ARTERIAL BLOOD PRESSURE
Introduction and principle
Artrial blood pressure is one of the essential parameters in
cardiovascular physiology . Learning the technique of how to measure the
arterial blood pressure is therefore very important clinically in medical
practice and experimentally in scientific research.
Objectives
To train the students how to measure the arterial blood pressure in
human beings and in experimental animals .
Methods
1-Indirect method
2- Direct method
Indirect method
This method is usually used for measuring the arterial
blood pressure in man .it is fairly accurate ,not invasive and relatively
easy .
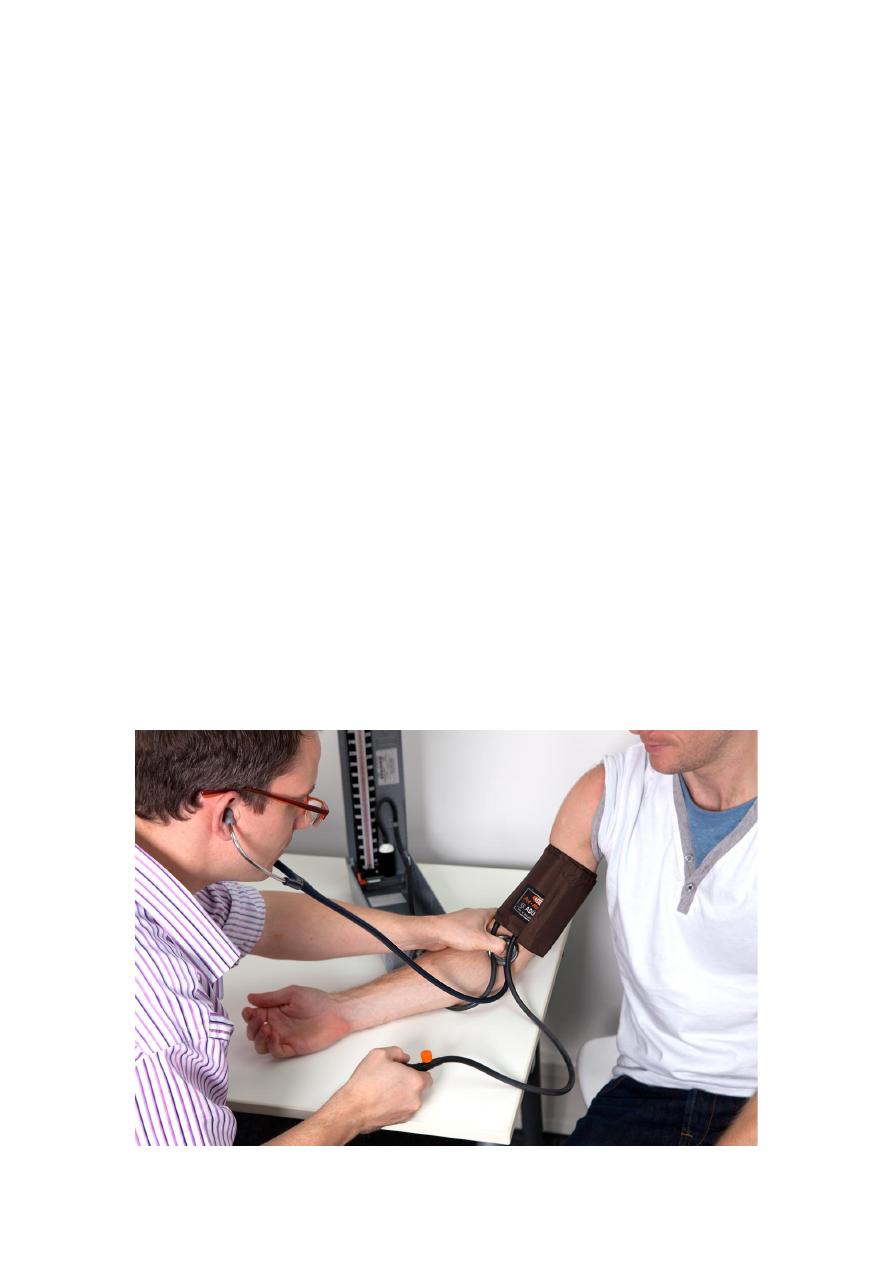
Materials and instruments
a-Sphygmomanometer .
b-Stethoscope .
c-A subject .
!
Procedure
The subject is in the lying or sitting position and relaxed .The
upper arm left or right is exposed .wrap the cuff of the
sphygmomanometer around the upper arm well above the elbow .The
wrapping should be neither tight nor loose ,and the middle part of the
rubber bag of the cuff should be placed along the course of the brachial
artery in the medial side of the upper arm .The cuff is fixed in position by
wrapping it with the cloth tail of the cuff . The tube of the cuff is
connected to the mercury manometer which should be at the level of the
heart ; in order to avoid the effect of the hydrostatic pressure of a column
of blood above or below the level of the heart . The arm of the subject is
supported at rest . Now the systolic arterial blood pressure is measured by
palpatory method , and the systolic and diastolic pressure by auscultatory
method .
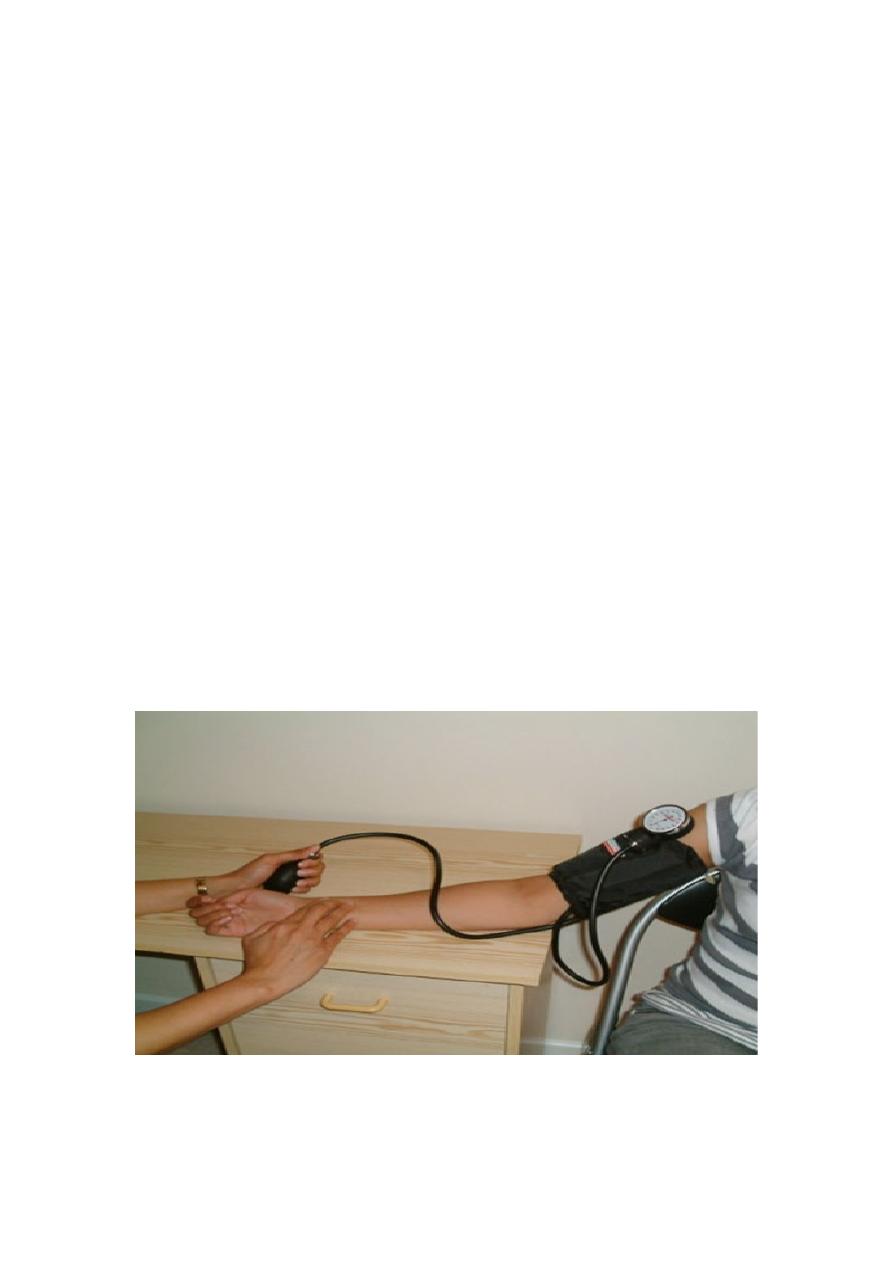
A. Palpatory method :
Feel the radial pulse of the subject by placing the three middle
fingers on the radial artery against the radius bone with mild pressure of
the distal finger, you can feel the radial pulse by the index finger. Raise
the pressure in the cuff to 200 mm Hg . start to lower the pressure slowly
while you are feeling the radial pluse. Once you feel the pulsation of the
radial artery, record the reading on the manometer. This reading gives you
the systolic pressure. Repeat this procedure many times and record your
result.
!
B- Auscultatory method :
From your surface anatomy knowledge of the antecubital fossa, put
the diaphragm of the stethoscope at the position of the brachial artery just

below the lower edge of the cuff (not underneath the cuff !). Raise the
pressure to 200 mm Hg, then lower the pressure slowly and steadily. The
following phases of the character of the sound will be heard by the
stethoscope:
phase 1 :If the pressure is above systolic no sound can be heard . when
the systolic pressure is reached , a clear loud sound is heard
with each heart beat .
phase 2:When you lower the pressure more the sound becomes softer.
Phase 3:As the pressure is lowered , the sound becomes louder and
banging in character.
Phase 4:Then the sound becomes soft and muffled. The point at which
the sound begins to fade is taken as the diastolic pressure.
Phase 5:The sound will disappear completely (sometimes this is taken as
the diastolic pressure).
Repeat this procedure many times and record your results .
Results
The arterial blood pressure is normally 120/80 in young student
Direct Method
This method is usually used for measuring the arterial blood
pressure in experimental animals .It is accurate, rather invasive including
the introduction of a needle inside the lumen of an artery usualy the
carotid or the femoral artery .
1
Note : Mean ABP = Diastolic pressure + pulse pressure.
3
pulse pressure = systolic – diastolic pressure.

