Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
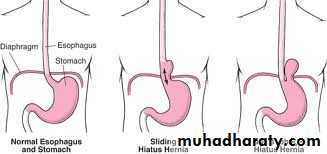
AnatomyHiatus Hernia
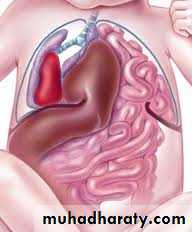
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Bochdalek Herniapostrolateral Morgagni Hernia
85-90% retrosternal
80-90% Lt. side 2-6%
Pathophysiology:- Pulmonary hypoplasia.- Pulmonary hypertension- Persistent fetal circulation
C/F:➣ Prenatal:US 24-26 wk ……. 50-60% polyhydraminous Echogenic chest mass bowel loops in the chest Mediastinal shift Intrathoracic liver
➣ Postnatal :Immediately after birth low Apgar score tachypnea grunting cyanosisLater in life incidentally recurrent chest infection
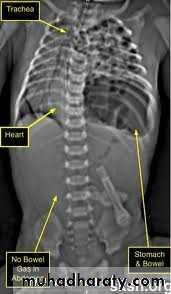
O/E:• Scaphoid abdomen.• Increased antero-posterior diameter of the chest.• Decreased air entry on the affected side with decreased tidal volume.• Bowel sound may be heard in the chest.• Shifting of cardiac impulse to the right.
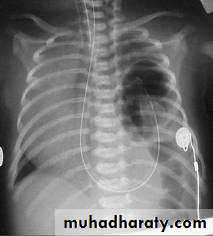
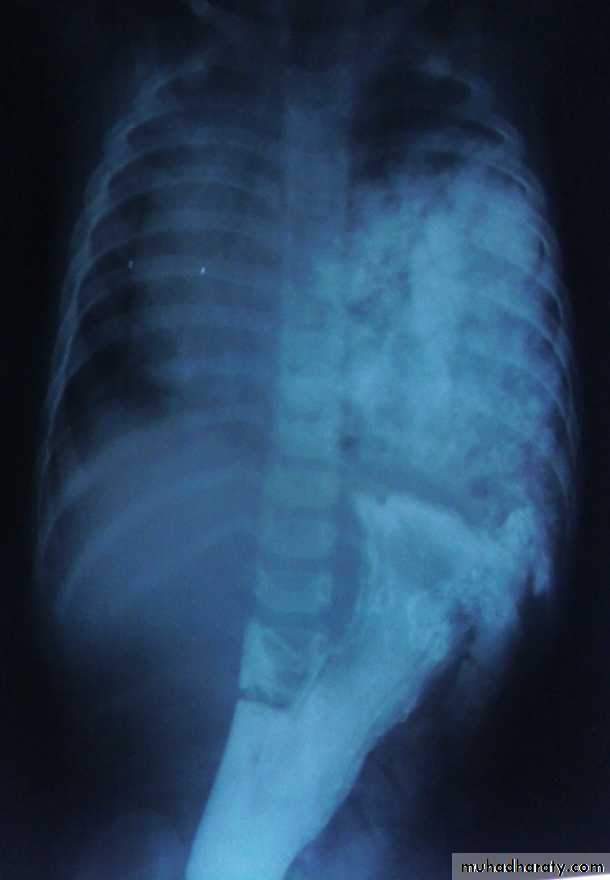
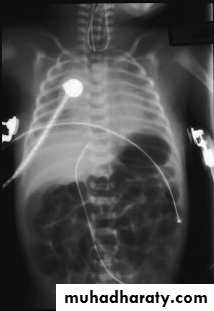
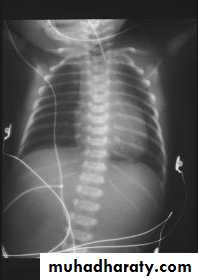
Diagnosis:-- CXRo Air & fluid filled loops of bowel in the chest.o Paucity of intestinal gas in the abdomen.o Mediastinal shift (heart shifted to the right).o Tip of NG tube seen in the chest.
-- Barium study
Treatment: ➣Resuscitation NG tube Bag mask ventilation is contraindicated Endotracheal intubation + oxygen. Urinary catheter Arterial & venous line Fluid therapy Echo study Refer to pediatric surgical center
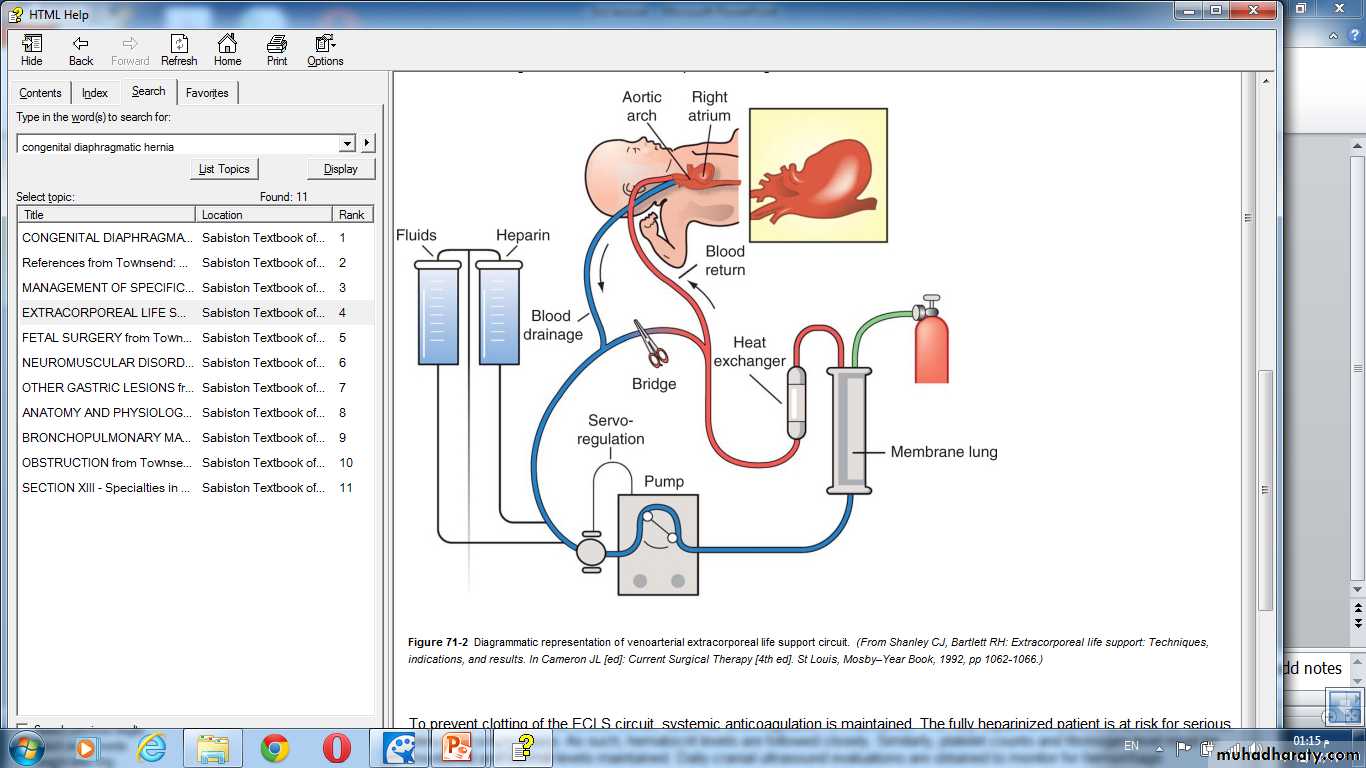
Therapeutic options for stabilization prior to surgery- mechanical ventilation: high frequency oscillatory ventilation(HFOV ).- inhaled nitric oxide (NO).- surfactant therapy.- ECMO ( extra corporeal membrane oxygenation ).
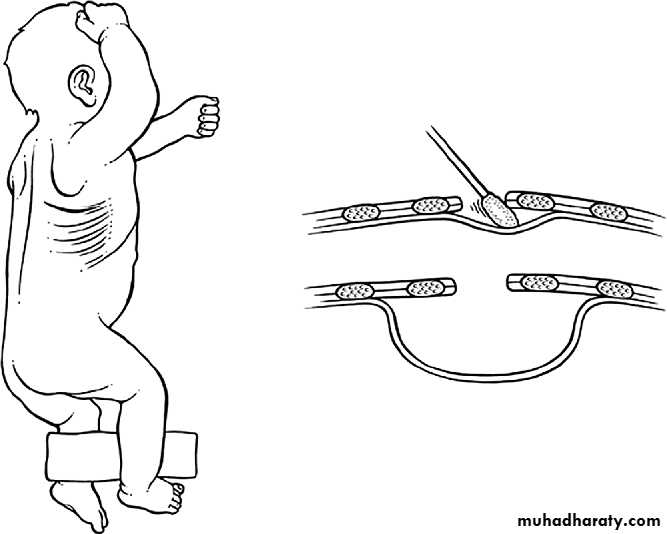
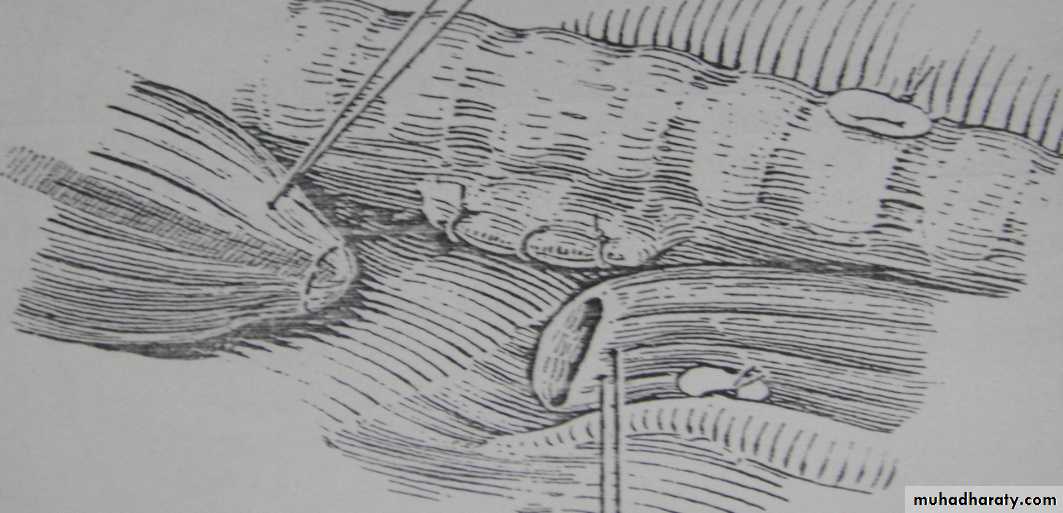
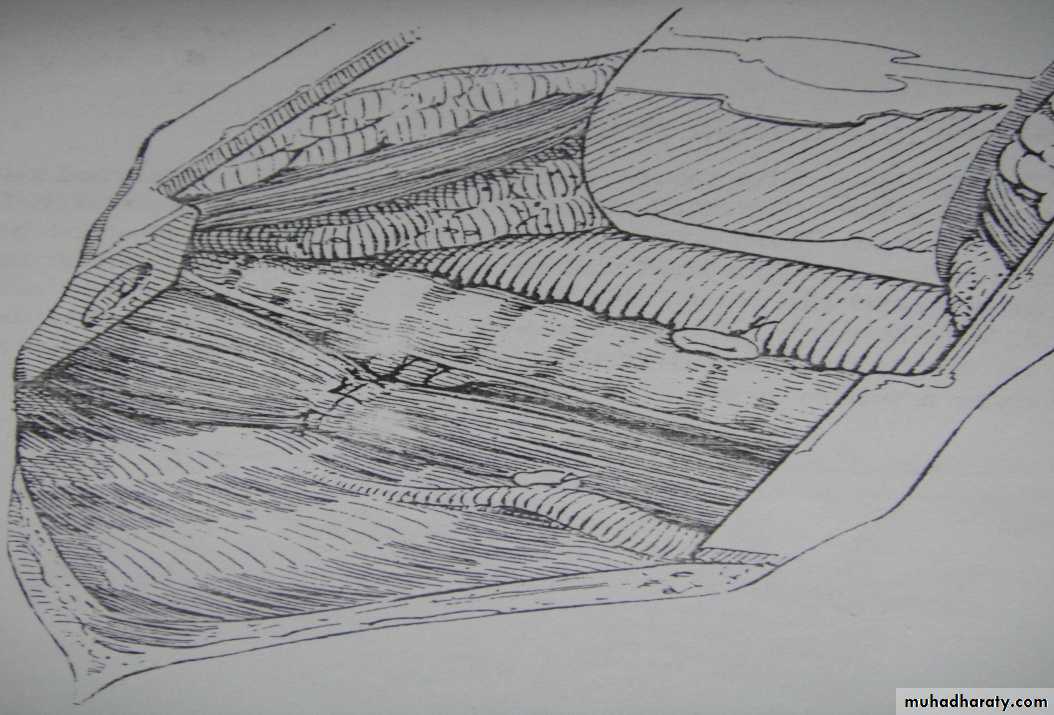
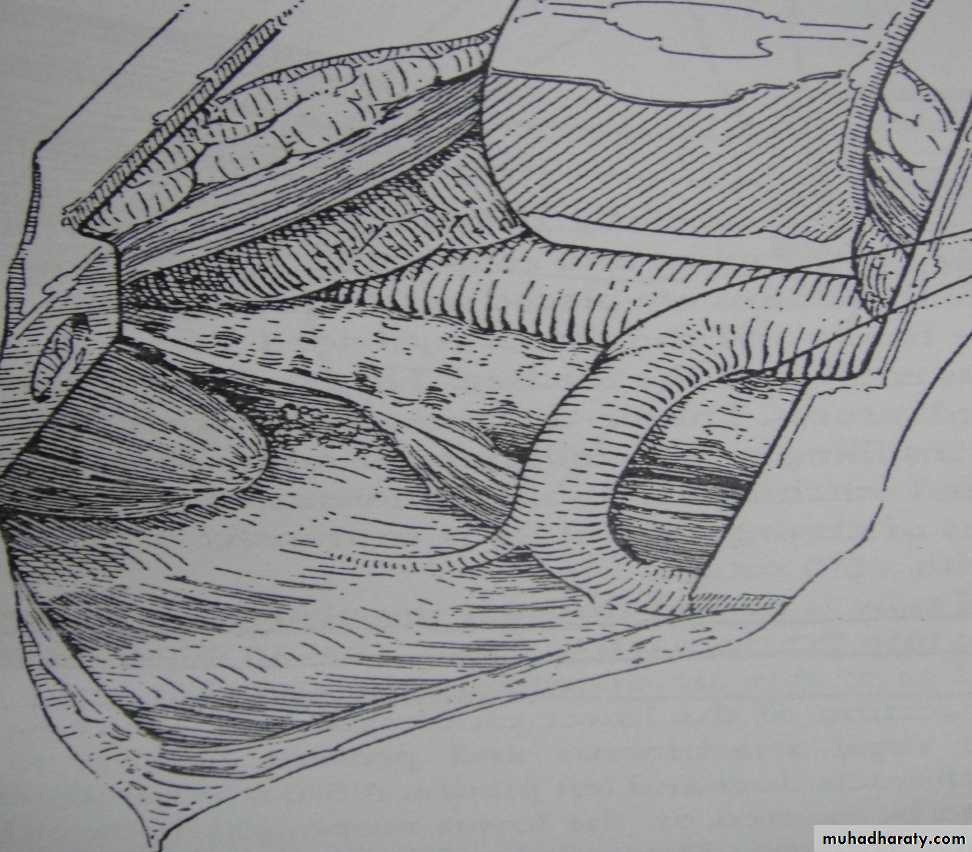
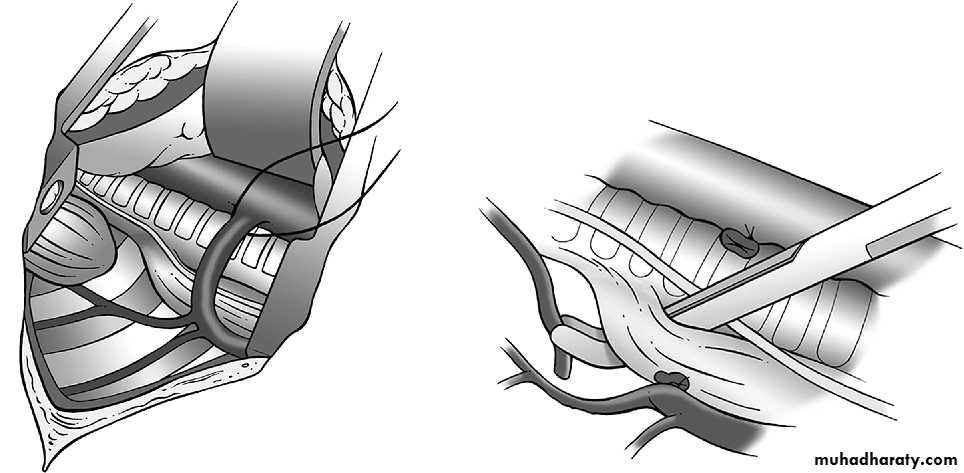
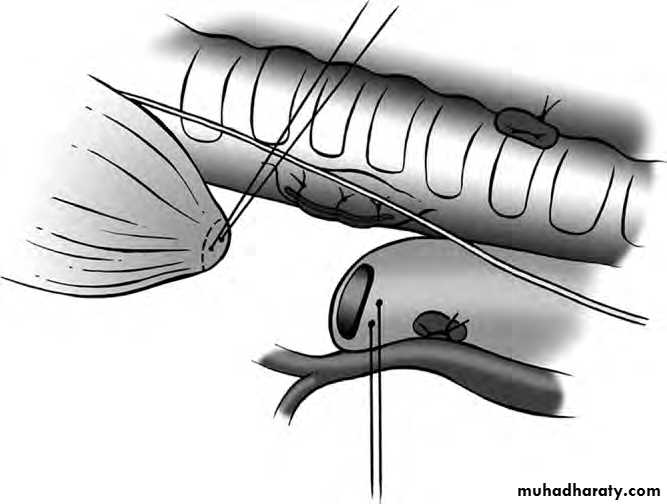
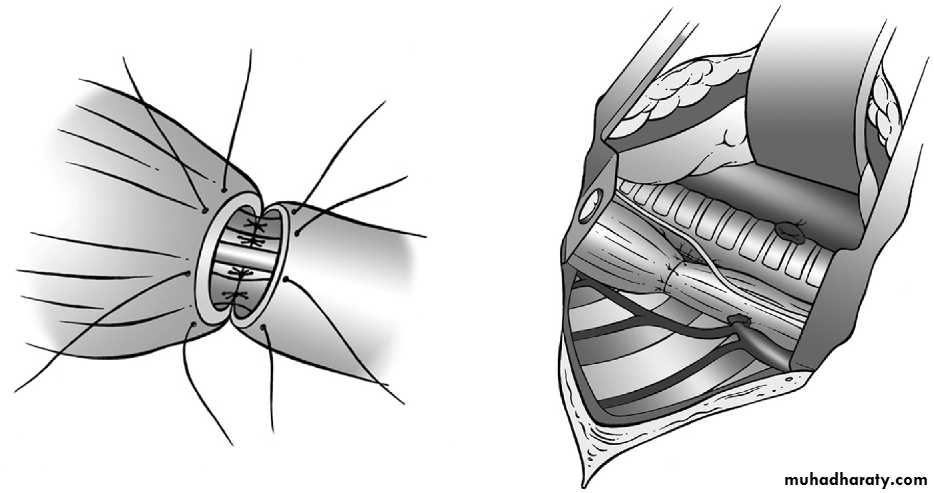
• SURGERY:delayed repairtransabdominal X transthoracicsubcostal incisionReduction of hernial contents10 closureProsthetic meshventral hernia for big defectsFetal intervention: 1. Tracheal occlusion.2. Prenatal steroid.3. Intrauterine surgical repair.
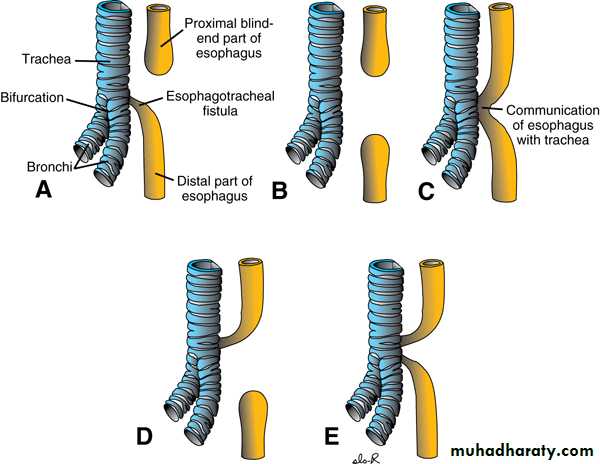
Esophageal Atresia + / ـــTracheoesophageal Fistula
ClassificationPathophysiology :-
Blind end esophageal pouch = pooled secretion.Fistulous connection with trachea = aspiration.
Disordered peristalsis in lower esophagus = GERD.Tracheomalacia = respiratory obstrucrtion.
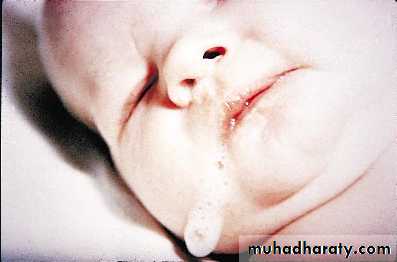
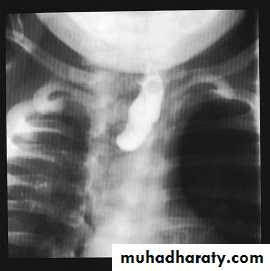
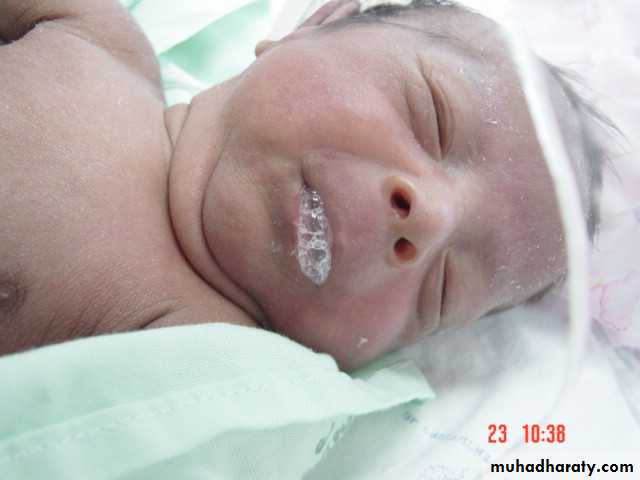
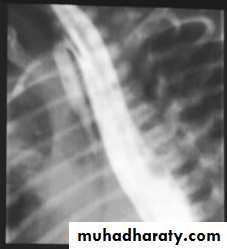
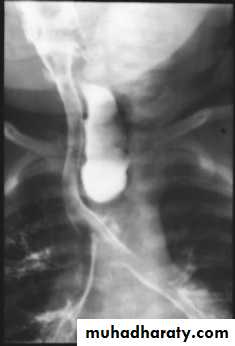
Presentation :-Polyhydraminous.Frothy secretion.Respiratory distress.Resistance to NG tube insertion.Plain X-ray.
Initial management :-Suctioning.Positioning.Vascular line.Endotracheal intubation.Incubator , warm , humidity.Check for associated anomalies.Referral to pediatric surgical center.
Operative management :-Pre-op. Echo study.Intra-op. Esophagoscopy.Intra-op. Bronchoscopy.thoracotomy.
Childhood tumors
The commonest malignancies in childhood are :-1- leukemia.
2- CNS tumors.
3- lymphoma.
4- neuroblastoma.
4- Wilm's tumor. (nephroblastoma).
5- the other are retinoblastoma, hepatic tumor, bone tumor, soft tissue tumor.
Neuroblastoma
Presentation :-Fever , weight loss , anorexia , sweating.
Skeletal involvement (bone and joint pain).Orbital sign (ecchymosis and proptosis).
Horner syndrome.
Pelvic involvement.
Investigation
24 hr urinary catecholamine metabolites (VMA & HVA)
Basic evaluation. (CBC, biochem., RFT, LFT, LDH, …)
Ultrasound.
Imaging. Abdominal X- ray.Biopsy. CXR.
CT , MRI.
MIBG scan.
TREATMENT
MDTChemotherapy.
Surgical intervention.
Radiotherapy.
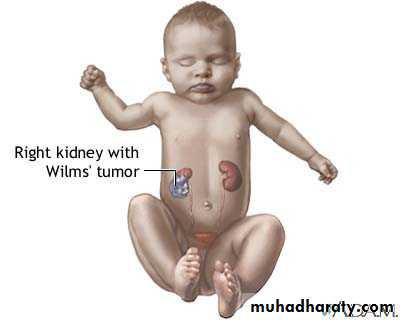
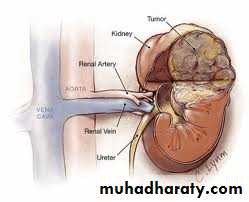
Nephroblastoma (Wilms' tumor).
Clinical presentation :-
80% asymptomatic flank mass.Hematuria.
Fever.
Hypertension.
TREATMENT
MDTCHEMOTHERAPY
SURGERY
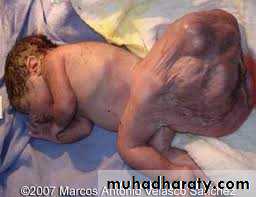
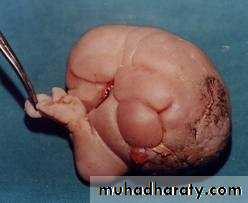
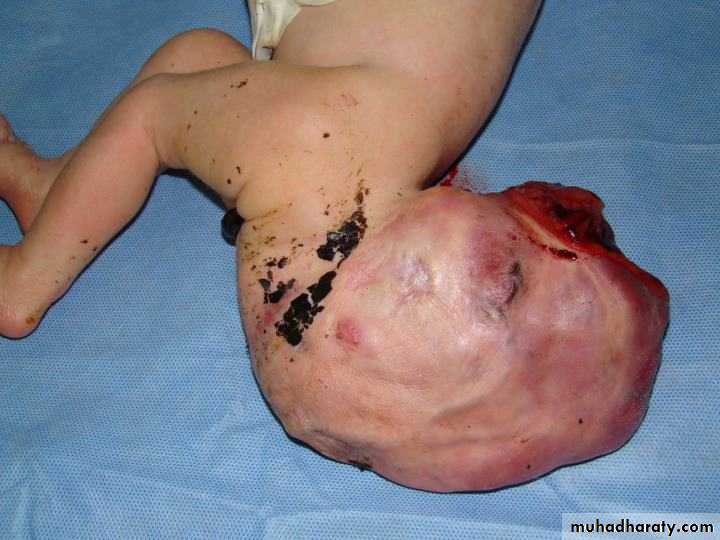
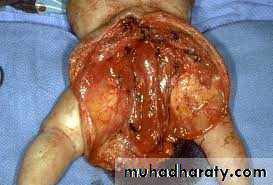
Sacrococcygeal teratoma
Teratos = monster.Onkoma = swelling.
The tumor is composed of multiple tissues foreign to the site of origin.
Teratoma
Clinical presentation :-Visible caudal mass.
Constipation.
Urine retention.
Leg edema.
High output cardiac failure.
Intrapartum complications.
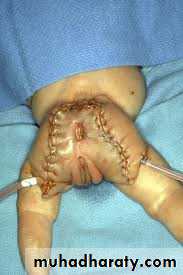
Surgery
Risk of malignancy. 10% birth-----75% 1 yearEn bloc excision with the coccyx.
Serum tumor markers. Carcinoembryonic Ag., HCG, AFP