Ari control and prevention
ARI control
Improving the primary medical care services and developing better methods for early detection , treatment and prevention of acute respiratory infection is the best way to control ARImortality rate due to pneumonia is reduced if treated correctly
Education of mothers about pneumonia because compliance with treatment and seeking proper care when child suffers determine outcome of the disease
WHO recommendation for management of ARI
Clinical assesmentHistory taking and management are very important
Note :1)age
2)feeding habits
3)fever
4)convulsions
5)irregular breathing
6)history of treatment during the illness
7)activity
Physical examination
1:count the breaths in one minuteBreathing count depends on the age of the child
Count respiratory rate for a minute
Fast breathing is present when RR is
-60 breaths /min or more in a child less than two months of age
-50/min or more in child aged 2months upto 12 months
-40 breaths/min or more in a child aged 12 months upto 5 years
Chest indrawing
Look for chest indrawing when child breaths INChild has indrawing if the lower chest wall goes in when the child breaths IN
Occurs when the effort required to breath in ,is much greater than normal
Stridor
Harsh noise while breathing IN is stridorOccurs due to narrowing of trachea ,larynx or epiglottis
These conditions often called croup
Wheeze
A child with wheeze makes a soft whistling noiseOR
shows signs that breathing OUT is difficult
This is due to narrowing of the air passages
Fever
Check for body temperature
Cyanosis
Sign of hypoxia
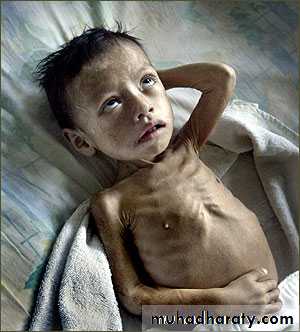
Malnutrition
If malnutrition is present its high risk and case fatality rates are higherIn severely malnourished:
1) children with pneumonia, fast breathing and chest indrawing may not be evident
2)Impaired or absent response to hypoxia and a weak or absent cough
reflex
3)Careful evaluation and
mangement
ARI control programmes
ARI control in childrenARI is an episode of acute symptoms & signs resulting from infection of any part of respiratory tract & related structures
Constitutes 22-66% of outpatients & 12-45% of inpatients
ARI control programmes
The aim of the program is to identify children with ARI at the community level by training the field workers to recognize easily & reliably identifiable clinical signs of ARI & early referenceWHO protocol comprises 3 steps:
Case finding & Assessment
Case Classification
Institution of appropriate therapy
Step 1: Case finding & Assessment
Cough & difficult breathing in children < 5 years ageFever is not an efficient criteria
Step 2: Case ClassificationChildren grouped into 2:
Infants < 2months & Older children
Specific signs to be looked: In younger children like feeding difficulty, lethargy, hypothermia, convulsions
In infants < 2 months
Pneumonia is diagnosed if RR 60/min with other clinical signsAll should be hospitalized
All should receive IV medications
Minimum duration of 10 days
Combination of Ampicillin & Gentamicin
step 3:Institution of appropriate therapy
AntibioticsPrevention of ARI
Breastfeeding infants exclusively (no other food or drinks, not even water) for the first six months breast milk has excellent nutritional value and it contains the mother’s antibodies which help to protect the infant from infection.Avoiding irritation of the respiratory tract by indoor air pollution, such as smoke from cooking fires; avoid the use of dried cow dung as fuel for indoor fires.
Immunization of all children with the routine Expanded Programme on Immunization
Feeding children with adequate amounts of varied and nutritious food to keep their immune system strong.
control the spread of respiratory bacteria by educating parents to avoid contact as much as possible between their children and patients who have ARIs.
people with ARIs should cough or sneeze away from others, hold a cloth to the nose and mouth to catch the airborne droplets when coughing or sneezing
Immunization also increases control, by reducing the reservoir of infection in the community and increasing the level of herd immunity
immunization
measles vaccine
Pneumonia is a serious complication of measlesReducing the incidence of measles helps reduce death from pneumonia
Live attenuated vaccine
Freeze dried product
0.5ml dose subcutaneously also effective intramuscularly
Schedule :9 th month
HIB vaccine
Haemophilus influenza B most important cause of death due to meningitis and pneumonia in developing countriesAvailable for more than a decade
Expensive
Included in the immunization schedule
combined preparation with DPT and poliomyelitis
Three or four doses are given dependin on type of vaccine
Schedule : 6 ,10, 14 weeks booster dose 12-18 months
Vaccine is not offered to children more than 24 months
Pneumococcal vaccine
A)ppv23: polysaccharide non conjugate vaccine containing capsular antigen of 23 serotypes against this infectionChildren under two years and immunocompromised do not respond well to this vaccine
Select groups –sickle cell disease ,chronic heart disease , DM, organ transplants etc
Dose -0.5ml
Administration – intramuscular in the deltoid
Pcv-7: pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
New vaccine suitable for infants and toddlersIt is included in the immunization schedule
Induces a t- cell dependent immune response
Prevents pneumococcal pneumonia and meningitis moderately effective against otitis media
dose- 1)6,10,14 weeks ,booster after 12 months
OR
2)2, 4,6 months and booster after 12 months
administration-intramuscular