1
Fifth stage
Psychiatry
Lec-13
.د
الهام
17/4/2016
Developmental Disease
Addiction is a Developmental Disease: It Starts Early
Basic Science Tells Us that Adolescents’ Brains Are Still Developing…
When Reading Emotion…Adults Rely More on the Frontal Cortex, While Teens Rely
More on the Amygdala
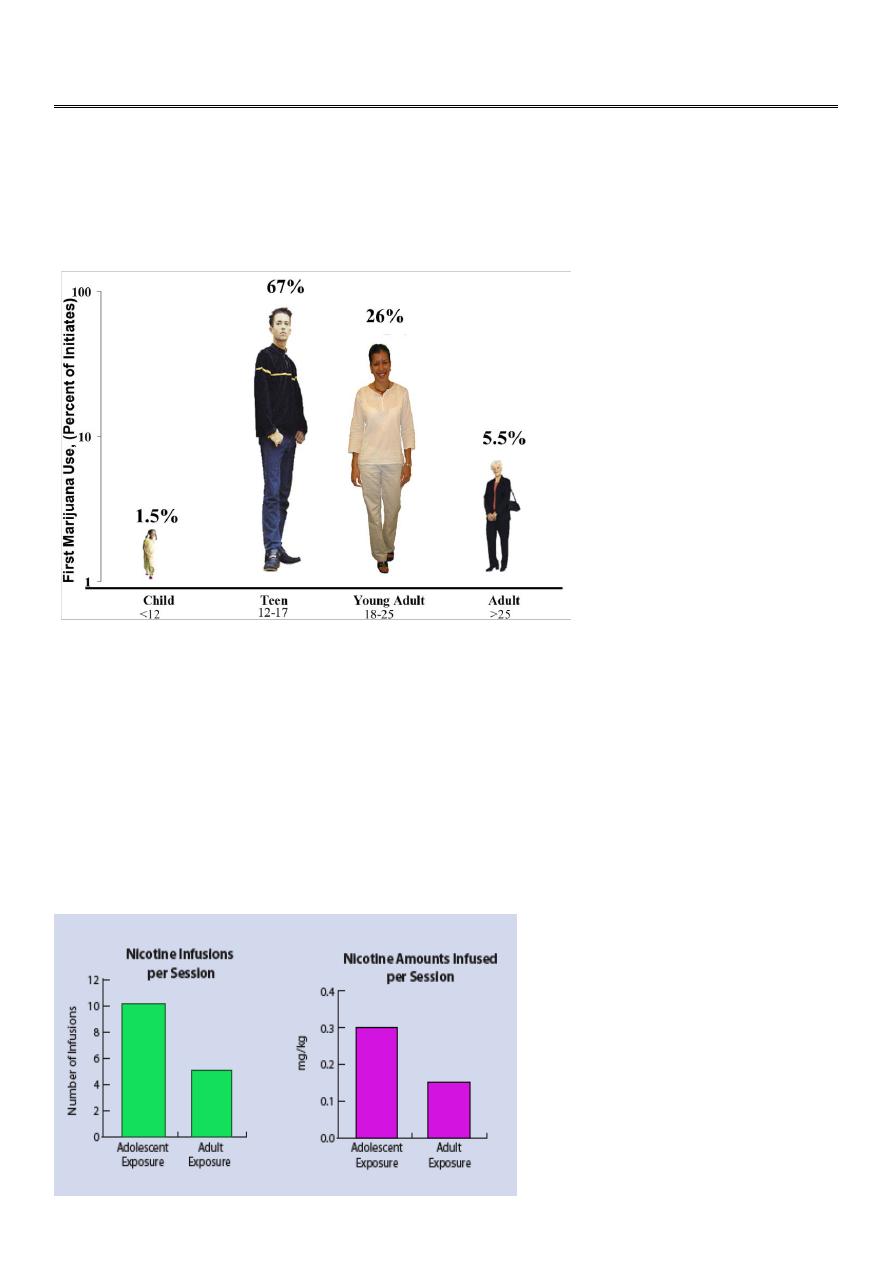
Do Adolescents React Differently than Adults to Substances of Abuse?
Rats Exposed to Nicotine in Adolescence Self-Administer More Nicotine Than Rats First
Exposed as Adults
2
Do We Need Fundamentally Different Strategies At Different Stages of Adolescence?
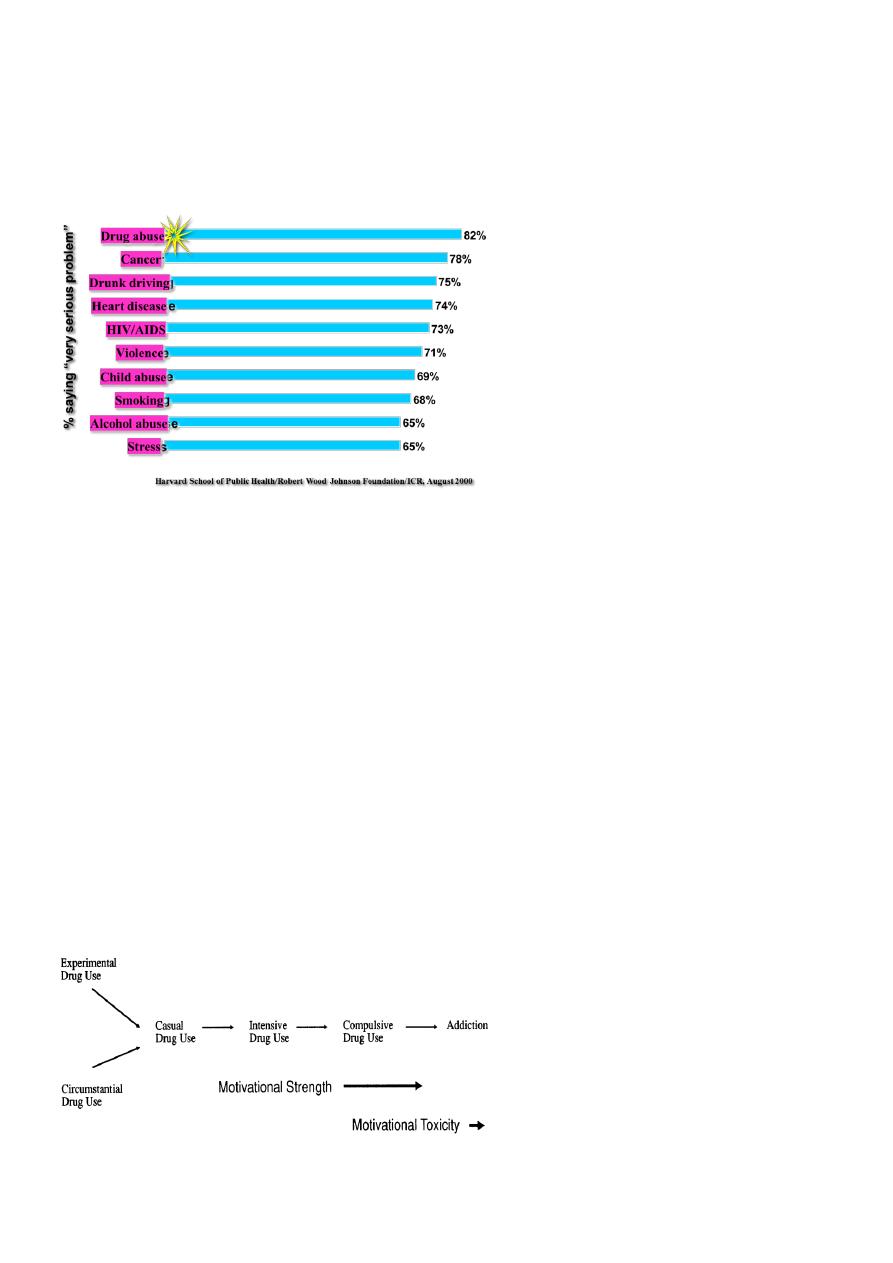
Americans’ Views of the Seriousness of Health Problems
(Top 10 of 36 Problems)
Definitions:
Drug Use
o Taking a psychoactive substance for non-medical purposes, out of curiosity
Drug Abuse
o Drug use that leads to problems (e.g. loss of effectiveness in society;
behavioral psychopathology, criminal acts)
Drug Dependence
o A maladaptive pattern of drug use leading to clinically-significant
impairment or distress, associated with difficulty in controlling drug-taking
behavior, withdrawal, and tolerance
o The state of needing a drug to function within ‘normal limits’
Nature of Addiction - a continuum of use?
However, addiction is more than mere drug use…
3
DSM-IV Criteria for Substance Dependence:
A maladaptive pattern of substance use, leading to clinically significant impairment or
distress, as manifested by three (or more) of the following, occurring at any time in the
same 12 month period:
• Tolerance
• Withdrawal
• Substance taken in larger amounts or over a longer period than intended
• Persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control substance use
• Great deal of time spent in activities necessary to obtain substance, use substance
(e.g., chain smoking), or recover from effects
• Important social, occupational, or recreational activities given up or reduced because
of substance use
• Substance use continued despite knowledge of persistent or recurrent physical or
psychological problem likely to have been caused or exacerbated by substance
Addiction Involves Multiple Factors:
Physical vs. Psychological Dependence:
• Physical Dependence
– Withdrawal symptoms in the absence of the drug
– Tolerance to its effects with repeated use
• Psychological Dependence
– “a relatively extreme, pathological state in which obtaining, taking, and
recovering from a drug represents a loss of behavioral control over drug taking

4
which occurs at the expense of most other activities and despite adverse
consequences” (Altman et al)
– “a situation where drug procurement and administration appear to govern the
organism’s behavior, and where the drug seems to dominate the organism’s
motivational hierarchy” (Bozarth)
Physical Dependence or Withdrawal Model
(Negative Reinforcement):
• Some drugs produce physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation
of drug-taking.
– Withdrawal symptoms are produced by the body in order to compensate for
the unusual effects of the drug.
– Withdrawal symptoms are generally the opposite of the effect produced by the
drug.
• Addicts continue to use drugs in order to avoid withdrawal.
• Over time, drugs no longer have the same rewarding effects - they merely allow the
person to feel “normal.”
Positive Incentive (Hedonic) Models
(Positive Reinforcement):
• Drugs produce pleasure - a “high.”
• Some drugs provide indirect positive incentive - they disinhibit behavior that is
normally suppressed (e.g., alcohol and social skills).
• Most drugs of abuse stimulate the brain’s reward circuits.
– All known drugs of abuse stimulate release of DA/opioids in the nucleus
accumbens
– Animals will work to micro-inject drugs of abuse and electrically stimulate the
same parts of the brain
– Normal rewards (food, drink, sex) also stimulate DA release
5
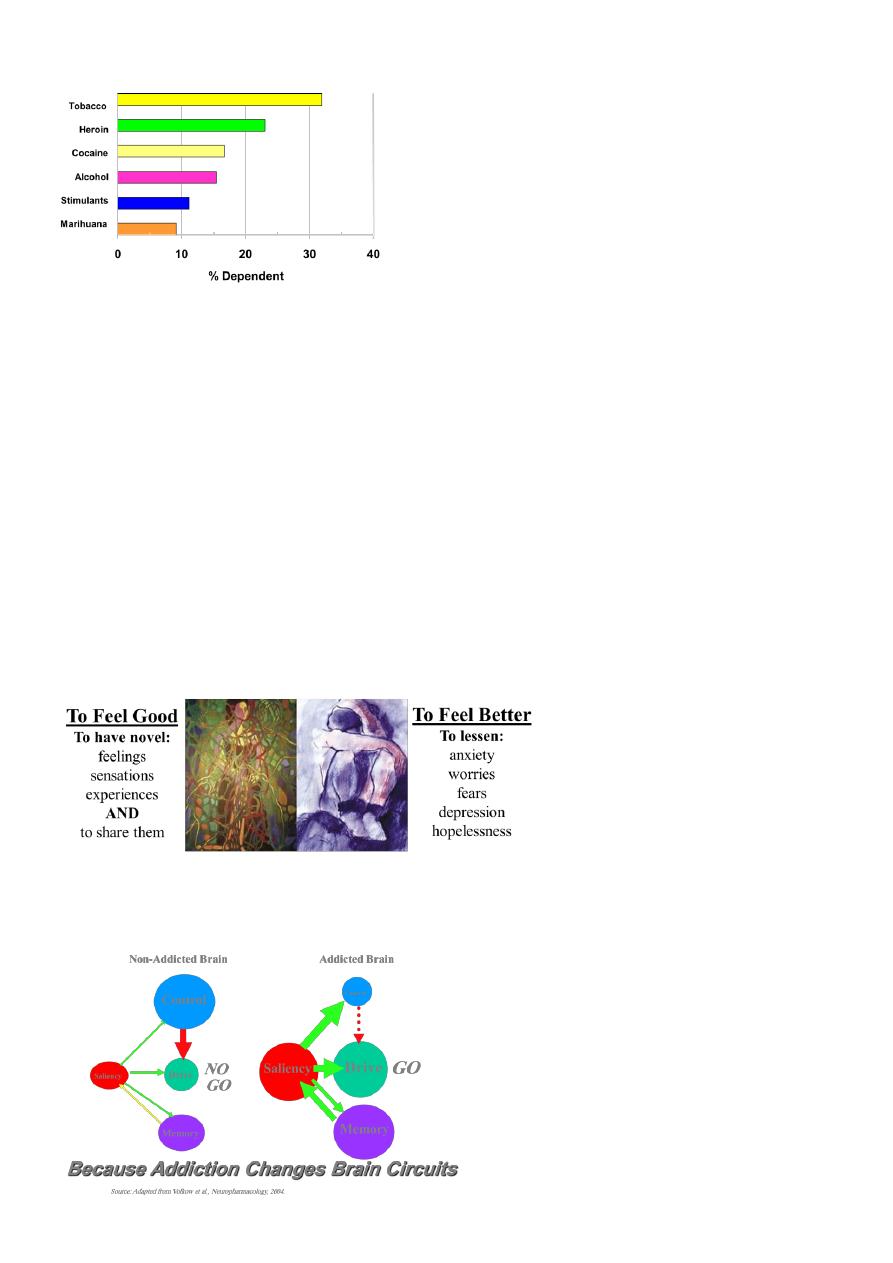
Drug Dependence Among Ever-Users:
Why do Mental Illnesses and Substance Abuse Co-occur?
• Self-medication hypothesis
– substance abuse begins as a means to alleviate symptoms of mental illness
• Causal effects of substance abuse
– Substance abuse may increase vulnerability to mental illness
• Common or correlated causes
– the life processes and risk factors that give rise to mental illness and substance
abuse may be related or overlap
Why Do People Take Drugs in The First Place?
Why Can’t Addicts Just Quit?

6
Treating a Biobehavioral Disorder Must Go Beyond Just Fixing the Chemistry
But, drug addiction is a chronic illness with relapse rates similar to those of hypertension,
diabetes, and asthma
Drug Use Has Played a Prominent Role in the HIV/AIDS Epidemic In Several Ways:
Disease Transmission
• IV Drug Use
• Drug User Disinhibition Leading to High Risk Sexual Behaviors
Progression of Disease
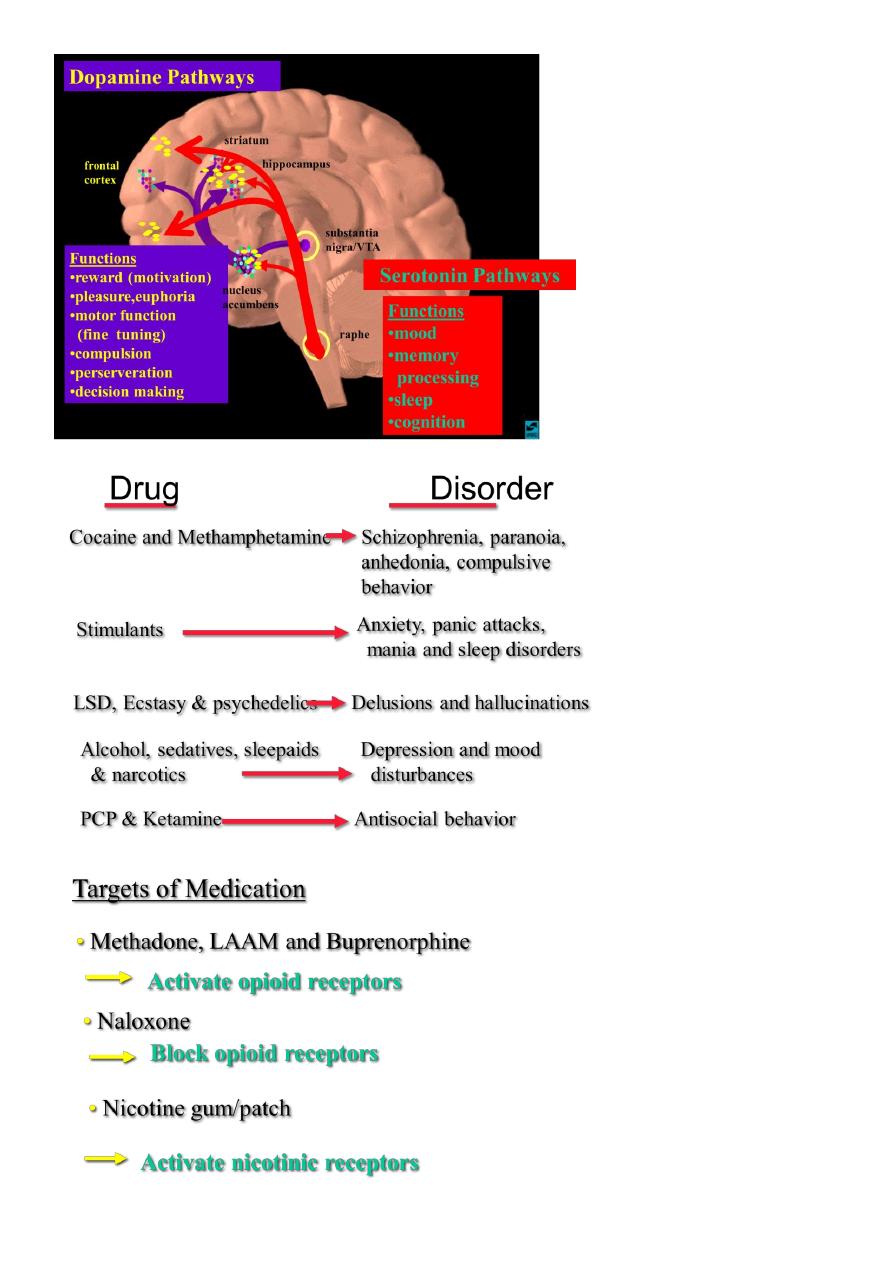
7
