PARATHYROID AND
ADRENAL GLANDS
Dr . zaeem dahla
General surgeon

EMBERIOLOGY
THE foramen
caecum at the base of the tongue is a
remnant of thyroglossal duct this hallow structure migrate
caudally and pass in close continuity with, and some times
through the developing hyoid cartilage.
The PTGs
develop from the 3rid&4
th
pharyngeal pouch.
The thymus
gland also develop from 3rid pharyngeal
pouch
As it descend to superior mediastinum , in thorax it take
with it the PTG which arise from 3rid pharyngeal pouch
take the inferior site in regards to it upper pouch.
•
THYROID GLAND
; usually arise from the 4
th
pharyngeal pouch.

Surgical anatomy &
physiology
•
The normal PTG weight up to 50mg with charterstic
orange\brown colour .
•
Most adult have 4 glands,2 superior,2 inferior , but
may have more than 4 glands,.
•
Superior PTG usually constant in its position , while
the inferior PTG have non fixed position.
• Upper PTH glands found in a fat tissue above on the
posterolateral border of the thyroid immediately
above the point of entry of the inferior thyroid
artery.
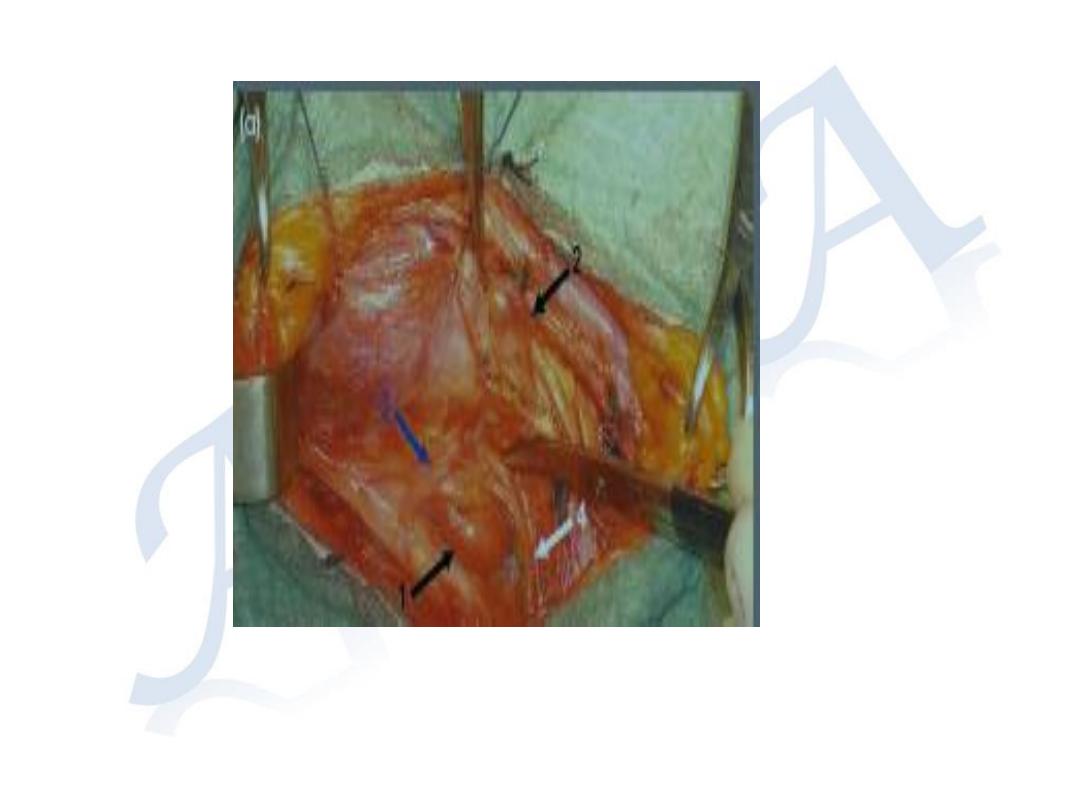

• The lower pair of PTG , more variable in
position , are usually found at the lower pole
of thyroid ,but may be found anywhere along
a line from this situation downwards to the
upper pole of thymus . Approximately 5% of
PTGs are found within the upper anterior
mediastinum . each gland has small capsule
and is supplied by a single leash of blood
vessels , theses glands are usually lie outside
thyroid gland capsule.

• Histology;
• The stroma consists of rich sinusoidal
capillary net work with islands of secretory
cells , two type of cells . The ‘ chief ’ cells or
principle cells are small with vesicular nuclei
and poorly staining cytoplasm. ‘oxyphil ’ cell
are less numerous and larger , with granular
cytoplasm and deeply staining .

• FUNCTION.
• Chief cells give P.T.H also called
parathormone, the hormone released
directly into the blood.the circulating level of
this hormone can be measured by radio-
immuno-assay.it is sufficiently reliable to
distinguish between high and low levels.

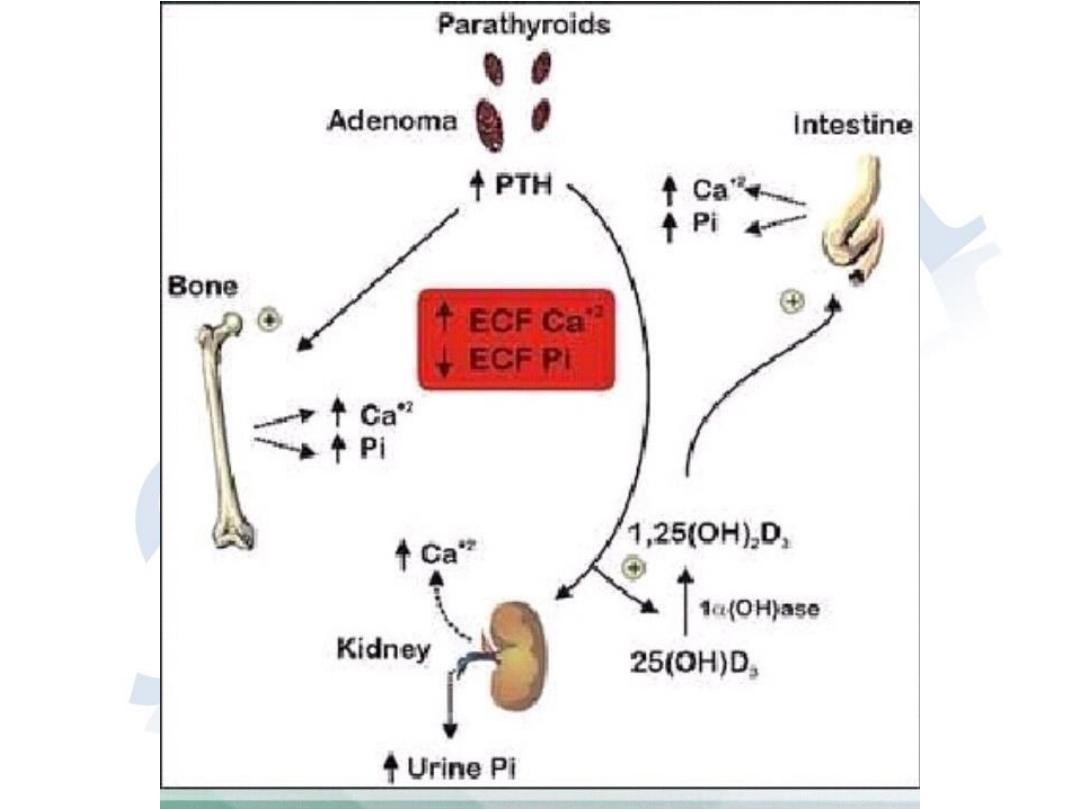
• FUNCTION OF PARATHYROID HORMONE
• Stimulate osteoclast activity, thereby increase bone
resorption by mobilizing calcium and phosphate.
• Increase the reabsorption of calcium by renal
tubules; thus reducing urinary secretion of calcium
• Augment the absorption of calcium from the gut.
• Reduce renal tubular re absorption of phosphate ,
thus promoting phosphate urea.

• Calcitonin hormone
• Was once thought to be the second
parathyroid hormone , but is now known to
be secreted by thyroid from the ‘parafolicular
cells ‘ ( c cell) its action quite the opposite
action of parathormone
.
Disease of parathyroid glands
Hypo parathyroidism
Hyper parathyroidism

hypoparathyroidism
• Parathyroid titany is a rare complication of subtotal
thyroidectomy (less than 1%)
• Symptoms usually appear on the 2
nd
or 3d post
oprative day, and are temporary .
• Permanent hypoparathyroidism, most commonly
encountered following radical thyroidectomy ,this
require constant supervision and treatment .
• Titany in newborn may occur within the first few
days of life in the child born of a mother with un
diagnosed hypo parathyroidism.

Clinical feature
• The 1
st
symptoms are tingling and numbness
in the face ,fingers, toes.
• In extreme cases cramps in the hands and
feet's are very painful ,the extended fingers
are flexed metacarpi- phalangeal joints with
thumb strongly adducted .
• This called ( capo pedal spasm)
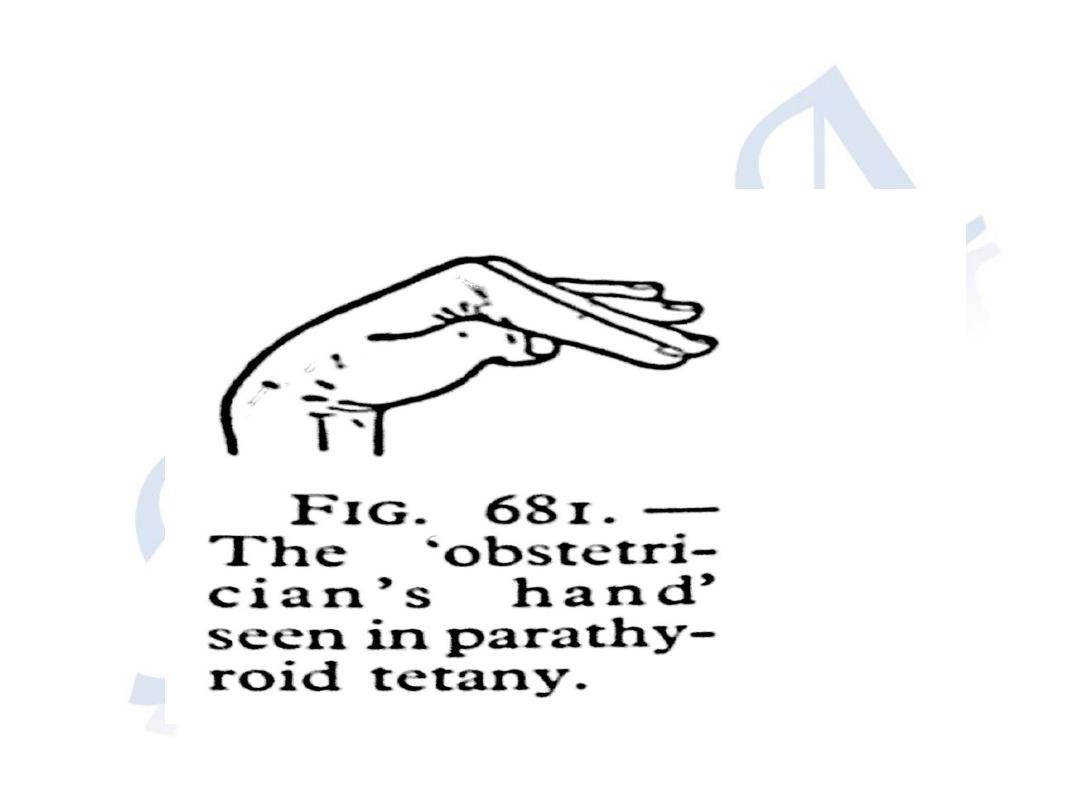

• Spasm of respiratory muscle.
• In infancy symptoms of titan may be mist
taken for epilepsy , though there is no loss of
consciousness.
• Latent titan maybe demonstrated by :
• # chvostek’s sign
• # trousseau’s sign

Treatment
• In acute cases the symptoms can be qiuckly and
effectively relieved by slow iv injection 10-20 ml
of 10% of calcium gluconate ,this can be
repeated till the serum ca level has been
established .
• Oral vitamen D
(increase ca absorption from GIT) and calcium
lactate .
• Initial dose 400000 units of calciferol may be
followed by 100000 units ,daily till serum ca
level become normal.


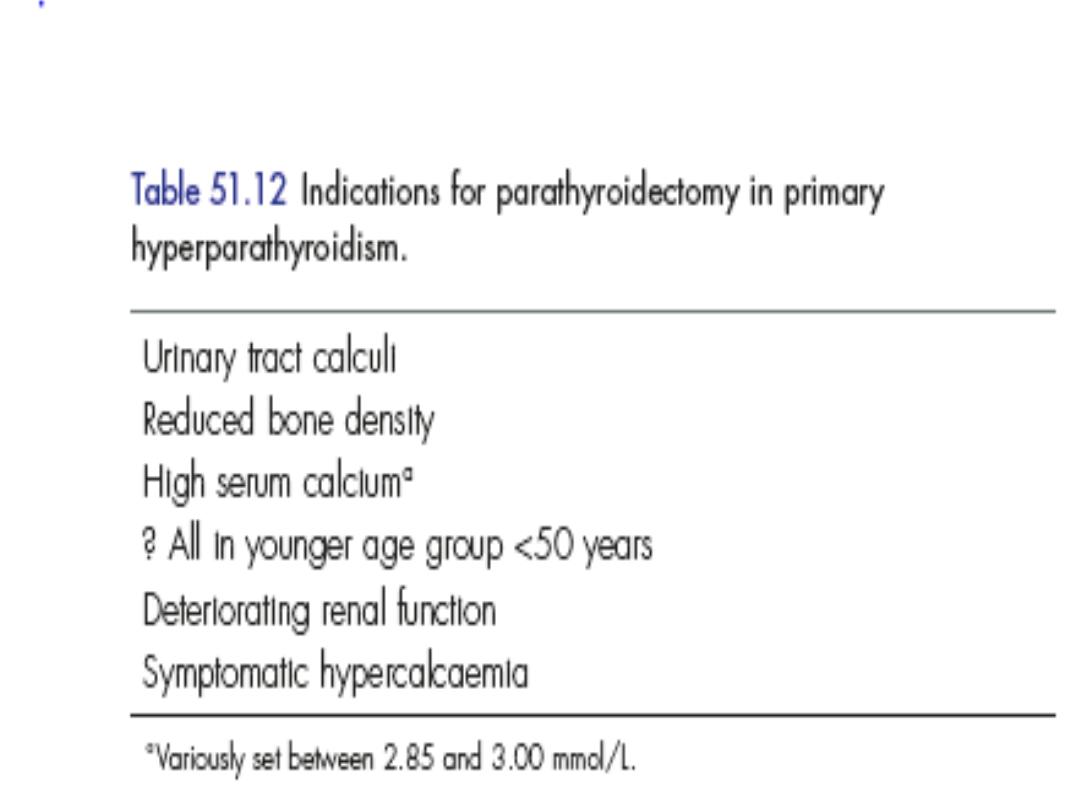
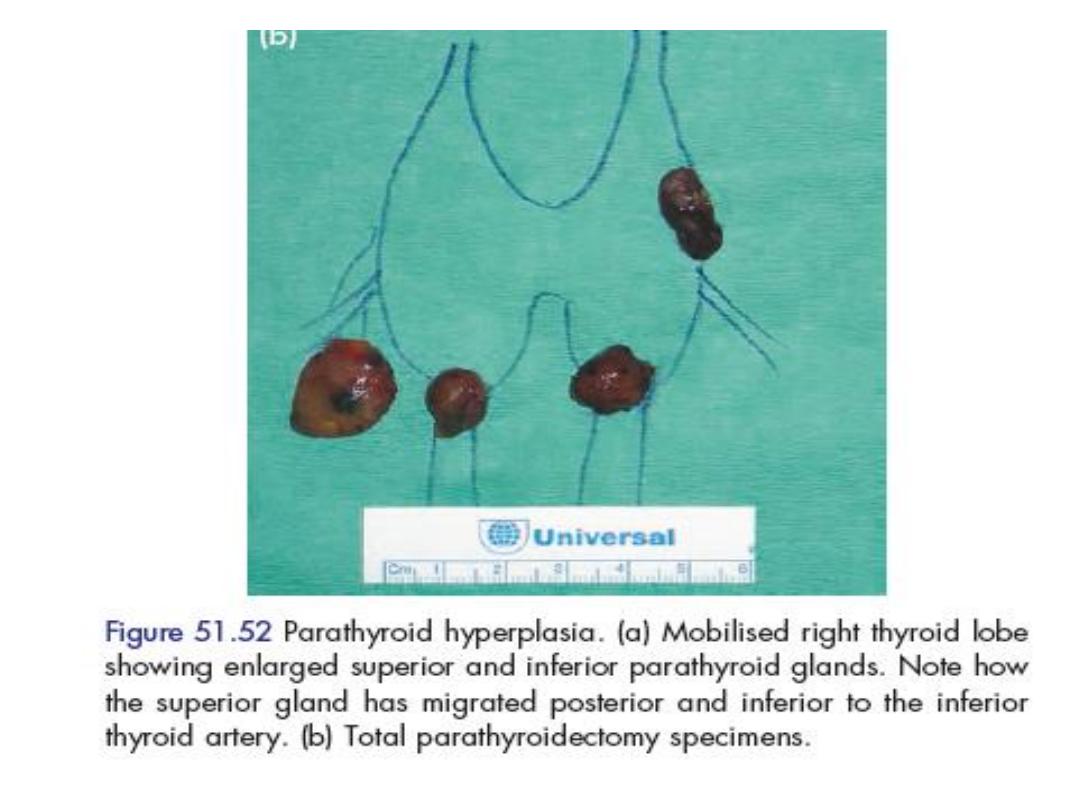
Hyperparathyroidism
• Symptoms of over activity of the para thyroid
gland may result from single or multiple
adenoma (85%)
• Hyperplasia of all 4 glands 13%
• Carcinoma more than 1% .
• That whole glands enlarged, darker in color.
Firmer and more vascular .

Clinical feature
• Hyperparathyrodism rarely found in 1
st
decade of life's.
• More common in women than men .
• Most commonly between the age 20 -60 y
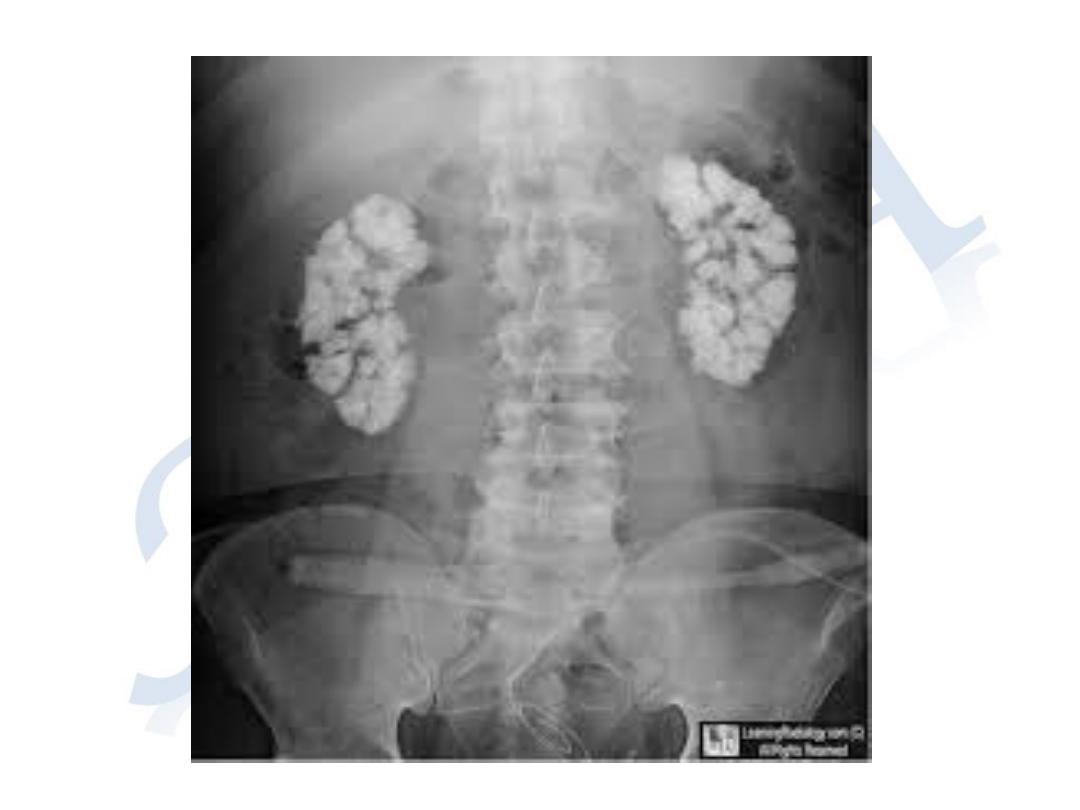
• The disease has been described as : bones
,stones , abdominal groans and psychic
moans
Parathormone increase
Bone disease
Renal stone
Psychic moans
Abdominal groans
•
Jonits, bones pain renal stone nausea ,vomiting, tiredness
•
density of bones nephroclcinosis anorexia personality
change
•
Otitis fibrosa cystica renal colic peptic ulcer
•
Bone cyst (jaw bones) pancreatitis

investigation
•
serum calcium upper limit (10.9 mg/dl)
• serum phosphate lower limit (3 mg/dl)
• excretion of ca in urine .
• serum alkaline phosphatase .
• serum PTH .

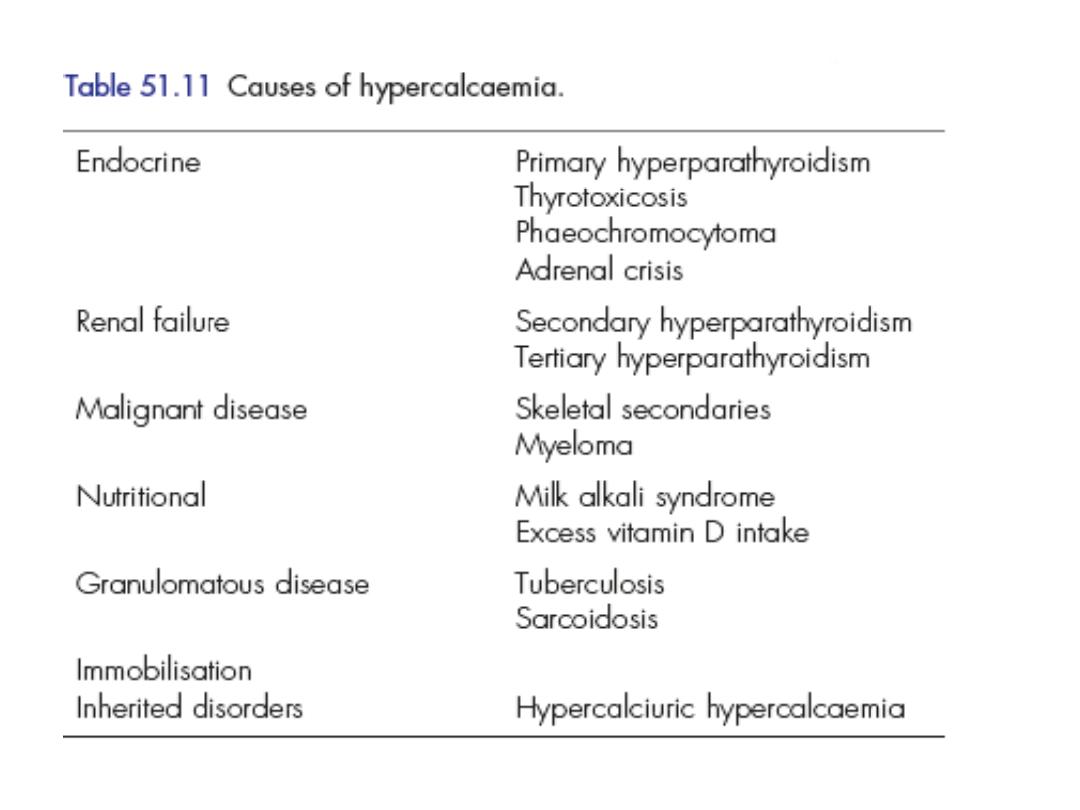
Differential diagnosis
• Secondary cancer in bones ( breast, prostate,
bronchus, kidney, thyroid)
• Carcinoma with endocrine secretion
(bronchus , kidney, ovary)
• Multiple myeloma
• Vitamin d intoxication
• Sarcoidosis
• Thyrotoxicosis

treatment
• Surgery is the only curative treatment
• Pre operative treatment is not usually
necessary.
• Occasionally patient with hypercalcemic crisis
need emergency treatment by fluids infusion
and biphosphate therapy .