
1
Fifth stage
Dermatology
Lec
د.عم
ر
2/3/2017
Vesiculobullous diseases
Classification of Vesiculobullous diseases :
INTRA EPITHELIAL VESICLES: The lesion is formed within the epithelium
Acantholytic vesicles : This is because of the break down of specialized attachments
called the desmosomes
Nonacantholytic vesicles: It is usually in the viral infections because of the death or the
rupture of the group of cells.
SUB EPITHELIAL VESICLES: Lesions formed between the epithelium and the lamina
propria eg:
Erthyma multifome
Phempegoid
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Epidermolysis bullosa
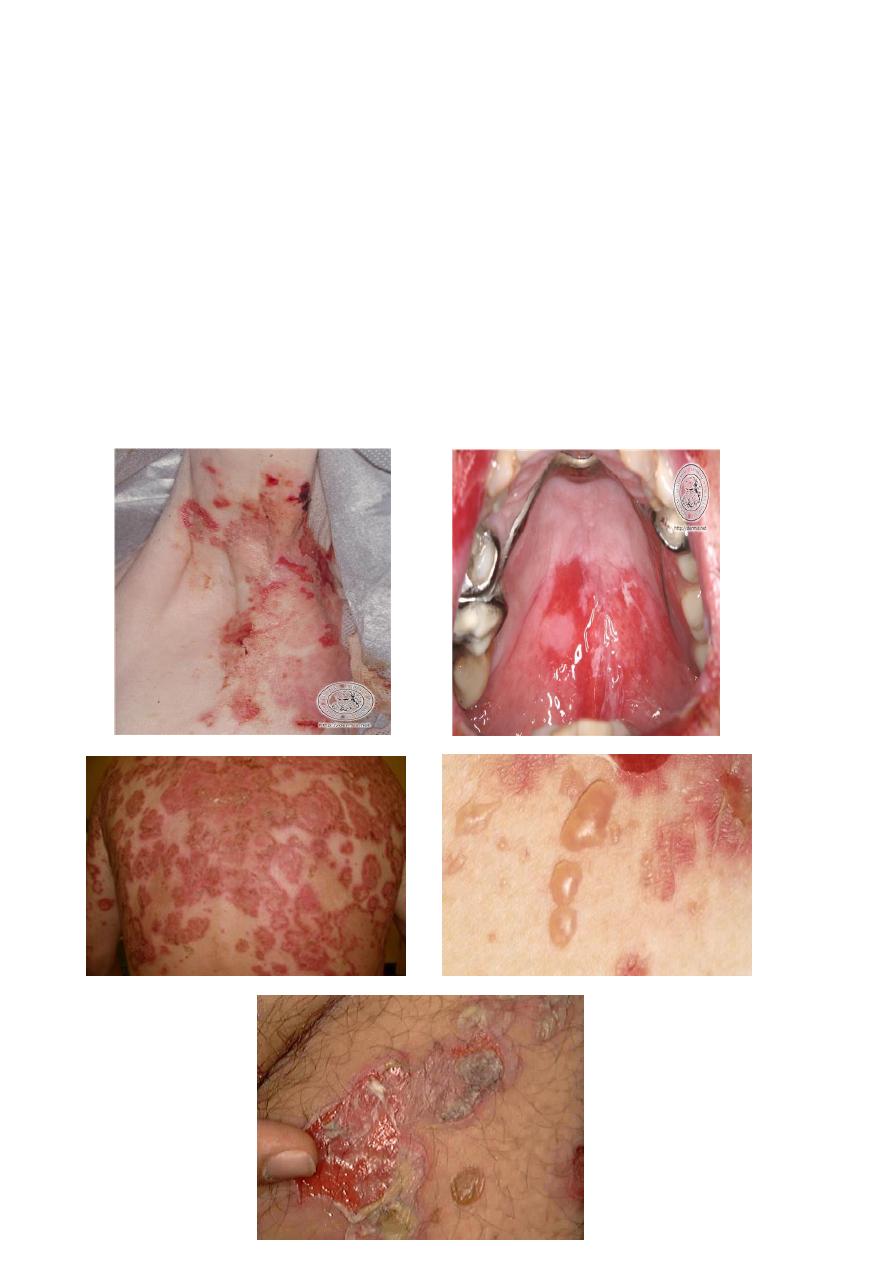
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS:
A rare autoimmune disease.
Common in Ashkenazi and Mediterranean jews
Middle aged and older
Other variants are:
o
Pemphius vegetans
o
Paraneoplastic pemphigus
2
CLINICAL FEATURES:
Painful erosions are formed in the oral cavity and skin.
The bulla is rapidly ruptured leaving a collapsed roof of grayish membrane with a red
ulcerated base. The ulcer may look like an apthous ulcer or may be large map shaped.
Nikolsky sign is positive.
Sometimes the ulcers are joined together to make a confluence. this condition is very
painful.
It has a variable course and might involve any mucous membrane as oesophagus,
cervix.
Protein/fluid,electrolyte and weight loss /secondary infections.
Fatal if untreated.
3
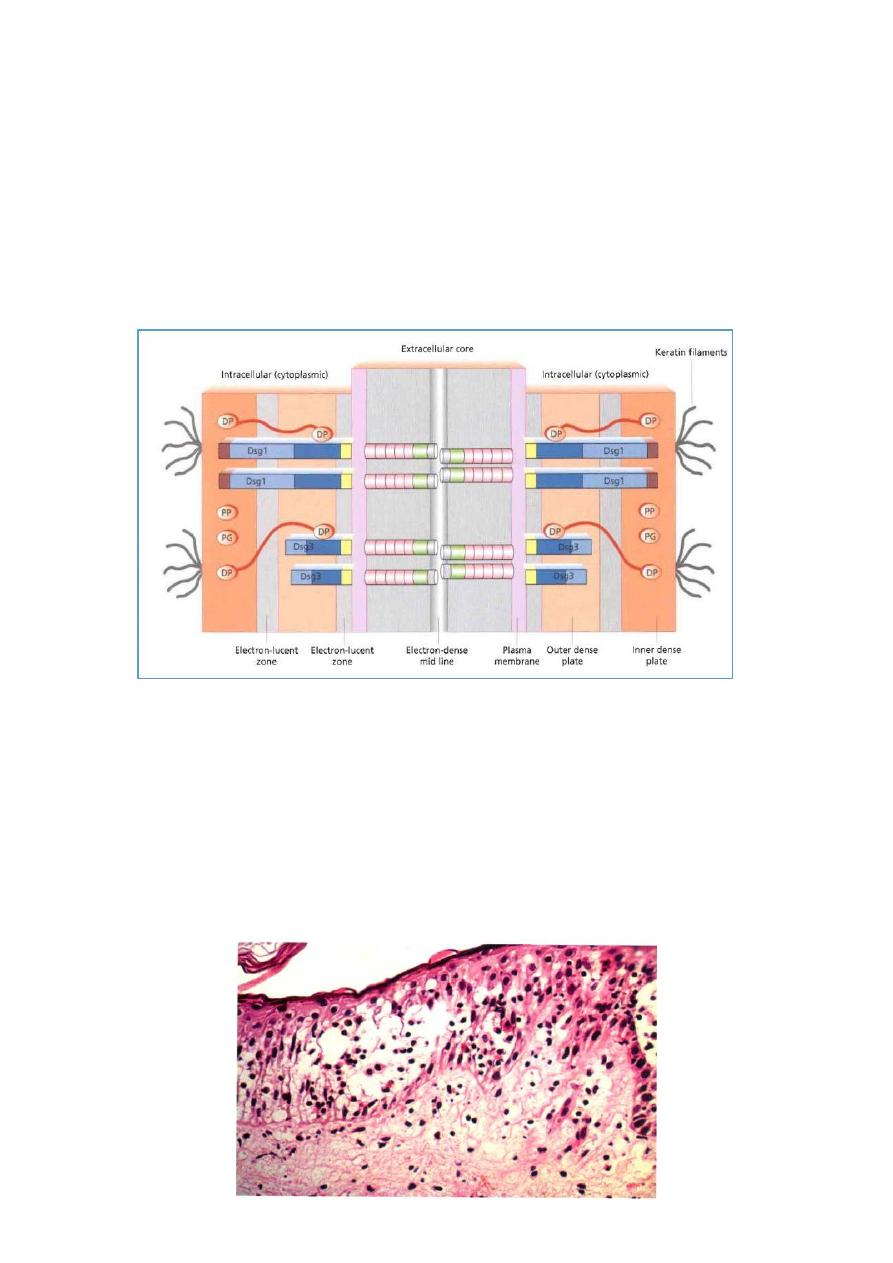
PATHOGENESIS:
It is an autoimmune disease
There are circulating antibodies of type IgG.
These antibodies are reactive against the desmosomes or the tonofilament complex.
There destruction or disruption of these tonofilament complex ,resulting in the loss of
attachment from cell to cell
HISTOPATHOLOGY
:
Intra epidermal (suprabasilar) vesicles or bulla and cleft like spaces are produced
(acantholysis).
These changes are in the stratum spinosum or the prickle cell layer.
Inflammatory cells are very scanty however eosinophils may be seen.

4
DIAGNOSIS:
Skin biopsy
Electron microscopy has shown that widening of the intercellular space is followed by
splitting of the desmosome junctions.
Direct & indirect immunofluorescence
ELISA
DIFFRENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
Bullous Pemphegoid
Erthema multiforme
Bullous lichen plannus
TREATMENT:
High mortality rates
Hospital admission
Topical potent steroids
Prednisolone plus azathioprine
Rituximab
Others
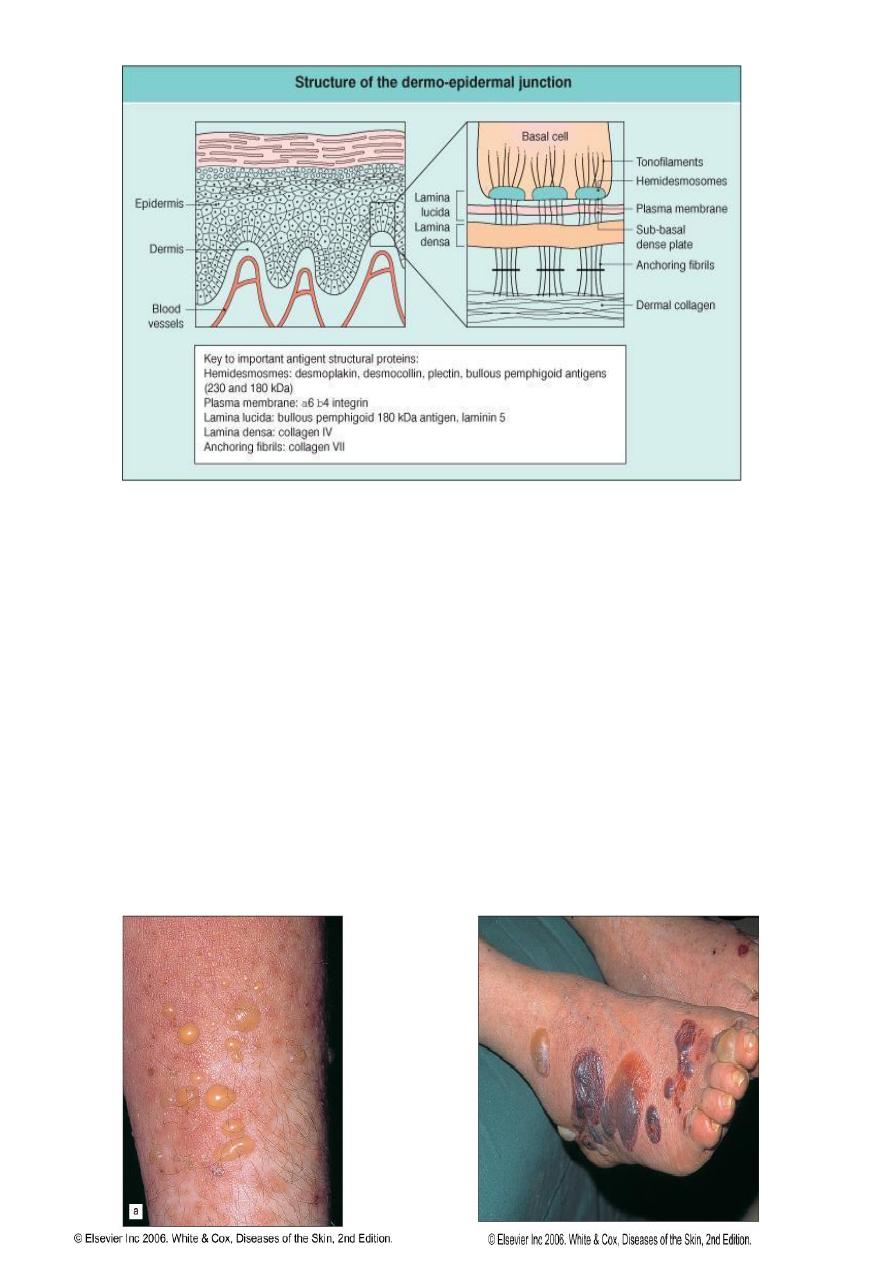
BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID:
Bullous pemphigoid is an affliction of elderly people,with onset usually after 60 years
of age.
The blister in bullous pemphigoid is subepidermal with an intact and often viable
epidermis forming the roof.
Bullous pemphigoid commonly starts with itching and a non-specific rash on the limbs
that may be either urticaria-like or occasionally eczematous and rarely may simulate
vesicular eczema.
5
PEMPHGOID
Blisters may arise on erythematous and on normal skin and may be associated with
dermal edema. The blisters are tense and dome shaped, obtaining a diameter of many
centimeteres.
The blisters are tough (Nikolsky sign negative) and may remain intact for several
days, the contents often becoming jelly-like with coagulated fibrin.
Mucosal lesions occur less frequently (25%) and are less severe than in pemphigus
vulgaris and are usually confined to the mouth
Untreated bullous pemphigoid runs a chronic, self limiting course over a number of
months or years.
The disease duration is usually 3-6 years, with most patients achieving complete
remission off treatment
.
3
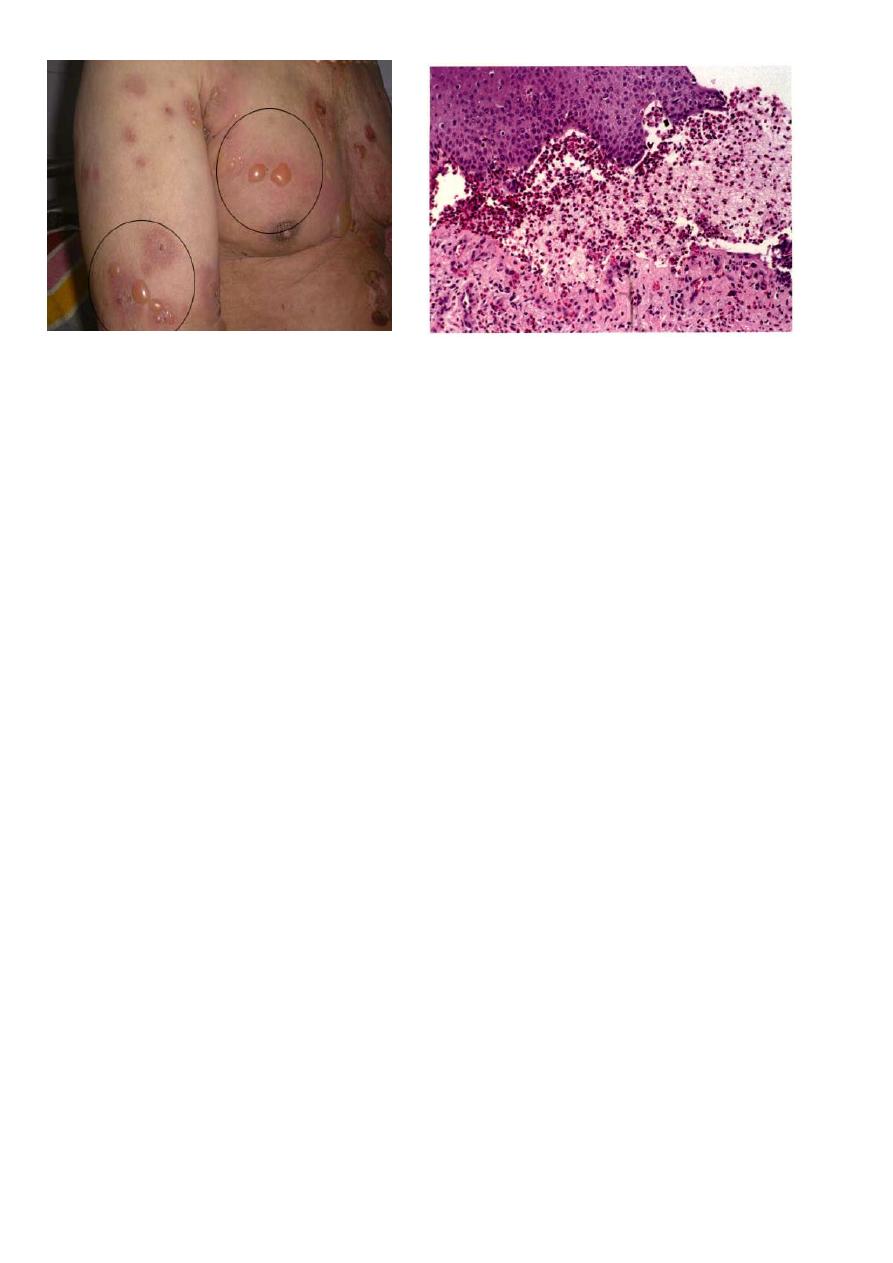
6
BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID HISTOLOGY
TREATMENT
Topical and systemic steroids are the mainstay of treatment.
For localized BP, very potent topical steroids are often sufficient.
Antibiotics
Systemic steroids
Immunsuppressives
IVIG
Plasmapheresis
