
1
Fifth stage
Surgery
Lec-1
د
.
محمد نزار
13/4/2011
Developmental dysplasia of the hip
Introduction
1- previously called CDH .
2- its incidence is 5-20/1000 live birth at time of delivery .
3- after 3 weeks of the delivery its incidence will be 1-2/1000 live birth .
4- girls affected more than boys 7:1 .
5- left hip affected more than the right .
6- in 1 of 5 cases the condition is bilateral .
AETIOLOGY
1- GENETIC FACTORS
2-HORMONAL FACTOR
3-INTRAUTERINE MALPOSITION
4-POST-NATAL FACTOR
PATHOLOGY
1- acetabular dysplasia
2- femoral head dysplasia
3- femoral neck antiversion
4- inverted labrum
5- long ligamentum teres
6- tight iliopsoas tendon
Clinical features
Any newborn baby should be examined for sign of hip instability , and we should
concentrate on babies which carry high risk example.
1- +ve family history .
2- baby with congenital anomalies .
3- baby with breech presentation .
symptoms
1- the mother may observe a short limb in unilateral DDH .
2- the mother may observe externally rotated limb .
3- asymmetry of the skin crease (folds) .
4- difficulty in changing the napkins .
5- delay walking mainly at 18 months or older .
6- wide perineum in bilateral DDH .
7- limping gate in neglected cases or when the patient presented after walking age .
examination
1- limb length asymmetry .
2- skin folds asymmetry .
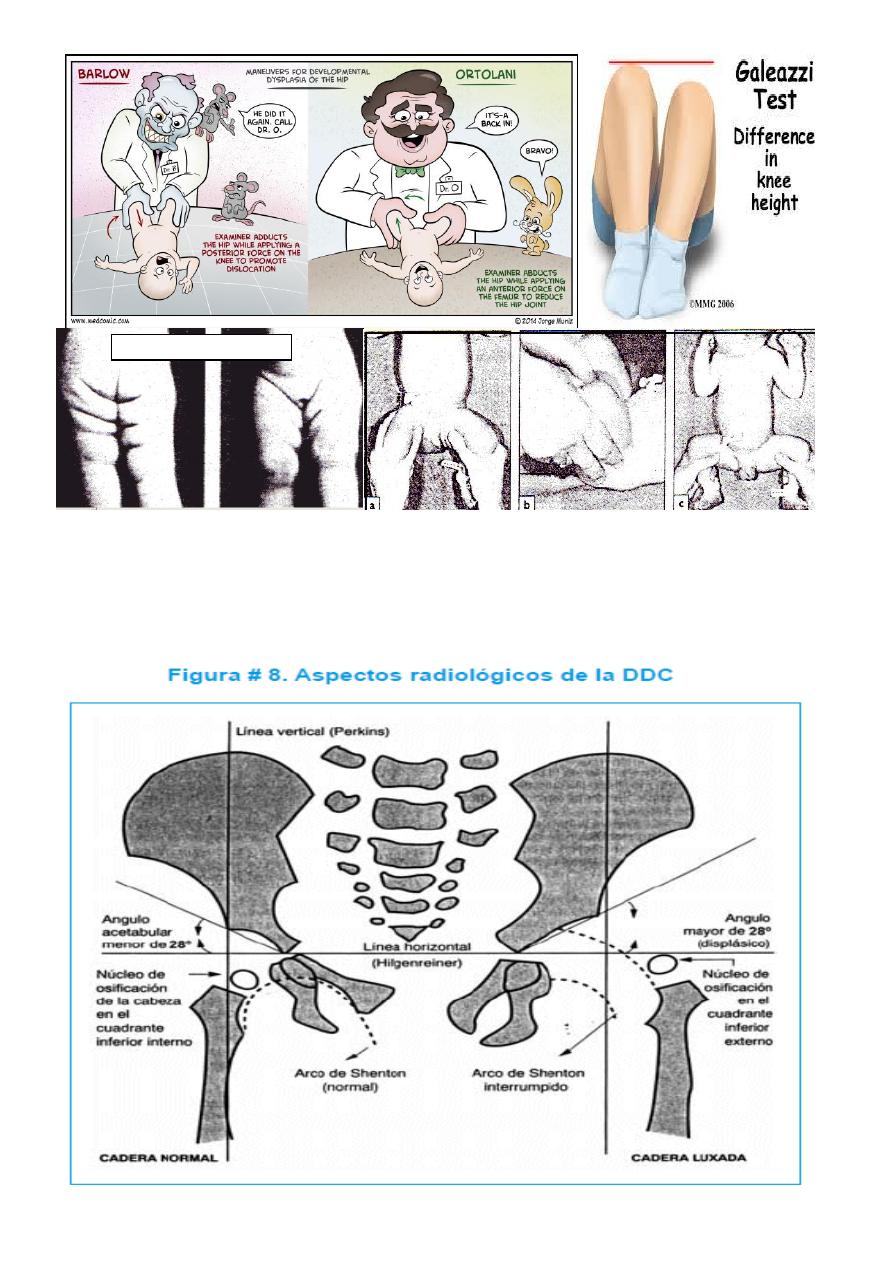
3- Barlow’s test .
4- Ortolani’s test .
2
Imaging
1- Ultrasound is used in the 1
st
6 months .
2- Plain x-ray is used as follow .
A- Von-rosen’s line in the 1
st
6 months .
B- Perkin’s line above the age of 6 months
C- shunton’s line above the age of 6 months.
Asymmetry of skin folds
3
Management
1-80-90% of unstable hip at birth will be stable spontaneously after 2-3 weeks .
2- baby with high risk of DDH should be examined by Ortolani’s and Barlow’s test
,ultrasound is much useful for diagnosis and follow up .
3- babies in the 1
st
month of life with +ve Ortolani’s or Barlow’s or ultrasound, should be
nursed by double napkins or abduction pillow for 6 weeks then reexamined
If:
A-the hip is stable :we should leave the patient free and follow him up for 6 months
B- the hip is still unstable: Abduction splint is used until the hip becomes stable
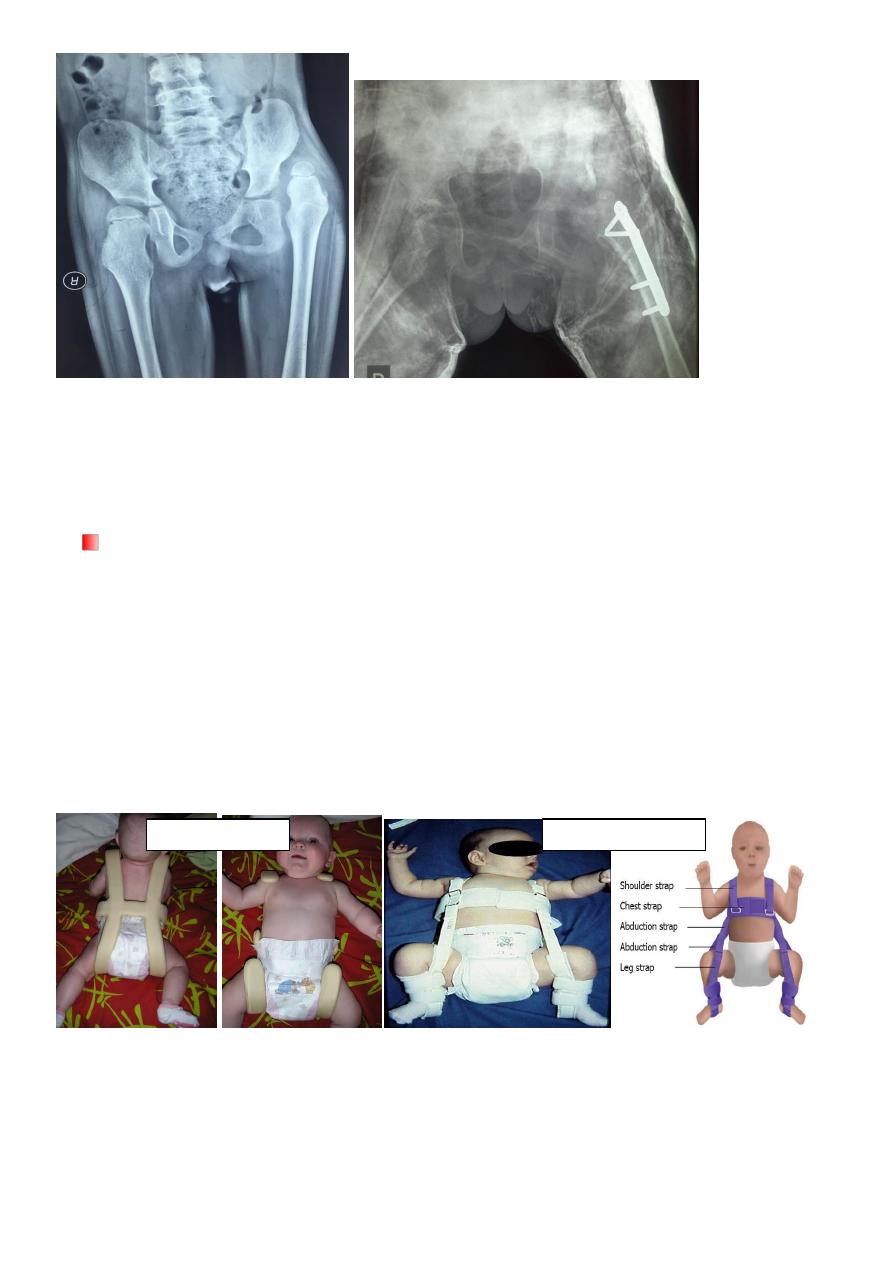
Types of abduction splints
1- Von-Rosen (H) shape malleable splint .
2- Pavlic Harness splint .
The splints should keep the limbs flexed 90* and abducted 45* .
C- if the hip is unredusable from the start or still dislocated after conservative treatment ;
then the treatment will be by manipulation under general anesthesia with or without
adductor tenotomy with hip P.O.P spica in flexion and abduction for 6 weeks .
D- if close reduction failed, then we should do open reduction
Von-Rosen splint
Pavlic harnes splint
