JABIR IBN HAYYAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITYCOLLEGE OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY
Histology of Endocrine SystemLecture By;
Dr. Hayder ALKifaee
20/4/2017
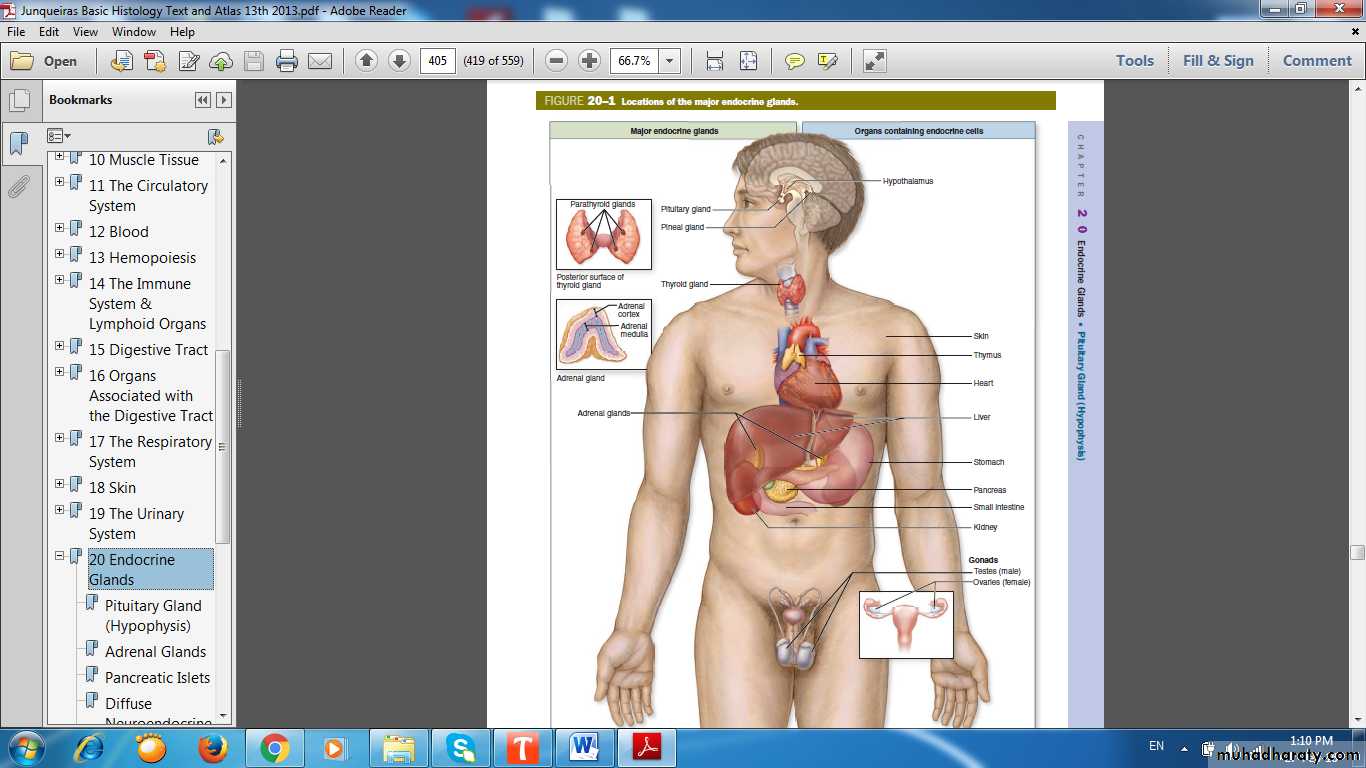
Endocrine Glands& Organs Containing Endocrine Cells
Primary Endocrine Organs
• Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri)• Pineal Gland (Epiphysis Cerebri)
• Thyroid Gland
• Parathyroid Gland
• Adrenal Gland
Secondary Endocrine Organs
• Kidney• Testes
• Ovaries
• Pancreas
• Stomach
• Intestines
• Thymus
• Heart
• Placenta
Typical Endocrine Glands
• Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri)
• Pineal Gland (Epiphysis Cerebri)
• Thyroid Gland
• Parathyroid Gland
• Adrenal Gland
Scattered Endocrine Masses
Islets of LangerhansCorpus luteum
Interstitial cells of Leydig
Placental lactogen secreting cells
Chorionic gonadotropin secreting cells
Juxtaglomerular cells
Isolated Endocrine Cells (Diffuse Neuroendocrine System)
Called APUD cells – Amine Precursor Uptake & Decarboxylation cells.Present within the lining epithelium of the digestive and respiratory system.
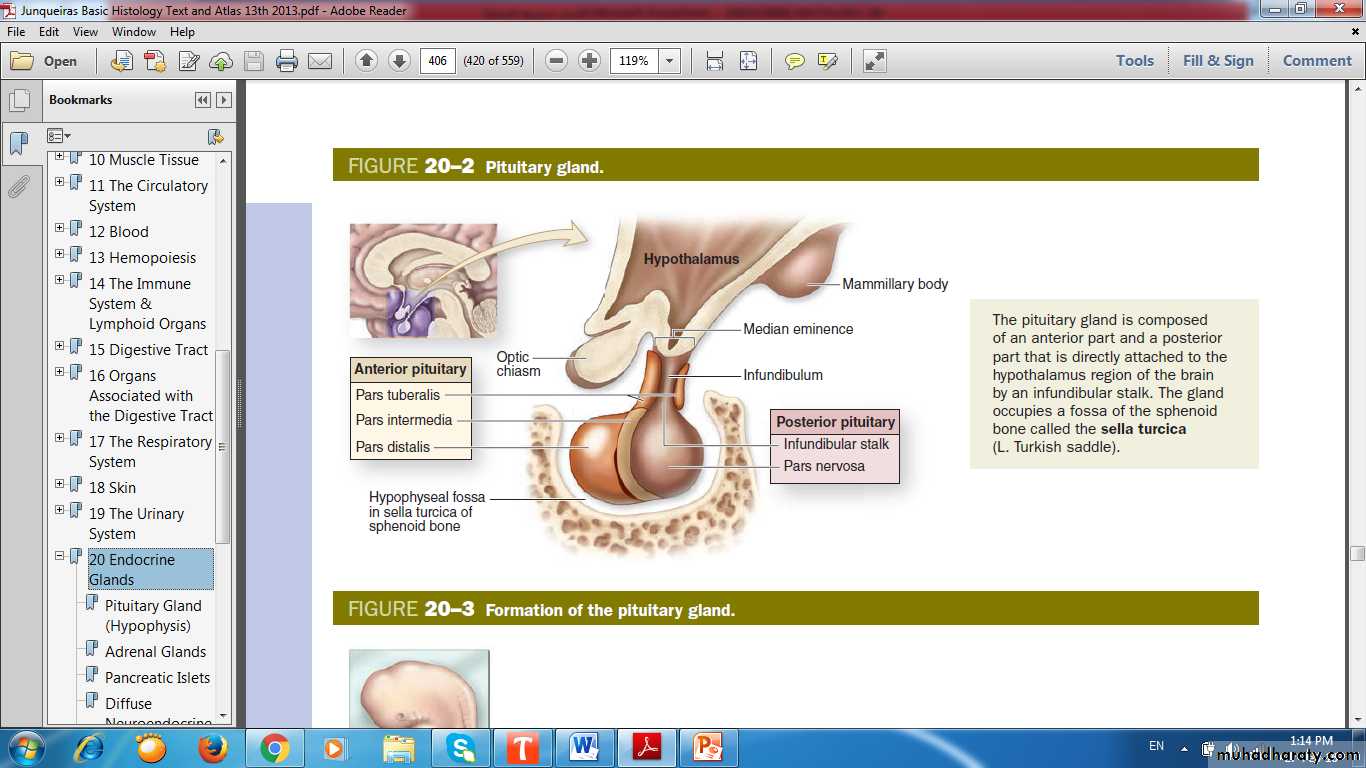
Pituitary Gland(Hypophysis Cerebri)
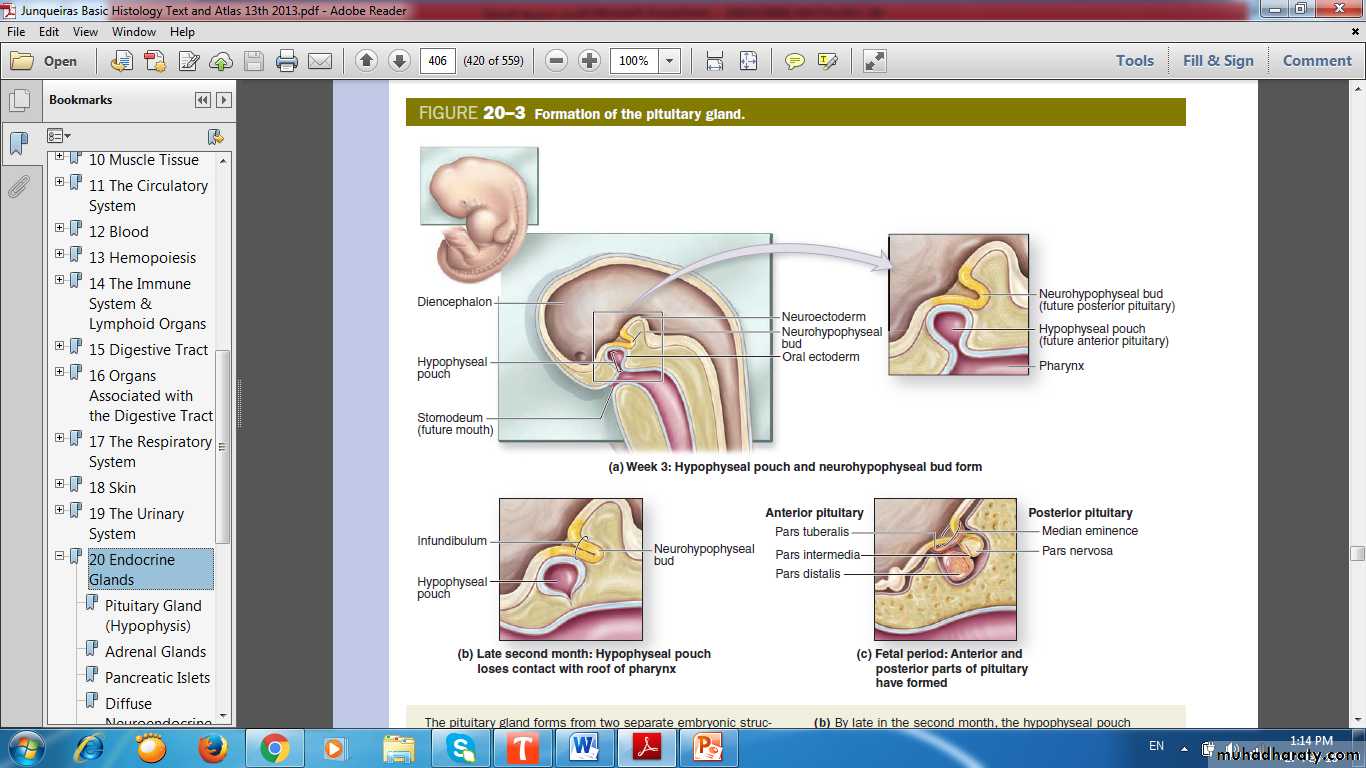
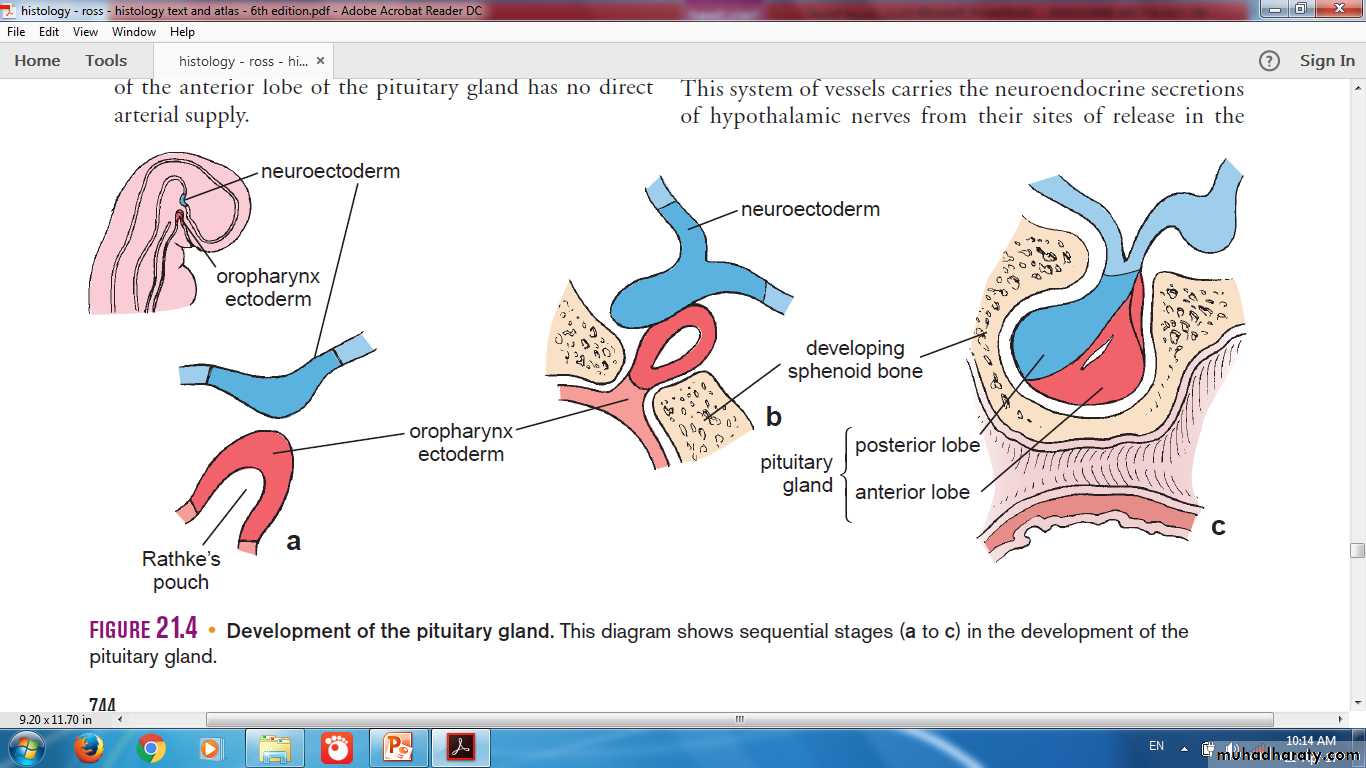
Dual Origin of Pituitary
Partly from the developing brain (Neurohypophyseal bud )Partly from the developing oral cavity (Hypophyseal ( Rathke ) pouch )
Formation of Pituitary Gland
Dual Origin of Pituitary GlandPituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland
AdenohypophysisPars distalis
Pars tuberalis
Pars intermedia
Neurohypophysis
Pars nervosaStalk (Infundibulum)
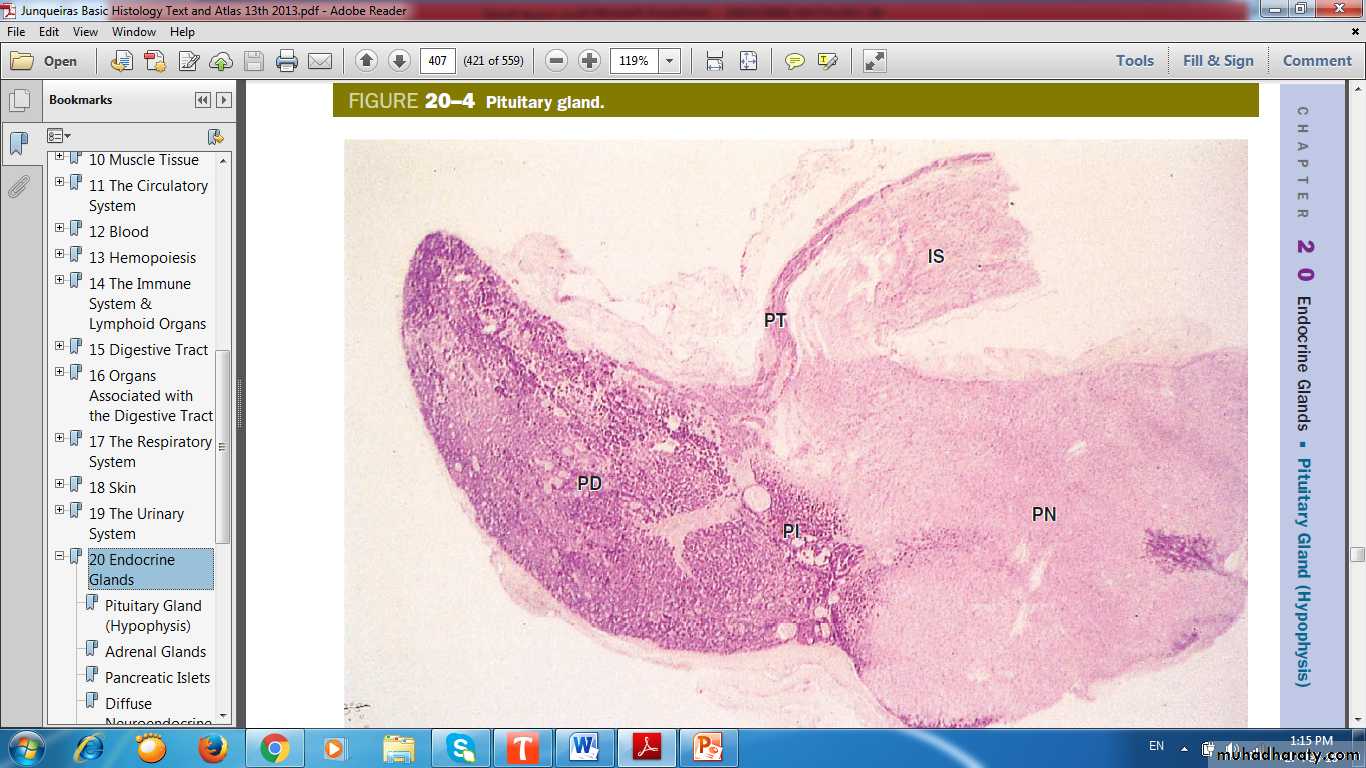
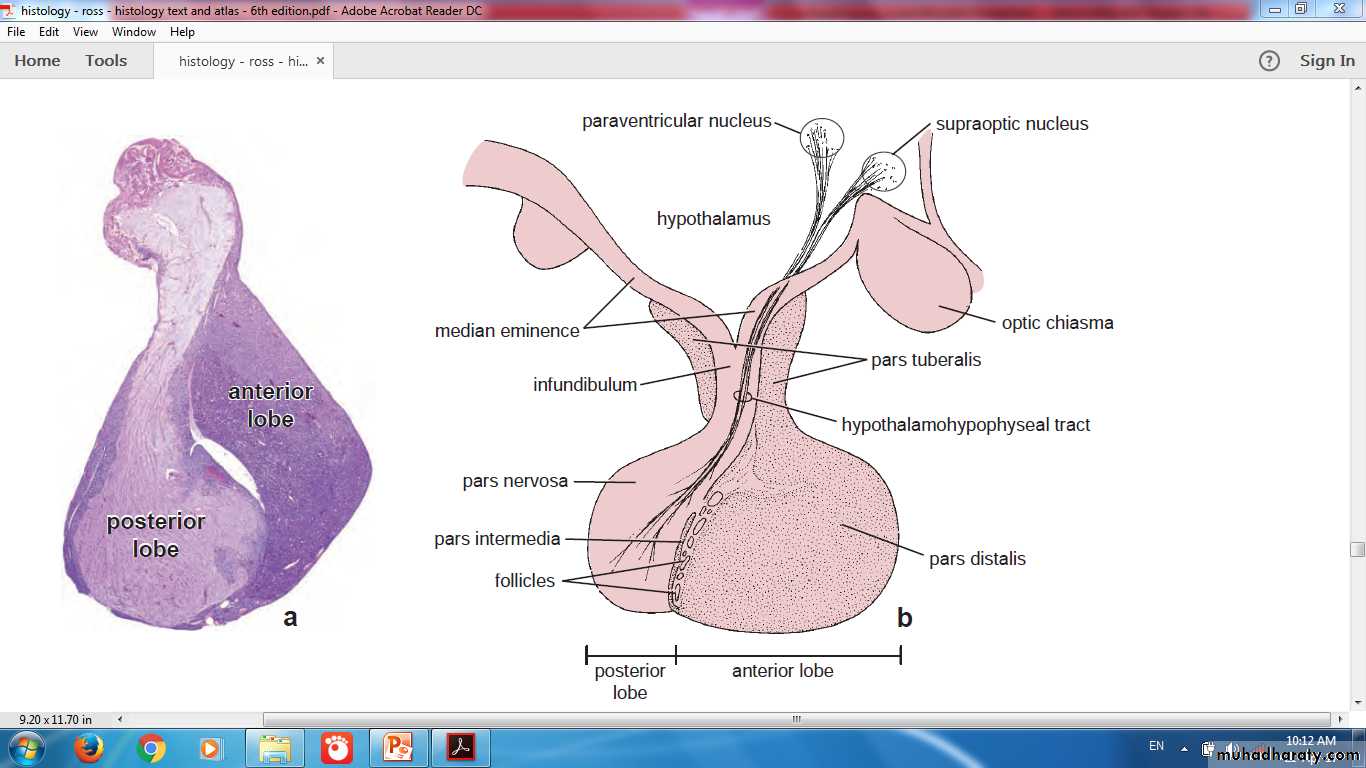
Pituitary Gland
infundibular StalkPars Nervosa
Pars Tuberalis
Pars Intermedia
Pars Distalis
Adenohypophysis
Neurohypophysis
Pituitary Gland
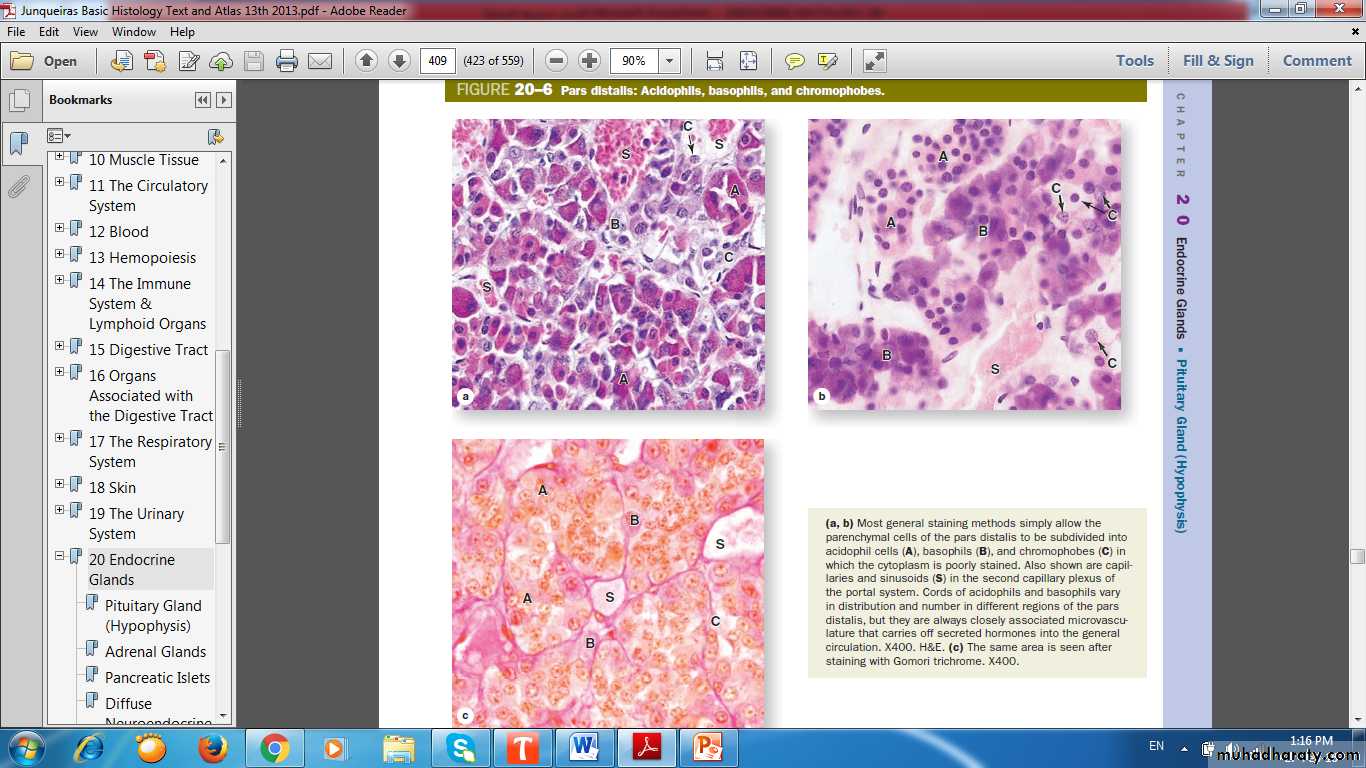
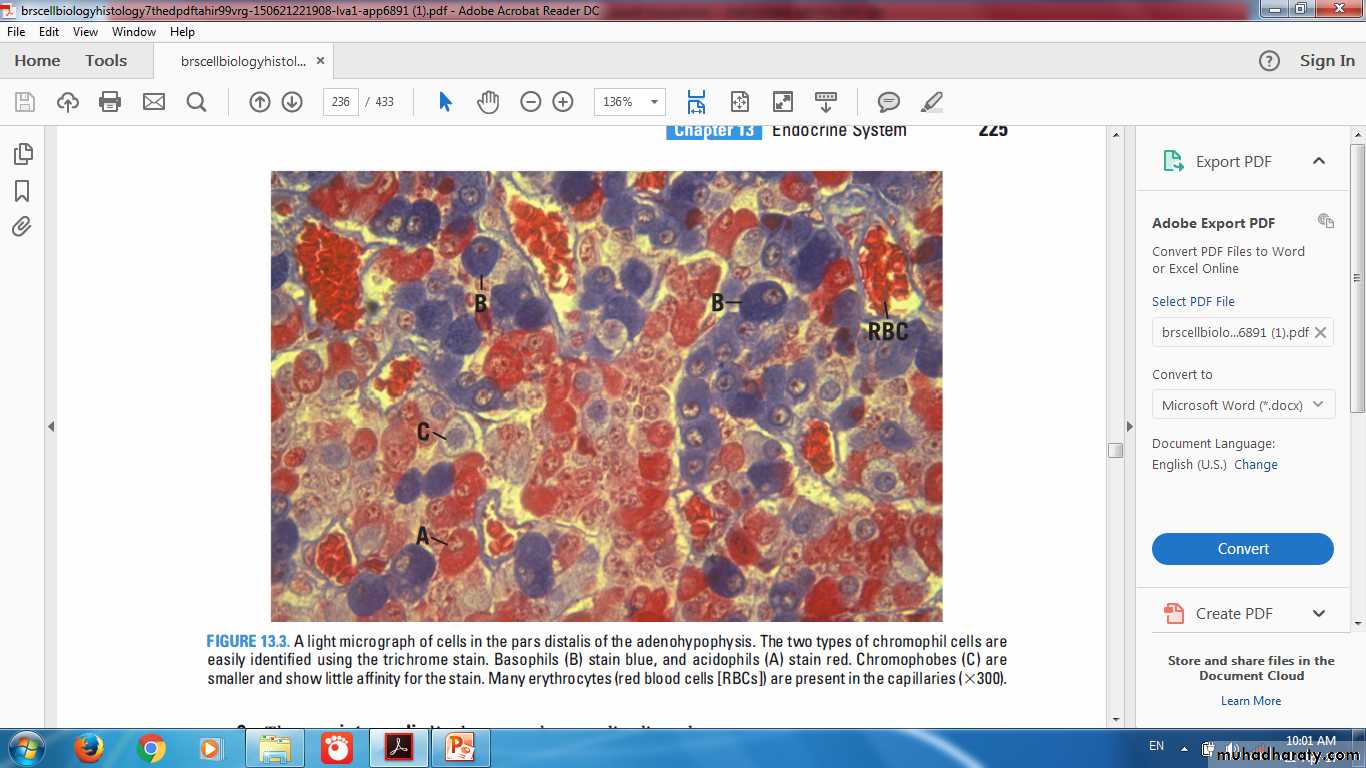
Pars distalisChromophils
Acidophils
Basophils
Chromophobes
Stain weakly
Few or no secretory granules
Stem & progenitor cells
Degranulated cells
Pars Distalis: Acidophil, Basophil & Chromophobe
ChromophilsAcidophils
Somatotrophs
Mammotrophs
Basophils
Gonadotrophs
Thyrotrophs
Corticotrophs
Acidophil, Basophil & Chromophobe
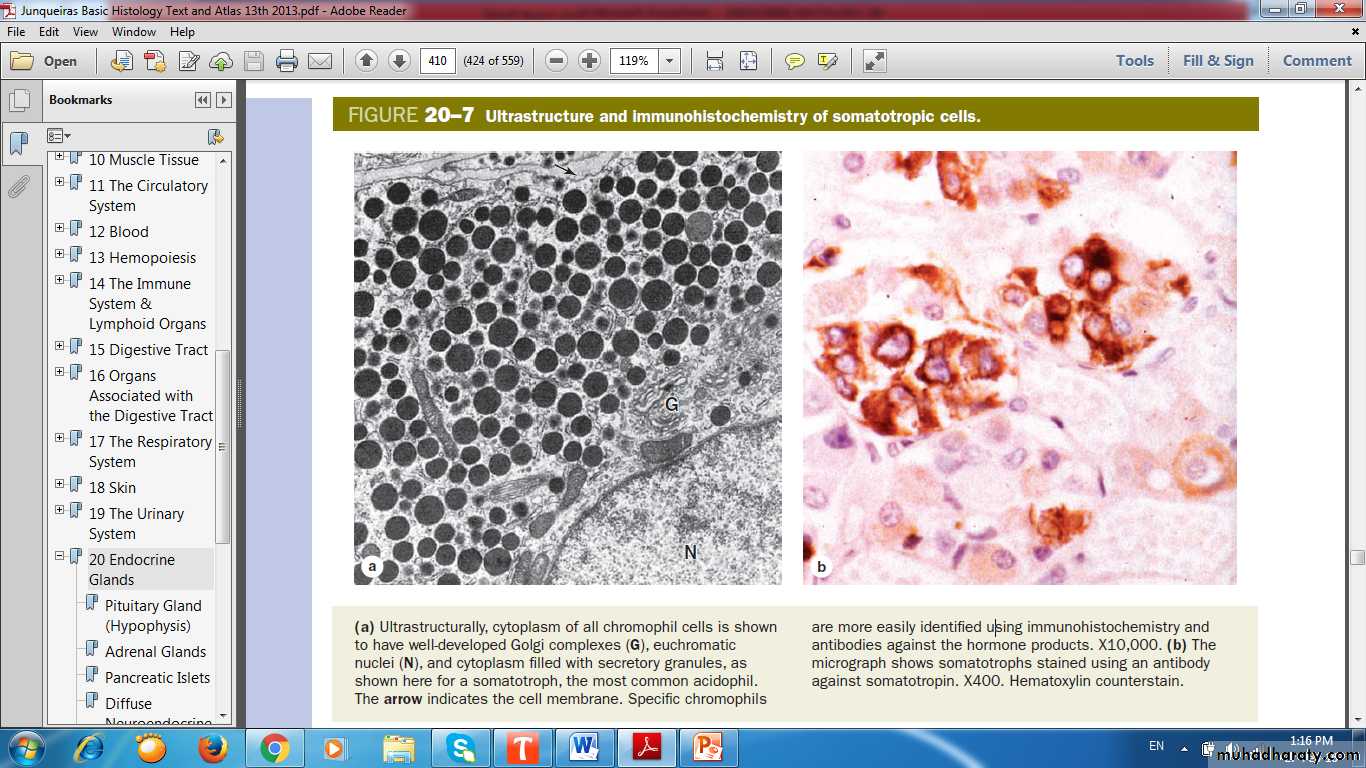
Somatotropic Cells
UltrastructureImmunohistochemistry
Control of the Pituitary
Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal TractHypothalamic-Hypophyseal Portal System
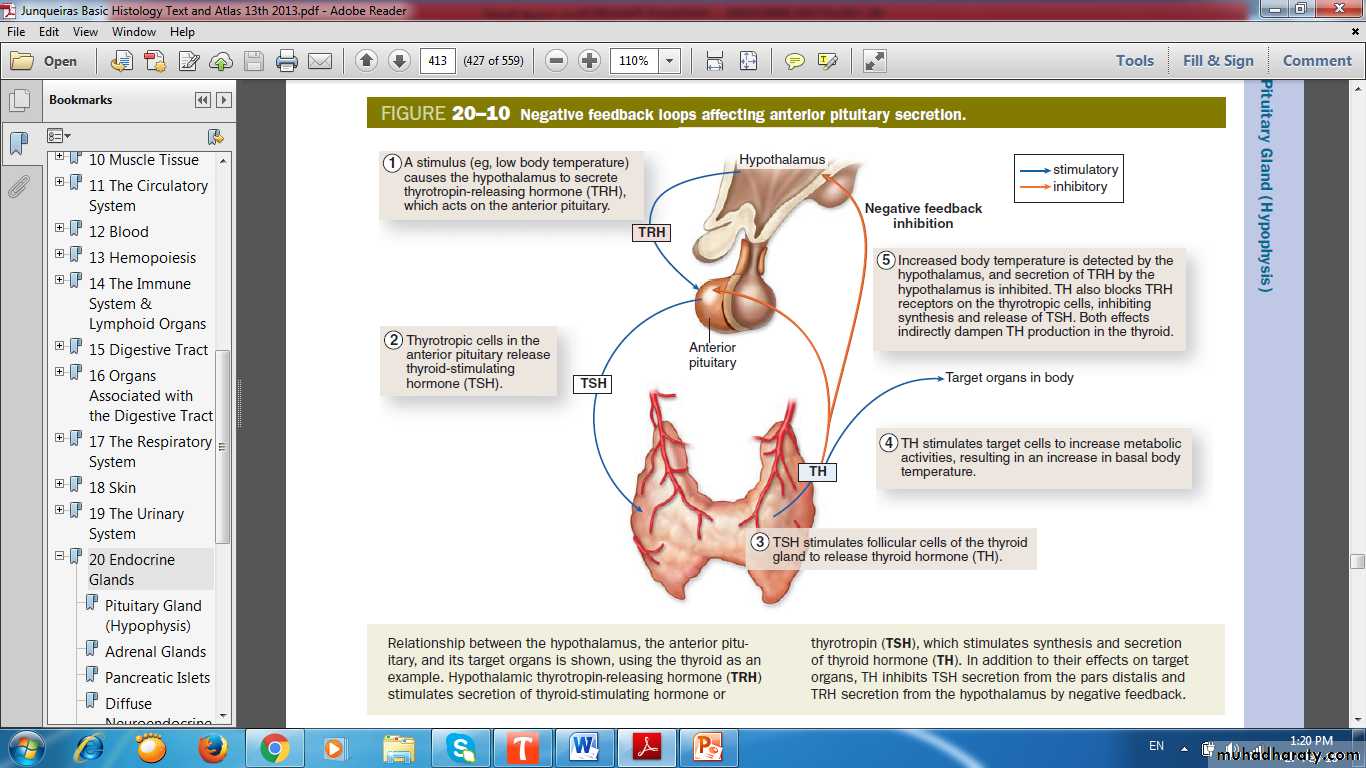
Negative Feedback Loops
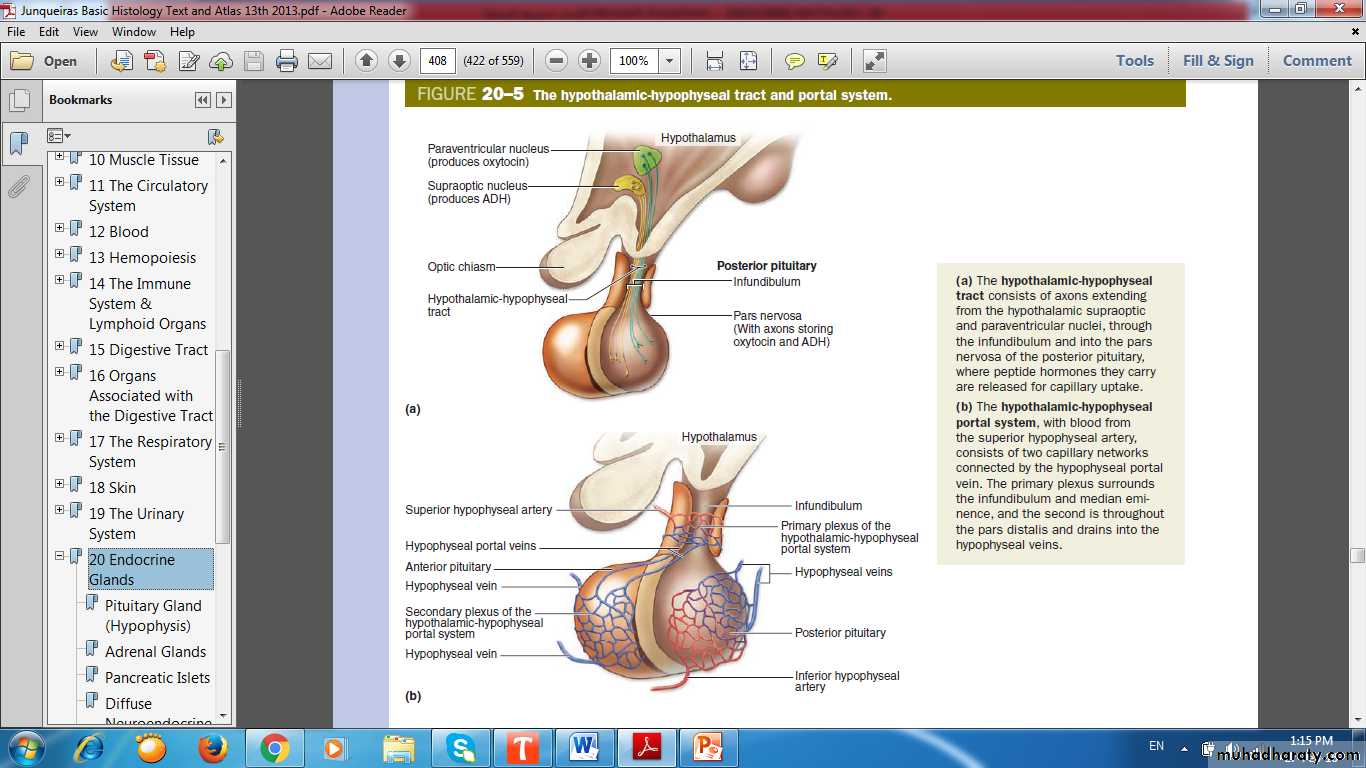
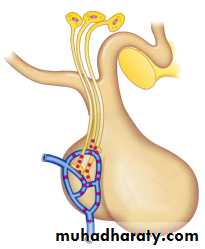
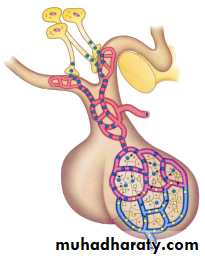
Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal Tract
Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal Tract
Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal Portal System
Hypothalamic Control of pituitary function
Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal Portal SystemHypothalamo-Hypophyseal Tract
Negative Feedback Loops Affecting Anterior Pituitary Secretion
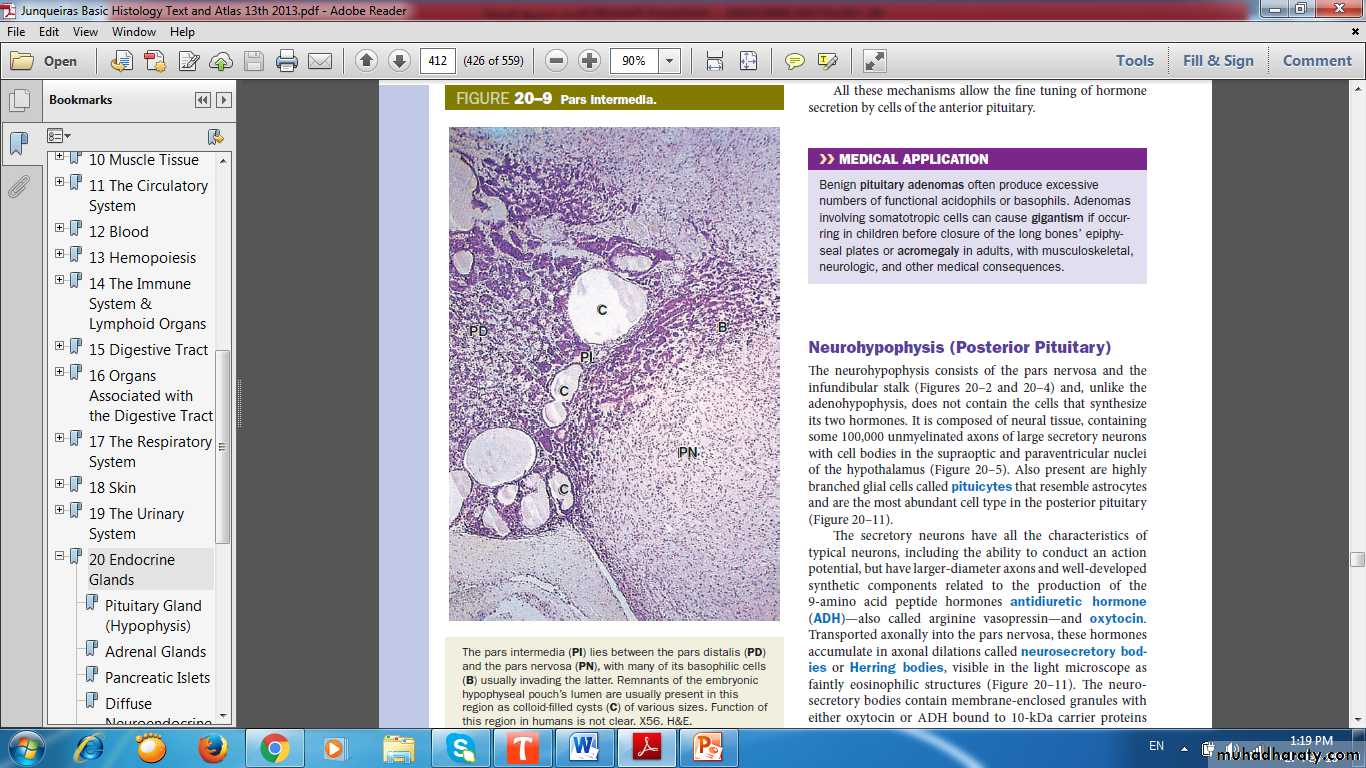
Pars Intermedia
Pars NervosaPars Distalis
Cyst
Basophilic cells
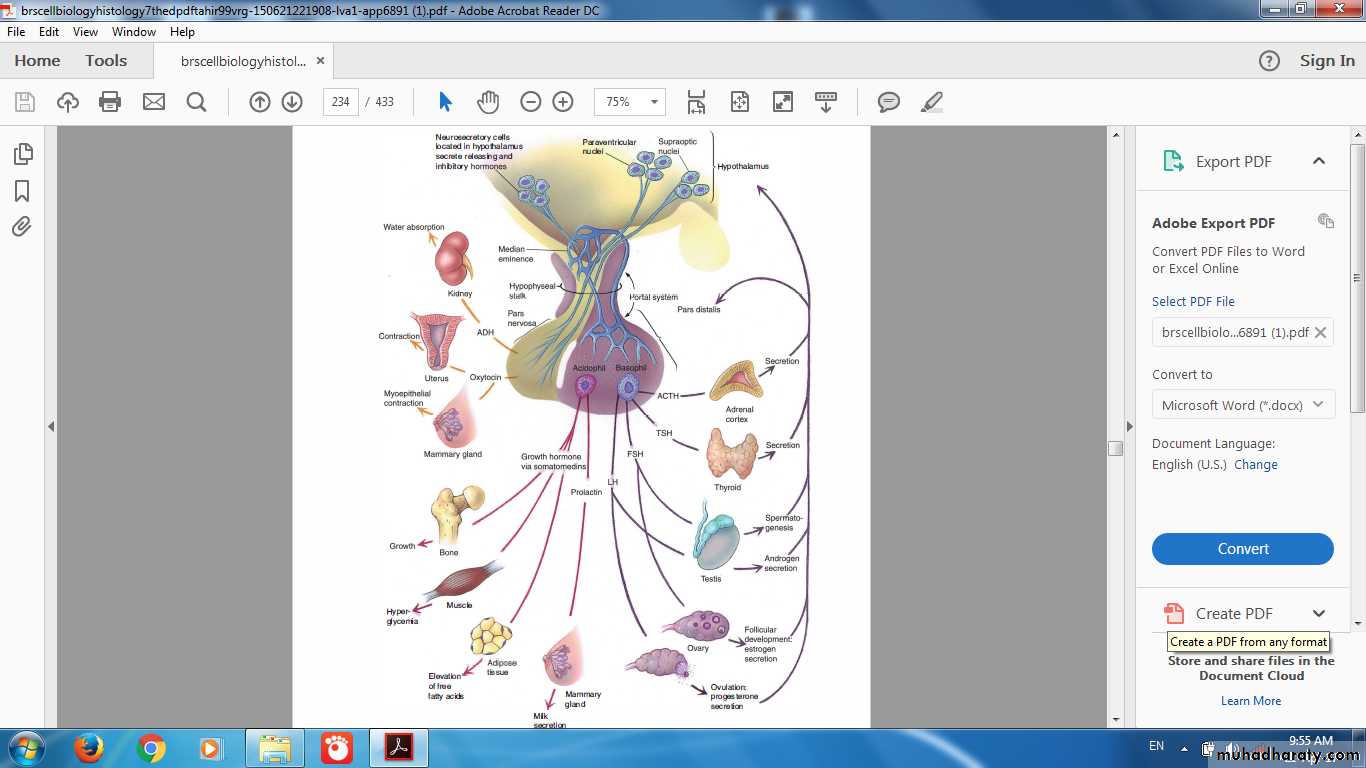
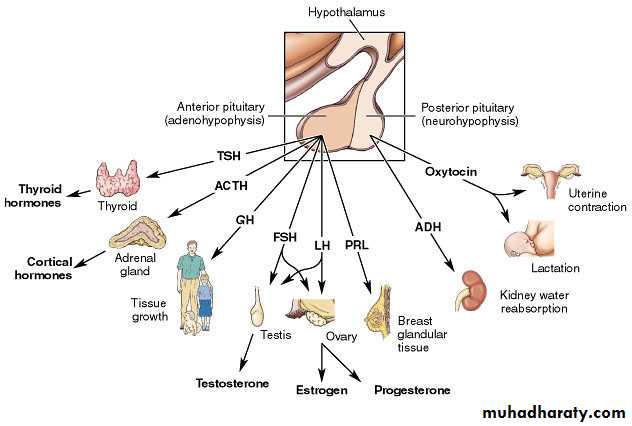
Hormones of Pituitary
Adenohypophysis• Growth hormone
• Prolactin
• FSH
• LH
• ACTH
• TSH
Neurohypophysis
• ADH
• Oxytocin
•
Gigantism & Dwarfism
Acromegaly
Pars Nervosa
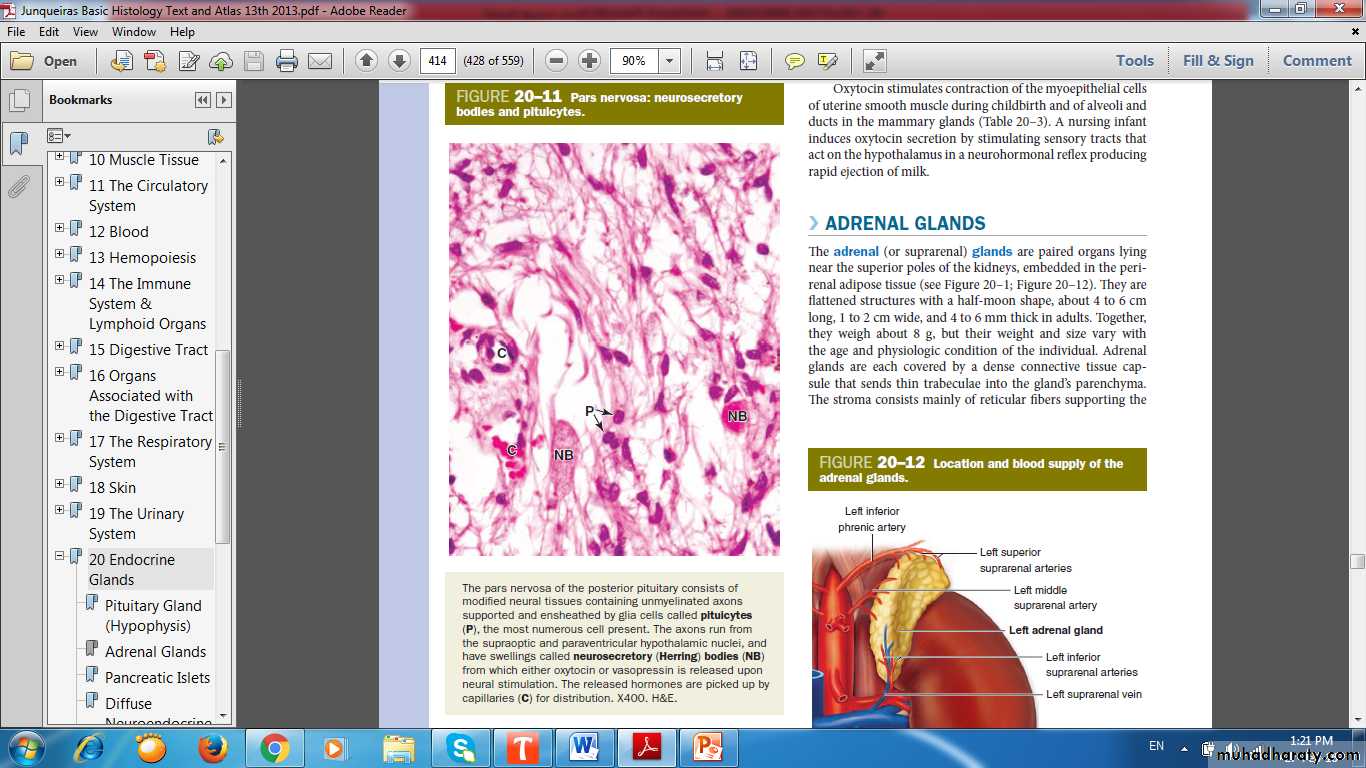
• Neurosecretory Bodies• Unmylinated axons
• Pituicytes
Neurosecretory Bodies
PituicytesCapillary
Hormones of Pituitary
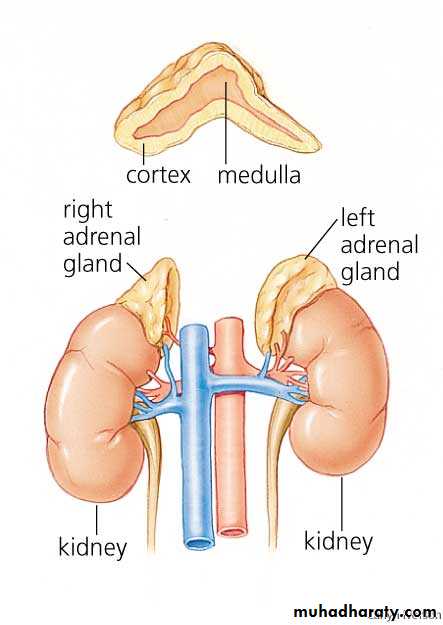
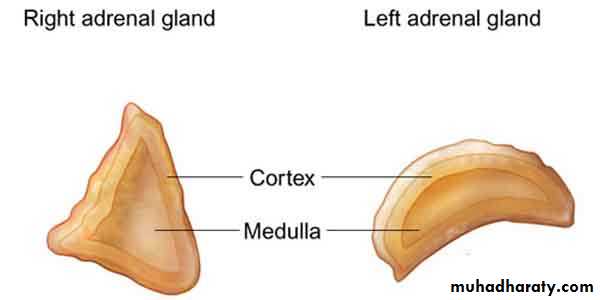
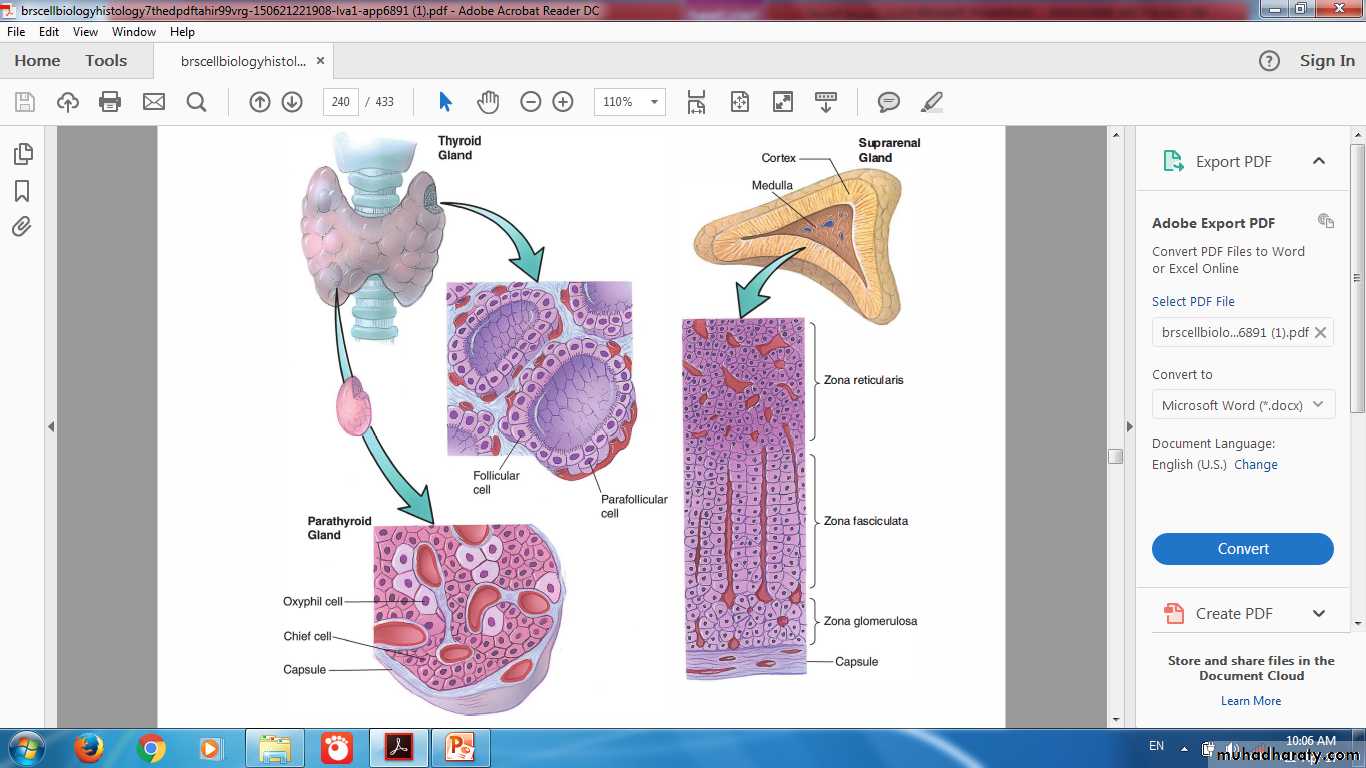
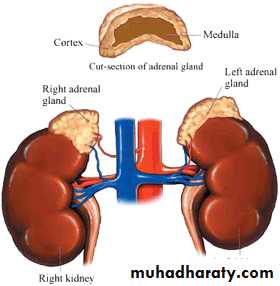
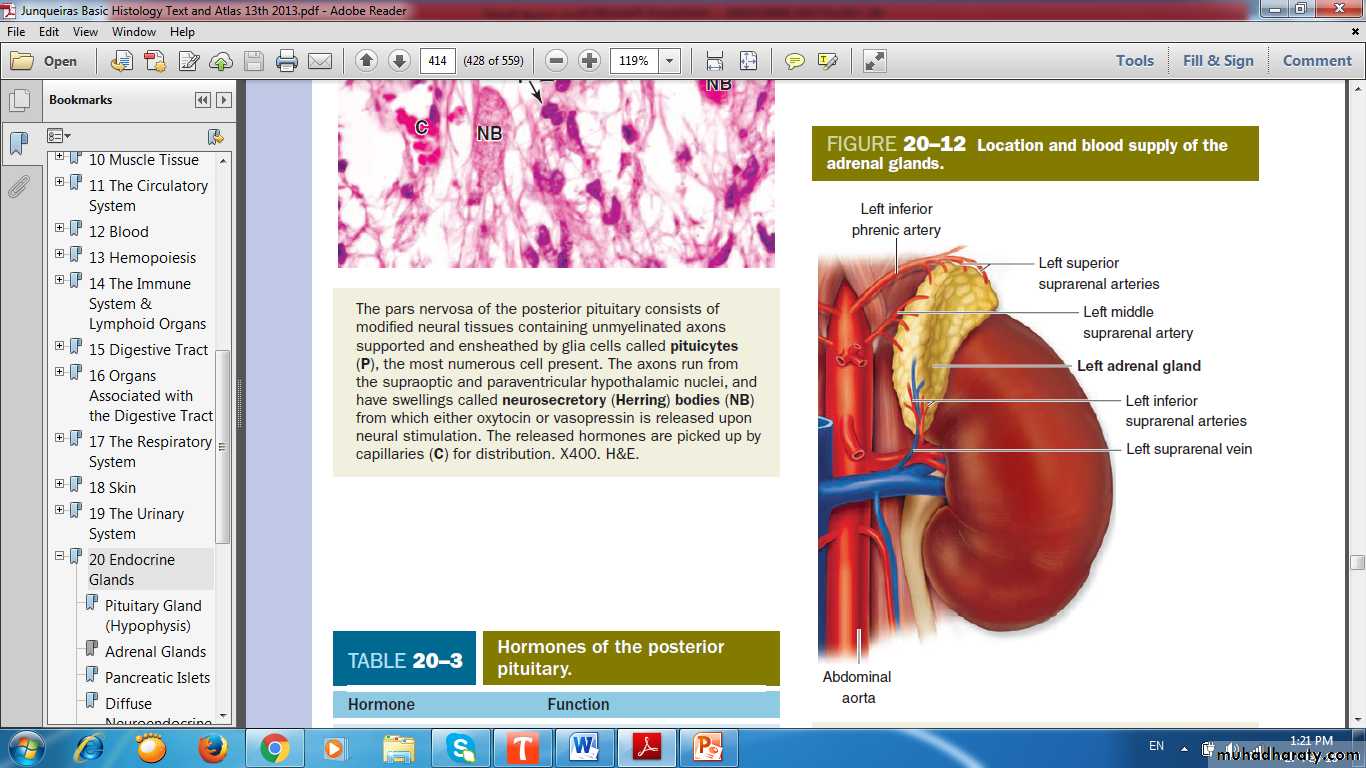
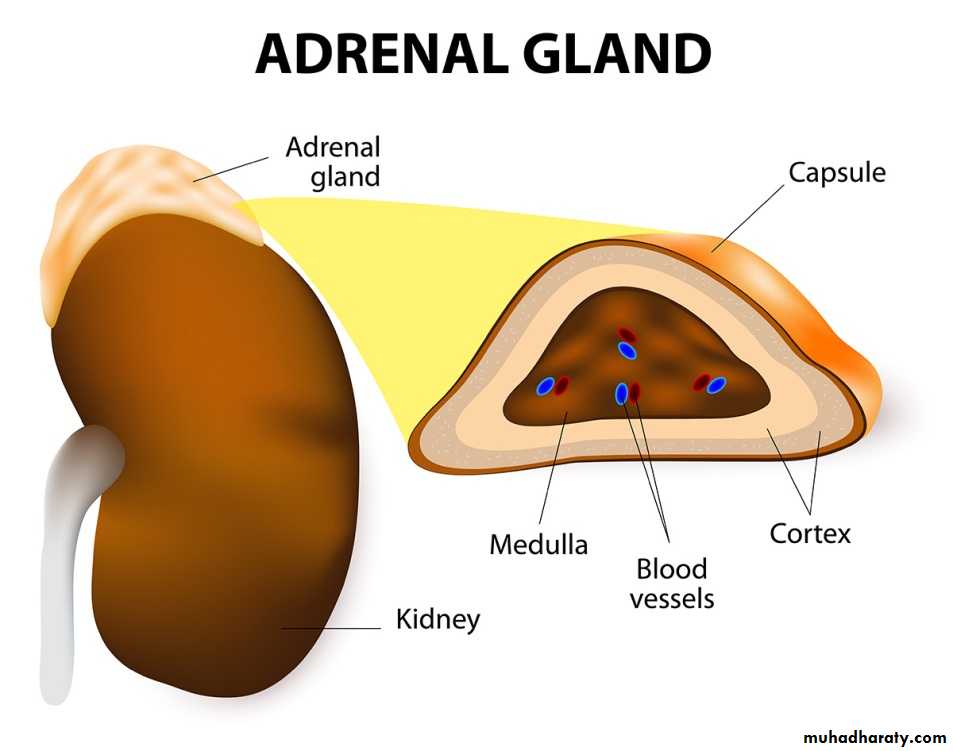
Adrenal Gland
Adrenal Gland
Adrenal Gland
Adrenal Gland
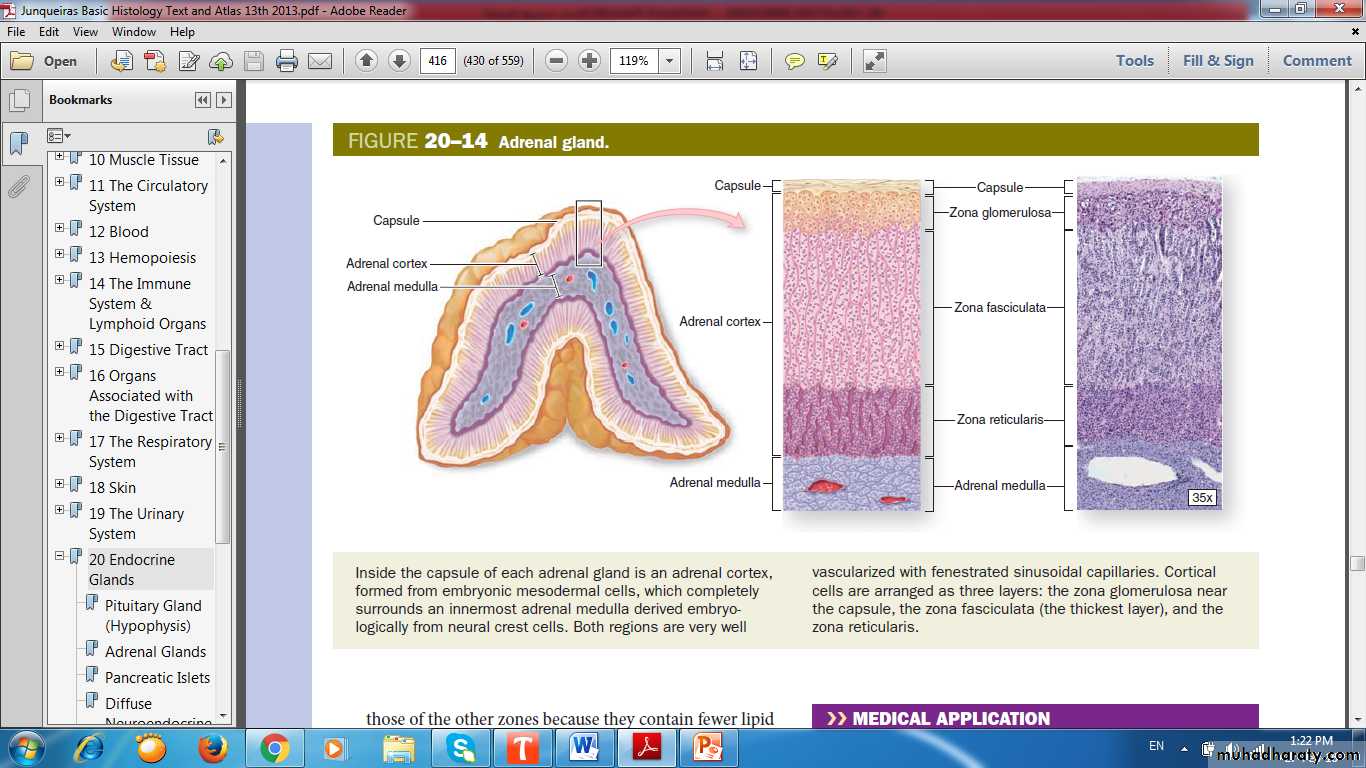
Adrenal CortexOrigin from mesoderm
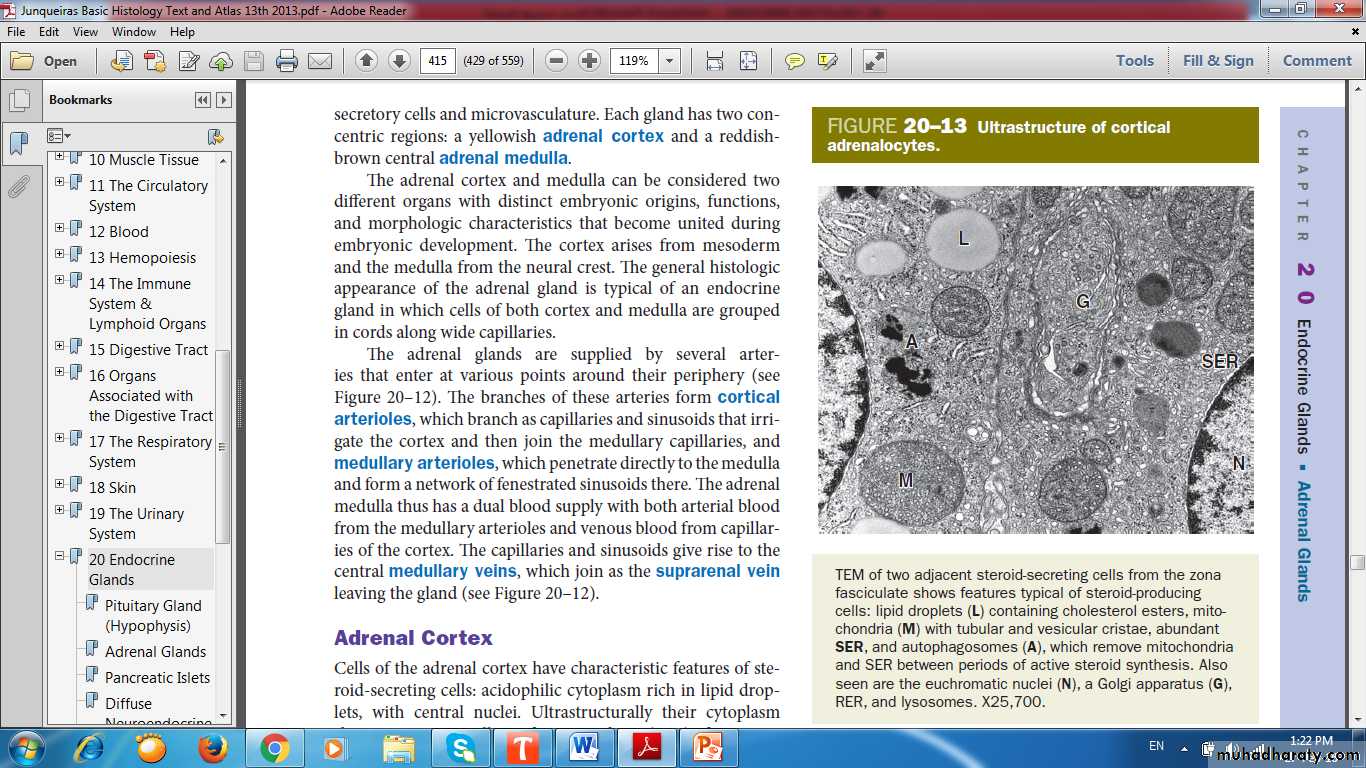
Features of steroid- secreting cells
Three concentric zones:
Zona Glomerulosa
Zona Fasciculata
Zona Reticularis
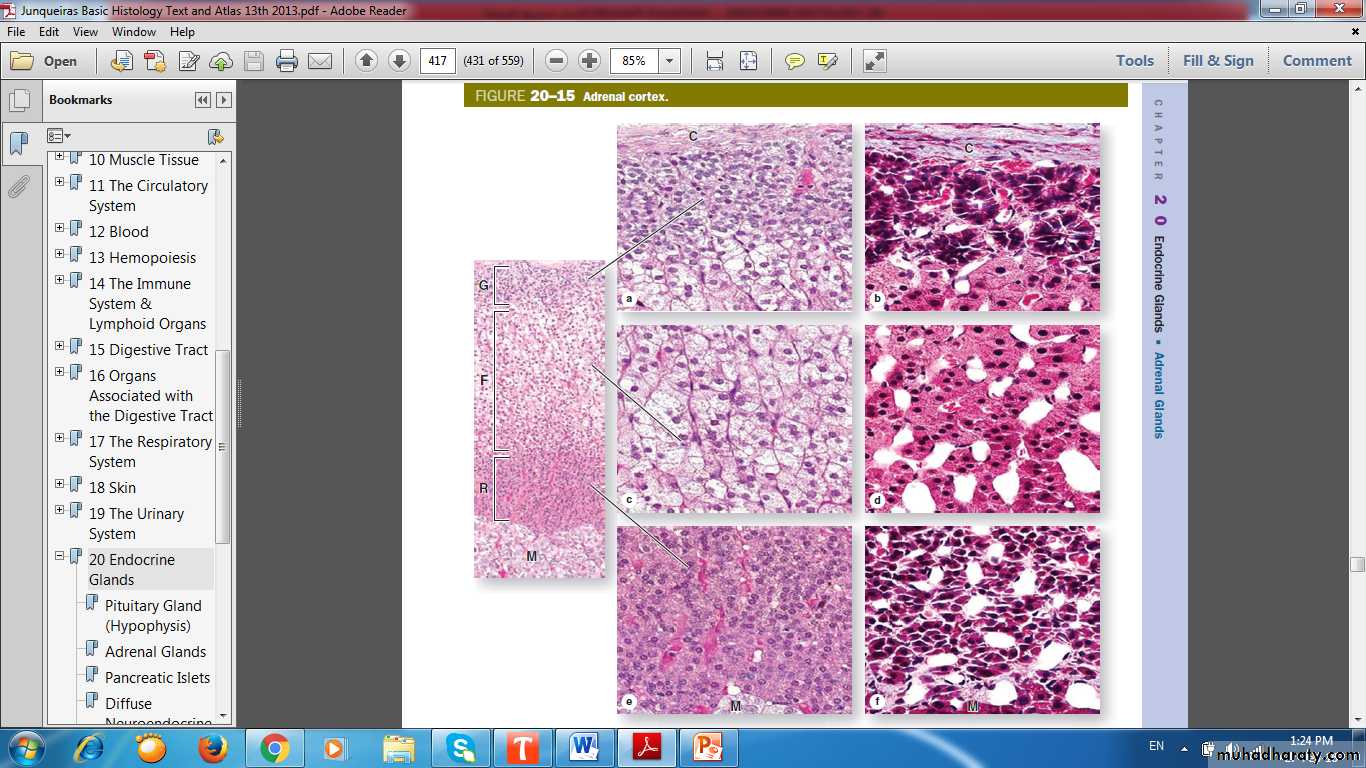
Adrenal Cortex
Zona Glomerulosa (15%): rounded or arched cords of columnar or pyramidal cellsZona Fasciculata (65-80%): long cords of large polyhedral cells, one or two cells thick
Zona Reticularis (10%): smaller cells in a network of irregular cords
Adrenal Cortex Zones & Function
Zona Glomerulosa:Aldosterone
Zona Fasciculata:
CortisolZona Reticularis:
Androgen
Ultrastructure of Cortical Adrenalocytes
Lipid dropletMitochondria
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
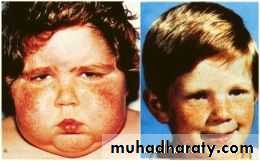
Cushing Syndrome
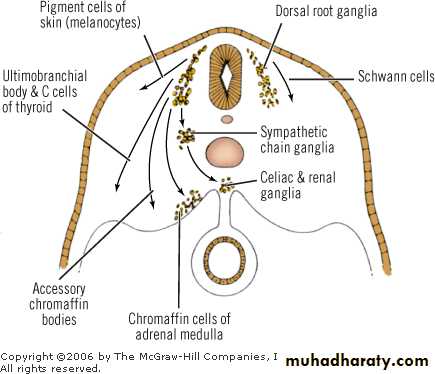
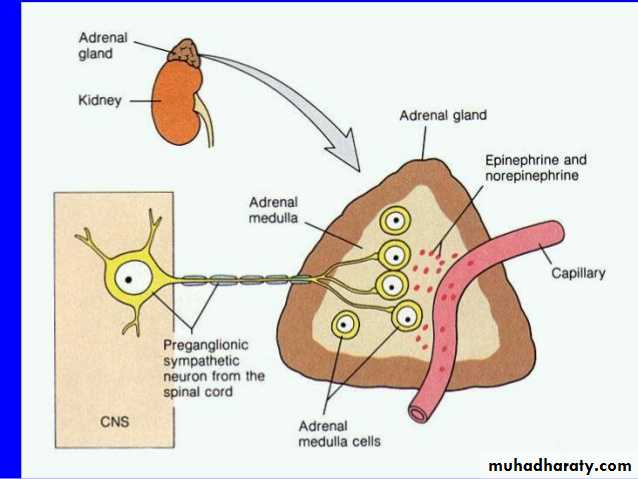
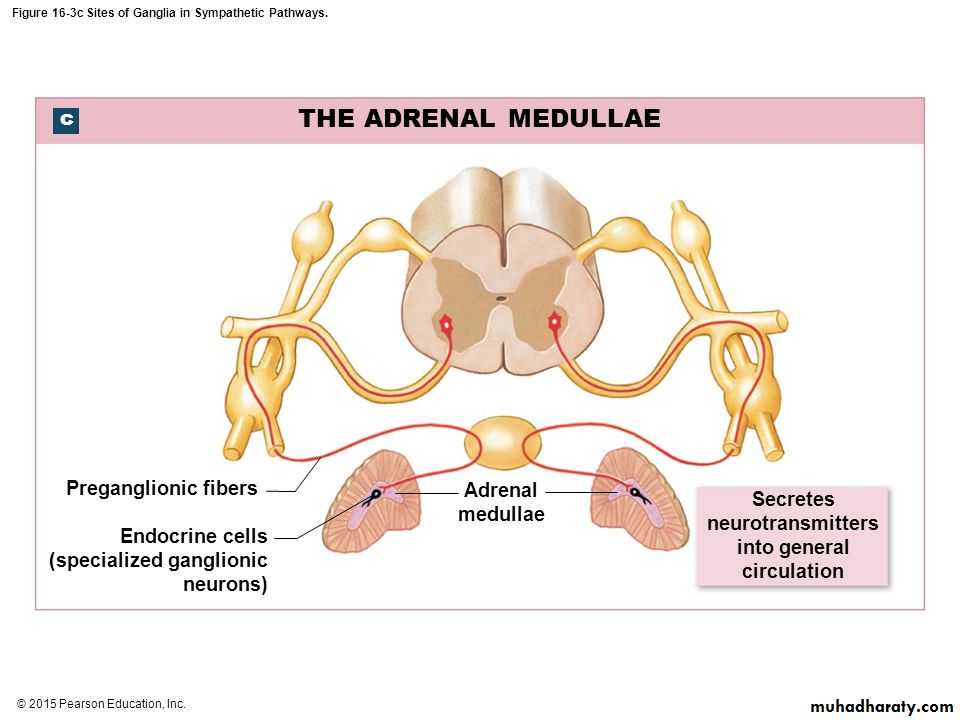
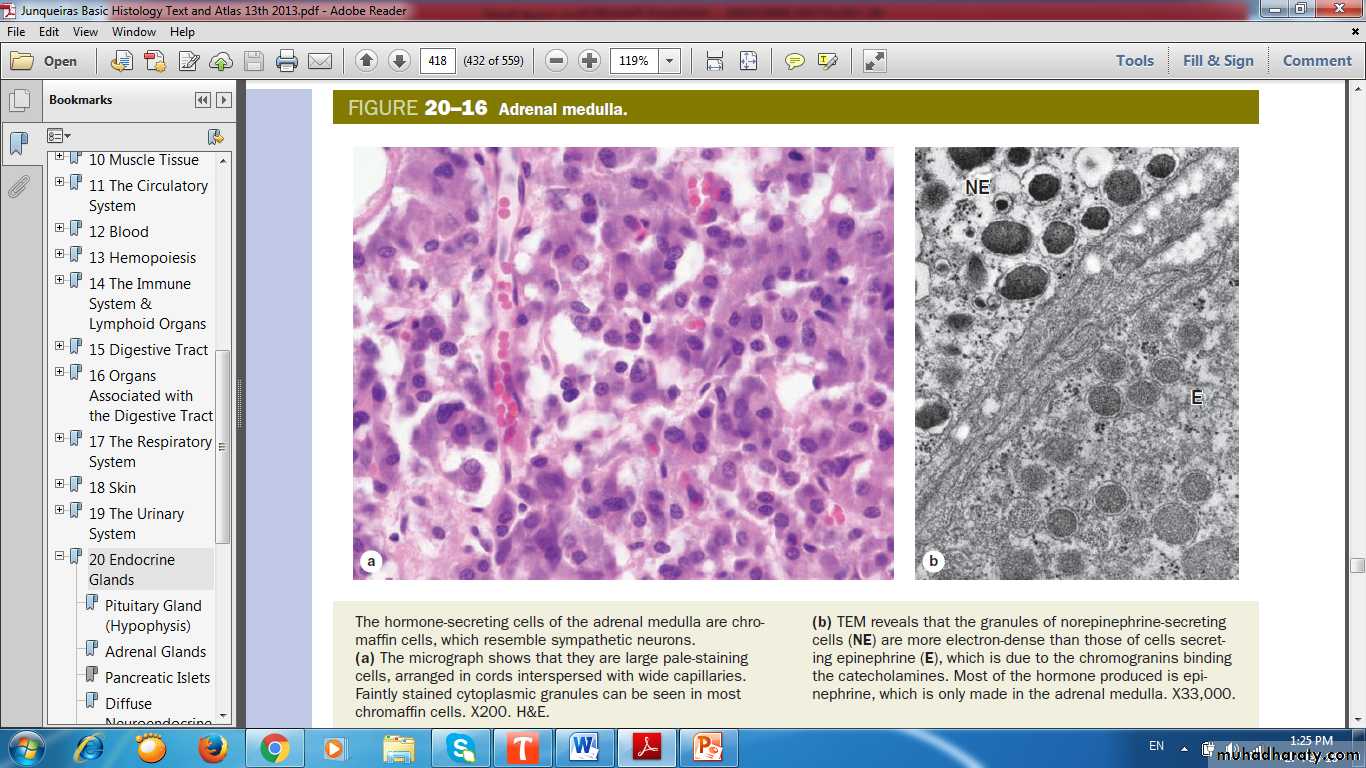
Adrenal Medulla
Adrenal Medulla
Origin from neural crestReddish brown in color
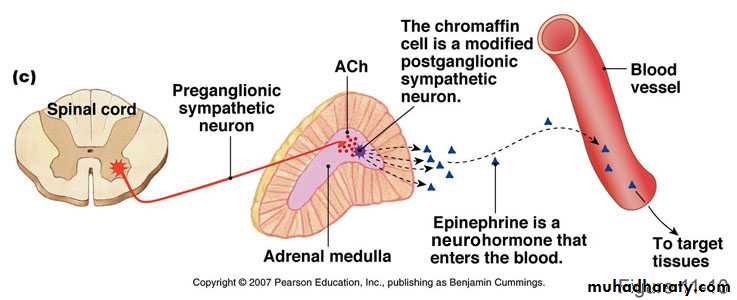
Cells called Chromaffin Cells
Profuse supply of sinusoidal capillaries
Adrenal Medulla Origin from Neural Crest
Chromaffin Cells
Modified neurons, lacking axons and dendritesSpecialized as secretory cells
Contain many electron-dense granules for storage and secretion of catecholamines
large, pale-staining polyhedral cells arranged in cords or clumps
Modified Neurons, Lacking Axons & Dendrites
Innervated by Preganglionic Nerve, which Trigger Hormone Release
Specialized as Secretory Cells
Chromaffin Cells are large, pale-staining polyhedral cells arranged in cords or clumps
NorEpinephreinEpinehrin
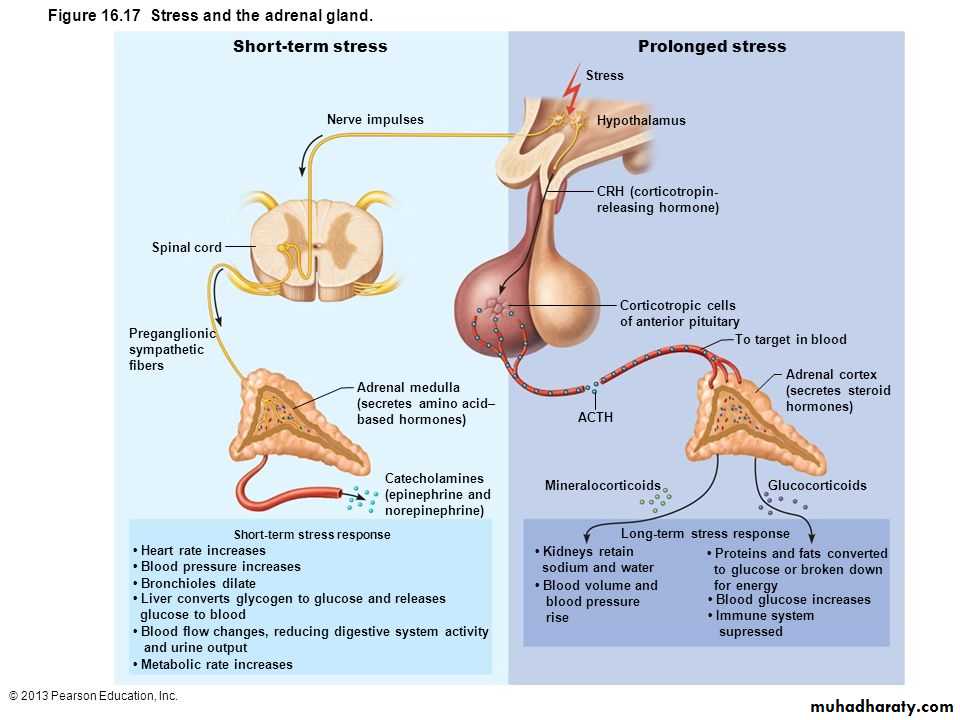
Stress & Adrenal Gland
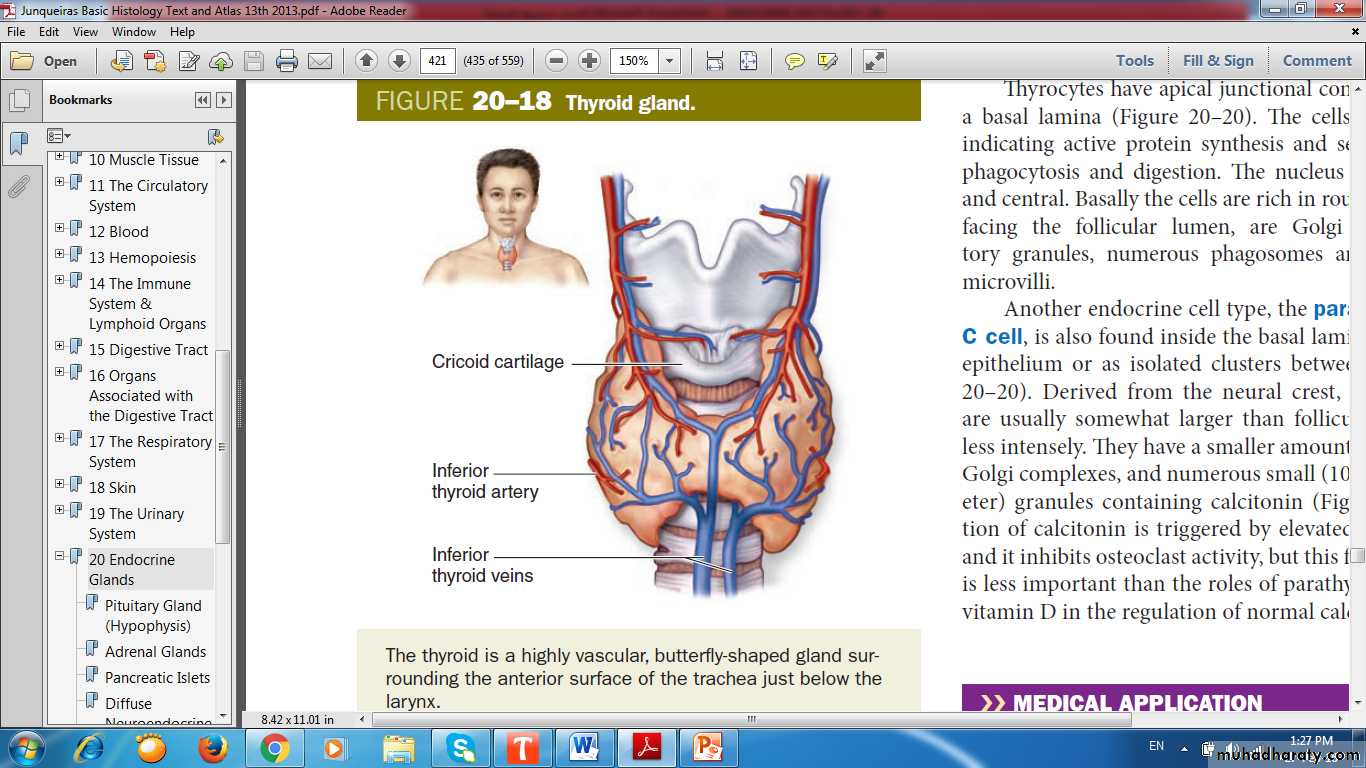
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
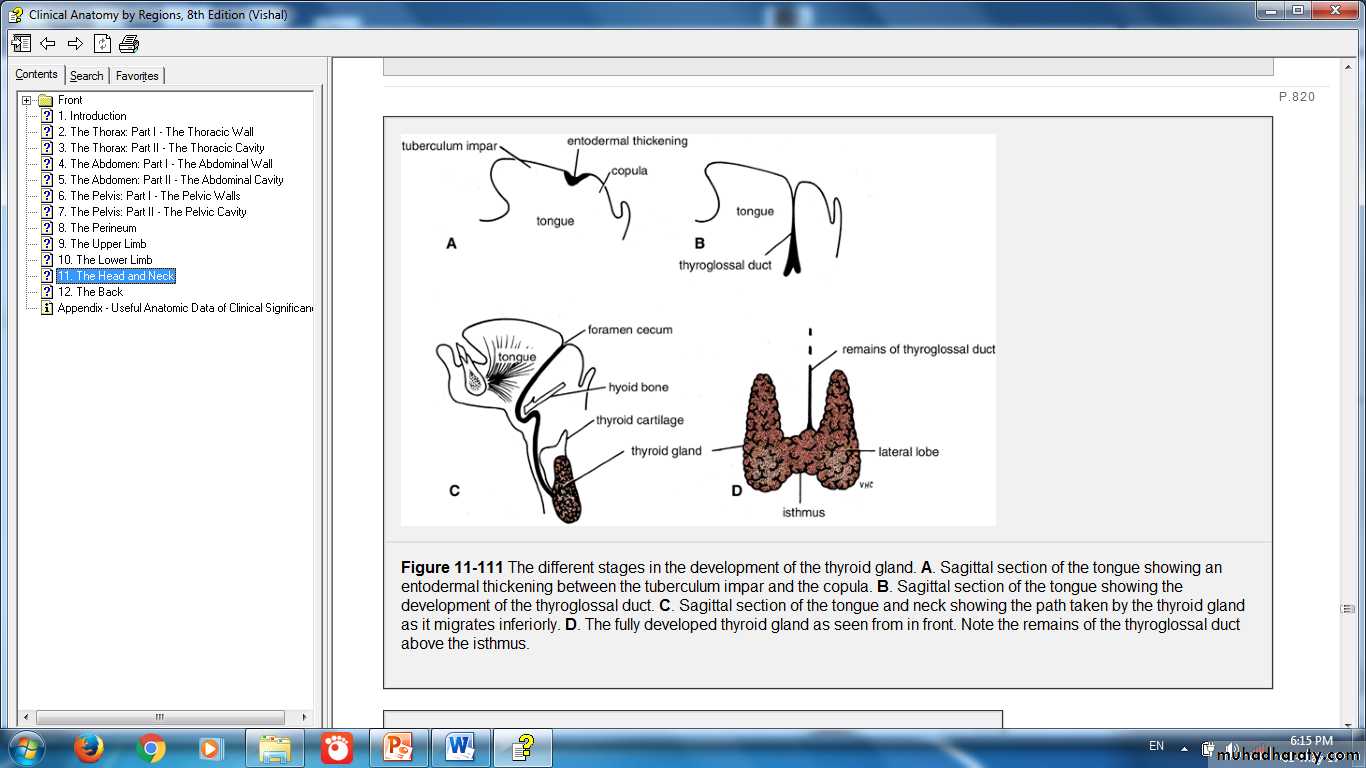
Thyroid GlandOrigin: foregut endoderm
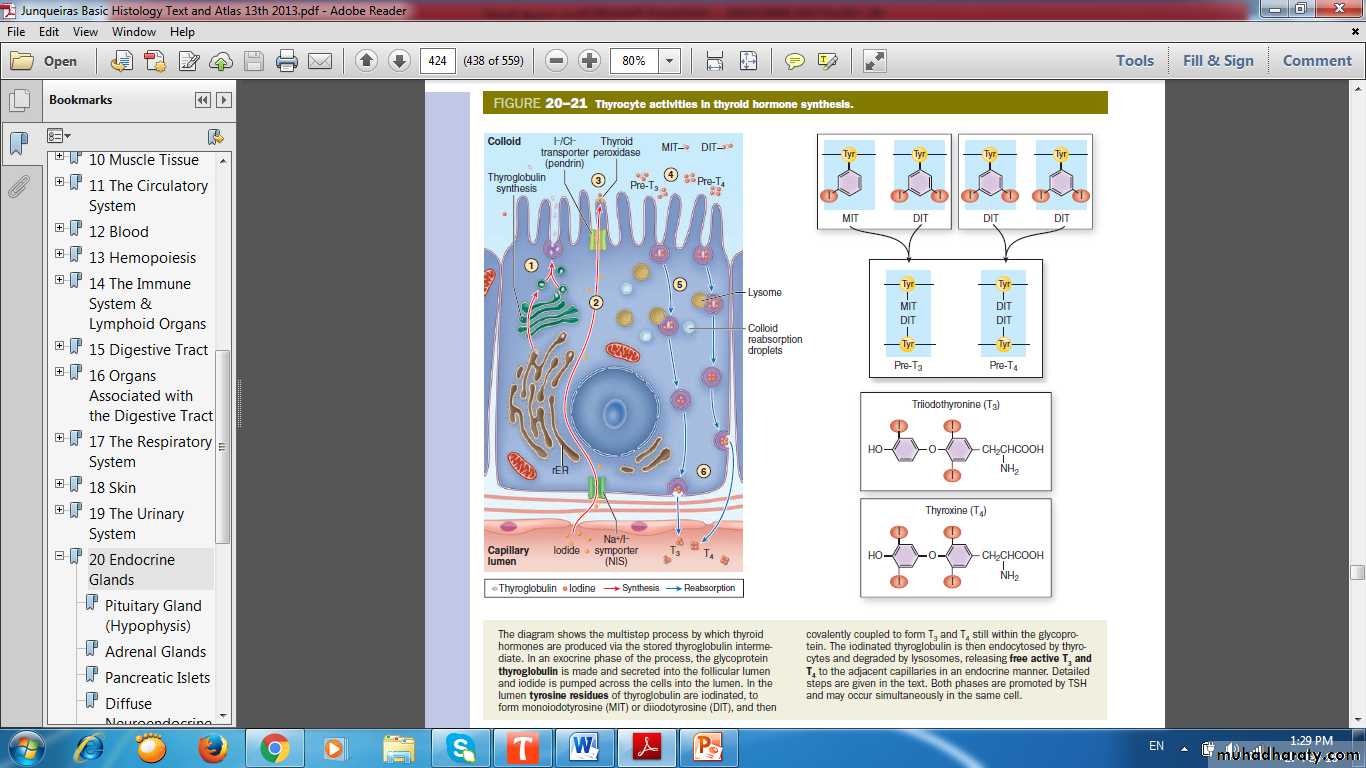
Hormones – (T3, T4 & Calcitonin)
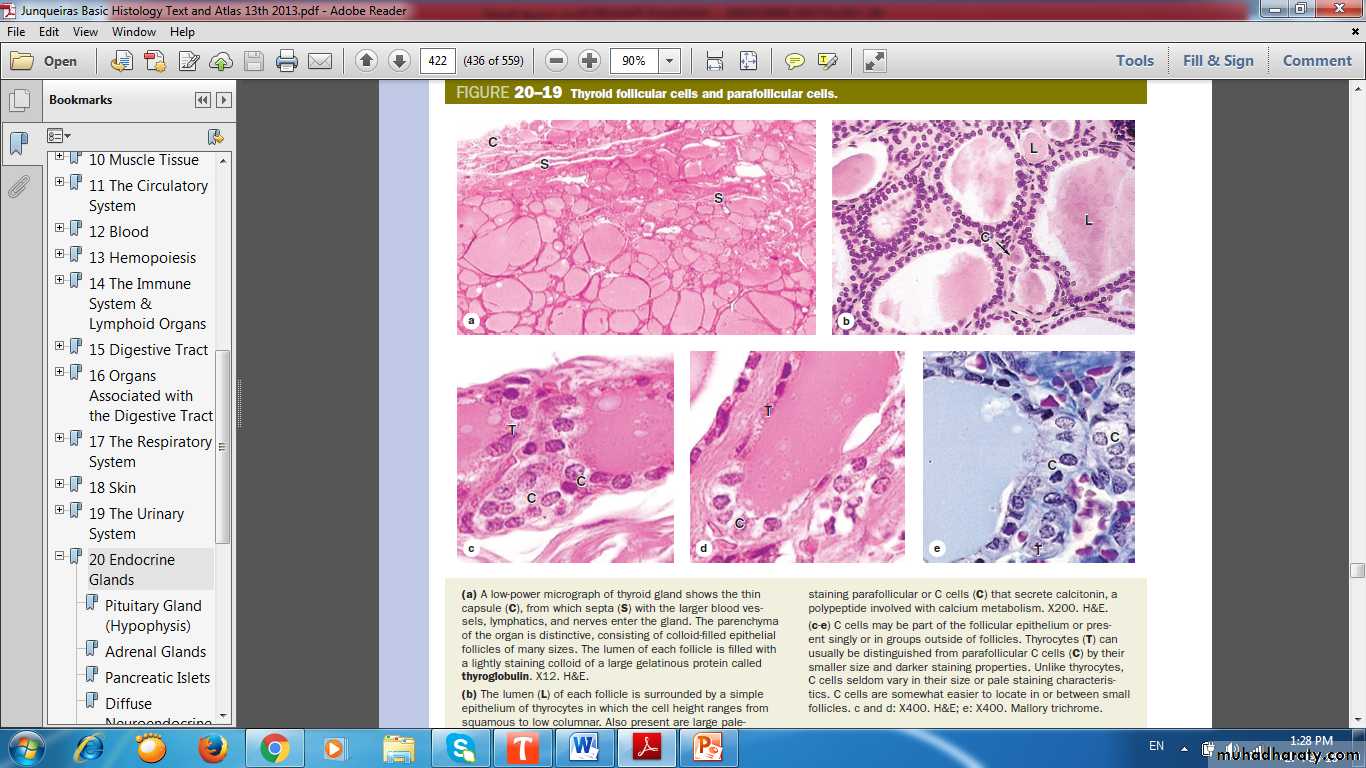
Thyroid follicles
Thyroglobulin
Parafollicular cell, or C cell
Origin of Thyroid: from foregut endoderm near the base of the tongue
Thyroid Follicular Cells & Parafollicular Cells
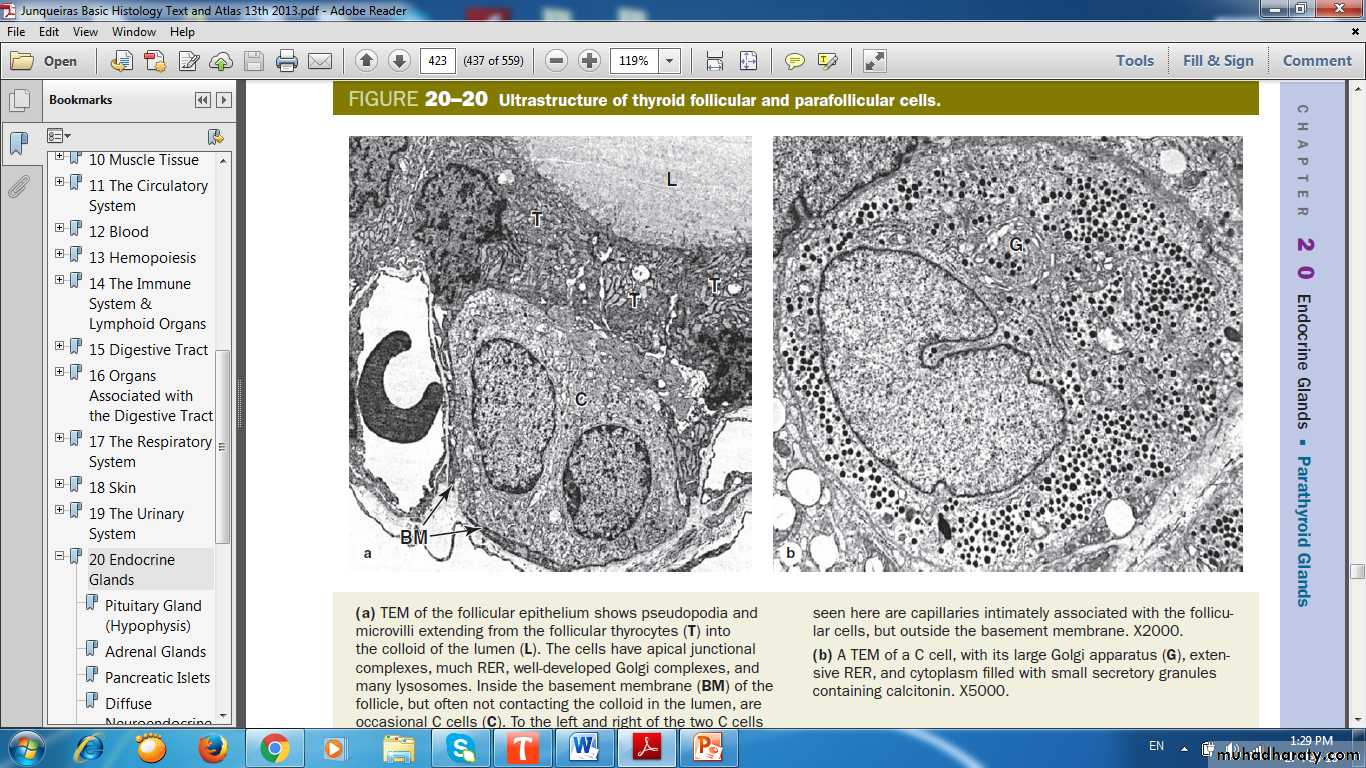
Ultrastructure of Thyroid Follicular Cells & Parafollicular (C) Cells
Thyrocytes Activities in Thyroid Hormone Synthesis
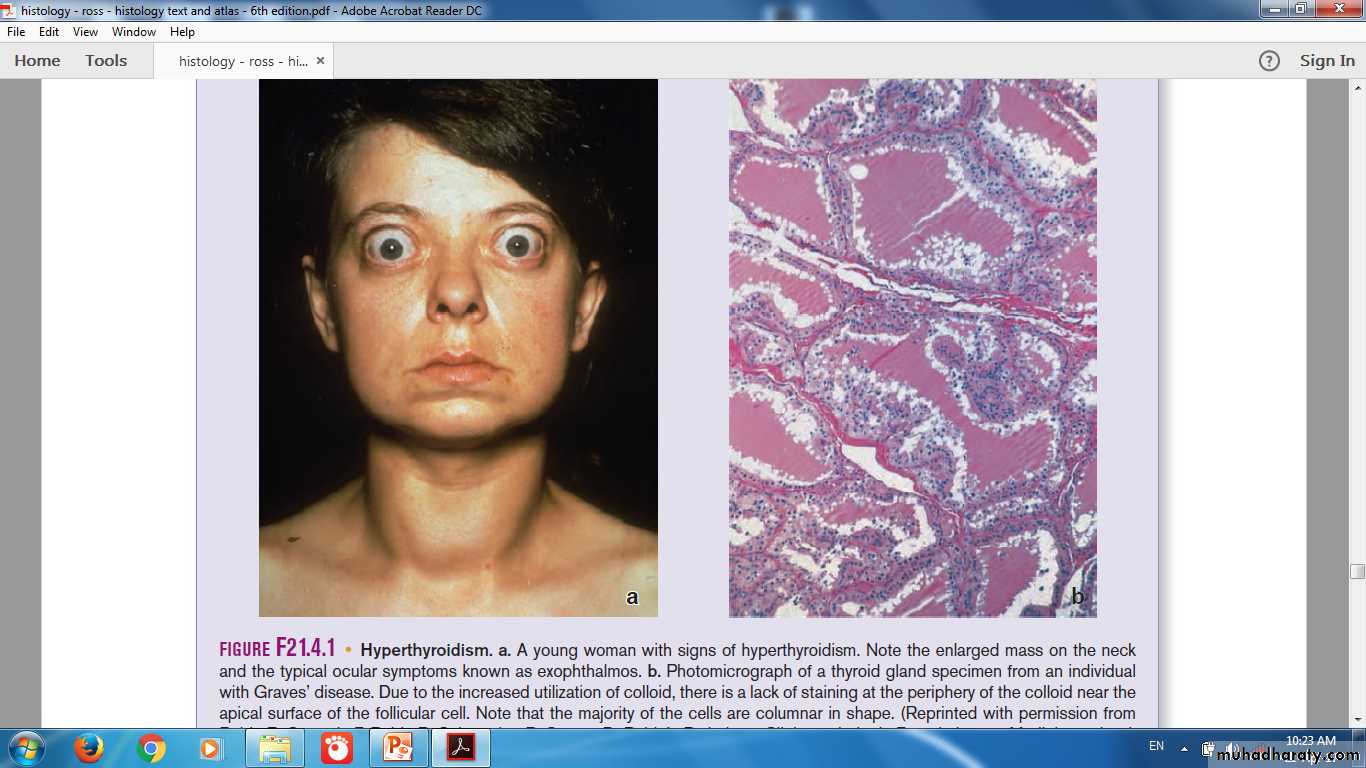
HyperthyroidismParathyroid Gland
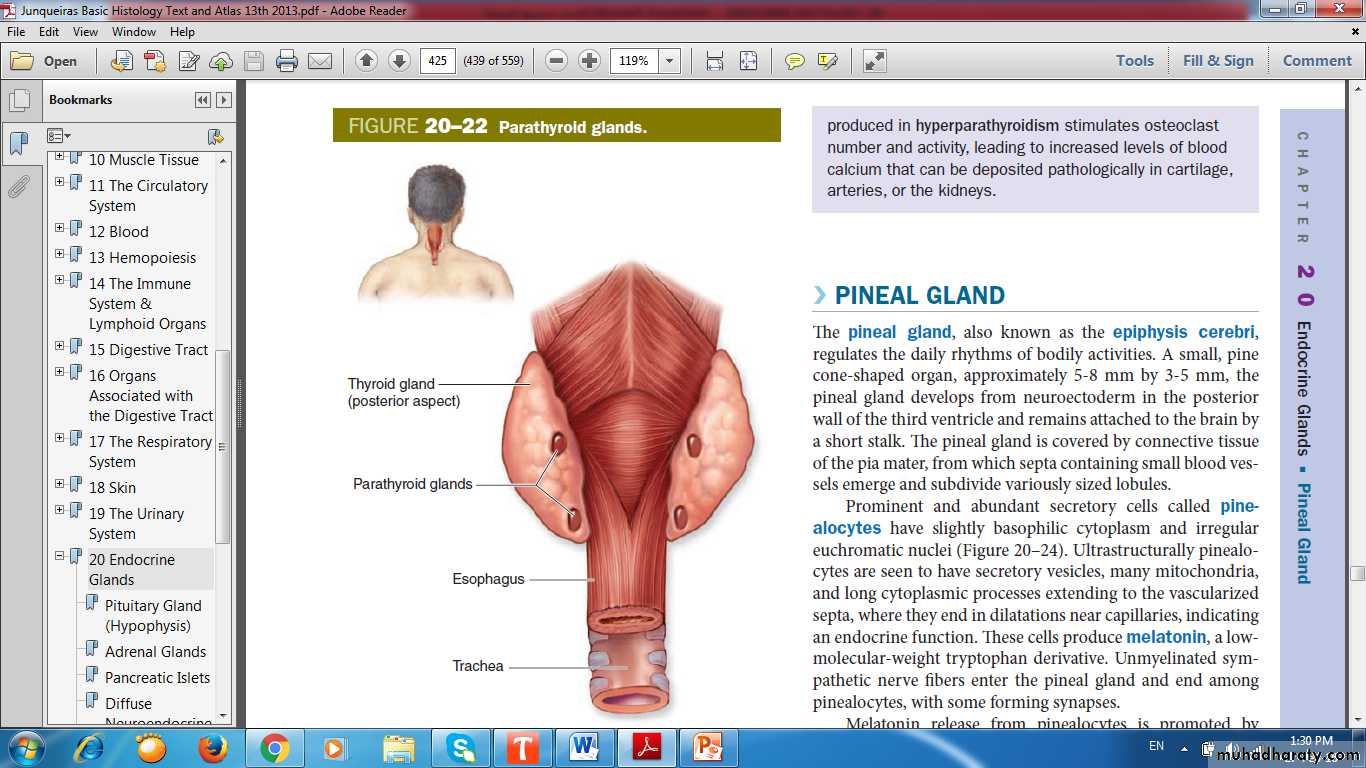
Parathyroid GlandFour small ovoid masses
Location
Origin
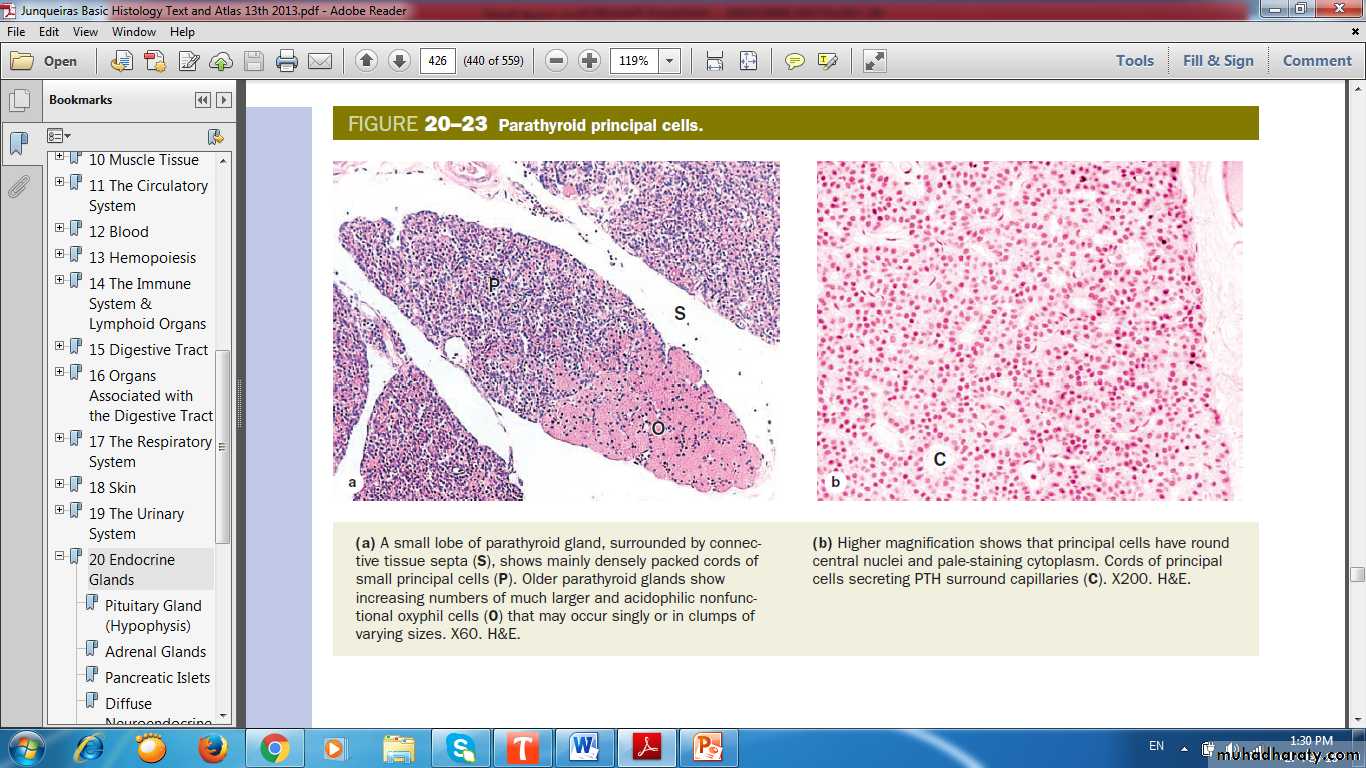
Principal (chief) cells
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Oxyphil cells
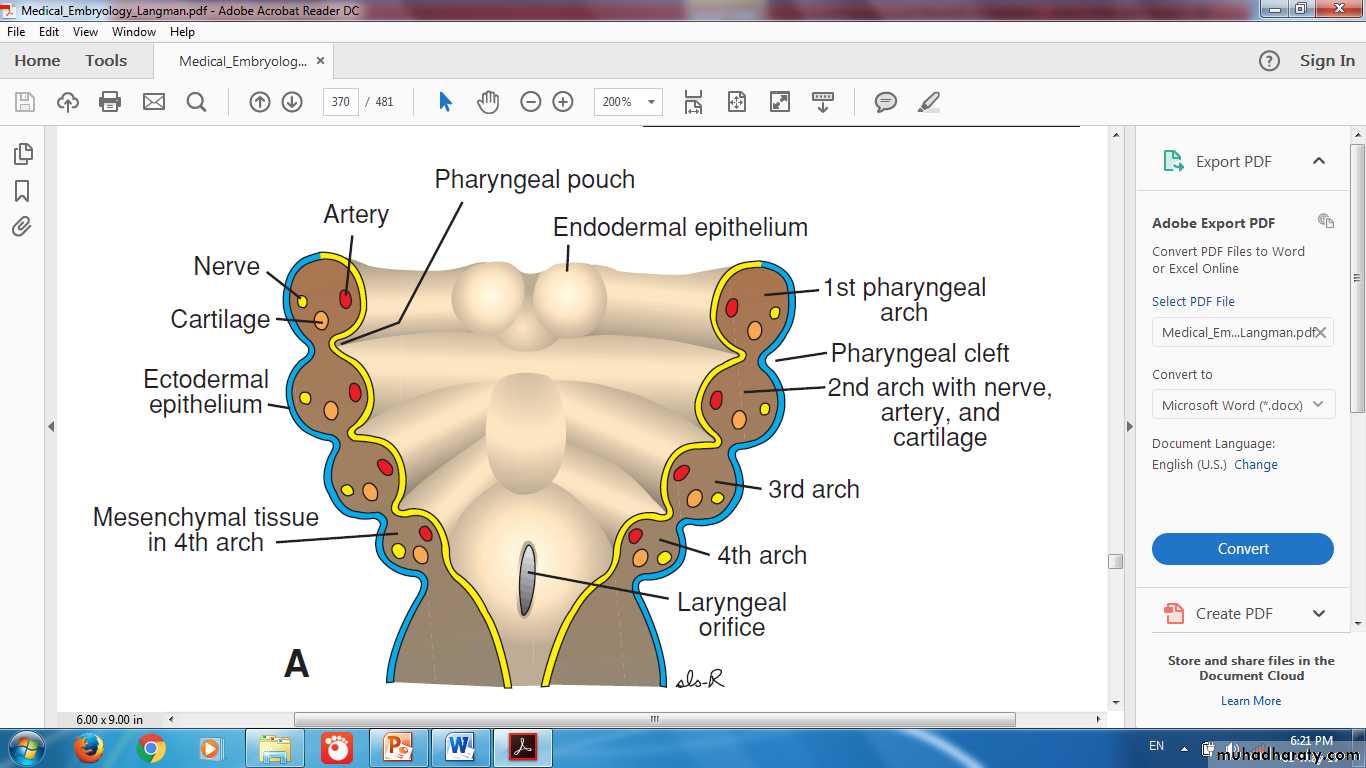
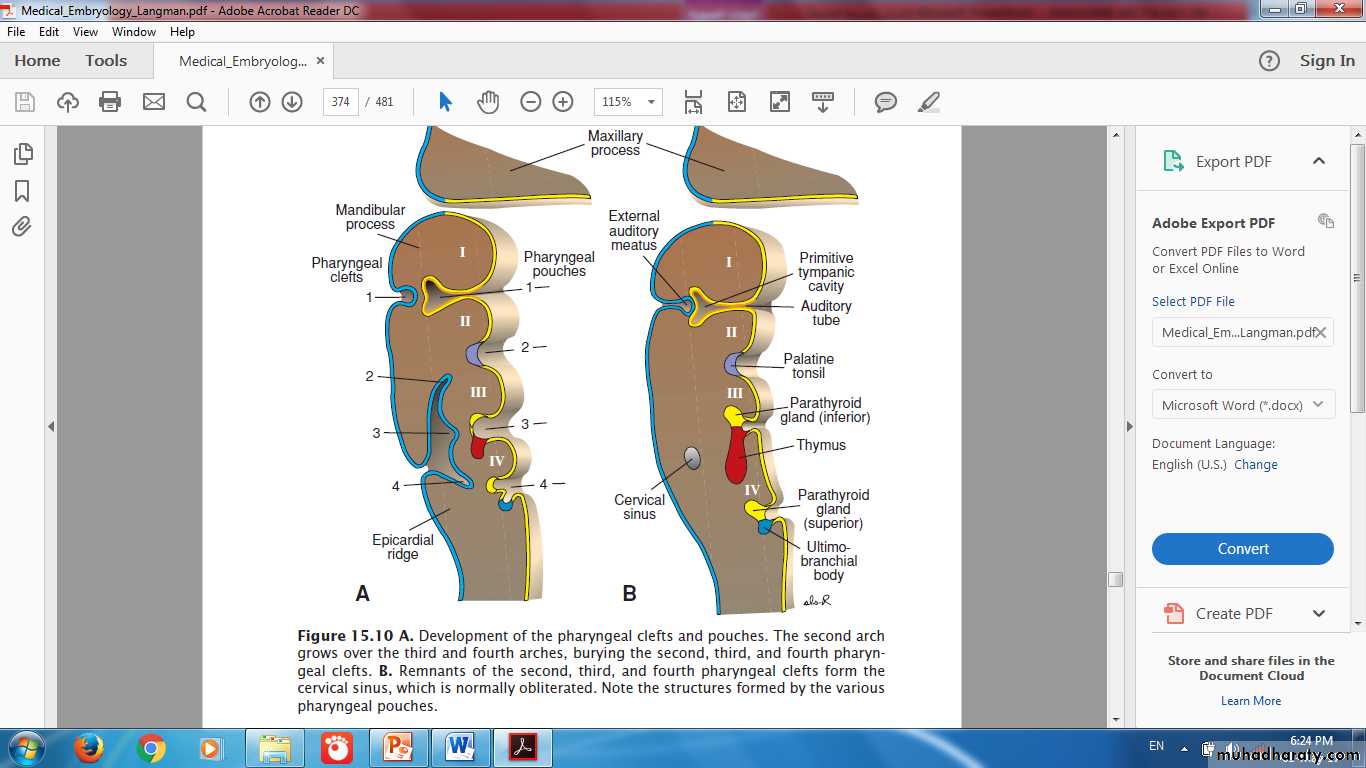
Pharyngeal Arches, Clefts & Pouches
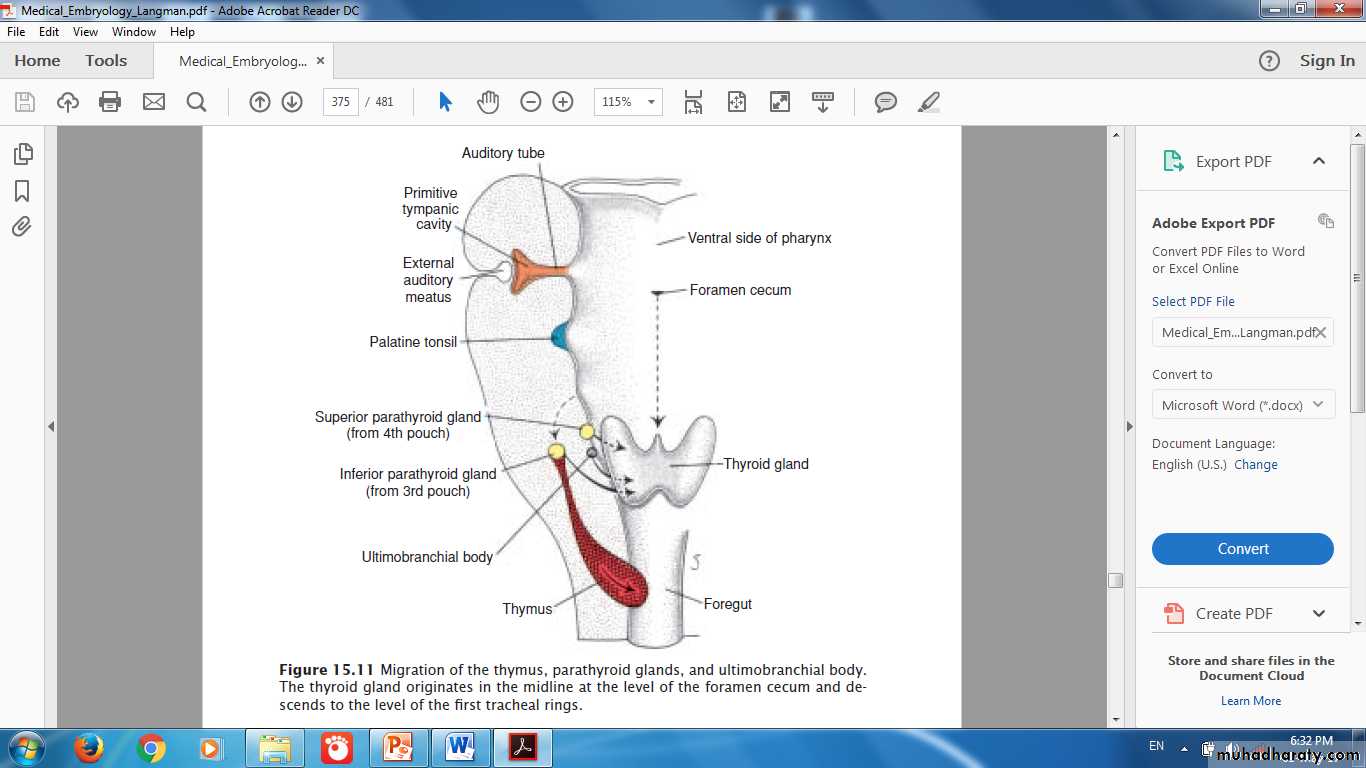
Origin of Parathyroid GlandsThymus & Inferior Parathyroid Gland
Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands
Parathyroid Principle Cells
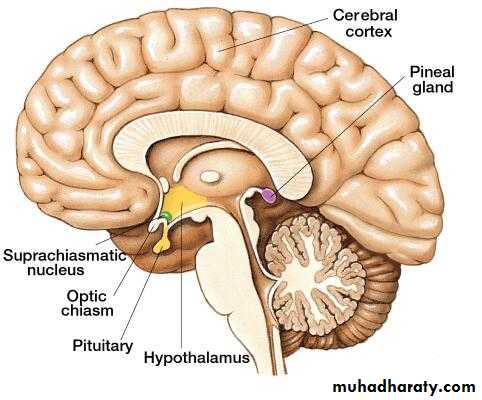
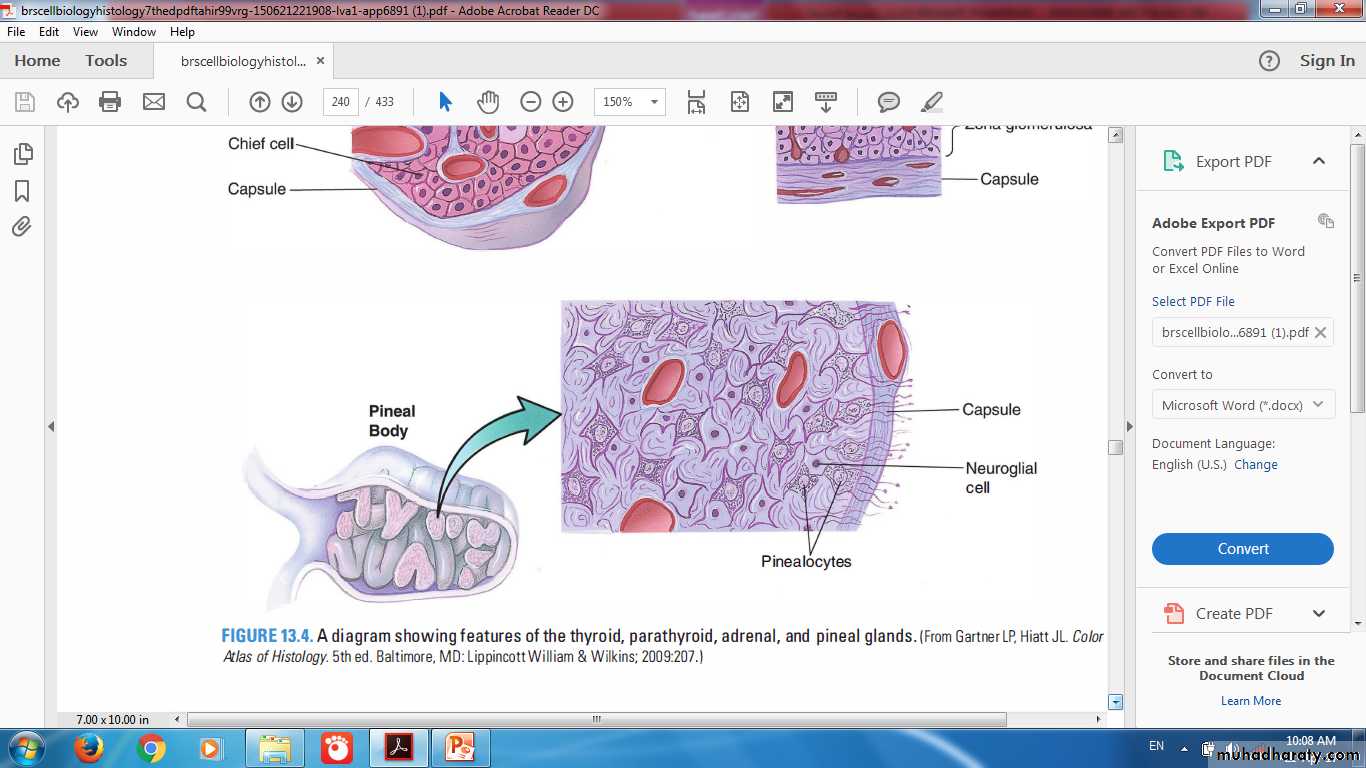
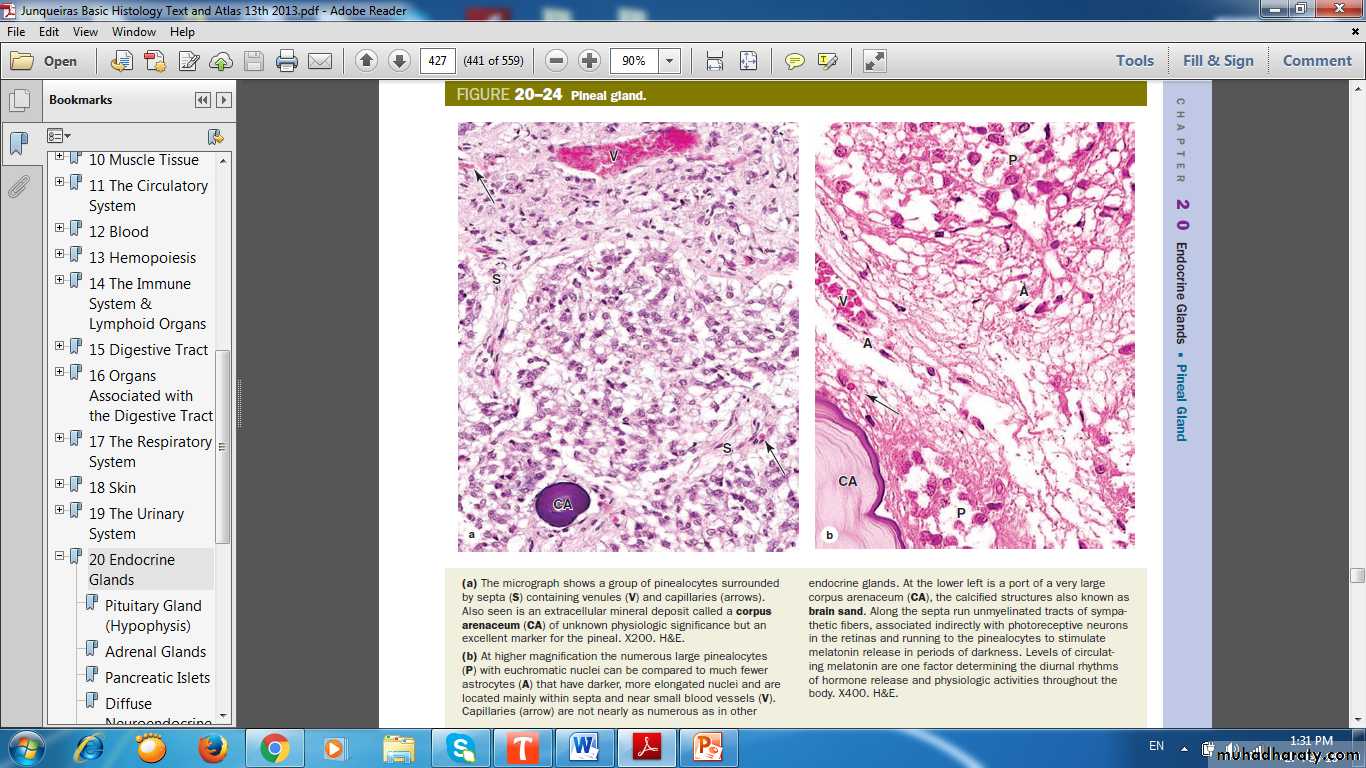
Pineal Gland (Epiphysis Cerebri)Pineal Gland
ShapeOrigin
Cells : Pinealocytes
Hormone: Melatonin
Glial cells: Modified astrocytes
Corpora arenacea (brain sand)
Neuroendocrine Transducer
Pineal Gland
Pineal Gland
Corpora ArenaceaSepta
Astrocyte
Pinealocytes