Salah M. Hassan
- A relatively slow-spreading viral disease characterised by skin lesions and/or plaques in the pharynx and affecting chickens, turkeys, pigeons and canaries worldwide.- Morbidity is 10-95% and mortality usually low to moderate, 0-50%.- Infection occurs through skin abrasions and bites, or by the respiratory route. - It is transmitted by birds, fomites, and mosquitoes (infected for 6 weeks).- The virus persists in the environment for months.
- It is more common in males because of their tendency to fight and cause skin damage, and where there are biting insects.- The duration of the disease is about 14 days on an individual bird basis.
Signs
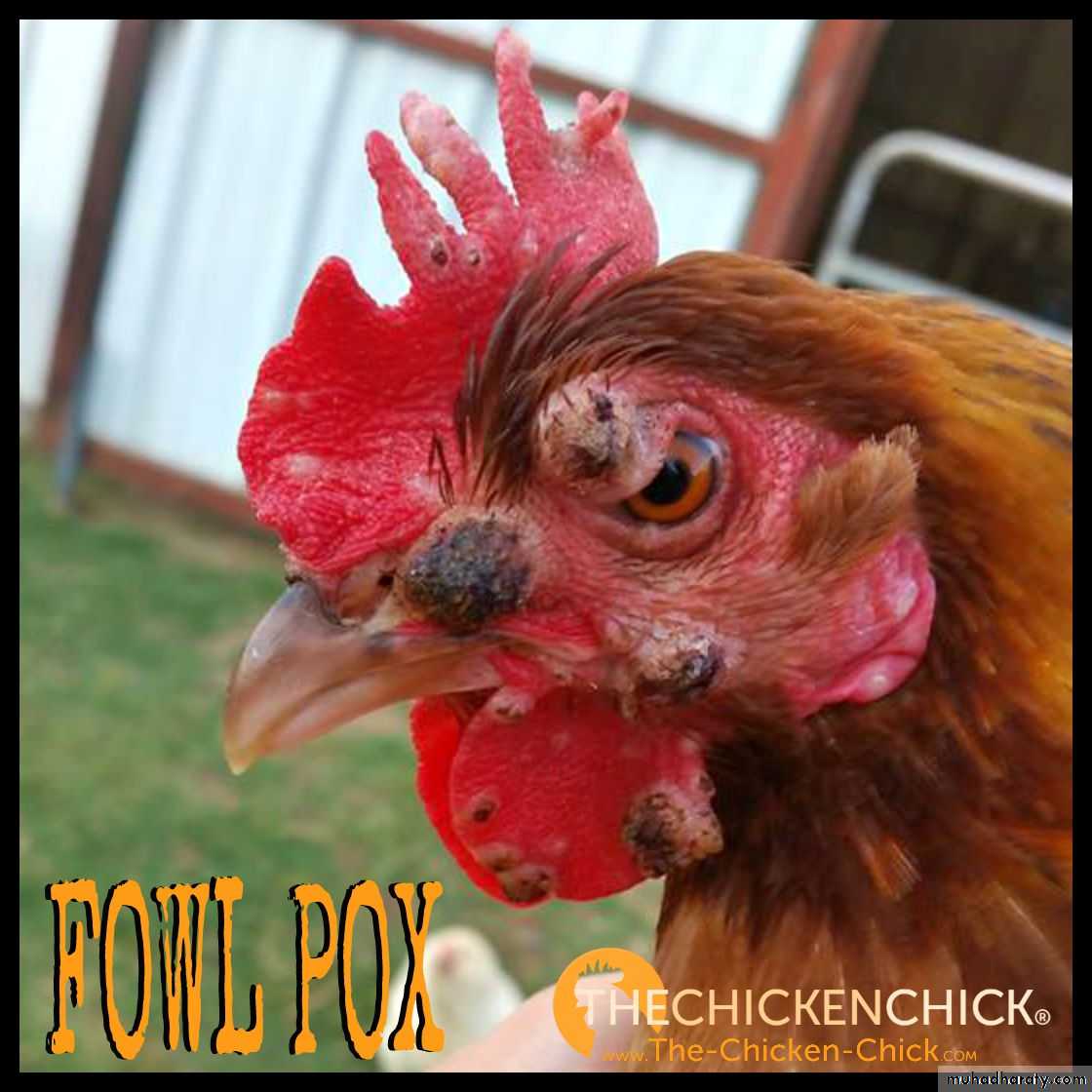
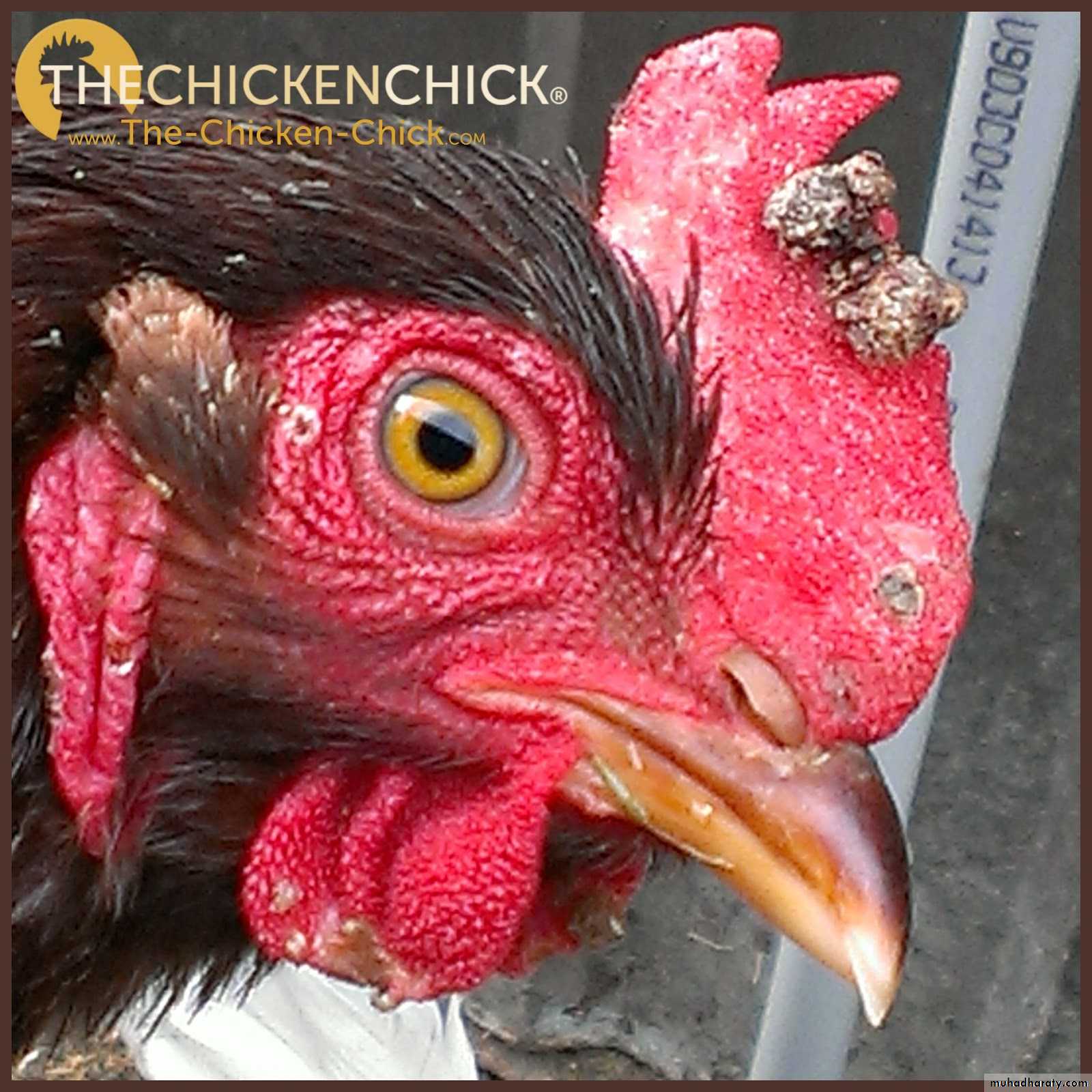
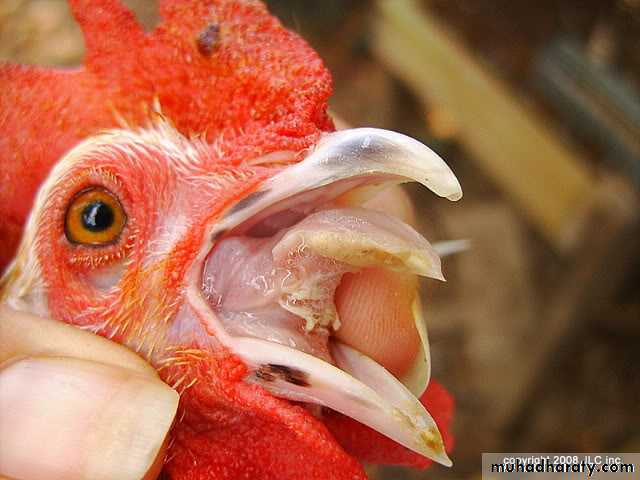
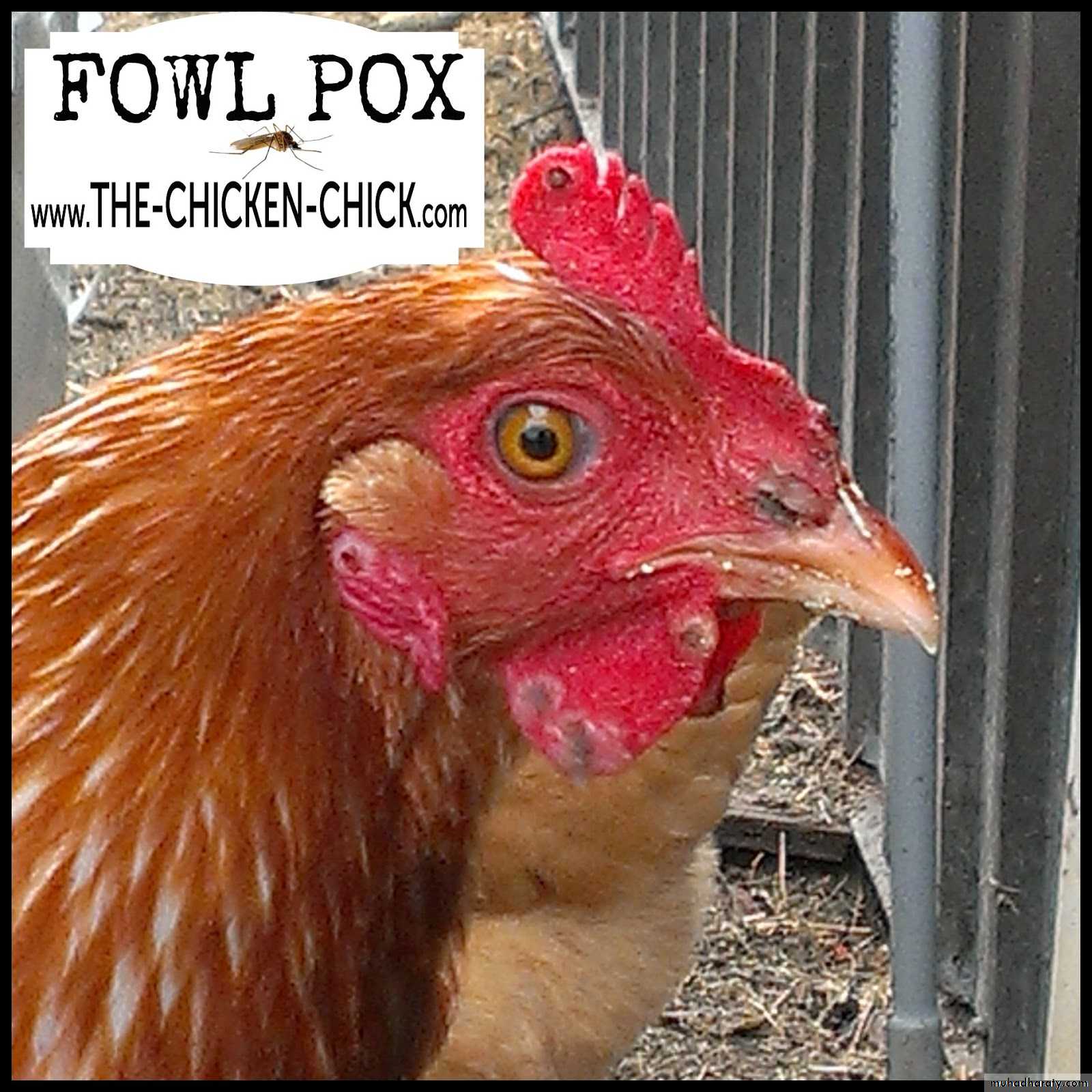
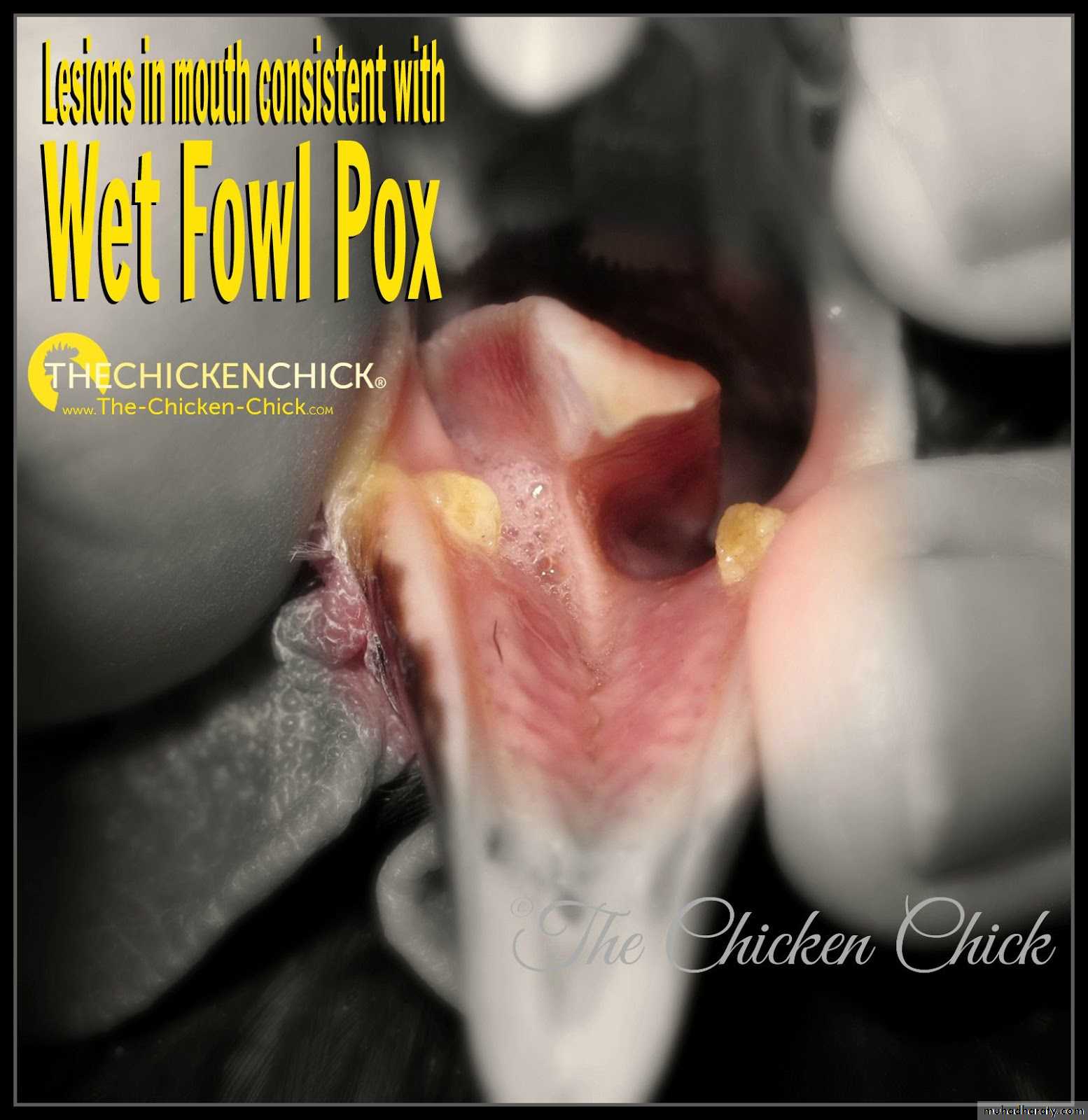
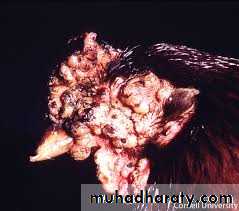
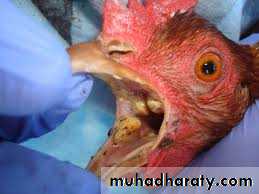
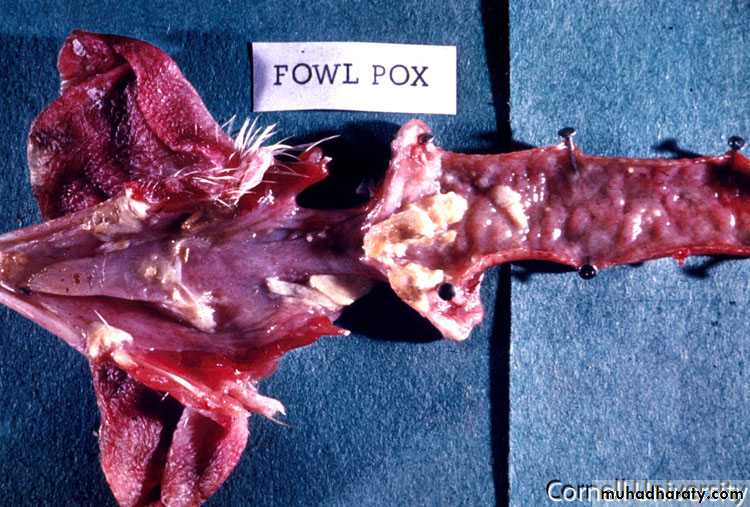
Warty, spreading eruptions and scabs on comb and wattles. ( Dry Form )Caseous deposits in mouth, throat and sometimes trachea. ( Wet Form )
Depression.
Inappetance.
Poor growth.
Poor egg production.
Post-mortem lesions
Papules progressing to vesicles then pustules and scabs with distribution described above.Less commonly there may, in the diptheritic form, be caseous plaques in mouth, pharynx, trachea and/or nasal cavities.
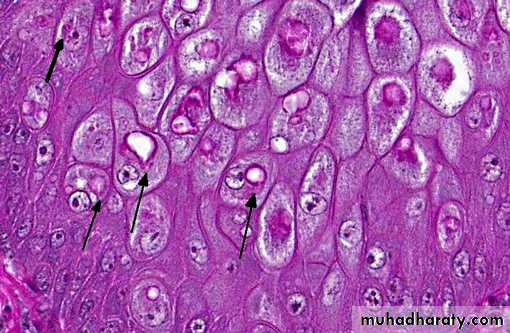
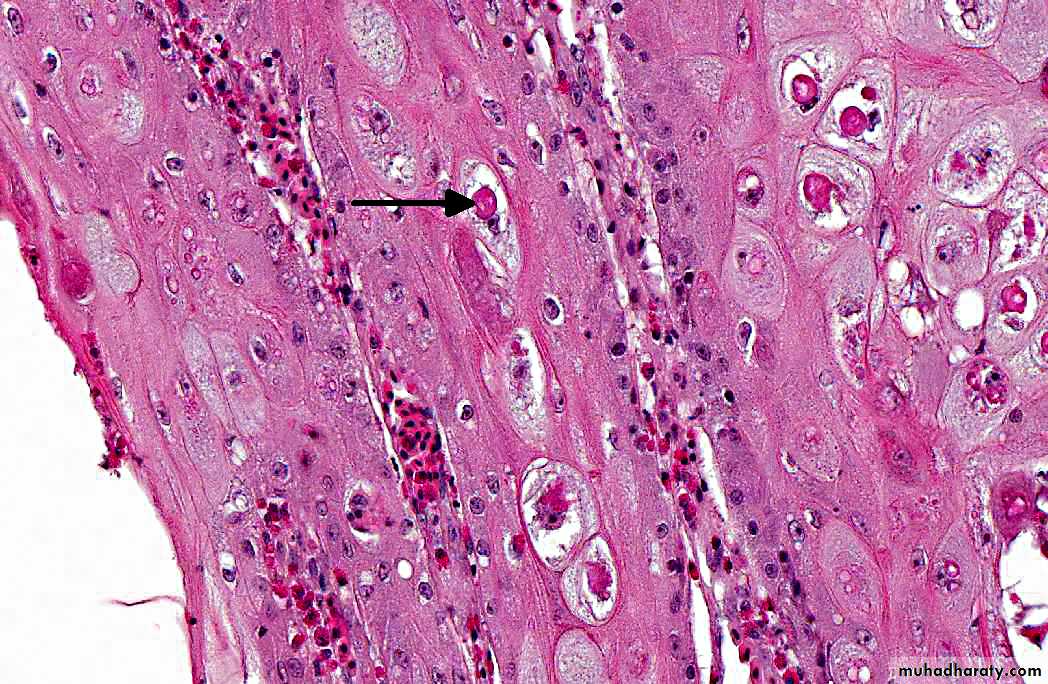
Microscopically - intra-cytoplasmic inclusions (Bollinger bodies) with elementary bodies (Borrel bodies).
Keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum contain large eosinophilic cytoplasmic viral inclusions (Bollinger bodies) (arrows).
Epithelial cells within the hyperplastic mucosa often undergo ballooning degeneration and contain a 15-30 um, eosinophilic, intracytoplasmic inclusion (Bollinger body). (arrow)
Diagnosis
- A presumptive diagnosis may be made on history, signs and post-mortem lesions.- It is confirmed by IC inclusions in sections/ scrapings, reproduction in susceptible birds, isolation (pocks on CE CAM) with IC inclusions. DNA probes.- Differentiate from Trichomoniasis or physical damage to skin.
Treatment
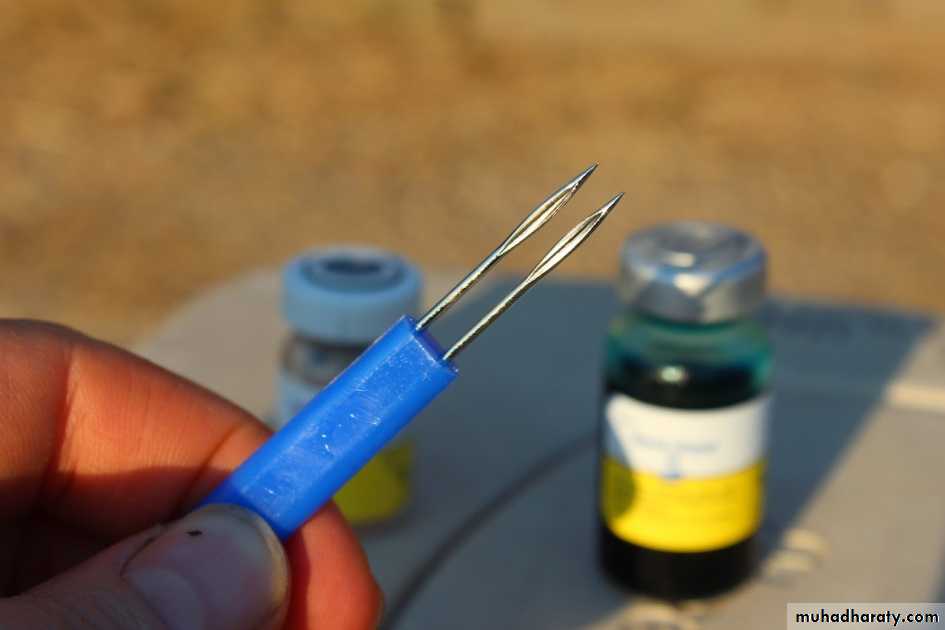
None.- Flocks and individuals still unaffected may be vaccinated, usually with chicken strain by wing web puncture.
- If there is evidence of secondary bacterial infection broad-spectrum antibiotics may be of some benefit.
Prevention
- By vaccination (except canary).- Chickens well before production. Turkeys by thigh-stick at 2-3 months, check take at 7-10 days post vaccination.
- There is good cross-immunity among the different viral strains.