
أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
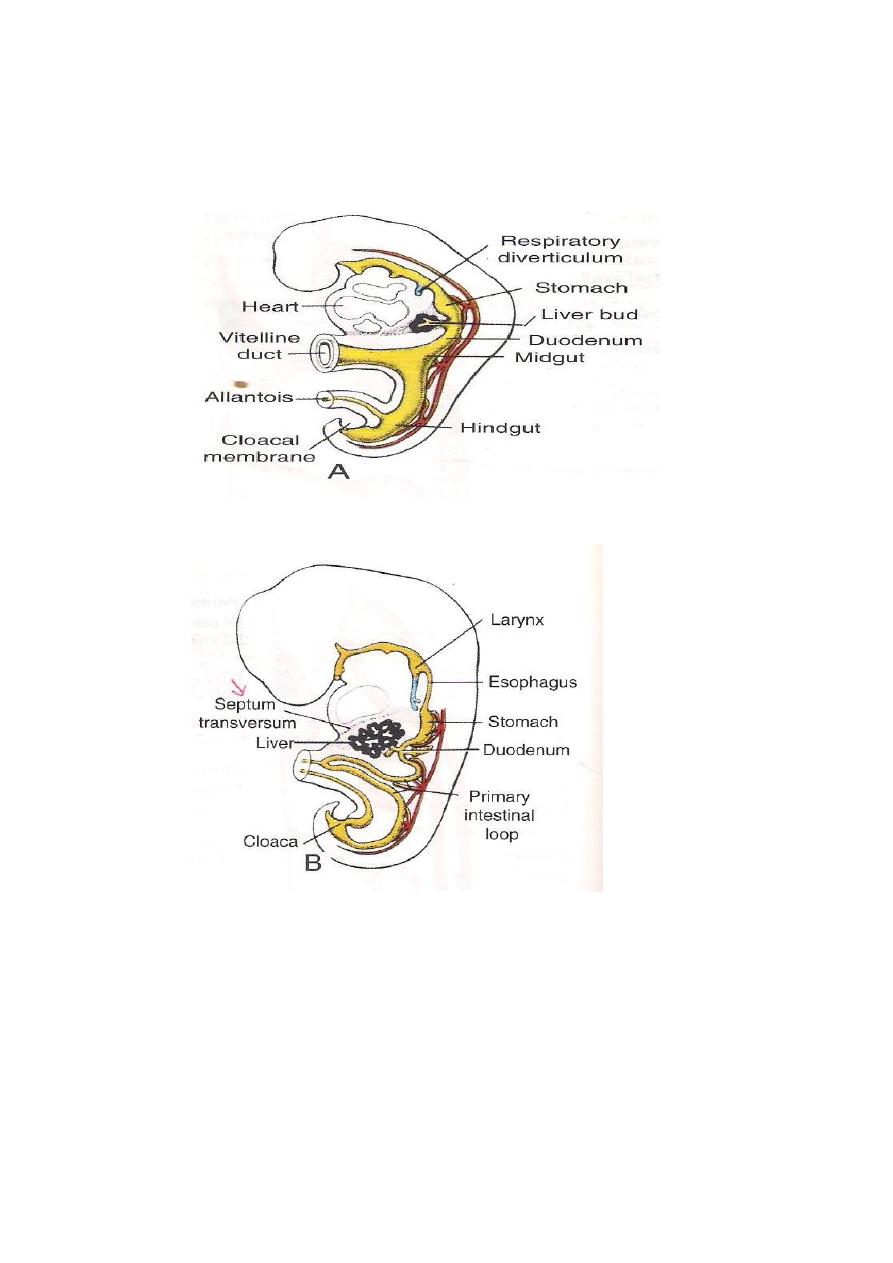
Development of The Mid-Gut
It grows faster than the vertebral column,thus it will become U-
Shaped structure with an inverted apex.This U-shaped structure
has a proximal(cranial) & distal (caudal)limbs with the superior
mesenteric artery running in between the 2 limbs,while the apex
is connected to the umbilicus by Vitelline ligament.
The cranial limb will give rise to the following parts of the
G.I.Tract:
1-The caudal half of the duodenum(The cranial half comes from
the fore-gut derivatives.
2-The Jejunum.
3-Most of the Ileum.
While the Caudal limb will give the following derivatives:
1-The terminal part of the Ileum.
2-The Caecum & Appendix.
3-The Ascending colon and 2 / 3 of the transverse colon.
The caecum with the apex attached to its tip arises a conical
diverticulum from the caudal limb close to the apex of the loop
i.ei near the point of attachment of Vitellointestinal duct.
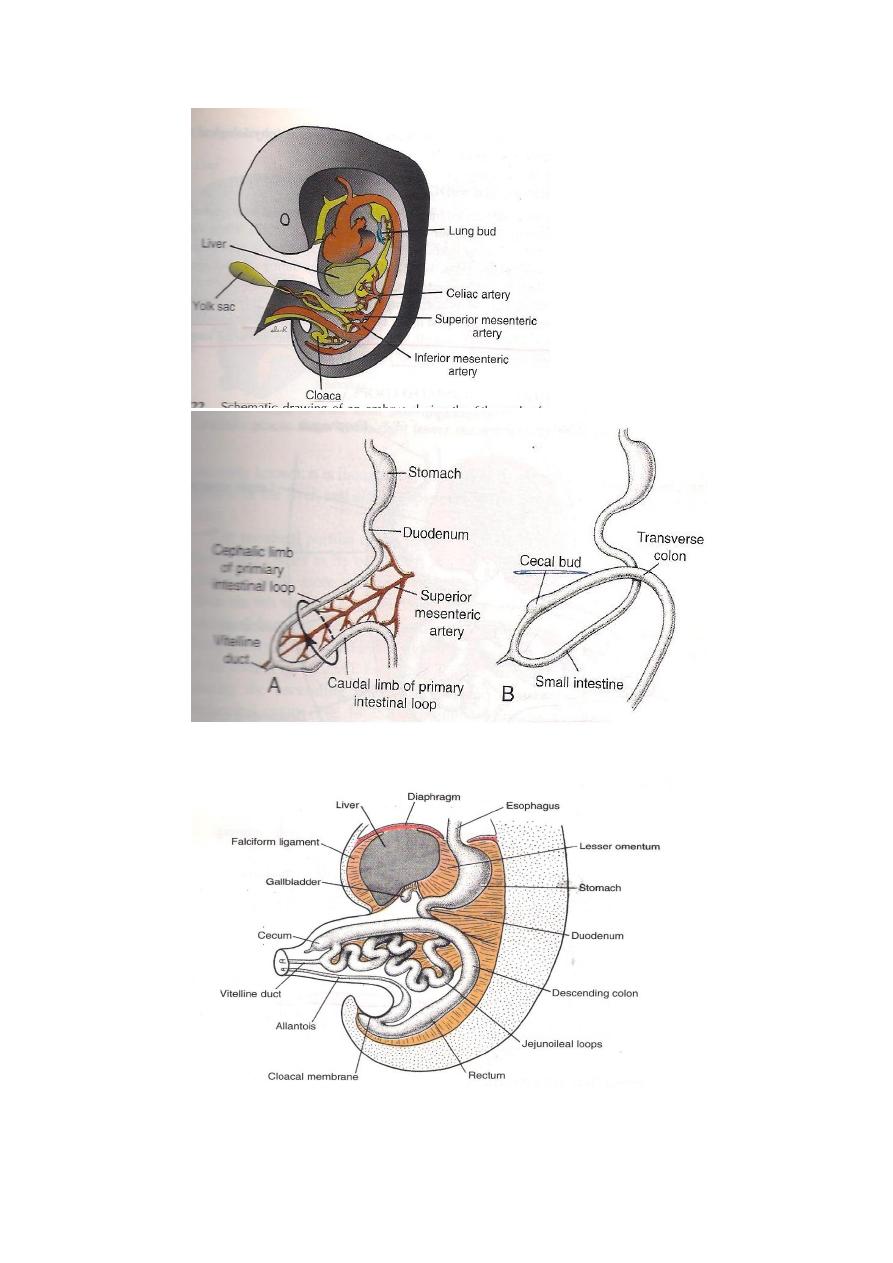
The U –shaped loop projects inside the umbilical cord to form
the umbilical hernia,which is a normal feature between 6
th
– 12
th
weeks of intra-uterine life.Such a hernia is due to the inadequacy
of the abdominal cavity which is largly occupied by the following
structures.
1-The rapidly growing liver.
2-The large sized mesonephros on each side of the vertebral
column.
By the end of the 12
th
weeks of development,the loop of the
intestine starts to return back in to the abdominal cavity because
of the following reasons:
1-Regression of the mesonephros.
2-No more increases in the size of the liver.
3-An increases in the expansion of the abdominal cavity with an
increase in the abdominal wall.

أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
Rotation of the loop & Reduction of the hernia
Just before the start of reduction,the loop will rotates 90 degree
Unti-clock wise,thus the original proximal limb comes to the
right ,while the distal limb comes to the left. Once
reduction starts the loop will complete its anti-clock wise rotation
to An angle of 270,so that the original cranial limb comes to the
left(deeper),while the original caudal Limb comes to the right
side(Superficial).
The original cranial limb (to the left & deeper)reurns first and
occupies the right side of The abdominal cavity(to form the coils
of small intestine).The caudal limb (left & superficial)
Re-inters superficial to the cranial limb and occupies the left side
of the abdominal cavity and forms the colon.The last segment to
inter is caecum which comes to lie superficial to the small
intestine,the caecum then descends from just below the liver to
reach its adult positrion in the right iliac fossa.
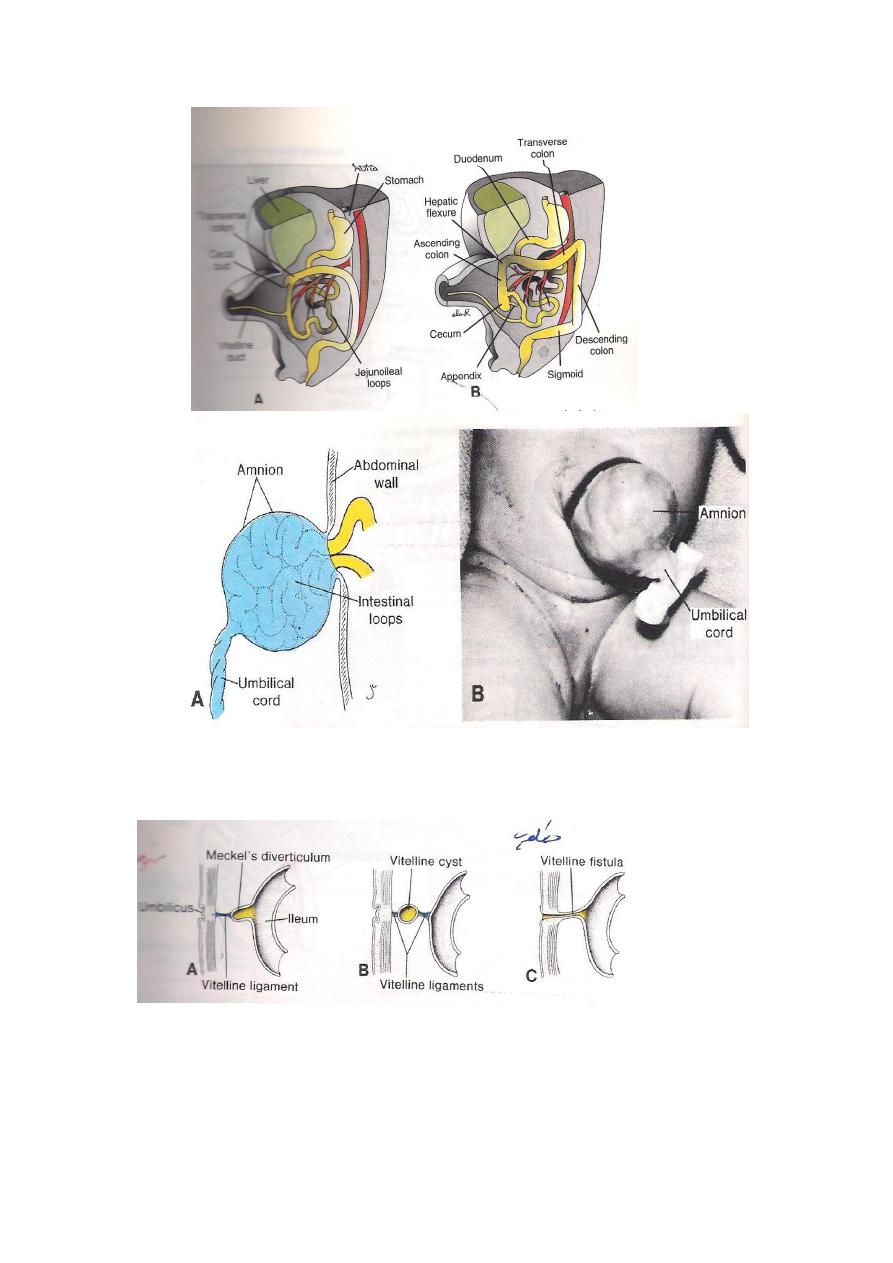
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF MID-GUT DEVELOPMENT
1-Omphalocele ,where the loop is trapped out side & covers only
by amnion due to incomplete reduction of the intestinal loop.
2-Congenital umbilical hernia ,which is mainly due to defects in
central part of the anterior abdominal wall and the skin around
the region of the umbilicus,thus the loop fails to completes its
reduction and stay out side and covers by peritoneum ,amnion
&skin.
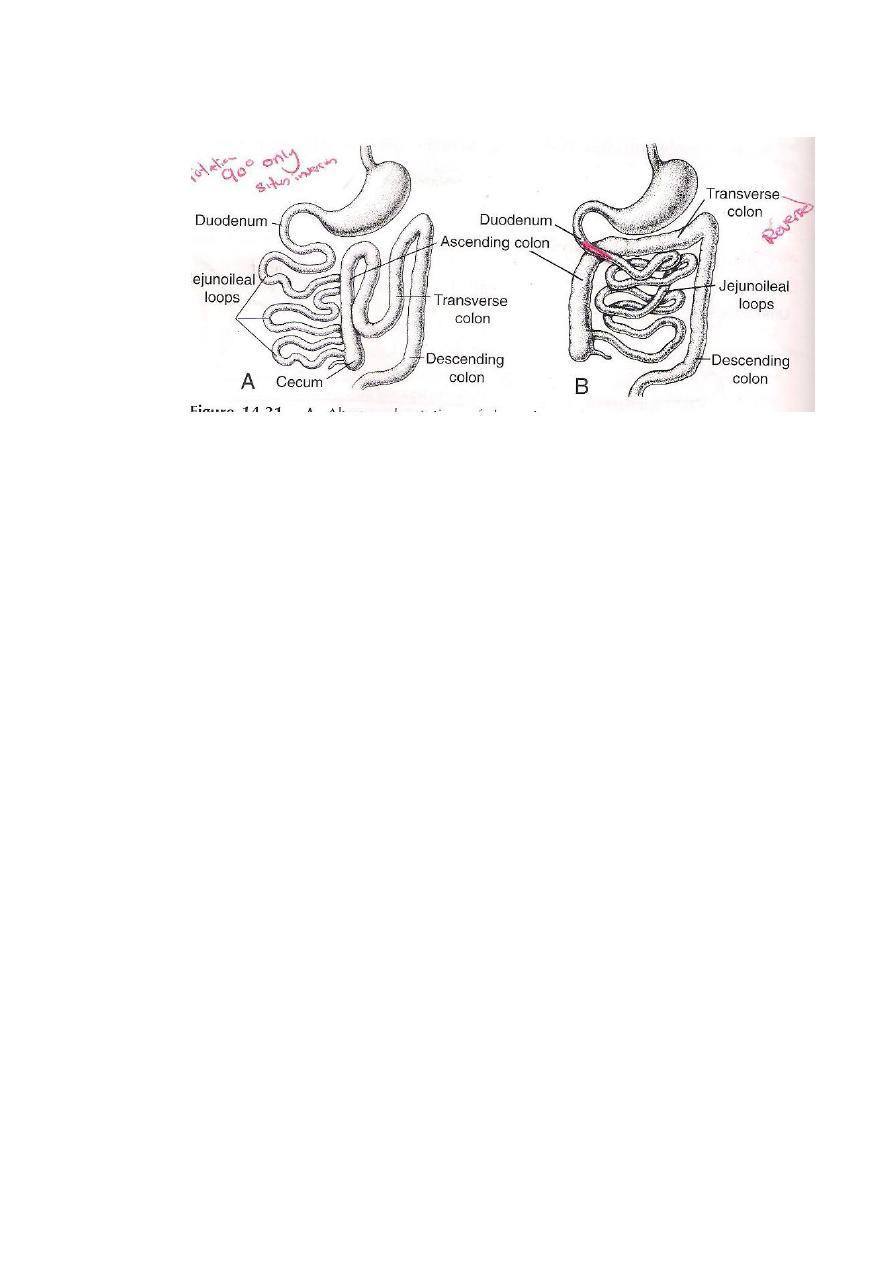
3-The loop may rotates in clock wise direction instead of being
roting in Anti-clock wise,thus the duodenum becomes in a
reversed position & superficial to the transverse colon.
4-Anti-clock wise rotation for only 90 degree leads to reversed
position of the abdominal contents and is usually associated with
congenital heart defect ( Situs inversus).
5-Sub hepatic position of caecum & appendix as it fails to descent
ro right iliac fossa.
6-Anomalies related to the Vetelline ligament including the
followings:

أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
A-Meckl's diverticulum is present 2 % of the population , 2 feet
from the ilio- caecal valve & is about 2 inches in length.
B-Vitello-intestinal fistula connects the intestine with the
umbilicus & discharge some of the Intestinal contents in to the
umbilicus.
C-The whole duct may persist as a fibrosed band extending from
the umbilicus to the ileum.
D-Part of the duct may persist & forms a vitelline cyst along the
course of the duct.
Development of the HIND-GUT
The hind gut gives rise to the following parts of the G.I.Tract:
1-The left one third of the transverse colon.
2-The descending colon.
3-The sigmoid colon.
4-The rectum.
5-The upper half of the Anal canal.
THE RECTUM & ANAL CANAL
The most caudal part of the hind gut(caudal to the origin of the
allantois) is known as Endodermal cloaca with the cloacal
membrane lying in its ventral wall.The Endodermal cloaca is
divided by mesodermal septum (Uro-rectal septum)in to two
parts;
A-Ventral part known as Urogenital sinus.
B-Dorsal part forms the rectum & upper half of the anal canal.
At the mean time the cloacal membrane is divided in to two parts
too :
A-Urogenital membrane ventrally.
B-Anal membrane dorsally.
The mesoderm surrounding the cloacal membrane thickened &
elevated,so the whole membrane comes to lie at the depression
of Ectodermal cloaca.The anal membrane becomes surrounded
by anal tubercle (mesodermal proliferation)that will form the
external anal sphincter.Thus the anal membrane becomes at the
bottom of the proctodeum(anal pit) Which gives rise to the lower

أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
half of the anal canal.Rupture of the membrane leads to
continuity between the 2 halves of the anal canal& the site of the
anal membrane represented in adult by anal valves.
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF HIND-GUT
1-Imperforated anus due to failure of rupture of the anal
membrane. 2-Congenital Recto-vaginal(in
females) or Recto-Vesical (in males) fistula due to defective Uro-
rectal septum.
3-Rectal atresia i.e obliteration of the lower part of the rectum
due to replacement of the caudal part of the ano-rectal canal by
fibrous tissues.
THE LIVER DEVELOPMENT
Starts as a ventral out growth (Diverticulum) from the ventral
aspect of the caudal part of the fore gut.It grows in to the ventral
mesogastrium & divides in to 2 Buds with a stem (stalk),these
buds are known as pars hepatica(develops in to R & L lobes of the
liver) and pars cystica which forms the gall bladder,while the stem
of the diverticulum forms the Bile Duct.The cells of the liver are
arranged in strands,which are separated from each other by blood
sinusoids(from mesoderm of septum transversum).The mesoderm
is also responsible for the formation of stroma & capsule of the
liver,while kupffer cells form from mesenchym .
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PANCREASE
It takes origin from 2 pancreatic Buds (from the endodermal lining
of the Duodenum),these buds are one dorsal & one ventral
buds.The dorsal pancreatic bud grows in to the mesoduodenum
& forms the tail,body & the major part of the head of the
pancrease.It also give the major part of the main pancic duct &
the accessory pancreatic duct.
The Ventral pancreatic bud accompanies the hepatic diverticulum
& forms the remaining part of the head of the pancrease and the
uncinated process,it also share in the formation Of the main

أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
pancreatic duct which drains the rest of the head &uncinated
process.
The endodermal cells of the pancreatic buds forms:
1-The secretory acini which secretes the pancreatic enzymes.
2-Islets of Langerhans that secretes insulin from B –cells &
Glucagon from Alpha cells.
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES
1-Pancreatic tissue may invade the pyloric part of the stomach.
2-Annular pancrease ,where a ring of pancreatic tissue surrounds
the whole circumference of the Duodenum due to a bnormal
migration of the pancreatic buds.
3-Cystic Fibrosis of the Pancrease results in very viscous
pancreatic secretions as a result of obstruction of the pancreatic
duct.
Development of the Spleen
It develops from the mesoderm in the dorsal mesogastrium which
becomes divided in to gastro-splenic and lieno-renal ligaments.It
is at first lobulated,but later on the lobes become confluent
together.The presence of notches in the upper border of the
adult spleen is an indication of its earlier lobulation.
The main Congenital Anomalies of Spleen are:
1-Lobulated spleen due to failure of the lobes to become
confluent. 2-Accessory splenules.
The Development of The Duodenum
Its cranial half develops from the fore-gut,while its caudal half
develops from the mid-gut.This explains its blood supply from
both Coeliac trunk & Superior mesenteric arteries. It is at first
has a dorsal mesenmtery known as Mesogastrium attacheit to the
posterior wall of the abdomen.As aresult of rotation of the
أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
stomach,the Duodenum comes to lie at the right side & becomes
C-shaped structure tjat loses its mesentery & becomes as
retroperitoneal structure exceopts its first one inch
أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
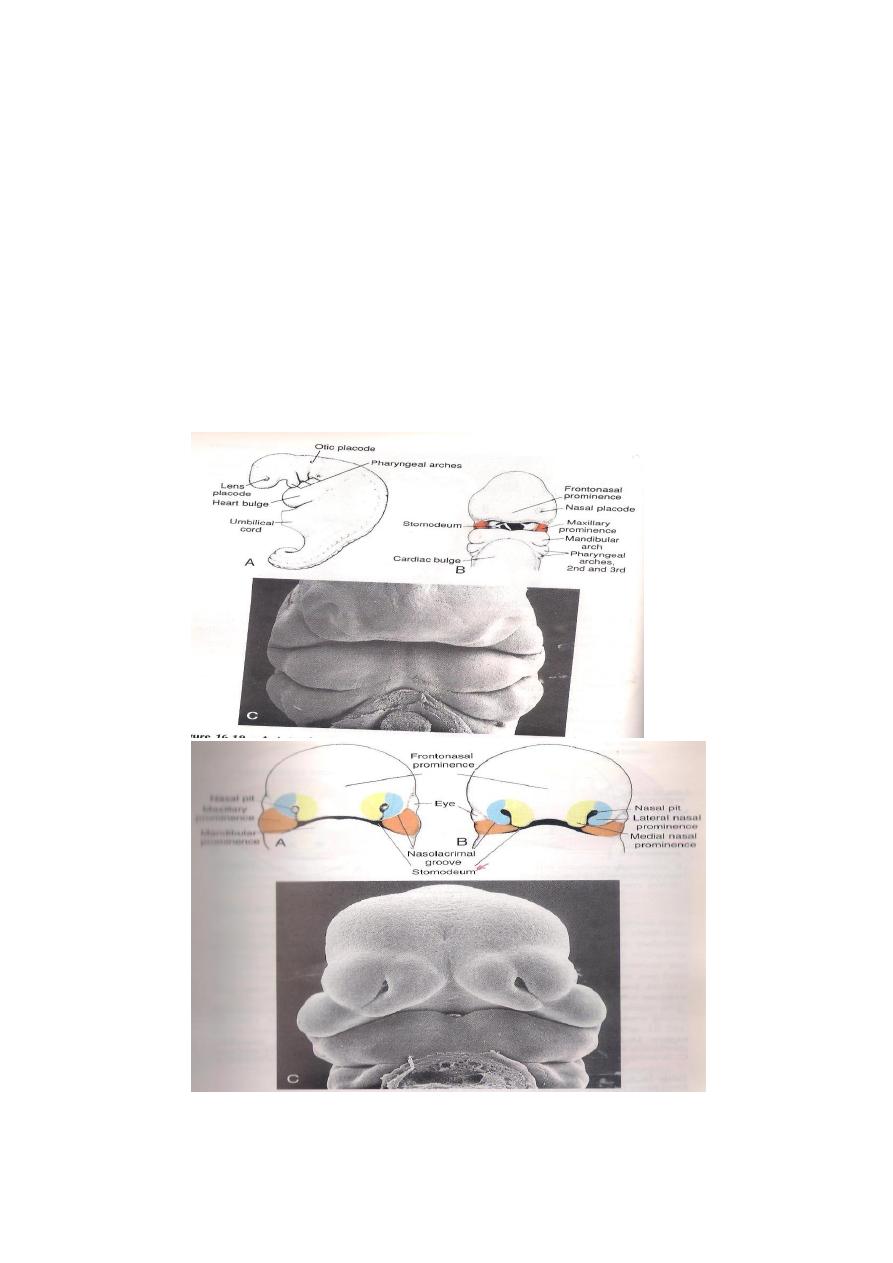
DEVELOPMENT OF THE FACE ,NOSE & PALATE
The face develops from five processes theses are the
followings 1-The Fronto-nasal Process.
2-Two Maxillary Processess.
3-Two Mandibular Processess.
The mesoderm covering the fore brain proliferates to form a
single median process termed the frontonasal process.On the
ventromedial part of the free end of the frontonasal process an
ectodermal thickening area termed olfactory placode(this will
become depressed to form the olfactory pit).The olfactory pit has
media &lateral folds.
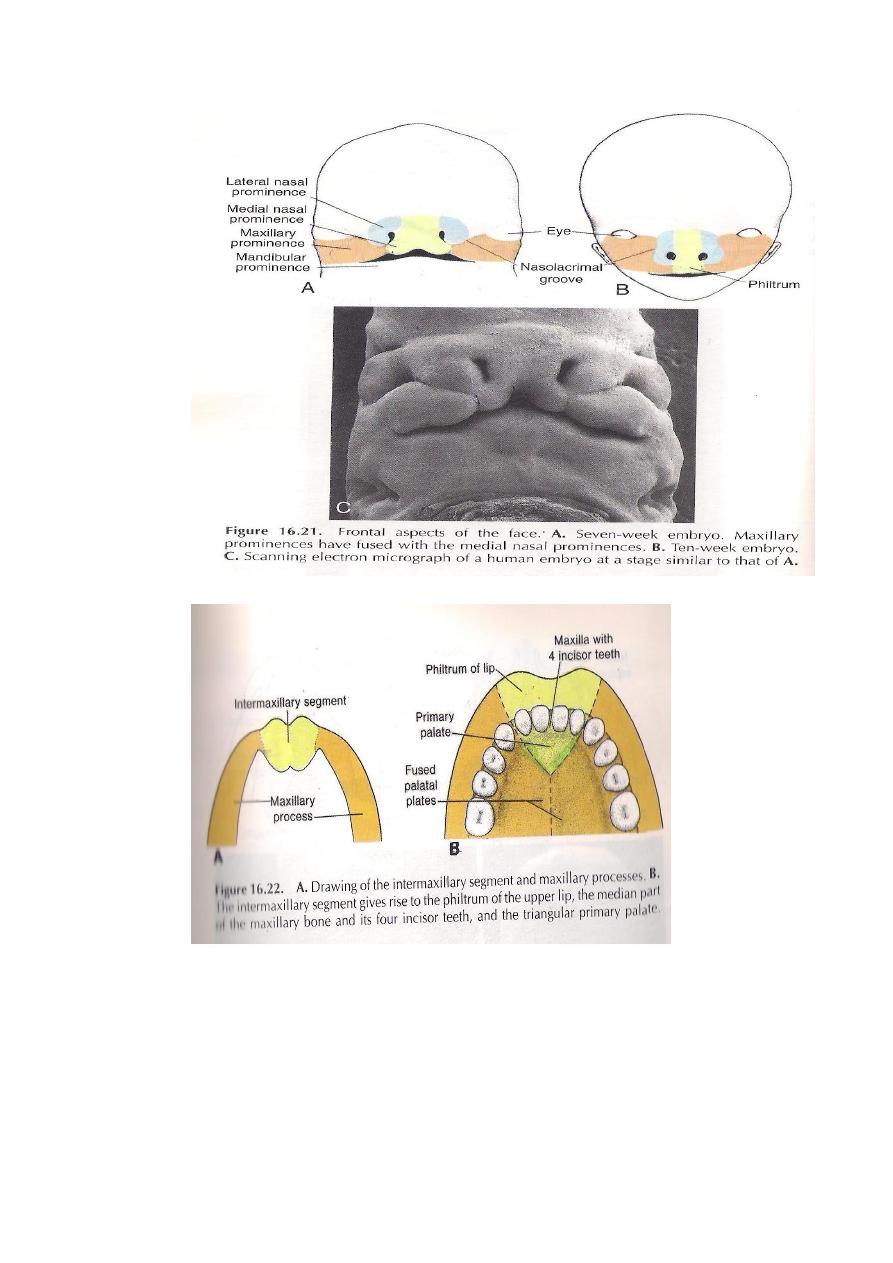
Part of the frontonasal process is called the intermaxillary
(Premaxilla)segment.It lies between the 2 maxillary processes &
gives rise to the followings: 1-Philtrum of the
upper lip.
2-Median part of the upper jaw.
3-The primitive palate.
On each side of the Stomodaeum the first branchial arch gives rise
to 2 processes.
A-Maxillary processes,which fuses with the lateral nasal fold.
B-Mandibular processes:The 2 meet together in the mid line.

أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
The maxillary process extends medially to fuse with the lower end
of the frontonasal process to form the lower lip & upper jaw.
DEVELOPMENT OF THE NOSE
Each maxillary process extends medially from below the olfactory
pit to fuse with the tends medial nasal fold.As a result the
olfactory pit becomes converted in to the primitive nasal cavity
with 2 openings,one leads to the surface called the primitive
anterior naris & another one opens in to the stomodaeum
( posteriorly) called the primitive posterior naris. Then the 2
primitive cavities are separated from each other by the primitive
nasal septum ( from the Frontonasal septum).
DEVELOPMENT OF THE PALATE
The lower end of the frontonasal process grows back ward to
form the primitive palate,which is limited anteriorly by the 4
incisors.It is derived from the intermaxillary segment. A horizontal
palatine process extends medially from the inner aspect of the
side of each maxillary process.In the mid line this palatine process
meets & fuses with each other as with the lower border of the
nasal septum.
Anteriorly each palatine process fuses with the primitive palate at
an oblique line.Posterior to the nasal septum ,the fused palatine
processes are not ossified & forms soft palate&uvula
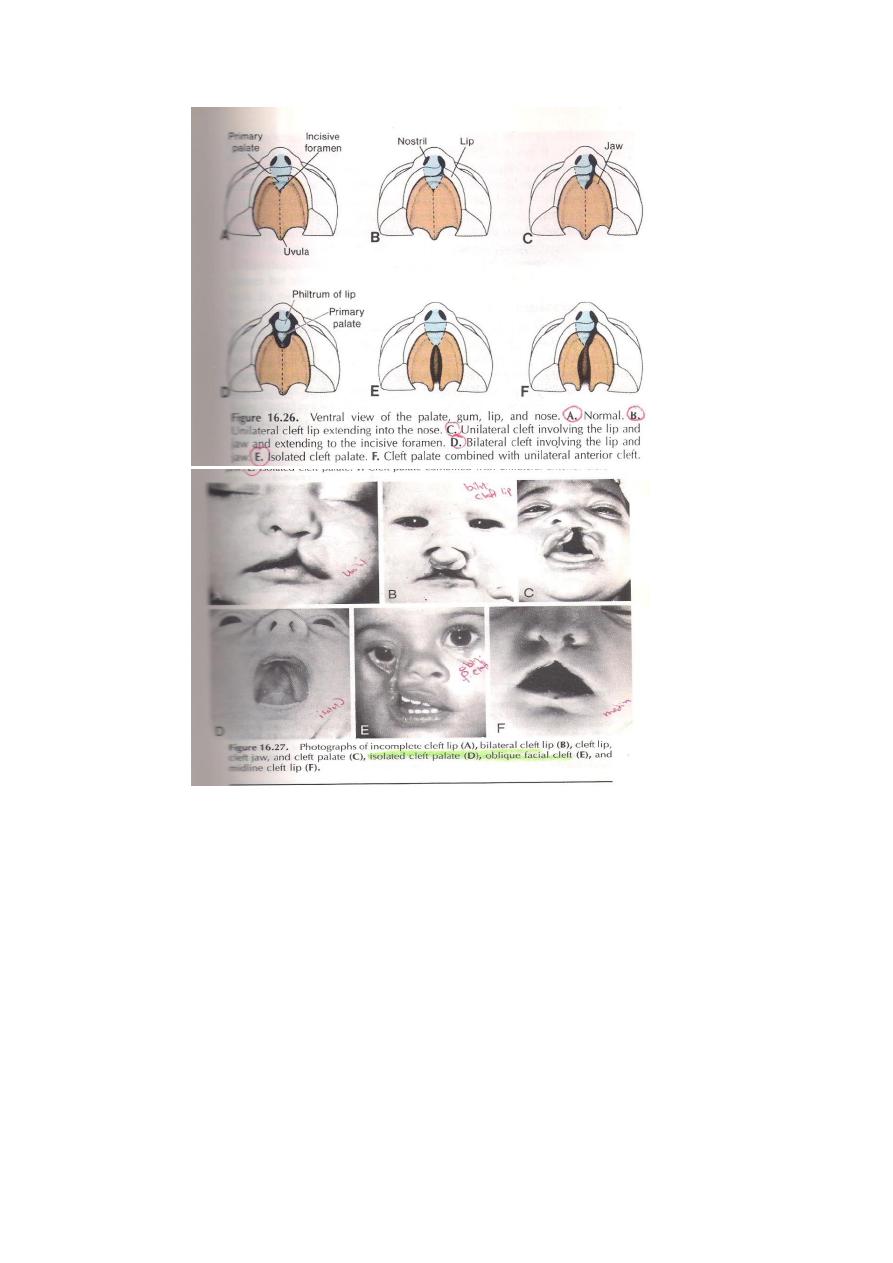
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF FACE & PALATE
1-Hare lip,is due to failure of fusion between the Maxillary
process & Medial Nasal fold..It leads to a fissure between the
philtrum & upper lip, it could be. A-Lateral
hare lip
BMedian hare lip.
C-Bilateral hare lip.
2-Oblique facial cleft,which is due to failure of fussion between
the maxillary process & the side of the frontonasal process along
أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
the side of the nose.
3-Cleft palate:
A-Unilateral ,due to failure of one horizontal palatine process to
extnd medially,thus failing to fuse with the primitive palate..
B-Bilateral cleft palate,,here the 2 palatine processes fail to fuse
with the primitive palate.
C-Isolated cleft palate,here the defect is in the mid line of the
palate behind incisive fossa.
D-Bifid soft palate ( Bifid Uvula ), here the 2 palatine processes
fail to fuse together in the mid line place in their most posterior
part.
أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)

أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
EMBRYOLOGY (Mid-Gut)
