Fifth stage
GynecologyLec-
9/5/2017
Metastatic Tumors of OvaryMETASTATIC TUMOR FROM BREAST CANCER
both ovaries replaced by pale, rather nodular tumor, with breast cancer cells arranged in long lines perpendicular to the surface of the ovarian cortex
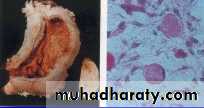
METASTATIC TUMOR FROM GASTRIC CANCER (Krukenberg )
gastric carcinoma of the fundus, with secondary ovarian tumor (Mucus-secreting signet-ring cells)
NeoplasticOvarian Tumours
Surface epithelial – 65-70%
Germ cell tumors – 15-20%
stromal – 10-15%
Metastatic tumors – 5%
Epidemiology
15,900 deaths annually4th common cause of cancer mortality
Most (70%) diagnosed at advanced stage where cure is uncommon.
23,000 cases annually
Ranks 3rd among gynecologic cancers
Ranks 5th among women cancers.
Risk Factors
Personal H :Any age ( common>40ys) .
Nulliparous.
Late age 1stpreg
History of breast or colon cancer.
Gonadal Dysgenesis
Talcum powder
Increased risk in women who use talc powder on genital area
M.H:
Early menarche.
Late menopause
prolonged use of fertility drugs without achieving pregnancy
Hormone replacement therapy > 10 years
Uninterrupted ovulation.
F.H
Mother, sister or daughter with ovarian cancer.
Protective factors
Multiparity: First pregnancy before age 30
Oral contraceptives.
Hysterectomy
Lactation
Bilateral oopherectomy
complications of benign ovTumours
torsion
hemorrhage
rupture
infection
incarceration
malignant change
complications during pregnancy
Diagnostic tools
HistoryExam (including rectal)
Investigations:-
TVS –masses and mass characteristics
Tumor markers – CA-125, LPA (plasma lysophosphatidic acid)
CT – assess spread to LN, pelvic and abdominal structures
MRI – best for distinguishing malignant from benign tumors
Clinical picture of benign ov tumors
Symptoms:
functioning tumors
nonfunctioning tumors
swelling
pressure symptoms
pain
menstrual disturbances
ovarian cachexia
Signs
small ov tumors
large ov tumors
DD:
from other pelvic swellings
from other abdominal swellings
Clinical picture cancer ovary
Benign ovarian Tumours + The following suggest malignancyage:mostly postmenopausal
pain: chronic and persistent
rapid course
bilaterality
Solidity ( variegated consistency )
fixity
metastases :nodules in DP, lymph nodes
ascitis
edema LL
cachexia
Staging:
Vertical incision.
Aspirate, or saline washing.
Careful assessment., Liver, rthemidaphragm, All other organs as omentum, intestine,….
Para aortic LN sampling.
Proper staging, for prognosis, selection of adjuvant therapy…..
Ovarian Cancer Staging
Stage 11A: One ovary
1B: Both ovaries
1C: with malignant ascites, rupture surface tumor
Stage 2
2A: Reproductive organs
2B: Other pelvic organs
2C: with malignant ascites or washings
Stage 3
3A: microscopic upper abdominal disease
3B: upper abdominal metastasis less than 2 centimeters
3C: upper abdominal metastasis greater than 2 centimeters
Stage 4 is disease outside the peritoneal cavity
Liver parenchymal metastasis.
Pleural effusion
Supraclavicular nodes
Treatment
Depends on
Staging
Tumor type
Age
Desire for future fertility
Include surgery, chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy
Surgery for ov. cancer
Complete surgery:TAH/BSO +omentectomy+lymphadenectomyother cases of stage Ia
Conservative surgery: unilateral adnexectomy indicated:
stage Ia: intact capsule, negative peritoneal washing, free omentum,
well differentiated T,
young patient with low parity
Stage Ib,c
Surgery for ov. Cancer cont…
Cytoreductive surgery: for all other stages
optimum cytoreduction leaving no macroscopic lesion or one less than 1.5 cm.
consist of TAH/BSO +omentectomy+lymphadenectomy+may be bowel resection &anastmosis.
Second look surgery after chemotherapy
Surgical treatment
Primary debulking and cytoreduction; may include:
Bilateral salpingo-oopherectomy
Hysterectomy
Lymphadenectomy (Para-aortic, inguinal)
Omentectomy
“brushing” of diaphragm
Examination of liver
Chemotherapy & radiotherapy for ov cancer
Chemotherapy:adjuvant to surgery to improve prognosis in early stages
induce remission in advanced cases
agents: alkylating agents,platinum: single drug and multible drug regimens
Radiotherapy:
has less place in modern practice, replaced by chemotherapy
was given for cases with small residual lesions (< 2 cm)
forms are:
radioactive isotope: intraperitoneal 32P ,
external-beam radiotherapy
Chemotherapy and Radiation
Usually 6 cycles of chemotherapy
Cisplatin (or Carboplatin) plus Paclitaxel most commonly used combination therapy
XRT