
د.احمد مؤيد
IHD
= المرحلة السادسة
C
Spectrum of coronary artery disease
-Silent ischemia
-Chronic stable angina
-Acute coronary syndromes (ACS)
NSTE-ACS (Unstable angina , NSTEMI)
STEMi
-Heart failure
-Arrhythmi
-Sudden death
Chronic stable angina
Angina pectoris is the clinical syndrome caused by transient myocardial ischaemia.
It may occur whenever there is an imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply
and demand. Coronary atheroma is by far the most common cause of angina.
Investigations
Resting ECG often normal.
Exercise ECG.
Myocardial perfusion scanning.
Stress echocardiography.
Coronary arteriography
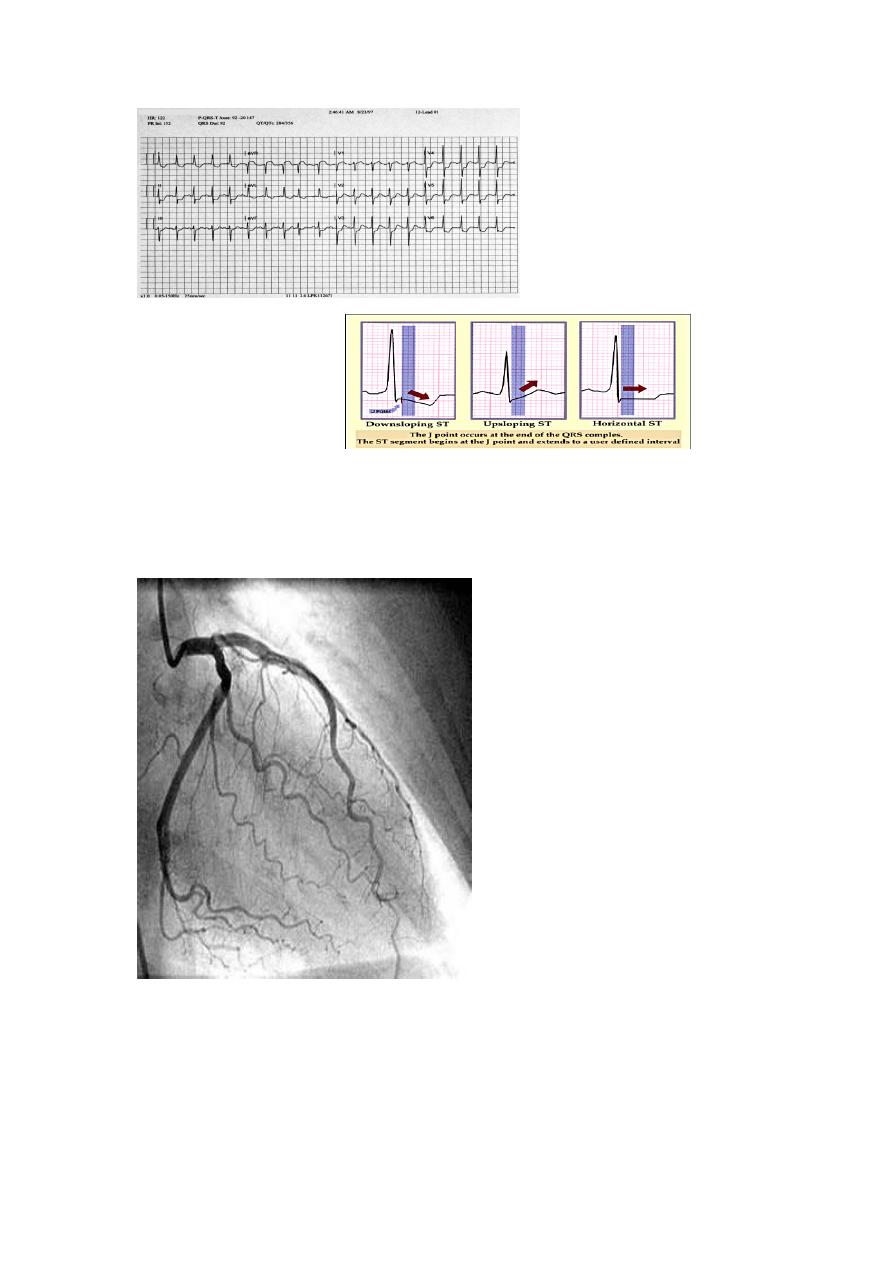
ST depression
1
.
Upward sloping depression of
ST segment is not indicative of IHD
2
.
It is called J point depression or sagging ST seg
3
.
Downward slopping or Horizontal depression of ST segment leading to T↓is
significant of IHD
Coronary Angiography

Management
Risk factors modification such as smoking, hypertension and hyperlipidaemia.
Drugs
Antiplatelet therapy
Low-dose aspirin reduces the risk of adverse events such as MI and should be
prescribed for all patients with coronary artery disease indefinitely .Clopidogrel
(75 mg daily) is an equally effective.
Anti-anginal drug treatment
Nitrates
Beta-blockers
Calcium channel antagonists
Potassium channel activators
Invasive treatment
Percutaneous coronary intervention PCI.
CABG
ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROMES
Pathogenesis of ACS
Sequence of events
•
Plaque Rupture
•
Platelet Adhesion
•
Platelet Activation
•
Platelet Aggregation

•
Thrombotic Occlusion
:
Differential diagnosis
•
Pericarditis
•
Pulmonary embolism
•
Pneumothorax
•
Aortic dissection
•
Esophageal spasm
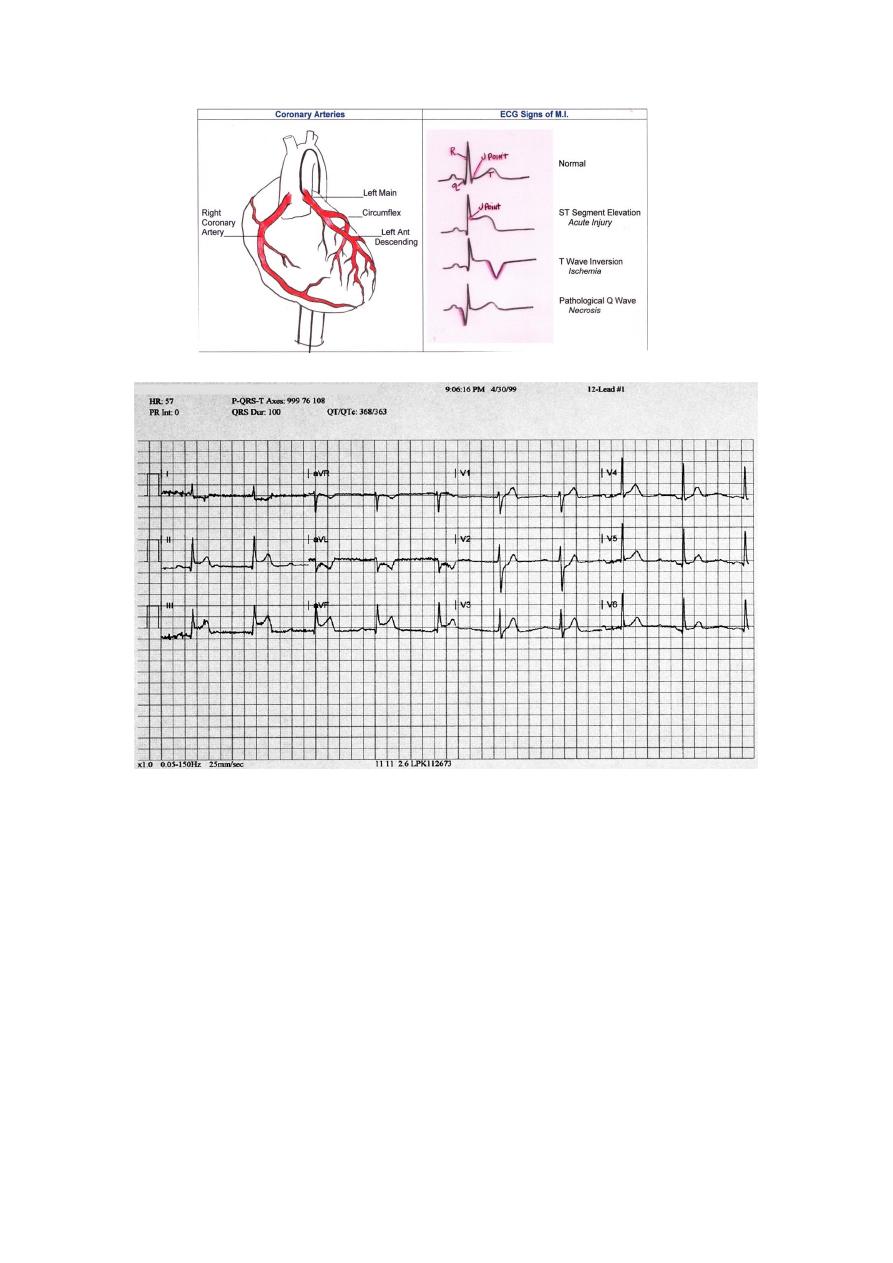
Ischemia and Infarction
Deep symmetric inverted T
waves
In more than 2 precardial leads
85% of the patients with such T wave↓had > 75% stenosis of the coronary artery
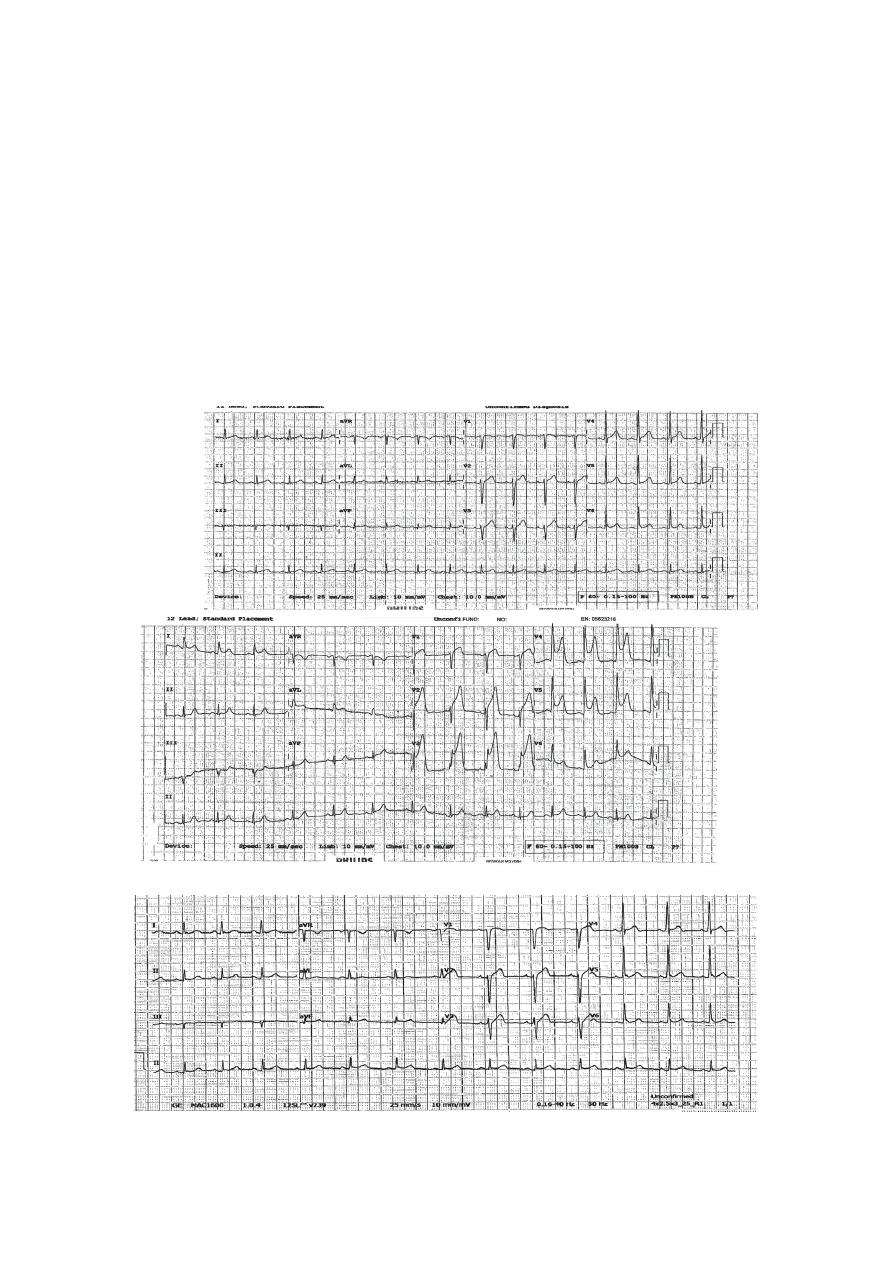
Stages of STEMI
ST
elevation
Arrangement of Leads on the EKG
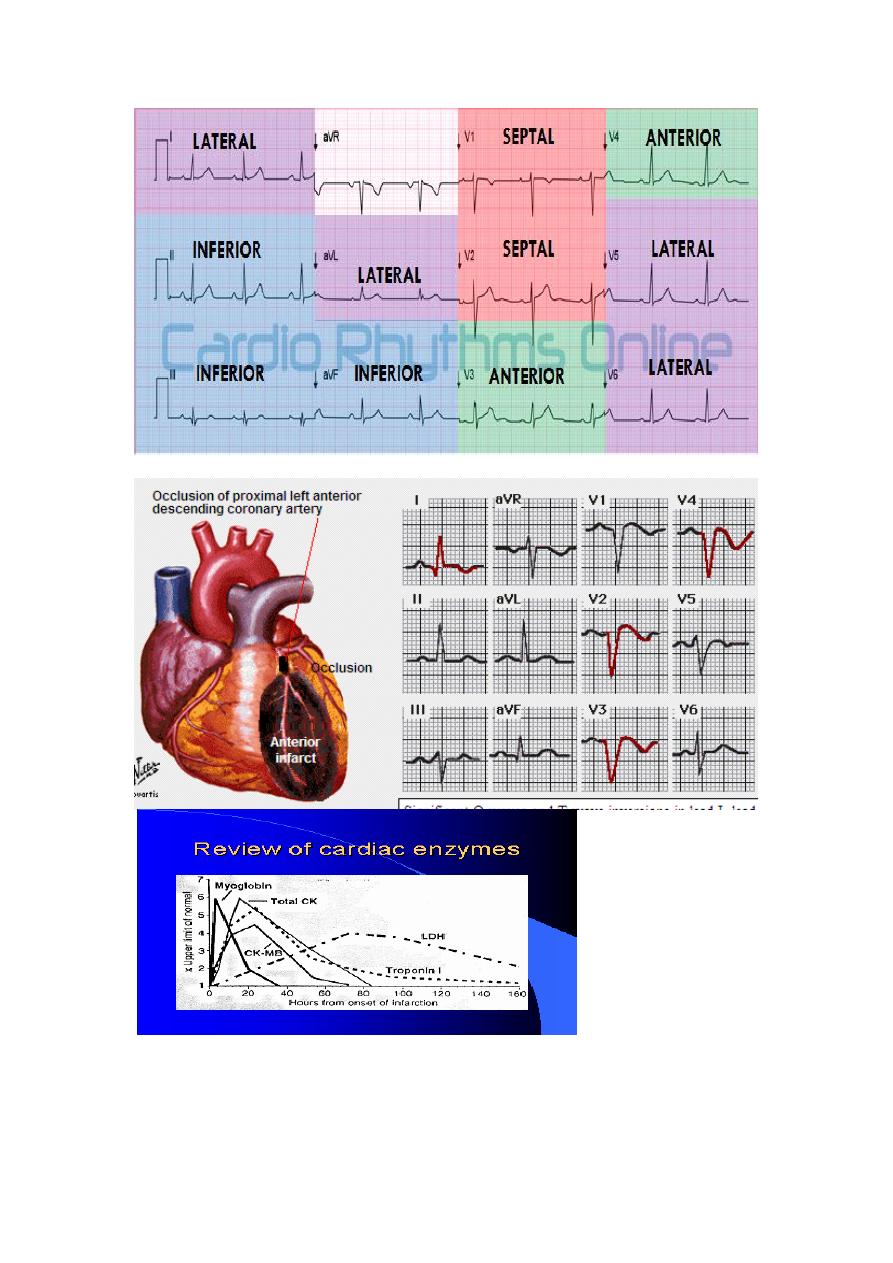
Acute Anterior MI
Cardiac Enzymes
Very Striking
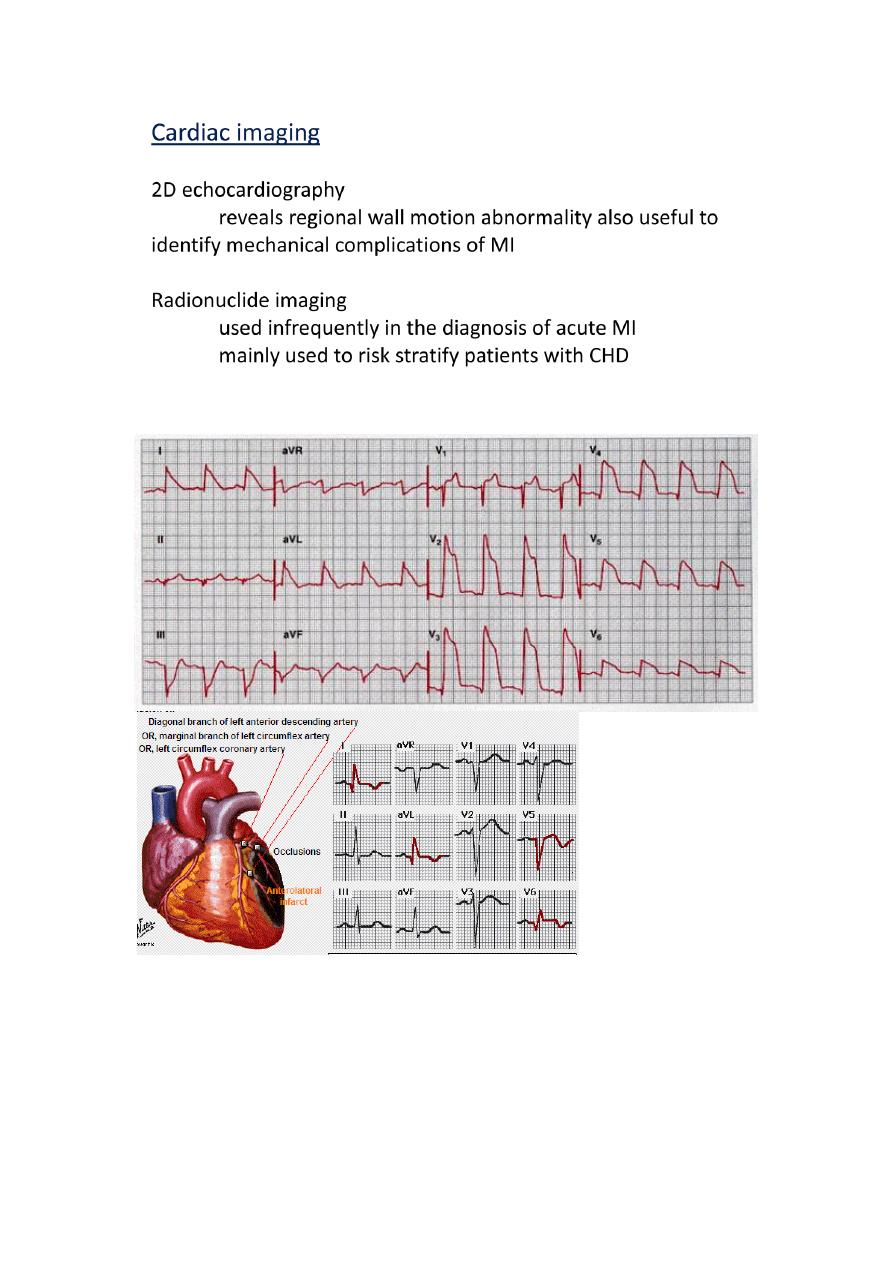
Acute Antero-Lateral MI
Severe Chest Pain – Why ?
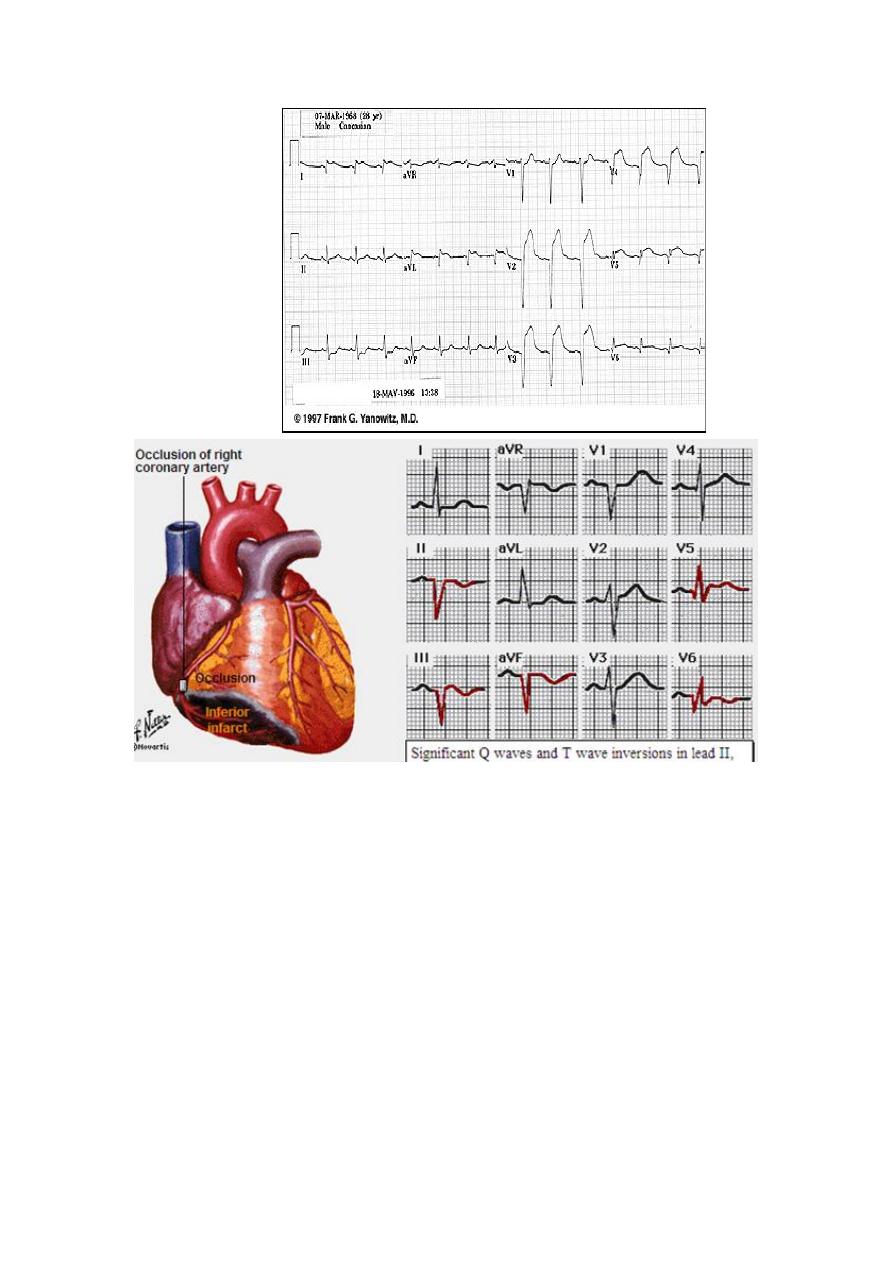
Acute Inferior wall MI
What is striking ?
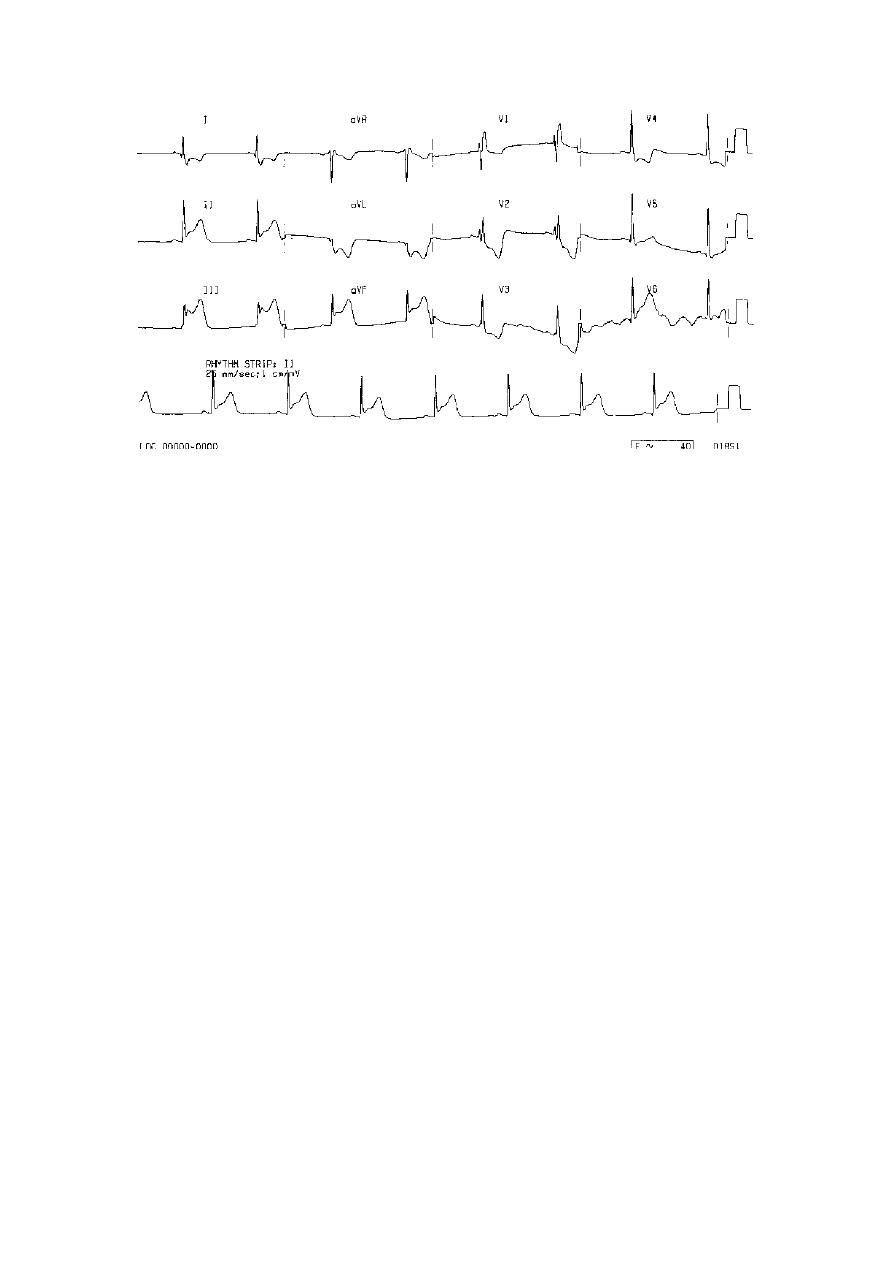
Where are the ST ↑ ?
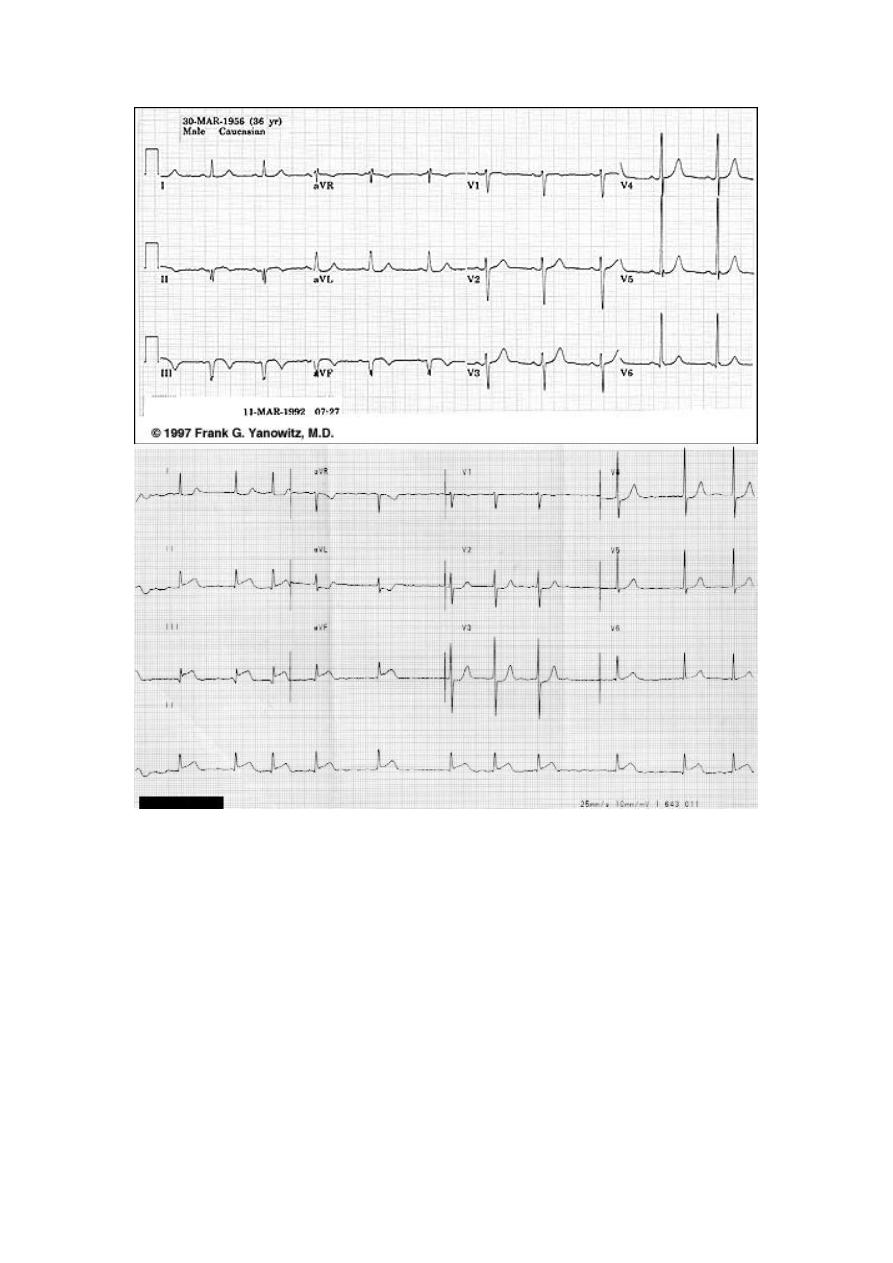
What changes we see ?
Why Acute changes disappeared
Guess How Old is this MI !
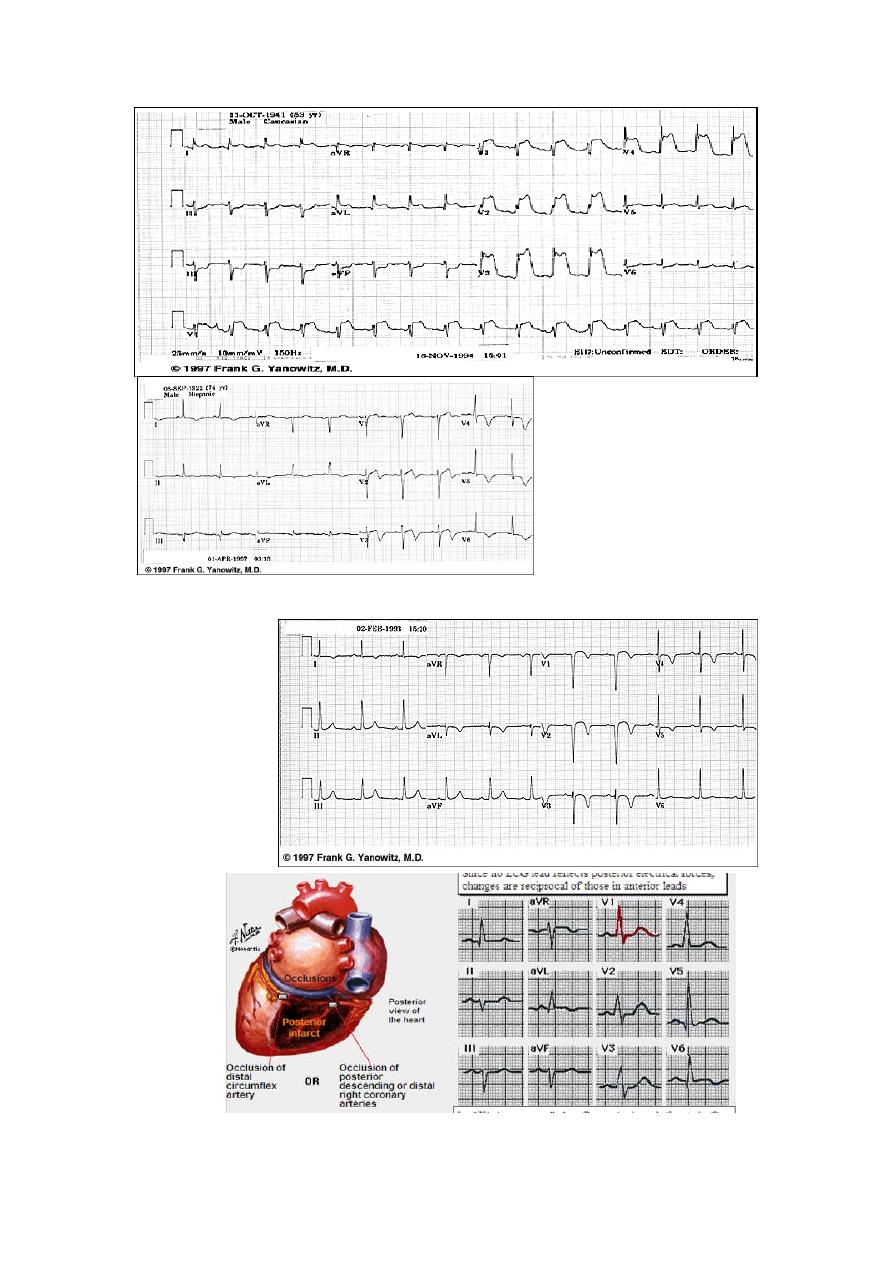
Acute True Posterior
MI
Decipher V1,
V2, V3
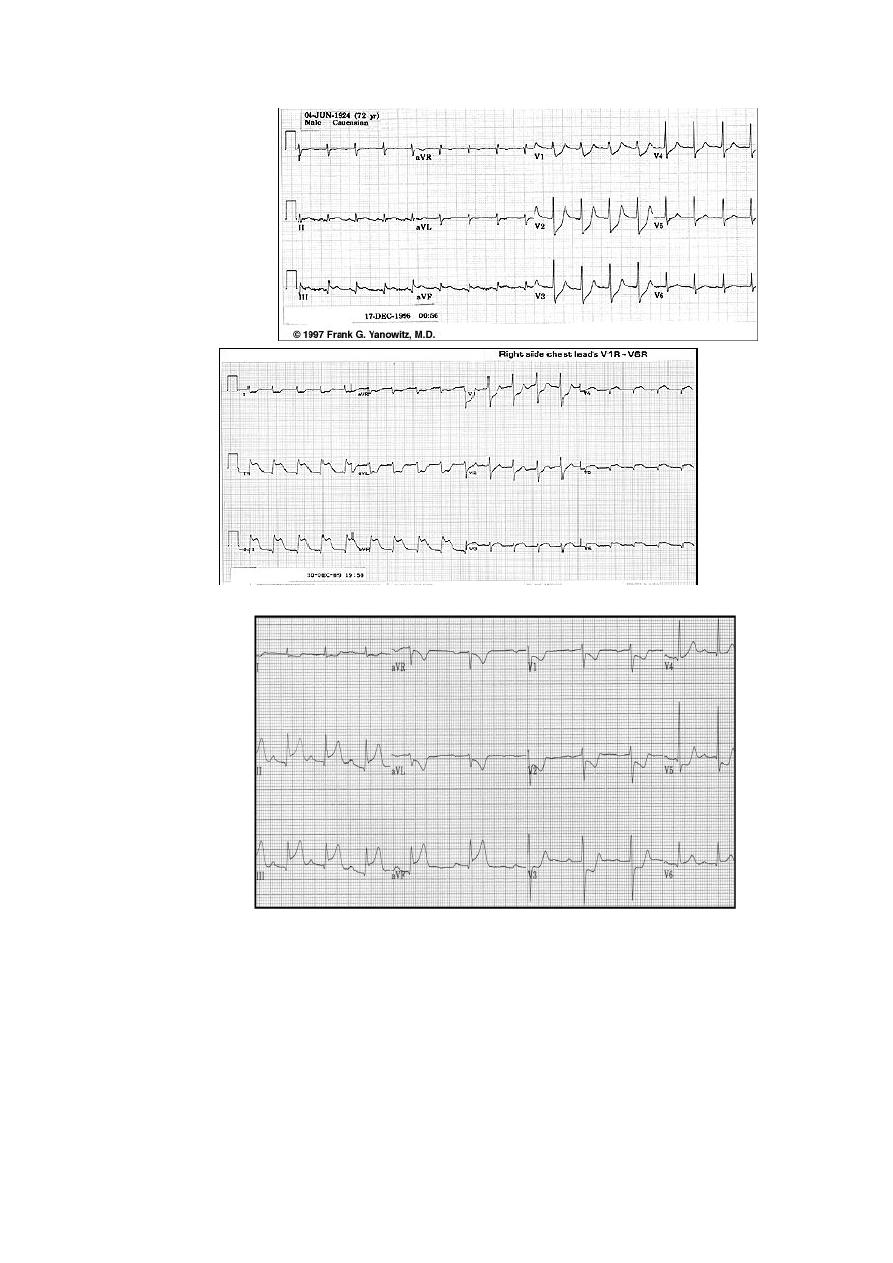
Identify the Double
wall MI
Inferior STEMI + Hypotension = ??
Look at the Right
Chest Leads
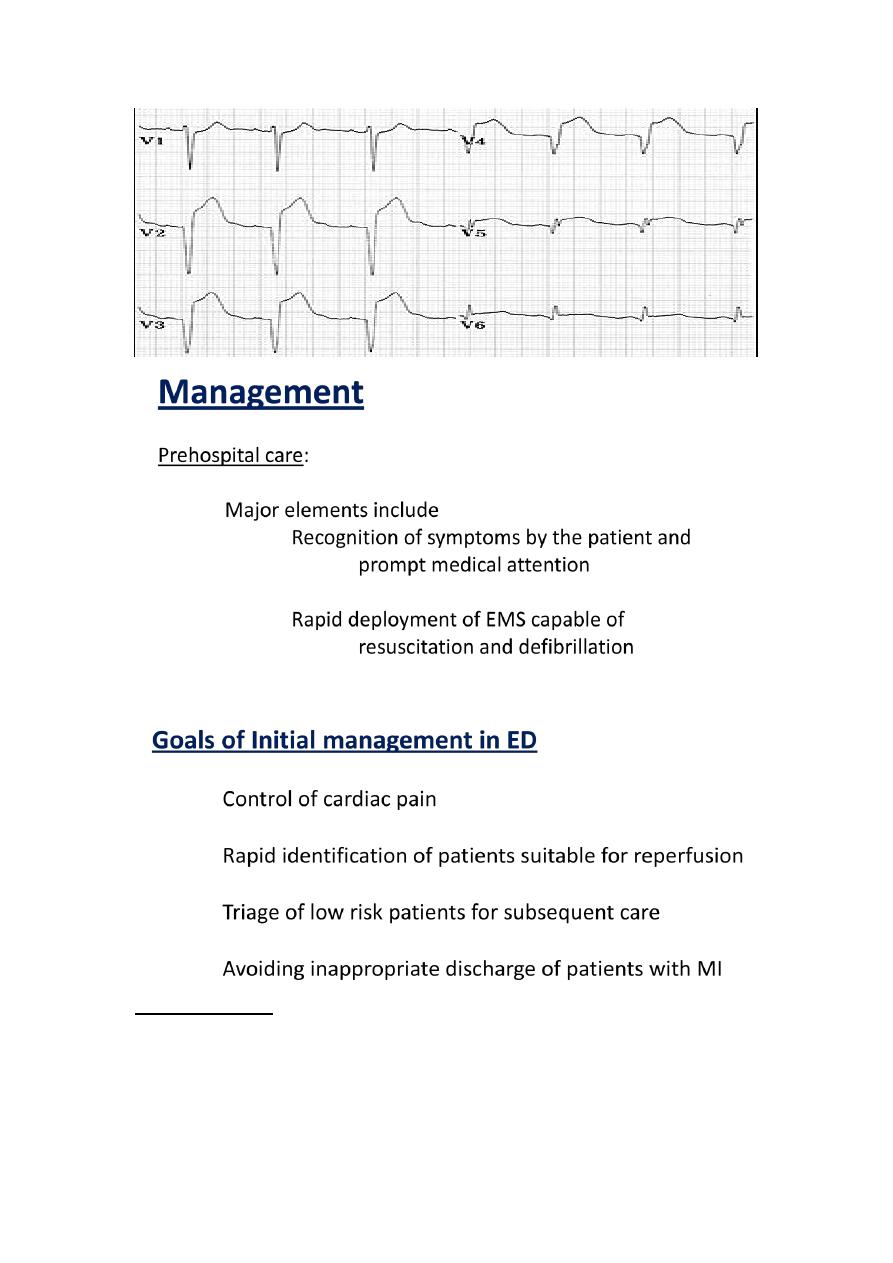
Initial management
•
Focused history and Focused examination
•
Reassurance
•
Ensure IV access + Basic investigations

•
aspirin + Clopidogril
chewable
325 mg
-
Aspirin: 160
•
Oxygen by nasal cannula if hypoxemia is present
•
Sublingual nitroglycerine followed by IV infusion if needed
•
Intravenous beta blockers (decrease myocardial oxygen demand, control chest pain
and reduce mortality)
•
in small doses)+ Metelopromide
given IV
Morphine for pain relief (
•
Monitor
•
12 Leads ECG
•
Consider Reperfusion
Reperfusion therapy
Primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI
Thrombolysis.
Absolute Contraindications
Any prior intracranial hemorrhage
Known structural cerebral vascular lesion (e.g., AV malformation)
Malignant intracranial neoplasm
Ischemic stroke in last 3 months
Suspected aortic dissection
Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis
Closed head or facial trauma in last 3 months
Relative Contraindications
Recent (3 weeks) major surgery
Recent (3 weeks) trauma
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation of >10min
BP > 180/110
Ischemic stroke more than 3 months old
Internal bleeding in last month
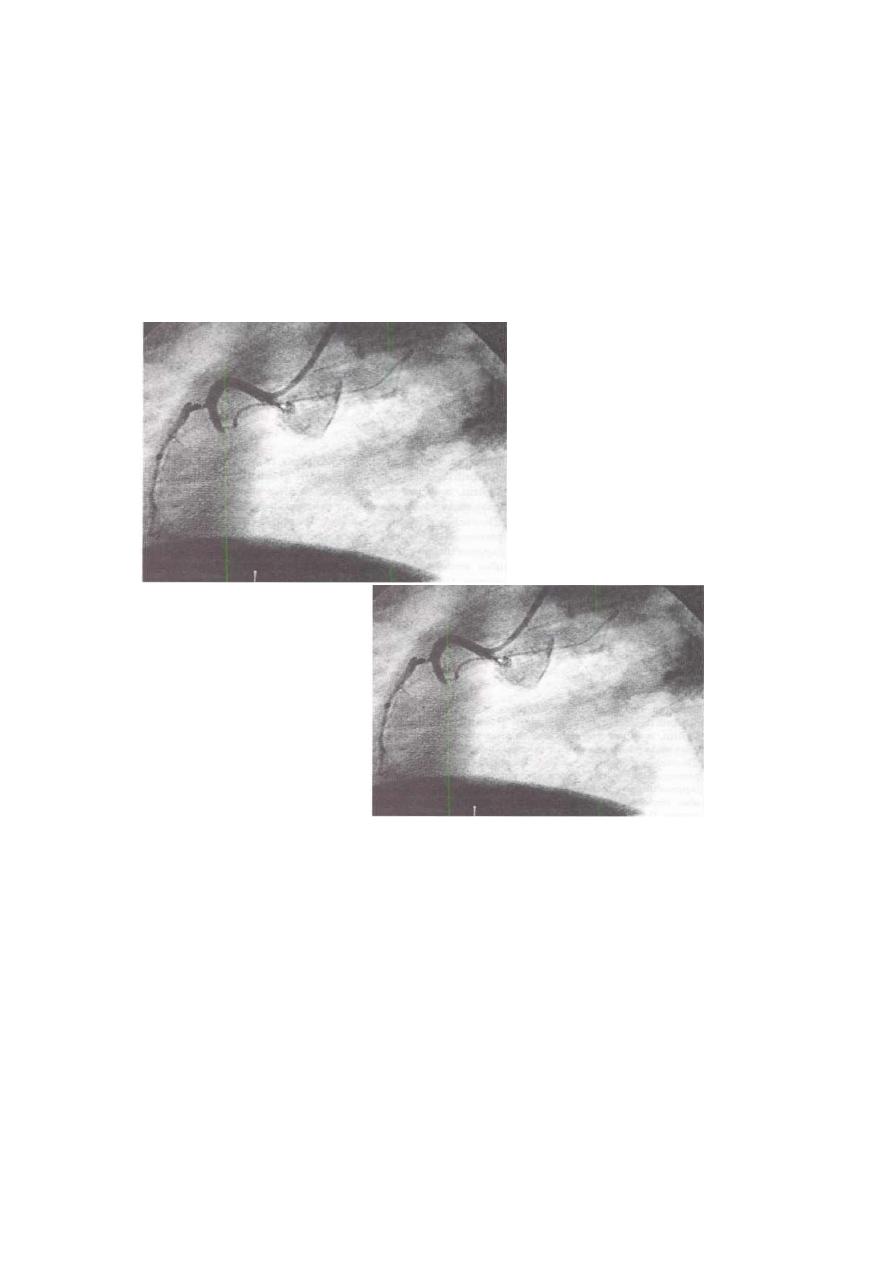
Noncompressible vascular punctures
For streptokinase/Anistreplase: prior exposure or allergy
Pregnancy
Active peptic ulcer
Currently on anticoagulants (sodium warfarin, Coumadin); the higher the INR, the
higher the risk
Complications of acute coronary
syndrome
Arrhythmias VF,AF, BRADYCARDIA
Ischemia
Acute circulatory failure
Pericarditis
Mechanical complications
Embolism
Impaired ventricular function HF
Ventricular aneurysm
Maintenance Therapy
Life style changes
Aspirin
Clopidogril
B blocker
ACE inhibitors
Calcium channel blocker
Statins ( Antilipids
Normal initial ECG exclude STEMI??
23 min.
later
1 hr post revascularization
