CORYNEBACTERIUM
MSc. Sarah AhmedMORPHOLOGY
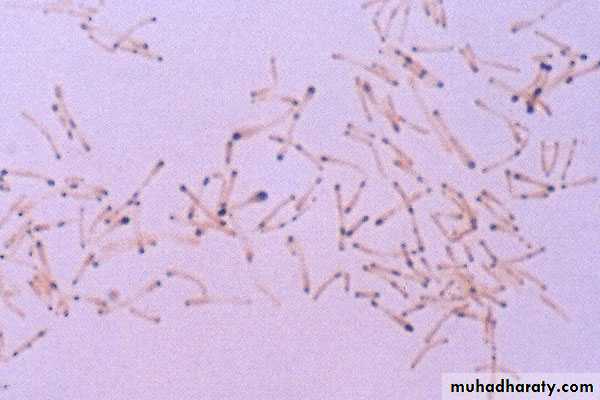
Special stains for demonstrating the granules :Albert’s stain
Neisser’s stain
Ponder’s stain
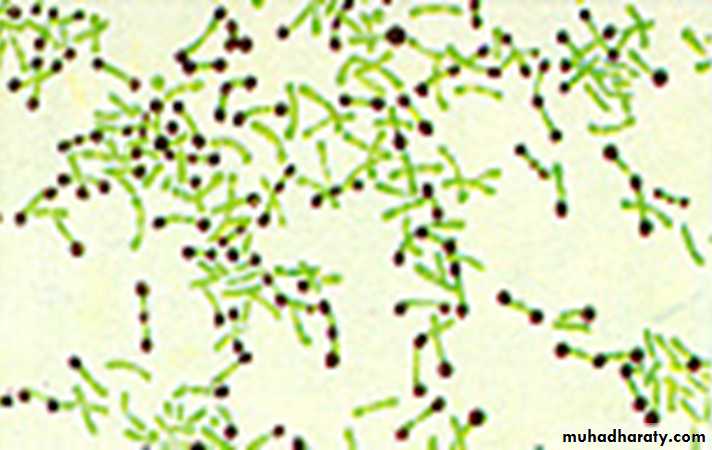
the bacilli lie at various angles to each other, resembling the letters, V or L;
This is called, “Chinese letter pattern” or “cuneiform pattern”;
COLONY CHARACTERISTICS
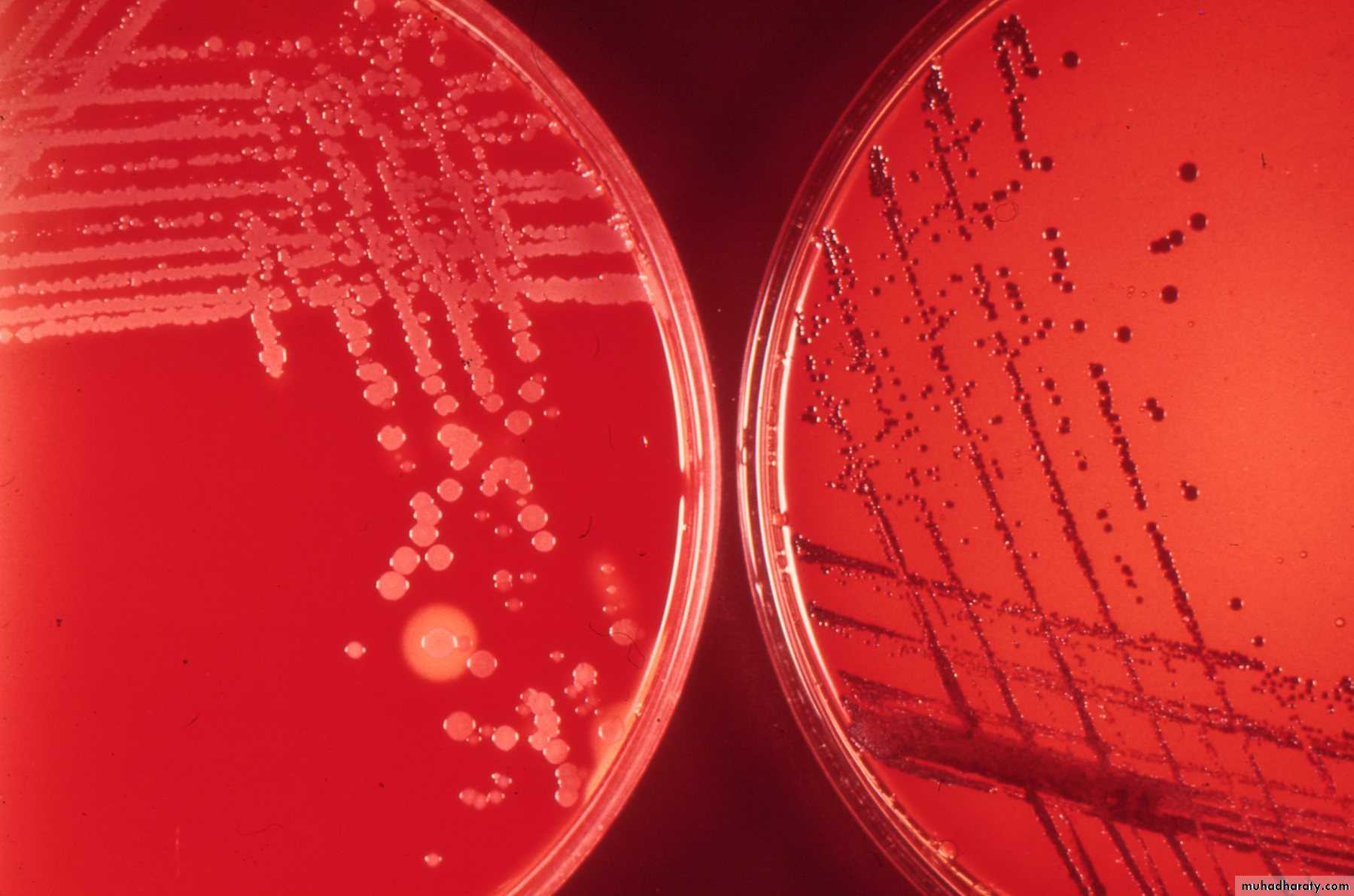
Blood agar : small, granular and gray with irregular edges; Hemolysis may or may not present;
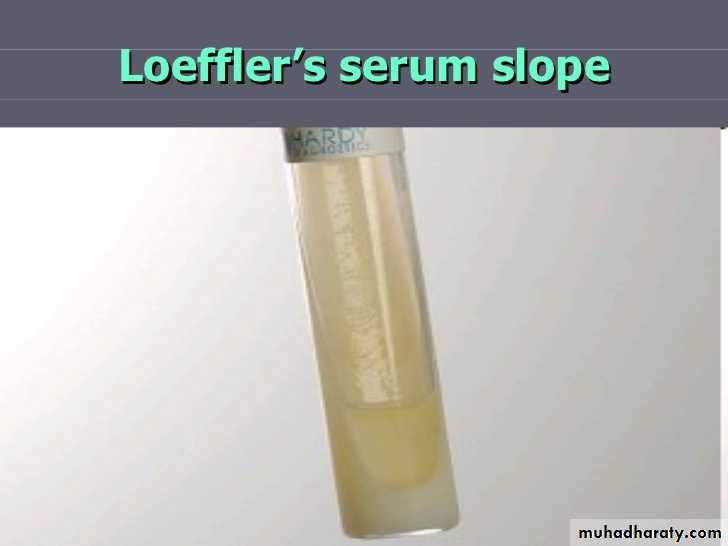
Loeffler’s serum slope:
Very rapid growth;
Colonies in 6-8 hrs
Initially circular white opaque colonies and acquire yellowish tint on incubation
COLONY CHARACTERISTICS
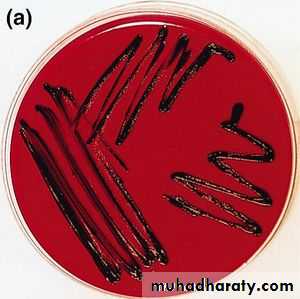
Tellurite blood agar:Growth slow; colonies seen after 48 hrs;
The colonies are brown to black with a brown-black halo because the tellurite is reduced to metallic tellurium;
Staphylococcus also produce such colonies
A diagrammatic representation
BIOCHEMICAL REACTIONS
Catalase positive, non-motile, non-spore formingFerment- glucose, galactose, maltose and dextrose; but not lactose, sucrose, mannitol;
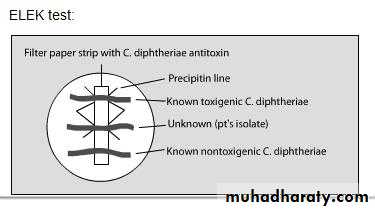
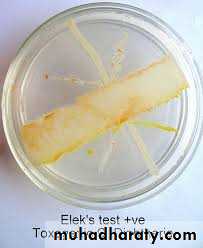
Do not hydrolyse urea;Elek’s gel precipitation test
In vitro test;A rectangular strip of filter paper is saturated with the diphtheria antitoxin(1000 units/ml);
This strip is placed on : agar plate with 20% horse serum, while the medium is setting;
The cultures to be tested are streaked at right angles to the filter paper strip;
A positive and negative control should be put;