ONCOLOGY2016-2017
BYDR. ATHL HUMO
Epidemiology
Cancer in patients younger than 20 yr of age is uncommon, it affect 1 in 500 by 15 year of age. Over all 5-year survival is 75%.leukemia is the most common malignancy in children followed by brain tumors ,then solid tumors like, Neuroblastoma, Willms T. lymphoma, bone tumors and retinoblastoma .
Preschool age < 5yr: ALL, Neuroblastoma, Willms, retinoblastoma.
School age: ALL, brain tumor.
Adolescent: ALL, Hodgkin lymphoma, bone tumor
Etiology
Involve an interaction between environmental factors (e.g. viral infection) and host genetic susceptibility (e.g. gene mutation).Clinical Presentations of Pediatrics Malignancy
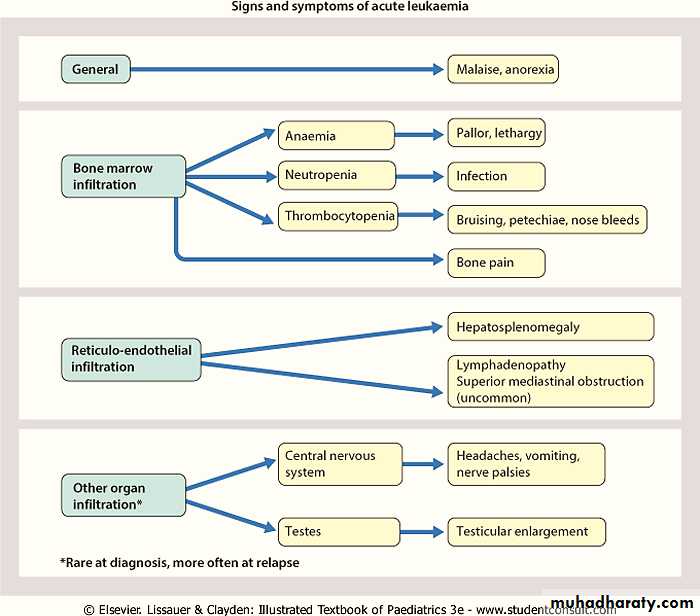
• Systemic: which is due to 1ry tumor, BM infiltration or metastasis any where. It include the followings:Fever, night sweats, fatigue, anorexia & weight loss.
Bone pain, limp, arthralgia(due to primary bone tumor, metastasis to bone).
Painless lymphadenopathy (Lymphoreticular malignancy, metastatic solid tumor)
Cutaneous lesion: bruising, petechiae.
Abdominal mass (Abdominal/pelvic organ tumor as neuroblastoma, Wilms tumor, lymphoma, hepatoblastoma)
Soft tissue mass (Local or metastatic tumor)
Hypertension (Sympathetic nervous system tumor as neuroblastoma, pheochromocytoma)
Diarrhea (Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide as neuroblastoma)
Increased intrathecal pressure
Endocrine manifestation as DI, poor growth due to involvement of hypothalamus or pituitary gland
• Hematologic:
• Ophthalmologic:• Thoracic: due to anterior & posterior mediastinal mass lead to compression s&s as cough, stridor, pneumonia, dysphagia & vertebral or nerve root compression.
LEUKEMIA
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) accounts for 80% of leukaemia in children.Acute myeloid leukaemia(AML) about 15%.
Chronic myeloid leukaemia and other myeloproliferative disorders.
Clinical Features of ALL
The initial presentation, usually is nonspecific as fever, anorexia, fatigue, malaise, and irritability. Bone or joint pain, particularly in the lower extremities, may be present.As the disease progresses, signs and symptoms of BMF become more obvious with the occurrence of pallor, fatigue, exercise intolerance, bruising, or epistaxis, as well as fever, which may be caused by infection or the disease.
Organ infiltration can cause
LAP
HSM
Exquisite tenderness over the bone, joint swelling and effusion.
Painless testicular enlargement
CNS involvement (cranial neuropathies, headache, seizures, papilledema).
Respiratory distress may be due to severe anemia or mediastinal node compression of the airways.
Investigations:
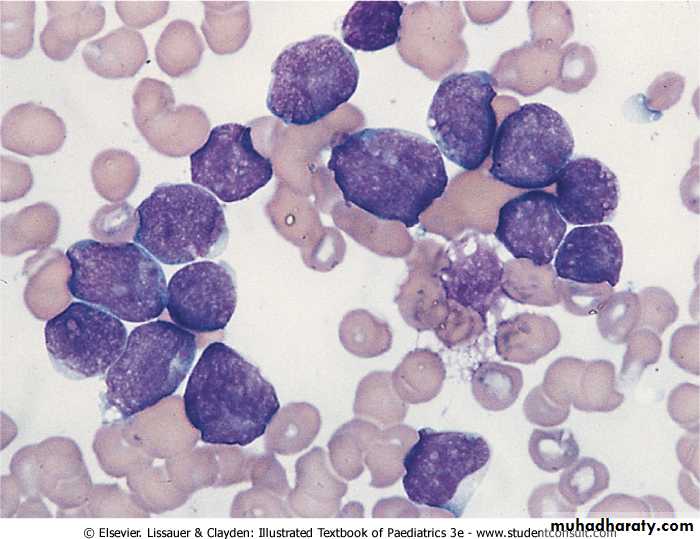
• The diagnosis of acute leukemia is confirmed by findings of immature blast cells on peripheral blood or BM aspirate.• CBC:
• Surface markers (immunophenotype) by flow cytometry
• Fluorescent in situ hybridization or PCR for chromosomal abnormalities.
• LP for CNS inolvement.
• CXR to exclude mediastinal mass.
• Electrolytes, calcium, phosphorus, uric acid, and renal and hepatic function should be monitored in all patients.
Leukaemic blast cells on a bone marrow smear
Treatment:
Before starting treatment of the disease, anaemia is corrected with blood transfusion, the risk of bleeding minimised by transfusion of platelets and infection is treated.Additional hydration and allopurinol (when the WBC is high) are given to protect renal function against the effects of rapid cell lysis.
• Initial therapy, remission induction, focus on eradication of leukemic cells from BM.[4 wk]
Vincristine weekly
Corticosteroid such as dexamethasone or prednisone
Single dose of asparaginase.
Patients at higher risk add daunomycin at weekly intervals.
Intrathecal chemotherapy is always given at the start of treatment and once more during induction.
NOTE: remission, defined by
<5% blasts in the marrow
Return of neutrophil and platelet counts to near-normal levels after 4-5 wk of treatment.
• Consolidation phase, focuses on intensive CNS therapy. Drug vary depend on risk group of patients (MTX, vincristine, asparaginase & cytarabine)
• Maintenance phase, which lasts for 2-3 yr, depending on the protocol used.
Daily mercaptopurineWeekly oral methotrexate
Intermittent doses of vincristine
Corticosteroid.
Co-trimoxazole is given routinely to prevent Pneumocystis jiroveci (carinii) pneumonia.
High Risk Group
• Age <1yr or >10 yr.• Initial WBC >50,000/μL.
• T-cell immunophenotype.
• Slow response to initial therapy.
• Chromosomal abnormalities, including hypodiploidy
LYMPHOMA
Lymphoma can be divided into:
Non Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL): more common in childhood.
Hodgkin's disease: more frequently in adolescence.
The etiologies are unknown, but evidence suggests that the EBV plays a causal role in both conditions.
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Presentation will depend on the site, staging & pathologic subtype of disease.The most common presentation is painless LN enlargement.
Systemic symptoms: fever and weight loss.
T-cell NHL, usually present as mediastinal mass with varying degrees of BM infiltration (same as T cell ALL).
B-cell NHL present more commonly with localised lymph node disease usually in the head and neck or abdomen. Abdominal disease presents with pain, a palpable mass or even intussusception in cases with involvement of the ileum.
NHL can present as a life-threatening oncologic emergency.
Superior mediastinal syndrome can occur as a consequence of a large mediastinal mass causing obstruction of blood flow or respiratory airways.Spinal cord tumors can cause cord compression and acute paraplegias.
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) can occur from rapid cell turnover, it can result in severe metabolic abnormalities including hyperuricemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperkalemia, and hypocalcemia. This can rapidly lead to renal insufficiency/failure as well as cardiac abnormalities if not aggressively treated.
Investigation:
• Diagnosis is established by LN or tissue biopsy or ascetic or pleural fluid analysis.• BM aspiration and bone biopsy examination to role out BM involvement.
• CSF examination to role out CNS involvement.
• CBP, S .uric acid, LDH….
• Whole body CT Scan , PET scan.
Treatment is multi-agent chemotherapy, a more intensive course being employed for advanced B-cell disease.