Embyrology
DEVELOPMENT OF THE GENITAL SYSTEM
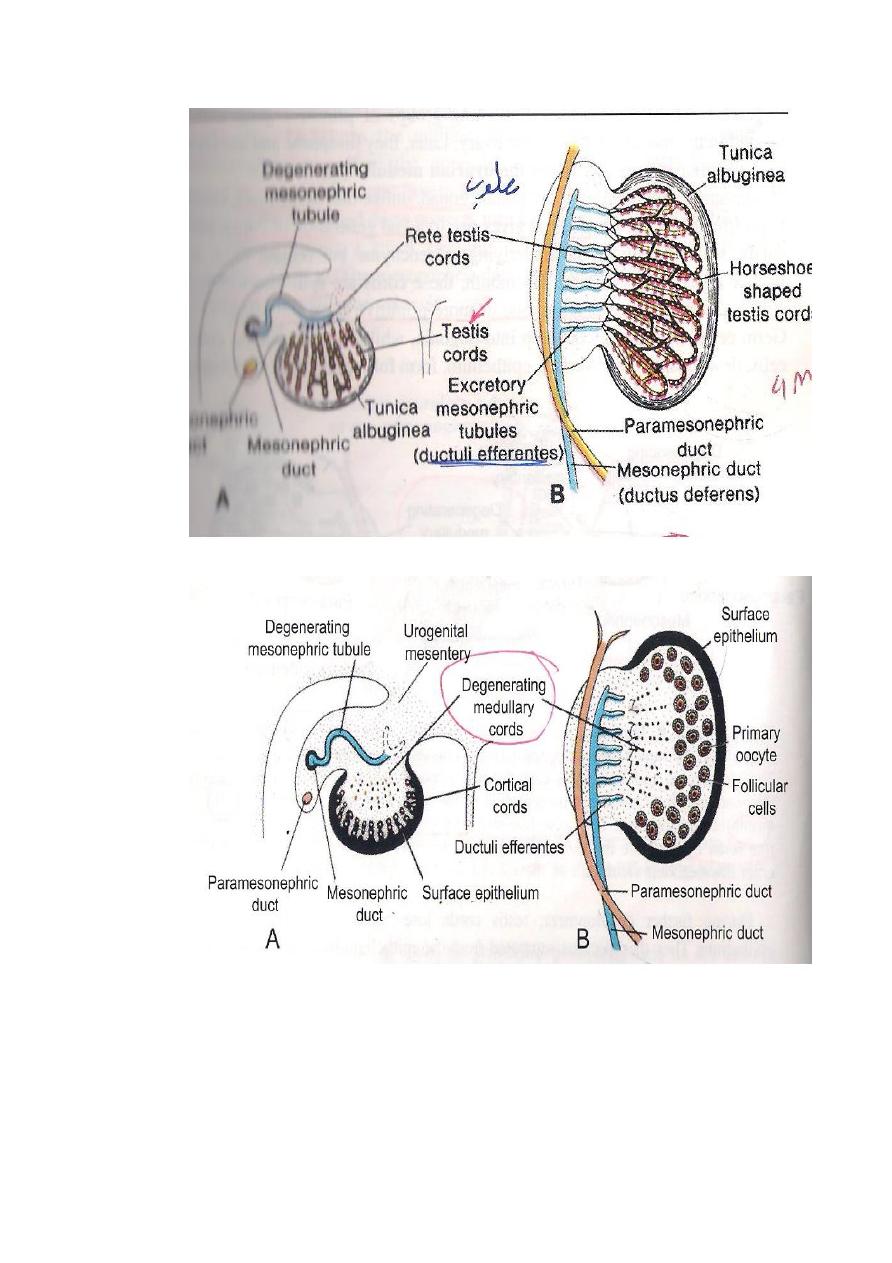
THE TESTES : It develops from the following sources:
1-From Coelomic epithelium.It gives rise to Sertoli Cells (sustentacular
cells).
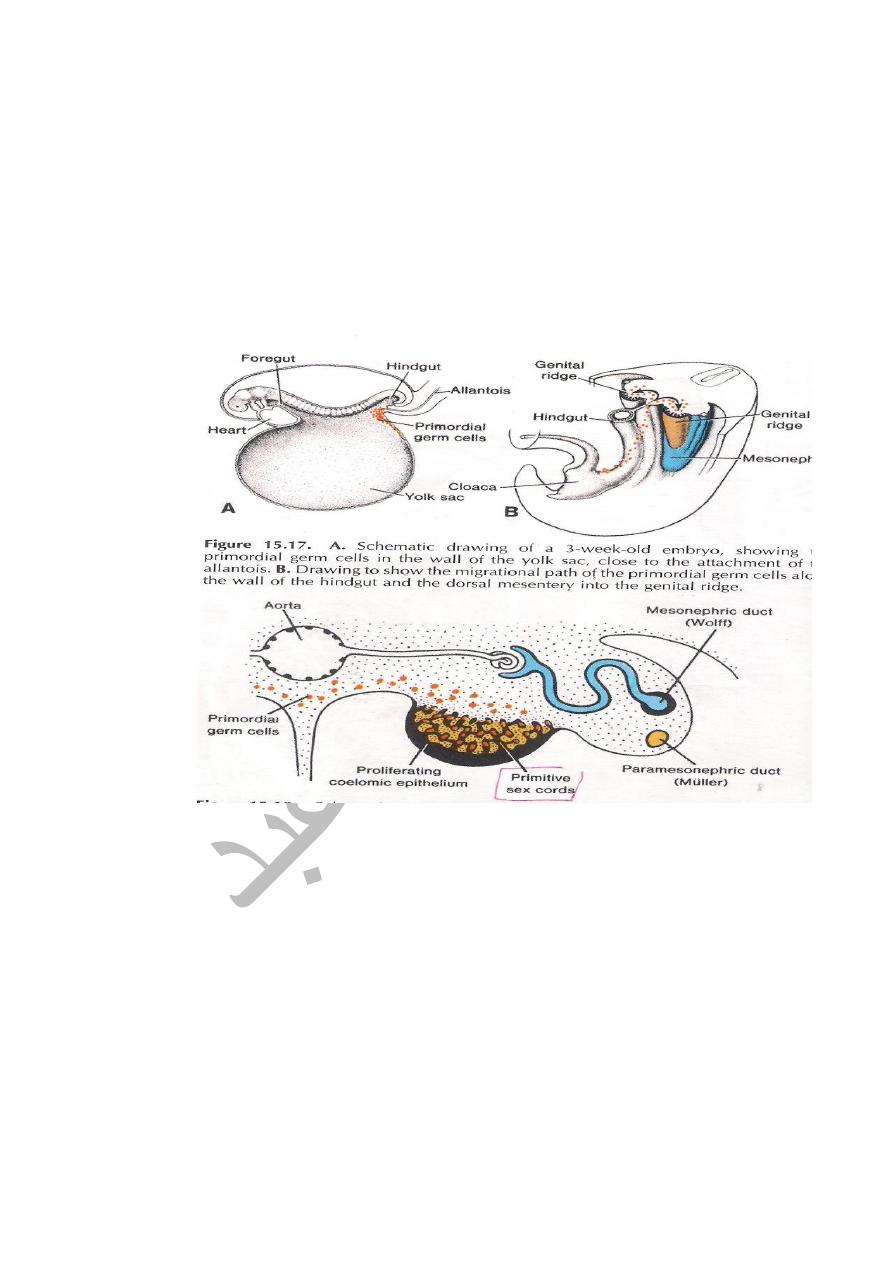
2-Primordial germ cells : are endodermal in origin and gives rise to
Spermatogonia.
3-The intermediate cell mass of mesoderm gives rise to C.T and tunica
albuginea.
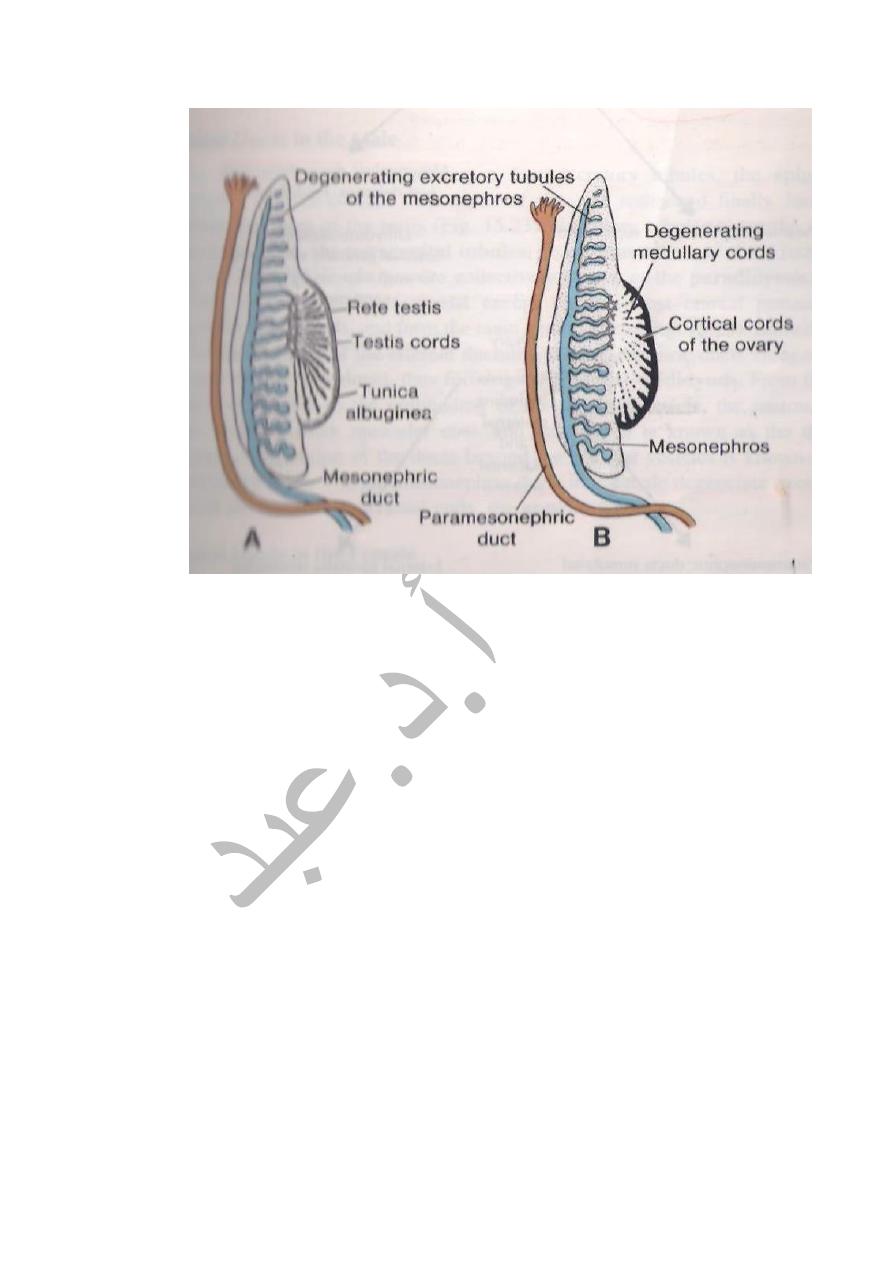
Both the Sertoli cells & Germ cells become arranged in the form of Cords
known as Testes Cords which becomes canalized later on to form the
seminiferous tubules. After its formation the Testes will start its Descend to
reach the scrotum..It is aided by:
A-Gubernaculum which is a fibrous cord extends from the lower pole of the
testes till the floor of the scrotal pouch.It traverses the muscles of anterior
abdominal wall (Inguinal canal ) to reach the scrotum.
B-Processus vaginalis : Is an evagination of peritoneal sac traped behind the
testes.
Shortening of Gubernaculum together with lengethening of the embryo help
the descend of the testes retroperitoneally to enter :
1-The inguinal canal at 7
th
month.
2-Inside the scrotum at birth ( 9
th
month )
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES
1-Congenital oblique inguinal hernia or congenital hydrocele due to patent
processus.
2-Cryptorchism.Failure of descend of testes and it stops at any of following
sits. a-Superficial inguinal ring.
b-Root of the penis.
c-Perineum.
3-Ectopic testes as in upper part of thigh or in the lower anterior abdominal
wall. 4-Gonadal dysgenesis;The genital ducts & external genitalia fail to
form properly. 5-Hermaphroditism : could be true (the gonads & external
genitalia are of both sexes),or pseudohermophroditism(the gonads of one
sex,while external genital are of other sex).
THE OVARY: It develops from the followings.
1-From Coelomic epithelium .It forms the Follicular cells.
2-From the Primordial cells which migrates from the wall of the Yolk Sac,it
forms oogonia.
3-From intermediate cell mass which forms the the stroma of the Ovary &
Tunica Albuginea.
The Primordial cells & Coelomic epithelium form Cords of Cells as separated
masses known as Primordial Follicles.Each follicle is formed from Oogonium
surrounded by follicular cells.
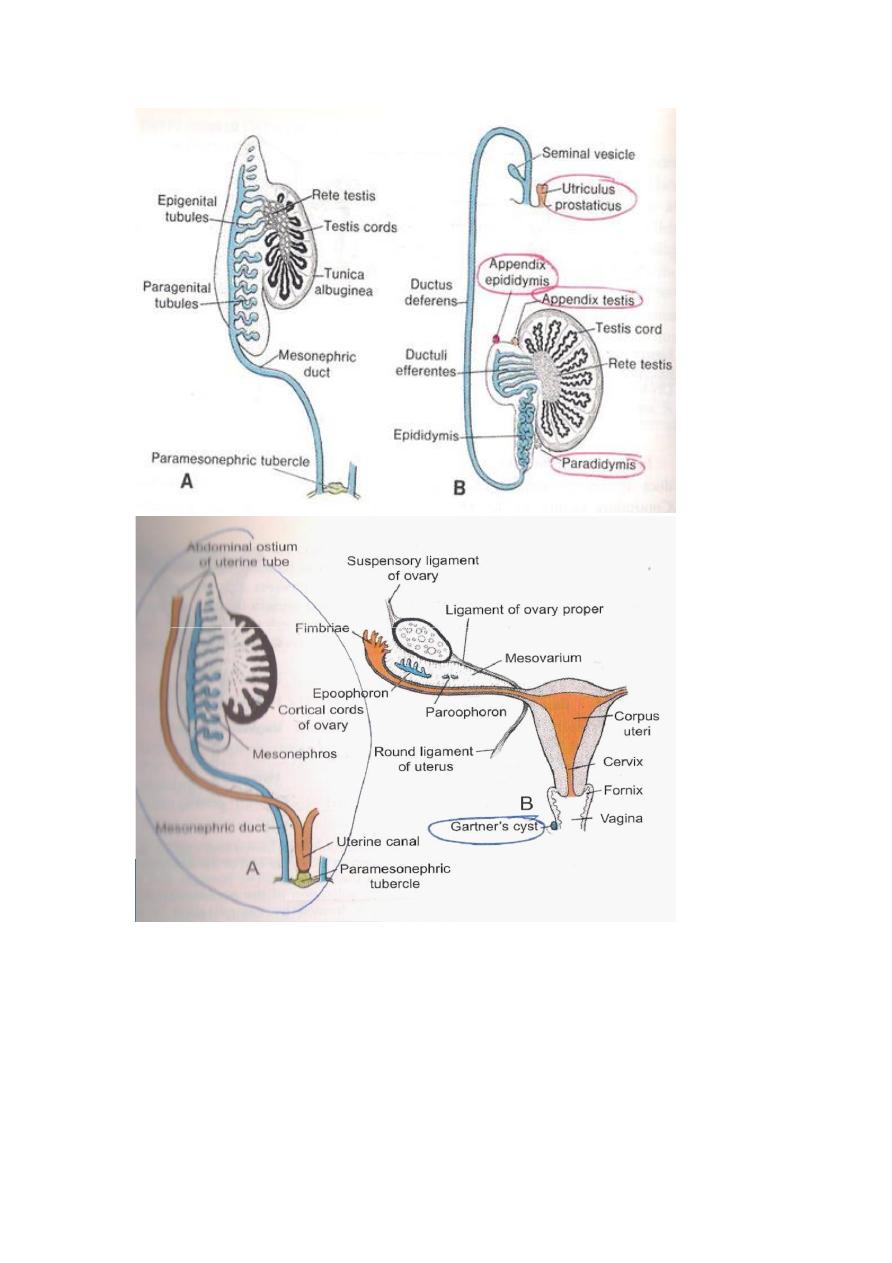
The Ovary is attached by Gubernaculum which traverses the ovary via the
anterior abdominal wall (in the inguinal canal) to reach the pelvic region
while gubernaculum will reach the labia majora.The Gubernaculum is
divided in to 2 parts:
1-The cranial part will form the ligament of the Ovary (between ovary and
uterus). 2-The caudal part forms the Round ligament of uterus
(between uterus & labia majora).
THE PARAMESONEPHRIC DUTS (MULLERIAN )
Two longitudinal ducts one on each side and descend very close to
Mesonephric(Wollfian)Duct.
Each duct has cranial end opens in to the peritoneal cavity & caudal end near
posterior wall of definitive urogenital sinus.In its course is divided in to 3
parts,cranial part descends vertically & lateral to mesonephric duct, an
intermediate part crosses transversely ventral to Mesonephric duct,while the
caudal part descends vertically & medial to Mesonephric duct.
Fate of the Paramesonephric ducts
1-In the Female.The cranial vertical part forms the uterine tube with its
lateral end opens in to the peritoneal cavity (coelomic cavity),its intermediate
transverse part forms the fundic region & upper part of the body of the
uterus,while the caudal parts are vertical and fuses together forming the
lower part of body of uterus & the cervix.
2-In the Male.It disappears completely except for 2 small parts at its ends
which gives off
A-Appendix of the testes from the cranial end.
B-The prostatic utricle ( Utriculus prostaticus ) from the caudal end.
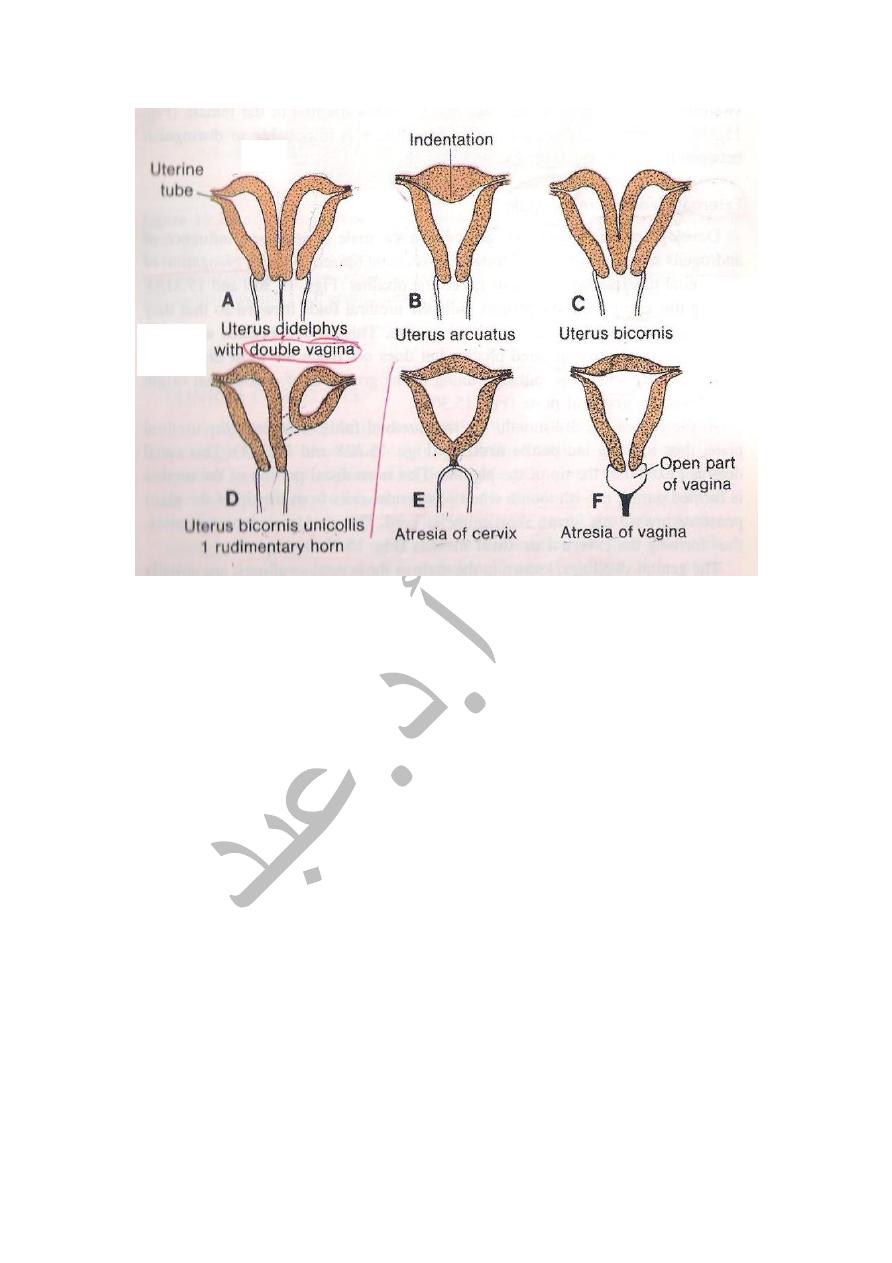
ANOMALIES OF UTERUS
1-Uterus Didelphys ( Double uterus ),here the 2 paramesonephric ducts
fail to fuse completely in the genital cord ,where each duct forms a
separate uterus & each one has its own Vagina.
2-Uterus Bicornis Bicolis.Double uterus with double cervix BUT single
CERVIX. 3-Bipartite Uterus.In this case the caudal parts of the 2
paramesonephric ducts fuse together but the septum in between persists
and thus there is a single uterus & its cavity is divided in to parts by a
septum. 4-Biconuate
Uterus.The uterus is single but has 2 separate horns due to improper
development of the Fundus.
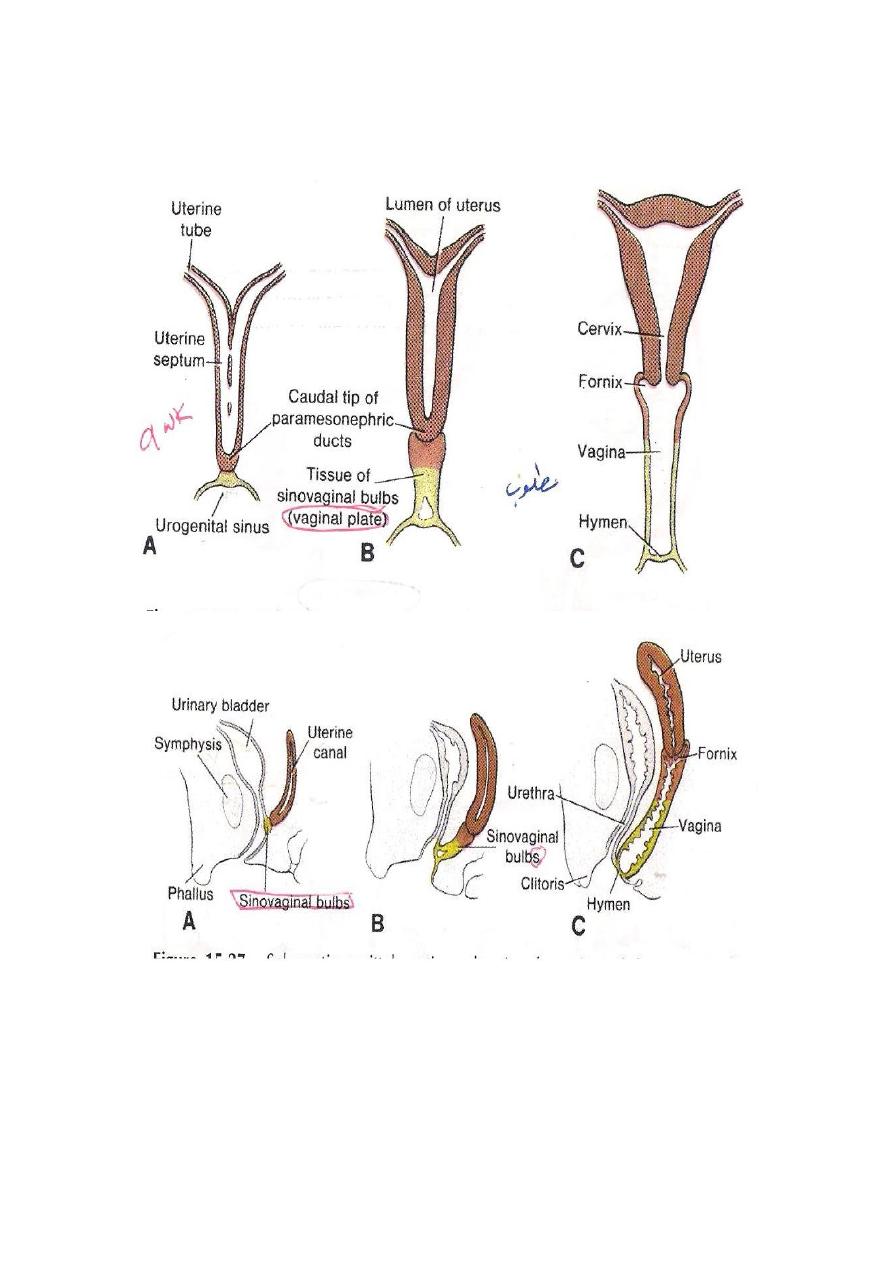
DEVELOPMENT OF THE VAGINA
The caudal part of the 2 Mullerian ducts fuses & produces the Mullerian
Tubercle( a bulg in to the cavity of the definitive urogenital sinus).At the
Mullerian tubercle the the endoderm lining the the urogenital sinus forms
2 Sino – Vaginal bulbs ,which fuses to form the Vaginal plate.The Vaginal
plate then becomes canalized forming the lumen of the Vagina .Its
expansion forms the followings: 1-
The Vaginal Orifices.
2-The Hymen.
Anomalies:
1-Absent Vagina due to failure of canalization of the Vaginal plate.
2-Imperforated Hymen.