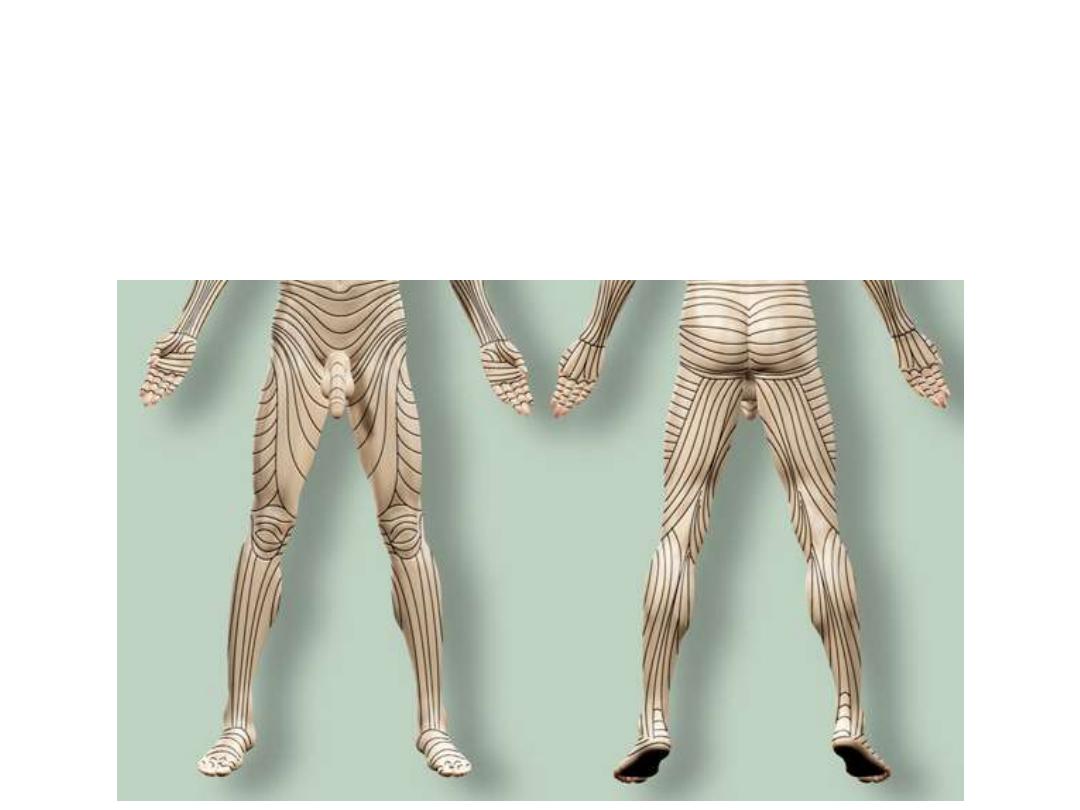
Langer lines:
•Invisible map of lines
•Follow collagen arrangement
•Incisions along them end with minimum scars
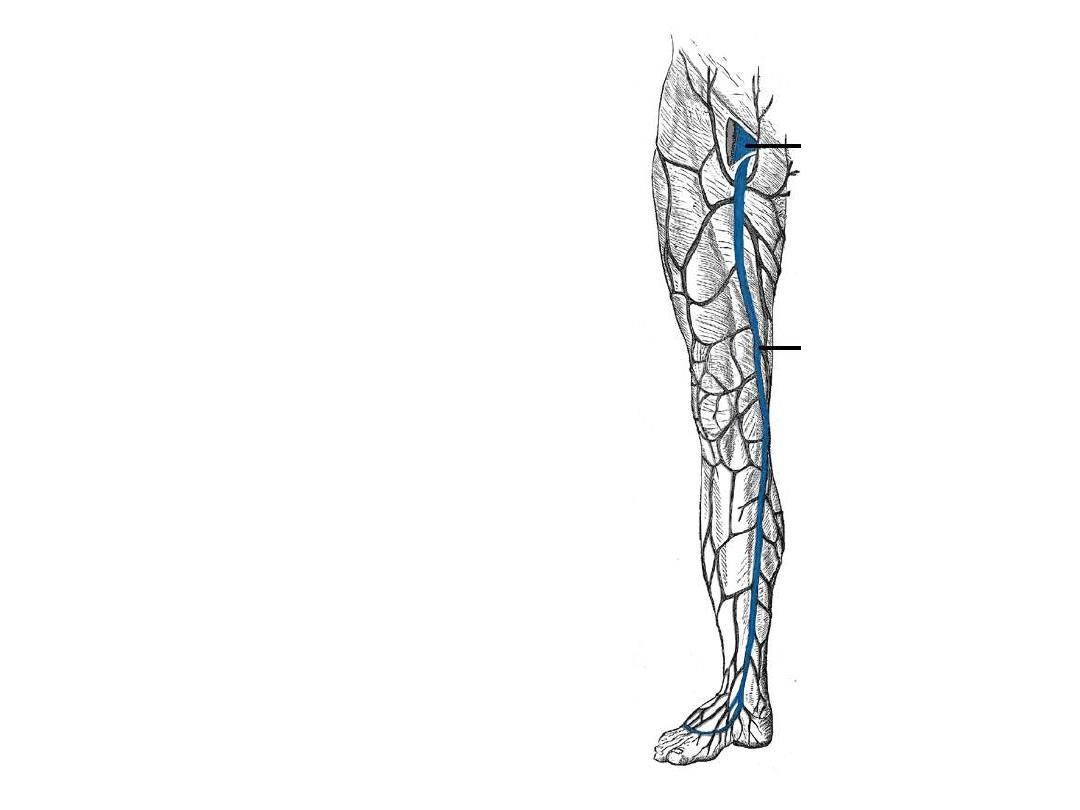
Superficial veins:
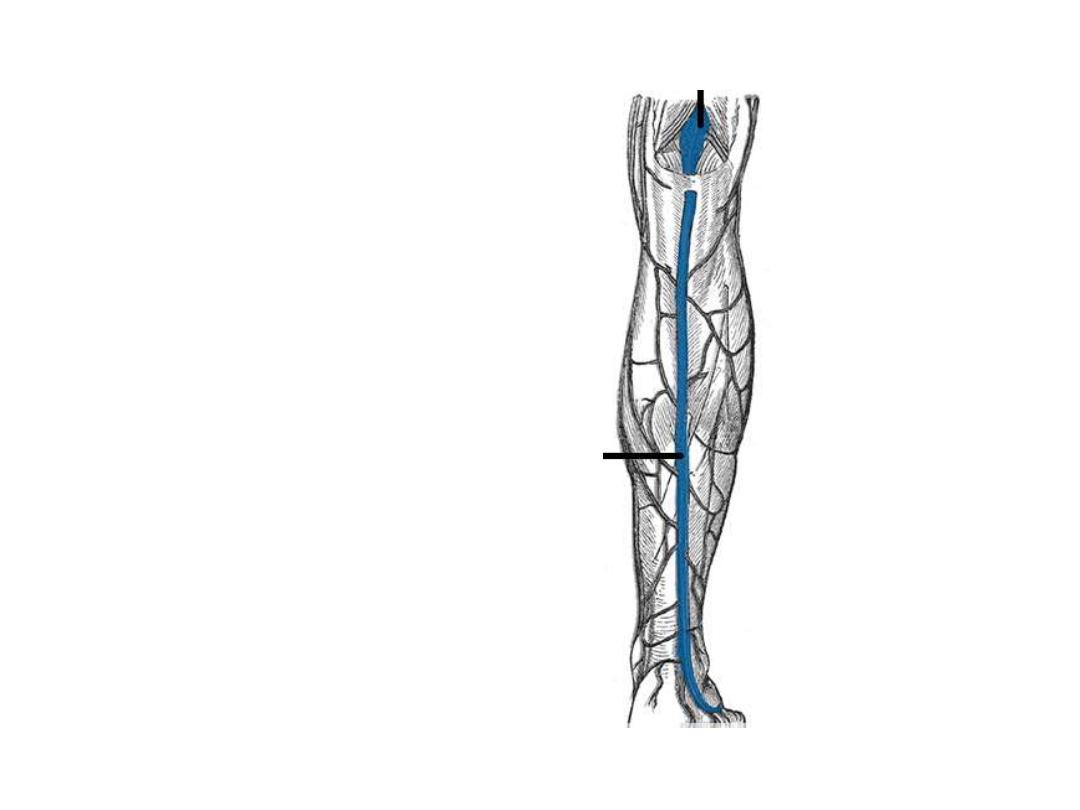
1- Great saphenous vein:
-Formed on the medial aspect of the
dorsal venous arch of the foot
-Passes in the superficial fascia
anterior to the medial malleolus
-Lies on the medial side of the leg,
knee, and thigh
-Enters
through
the
saphenous
opening to join with the femoral vein
below the IL
-In
part
of
its
course,
it
is
accompanied by saphenous nerve
-Used in venous cut down
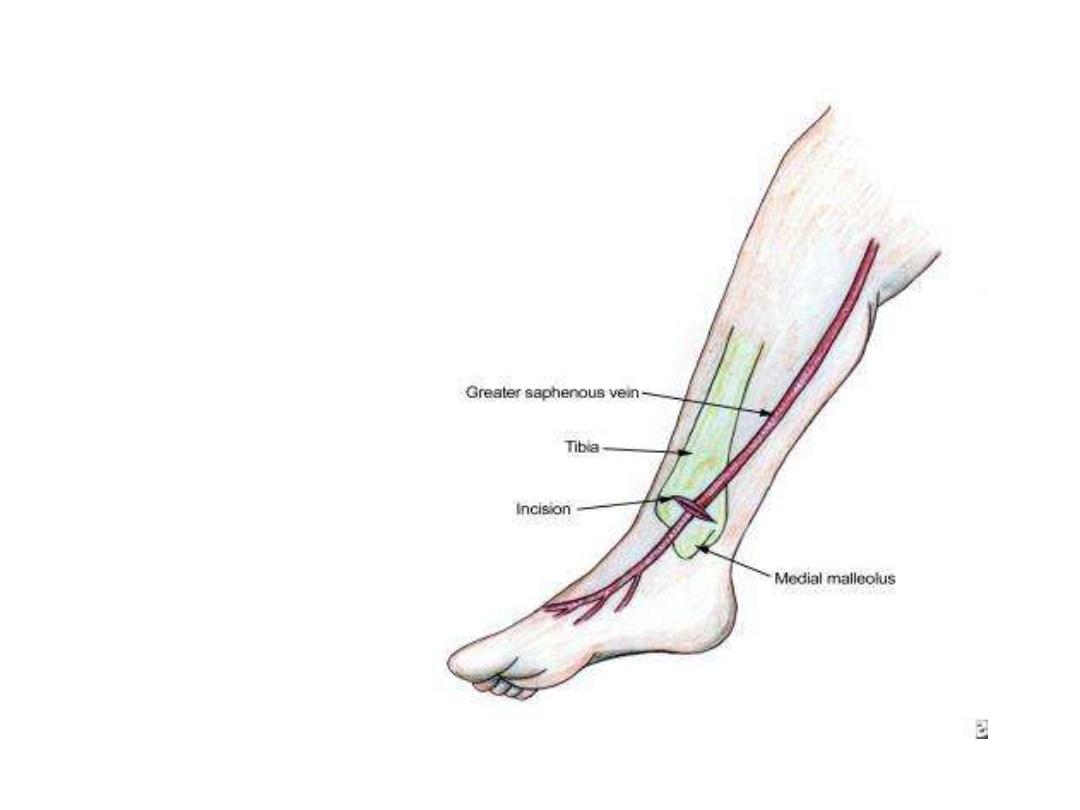
Venous cut down:
Used
as
an
emergency
establishment of a parenteral
route
2- Small saphenous vein:
-Formed on the lateral aspect of
the dorsal venous arch of the foot
-Passes in the superficial fascia
behind the lateral malleolus
-Lies on the back of the calf
-Pierces the roof of popliteal fossa
& empties in the popliteal vein
-In part of its course, it is
accompanied by the sural nerve
Superficial lymph nodes:
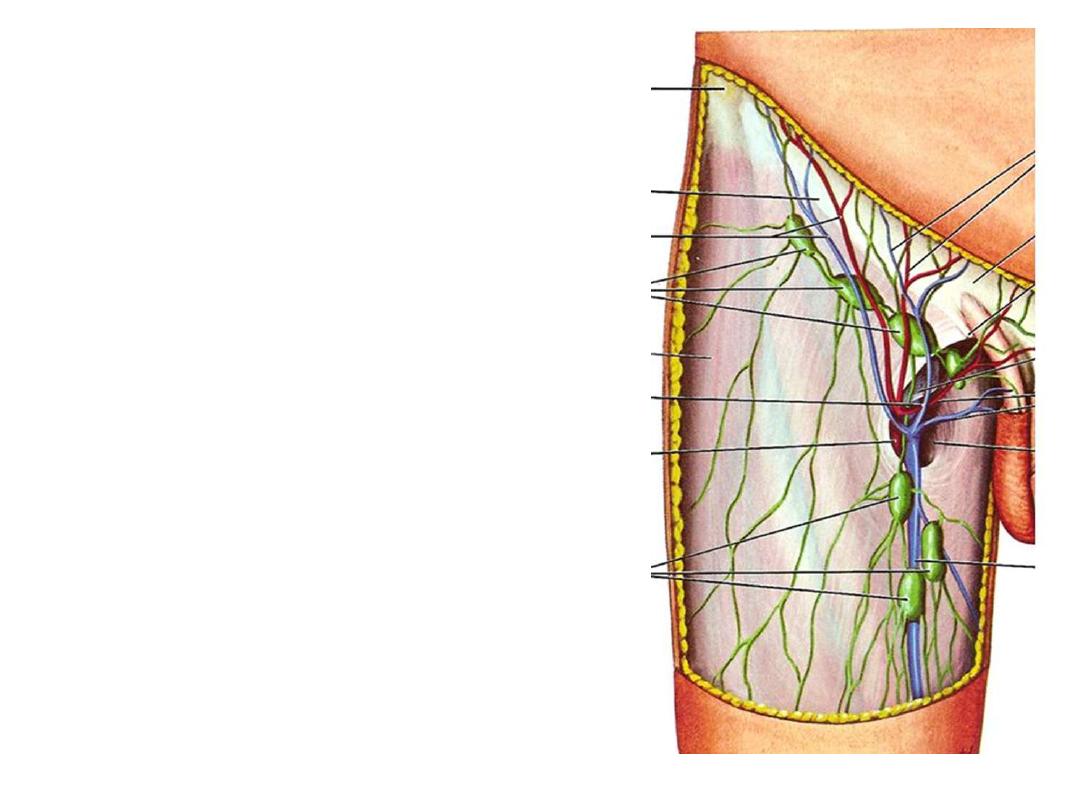
Superficial inguinal nodes:
Arranged in the form of (T) letter around the
termination of great saphenous vein
Divided into:
1- Vertical group: along the vein, receives from
superficial structures of lower limb except the heel
2- Lateral group: below the lateral end of inguinal
ligament, receives from posterior abdominal wall
below the waist
3- Medial group: below the medial end of inguinal
ligament, receives from anterior abdominal wall
below the waist
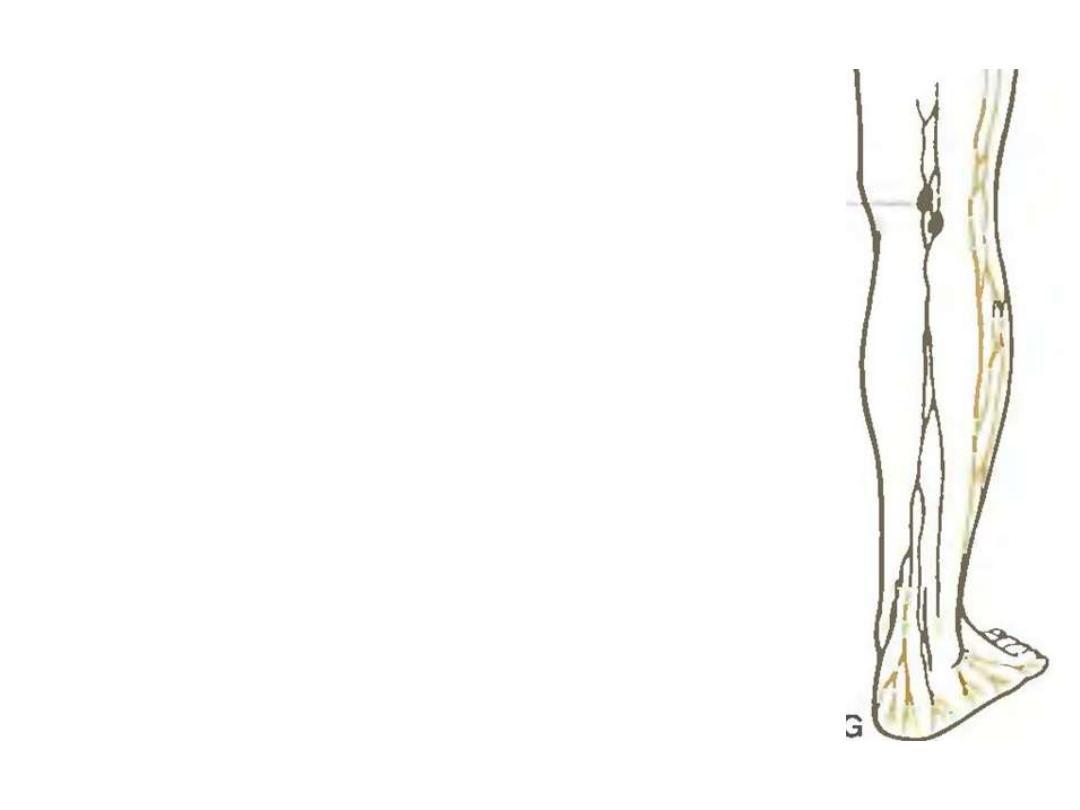
Popliteal nodes:
Lie in the roof of popliteal fossa
Receive
from
lymphatic
accompanying
the
small
saphenous vein
Drain the lateral foot, heel &
lower part of lateral leg
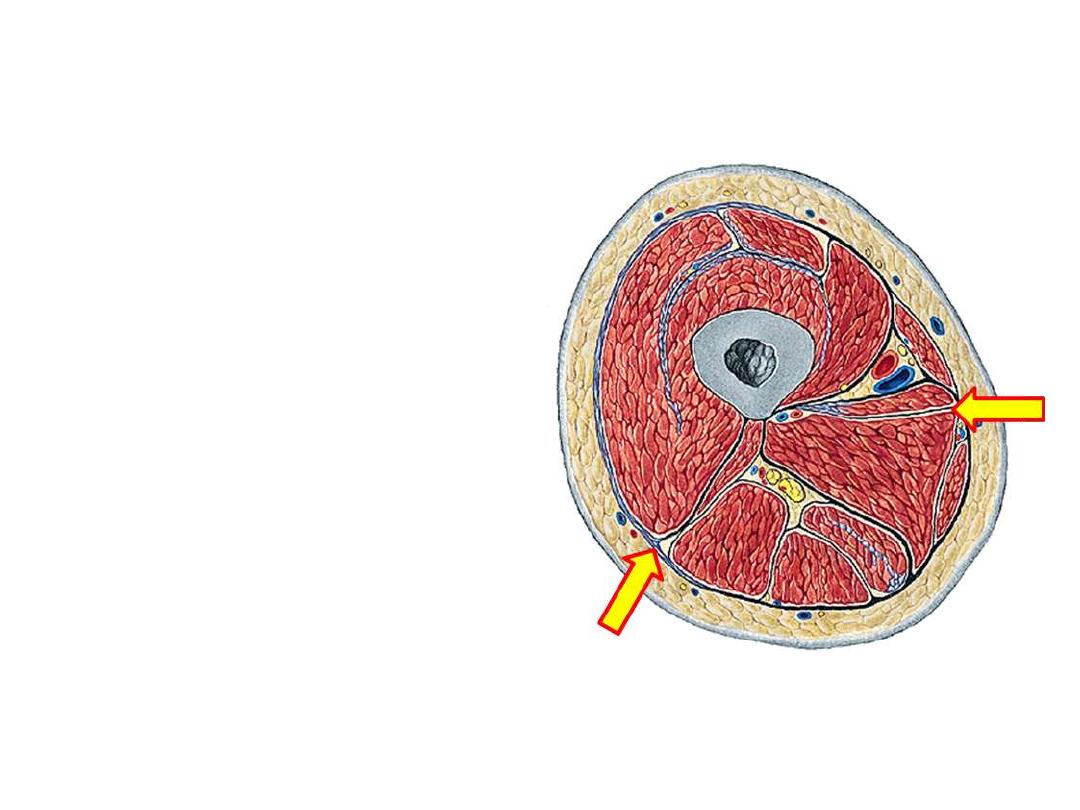
Fascia lata (deep fascia of the thigh):
-Is a strong membrane that encircles
the soft tissues of the thigh like a
stocking
Upper attachment;
Pubic symphysis
– pubic crest –
ischiopubic
ramus
–
ischial
tuberosity
– sacrotuberous ligament
– PSIS – iliac crest – ASIS – inguinal
lig.
– pubic tubercle – pubic crest –
iliopectineal line
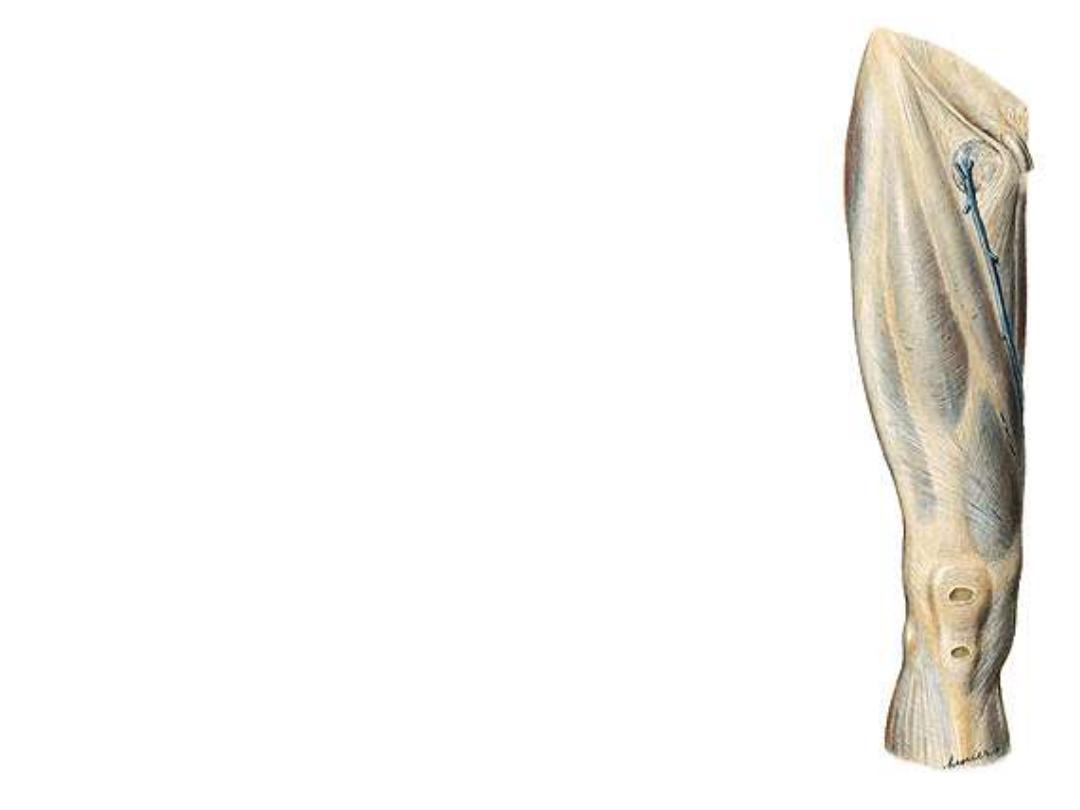

Lower attachment;
Patella
– tibial condyles – tibial tuberosity – fibular head
Structures enclosed by the fascia:
• Gluteus maximus
• Tensor fascia latae
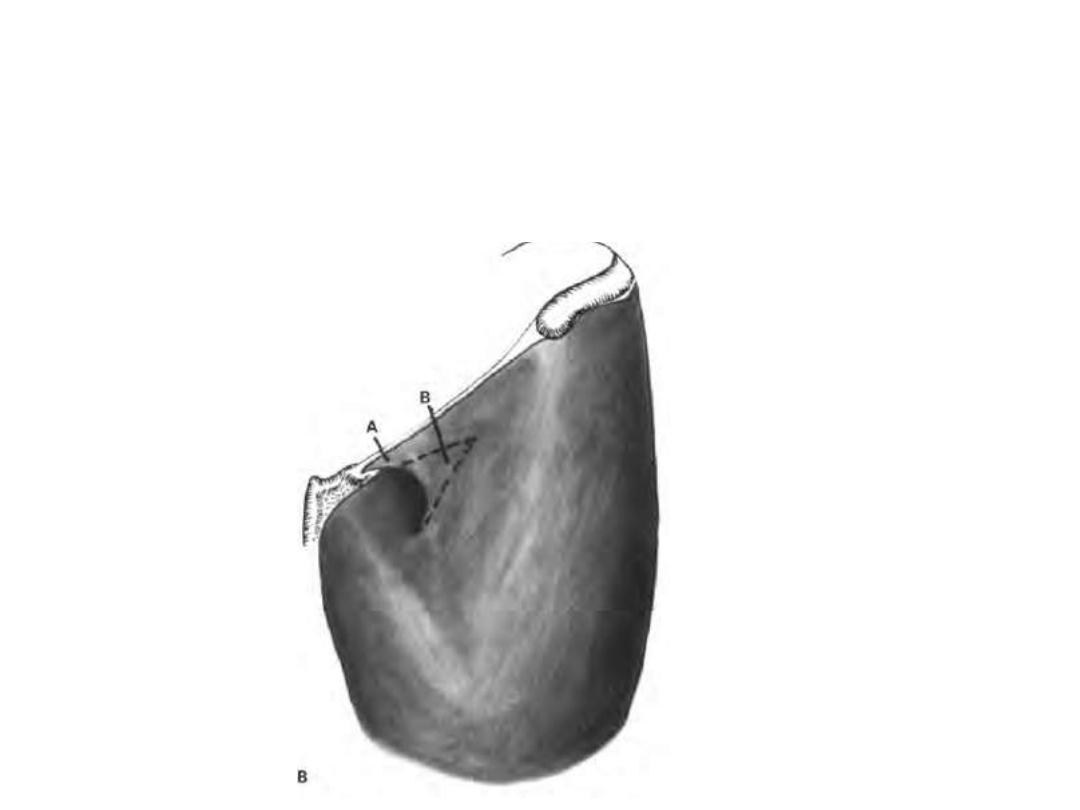
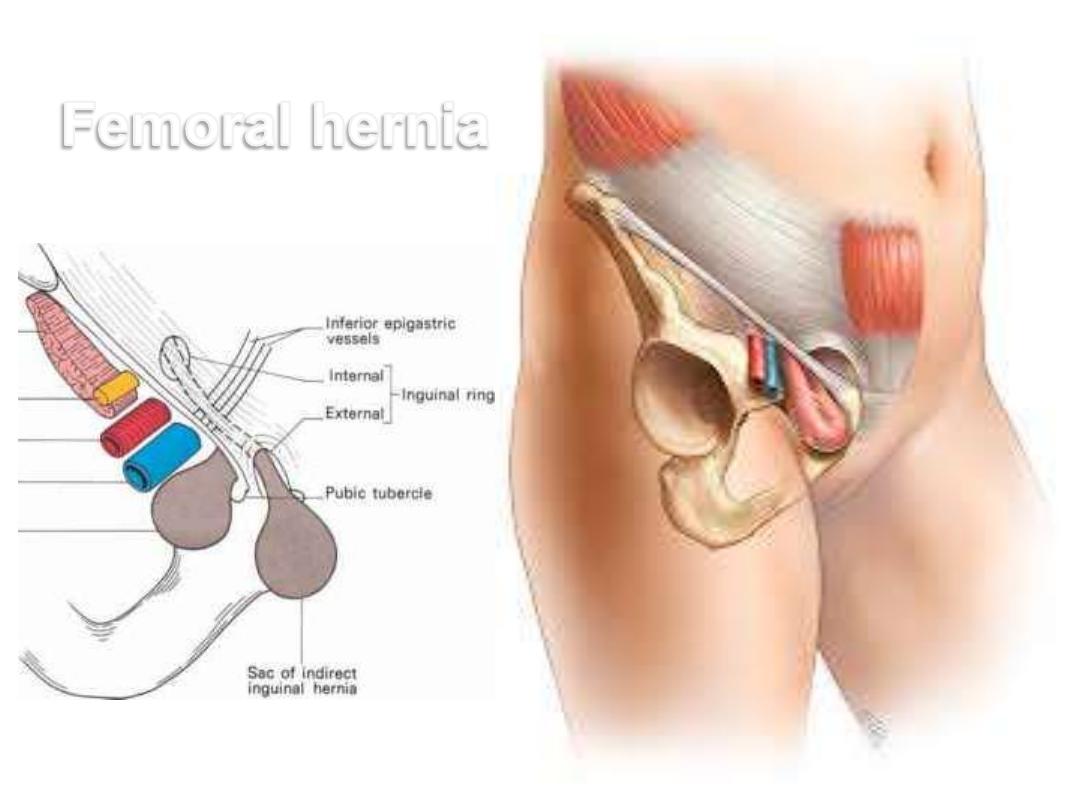
Saphenous opening;
•Lies below the medial end of IL for entrance of great saphenous vein &
lymphatics
•Its lateral edge is called the falciform margin
•Femoral hernia may get out of it
Derivatives:
1- Intermuscular septa;
• Lateral & medial septa project
from the fascia to lineal
aspera
• They divide the thigh into
three compartments, anterior,
posterior & medial
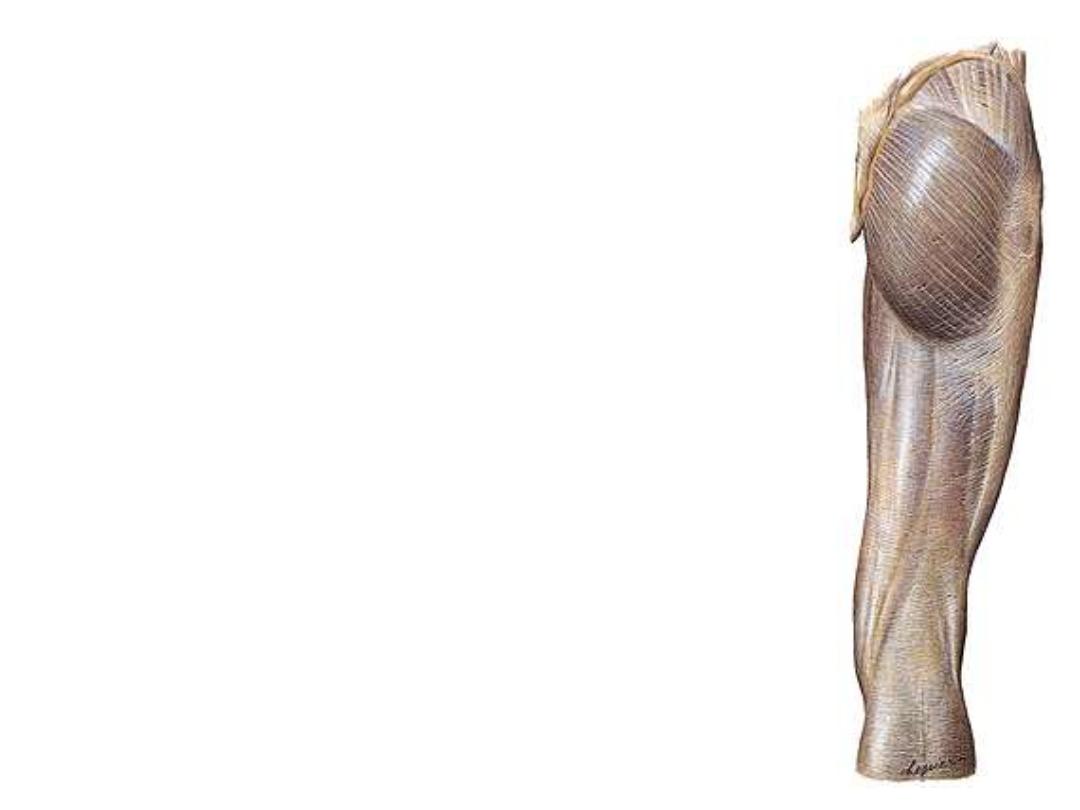

2- Iliotibial tract;
thickening in
the lateral part of the fascia
below tensor muscle, extends
down to the lateral tibial condyle
Functions of ITT:
-Maintains extended knee in
position as it passes anterior to
F-E axis
-It is mainly in action when the
slightly flexed knee is carrying
the
body
weight
so
it
is
important in walking, running &
standing from sitting position
2
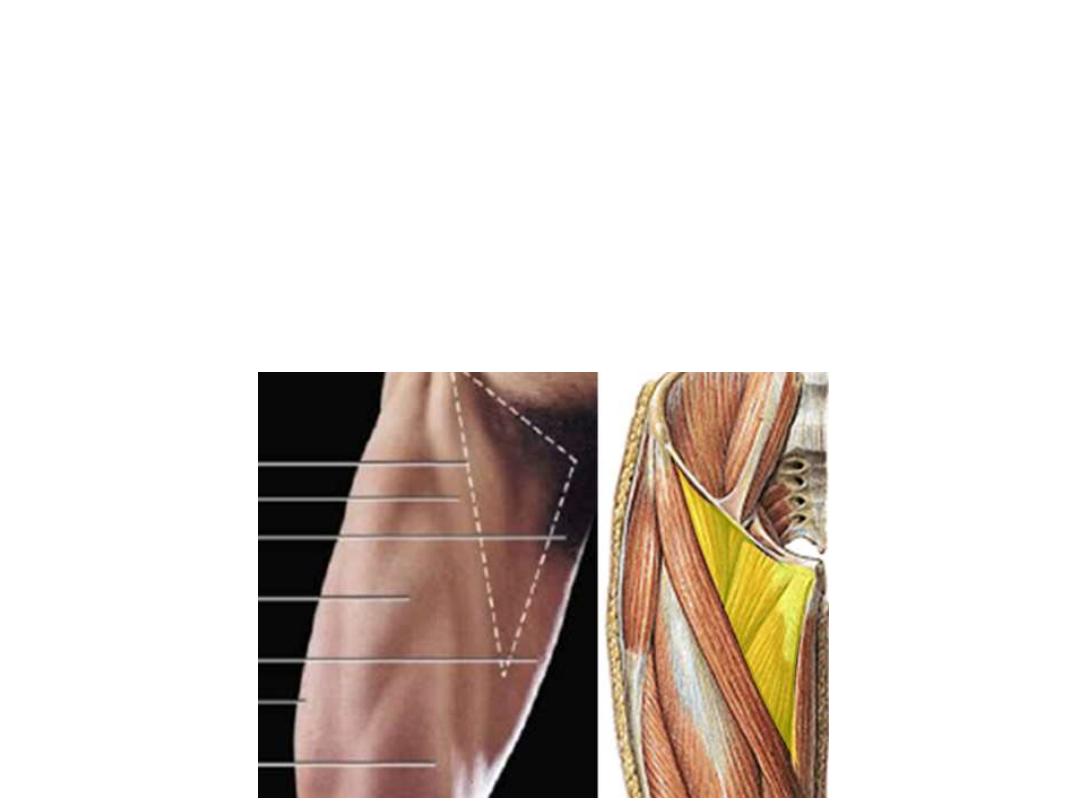
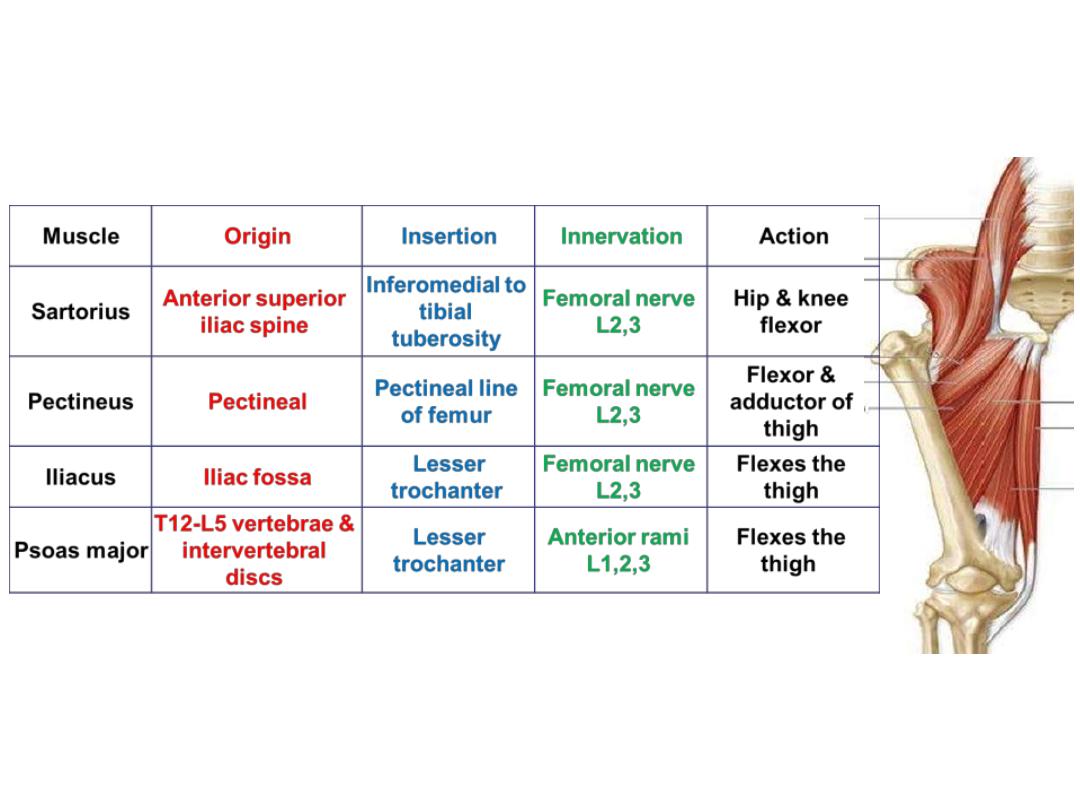
The femoral triangle:
A triangular gutter-like muscular depression whose base is formed by
inguinal ligament & apex downwards, roofed by fascia lata
Boundaries:
-Medially; medial border of adductor longus
-Laterally; medial border of sartorius
-Superiorly; inguinal ligament
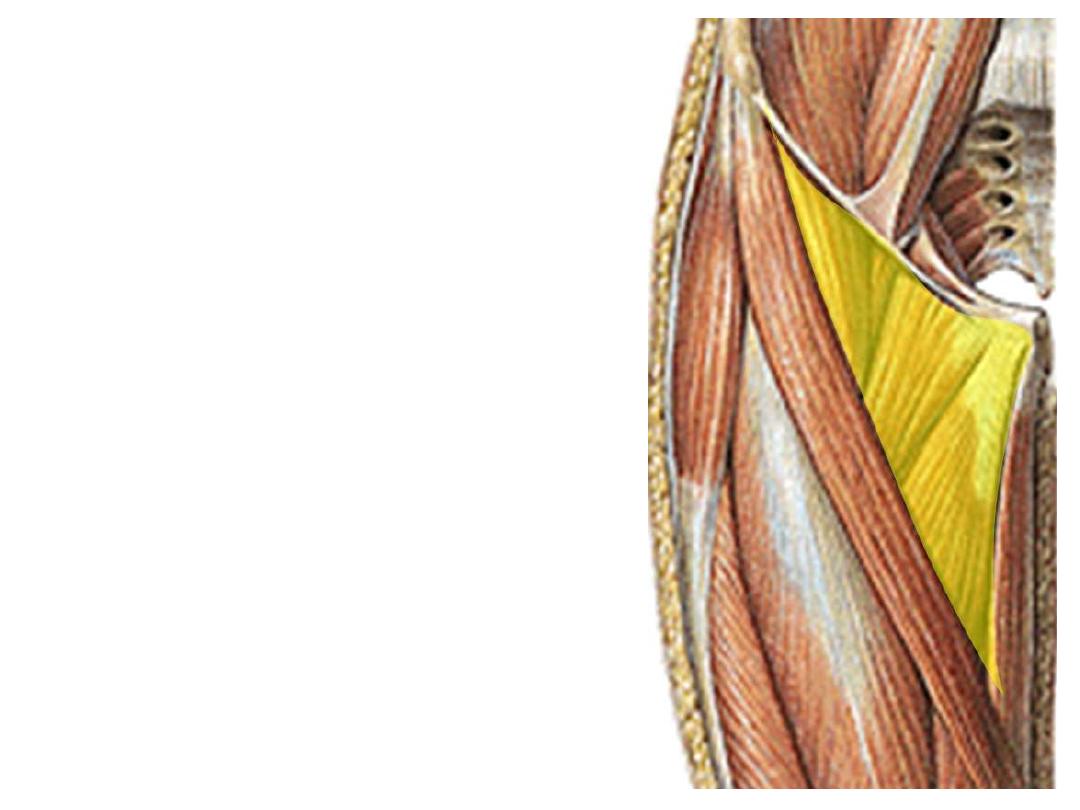
Floor:
1.
Adductor longus
2.
Pectineus
3.
Psoas
4.
Iliacus
Contents:
1- Femoral sheath & its contents
2- Femoral nerve
1
2
3
4
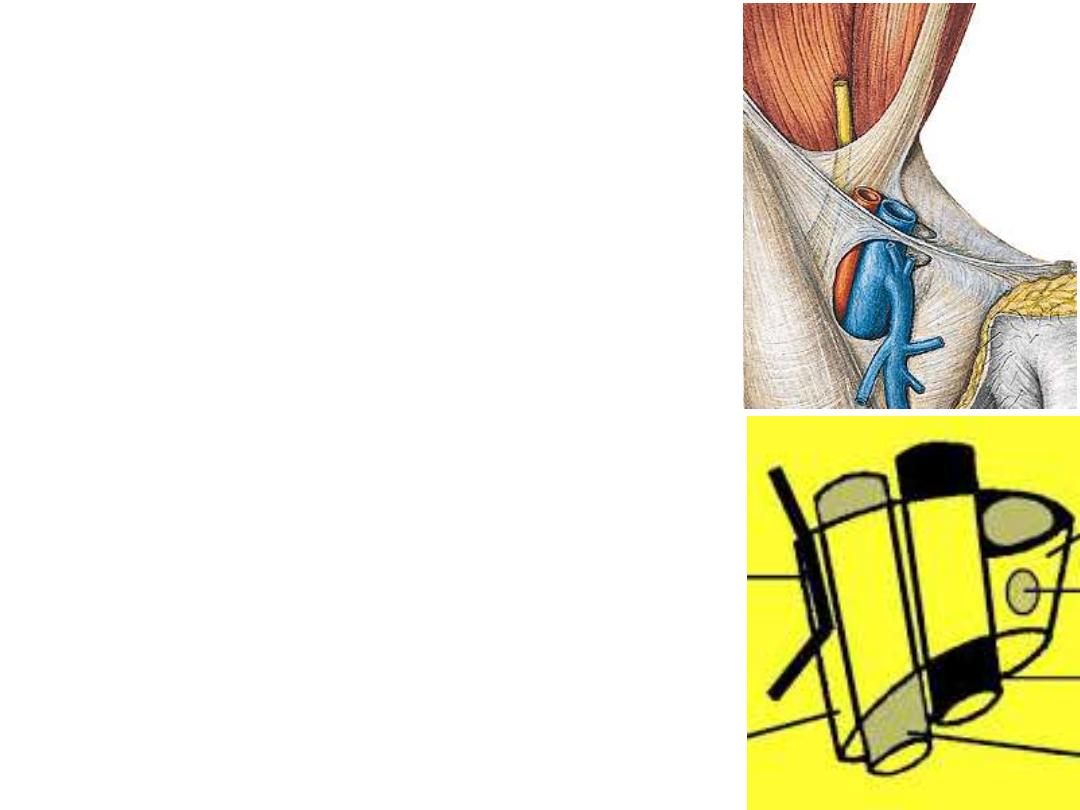
The femoral sheath:
-A funnel-shaped extension of abdominal fascia
which descends 2-3 cm beyond the inguinal
ligament
-This cylinder is divided into 3 compartments:
The lateral is for the femoral artery
The middle for the femoral vein
The medial is a dead space contains the deep
inguinal lymph node (femoral canal)
Femoral nerve is outside the sheath
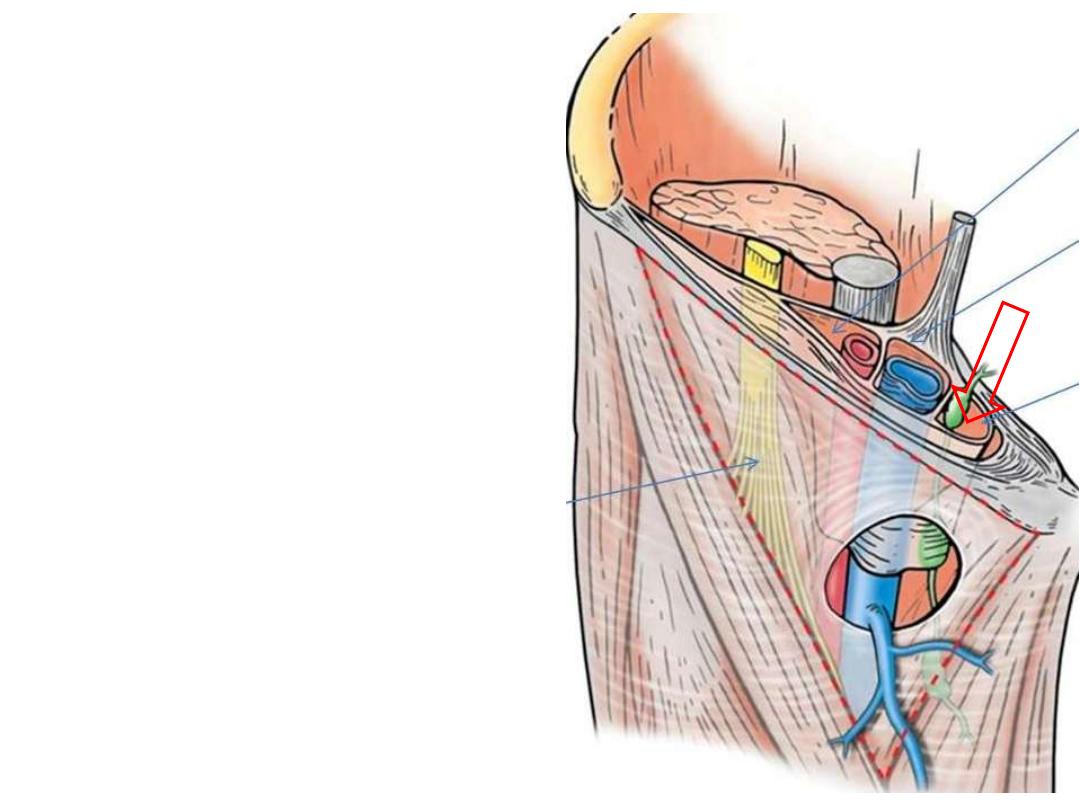
Femoral ring:
The pelvic mouth of the femoral
canal
It is closed by fascial condensation
Bounded medially by the lacunar
ligament & laterally by femoral vein