Basics of RNA structure and modeling
Dr. MAHA SMAISMTranslation - making proteins
Nuclearmembrane
Transcription
RNA ProcessingTranslation
DNAPre-mRNA
mRNA
Ribosome
ProteinEukaryotic Cell
RNA types & functions• Types of RNAs
• Primary Function(s)• mRNA - messenger
• Transfers genetic information from genes to ribosomes to synthesize protein
• rRNA - ribosomal
• Provides structural framework for ribosomes & catalytic role
• t-RNA - transfer
• Transfers a.a to mRNA for synthesis of protein.
• hnRNA - heterogeneous nuclear
• precursors for mRNAs & other RNAs
• scRNA - small cytoplasmic
• involved in selection of protein for export ,signal recognition particle (SRP)
• snRNA - small nuclear
• snoRNA - small nucleolar
• mRNA processing, poly A addition <catalytic>
• rRNA processing/maturation/methylation
• regulatory RNAs RNA
• regulation of transcription and translation, other??
Major Types of RNA
Three types of RNA:
A. messenger RNA (mRNA)
B. transfer RNA (tRNA)C. ribosome RNA (rRNA)
Remember: all produced in the nucleus!rRNA
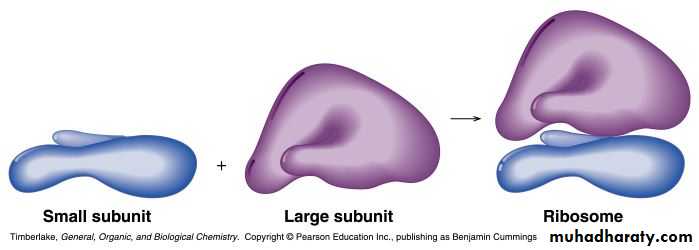
Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis- they consist of ribosomal RNA (65%) and proteins (35%)
- they have two subunits, a large one and a small one
rRNA functions
Structural
rRNA is the major structural component of ribosomesBUT - its role is not just structural, also:
Catalytic
RNA in the ribosome has peptidyltransferase activityEnzymatic activity responsible for peptide bond formation between amino acids in growing peptide chain
Ribosomes
P
Site
A
Site
Large
subunit
Small subunit
mRNA
AU
G
C
U
A
C
U
U
C
G
Transfer RNA
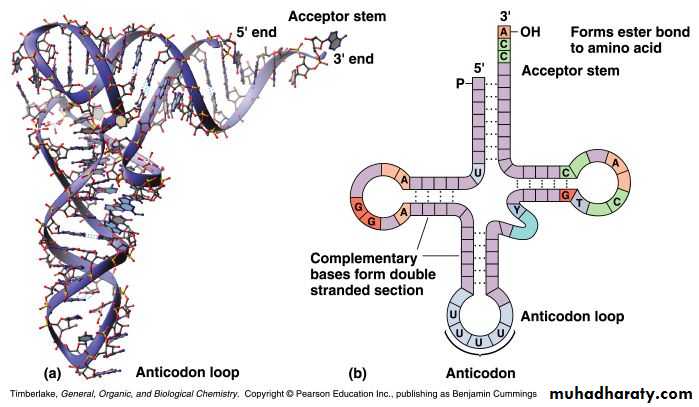
Transfer RNA- Consists of a single RNA strand that is only about 80 nucleotides long
translates the genetic code from the mRNA and brings specific amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis
Each amino acid is recognized by one or more specific tRNA
Each carries a specific amino acid on one end and has an anticodon on the other end
tRNA has a tertiary structure that is L-shaped
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
amino acid
attachment siteU
A
anticodon
methionineC
pre-RNA molecule
intronintron
exon
exon
exon
exon
exon
exonMature RNA molecule
exon
exonexon
intronintron
splicesome
splicesomeIntrons are pulled out and exons come together.
End product is a mature RNA molecule that leaves the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
methionineglycine
serineisoleucine
glycinealanine
stopcodon
protein
A
U
G
G
G
C
U
C
C
A
U
C
G
G
C
G
C
A
U
A
A
mRNA
start
codon
Primary structure of a protein
aa1
aa2
aa3
aa4
aa5
aa6
peptide bonds
codon 2
codon 3codon 4
codon 5
codon 6
codon 7
codon 1
codon 5
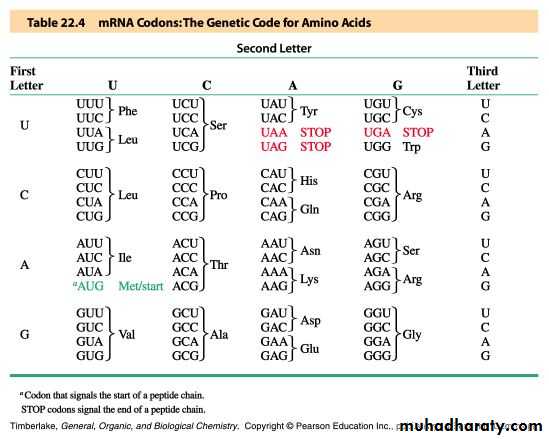
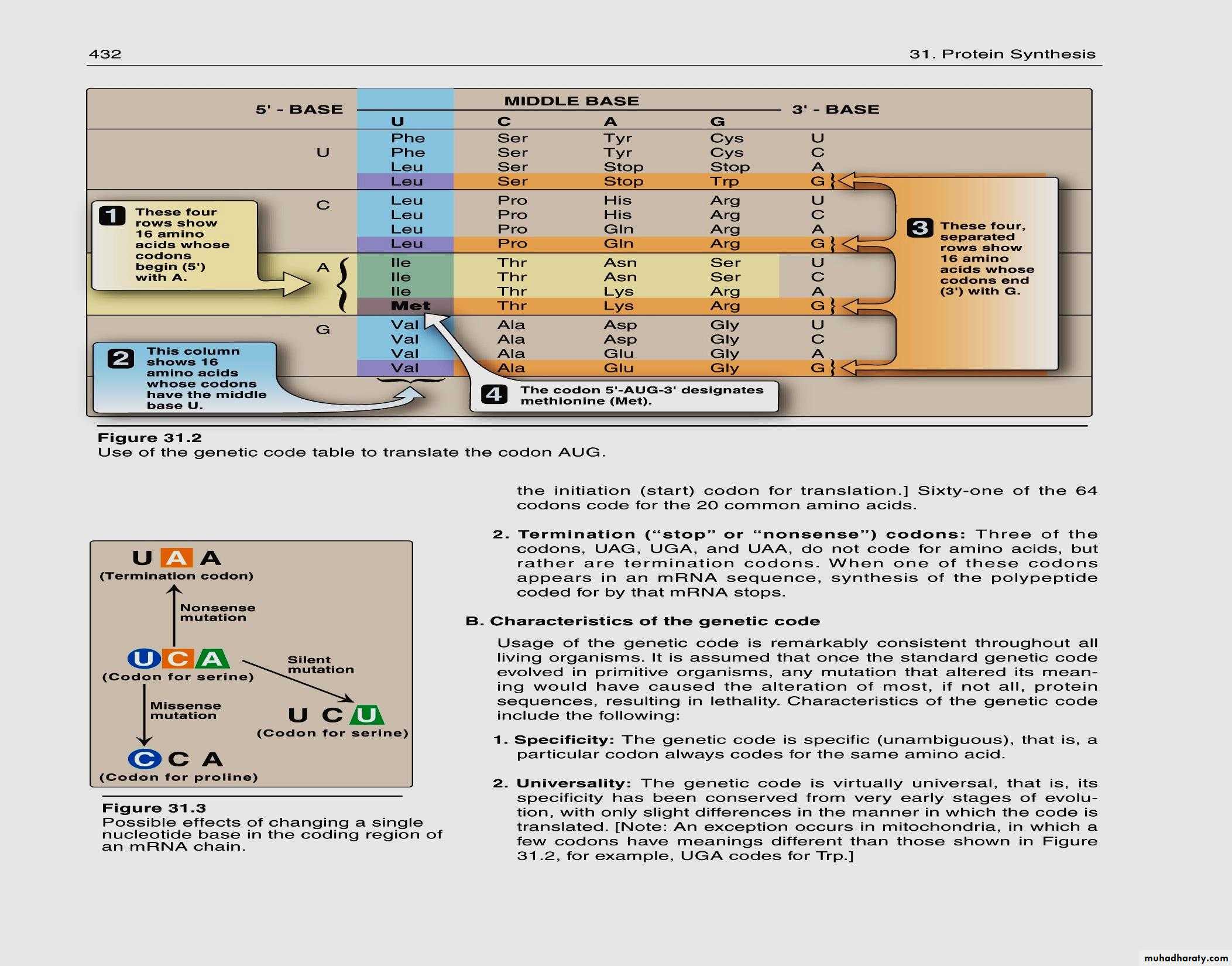
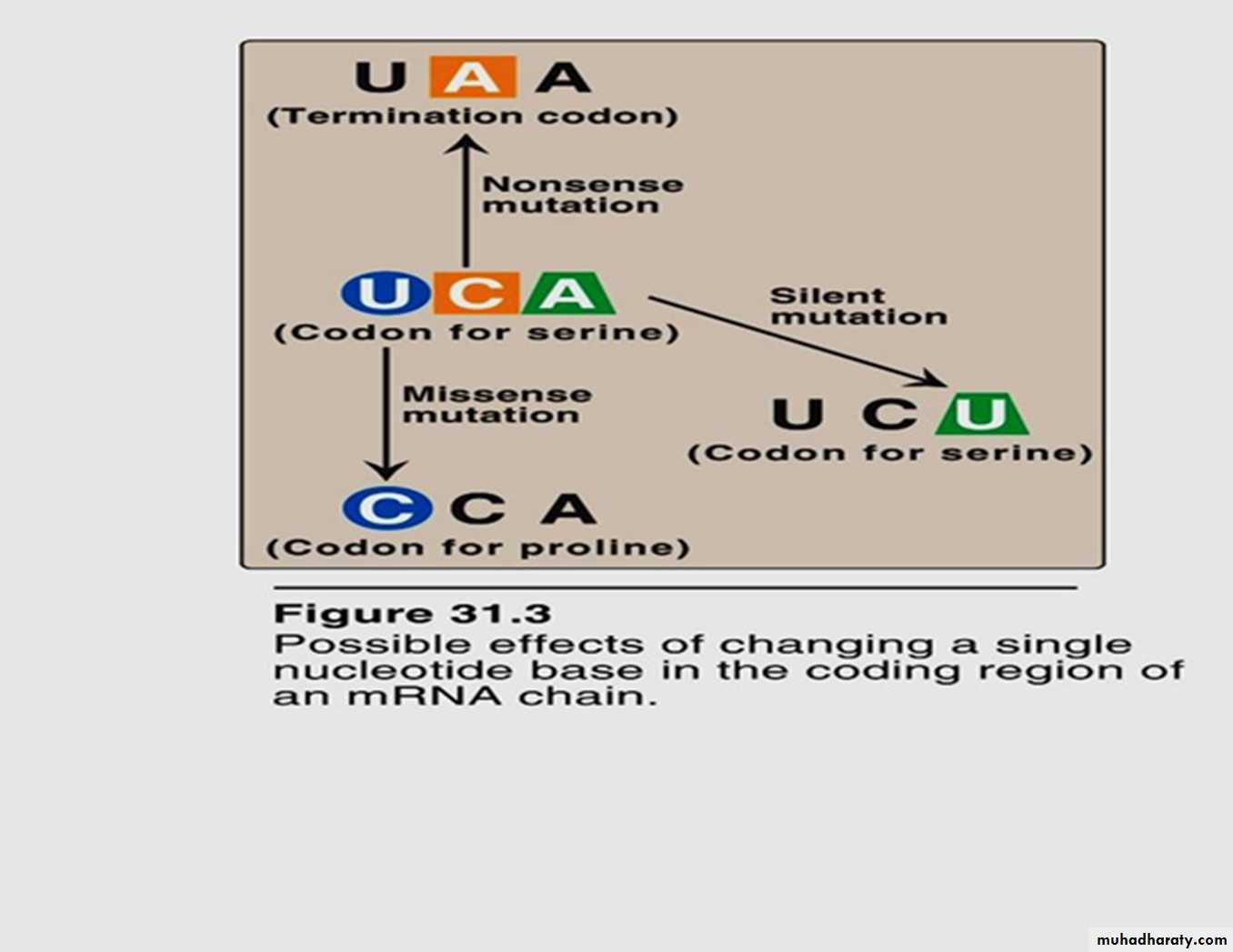
The Genetic Code
The genetic code is found in the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA that is transcripted from the DNAA codon is a triplet of bases along the mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid
Each of the 20 amino acids needed to build a protein , has at least 2 codons
There are also codons that signal the “start” and “end” of a polypeptide chain
mRNA Codons and Associated Amino Acids
Translation and tRNA Activation
Once the DNA has been transcribed to mRNA, the codons must be tranlated to the amino acid sequence of the proteinThe first step in translation is activation of the tRNA
Each tRNA has a triplet called an anticodon that complements a codon on mRNA
A synthetase uses ATP hydrolysis to attach an amino acid to a specific tRNA
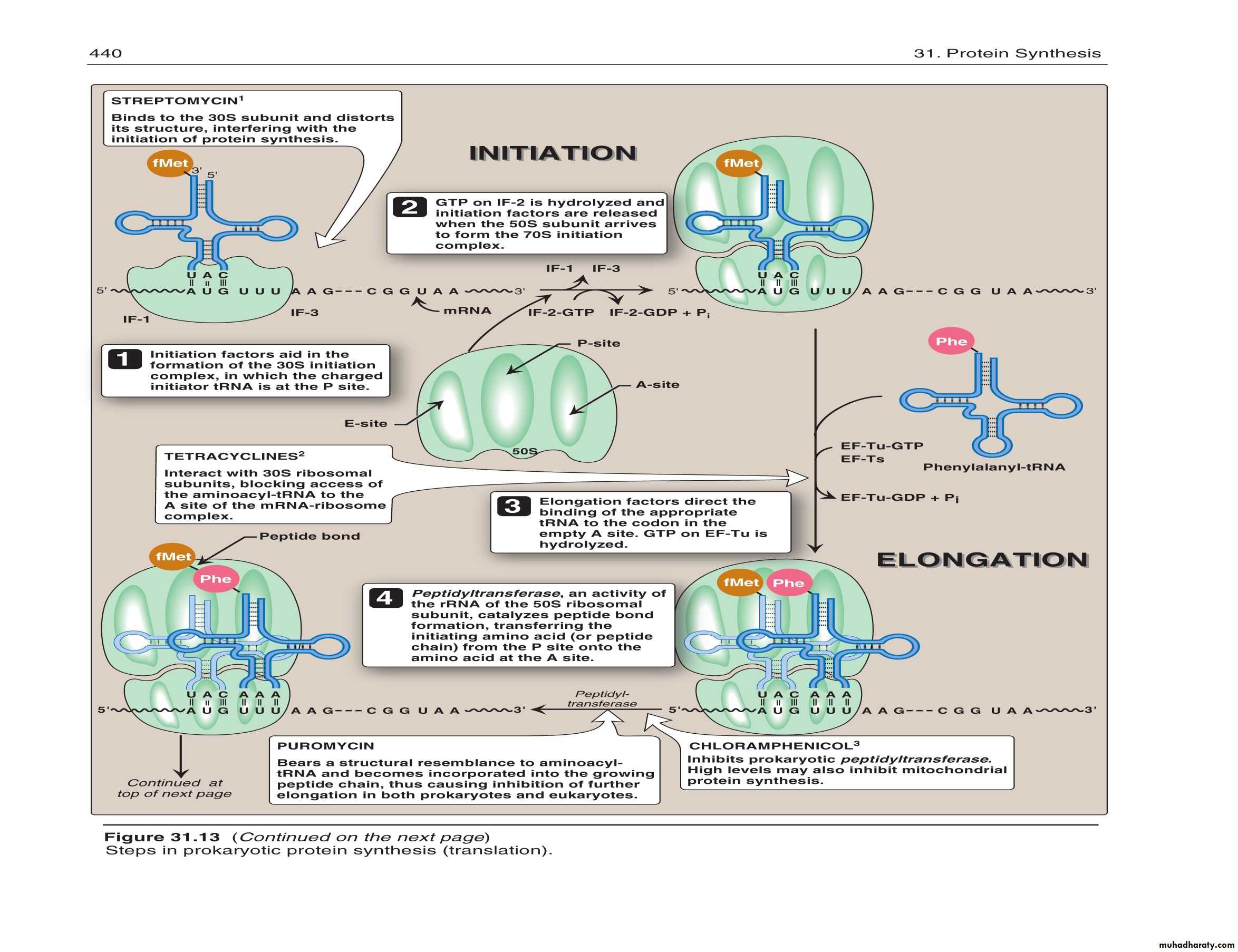
Initiation and Translocation
Initiation of protein synthesis occurs when a mRNA attaches to a ribosome
On the mRNA, the start codon (AUG) binds to a tRNA with methionine
The second codon attaches to a tRNA with the next amino acid
A peptide bond forms between the adjacent amino acids at the first and second codons
The first tRNA detaches from the ribosome and the ribosome shifts to the adjacent codon on the mRNA (this process is called translocation)
A third codon can now attach where the second one was before translocation
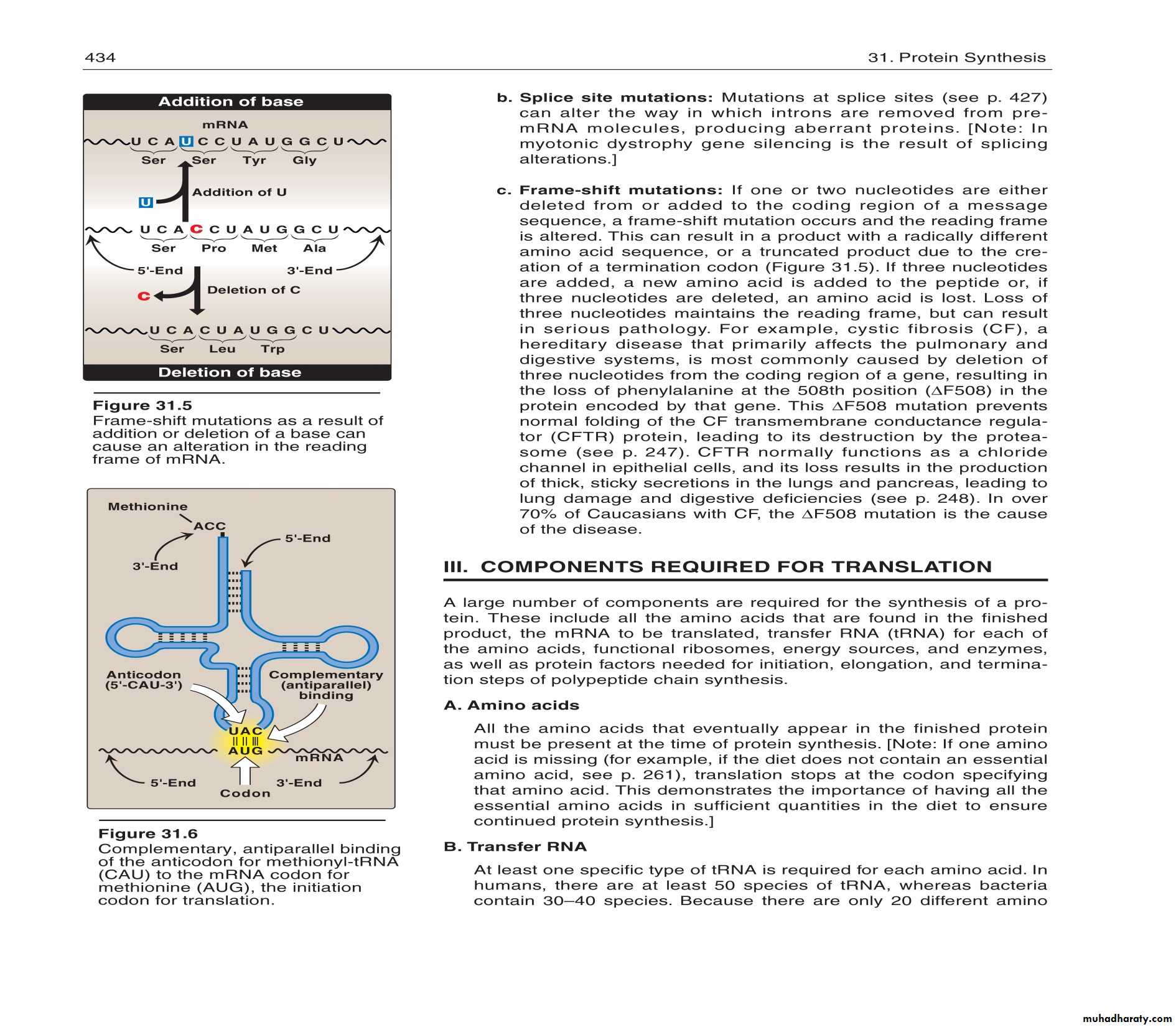
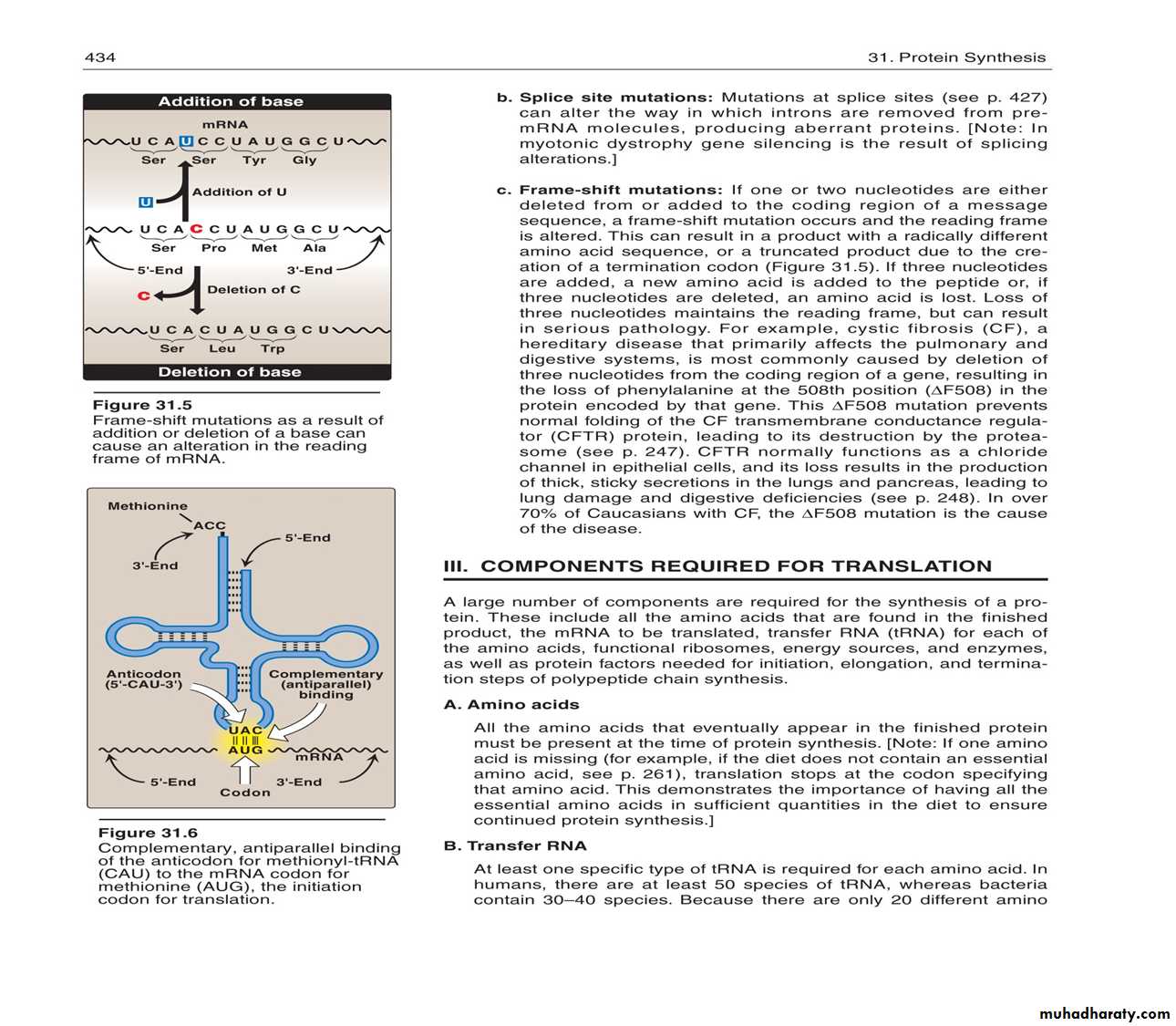
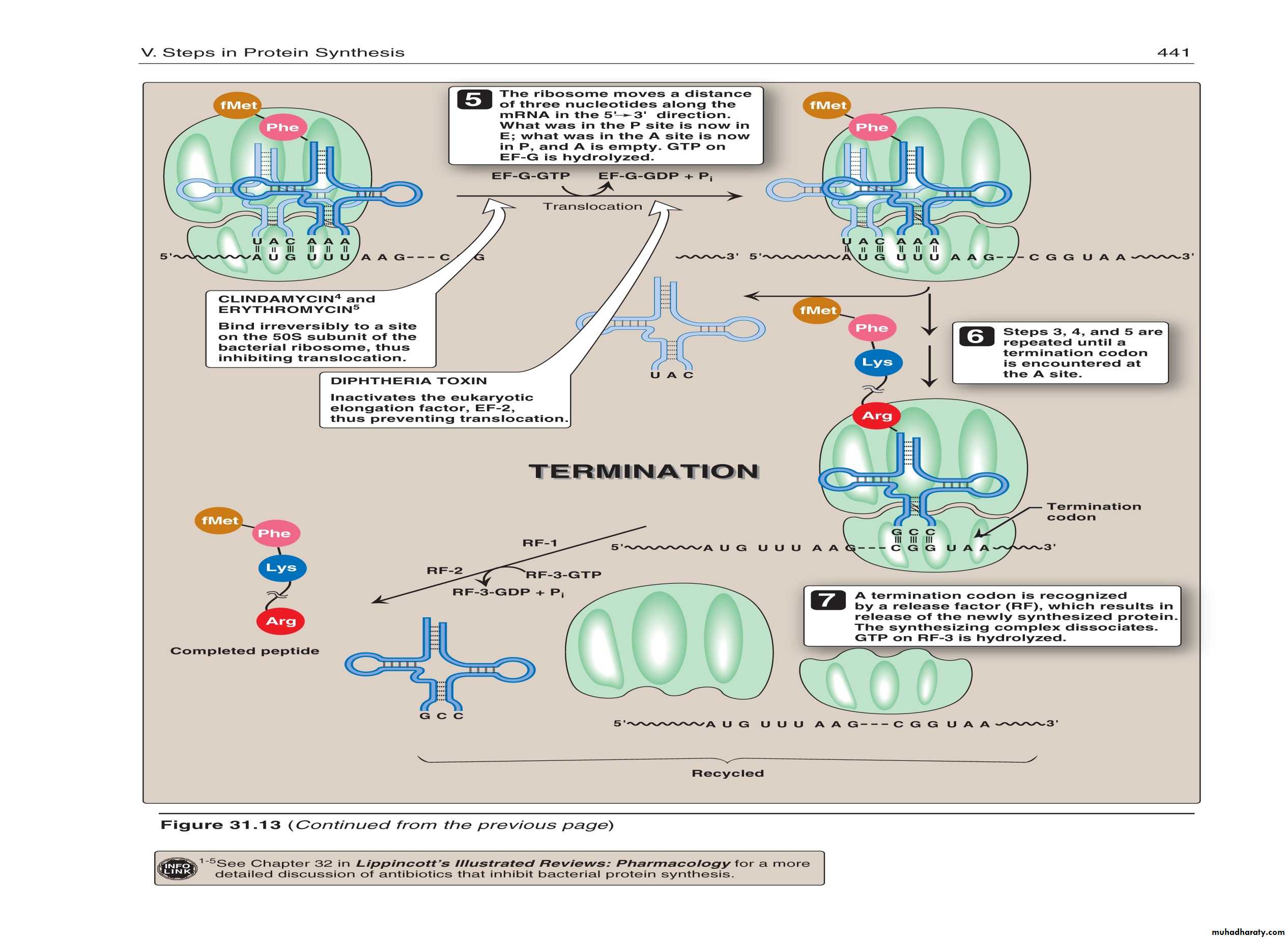
Termination
After a polypeptide with all the amino acids for a protein is synthesized, the ribosome reaches the the “stop” codon: UGA, UAA, or UAGThere is no tRNA with an anticodon for the “stop” codons
Therefore, protein synthesis ends (termination)
The polypeptide is released from the ribosome and the protein can take on it’s 3-D structure
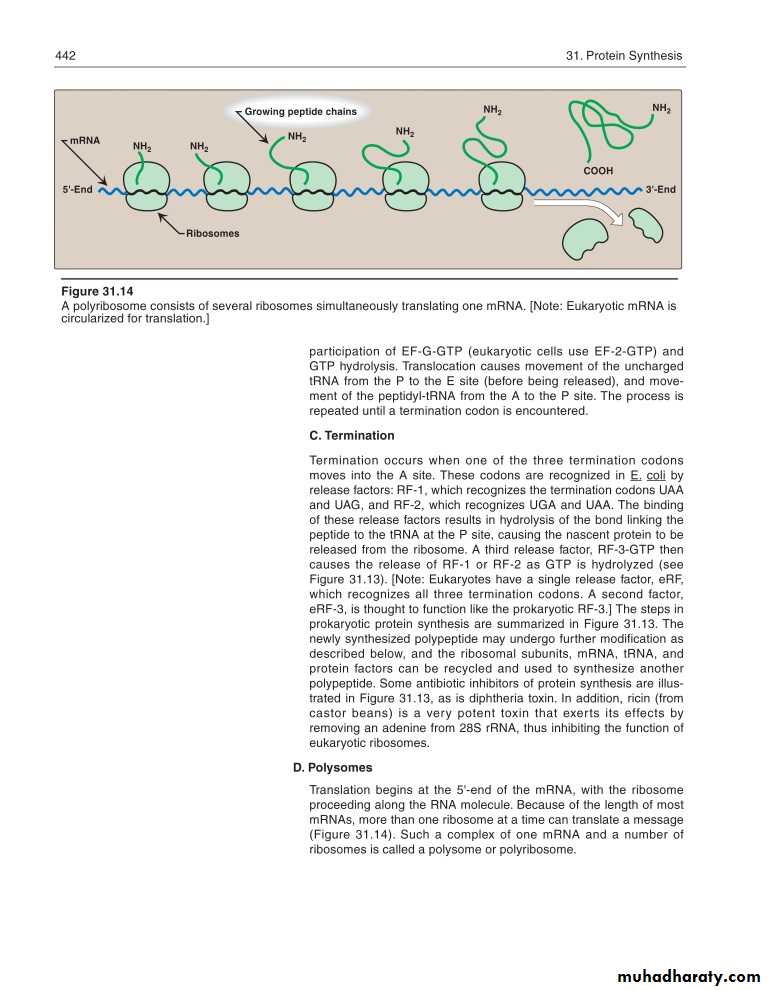
(some proteins begin folding while still being synthesized, while others do not fold up until after being released from the ribosome)