ORAL HABITS
Dr.Omar S.M.J.AliOral habits are habits that frequently children acquire that may either temporarily or permanently be harmful to dental occlusion for and to the supporting structures.
When habit cause defect in orofacial structure it is termed as pernicious oral habit.
ORAL HABITS
Introduction
It is observed that most children below 3 year suck their thumbs & finger.
Thumb sucking in infants is common and is meant to meet both psychological and nutritional needs.Most children discontinue the habits 3-4 year of age.
A study by Nowak and Warren (2000) found that 50% of children discontinued use by 28 months of age, 71% discontinued use by 36 months of age, and 90% discontinued use by 48 months.
If habit continues beyond this period there is definite chance that may lead to dentofacial changes.
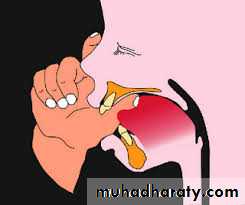
THUMB SUCKING
Introduction:-
Diagnosis of thumb sucking
• History• Determine the psychological component involved.
• Question regarding the frequency, intensity and duration of habit.
• Enquire the feeding patterns, parental care of the child.
• The presence of other habits should be evaluated.
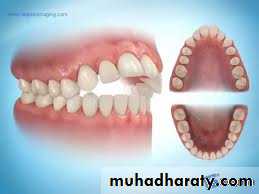
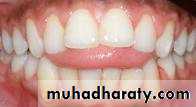
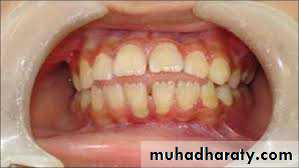
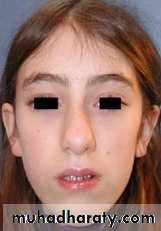
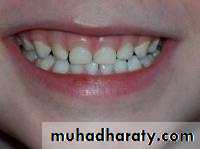
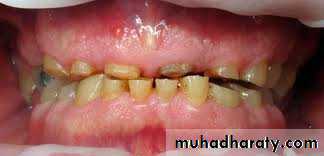
Labial flaring of maxillary anterior teeth.
Lingual collapse of mandibular anterior teethIntra oral
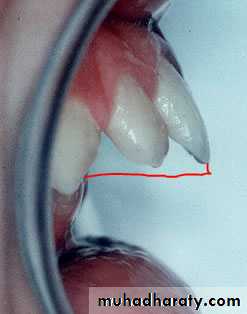
Increased overjet (The distance between the front surface of the lower incisors and the front surface of the upper incisors. The front surface of the upper incisors is usually 2-4 mm ahead of the front surface of the lower incisors)
Intra oral
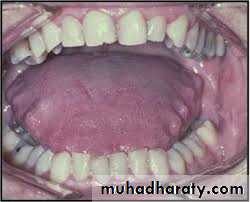
Tongue placed inferiorly leading to posterior cross bite due to maxillary arch contraction.
Intra oral
High palatal vault.
Intra oralFungal infection on thumb
Extra oral• Extraoral Examination :-
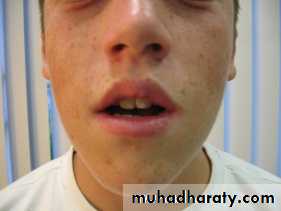
• Lips• Upper lip may be short and hypotonic.
• Lower lip is hyperactive .
• Facial form analysis:-
• Check for mandibular retrusion.
• Maxillary protusion.
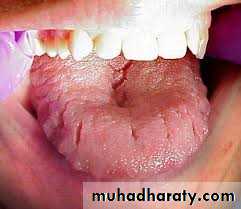
• States tongue thrust as forward movement of tongue tip between the teeth to meet the lower lip during deglutition and in sounds speech so that tongue becomes interdental.
Tongue thrusting
Definition:-Classification:-
• Physiologic:-
• This comprises the normal tongue thrust swallow of infancy.
• Habitual:-
• The tongue thrust swallow is present as a habit even after the correction of the malocclusion.
• Functional:-
• When the tongue thrust mechanism is an adaptive behaviour developed to achieve an oral seal, it can be grouped as functional.
• Anatomic:-
• Persons having enlarged tongue can have an anterior tongue posture.
•
(1) Retained infantile swallow:-
Retention of infantile swallow mechanism. With eruption of incisor at six months of age, tongue does not drop back as it should & continues to thrust forward.(2) Upper respiratory tract infection:-
Upper respiratory tract infection such as mouth breathing, allergies etc, promote forward movement of tongue due to pain.
It may also present due to physiological need to maintain adequate airway.
(3)Neurological disturbances:-
Hyposensitive palate, disruption of sensory control & co ordination of swallowing .
(4) Feeding practice:-
• Bottle feeding is more contributory than breast feeding to tongue thrust development.
Etiology :-
(5) Induced due to other oral habits :-
Thumb sucking & finger sucking may prevalent in many childrenHabits created malocclusion (anterior open bite)
Tongue is protrude between anterior teeth during swallowing,when habit corrected than change in protrusive tongue activity take place.(6) Heriditary
(7) Tongue size:- macroglossia can have an effect on the dentition.
• Facial form :- increase anterior facial height
• Intraoral• (1) Tongue posture:-
• Tongue tip at rest is lower because of anterior open bite present
• Tongue movement :-
• Movement is irregular from one swallow to another.
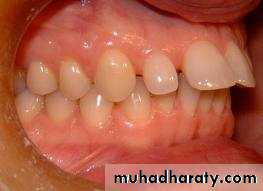
• Malocclusion:- In maxilla
• Proclination of maxillary anterior .
• An increase overjet
• Maxillary constriction
• Generalized spacing between teeth.
Clinical features :-
Extra oral-In Mandible :- Retroclination of mandible
Diagnosis :-
History :-
Determine swallow pattern of siblings & parents to check for hereditary etiologic factor.
Information regarding upper respiratory infection, sucking habits
Finally past & present information regarding the over all abilities , interest ,motivation of patient should be noted .
Examination :-
Patient seated upright :-A little water is placed in patient mouth & patient is asked to swallow it.
During normal swallowing pattern :-
Lip touch each other tightlyMandible rise as teeth are brought together
Facial muscle do not show any marked contraction.
During abnormal swallowing:-
Teeth are apart.Lip do not touch each other.
Facial muscles show marked contraction.
Definition:-
• Mouth breathing as habitual respiration through the mouth instead of the nose.Etiology:-
• It is estimated that 85% mouth breather suffer from some degree of nasal obstruction
• Developmental Anomalies like abnormal development of nasal cavities .
• Partial obstruction in deviated nasal septum and Localized benign tumor.
• Infection inflammation of nasal mucosa as:- Chronic allergic, chronic atrophic Rhinitis, Enlarged adenoid tonsils
• Traumatic injures of nasal cavity
• Genetic Pattern
Mouth breathing habits
• Classification:-
• Anatomic
• Mouth breather is one whose short upper lip does not permit complete closure
• Habitual
• Persistence of habit even after the elimination of obstructive cause
• Obstructive
• Increased resistance to complete obstruction of normal airflow to nasal passage
• Clinical Features:-
• Facial appearance of child with mouth breathing habit is termed as Adenoid facies.
• Long narrow face, narrow nose and nasal passage.
• Short upper lip.• Nose tipped superiorly
• Expressionless face.
• Dental effect (intra oral)
• Protusion of maxillary incisors
• Palatal vault is high.
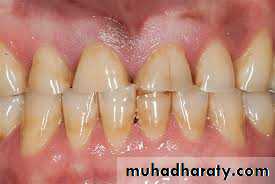
• Increase incidence of caries.
• Chronic marginal gingivitis.
• Examination:-
• Observe the patient unknowingly while at rest• In a nasal breather – lip touch lightly
• In mouth breather – Lip are kept apart.
• Patient asked to take deep breath
• Nasal breather keep the lip tightly closed
• Mouth breather take deep breath keeping mouth open.
Bruxism
• Definition:
• Given by Ramford 1966
Bruxism is habitual griding of teeth when the individual is not chewing or swallowing.
Classification:-
• Day time Bruxism.It can be conscious & subconscious and may along with parafunction habit such as chewing pencil, nails, cheek & lips• Night time Bruxism/Nocturnal Bruxism:-
It is subconscious griding of teeth characterized by rhythmic pattern of masseter muscle activity.
Etiology:-
• It was found in children with cerebral palsy & mental retardation.• Psychological:-
A tendency of grind teeth associated with feeling of hunger and aggression, hate,anxiety etc.
• Occlusal discrepancy
Improper interdigitation of teeth lead to bruxism.
• Systemic factor:- Mg++ deficiency may lead to bruxism.
• Genetic.
• Occupation:- Overenthusiastic student or competitive sports lead to clenching .
Clinical features:-
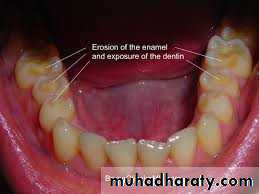
• Occlusal trauma:- occlusal surface is worn considerably with exposing dentin extreme sensitivity.• Toothache, mobility.
• Pain in TMJ
• Trauma to periodontium.
• Masticatory muscle soreness.
• Headache.
•
Lip Habits
Definition:-Habit involve manipulation of lips and perioral structure are termed as lip habits.
Etiology :- Malocclusion
HabitEmotional Stress
Lip biting
Classification:-
• Wetting the Lip with the tongue.
• Pulling the lip into mouth between the teeth.
•
Clinical features:-
Protrusion of upper anteriors & retrusion of lower anteriors.Lip trap
Muscular imbalance
Lower incisor collapse with lingual crowding
Mentolabial sulcus become accentuated.
It is most common habit in children
It is sign of internal tensionEtiology :-
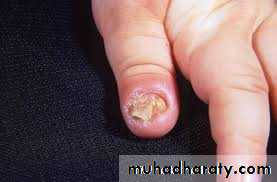
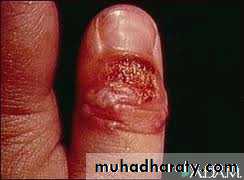
Persistence nail bitting may be indicative of emotional problem.Psychosomatic
Successor of thumb sucking.
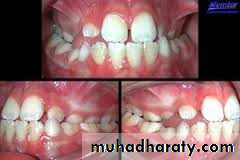
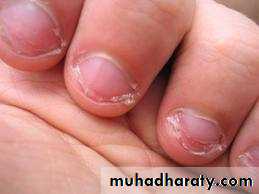
Clinical features:-
Crowding
Rotation
Alteration of incisal edge of incisor
Inflammation of nail bed.