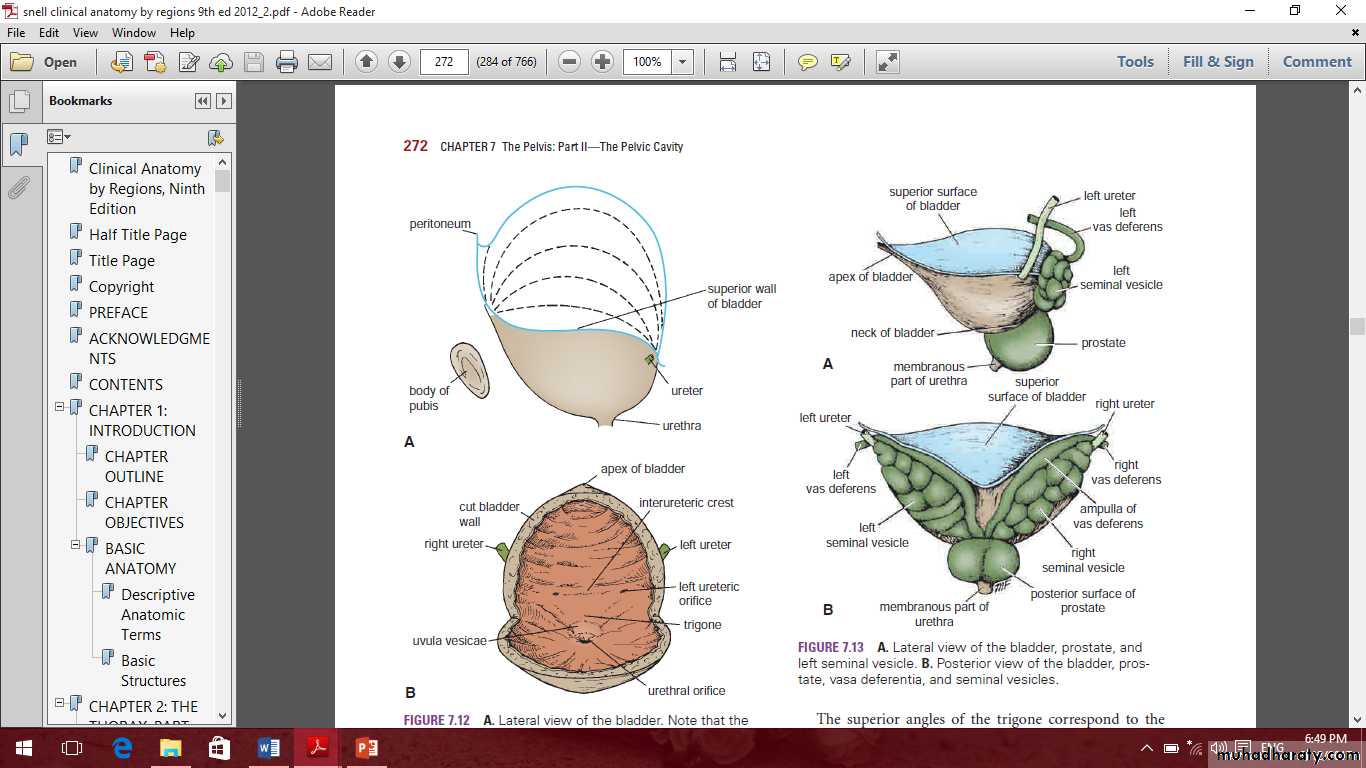
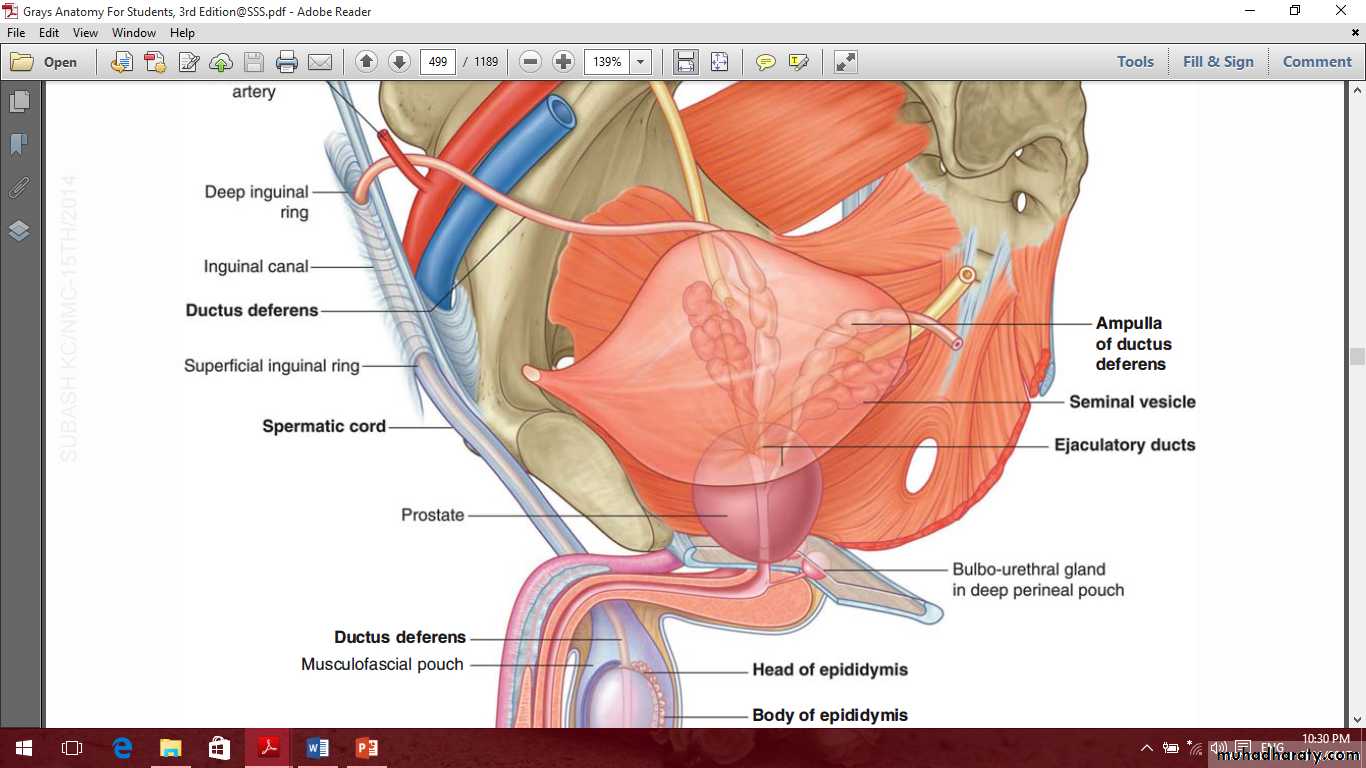
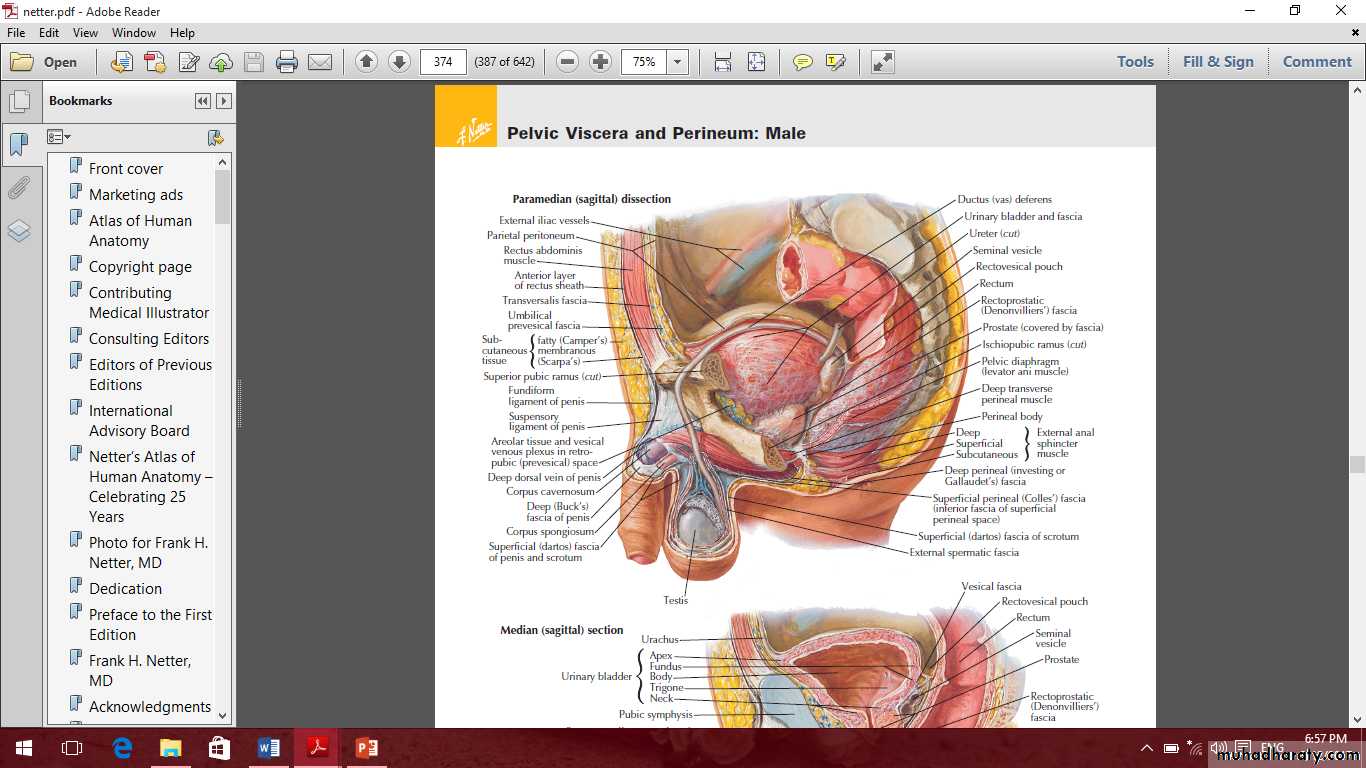
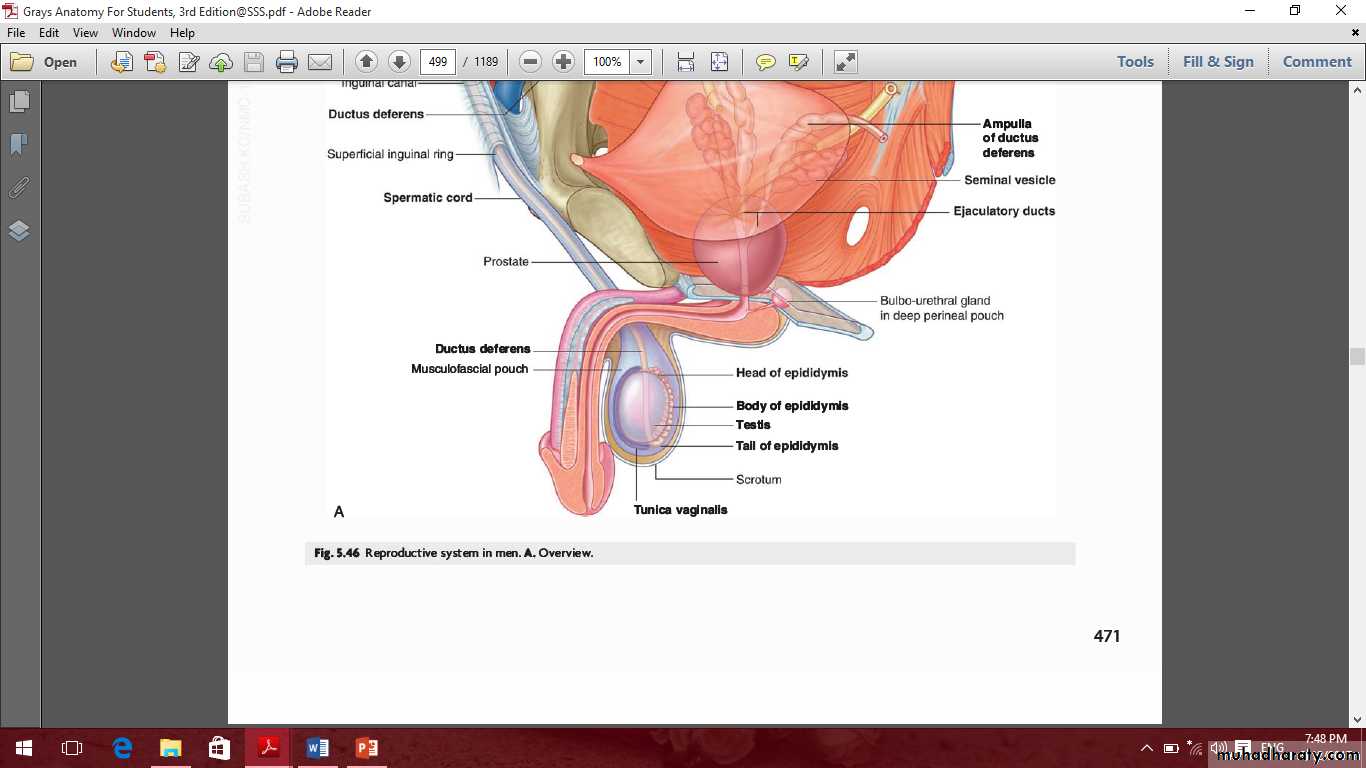
Male internal genital organs
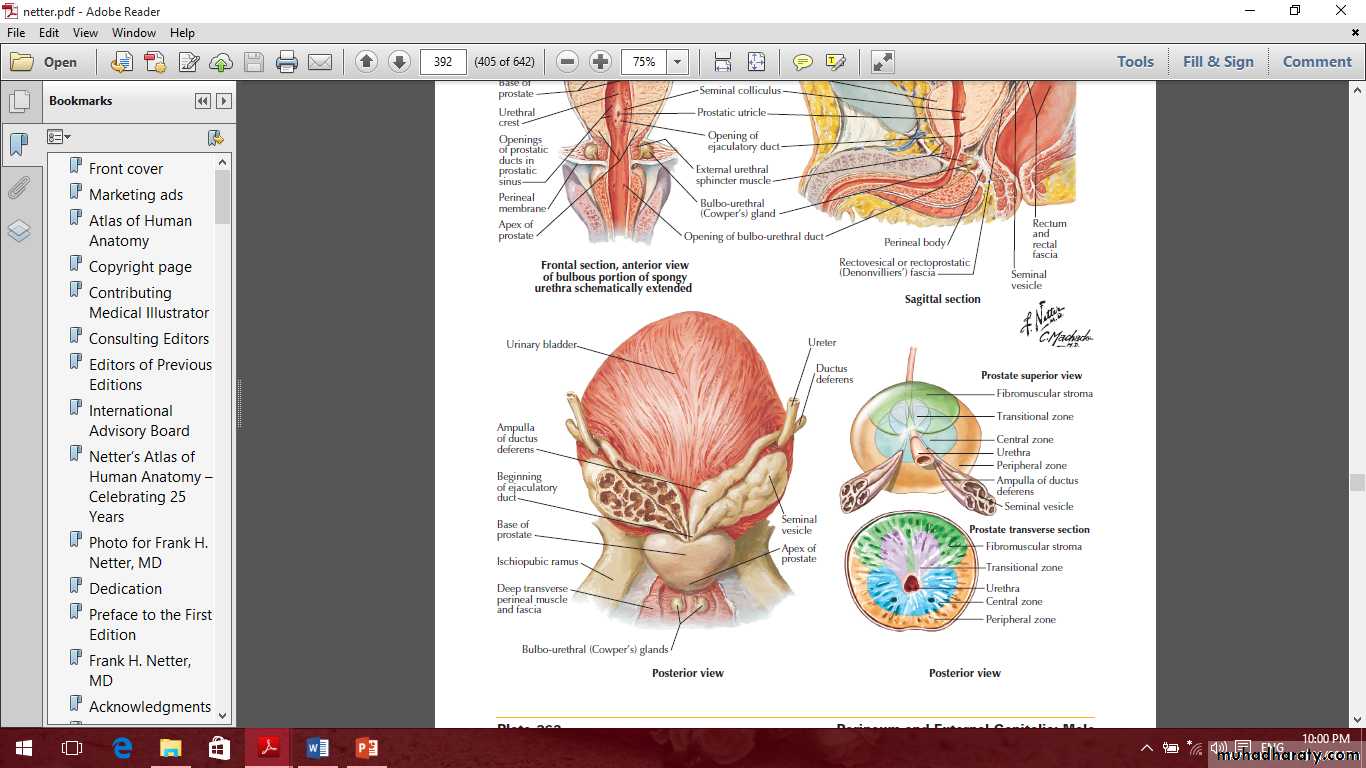
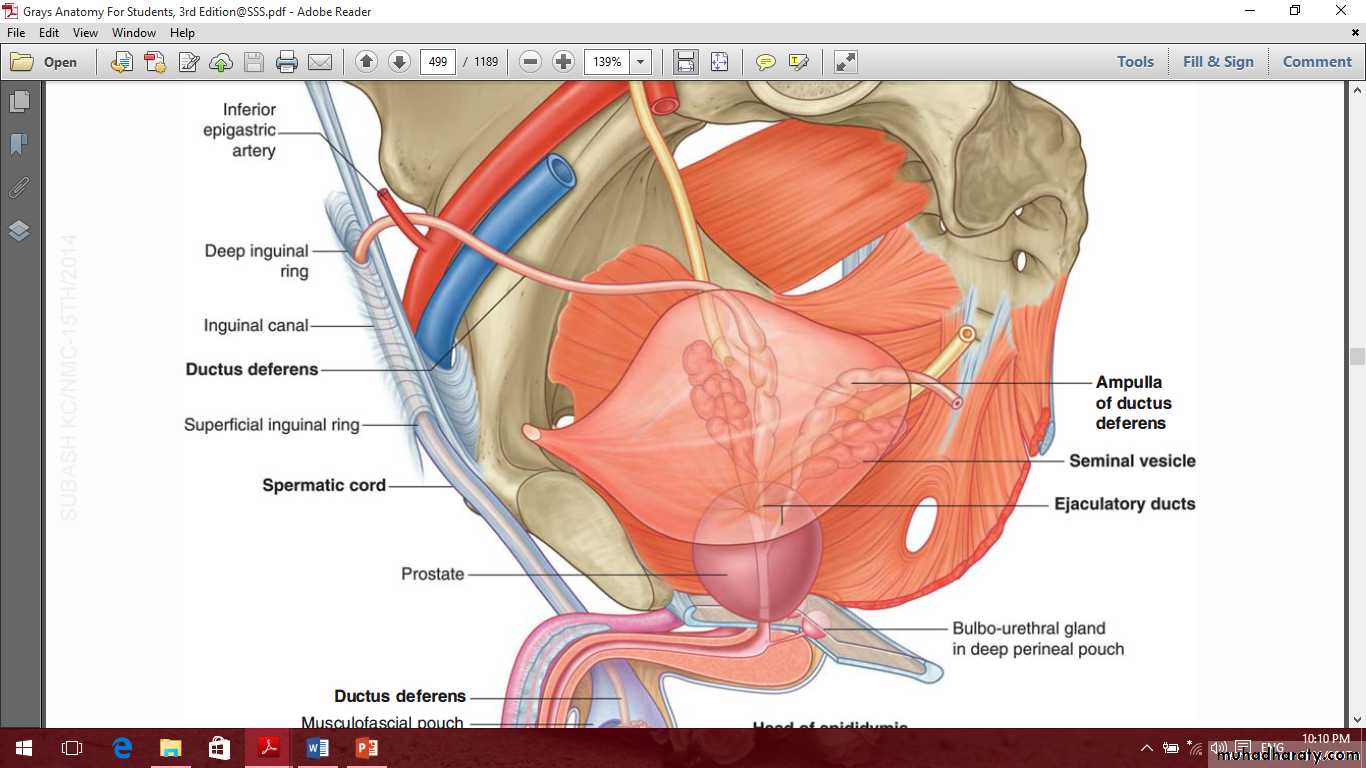
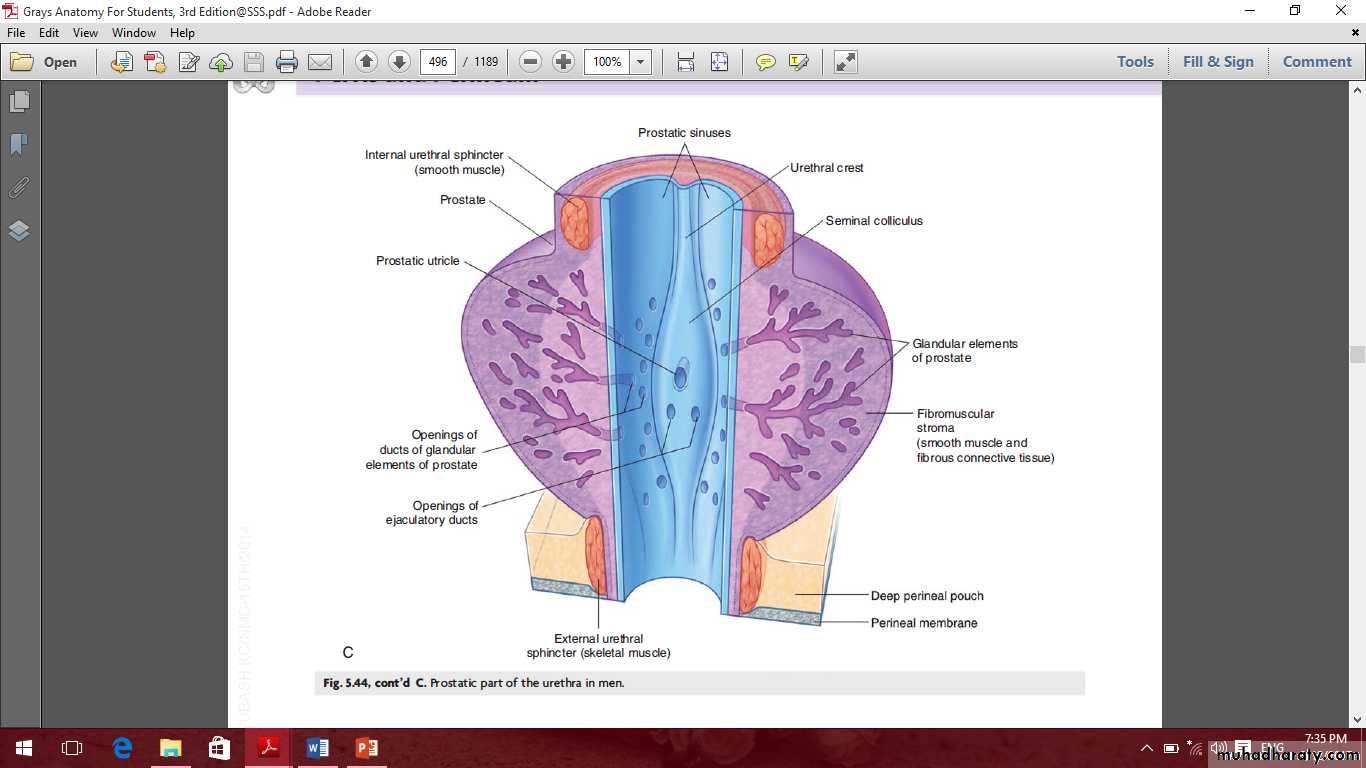
IncludeProstate
Seminal vesicle
Ductus deferens
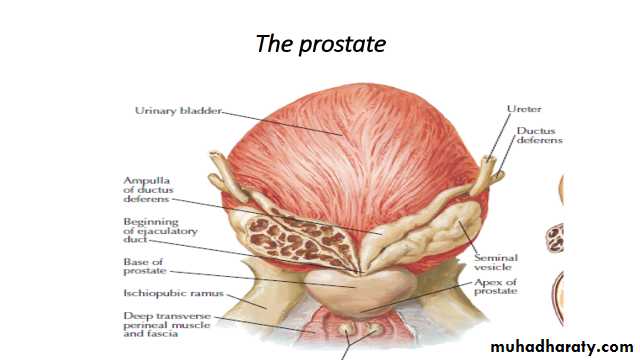
Prostate
Seminal vesicle
Ductus deferens
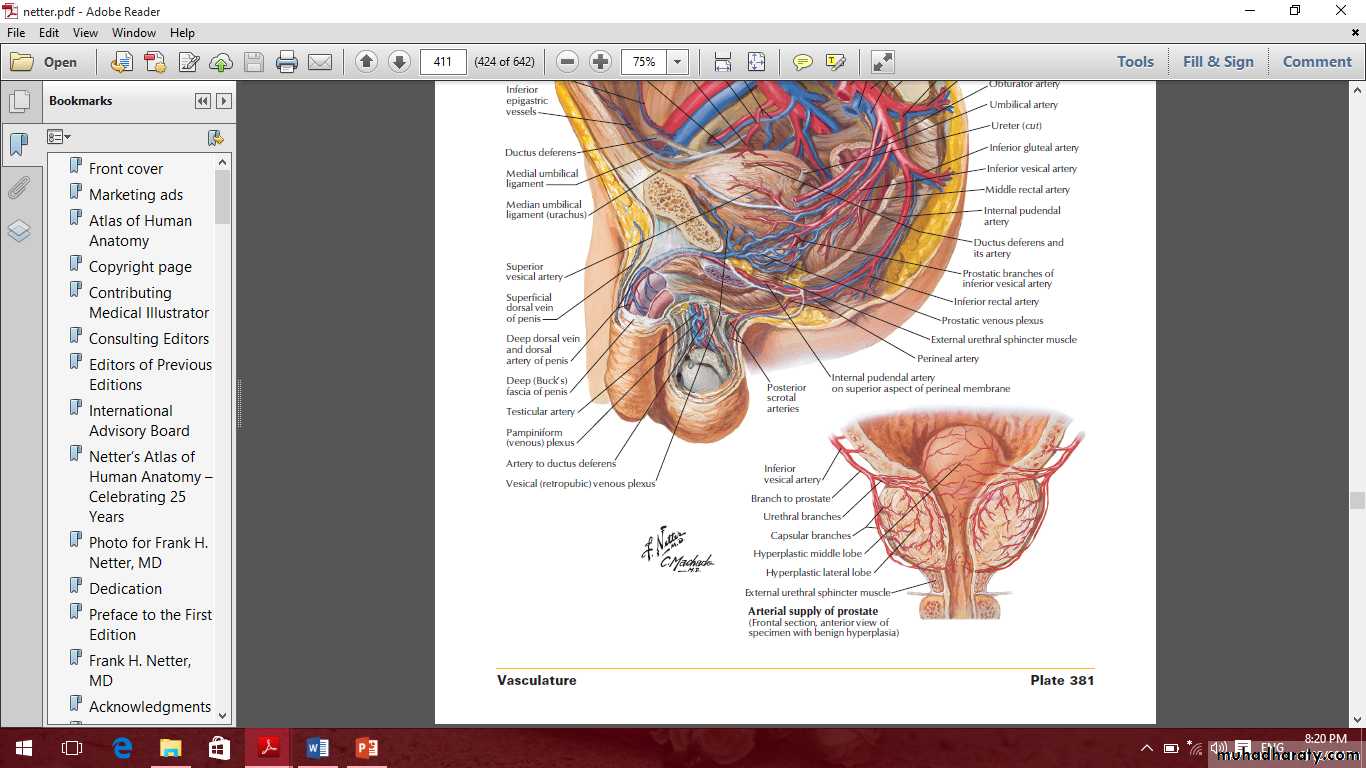
Blood supply of the prostate, seminal vesicle and ductus deferens
1- Superior vesical artery supply the superior part of the bladder, seminal vesicle and ductus deferens.2- Inferior vesicle artery supply the base of the bladder, Seminal vesicle and ductus deferens through a slender branch called the deferential artery.
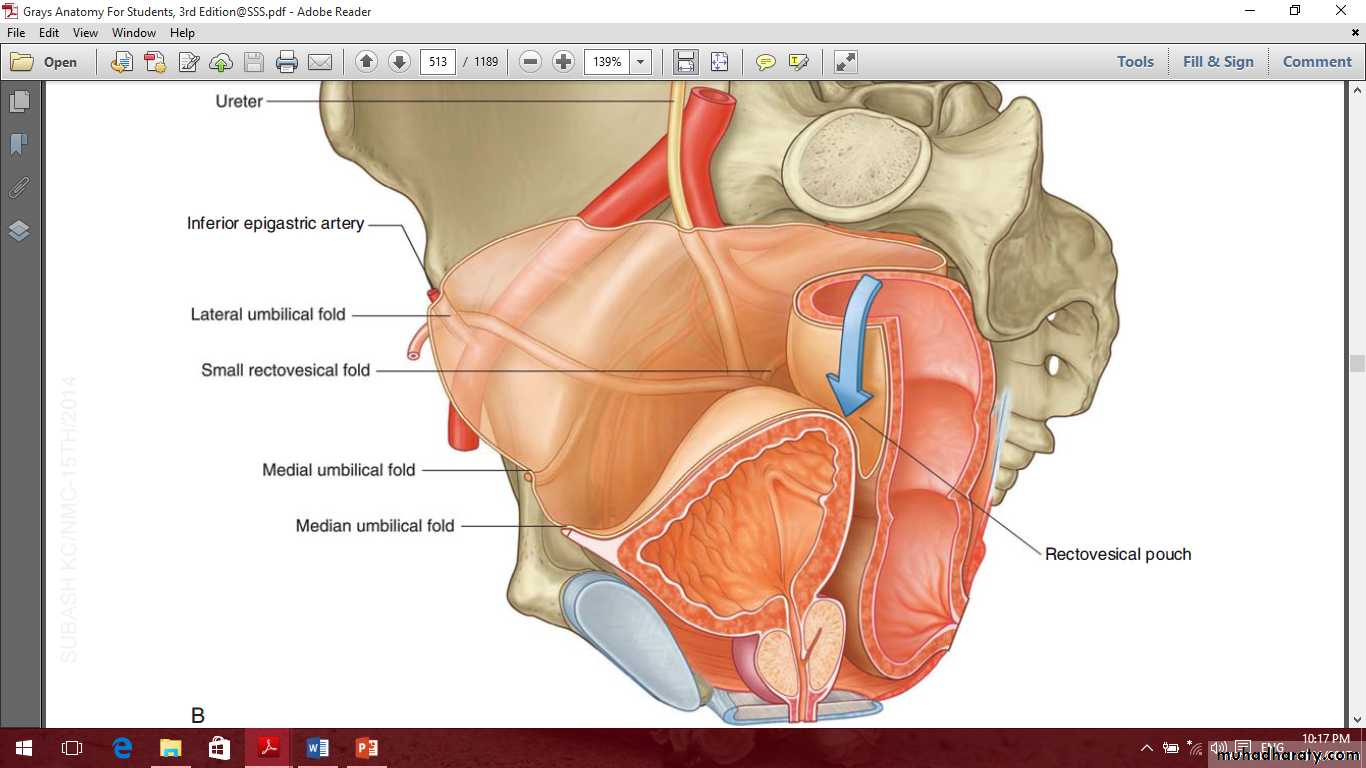
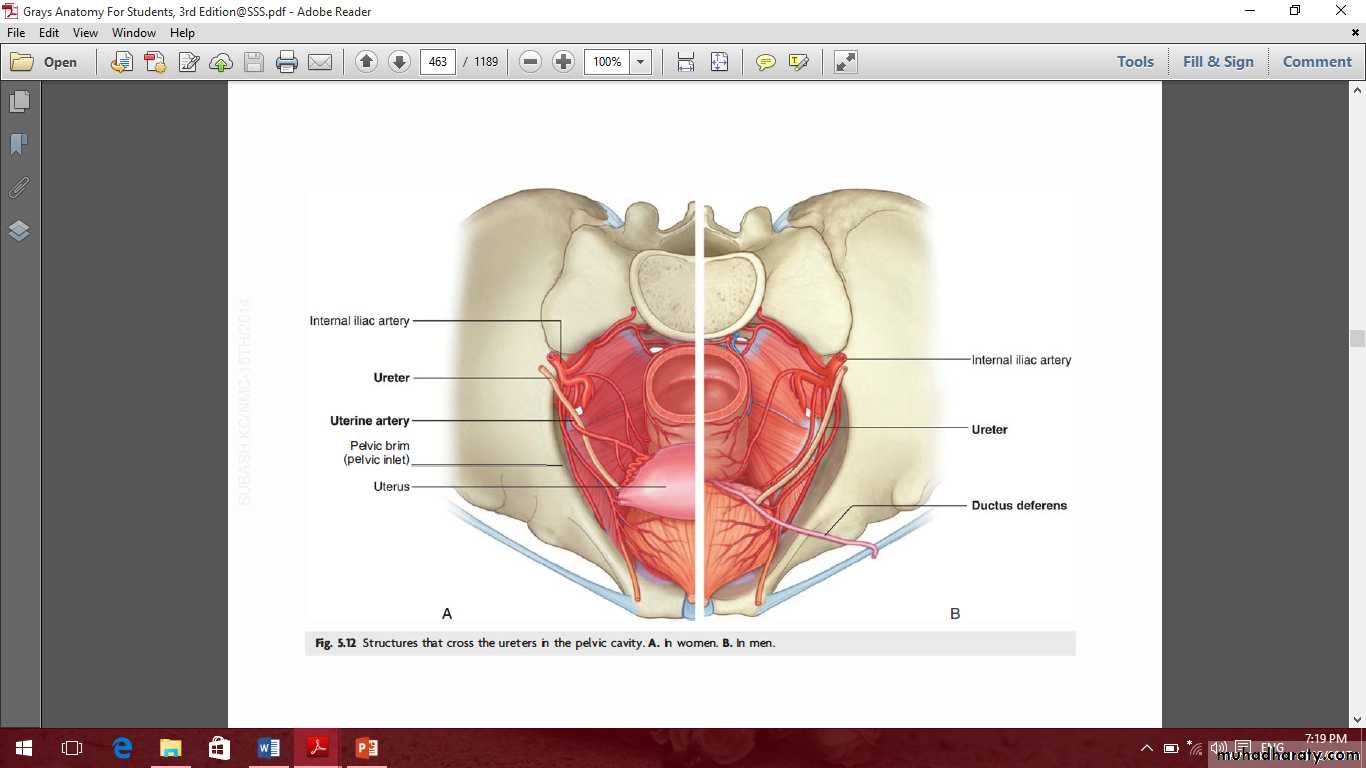
Pelvic ureter in male
Pelvic ureter
Pelvic ureter in female
Pelvic ureter in female
Blood supply of the ureter
1- From the superior vesical artery.2- From internal or common iliac artery.
3- In female it receives branches from the uterine artery.
Venous drainage
The inferior part drain into the internal iliac vein.
The superior part to the ovarian or testicular vein.
Lymphatic drainage pass to the lumbar nodes.
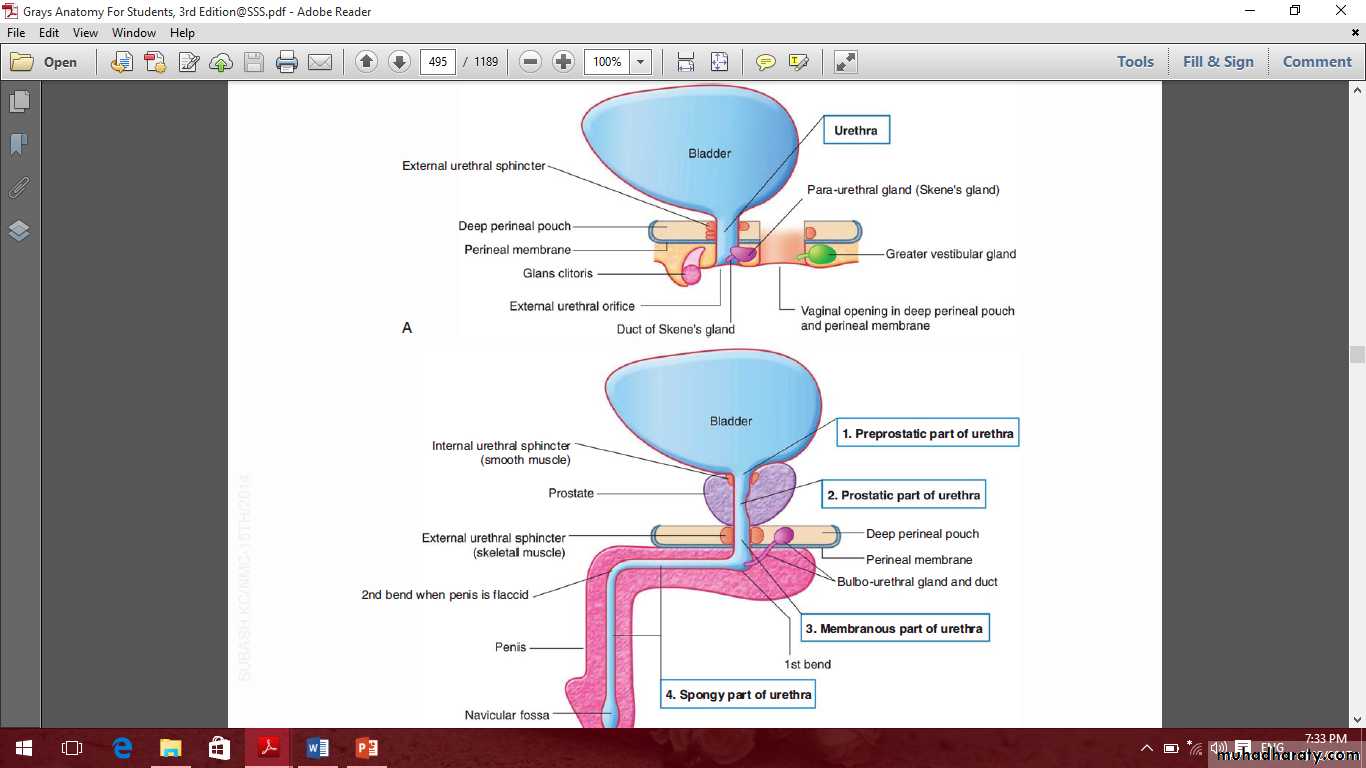
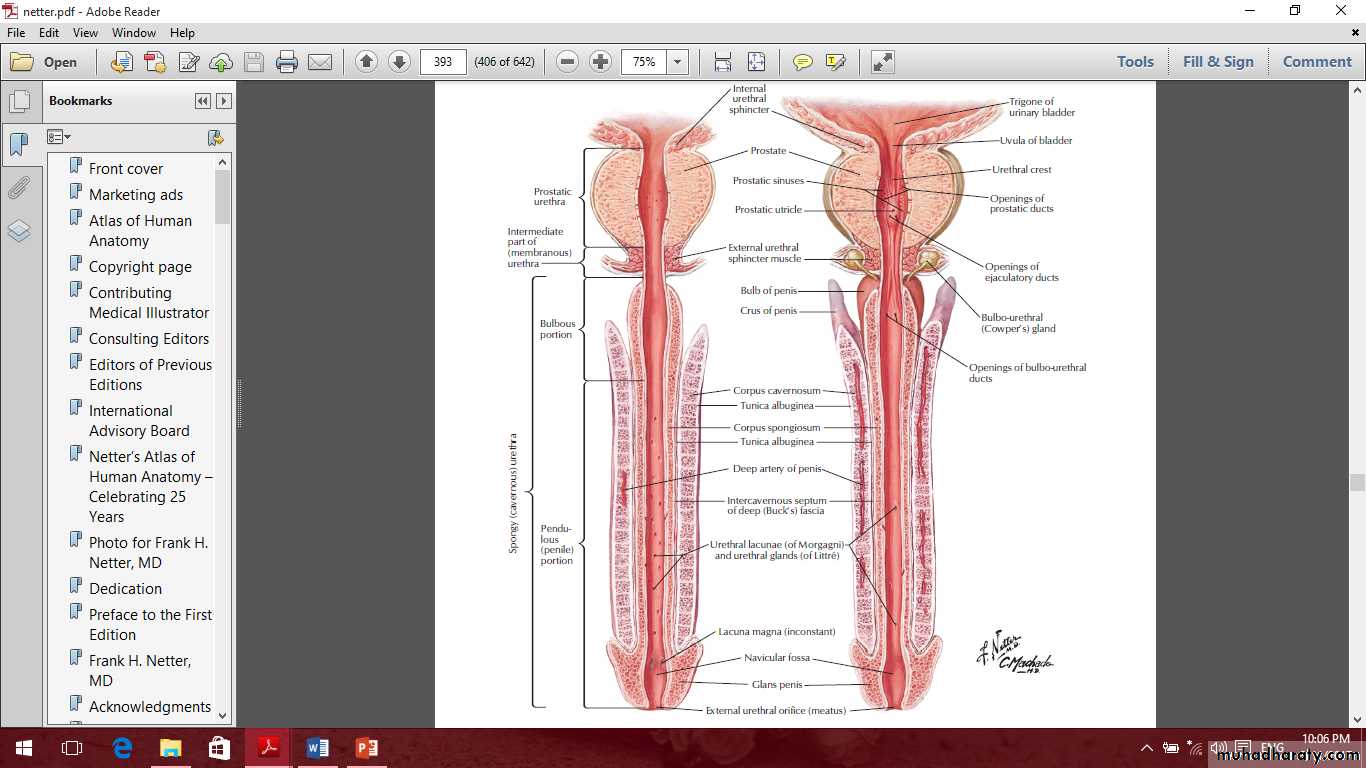
Male urethra
Prostatic urethra
Membranous and spongy urethra
Membranous and spongy urethra
Blood supply of male urethra
1-The prostatic part through prostatic artery from the inferior vesical artery.2-The membranous and spongy parts through the artery of the bulb of the penis from the internal pudendal artery.
Venous drainage through internal iliac vein.
Lymphatic drainage
To the internal iliac nodes from the distal part of the spongy urethra pass to the deep inguinal nodes.
Female urethra
Blood supply of female urethra
Branches from vaginal artery
Branches from internal pudendal artery.
Venous drainage to the internal iliac vein
Lymphatic drainage to the internal iliac nodes.
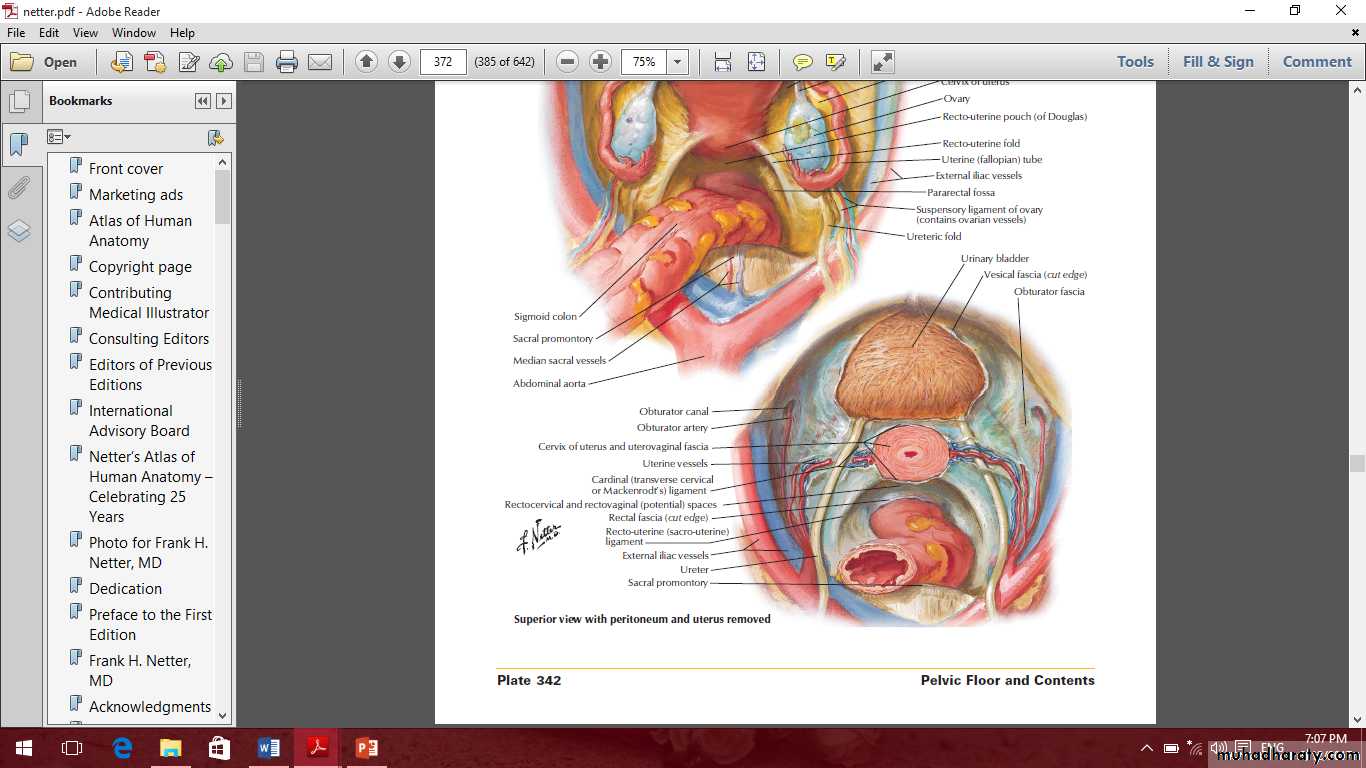
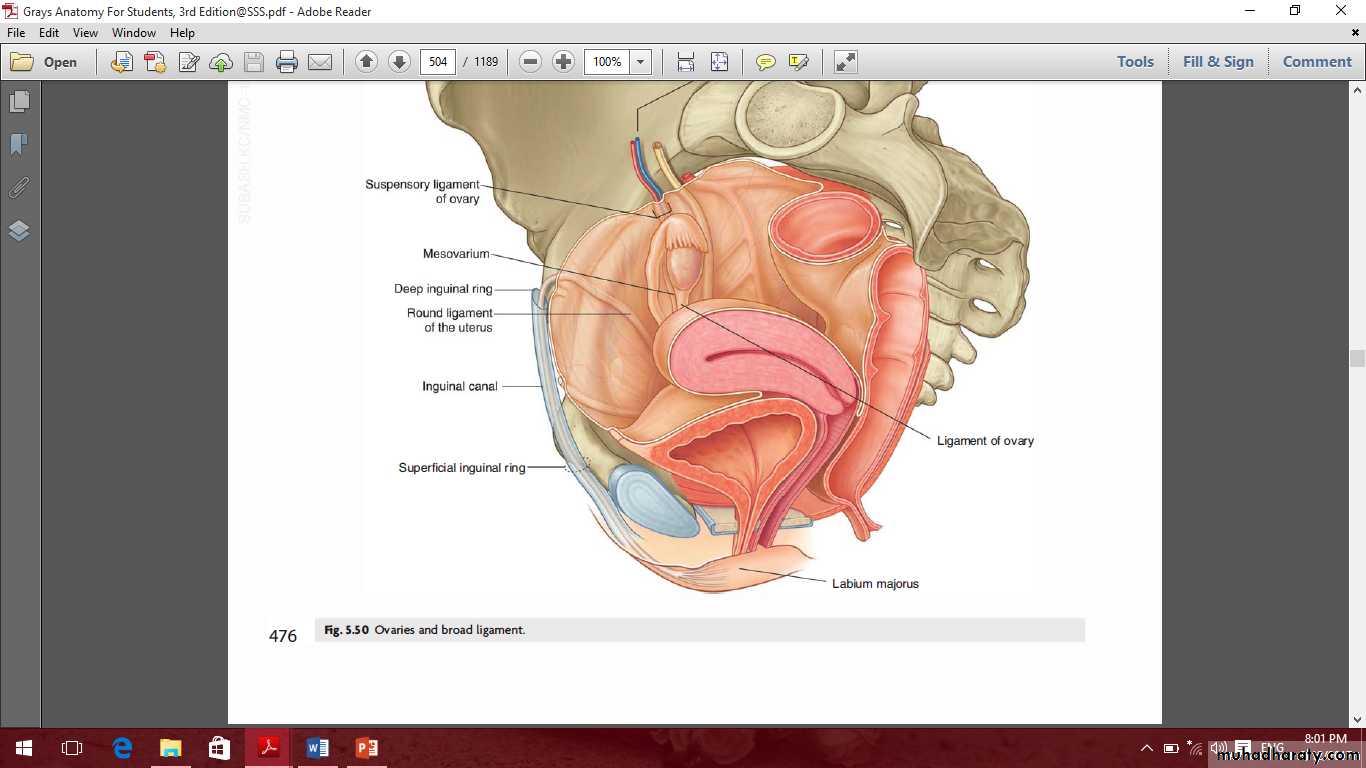
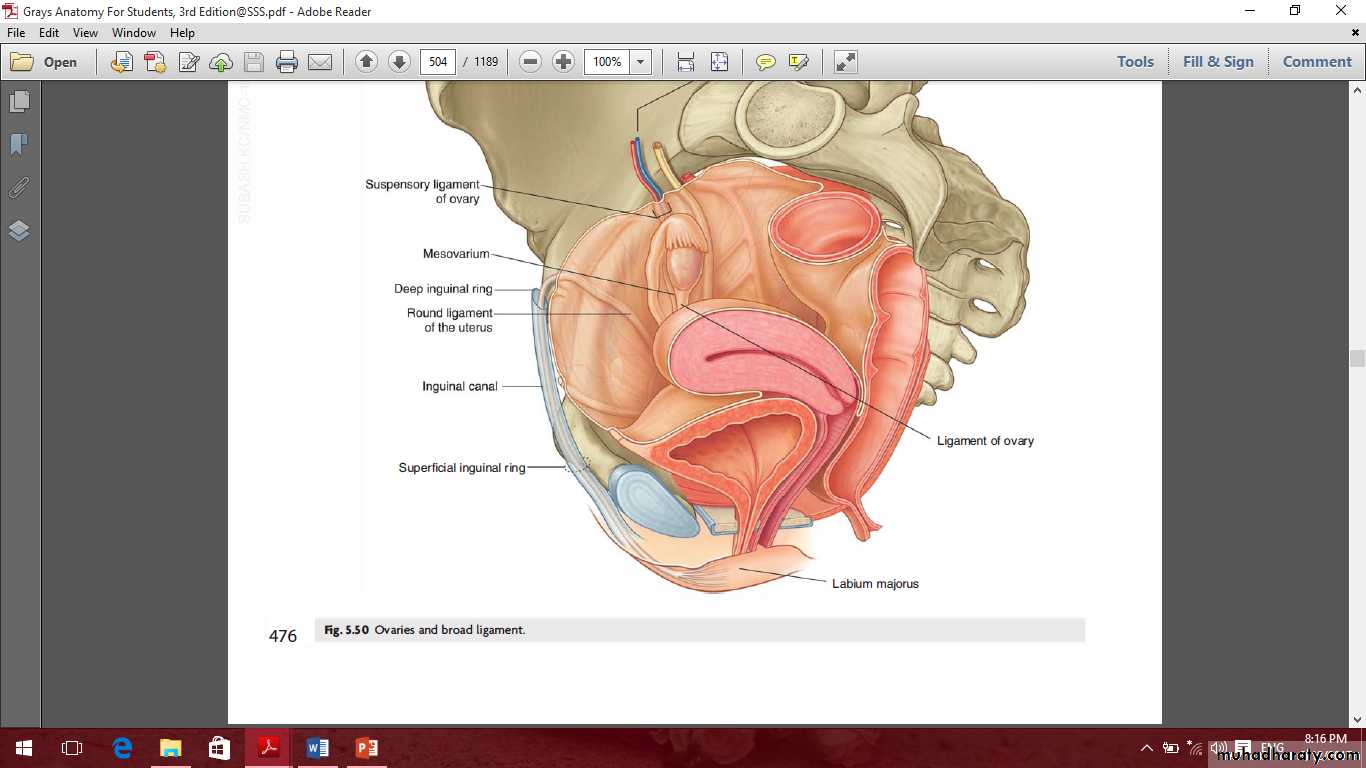
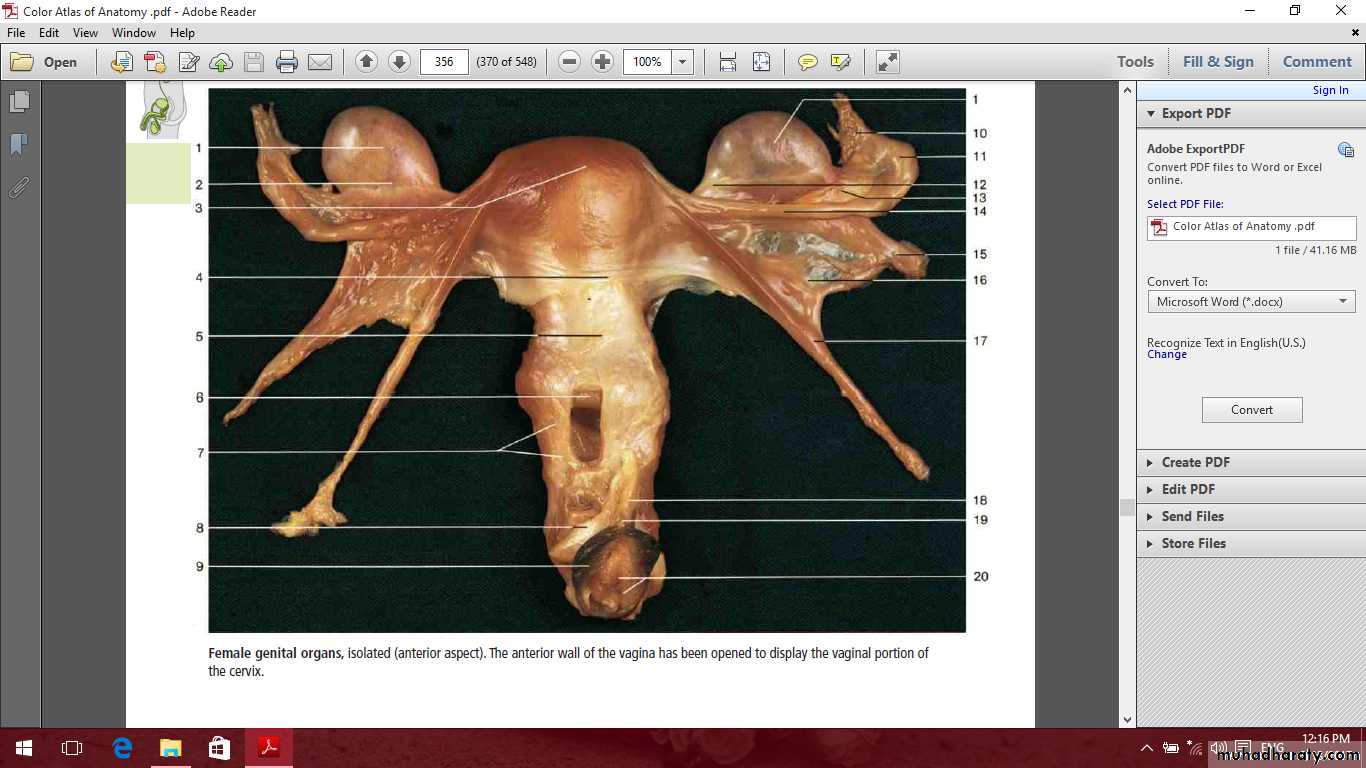
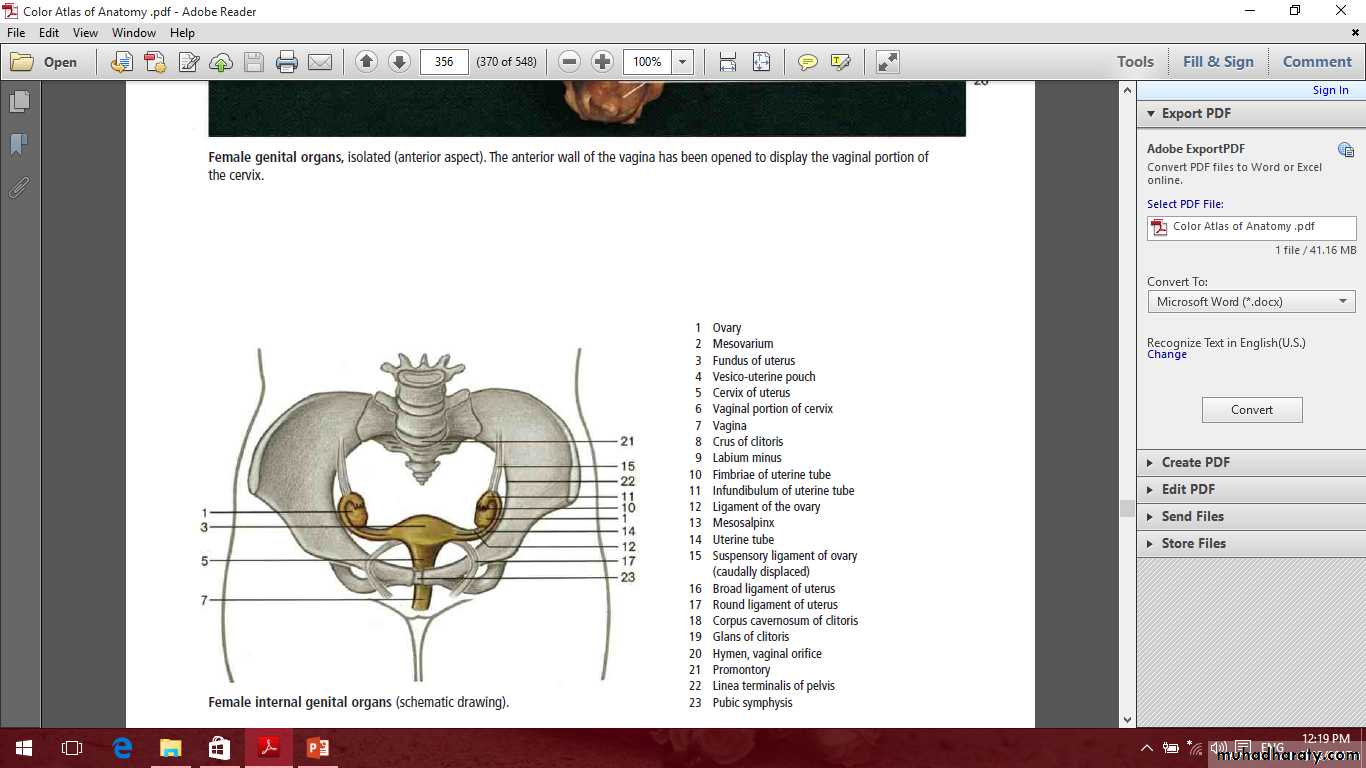
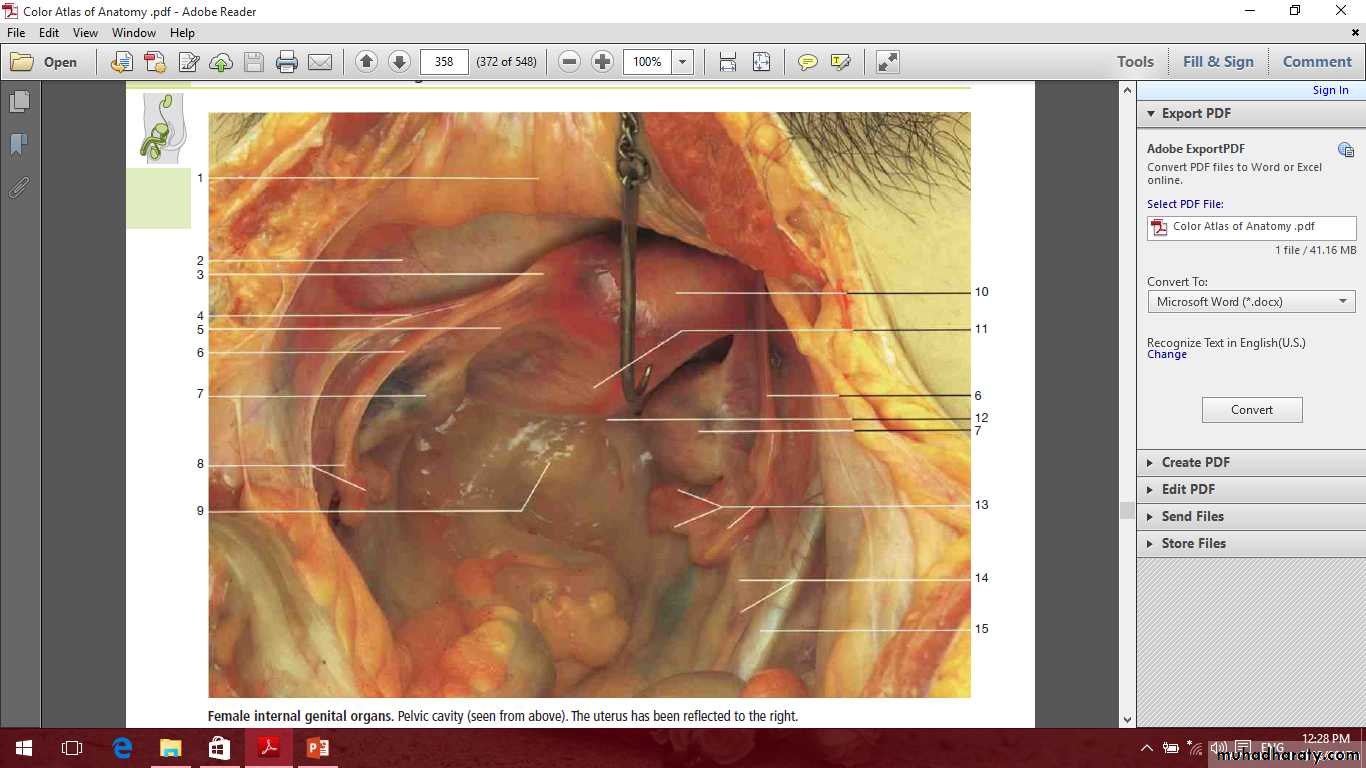
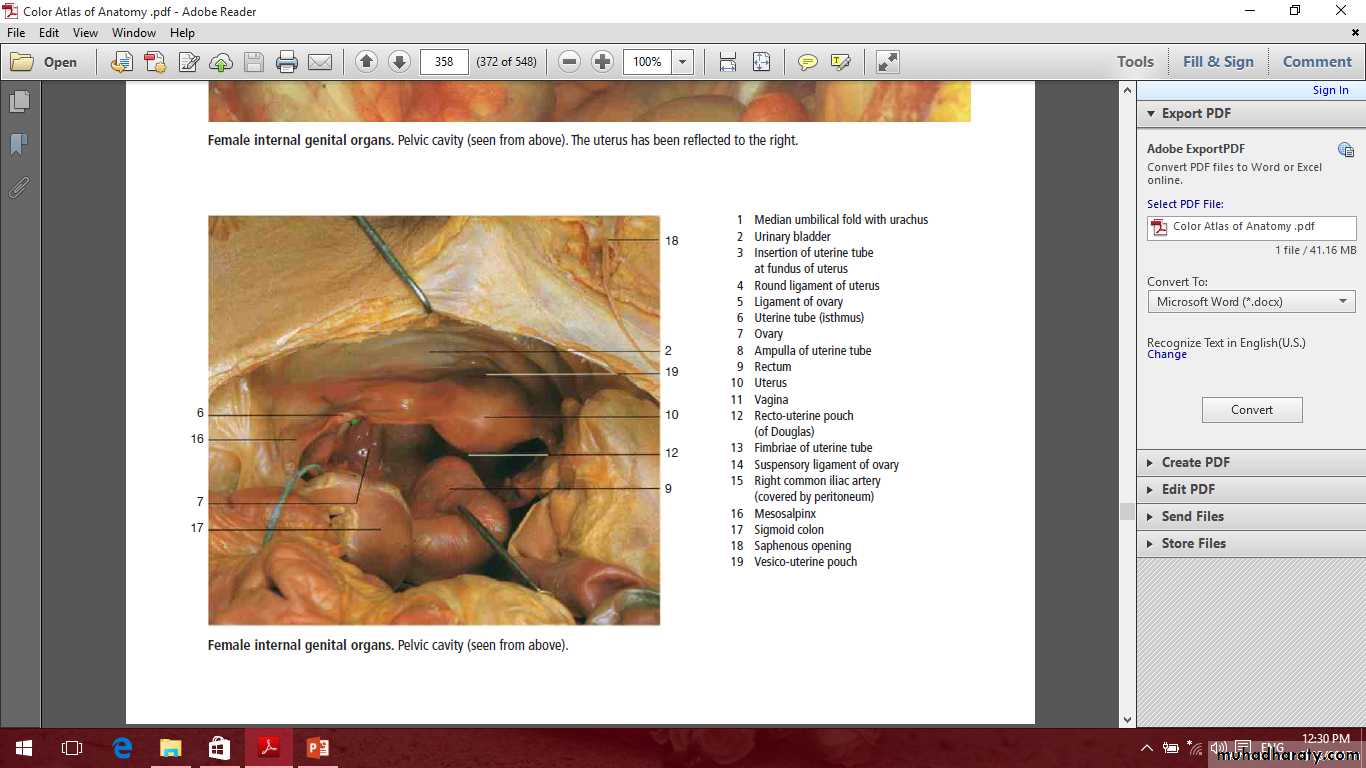
Female internal genital organs
Include the
Ovaries
uterine tubes
uterus
vagina.
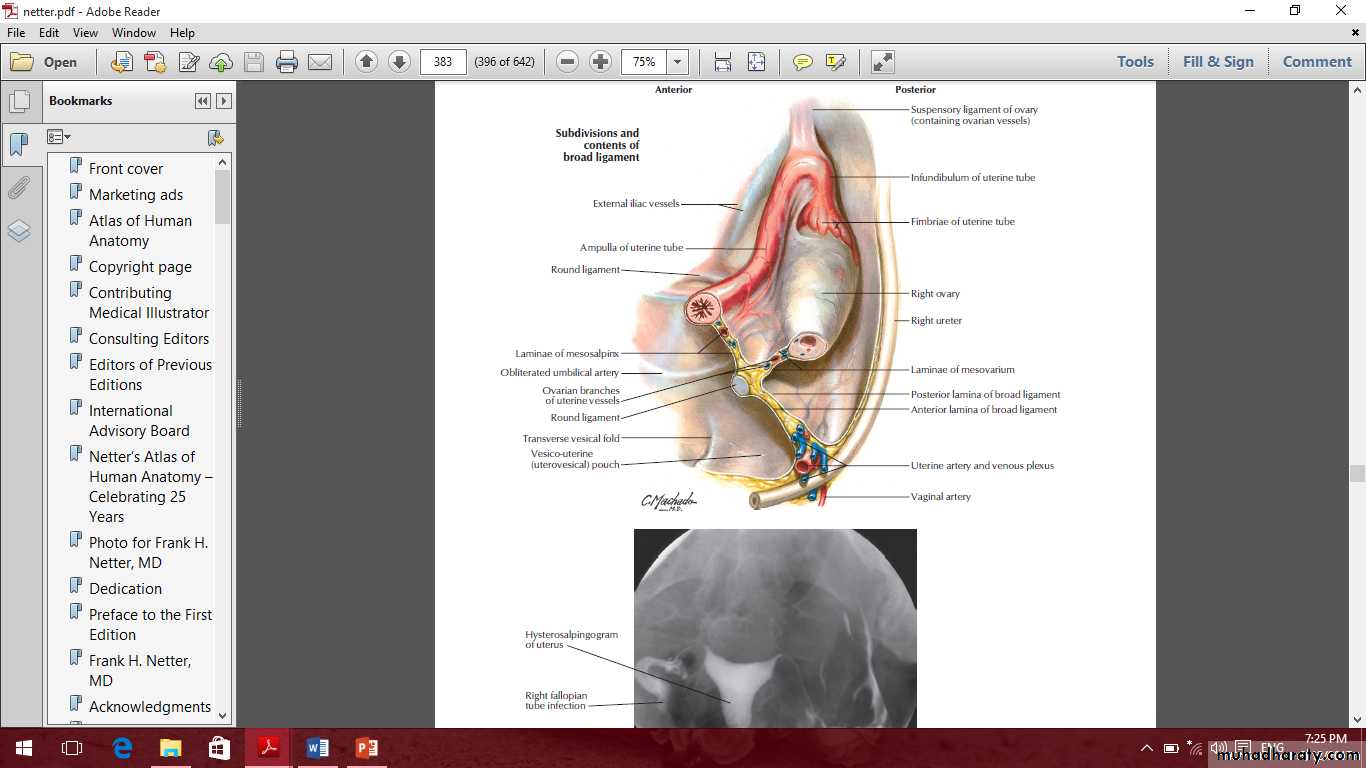
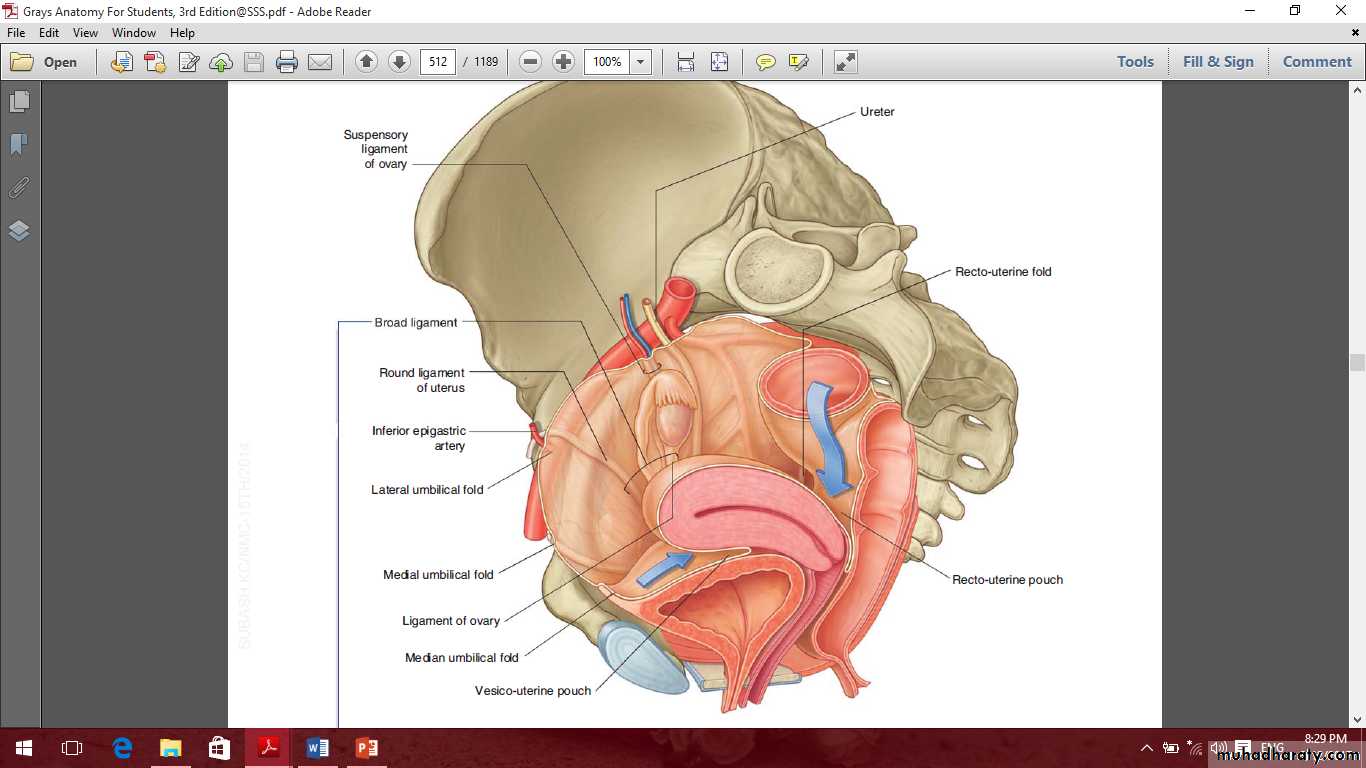
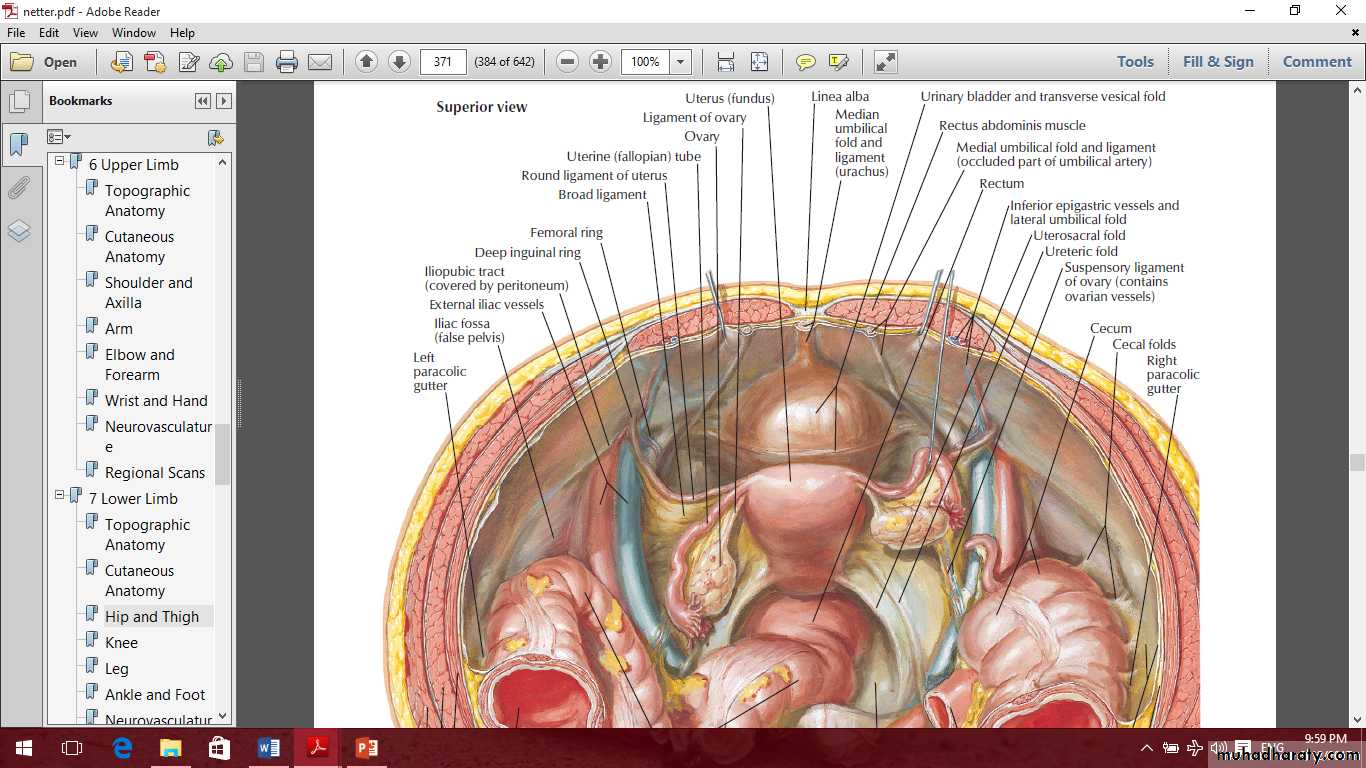
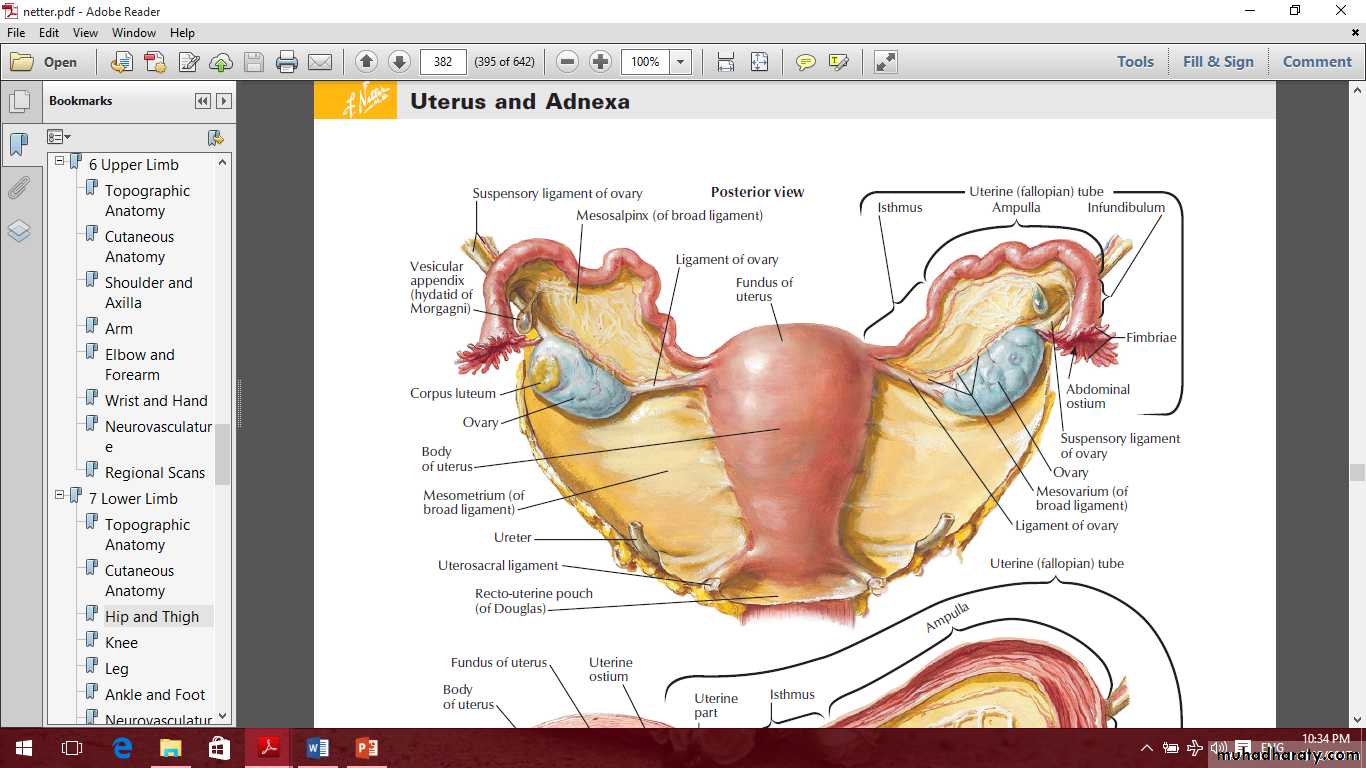
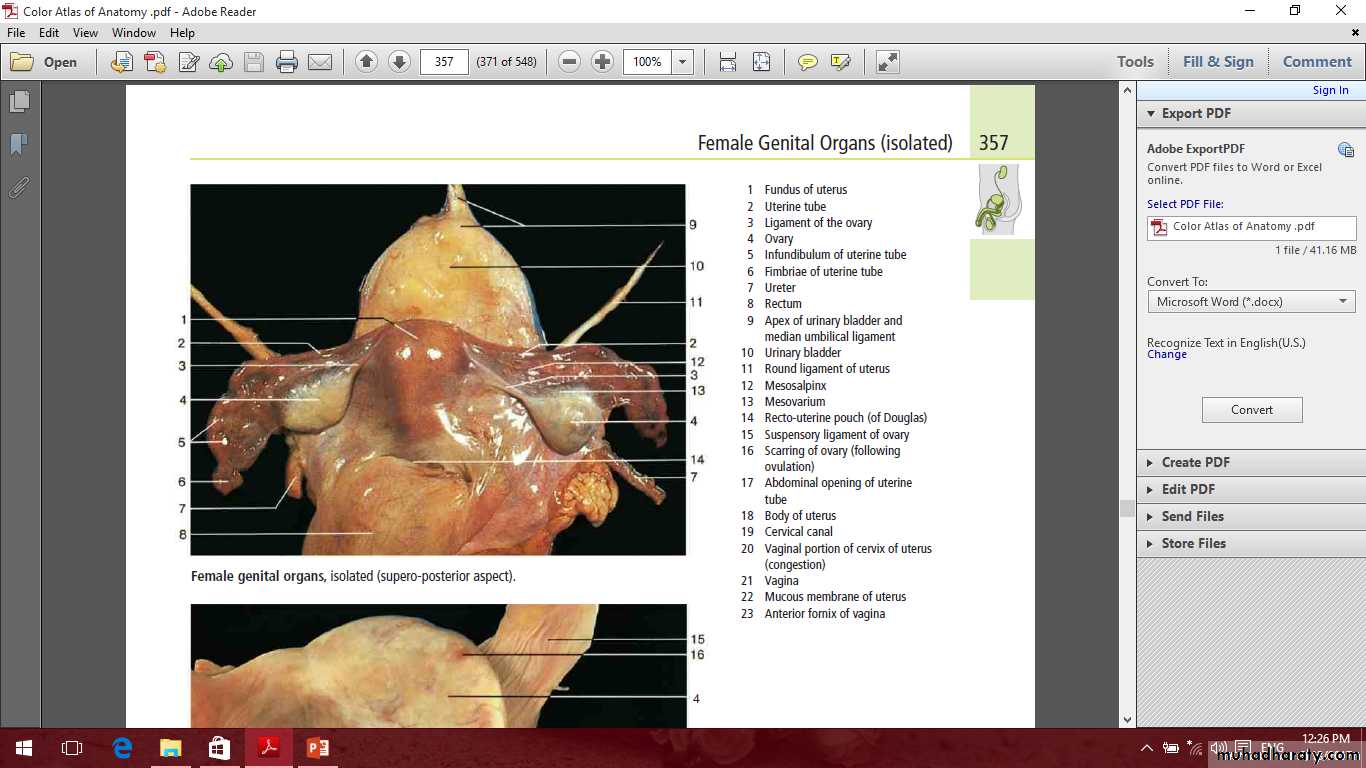
The ovaries
Ovarian fossa
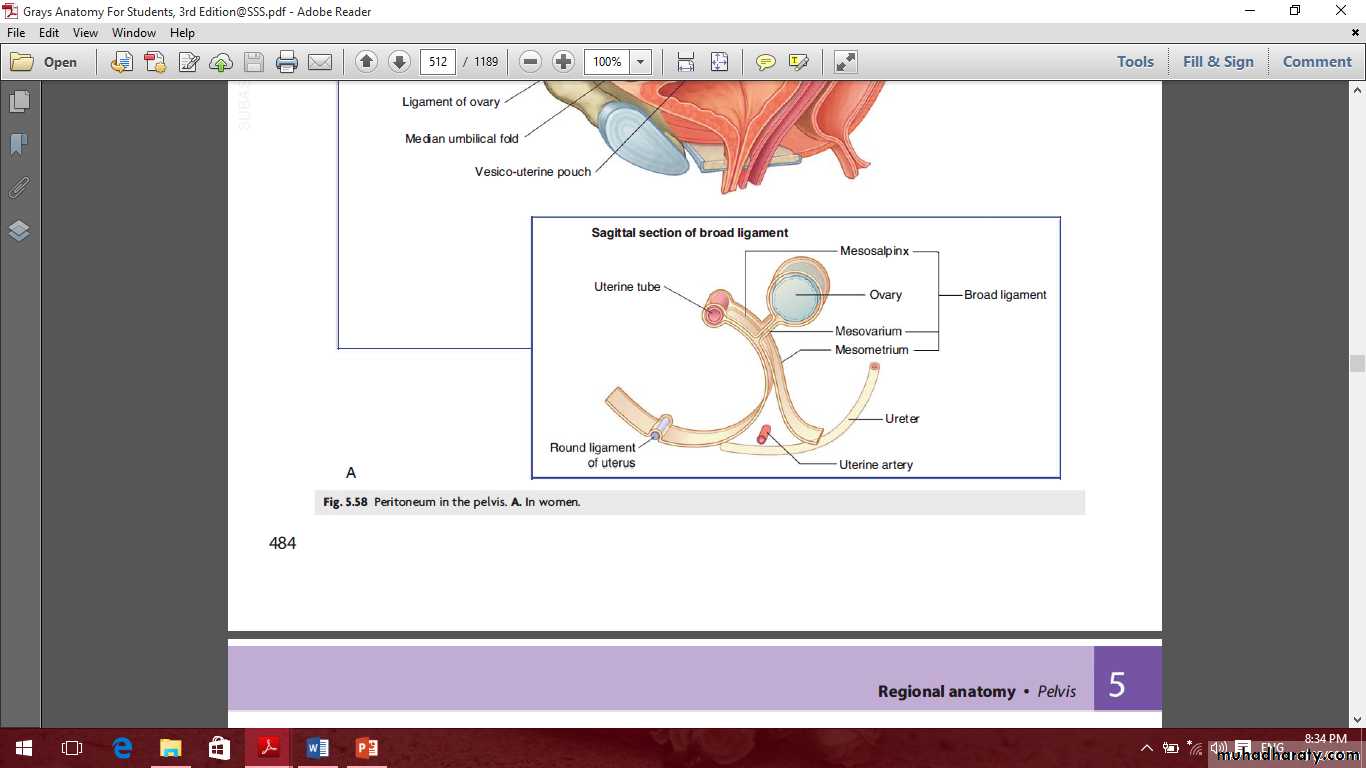
Ligaments of the ovary
MesovarianOvarian ligament
Suspensory ligament of the ovaryOvarian fossa
Blood supply of the ovary
Through the ovarian artery which arise from the aorta below the renal artery passes to the lateral pelvic wall enters the suspensory ligament of the ovary.Venous drainage
Through a plexus of veins called pampiniform plexus then the ovarian vein formed from the plexus , the right ovarian vein ends in the inferior vena cava while the left one ends in the left renal vein.
Lymphatic drainage
Pass to the lumbar nodes.
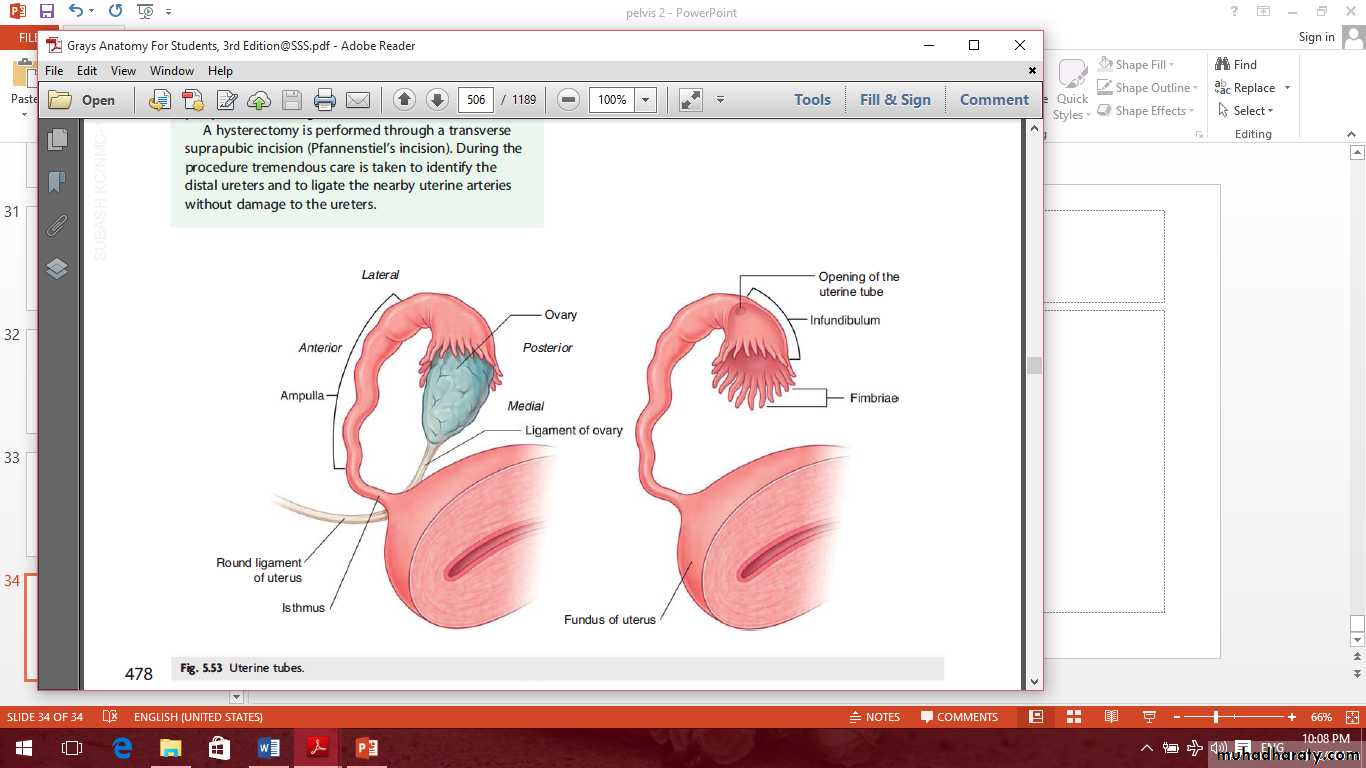
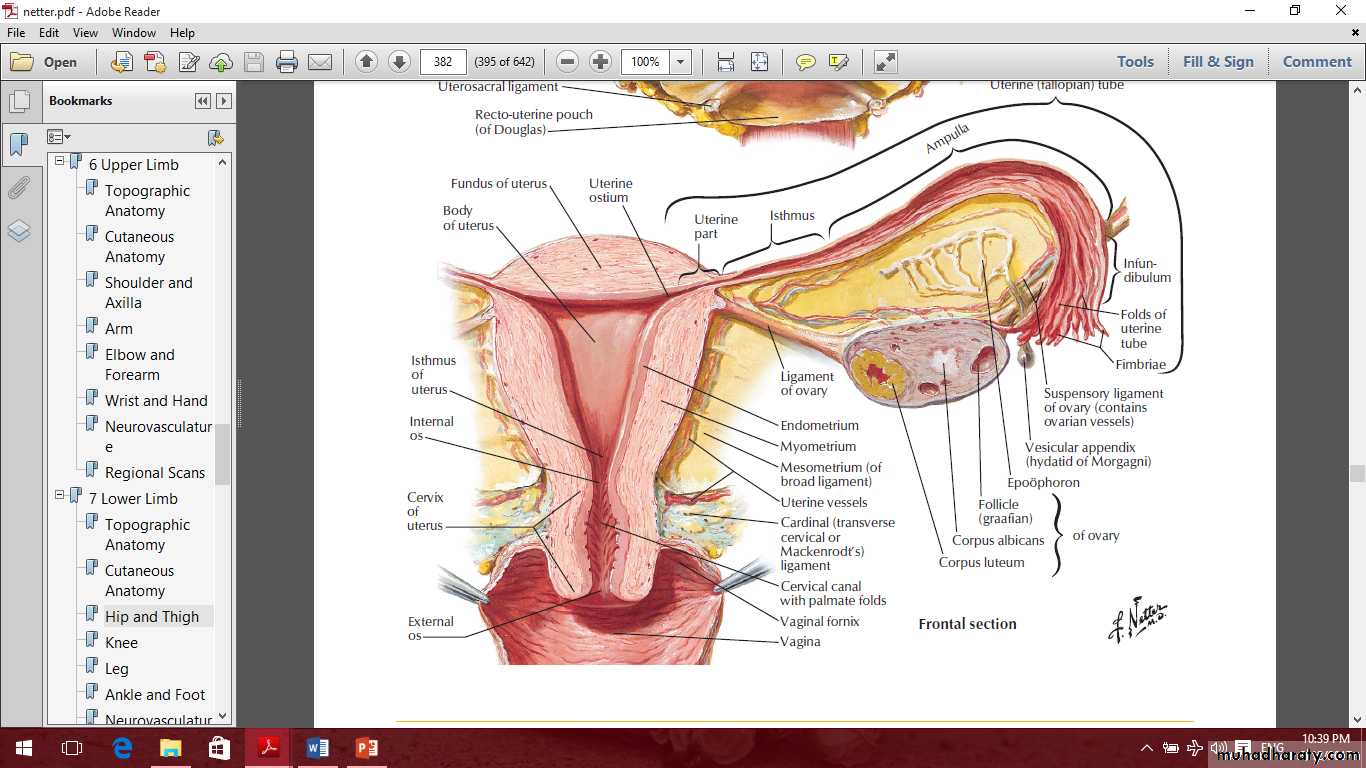
Uterine tubes
Parts of uterine tubes are:1- Intramural
2- Isthmus
3- Ampulla
4- Infundibulum and fimbria.
Parts of uterine tubes
Blood supply of uterine tubes
Blood supply through ovarian and uterine arteries.Venous drainage to the internal iliac vein.
Lymphatic drainage to the lumbar nodes.
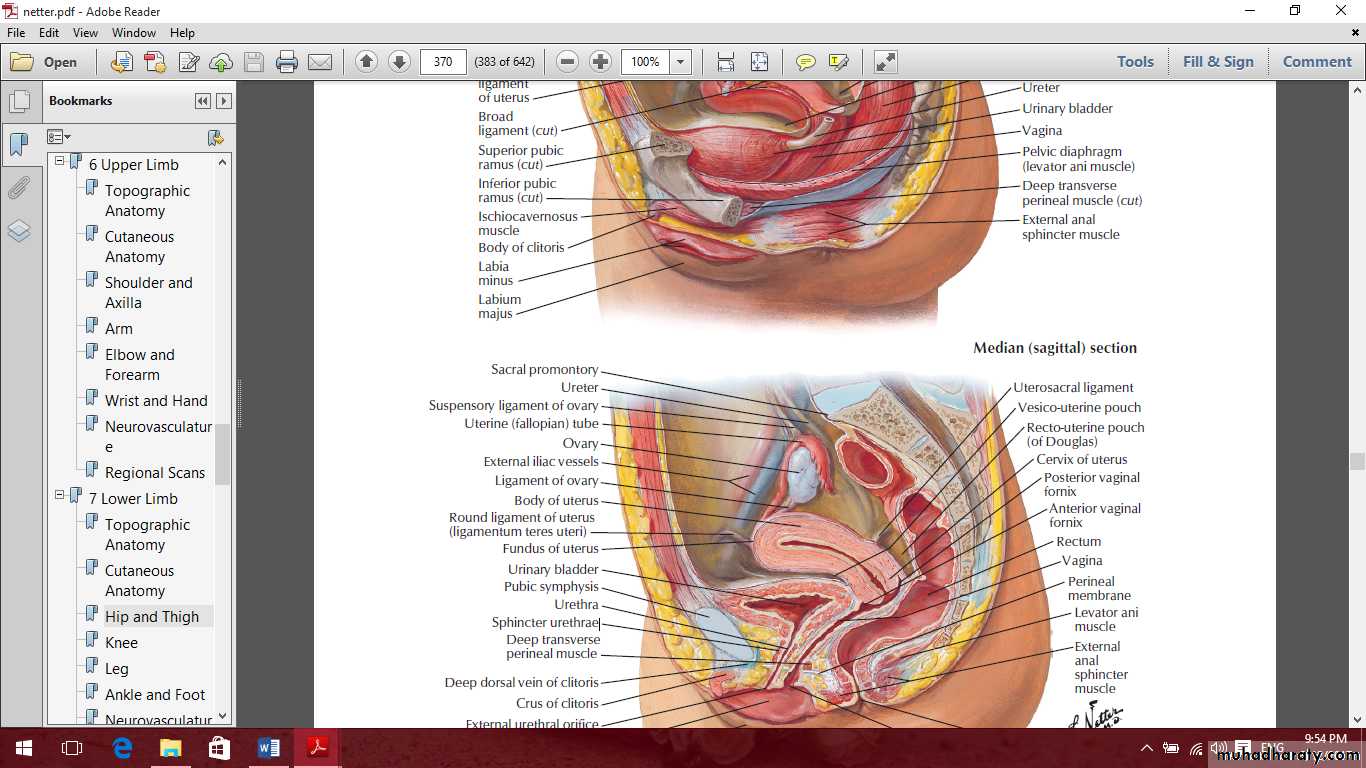
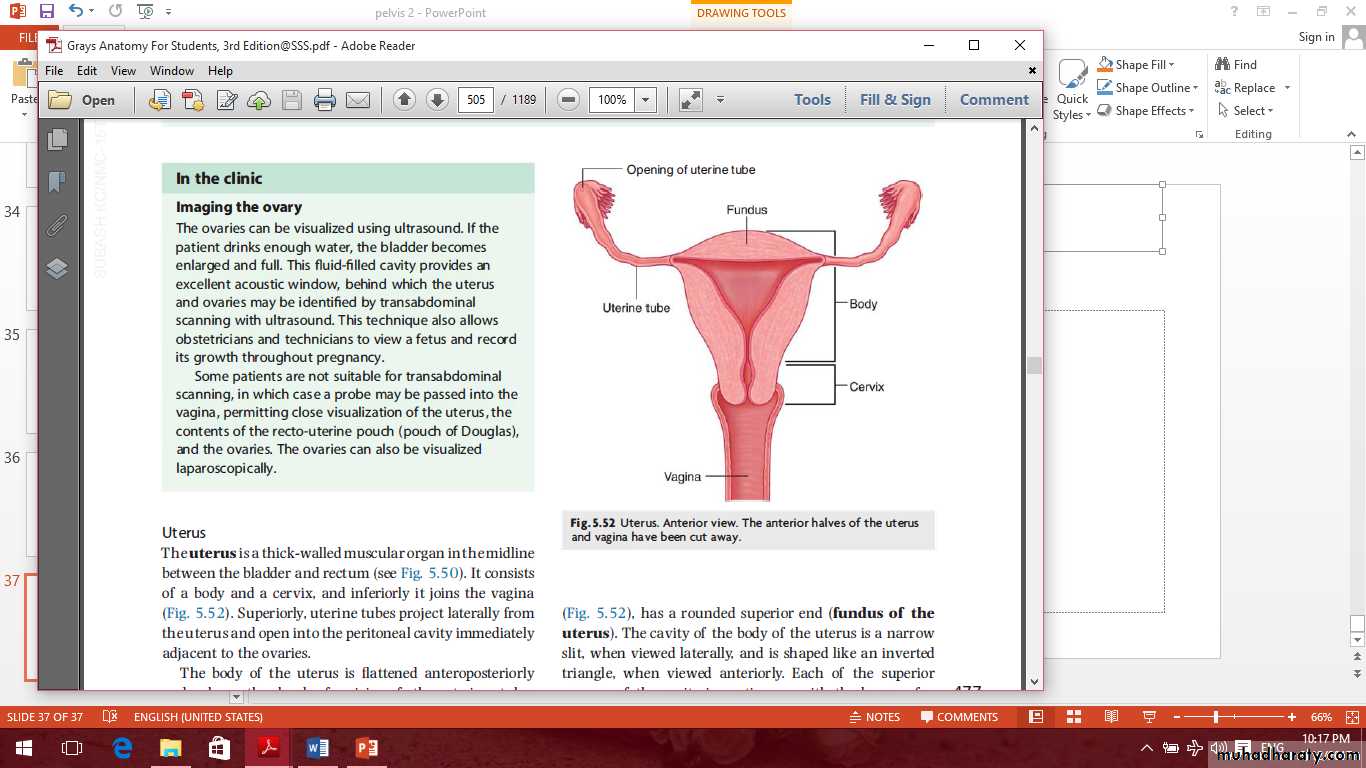
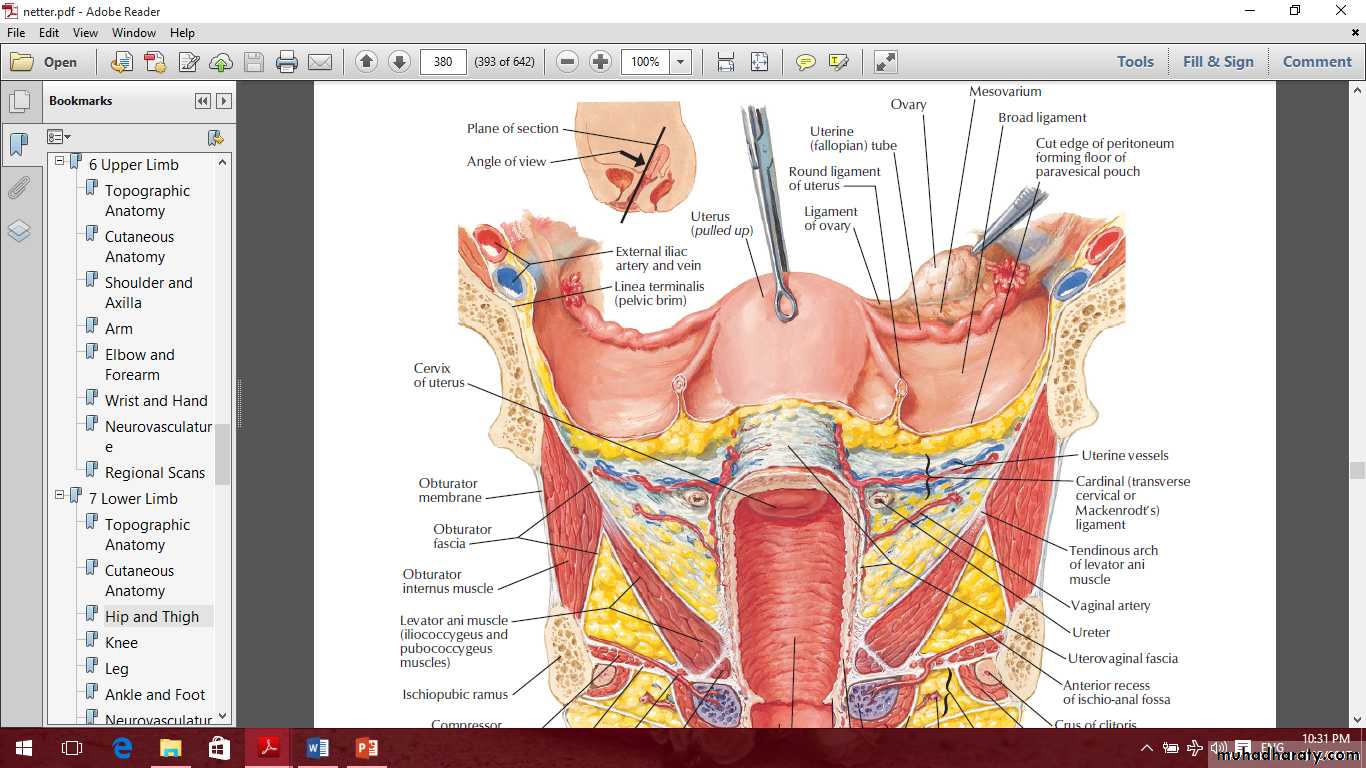
The uterus
Parts of the uterus are1- Fundus
2- Body
3- Cervix
Parts of the uterus
Body of the uterus
The structure which support the uterus are:
1- The urinary bladder2- The ampulla of the rectum.
3- The pelvic diaphragm.
4- The perineal body.
Perineal body
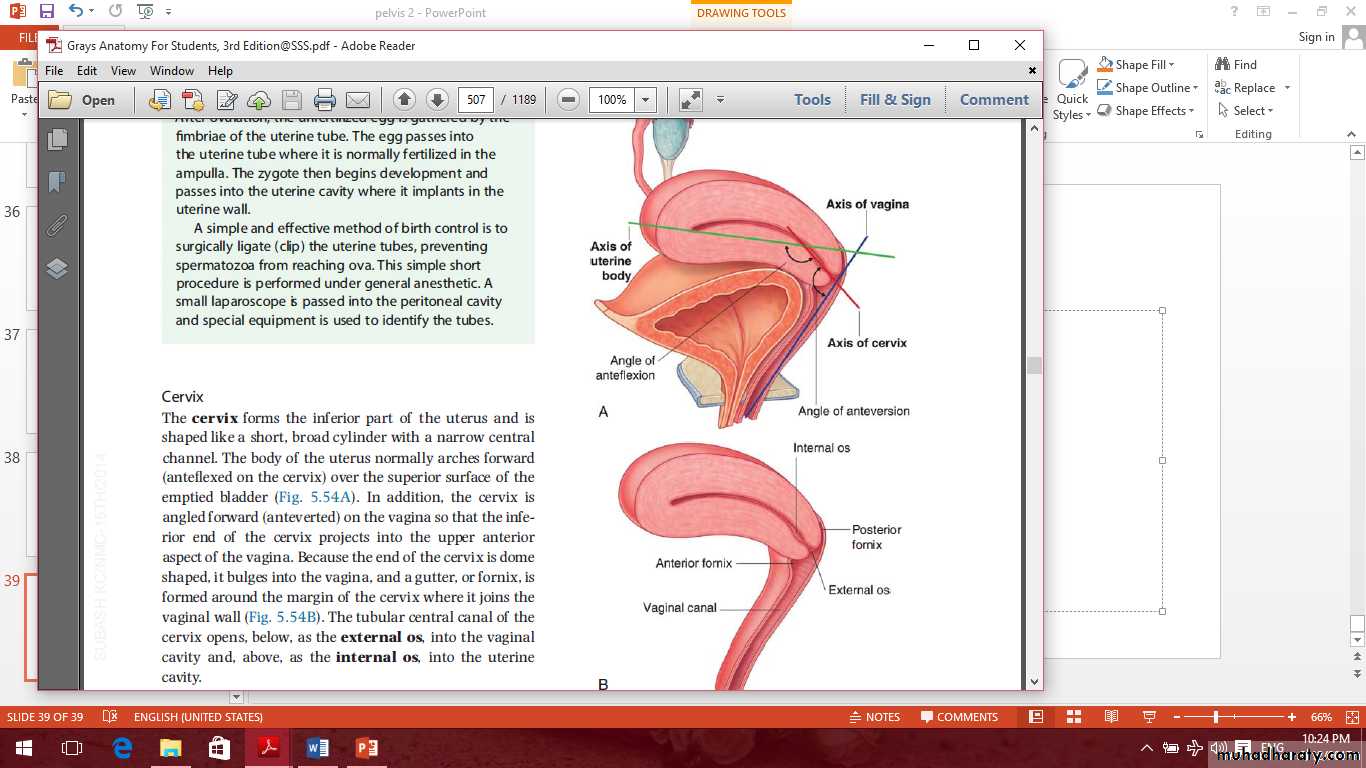
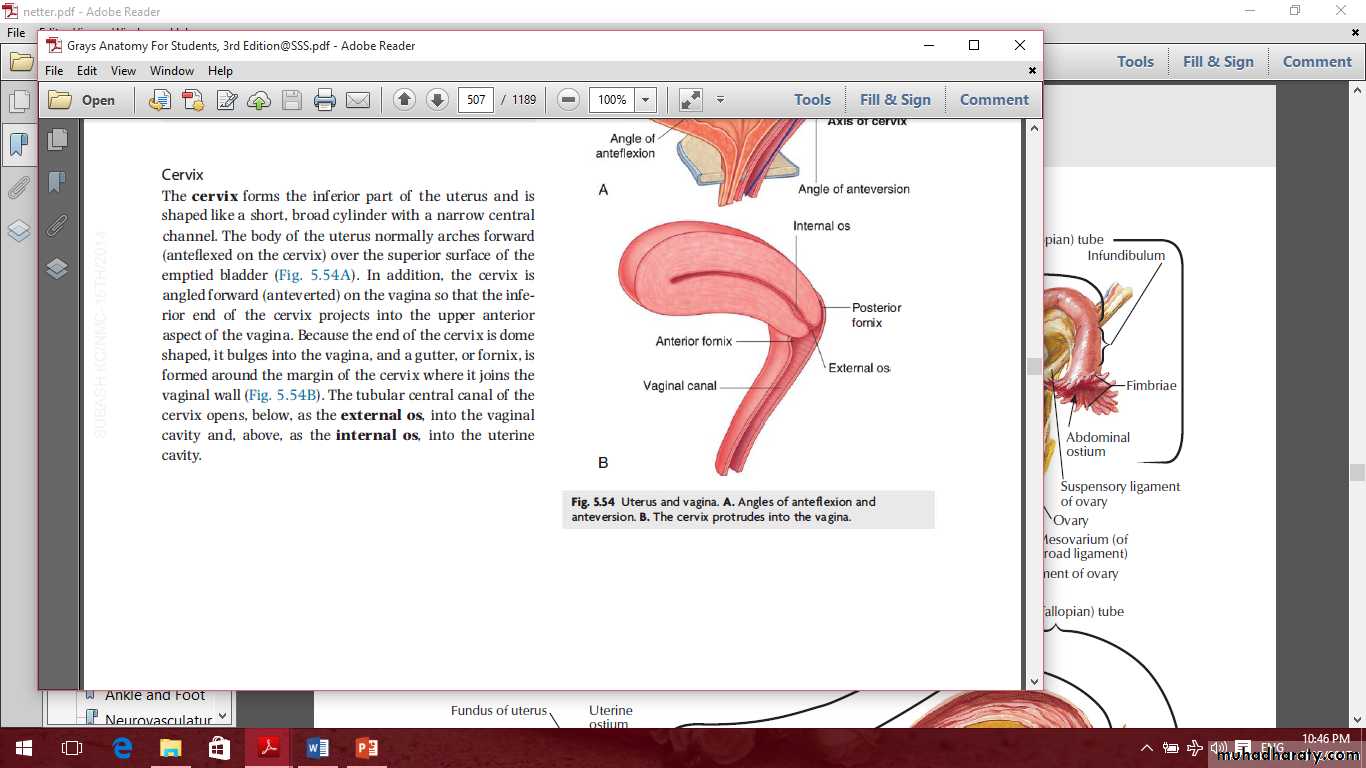
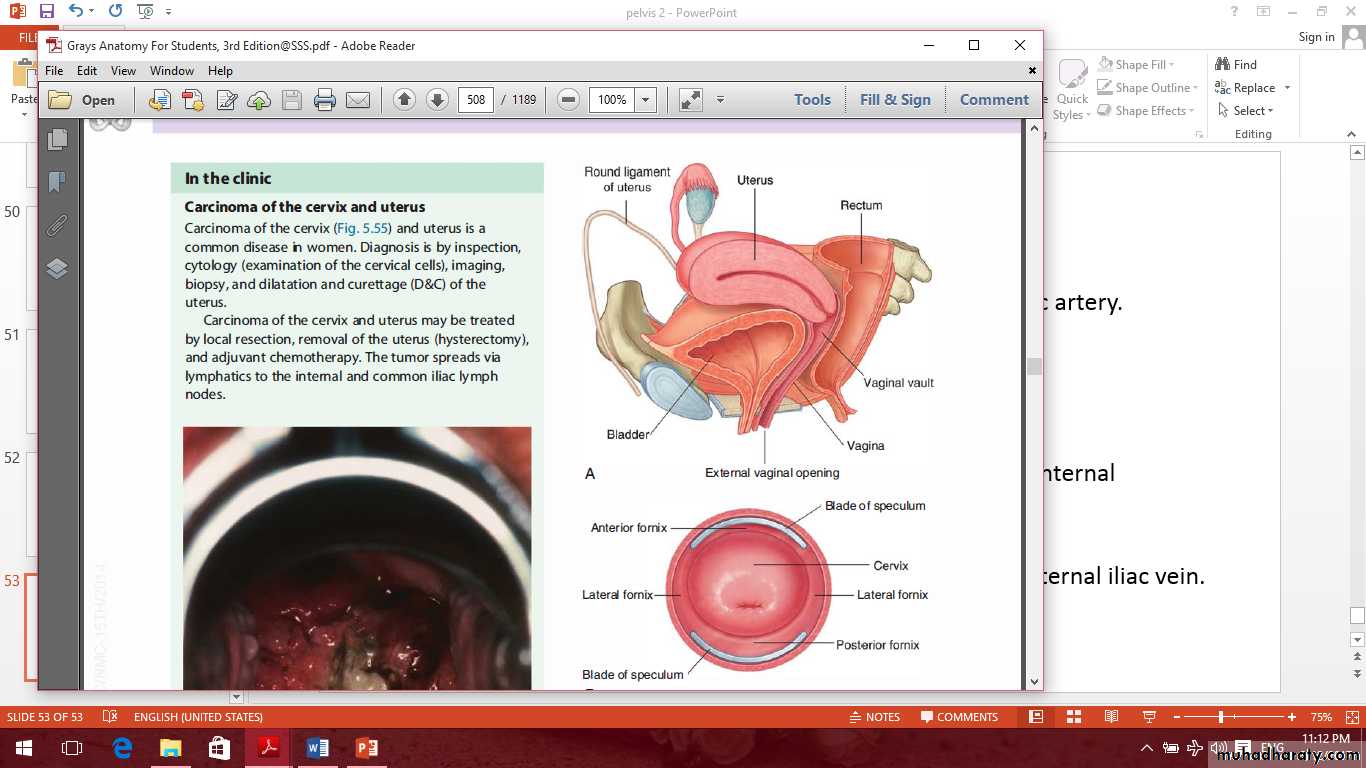
The cervix
Parts of the cervix are:
Vaginal
supravaginalThe cervix
The cervix held in position by
1- Transverse ligament of the cervix which pass to the lateral pelvic wall.2- Uterosacral ligament.
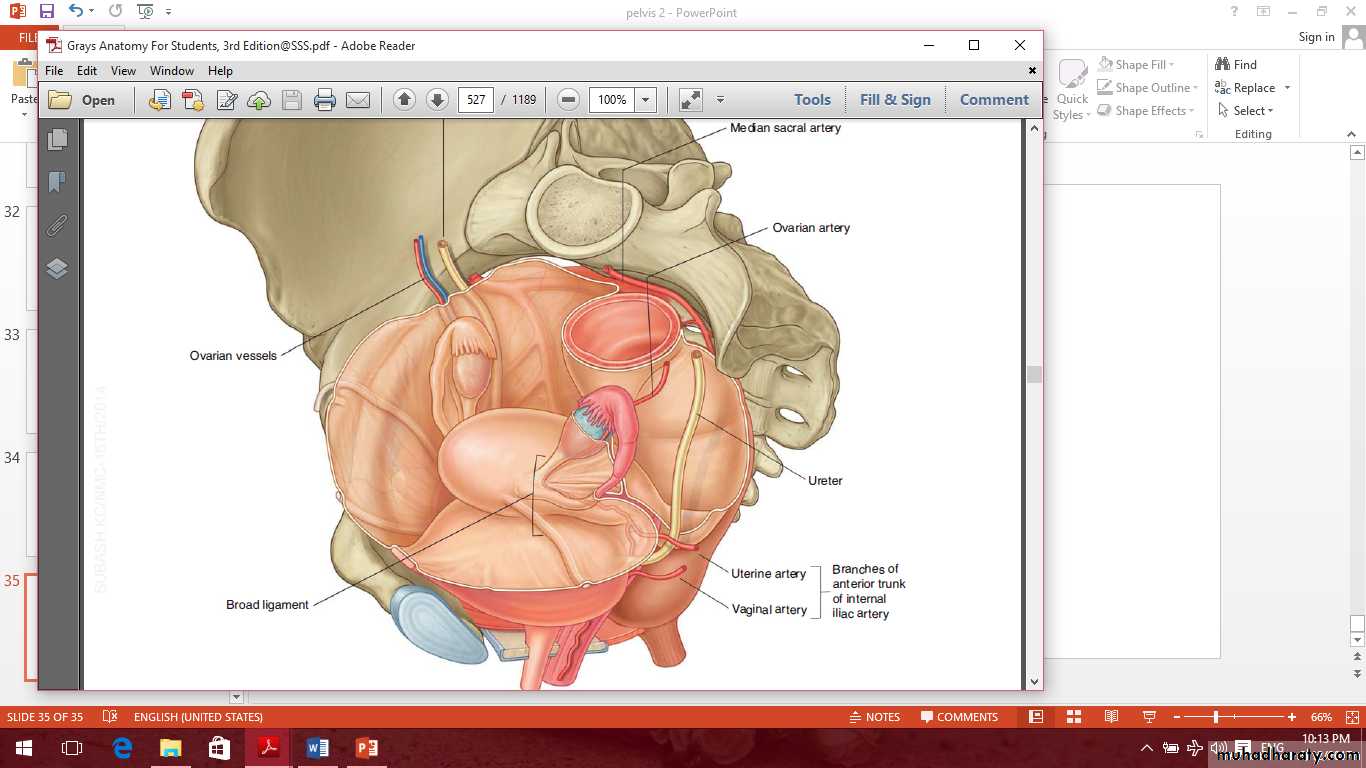
Blood supply of the uterus
1- Uterine artery branch from the internal iliac artery enters broad ligament divided into ascending and descending branches.2- Ovarian artery gives branches to the upper part of the uterus.
The venous drainage through uterine vein to the internal iliac vein.
Blood supply of the uterus
Lymphatic drainage
1- The fundus drains to the lumbar nodes through the ovarian vessels.2- Some lymphatic from the fundus pass through the round ligament to the superficial inguinal nodes.
3- Lymphatics from the body drains to the internal or external iliac nodes.
4- The cervix drains to internal iliac and lateral sacral nodes.
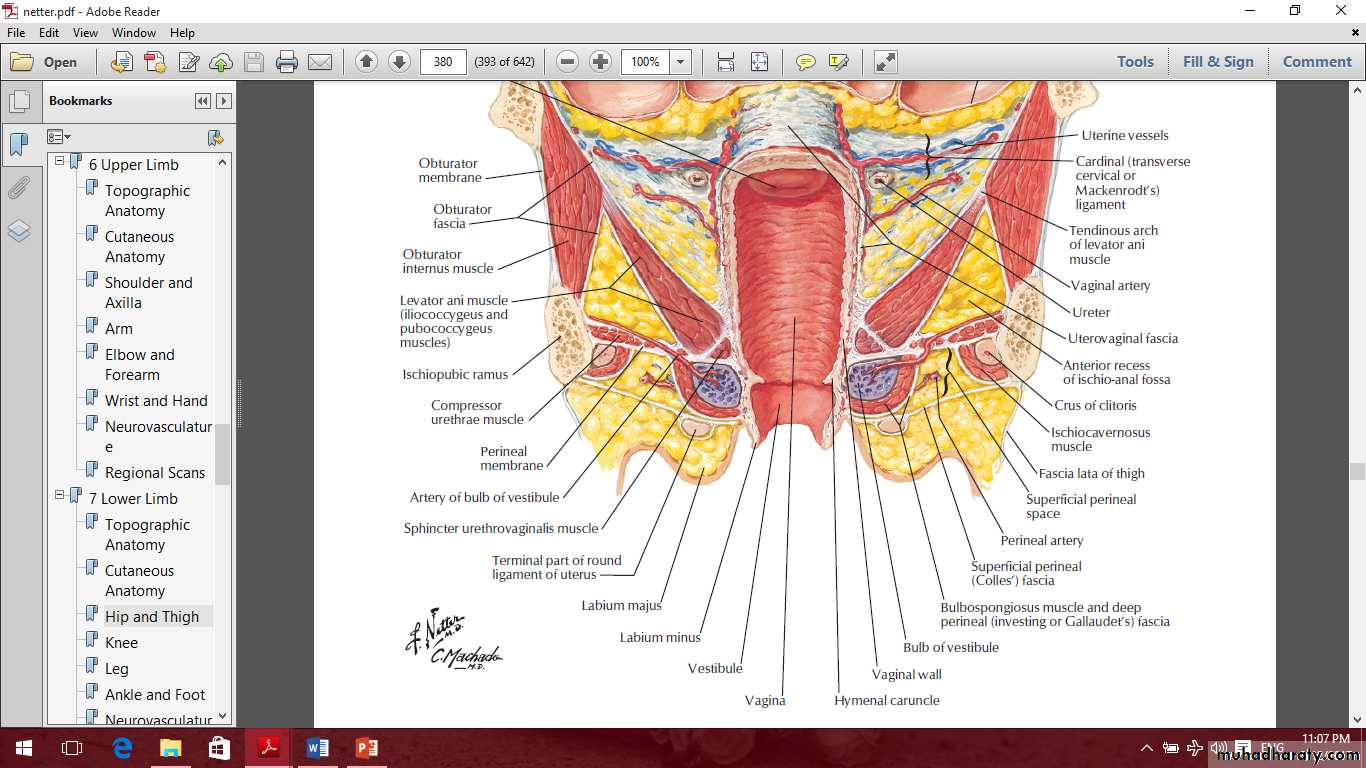
The vagina
Relations of the vagina
Vaginal fornices
Blood supply of the vagina
1- The vaginal artery which is a branch from the internal iliac artery.2- Twigs from middle rectal artery.
3- The descending branch of the uterine artery.
4- The lower part of the vagina receives branches from the internal pudendal artery.
Venous drainage through vaginal and uterine veins to the internal iliac vein.
lymphatic drainage of the vagina
1- The upper part drains to the internal iliac or sacral nodes.2- The middle and lower part to the internal or external nodes.
3- The lowest part to the superficial inguinal nodes.
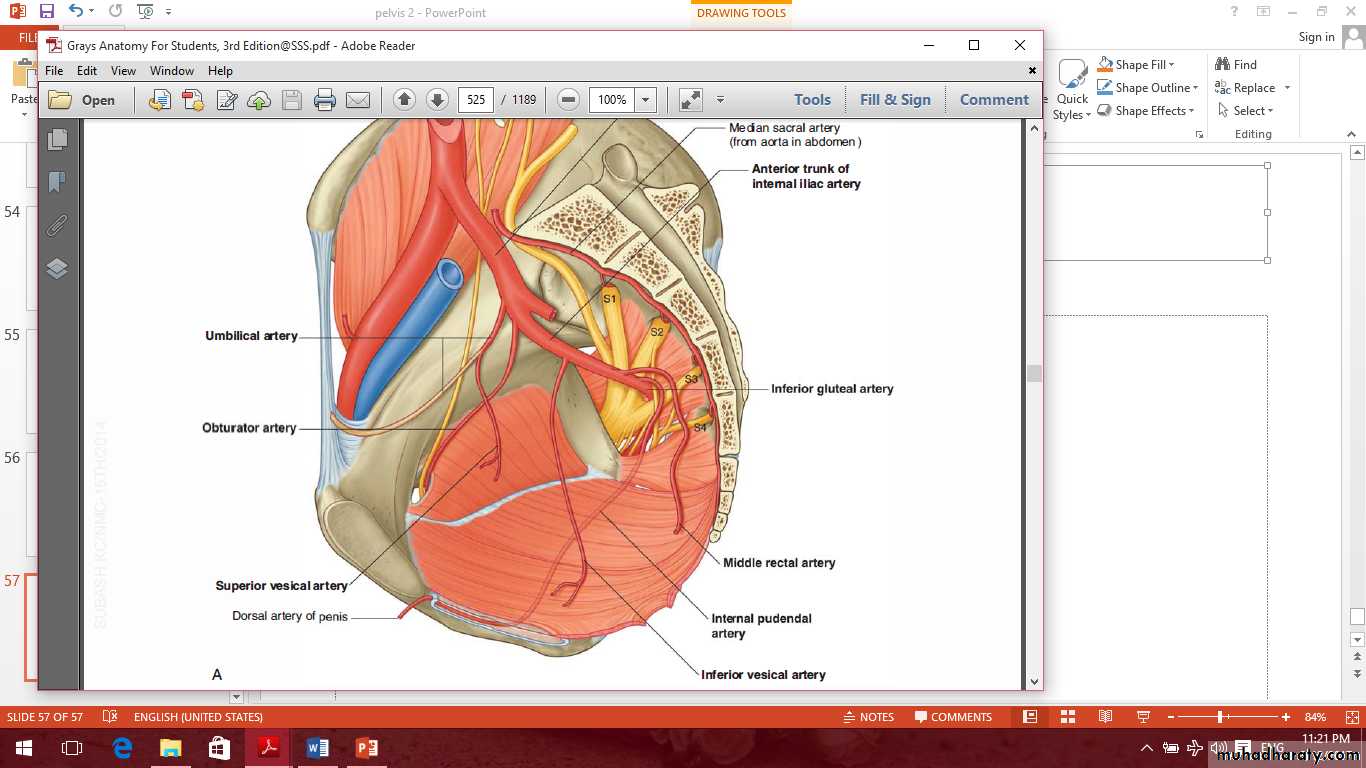
Vessels of the lesser pelvis
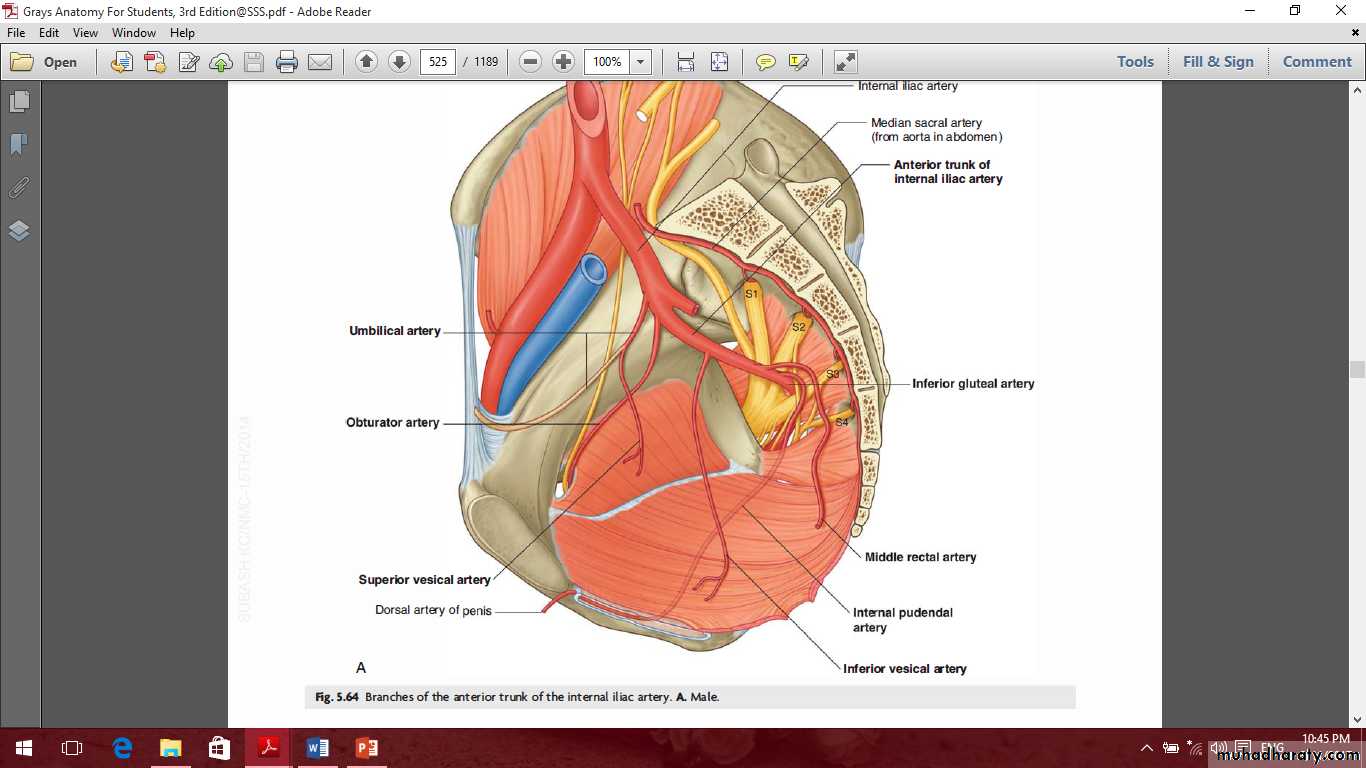
Internal iliac artery gives anterior branches include
1- Umbilical artery gives superior vesical arteries.
2- Obturator artery.
3- Inferior vesical or vaginal artery.
4- Uterine artery.
5- Middle rectal artery.
6- Internal pudendal artery.
7- Inferior gluteal artery.
Anterior branches of internal iliac artery
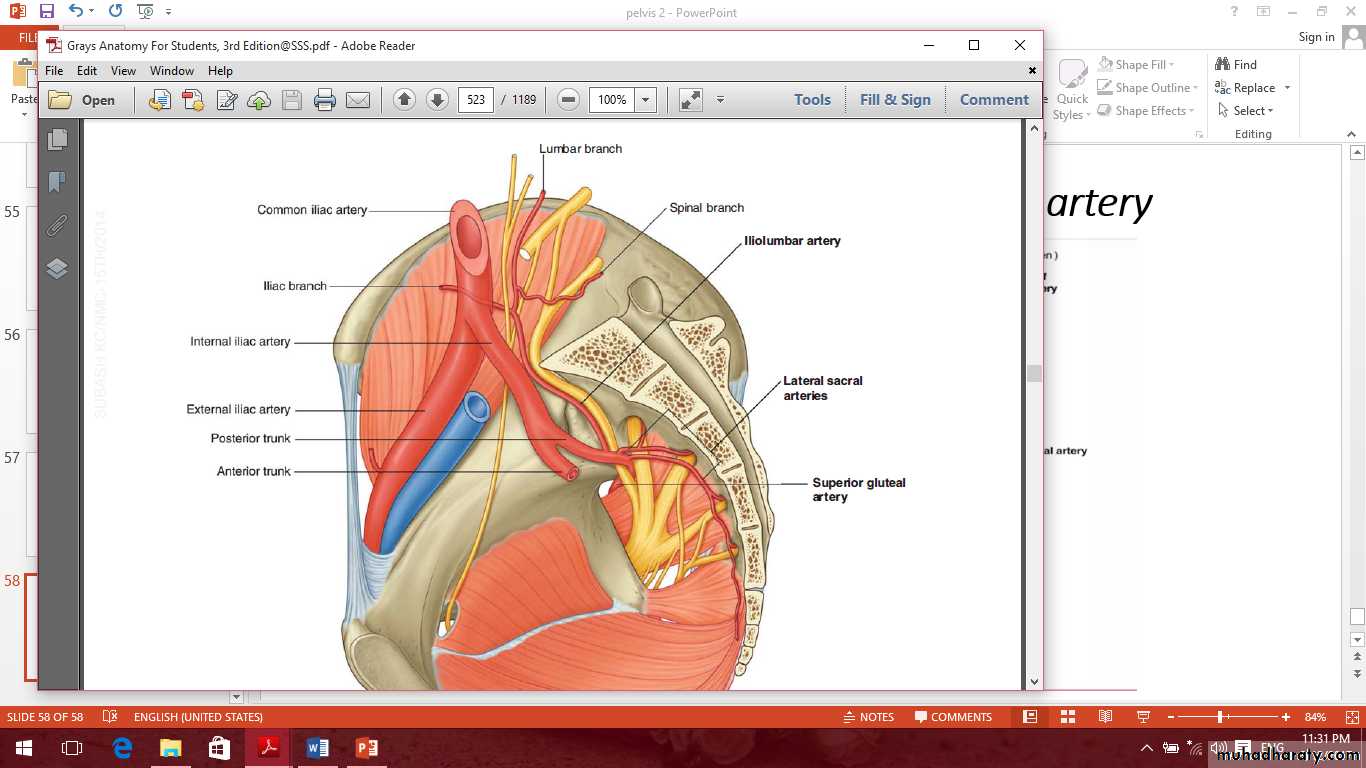
Posterior branches of the internal iliac artery
1- superior gluteal artery.2- iliolumbar artery.
3- lateral sacral artery.
Posterior branches of internal iliac artery
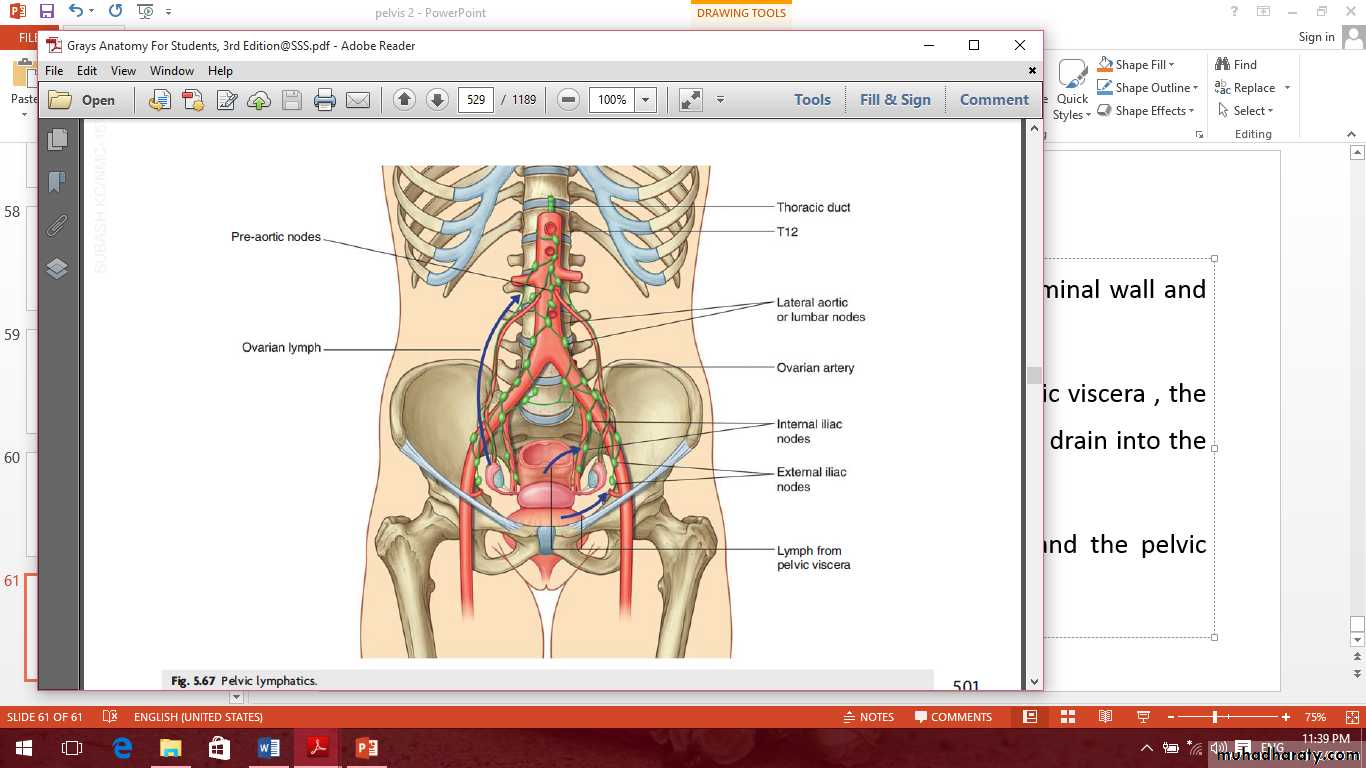
Lymph nodes of lesser pelvis
1- The external iliac nodes drain the lower limb, abdominal wall and pelvic viscera drain into the common iliac nodes.2- The internal iliac nodes receive the lymph from pelvic viscera , the perineum, the gluteal region and the back of the thigh drain into the common iliac nodes.
3- The sacral nodes drain the posterior pelvic wall and the pelvic viscera.
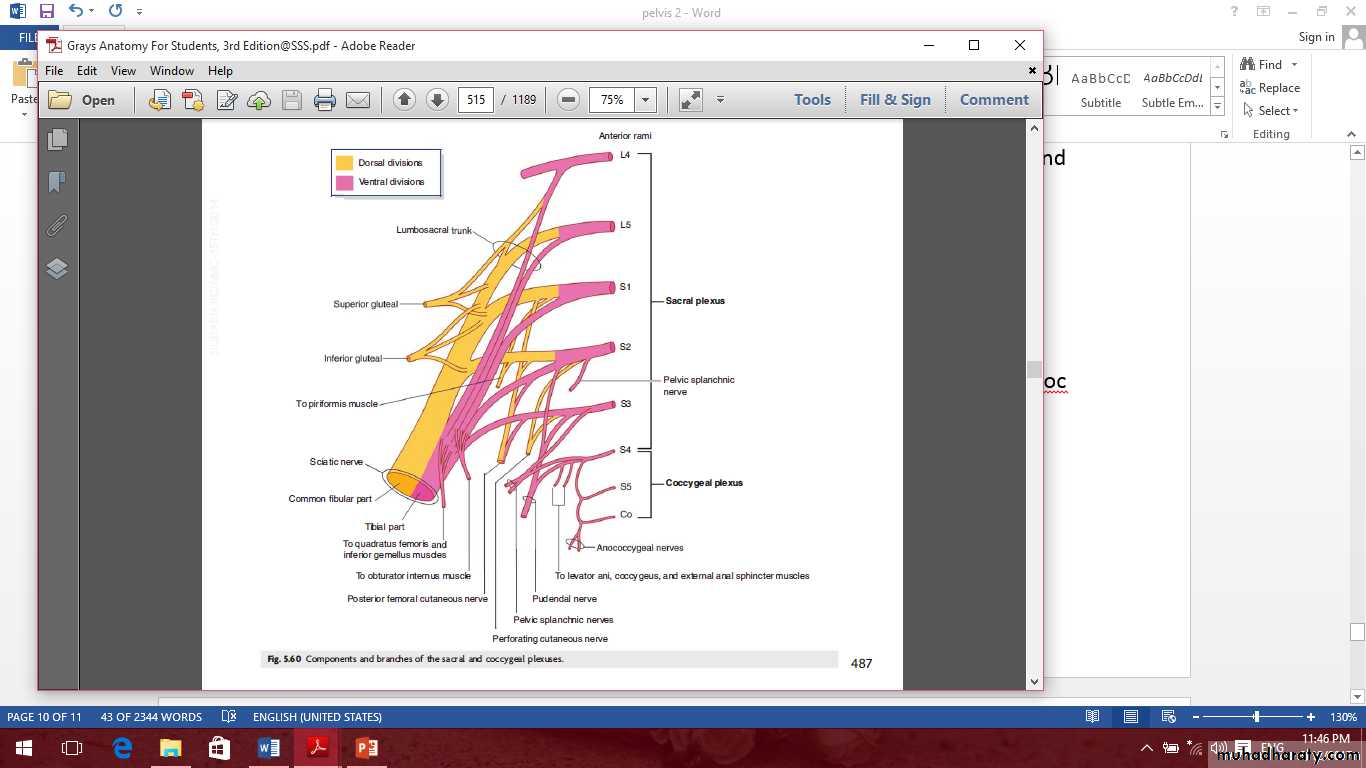
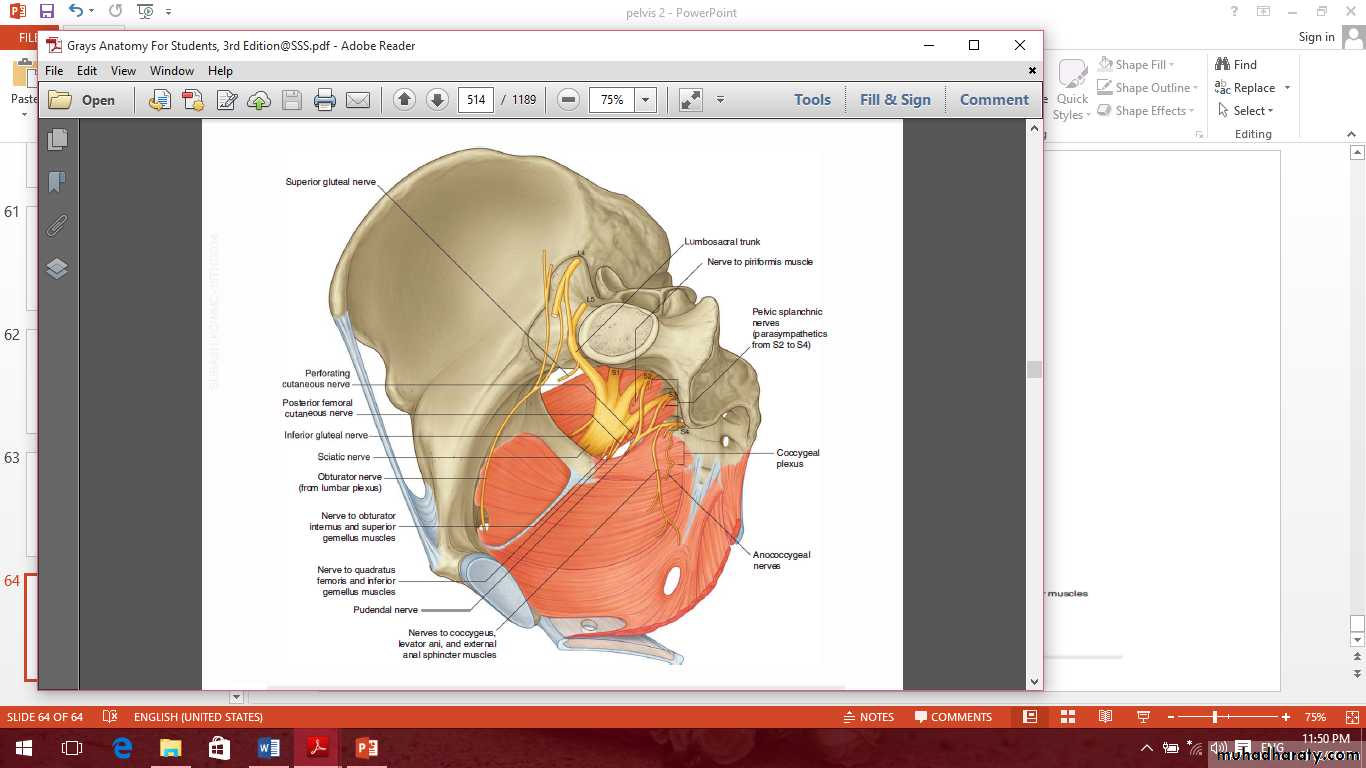
Sacral plexus
Branches from the ventral rami before it form the plexus are:1- nerve to piriformis muscle.
2- nerves to coccygeus and levator ani muscle.
3- Pelvic splanchnic nerves from S2, S3 and S4 contain preganglionoc parasympathetic nerve fibers to the inferior hypogastric plexus.
Sacral plexus
Branches arise from the anterior surface of the plexus
1- Nerve to quadratus femoris muscle.2- Nerve to obturator internus muscle.
Branches from the dorsal surface of the plexus
1- The superior gluteal nerve.2- The inferior gluteal nerve.
3- The perforating cutaneous nerve to the gluteal skin.
4- The perineal branch.
Terminal branches of the sacral plexus
1- Sciatic nerve.
2- Pudendal nerve.
Sacral plexus
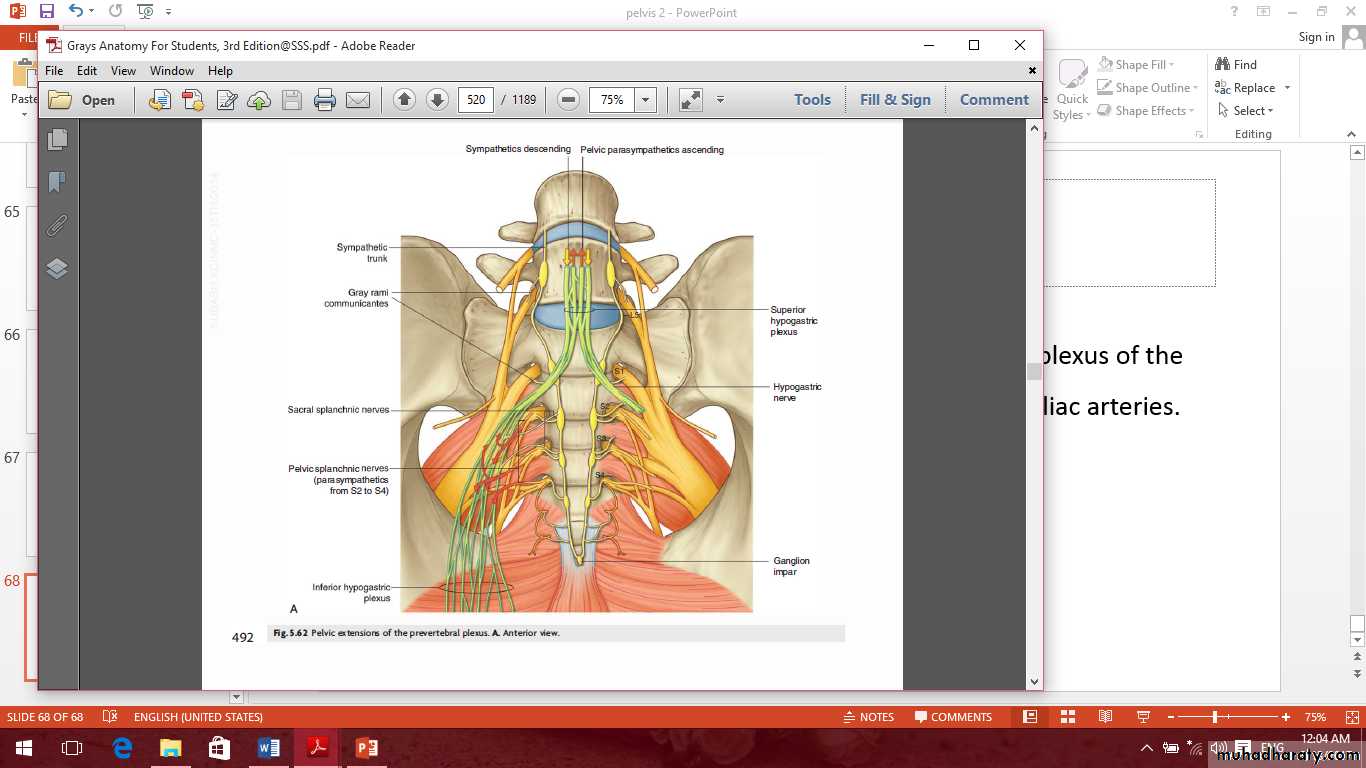
The inferior hypogastric plexus of nerves
It is the direct continuation of the superior hypogastric plexus of the abdomen divided into two plexuses surrounded the common iliac arteries. They receive the pelvic splanchnic nerves.The visceral plexus
1- The rectal plexus supply the rectum, sigmoid and descending colon.2- Vesical plexus urinary bladder, seminal vesicle and ductus deferens.
3- The prostatic plexus supply the prostate, membranous urethra and the penis.
4- The uterine and vaginal plexus.