1
Fifth stage
Surgery
Lec-
د.يقظان
12/3/2017
Pelvic fractures
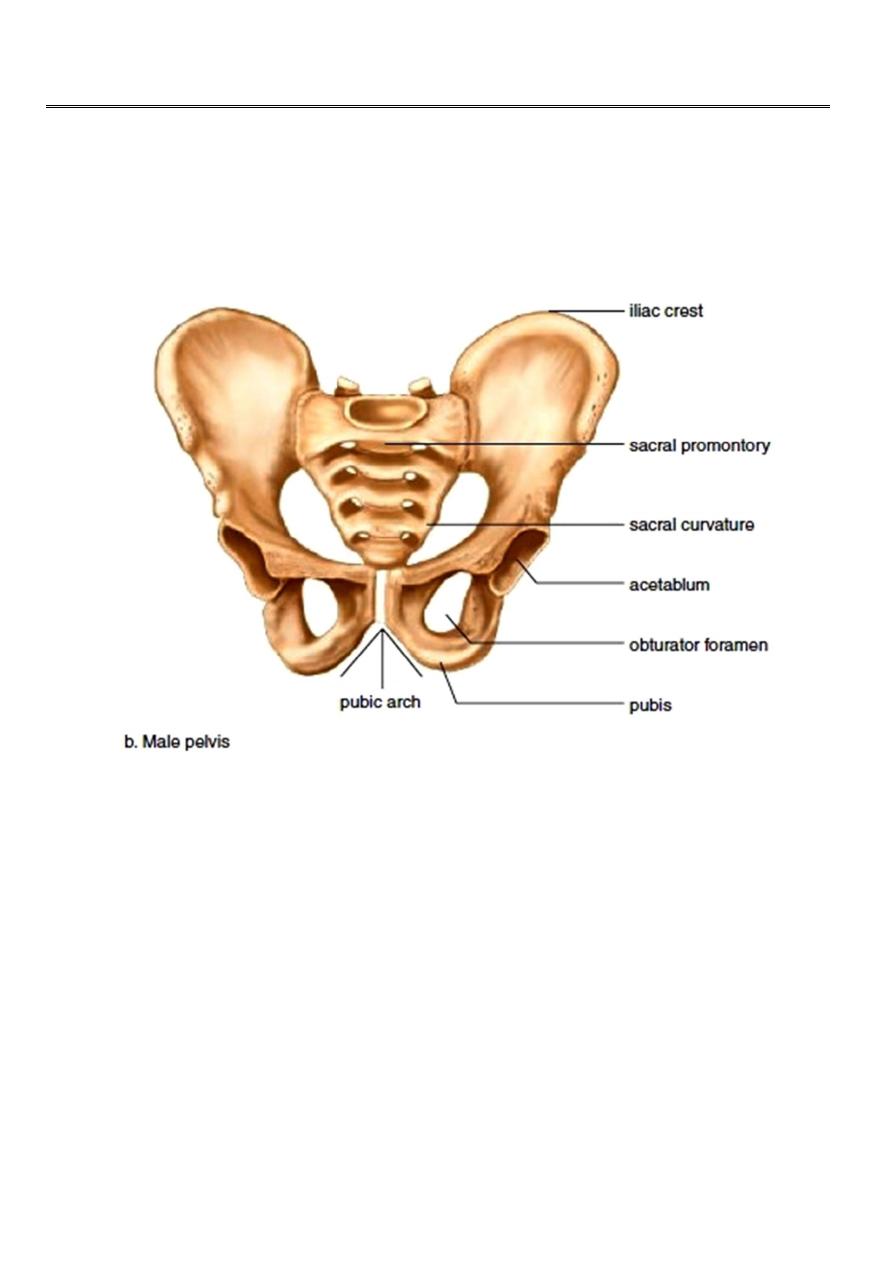
Anatomy of pelvis :
The pelvic ring is made of the two innominate bones and the sacrum. Articulating in front at
the symphysis pubis , posteriorly articulating with sacroiliac joints.
Fractures of the pelvis :
5% of all fractures
2/3 caused by road accident
Carried high rate of mortality in -sever type, 10%.
(unstable type)
Types of fractures pelvis :
1. Isolated fractures (with an intact ring).
2. Fracture with broken ring. (stable, unstable). If the pelvis can withstand weight
bearing loads without displacement, it is stable
3. Fracture of acetabulum.
4. Sacrococcygeal fracture.
2
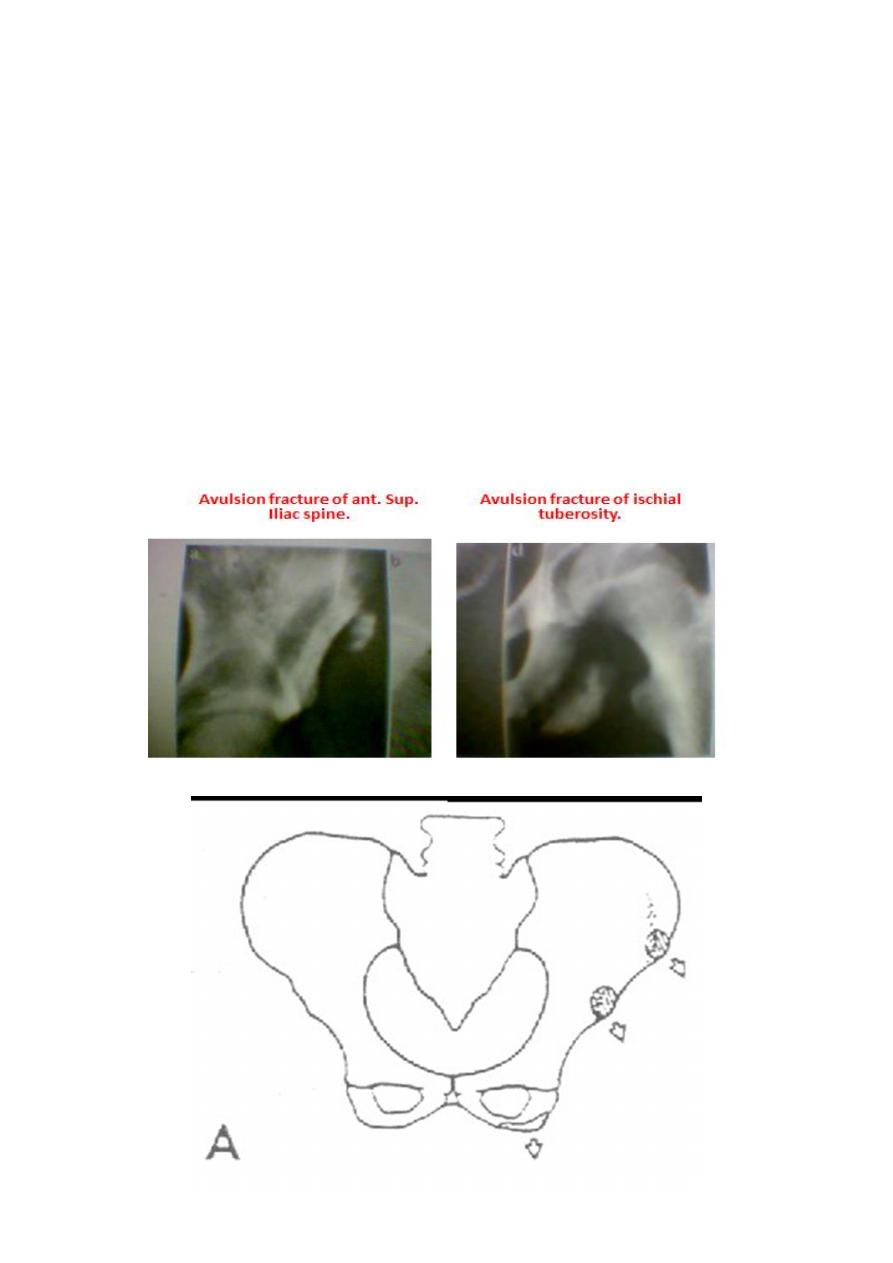
Isolated fractures with intact ring :
• Avulsion fractures: e.g avulsion of anterior sup. iliac spine by strong contraction of
Sartorius muscle.
• Direct fractures: e.g. fall from height lead to fracture of iliac blade, ischium.
• Stress fractures: e.g. fracture pubic rami in osteoporotic patients .
Clinically in Isolated fractures with intact ring The patient is not severely shocked but has
pain on attempting to walk. There is localized tenderness but seldom any damage to pelvic
viscera. Treated by pain relieve, bed rest , for 1-3 weeks, physiotherapy of the lower limb
from the beginning.
3
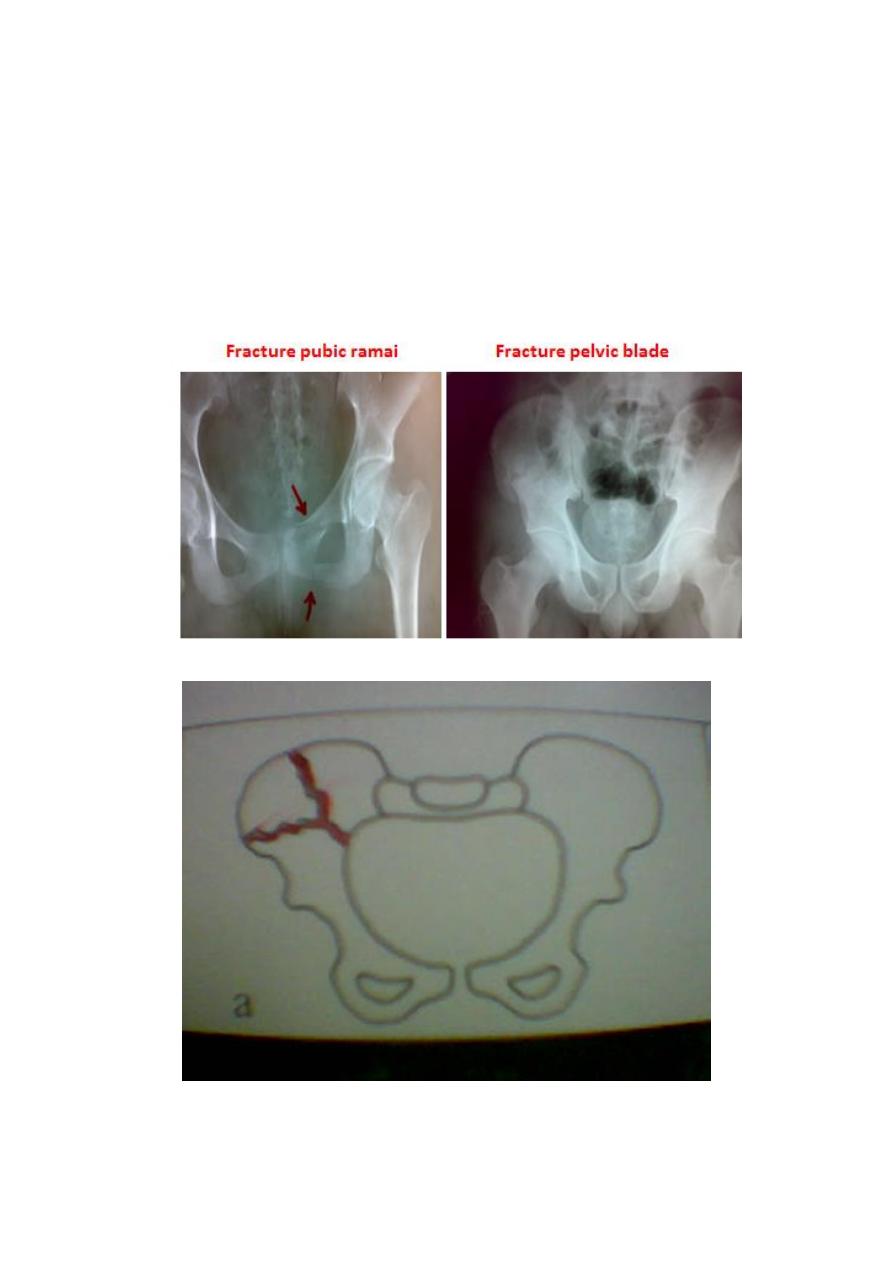
Fractures with a broken ring :
1. Stable ring fractures
2. Undisplaced fractures of one or two ipsilateral pubic rami.
3. Fractures of the blade of ilium.
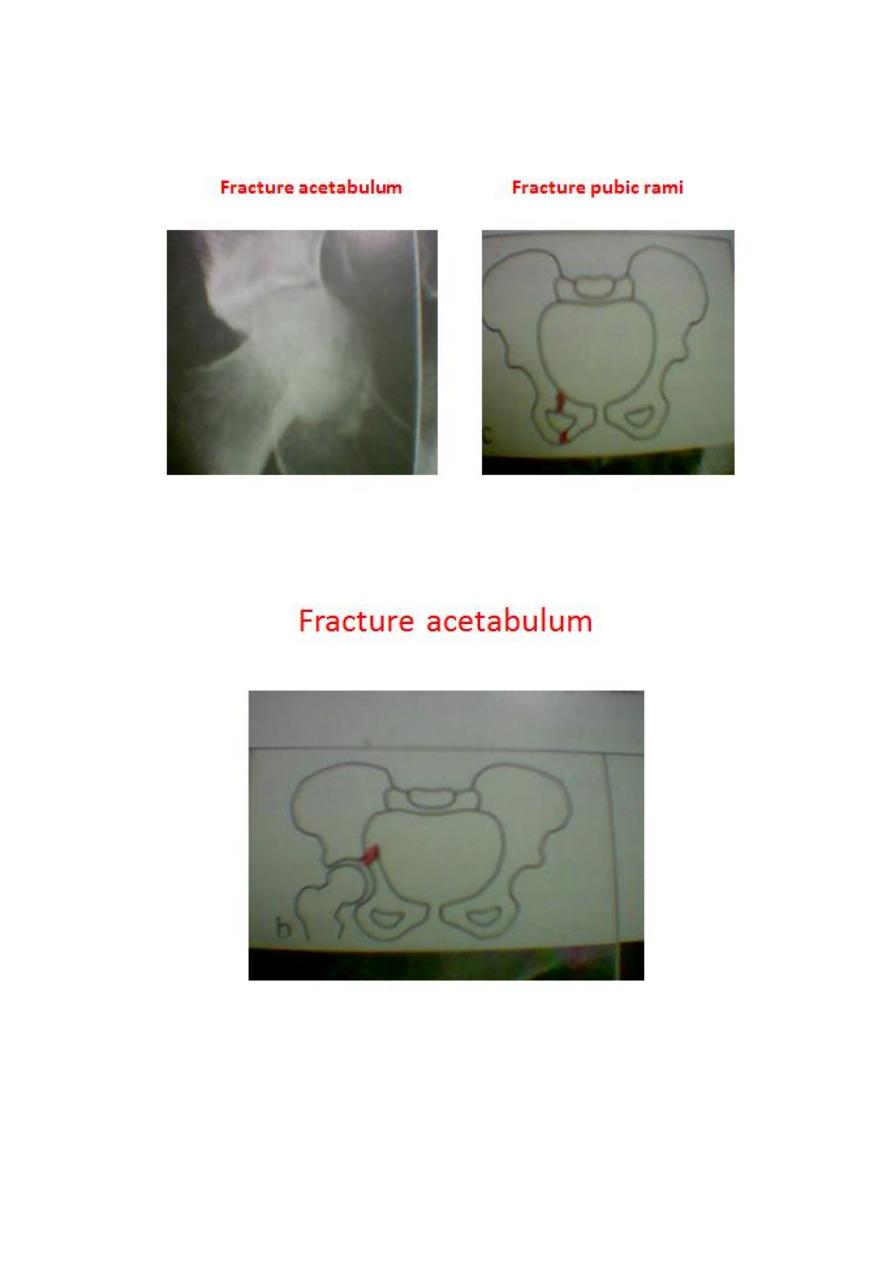
4.
Fractures of acetabulum
.
4
Unstable ring fractures :
1. Caused by sever trauma.
2. Extremely serious.
3. Carries high risk of visceral injuries.
4. There are fractures around or separation of symphysis pubis or sacroiliac joint.
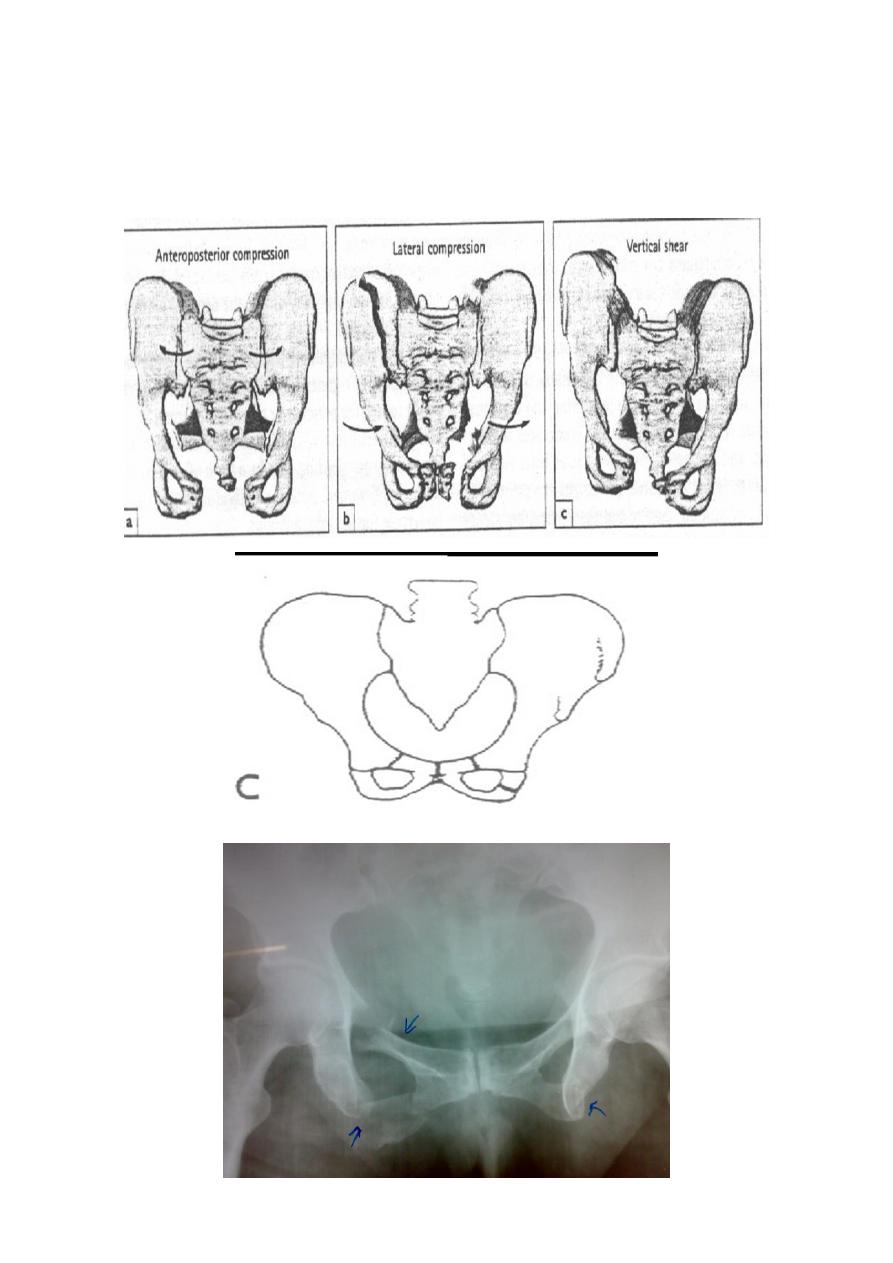
5
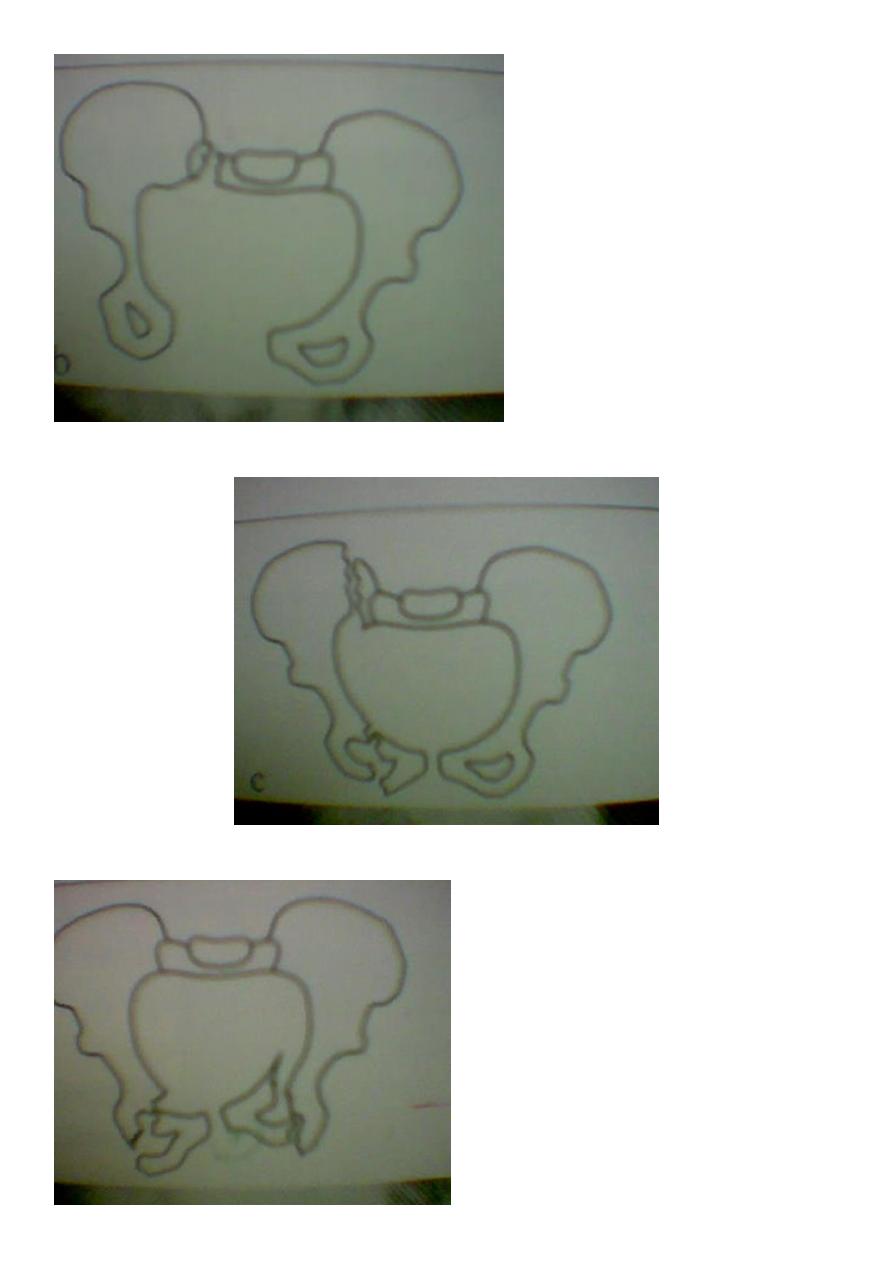
Types of unstable fracture pelvic ring :
1. antero-posterior compression (open book).
2. lateral compression (closed book).
3. Vertical force cause vertical displacement of the innominate bone on the same side.
4. combination injuries.
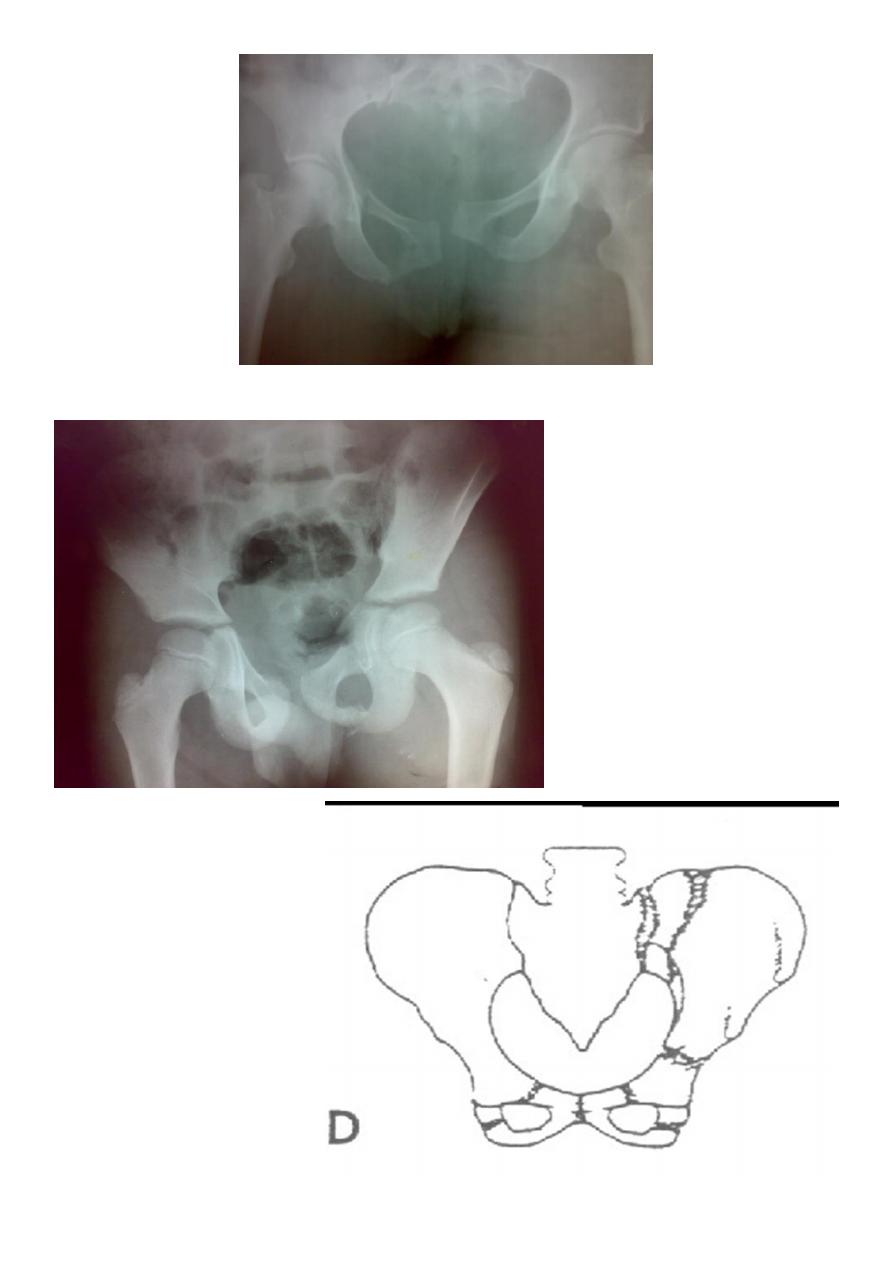
6

7
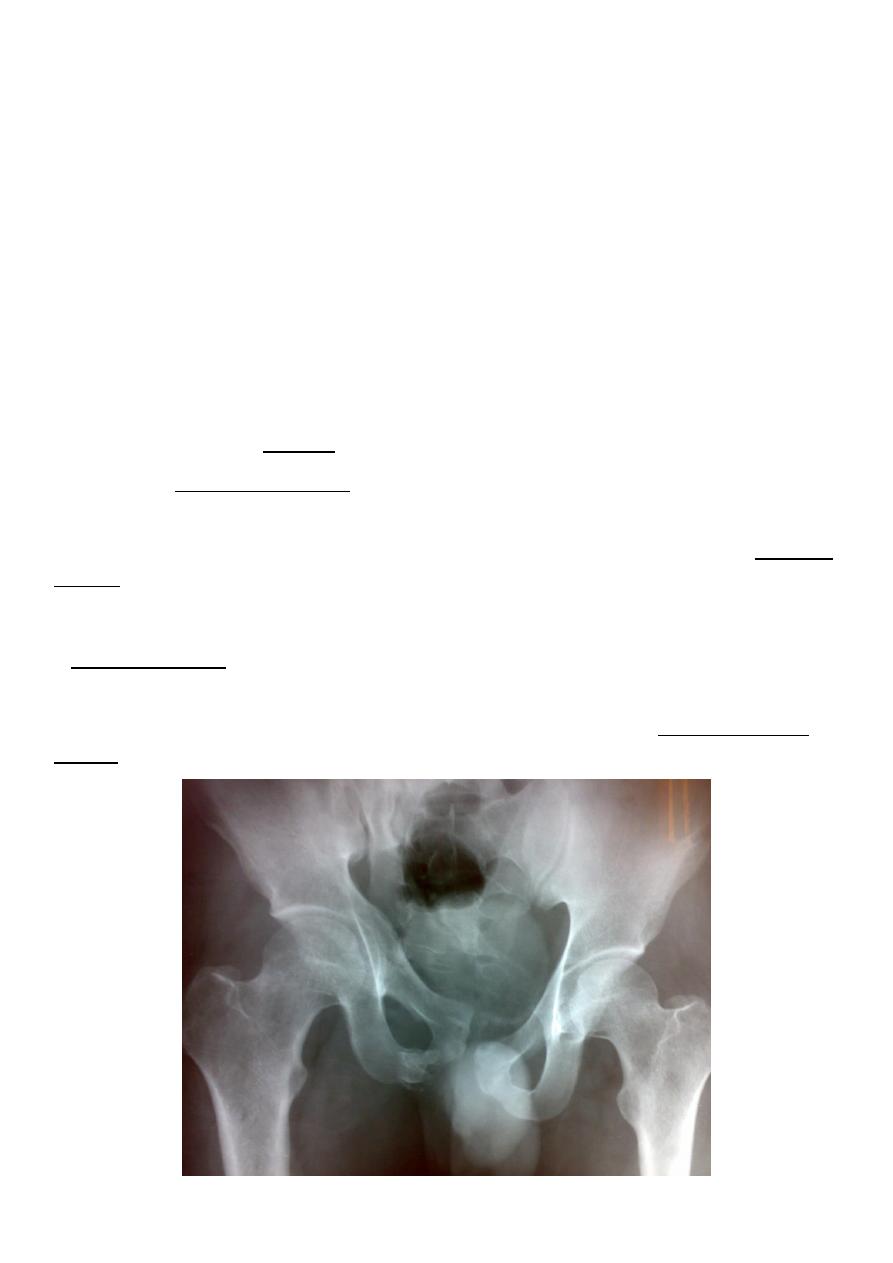
8
Clinically : These injuries caused by severe trauma, extremely serious, carries high risk of
visceral injuries. There are fractures around or separation of symphysis pubis or sacroiliac
joint. With unstable injuries, the patient is
a) severely shocked.
b) in great pain.
c) unable to stand.
d) Patient may be unable to pass urine(blood at external meatus).
e) wide spread tenderness.
F) one leg may be partly anaesthetic due to sciatic nerve injury.
Patient may be severely shocked due to blood loss or visceral injury.
There may be swelling or bruising of the lower abdomen, the thighs, the perineum, and the
scrotum or the vulva.
An inability to void and blood at the external meatus, are the classic features of a ruptured
urethra (NO CATHETERIZATION).
A ruptured bladder should be suspected in patients who do not void or in whom a bladder
is not palpable after adequate fluid replacement.
Abdominal tenderness and guarding suggests intraperitoneal bleeding (ruptured liver or
spleen) .

9
On examination :
Pain may be elicited by gentle but firm pressure(from side to side on iliac crest), then
outwards, and then directly on symphysis pubis.
Rectal examination is mandatory (High prostate = urethral injury).
Neurological examination is essential to detect lumbosacral plexus damage.
X- ray:
Ideally five views should be obtained : Standard anteroposterior view, inlet view, outlet
view, right oblique view, and left oblique view, but x-ray shouldn't be done until the patient
become stable .
Treatment :
The first step make sure that airway is clear. Active bleeding should be controlled.
shock treatment is the essential part of management .
Severe bleeding is the main cause of death following high-energy pelvic fractures. If there is
an unstable fracture of the pelvis, hemorrhage will be reduced by rapidly applying a pelvic
binder or an external fixator.
Treatment of the fracture :
Open book injuries with a gap of less than 2cm at the symphisis pubis can be treated with
bed rest for 6 weeks. If the gap is more than 2cm, external fixator with pins in the iliac
blades and anterior bar may be used for 8-12 weeks. The other option is anterior plating.
Severe vertical shear and compression injuries are the most dangerous and most difficult to
treat. The fracture or dislocation must be stabilized by external fixation or posterior
iliosacral screw or anterior plating with posterior iliosacral screw . Vertical force fractures
may be treated by open reduction and internal fixation or skeletal traction and non
weight bearing for 3 months .
