Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease(COPD)
Prof. Dr. Abdul Hameed Al QaseerChronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined as a disease state characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully reversible COPD includes emphysema, an anatomically defined condition characterized by destruction and enlargement of the lung alveoli; chronic bronchitis, a clinically defined condition with chronic cough and phlegm; and small airways disease, a condition in which small bronchioles are narrowed. COPD is present only if chronic airflow obstruction occurs; chronic bronchitis without chronic airflow obstruction is not included within COPD.
Global Strategy for Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD. Updated 2011
Risk Factors for COPDGenes
Exposure to particles
• Tobacco smoke
• Occupational dusts
• Indoor air pollution from heating and cooking with biomass in poorly ventilated dwellings
• Outdoor air pollution
Lung growth and development
GenderAge
Respiratory infections
Socioeconomic status
Asthma/Bronchial hyperreactivity
Chronic Bronchitis
Risk Factors in COPD
COPD – and why?
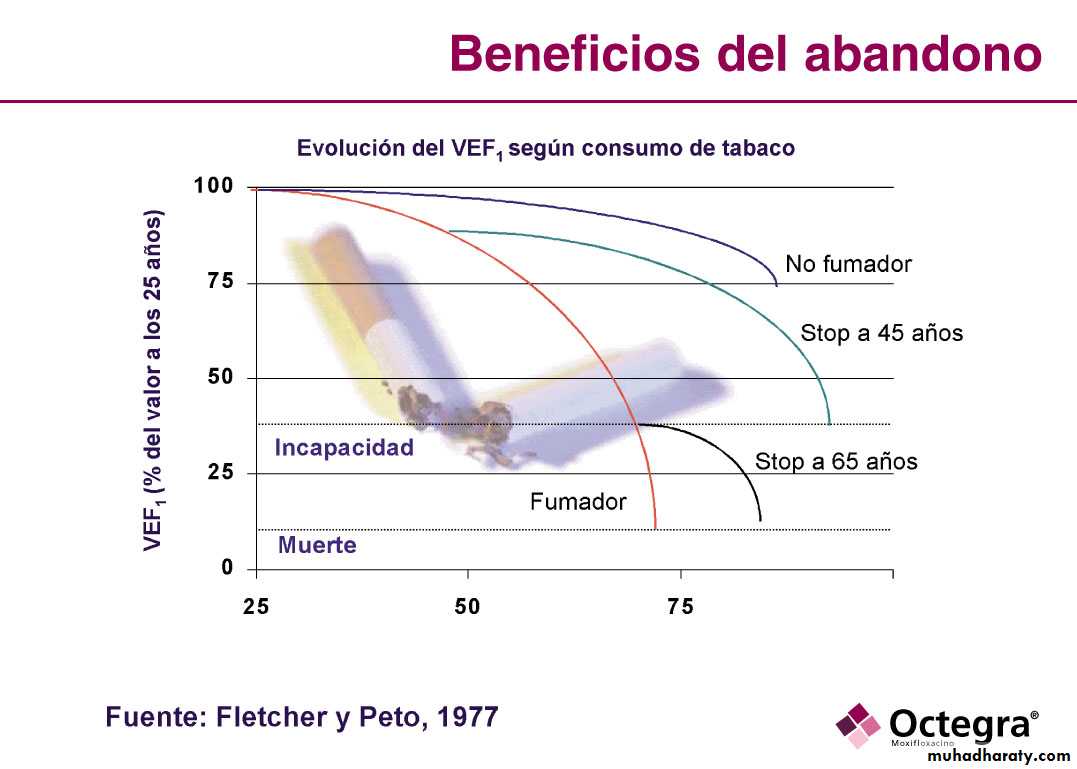
Fletcher, Peto 1977
No smoker
No smokerStop 45 years
Stop 65 years
Current smoker
Disability
Dead
FEV1
YEARS
Pathogenesis of Emphysema
Breathlessness is the cardinal manifestation of COPDIt is a slowly progressive .However , it can acute during exacerbation
The patient may presented with leg edema with or without right sided heart failure ( core pulmonale)
Physical examination : may be minimum
wheeze , rals ……
Clinical Spectrum of COPD ( pink puffers(A)& blue bloaters(B)
PINK PUFFERS (EMPHESYMA)
BLUE BLOATERS ( CHROIN BRONCHITIS)Modified Medical Council Research Dyspnea
InvestigationChest X-ray
Spirometry
High resolution CT
Arterial Blood Gas
Bacteriologic , CBC ……
Global Strategy for Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD. Updated 2011
Diagnosis: SpirometryVolume, liters
Time, seconds5
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
FEV1 = 1.8L
FVC = 3.2L
FEV1/FVC = 0.56
Normal
Obstructive
Spirometric classification of COPD
Classification of Severity of Airflow Limitation in COPD*In patients with FEV1/FVC < 0.70:
GOLD 1: Mild FEV1 > 80% predicted
GOLD 2: Moderate 50% < FEV1 < 80% predicted
GOLD 3: Severe 30% < FEV1 < 50% predictedGOLD 4: Very Severe FEV1 < 30% predicted
*Based on Post-Bronchodilator FEV1CT of chest shows emphysema
Differential Diagnosis of COPDChronic Asthma
Bronchiectasis
Bronchial carcinoma
Heart failure
Pulmonary TB
ILD
What are the deference between asthma & COPD(ch.bronchitis)?
ASTHMA
COPDONSET
Mainly childhood
mid-late adult life
smoking
Usually nonsmoker
almost invariably smoker
Chronic cough & sputum
Absent
Frequent
Dyspnea on effort
Variable & reversible
constant , poorly reversible
Nocturnal symptoms
Relatively common
Uncommon
Airflow limitation
Diurnal variability
Normal
Response to bronchodilator
Good
poor
Ancillary tests in the D. Dx. between stable asthma & COPD
TEST
ASTHMA
COPD
Reversibility to bronchodilator & /or corticosteroids
Usually present
usually absent
TLV + RV
usually normal
Increase
DLco
normal
AHR
might be increase
allergy testOften +
often -
CXR
usually normal
usually abnormal
sputum
eosinophilia
neutrophilia
Exhaled NO
increase
usually normal
Management of COPD
Stop smoking
Vaccination
Bronchodilators
Corticosteroids
Oxygen therapy
Rehabilitation
Others
Smoking cessation
Every attempt should be made to highlight the role of smoking in the development and progress of the disease and encourage, advise and assist the patient toward smoking cessation. On cessation, patients should be warned to expect an apparent worsening of chest symptoms and reassured that this is temporary. Cessation is difficult but highly rewarding and remains the only intervention proven to decelerate the decline in FEV1.COPD Assessment Score ( CAT)
Smoking cessationPharmacological Management of COPD
In advanced disease Long – term oxygen therapy is necessaryCOPD in Old age
Management of acute exacerbation of COPD
1. Oxygen therapy : 24%---28% ---
2. Inhaled bronchodilators : SABA , SAMA , LABA ,LAMA
3. Oral corticosteroid: prednisolone 30 mg/d for 10 days
4. Antimicrobial drugs