27/3/2016
Antenatal Assessment of Fetal Well-being
DR.SHAIMAA
1
BY : TAHER ALI TAHER
Obstetrics
The aim:
Using tests to clearly identify the compromised fetus at a stage at which
intervention will improve the outcome.
What is fetal compromise?
A fetus that is at risk of damage from hypoxia.
Causes of hypoxia:
1 - Uteroplacental insufficiency, fetal growth restriction.
2 - Decreased maternal oxygenation.
3 - Impaired fetal blood supply to the placenta.
4 - Intrinsic fetal conditions.
Physiologically:
The production of ATP requires O
2
Hypoxia leads to anaerobic metabolism with decreased production of
ATP ( 2 molecules vs. 24).
Lactic acid accumulation leads to metabolic acidemia, eventually cell
damage and death.
The brain, myocardium and kidneys are the most sensitive organs,
eventually fetal death may occur.
Fetal response to hypoxia:
The human fetus demonstrates complex patterns of activity including
breathing movements, gross body movements and fine motor
movements.
27/3/2016
Antenatal Assessment of Fetal Well-being
DR.SHAIMAA
2
BY : TAHER ALI TAHER
The fetus exposed to hypoxia, will demonstrate adaptations designed to
conserve energy and decrease O
2
consumption. These include:
-decreased fetal movement.
-redistribution of blood.
-decreased urine output leading to oligohydramnios.
-since fetal growth accounts for substantial fraction of energy of total
substrate consumption, therefore in hypoxia growth is decreased
leading to fetal growth restriction.
The majority of currently available tests of fetal well-being are
designed to detect these adaptive changes , these tests include:
1- Fetal movement counting (kick count):
Depends on maternal perception of fetal movement, therefore it should
not be routinely provided.
But those women at high risk of fetal compromise are advised to pay
attention to their fetal movement and it is recommended that pregnant
females who report a reduction or an alteration in the movement of
their fetuses, should be offered some other forms of assessment of fetal
well-being.
2- Fetal heart rate recording: which include
cardiotocography (CTG) and computerized CTG.
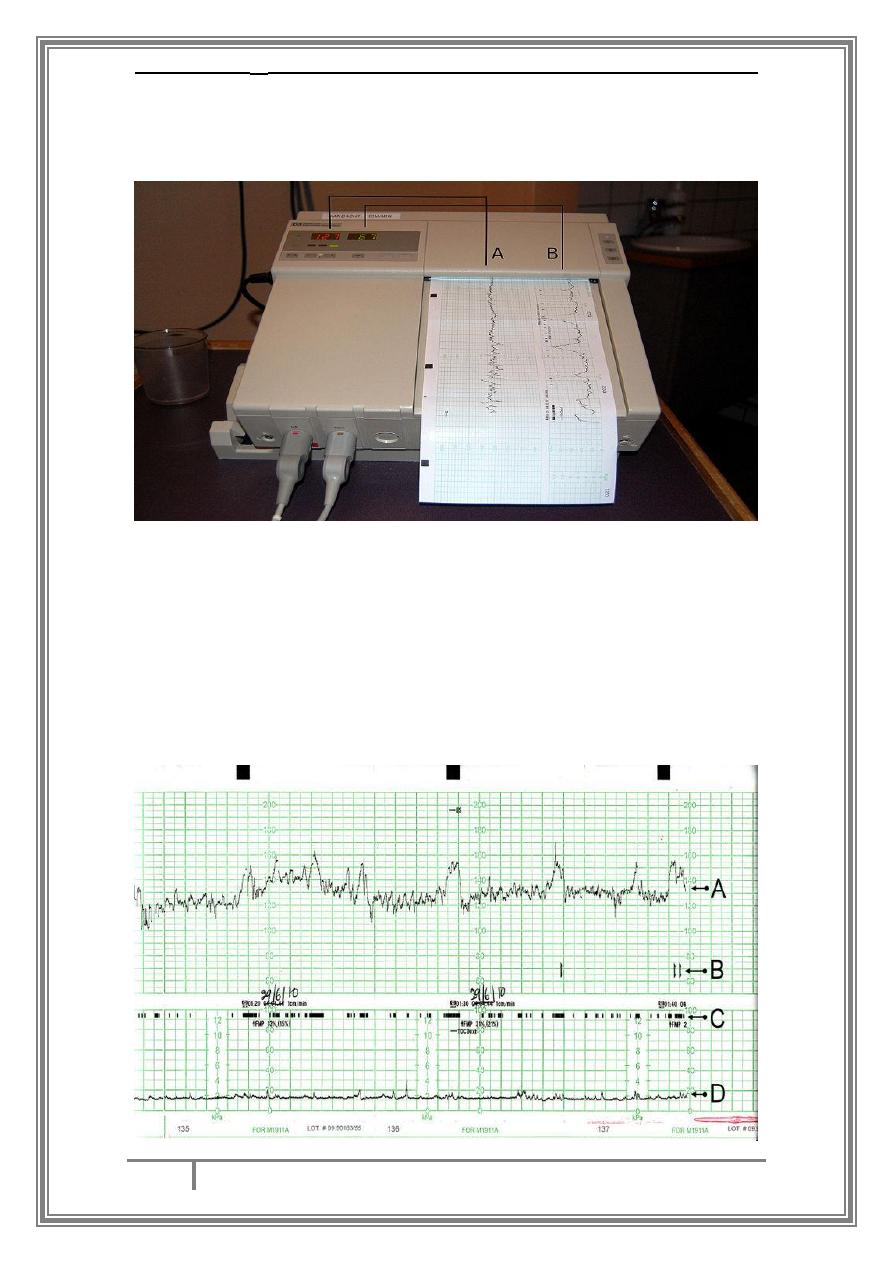
A - Cardiotocography:
Indirect method of monitoring of fetal heart rate. It uses the physical
principle of doppler effect to detect fetal heart motion.
physiologically, the fetal cardiac activity is regulated through
sympathetic and parasympathetic signals and by vasomotor,
chemoreceptors and baroreceptors mechanisms, so pathological events
27/3/2016
Antenatal Assessment of Fetal Well-being
DR.SHAIMAA
3
BY : TAHER ALI TAHER
such as hypoxia modify these signals and eventually alters the fetal
cardiac response
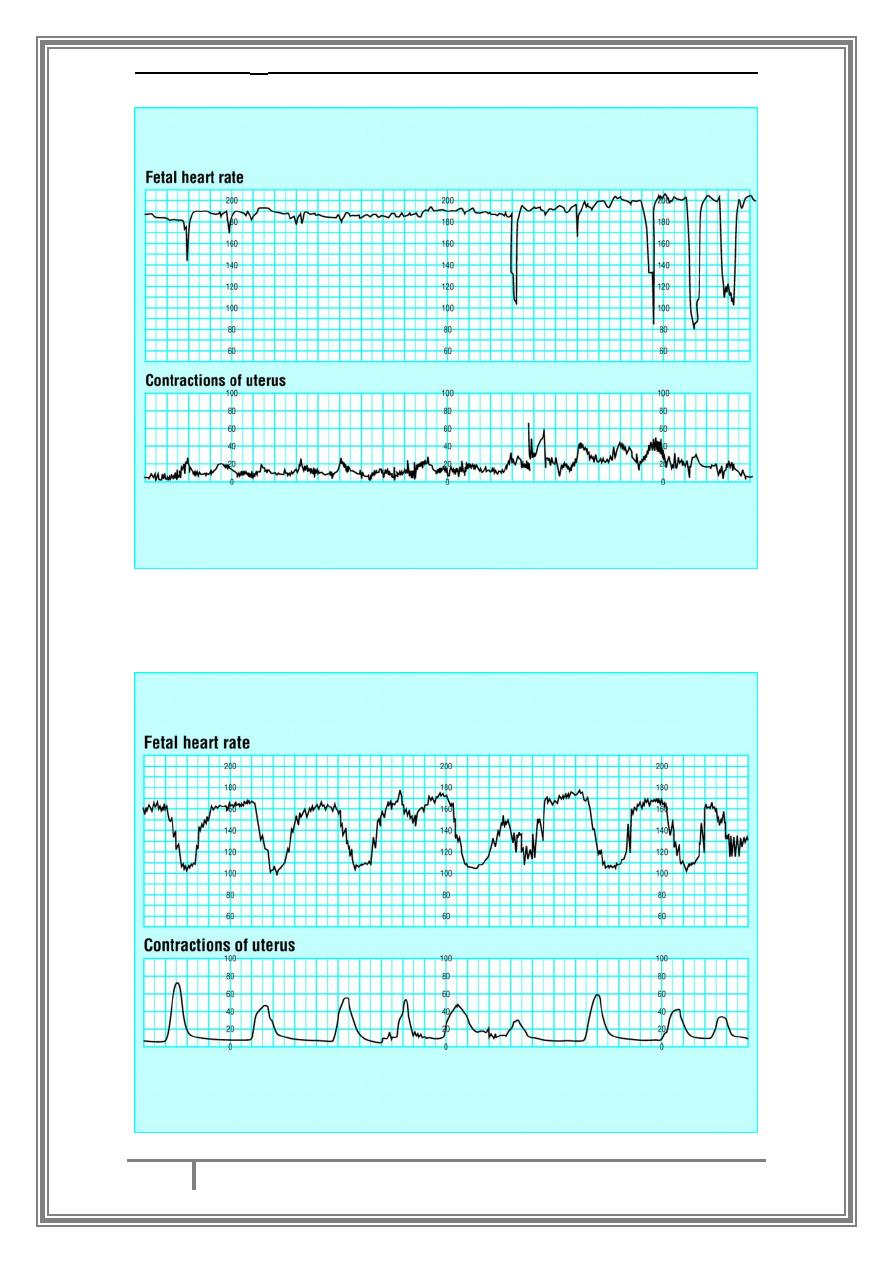
What are the parameters to look for in a CTG trace?
-Baseline fetal heart rate.
Fetal heart rate variability.
-
Fetal heart rate acceleration.
-
Fetal heart rate deceleration.
-
27/3/2016
Antenatal Assessment of Fetal Well-being
DR.SHAIMAA
4
BY : TAHER ALI TAHER
Normal CTG :
Baseline rate 110 – 160 bpm.
-
variability 10 – 25.
-
2 accelerations in a 20 – 30 min trace.
-
No deceleration.
-
Suspicious CTG:
Abnormal baseline rate.
*
reduced variability < 10 bpm.
*
absence of acceleration.
*
variable deceleration.
*
Abnormal CTG:
No accelerations and two or more of the following:
abnormal baseline rate.
-
abnormal variability.
-
repetitive late decelerations.
-
-variable decelerations with duration > 60 sec, late recovery to
baseline, late deceleration component, poor variability between and
during decelerations.
27/3/2016
Antenatal Assessment of Fetal Well-being
DR.SHAIMAA
5
BY : TAHER ALI TAHER

27/3/2016
Antenatal Assessment of Fetal Well-being
DR.SHAIMAA
6
BY : TAHER ALI TAHER
Non stress and stress CTG:
Non stress: when the patient is positioned comfortably without
contraction.
Stress test: refers to what the fetus is experiencing where contractions
are stimulated either by nipple stimulation or by oxytocin. A positive test
is fetal cardiac decelerations in response to uterine contractions.
B) Computerized CTG:
computer programs have been developed to analyze fetal heart rate
recording. By this we can assess short – term variability.
3) Biophysical profile:
It depends on ultrasonic assessment over 30 min of 5 parameters then
scoring is done so that each parameter is given a score of 2 when normal
and zero when abnormal producing a total score of 10.
The parameters are:
Fetal breathing movement.
*
Gross body movement.
*
Fetal tone.
*
Non stress test.
*
Qualitative amniotic fluid assessment.
*
27/3/2016
Antenatal Assessment of Fetal Well-being
DR.SHAIMAA
7
BY : TAHER ALI TAHER
4) Fetal biometry and doppler ultrasonography:
Doppler ultrasound makes use of the phenomenon of doppler
frequency shift, where the reflected wave will be at a different
frequency from the transmitted one if it interacts with moving
structures.
Wave forms from umbilical artery provide information on the
fetoplacental blood flow and should be performed on high risk
pregnancies.
So if the resistance index measured in the umbilical artery rise above
the 95
th
centile this means faulty perfusion of the placenta with fetal
hypoxia. Absent or reversed end diastolic flow in the umbilical artery
is particularly serious with correlation to fetal distress and
intrauterine death.
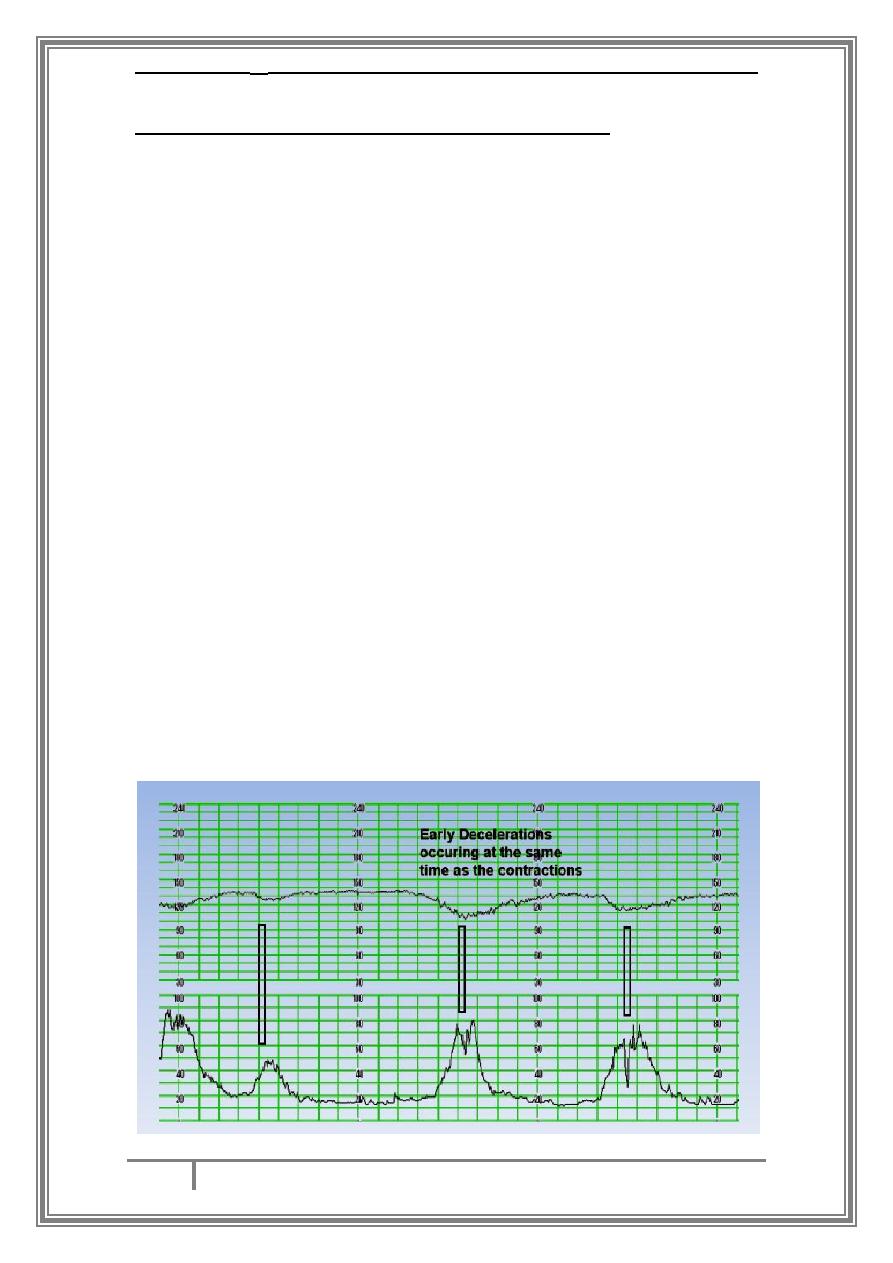
Types of deceleration on CTG and there causes :
Early decelerations : are benign , They are caused by head compression
and in general are a normal physiological response to a mild increase in
intracranial pressure. Importantly they are uniform in shape and start
and finish with the contraction. They may be said to mirror the
contraction.
27/3/2016
Antenatal Assessment of Fetal Well-being
DR.SHAIMAA
8
BY : TAHER ALI TAHER
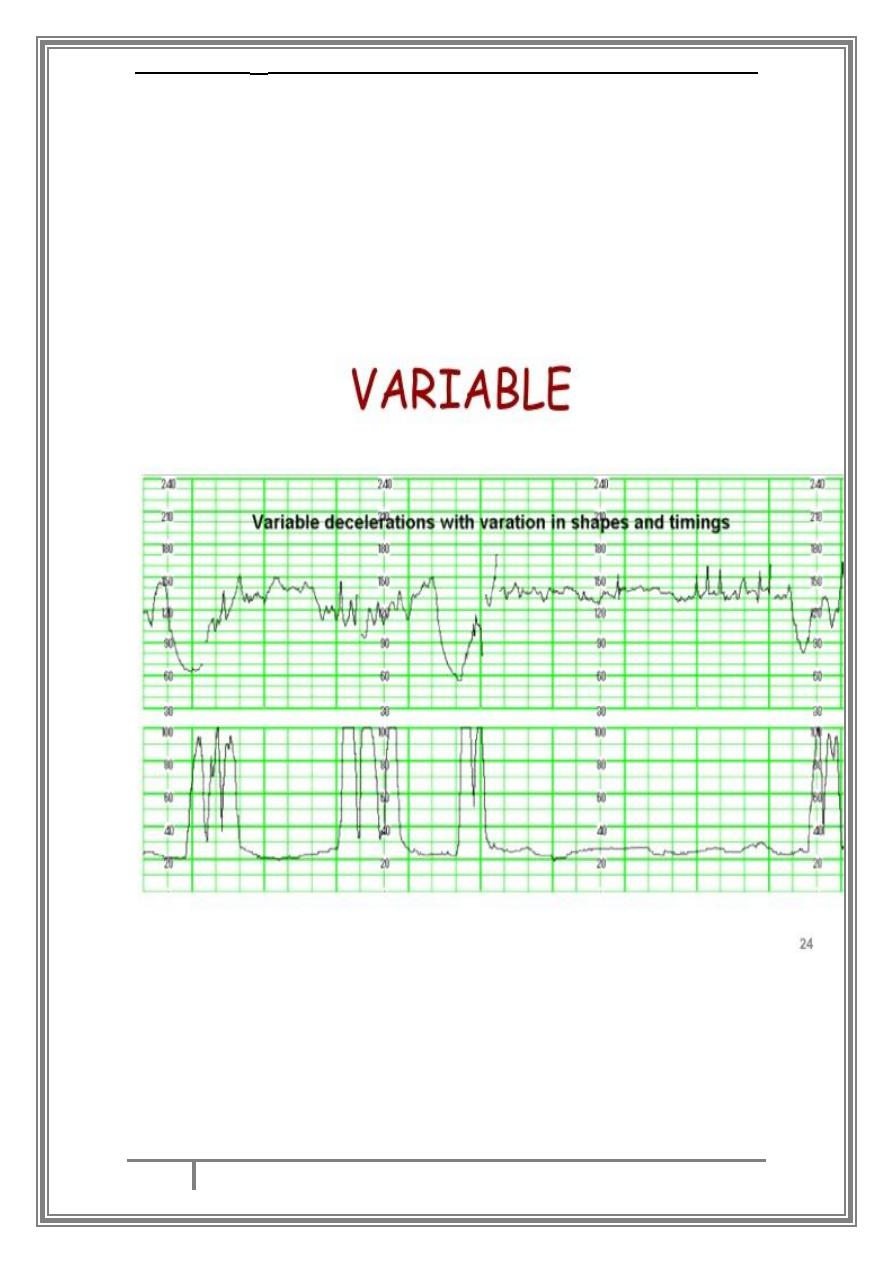
Variable decelerations are a repetitive or intermittent decreasing of FHR
with rapid onset and recovery. Time relationships with contraction cycle
may be variable but most commonly occur simultaneously with
contractions. The significance of variable decelerations depends on the
overall clinical picture and specific features of the decelerations
themselves, as well as other features of the CTG. Variable decelerations
in association with other non-reassuring or abnormal features change
the category of the deceleration to ‘complicated.
27/3/2016
Antenatal Assessment of Fetal Well-being
DR.SHAIMAA
9
BY : TAHER ALI TAHER
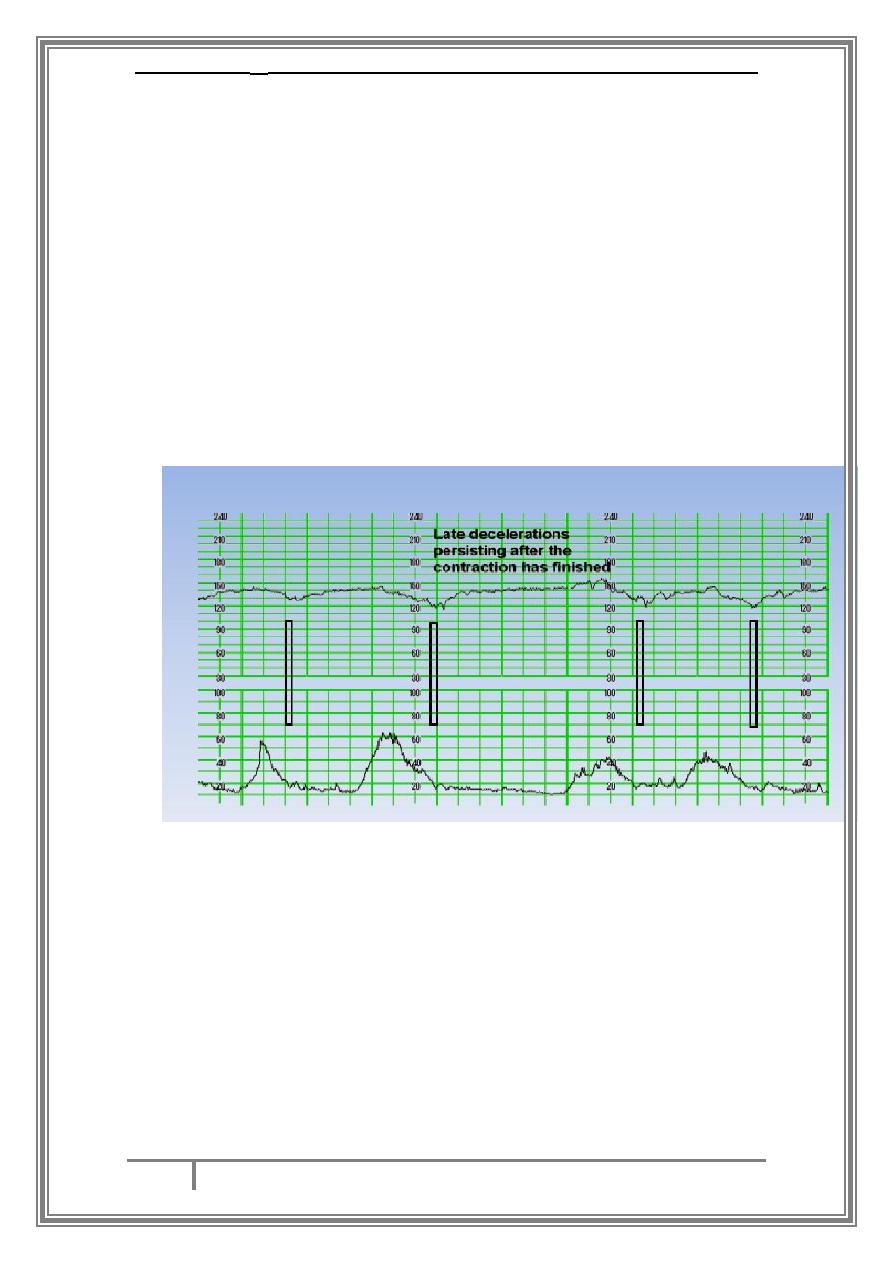
Late decelerations are defined as uniform, repetitive decreasing of FHR
with, usually, slow onset mid to end of the contraction and nadir more
than 20 seconds after the peak of the contraction and ending after the
contraction1. Late decelerations are caused by contractions in the
presence of hypoxia. This means that they will occur with each
contraction and the fetus is already hypoxic. There will be no features of
a well oxygenated fetus, like early or typical variable decelerations,
normal baseline variability or shouldering. They start after the start of
the contraction and the bottom of the deceleration is more than 20
seconds after the peak of the contraction. Importantly, they return to
the baseline after the contraction has finished. In the hypoxic fetus, this
will include decelerations of less than 15bpm (and occasionally less than
5bpm)
… THE END …
