Extra-oral Prostheses
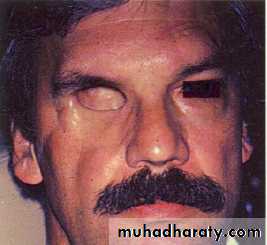
Restoration of eye defects
Types of eye defects
acquiredCongenital
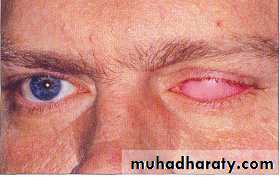
Enucleated eye
Eviscerated eyeextenerated eye
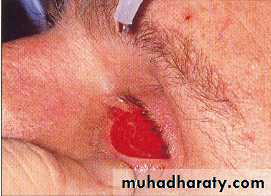
It is evacuation of the intra-occular content through corneal incision or excision
leaving intact optic nerve, extra-occular muscles, Tenon’s capsule and conjunctiva.
due to Endo-ophthalmitis
EviscerationIt is the surgical removal of the eye ball after separation of the eye muscles and optic nerve leaving only Tenon’s capsule and conjunctiva.
Irreparable trauma
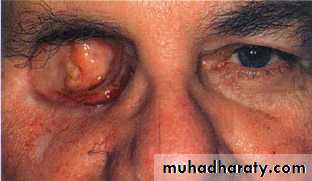
Blind painful eyeMalignant tumor
EnucleationIt is resection of the entire contents of the orbit including eyelids, eye ball, optic nerve, the extra-ocular muscles.
due to malignant tumor
orbitotomy may be accompanied with partial or total maxillectomy.
Orbital extenration
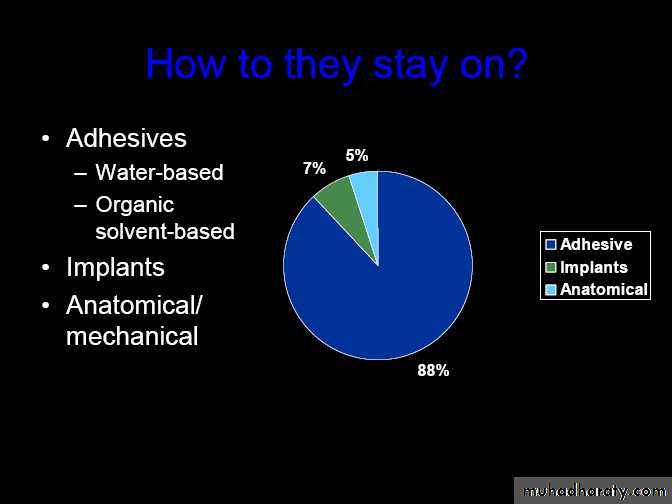
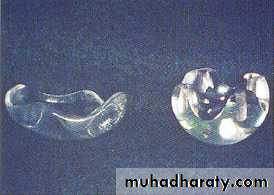
Types of eye prosthesis
Ocular conformerOcular shell
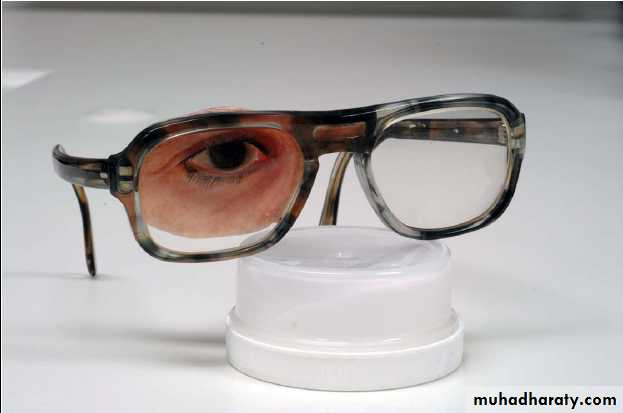
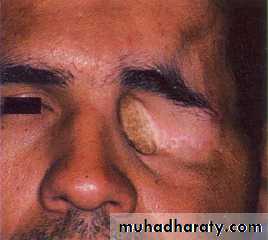
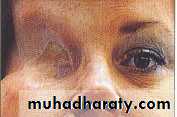
Ocular prosthesis
Orbital prosthesisOcular conformer
Types of occular conformer
Ocular shell
Ocular prosthesisOrbital prosthesis
Electronic visual prosthesisCustom made
Ready madeOcular prosthesis
Fabrication of custom ocular prosthesis
Retains the shape of the defect socket.
Prevents collapse or loss of shape of the lids.
Provides proper muscular action of the lids.
Prevents accumulation of fluid in the cavity.
Maintains palpebral opening similar to the natural eye.
Mimics the coloration and proportions of the natural eye.
Has a gaze similar to the natural eye.
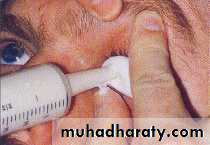
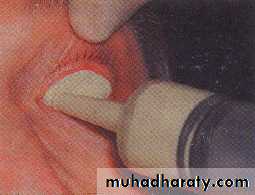
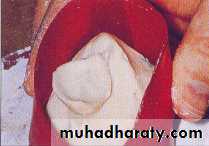
Impression
While going through the available literature, we came across numerous ocular impression techniques as various ocular impression techniques proposed by different authors based on impression materials used by them.External tray technique
Stock ocular tray techniqueOcular impression techniques
Patient evaluation
Stock ocular tray technique(Molded shell)
The patient is instructed to look to the right, left, up, and down without moving the head. If the impression was properly oriented and extended into all available areas, the stem of the tray should follow the movement of the pupil of the natural eye
The external tray technique
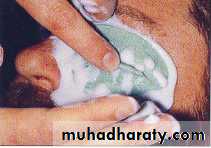
Once set, the impression is removed by having the patient wiggle the face to break the seal.
The impression is removed from the lower, shallower sulcus first, then rotated out of the deeper, upper suIcus.
Wax pattern
Fitting the Scleral Wax Pattern
black iris disk techniquePaper iris Disk Technique
Custom Ocular Prosthesis Fabrication
Digital imaging
Custom Ocular Prosthesis Fabrication• The paper iris disk technique utilizes readily available materials and techniques familiar to the dental office and allows almost limitless adjustment of coloration. The black iris disk technique requires significantly greater mastery of color matching and painting skills but produces a three dimensional value to the resulting iris-lens assembly because of a laminating effect in the painting
difference
A feeling of fullness is natural upon placement. Adjustment is contraindicated for the first few days unless obvious irritations are detected.
The patient should be instructed on how to remove and place the prosthesis.
The patient should return in 1 day, 3 days, and 1 week for follow-up.
There is no need for the patient to remove the prosthesis except for cleaning. Once a week the prosthesis should be removed by the patient and cleaned with mild soap and rinsed well.
Placement of the Custom Ocular Prosthesis
The prosthesis should be inspected for scratches or deposits.The patient should return to have the prosthesis re-polished.
The patient should return at about 6-month intervals to have the defect and pros thesis evaluated and adjusted as necessary.
Placement of the Custom Ocular Prosthesis
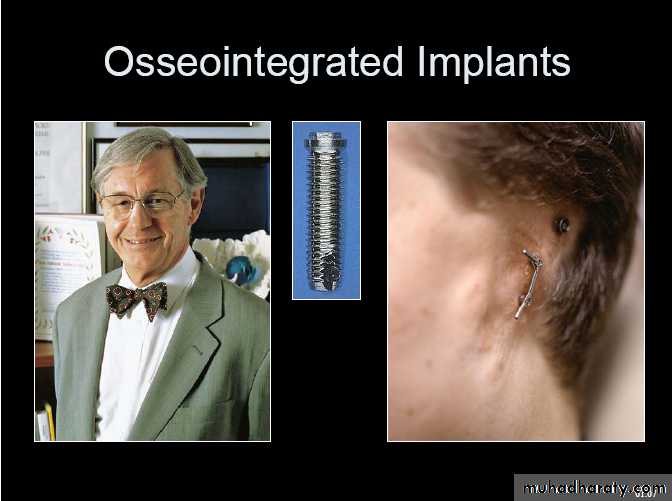
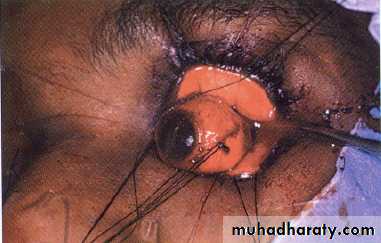
An ocular implant is a body implanted inside the bed on anophthalmic socket during surgically removing the globe in order to prevent :atrophy of the orbital tissues
dropping of upper lid
slower growth rate of the orbit in children.
ocular implants supporting ocular prosthesis
During the recent years, there have been attempts to improve the cosmetic appearance by implanting a foreign material into eye socket, which render the ocular prosthesis
to be less shrunken
appear natural
have better mobility as implant transmits movement of ophthalmic socket to ocular prosthesis.
The material should not be irritant, allergic or carcinogenic.
It has a mean of attachment with extra-occular muscle..
Able to move the prosthesis.
Sufficient volume to replace the lost tissue without being shrunken.
Requirements for an ideal ocular implant
Fabrication of esthetic orbital prostheses is a most difficult challenge.
Orbital prosthesis fabrication
impression and working-cast fabricationSculpture and formation of the pattern
Mold fabrication.
Processing of the prosthesis material.
Orbital impression
Impression materials
Irreversible hydrocolloidElastomeric materials poly vinyl siloxane
reversible hydrocolloid
Impression
Digital imaging in formation of the prosthesis patternComputer imaging may be used to assist establishment of the correct ocular positioning
Using a digital camera, an image of the patient is made. Using image-editing software the normal eye can be reversed and superimposed over the orbital defect
A similar image is made of he working cast at the same object-lens distance with the ocular segment positioned in the wax up
Simple cut and paste operations allow the image of the actual eye to be superimposed over the orbital prosthesis to verify the ocular and eye lid position
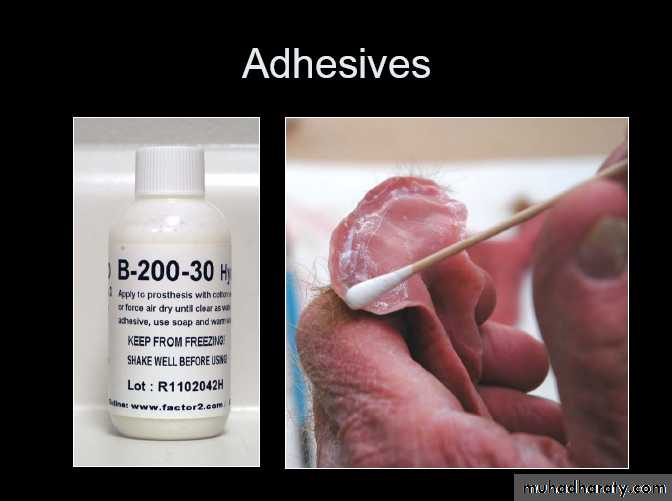
Improved retention and stability of the prosthesis,
Elimination of occasional skin reaction to adhesives,Ease and enhanced accuracy of prosthesis placement,
Improved skin hygiene and patient comfort
Advantages of osseointegrated implants
decreased daily maintenance associated with removal and reapplication of skin adhesives,
increased life span of the facial restoration (when skin adhesives are used for retention, they must be removed and reapplied each day, leading to loss of colorants at the margin of the prosthesis and rendering the prosthesis un acceptable,
Enhanced esthetics of the lines of junction between the prosthesis and skin. When an implant-borne prosthesis is fabricated, its margins can be made thinner, and positive pressure can be developed by the margins of the prosthesis with the movable peripheral tissues.
Advantages of osseointegrated implants
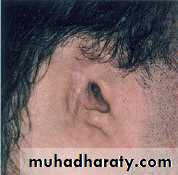
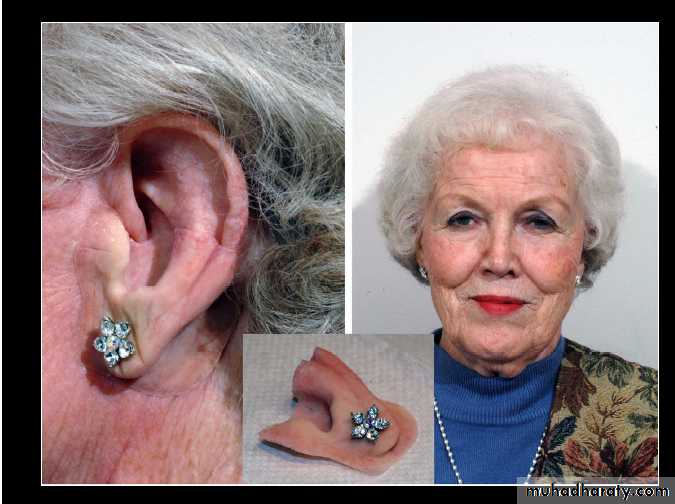
Restoration of ear defects
acquiredCongenital
Trauma
Neoplasm
Tragus should be retained because it creates less obvious anterior line between prosthesis and skin.
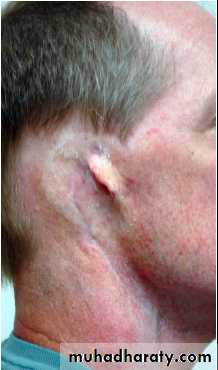
If surgical reconstruction of auricle is not intended, the entire ear should be removed leaving flat tissue bed.
Tissue bed should be lined with split thickness skin graft or full thickness skin graft or pedicle graft.
Hair bearing flaps should be avoided because:
It prevents placement of implants.
It interfere with the use of skin adhesives for prosthesis retention.
In patients with benign tumors implant can be placed in the same session of tumor resection.
Surgical modifications to enhance prosthetic prognosis
Definitive
Temporary
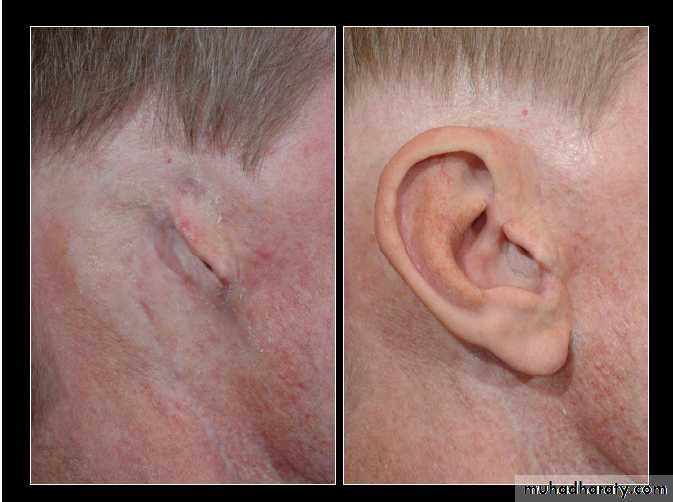
Types of ear prosthesis
Temporary auricular prosthesis
Definitive auricular prosthesisAuricular impression
Auricular impressionSeveral impression techniques have been advocated aiming for minimal distortion of the impression and cast accuracy as important criteria for achieving a successful prosthesis, the most familiar technique with the:
- Irreversible hydrocolloid reinforced by a plaster matrix.
- Rupper base impression material.
Irreversible hydrocolloid reinforced by a plaster matrix
Rubber base impressionSculpting:
SculptingSculpting
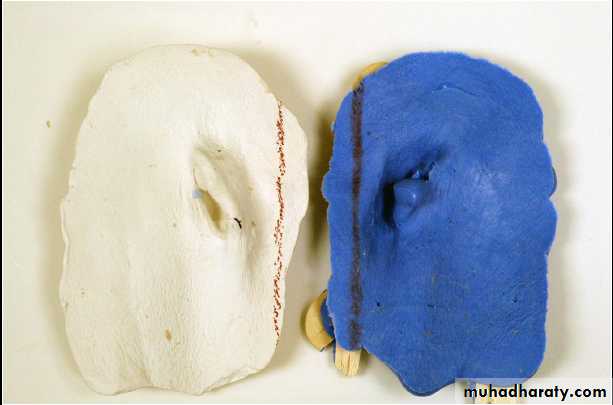
Mould fabricationThree-piece mold for auricular prosthesis.
Processing with intrinsic and extrinsic colorationAdvantages of ear prosthesis