
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
(pseudotumorcerebri)
papilloedema with symptomatic raised ICP more than 20cm with
normal imaging study of the brain ( absent intracranial mass or
infection)
more common in obese women of childbearing age
usually self limiting, recurrence is common
a preventable cause of blindness from optic atrophy
perimetry is the best test to detect and follow visual loss
clinical features
symptoms and signs of raised ICP headache with papilloedema and no focal
neurological deficit apart from abducent palsy (false localizing sign)
i.e. headache, diplopia, papilloedema, enlarged blind spot with conspicuous
absence of altered level of consciousness in spite of raised ICP
Diagnosis
1. clinical symptoms and signs
2. CSF pressure, more than 20cm H2O
3. CSF normal cytology and biochemistry some time low protein
4. Normal imaging study of the brain except for slit ventricles
Associated conditions
1. Obesity
2. Drugs tetracyclines, nalidixic acid, ciprofluxacine, danazol, lithium,
amiodarone, phenytoin, nitrofurantoin, nitroglycerine and steroids
3. Steroid withdrawal
4. Hypervitaminosis A
5. Hypoparathyroidism and hyperthyroidism
6. Addison disease and cushing disease
7. Uremia
8. Iron deficiency anemia
9. Menstrual irregularity
10. Oral contraceptive
Differential diagnosis
1. Brain mass, may be nonvisible on non enhanced CT scan
2. Dural sinus thrombosis
3. Meningeal carcinomatosis
4. Pseudopapilloedema: anomalous elevation of optic nerve head
associated with hyperopia and drusen, but here there is positive retinal
venous pulsation
5. Malignant hypertention
Treatment
Spontaneous resolution is common between 1 month – 1 year
Recurrence rate 10 %
There is no reliable predictor of visual loss, i.e visual loss is unrelated to
severity of headache, papilloedema, duration of symptoms.
1. Repeated ophthalmplogical examination by perimetry
2. Treat offending factor
3. Weight loss
4. Medical treatment
Diuretics
Carbonic unhydrase inhibitors
acetazolamide start by 250 mg PO q 8-12 hr
increasing the dose till symptomatic relief or side
effects or 2 gm is reached. Contraindicated in renal
calculi and allergy to sulpha
topiramate(topomax) anticonvulsant with carbonic
unhydrase inhibition 200 mg PO BID
frusemide( Lasix )start 160 mgup to 320 mg
5. surgical
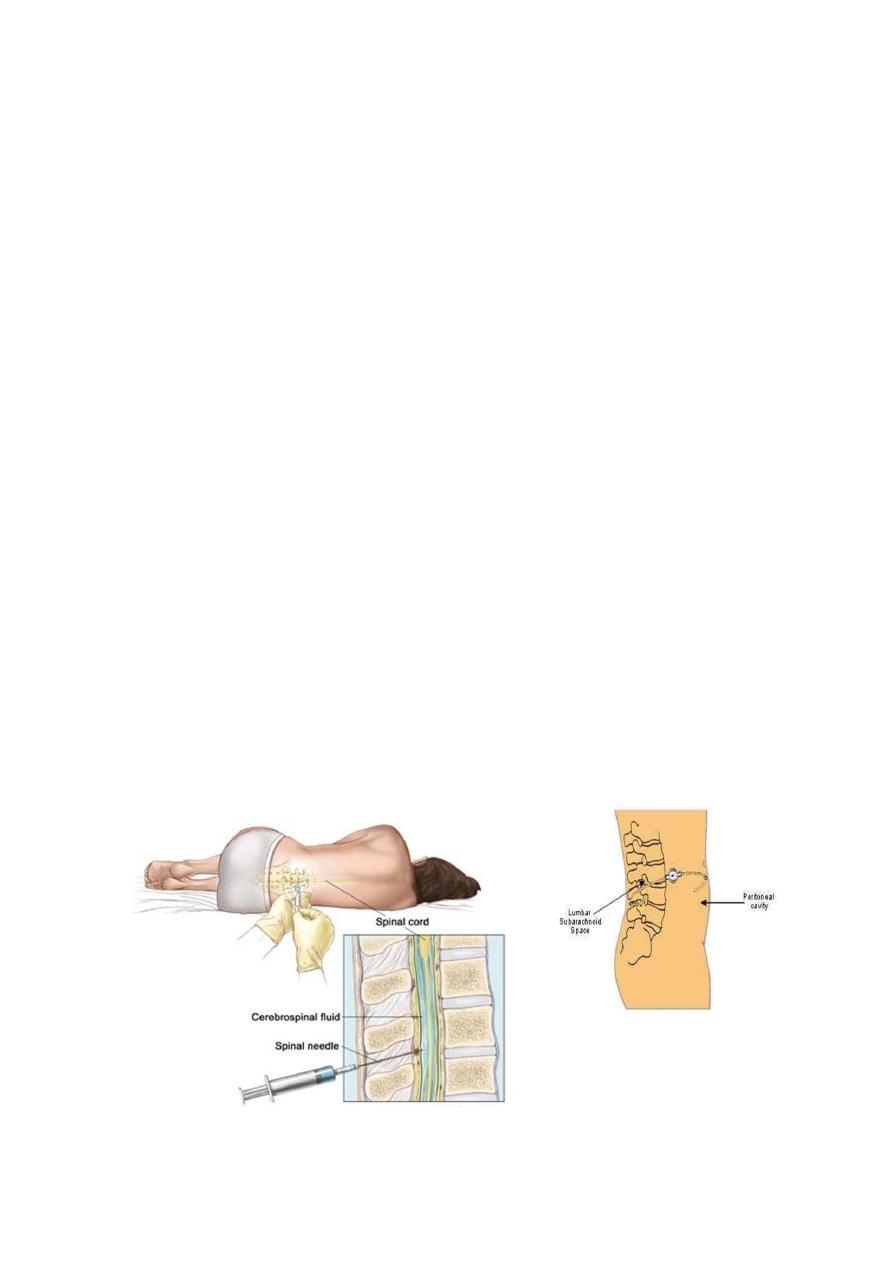
a. serial LP till remission 25% remit by 1
st
LP, aspirate 30cc daily
till opening pressure be bellow 20cm then aspirate weekly with
follow up
b. lumboperitoneal shunt
