1
Fifth stage
Dermatology
Lec-12
.د
عمر
10/4/2016
Melasma
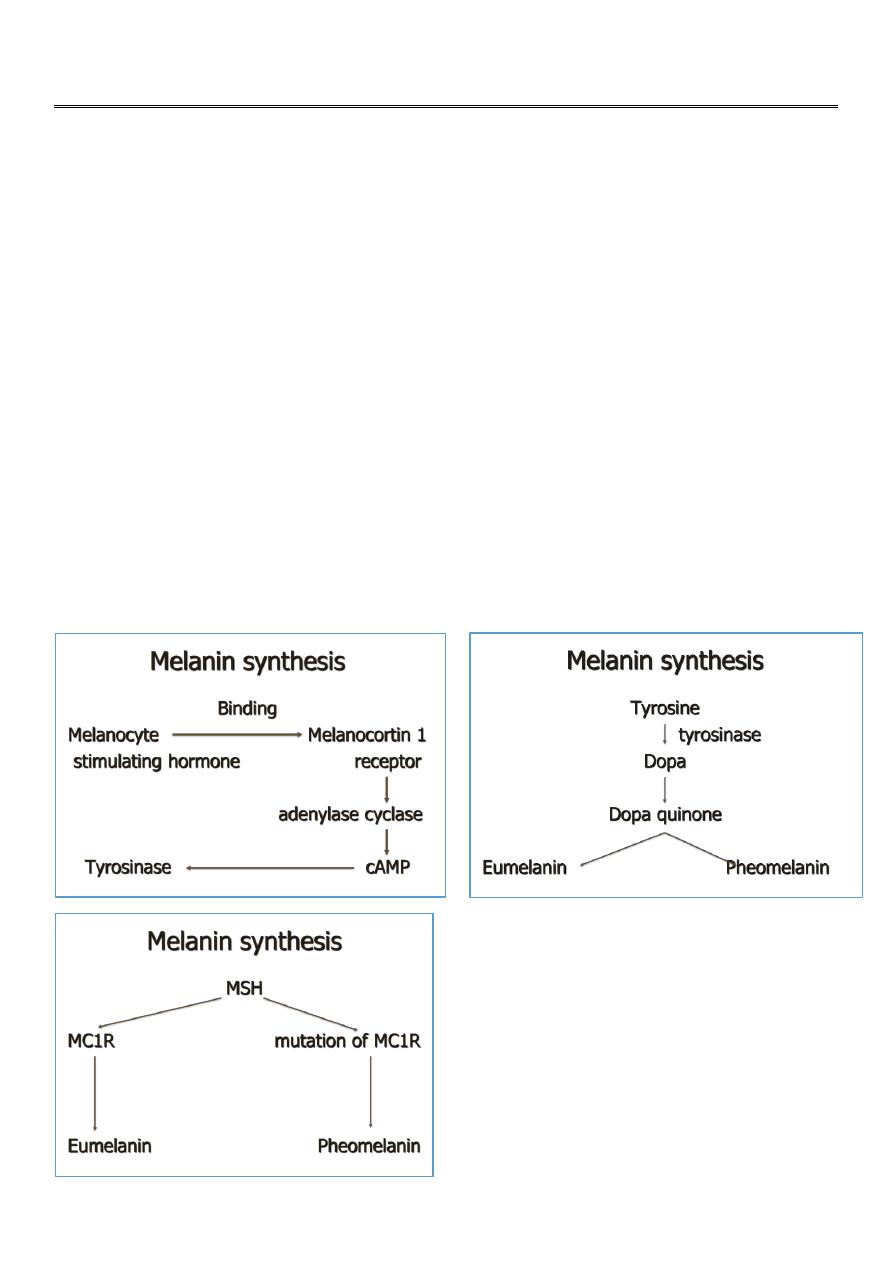
Biology of melanocyte
Dendritic cell at basal layer of epidermis
Produce melanin and send to surrounding keratinocyte
Epidermal melanin unit (melanocyte:keratinocyte) = 1:36
Biology of melanin
Synthesis from melanosome
Transport to keratinocyte via dendritic process of melanocyte
2 type
: eumelanin
: pheomelanin

2
Melanin transfer
Phagocytosis
: melanin transfer to dermis
: phagocytose by melanophage
Endocytosis
: melanin transfer to keratinocyte via intercellular space
Melasma
Acquired bilateral symmetrical hypermelonosis
Irregular light to gray brown macule and patch
Ill defined margin
Involved sun exposure area
Most common in women
Melasma is a common acquired pigmentary disorder that occurs mainly in women
(more than 90% of cases) of all racial and ethnic groups, but particularly affects those
with Fitzpatrick skin types IV–VI
Distribution of melisma
Central facial pattern (63%) : cheek, forehead, nose, chin
Malar pattern (21%) : cheek, nose
Mandibular pattern (16%) :chin
Cause of melisma
Light : UVA, UVB, visible light
Hormone : pregnancy, contraceptive pill
Drug : dilantin, anti-malarial drug, tetracycline, minocycline
Cosmetic : perfume, color
Genetic
Malnutrition : liver dysfunction, B12 def.
Types of melisma
Epidermal melasma
Dermal melasma
Mixed epidermal dermal melasma

3
The use of a Wood’s lamp can often be very beneficial in determining the location
of melanin deposition showing enhancement of color contrast in lesional skin for
the epidermal type, but not the dermal types. The mixed type has enhancement in
some areas of lesional skin, but not in other areas.
Estrogen may play a role in melasma induction(OCP,HRT,pregnancy)
Pregnancy induced melasma will recover after some months (but not completely).
Epidermal melisma
Light or dark brown color
Melanin deposition in basal, suprabasal layer of epidermis
Larger melanocyte with more noticeable dendritic process
Dermal melisma
Blue gray color
Perivascular melanophage at superficial and middermis
Melanin granule in dermis
Whether the melanin is deposited in the epidermis or dermis is important therapeutically
because dermal hyperpigmentation is much more challenging to treat
Topical Treatments for Melasma
In those patients with epidermal type melasma, there are multiple treatments available
(see Table 2).6 Topical agents include phenols, e.g., hydroquinone (HQ); retinoids, e.g.,
tretinoin; azelaic acid; kojic acid (KA); and glycolic acid (GA).
Hydroquinon
2%–4% has been widely used for melasma therapy.
inhibits the conversion of dopa to melanin by inhibitin theactivity of tyrosinase.
may interfere with DNA and RNA synthesis, degrade melanosomes, and destroy
melanocytes.
Reports of contact dermatitis in up to 25%
As an itchy eruption
it is best to be tested in a hidden part before use

4
Side-effects included irritant and allergic contact dermatitis, PIH, nail bleaching and rarely,
ochronosis-like pigmentation.
Retinoids
0.05-0.1%
inhibiting tyrosinase transcription,interrupting melanin synthesis.
While tretinoin may be effective in reducing melasma, it typically takes at least 24
weeks to see clinical improvement.
azelaic acid
1) 15%–20% a dicarboxylic acid, is a reversible inhibitor of tyrosinase
2) shown to be as effective as HQ 4% but without its side effects.
3) The combination of azelaic acid with 0.0a5% tretinoin or 15%–20% glycolic acid may
produce earlier, more pronounced skin lightening. Adverse effects include pruritus, mild
erythema, scaling, and burning.
KOJIC ACID
KA 2% is generally equivalent to other therapies but may be more irritating.
Glycolic acid
GA 5%–10% is an alpha-hydroxy acid
It decreases pigment by many mechanisms including thinning the stratum corneum,
enhancing epidermolysis, dispersing melanin in the basal layer of the epidermis, and
increasing collagen synthesis in the dermis.
HQ 5%, tretinoin 0.1%, and dexamethasone 0.1%, was first introduced in 1975 and
termed the Kligman formula
combination of HQ 4%, tretinoin 0.05%, and fluocinolone acetonide 0.01% (Tri-Luma®,
Galderma) proved better than any combination of two of the above agents, with 77%
of patients showing complete or nearly complete clearing.
Laser treatment for melisma
Target chromophore is melanin
Should destroy melanocyte in hair follicle
Good in dermal and mix melasma
Epidermal melanin removal : lPL
Dermal melanin removal : Q-switched Ruby, Q-switched Alexandrite, Q-switched
Nd:YAG
