
gynecology
oj
kk
Total Lectures :18
Dr. Maad
BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE
CERVIX & UTERUS
Lec . 3
Done by :
Ali Faleh
2016-2017
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ

BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
1
By : Ali Faleh
Dysplasia
Dysplasia – change of phenotype (size,shape and organization of tissue).
is a term used in pathology to refer to an abnormality of development. This generally
consists of an expansion of immature cells, with a corresponding decrease in the
number and location of mature cells. Dysplasia is often indicative of an early neoplastic
process. The term dysplasia is typically used when the cellular abnormality is restricted
to the originating tissue, as in the case of an early, in-situ neoplasm.
Dysplasia are now usually referred as
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)
.
They are regarded as mild, moderate or sever, depending on the degree of cytological
atypia and also the thickness of the epithelium involved :-
CIN I : affecting the deepest 1/3 of the epithelium from the basal layer up ward
CIN II : Affecting 2/3 of the thickness
CIN III: Affecting full thickness
HPV infection alone and CIN I are grouped together as ‘low – grad squamous
intraepithelial.
Lesions (LSIL) and CIN II and CIN III as ‘high –grade SIL (HSIL)
Microscopic changes :
Dysplasia is characterized by four major pathological microscopic changes:
Anisocytosis (cells of unequal size)
Poikilocytosis (abnormally shaped cells)
Hyperchromatism (excessive pigmentation)
Presence of mitotic figures (an unusual number of cells which are currently dividing).
Dysplasia is the earliest form of pre-cancerous lesion which pathologists can recognize
in a pap smear or in a biopsy. Dysplasia can be low grade or high grade. The risk of low
BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
2
By : Ali Faleh
grade dysplasia transforming into high grade dysplasia, and eventually cancer, is low.
Treatment is usually straightforward. High grade dysplasia represents a more advanced
progression towards malignant transformation.
Invasive carcinoma
is the final step in this sequence. It is a cancer which has
invaded beyond the basement membrane and has potential to metastasize (spread to
other parts of the body). Invasive carcinoma can usually be treated, but not always
successfully. However, if it is left untreated, it is almost always fatal.
Carcinoma in situ
, meaning "cancer in place", represents the transformation of a
neoplastic lesion to one in which cells undergo essentially no maturation, and thus may
be considered cancer-like. In this state, epithelial cells have lost their tissue identity and
have reverted back to a primitive cell form that grows rapidly and with abnormal
regulation for the tissue type. However, this form of cancer remains localized, and has
not invaded past the basement membrane into tissues below the surface.
Metaplasia
Metaplasia (Greek: "change in form") is the reversible replacement of one differentiated
cell type with another mature differentiated cell type. The change from one type of cell
to another may generally be a part of normal maturation process or caused by some
sort of abnormal stimulus.
In simplistic terms, it is as if the original cells are not robust enough to withstand the
new environment, and so they change into another type more suited to the new
environment. If the stimulus that caused metaplasia is removed or ceases, tissues return
to their normal pattern of differentiation. Metaplasia is not synonymous with dysplasia
and is not directly considered carcinogenic.
Causes :
When cells are faced with physiological or pathological stresses, they respond by
adapting in any of several ways, one of which is metaplasia. It is a benign (i.e. non-
cancerous) change that occurs as a response to change of milieu (physiological
metaplasia) or chronic physical or chemical irritation (pathological metaplasia). One

BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
3
By : Ali Faleh
example of pathological irritation is cigarette smoke that causes the mucus-secreting
ciliated pseudo stratified columnar respiratory epithelial cells that line the airways to be
replaced by stratified squamous epithelium, or a stone in the bile duct that causes the
replacement of the secretory columnar epithelium with stratified squamous epithelium
(Squamous metaplasia). Metaplasia is an adaptation that replaces one type of
epithelium with another that is more likely to be able to withstand the stresses it is
faced with.
DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAP SMEAR
In 1928 George Papanicolaou initiated the a sampling of vaginal cells, speculating that
these cells would predict which women develop cervical cancer.
Together with Dr Herbert Traut , published a monograph in 1947 that eventually
resulted in Pap smears becoming the standard of care in cervical cancer screening
The procedure they outlined was modified in 1947 by Ayre,who collected cervical cells
directly using a wooden spatula.
In1988 ,a workshop was held in Bethesda, Maryland, that provided a general consensus
on how to read Pap smears and initial guidelines designed to decrease the variability
among laboratories in reporting of result
A second workshop in 1991 modified these guidelines based on actual practice and
clinical experience
The Bethesda 1988 and 1991 guidelines both emphasized delineating SQUAMOUS
INTRAEPITHELIAL LESION ---Low grade {LSIL} and high grade {HSIL}----from atypical
squamous cells of unclear significant {ASC—US}and normal Pap smears.
The Bethesda 2001 consensus panel resulted in the
following revisions
in the
terminology used to report Pap smear results:
1-
Significant changes were made in the management of atypical squamous cells. The
guidelines retained the and added the subcategory of “ atypical squamous cells
favoring HSIL” [ASC-H] . ASC-US carries a moderately low incidence of CIN 2 or CIN 3

BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
4
By : Ali Faleh
[10%] and very low incidence of cancer [0.1%],whereas ASC-H is associated with a much
higher incidence of CIN 2 or 3.
2-
The Bethesda 2001 guidelines also eliminated the categories of “reactive change Pap
smear” and “atypical squamous cells of unclear significance favoring reactive change
Pap smear.
3-
AGC-US” atypical glandular cell of unclear significance ‘ was eliminated , primarily to
avoid confusion with ASC-US. On average 44% of women with AGC-US have subsequent
tissue examination that yields a diagnosis of cervical dysplasia, and cancer is diagnosed
in 8%.
4-
The finding of AGC was made more specific in the 2001 guidelines with the inclusion
of two categories:”AGC favoring neoplasia and “adenocarcinoma in situ”[AIS]
Pap smear Technique and Interpretation
Frequency of screening:
1- In USA the most recent recommendation is to screen for the first time 3 years after
the onset of sexual activity Or before age 21 ,which ever comes first.
2- ACOG recommends annual Pap smear screening /
AMERICAN CANCER SOCITY recommends every –other-year screening when using liquid
–based cytology
3- after age 30 , the interval between screening can be increased to 2-3 years .
4- More frequent i.e. annual Pape smears are recommended for women :
a- using DSE
b - immunocompromised
c- previous history of stage 2 or 3 cervical intraepithelial neoplsia CIN

BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
5
By : Ali Faleh
INTERPRETATION
The Bethesda guidelines recommend that 8000—12,000 squamous cells be obtained for
conventional Pap smear but only 5000 cells for a liquid- based sample
Cells can obscured by blood , mucous and inflammatory cells
If more than 75% of the cells are obscured , the sample is inadequate and a new sample
must be tested.
If 50—75% of the cells are obscured ,the sample is adequate but partially obscured.
The presence of endocervical cells [ at least 10] is recommended but not required in
samples from women younger than 40 years of age but required from women older
than 40 .
1- Negative result :
NILM: negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy.
the normal cells; is optional for the pathologist to add information about other
infection :
Candidiasis ,, Tricomoniasis ,,, Herpes simplex virus ,,,, Bacterial vaginosis
2- ASC :
The Bethesda guidelines regarding atypical squamous cells [ ASC ] emphasize the ability
to distinguish between HSIL and LSIL .
Overall it is thought that 10– 30% of women with a finding of ASC on a Pap smear have
underlying CIN grade 2 or 3 , and 0.1% may invasive cancer . classified in to :
(a) ASC-US
It is estimated that 90- 95% of all finding of ASC fall into this category of ASC-US .
Women with a Pap smear result of ASC-US have a 5-7% of having CIN 2 and 3 and
39% of women with CIN 2 or 3 have a previous finding of ASC-US on Pap smear

BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
6
By : Ali Faleh
ASC-US is associated with HPV in about 33- 67% of cases .
(b) ASC-H
The category of ASC-H describes atypical cells that are morphologically suspicious of
HSIL but too few in number to qualify as HSIL .
ASC-H is more highly associated with HSIL than ASC-US and is the most common
precursor lesion for CIN . Follow –up of women with a finding of ASC-H leads to
diagnosis of CIN 2 & 3 in 68%.
3– LSIL and HSIL
Studies have shown that the finding of LSIL is more variable and less reproducible than
HSIL, and repeatable in only 80% of smear.
Bethesda guidelines further specify [with features suspicious of invasion ] when
histologic evidence supporting cancer is present.
counseling women with abnormal Pap smear :-
Women with abnormal Pap smear findings should be counseled that HPV infection has
been linked with the development of cervical cancer, and that HPV is the most common
viral STD , affecting up to 70% of the sexually active population .
Additional Test & Examination
:-
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS DNA TESTING and COLPOSCOPY :----
Extensive molecular and biologic and epidemiologic research confirms certain HPV types
to be carcinogenic in human .the four steps in the development of cervical cancer are :
A- infection of the metaplastic epithelium of the transformation zone with one or more
carcinogenic HPV types
B- viral persistence rather than clearance reflecting the host immune response

BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
7
By : Ali Faleh
C- clonal progression of persistently infected epithelium to cervical precancer ( CIN 3)
F- invasion .
HPV 16 type is detected with greatest frequency in high –grade intraepithelial neoplasia
and invasive cancer.
It is associated with 50% of cervical squamous cervical cancers and more than 30% of
adenocarcinomas .
HPV 18 is the second most common (25%) HPV type in invasive cervical cancer . Most
HPV infection , whether associated with a cytological abnormality or not ,are transient ,
being cleared or suppressed by cell- mediated immunity , within several months to 2
years & 90% of women clearing a specific HPV- type after 2 year observation.
Viral clearance is not often associated with reappearance of the same HVP type.
Occasionally the same HPV type will reappear.
The high rate of infection among immunosuppressed HIV- infected women supports the
concept of latency Secondary peaks of HPV infection in older or postmenopausal
women suggest the possibility of reactivation of latent reservoir duo to senescence of
cell-mediated immunity
Only persistence high –risk HPV infection of the cervical epithelium appears to trigger
neoplastic progression ,follow-up strategies suggest persistence beyond 2 years defines
a greater risk to patients.
The type of HPV is the strongest factor affecting risk of viral persistence , HPV 16 is
highly carcinogenic with an absolute risk of CIN 3 approaching 40% at 3-5 years.
The time from HPV infection to the development of CIN 3 is from 5 to 15 years and up
to 25-30 years when infection occur in late teens or early twenties.
The transient time for CIN 3 to be invasive cancer is variable ,taking as little as 12 to 18
months or as long as several decades.

BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
8
By : Ali Faleh
Cofactor Interaction with HPV
1-
cigarette smoking:
The detection of high level of genotoxic breakdown product of cigarette smoke –
including nicotine, cotinine, hydrocarbone,tars
in cervical secretion , these will influences epithelial immunity by decreasing the
numbers of antigen-presenting Langerhans cells in the genital epithelium, this could
favor viral persistence , contributing to malignant transformation .
2- infection :
Chlamydia trachomatis ,Neisseria gonorrhea, heroes simplex,Trichomonas
vaginalis causing disruption of epithelial integrity and reparative metaplasia associated
with acute cervcitis .
3- sex hormone:
Condylomata accuminata increase rapidly in size and in number in pregnancy, those
in prolong –term oral contraceptive pill(ocp),
That increased risk of CIN to twofold for 5 or more of OCP use,
CIN and cervical cancer are more frequently found in women with increased parity.
4- Exogenous and Endogenous immunosuppression
a- HIV b- Renal transplant c- Leukemia
5-
Dietary deficiencies of vitamin A or beta- carotine
Treatment
Based on Pap smear :
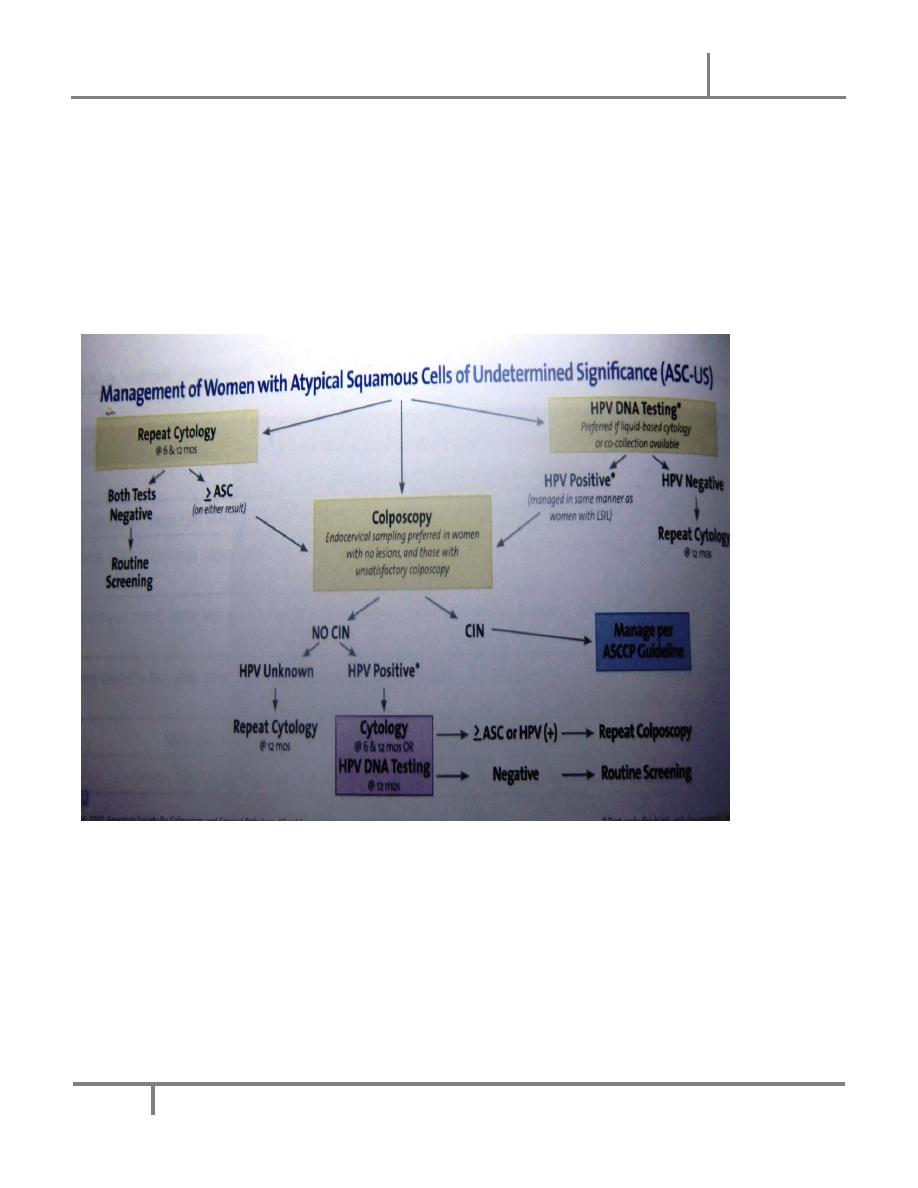
A– ASC-U:
Women with a finding of ASC-US are now managed in private practice, and increasingly
in the public sector ,primarily through reflex HPV DNA testing .

BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
9
By : Ali Faleh
This approach leads to overall cost saving And fewer referrals for colposcopy .
More specifically ,72% of women with CIN 3 are diagnosed by DNA testing ,which is
superior to colposcopy or Pap smear alone.
DNA testing also results in 50% fewer referrals for colposcopy.
Women with a positive HPV DNA test result are referred for colposcopy Pap smear in 12
months.
Alternatively, ASC-US can be managed by either IMMEDIATE referral for colposcopy
Or REPEAT Pap smear testing in 3-6 months .
If colposcopy is used and CIN is not found on examination of a biopsy specimen , the
women can resume routine screening at 12-month intervals. If CIN found , it is managed
accordingly.
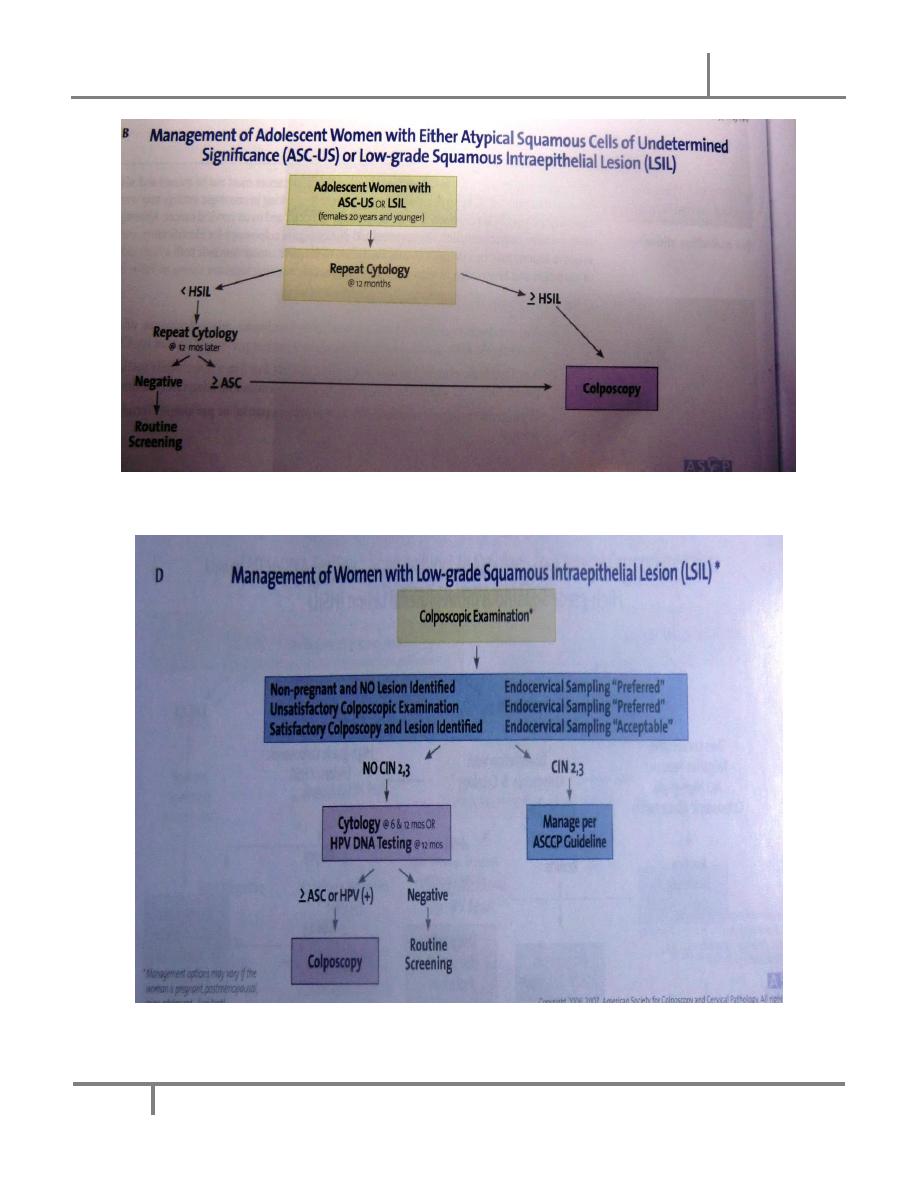
D. LSIL:
This is noted in 1.6% of all Pap smears
Between 15% and 30% of women with a finding of LSIL on Pap smear have CIN 2 OR 3
on subsequent examination of cervical biopsy specimen and 12% of women with LISL
and CIN 1 on tissue examination progress to CIN 2 or 3 over the next 2 years.
All women with LSIL should therefore be referred for colposcopy and biopsy
If tissue examination is positive for CIN 2 or 3 , the women should be managed as the
guidelines
If negative, follow up Pap smear at 6 months and 12 months and HPV DNA testing at 12
months are recommended . Women with ASC-US or higher on follow up Pap smears or a
positive HPV DNA test should referred for colposcopy .The routine use of DNA HPV
testing for LISL is not indicated , because more than 80% of women with this finding on
Pap smear have a positive HPV DNA .
BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
10
By : Ali Faleh
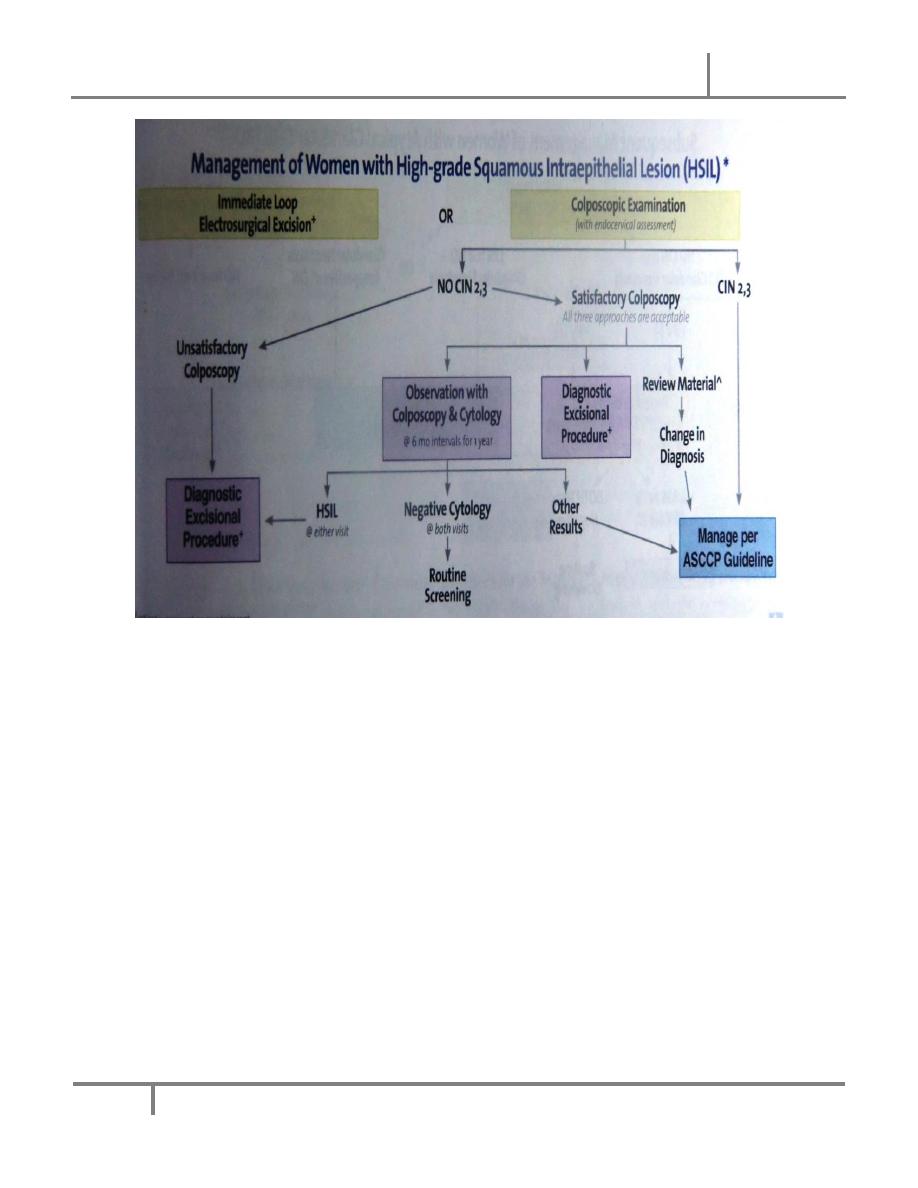
HSIL
All women with HSIL should undergo prompt colposcopy evaluation and biopsy , it
accounts for only 0.45% of all Pap smear results ,but CIN 2 or 3 is seen in 70% of women
with this finding, and 3% have invasive cancer
. Similarly to LSIL , the routine use of HPV DNA testing is not recommended ,because
more than 95% of women with this finding on Pap smear have a positive HPV DNA test.
BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
11
By : Ali Faleh
BEGNIN DISEASE OF THE THE CERVIX & UTERUS Dr. Maad
[Year]
12
By : Ali Faleh
