Haemangioma
Its benign endothelial tumor of blood vessels.-common skin lesion.
-1% newborn,10% infant.
-60% =head.
- female/male=3/1.
-Grow rapidly in first year then slowly involute.70% at 7 years.
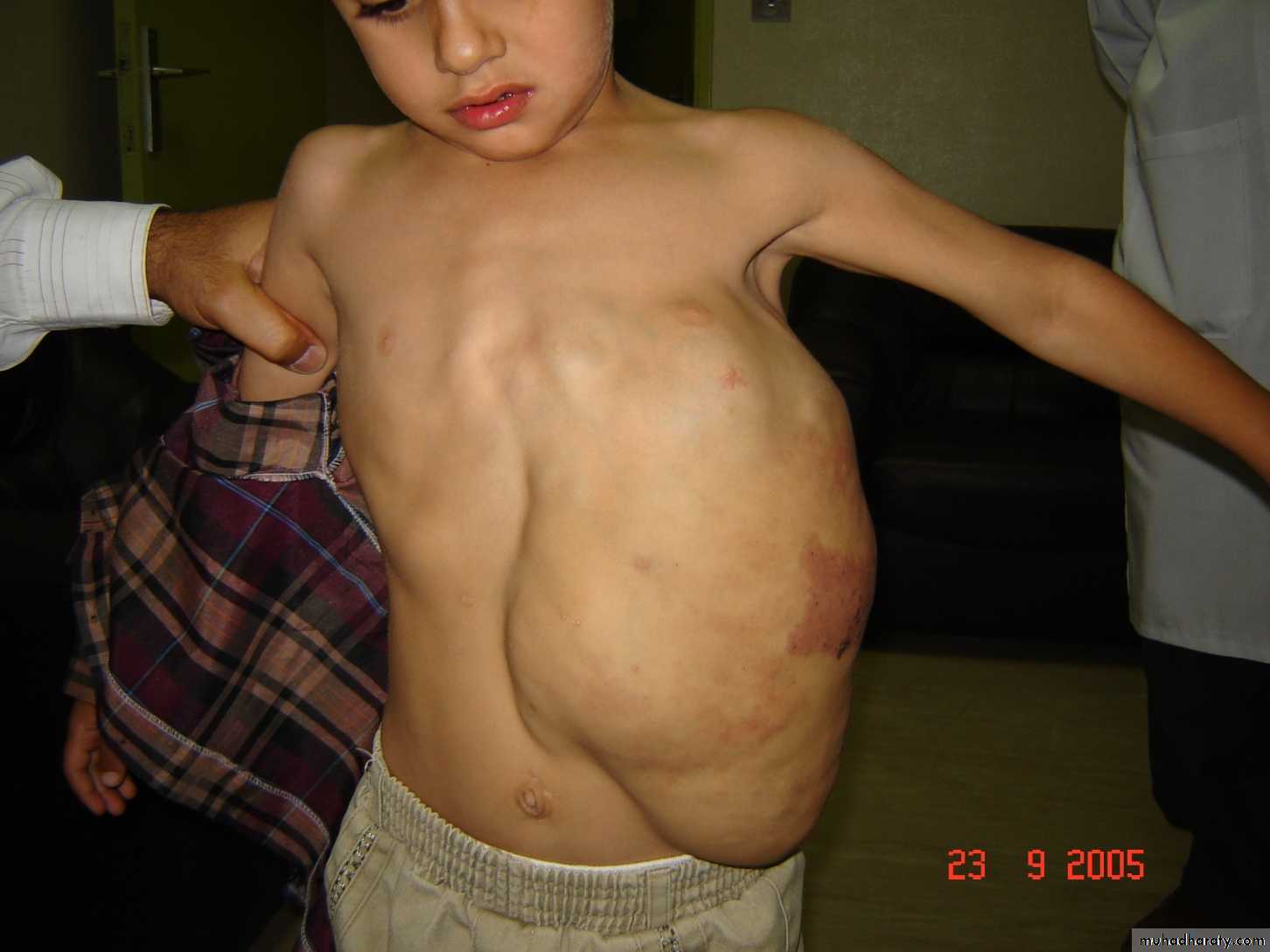
-80% solitary lesion &20%are multiple(viscera).
Classification
Mullikan classify haemangioma into 2 groups:1- vascular tumor:
- rapid growth.
-involutes ,leaving fibrosed skin +fat deposition.
-increase endothelia cell activity.
- increase number of mast cells.
- capillary.
2-vascular malformation:
-not regress with time.
- not hyper cellular.
-flat mature endothelium.
- not proliferative.
-cavernous
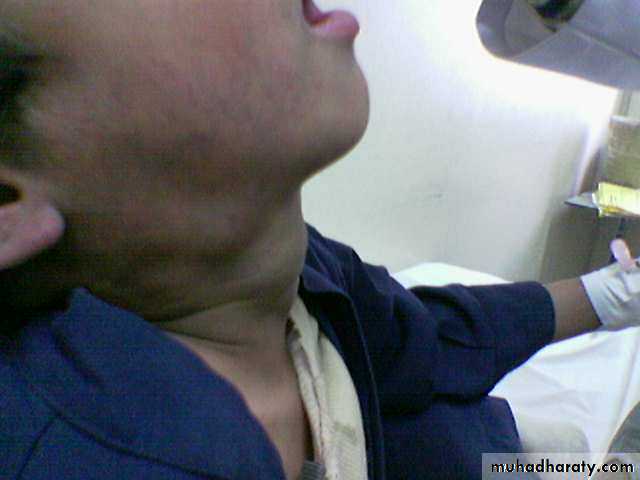
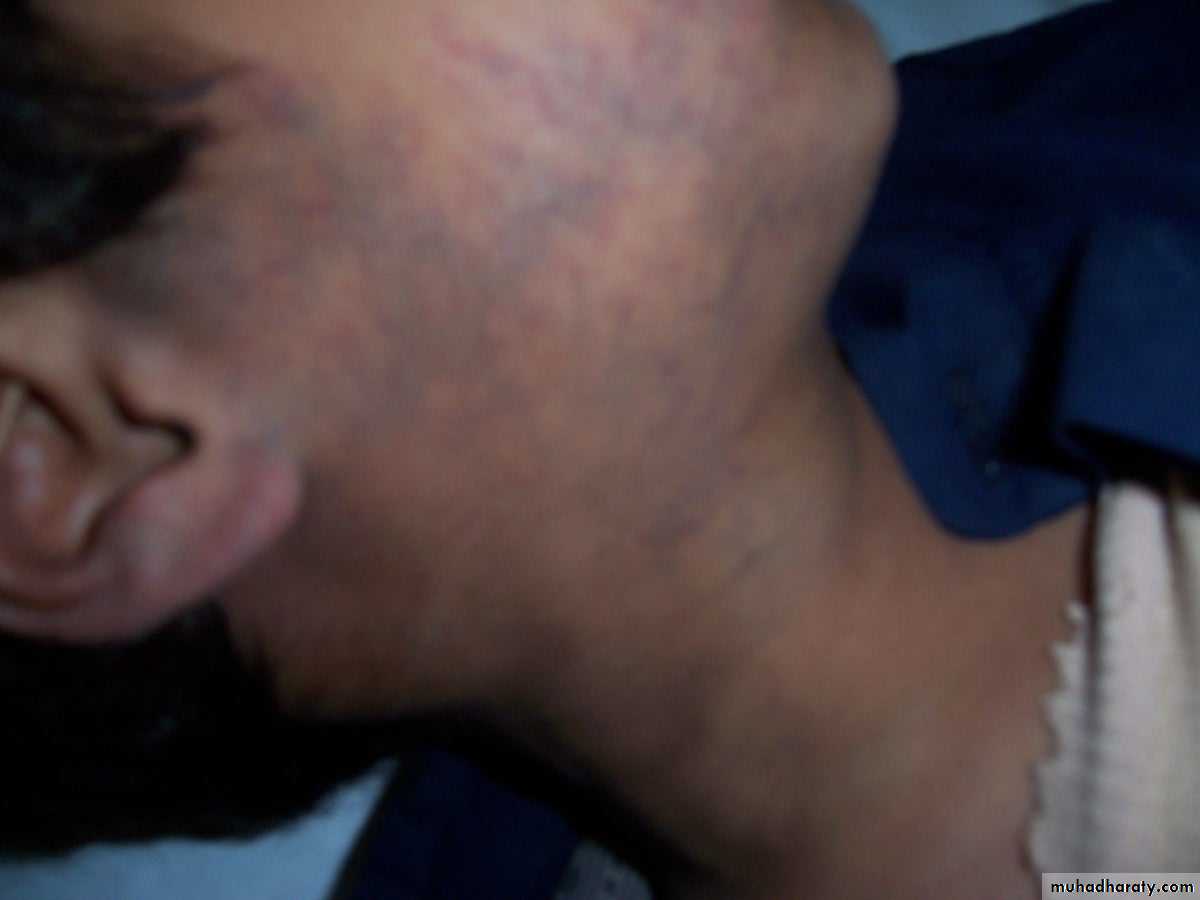
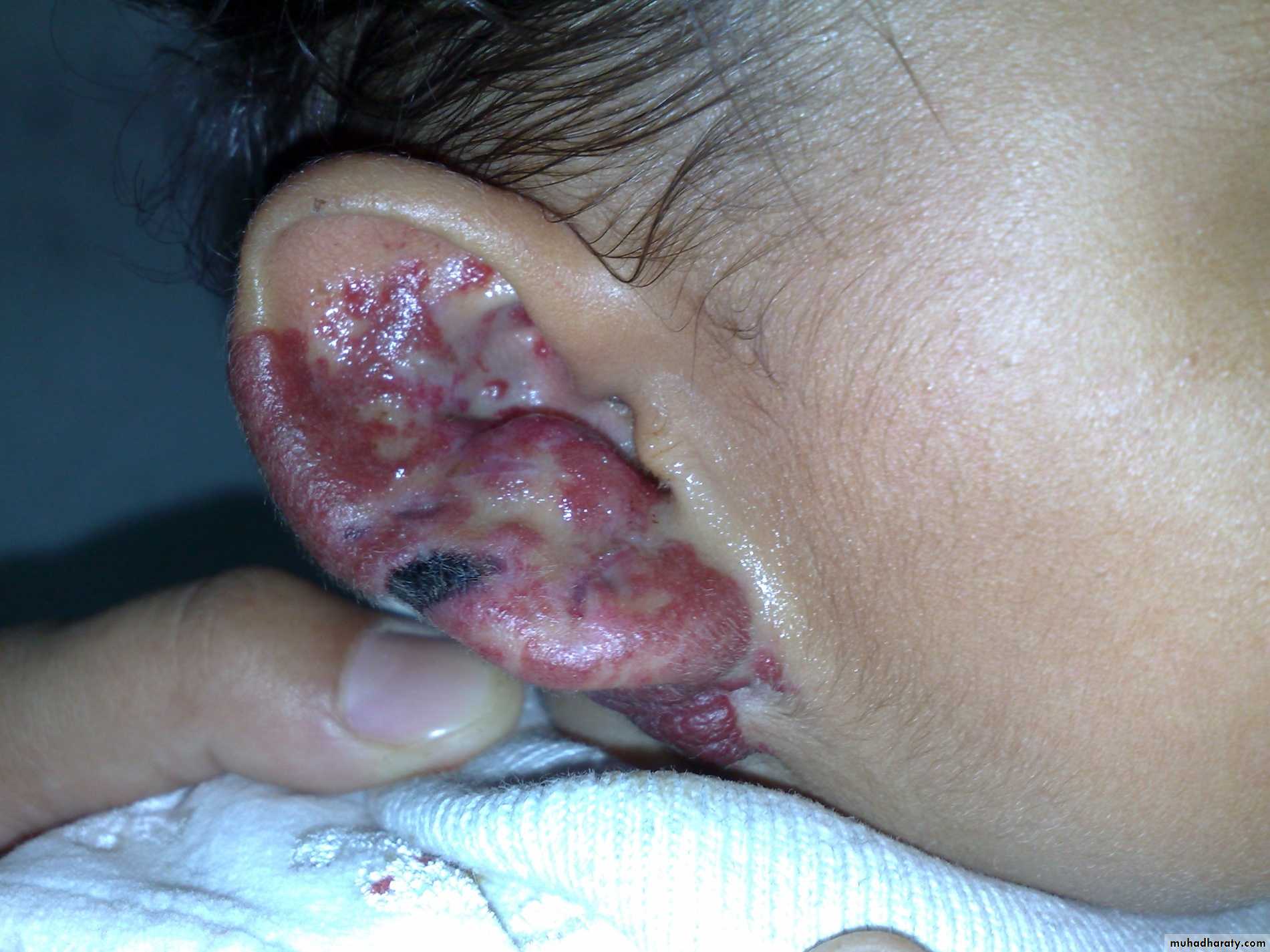
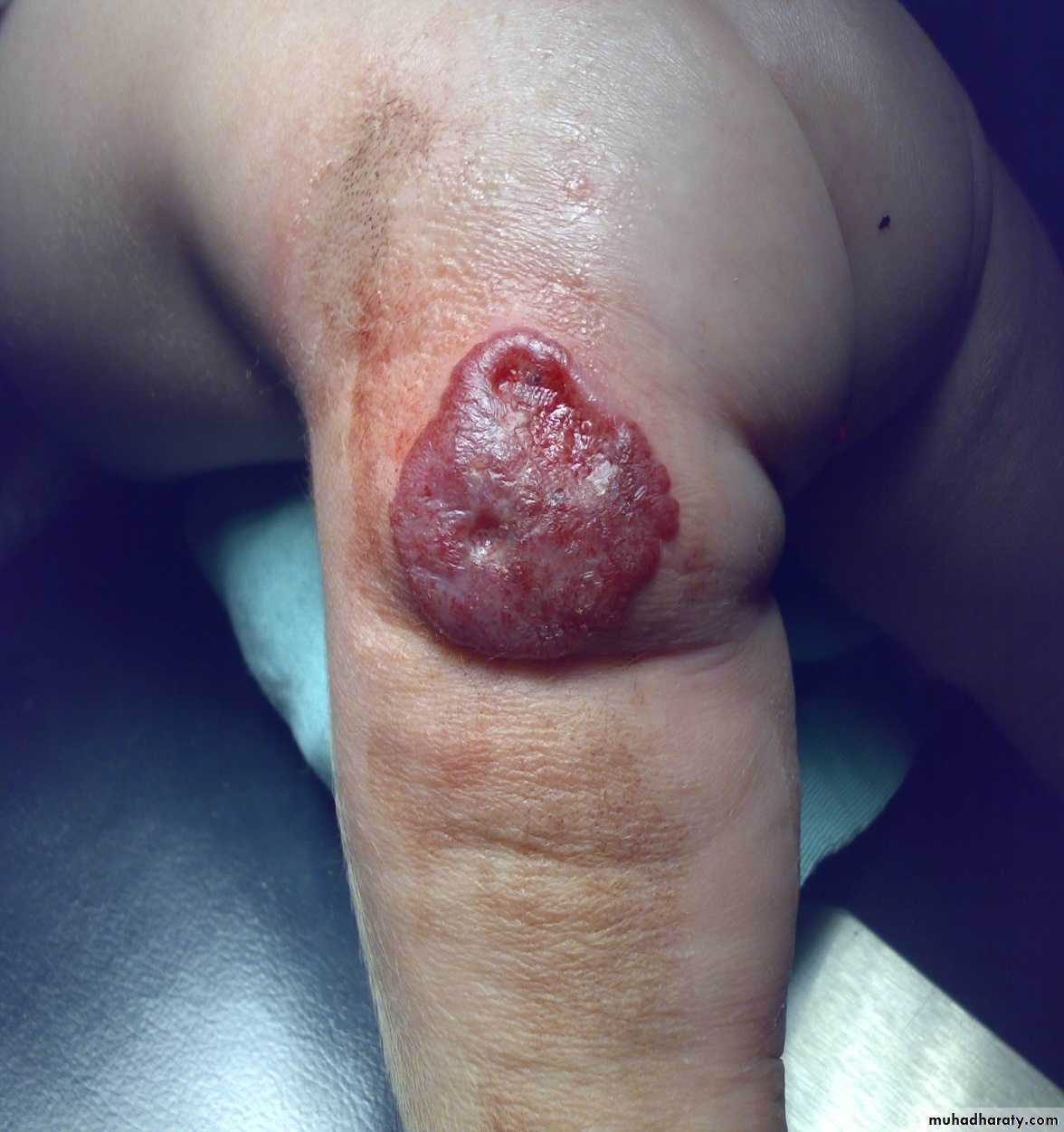
Clinical appearance
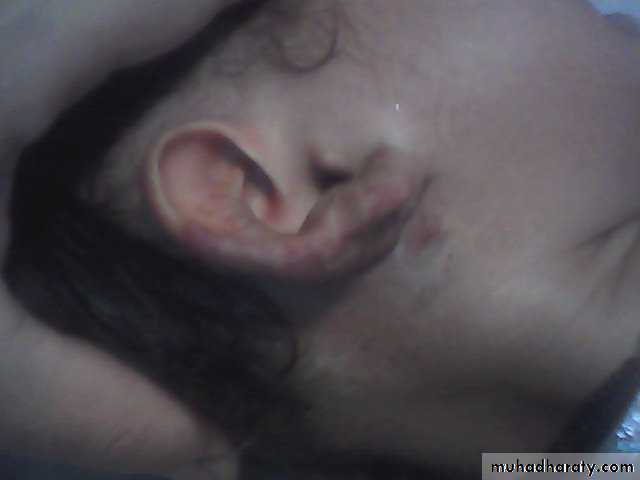
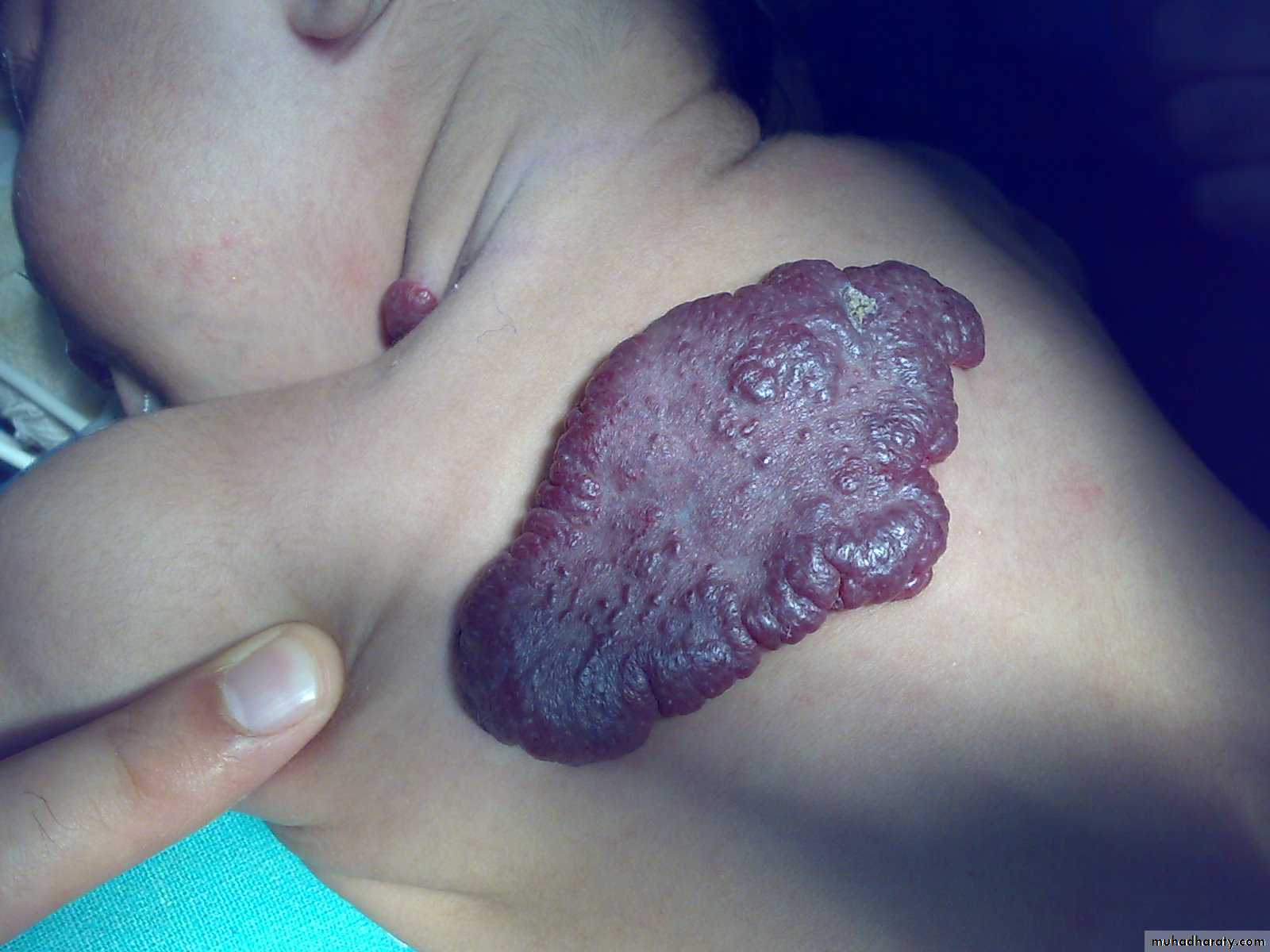
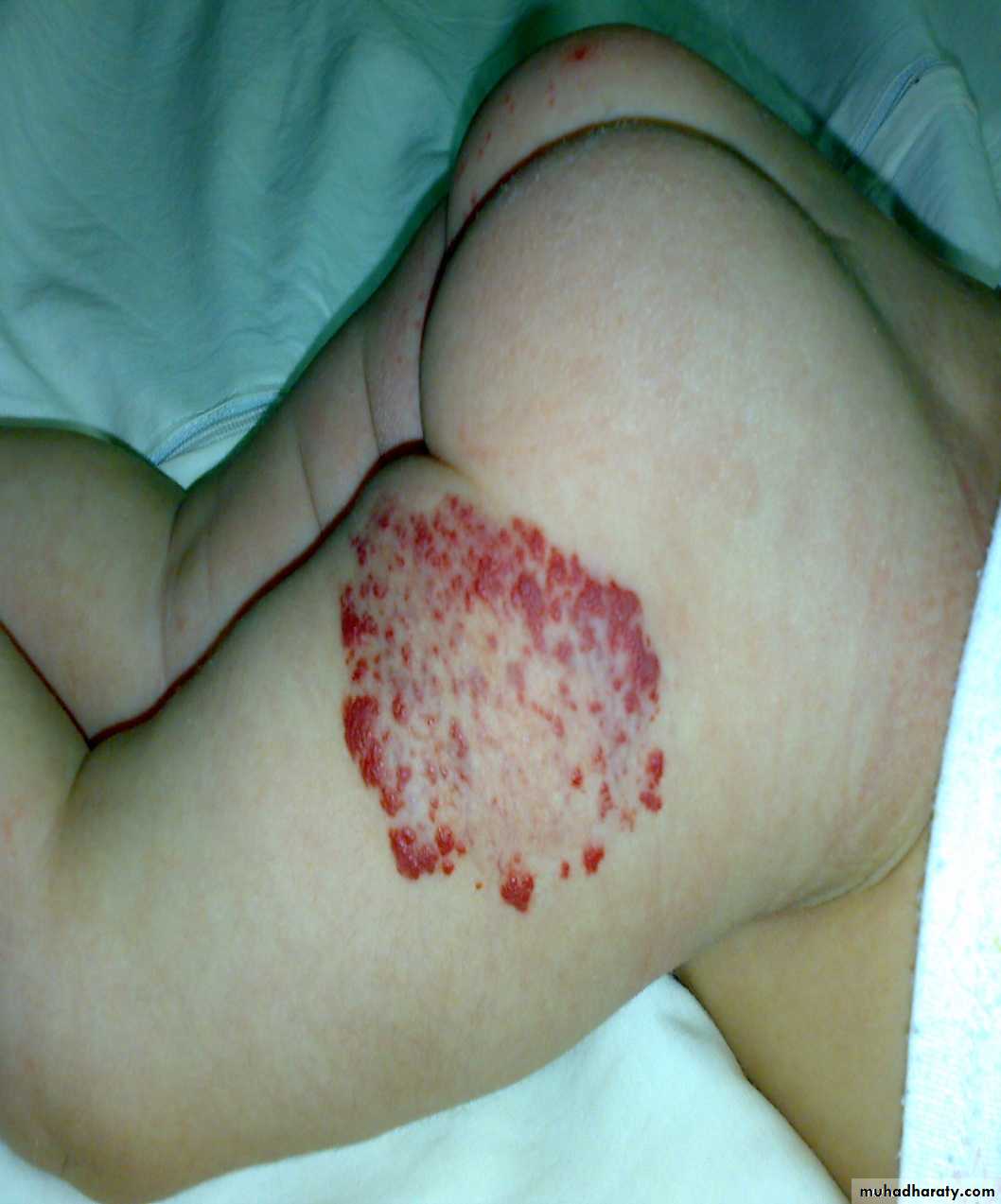
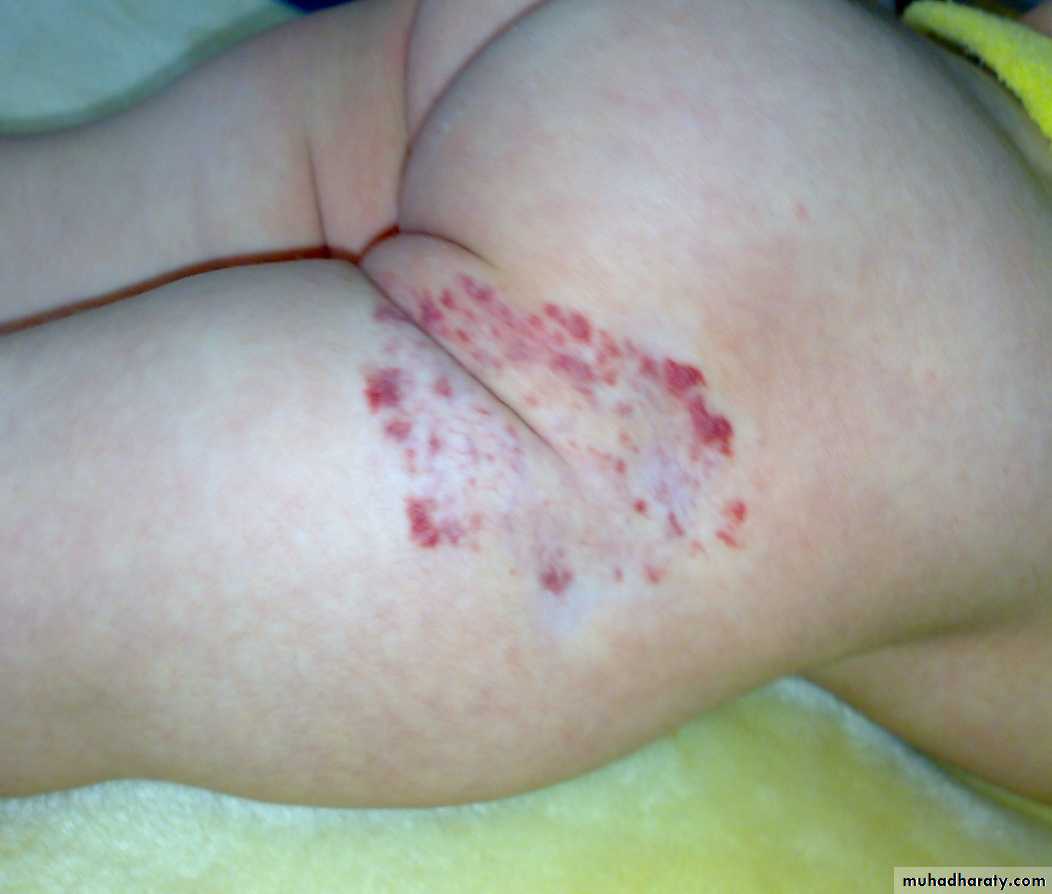
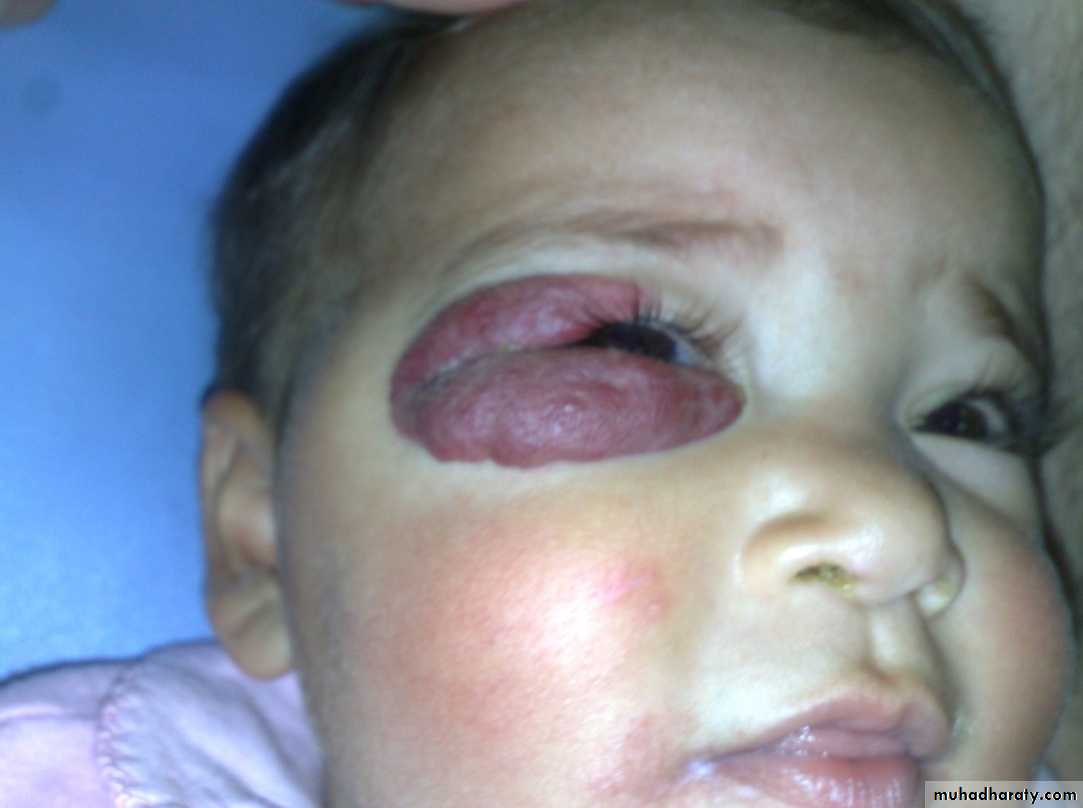
-depend on the depth &growth phase.-early lesion as strawberry ,elevated ,irregular.
- size= small red elevated mark to huge tumor .
- Deep lesion = blue or skin color.
- on examination: comprisable but slowly refill .
- Difficult to differentiate between cavernous and capillary haemangioma.
-Microscopically: dilated vascular spaces within dermis and subcutaneous tissue.
Rapid growth result from :
- canalization.- proliferation of angioblast.
Regression result from:
1- thrombosis.
2- sclerosis.
3-infarction.
- Most complications occur during proliferative phase.
Location
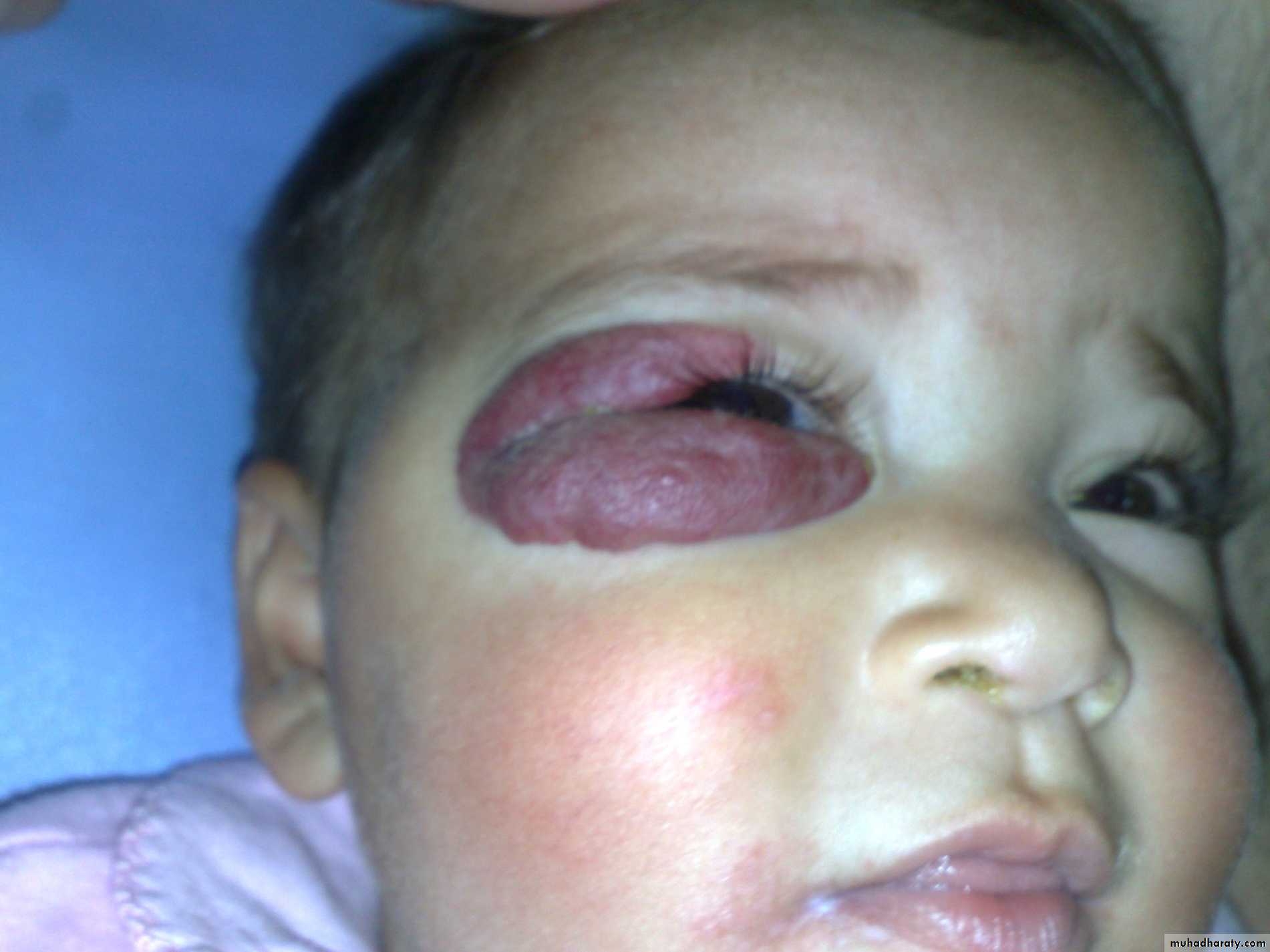
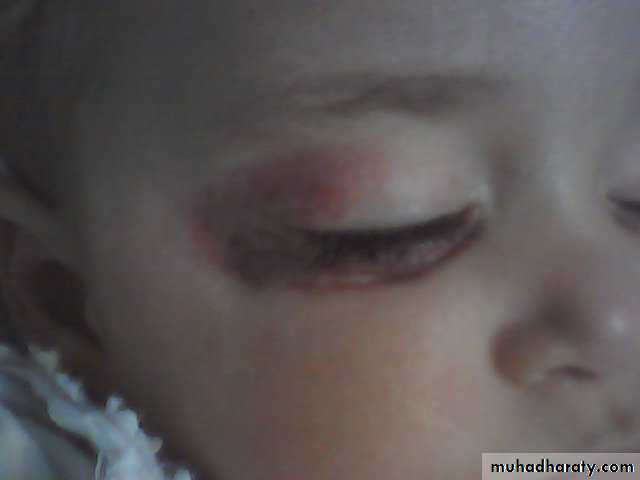
In addition to size &complications it dictate the urgency of treatment?1- periorbital lesion visual obstruction ambylopi a & sometimes visual impairment.
2- nasal opening obstruction apnea in neonates.
3- external auditory meatus conductive hearing loss.History
1- proliferating phase:- a small sot appear several weeks after birth.
- grow rapidly for several months(8-12).
2- plateau phase :
- size not increase or decrease up to 2 years.
3- involution phase:
- started at 2-3 years .
- disappears by 5-7 years;
- leaving a patch of pale flaccid skin( fibro fatty tissue)
Complications
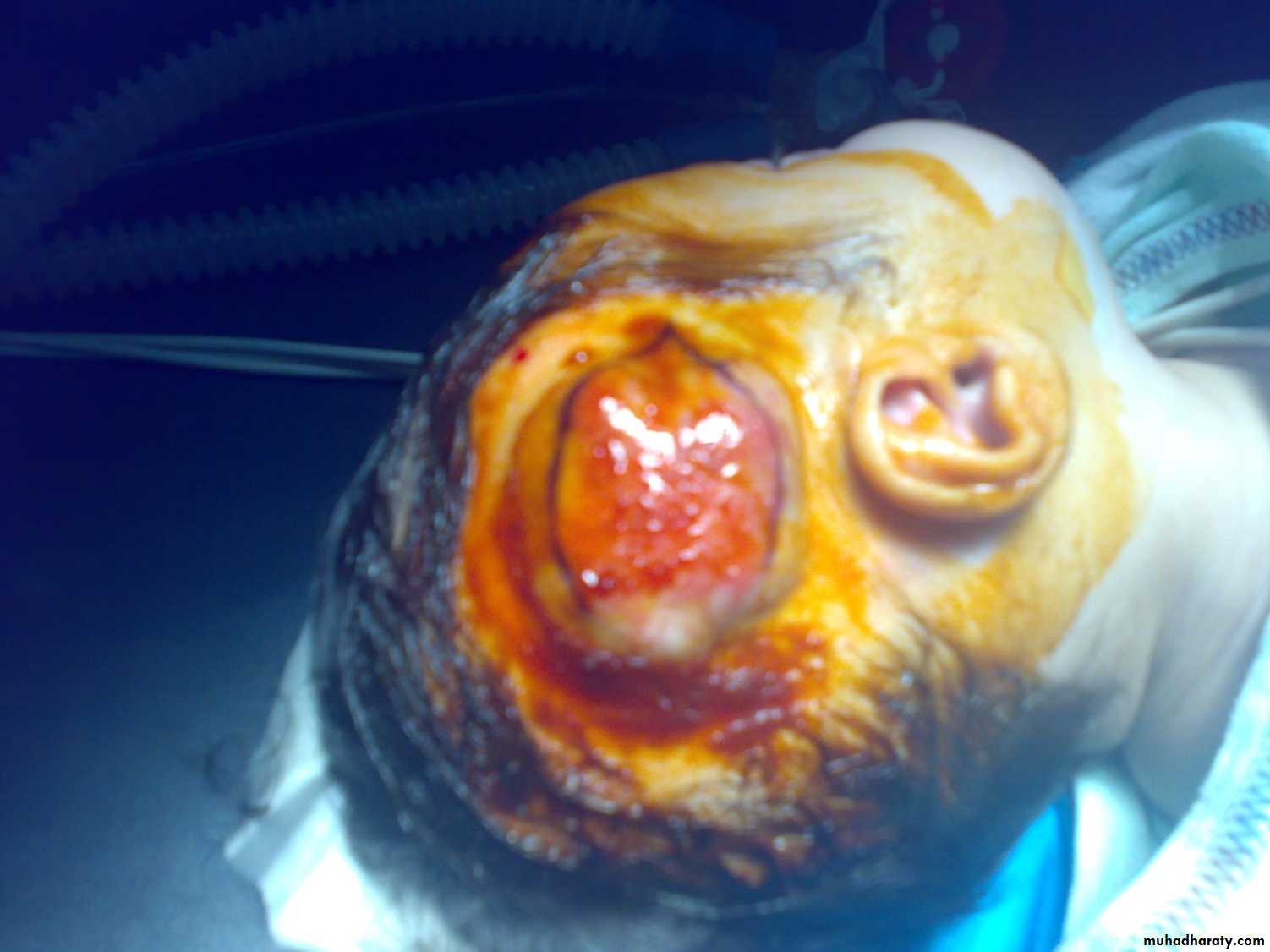
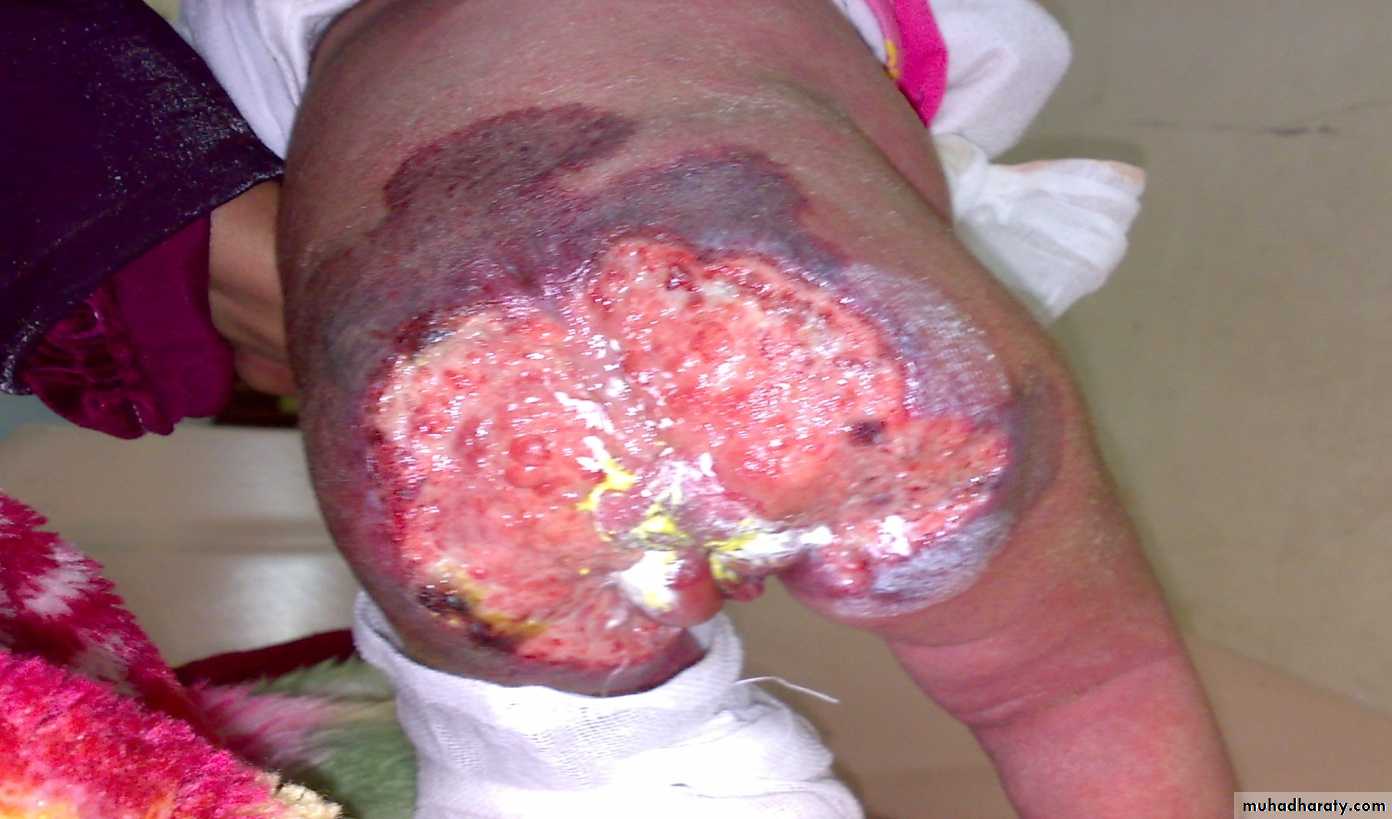
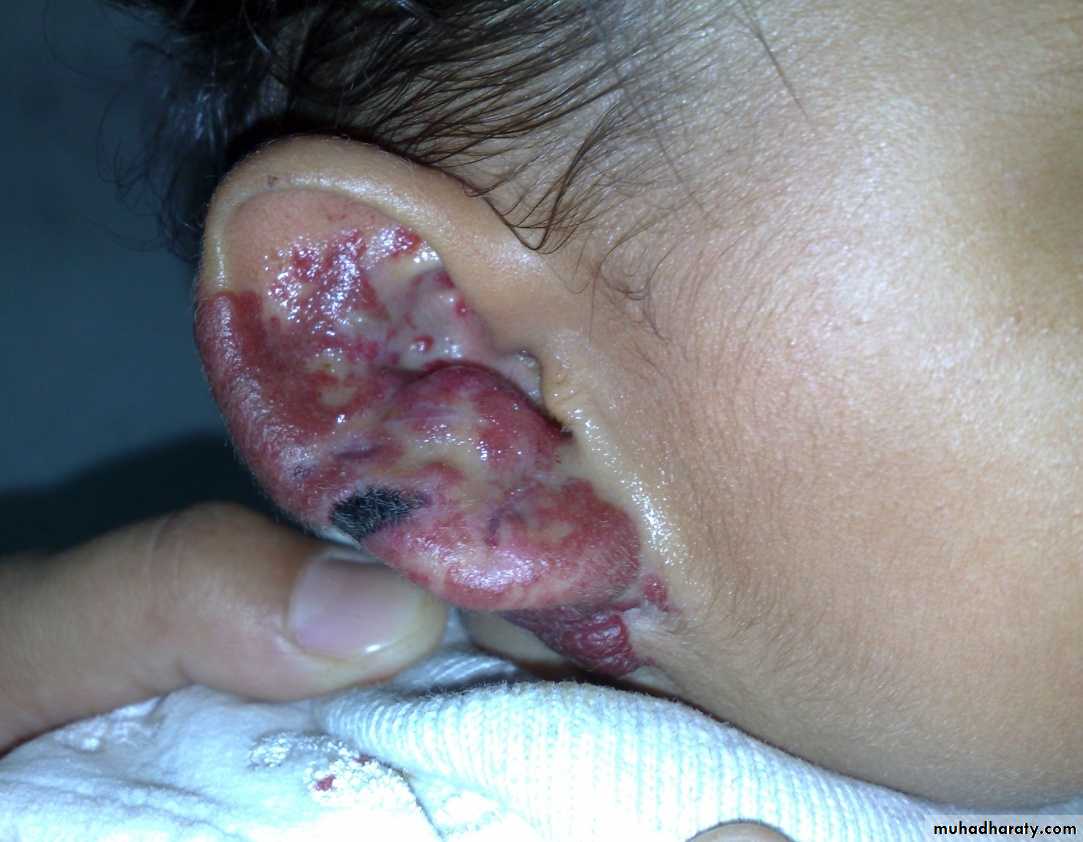
1-superficial ulceration:-common.
- my cause necrosis and bleeding.
- Can be treated by dressing & systemic antibiotics.
- Large ulcer need aggressive treatment.
2- bleeding :
can stop with compression or fibrin glue.
3- infection:
-blood born.
- May cause septicemia or local necrosis.
- Treated by antibiotics.
4-Kassabach-meritt syndrome:
-large size haemangiom secondary to traped platelets. - thrombocytopenia , coagulopatthy and hemolytic anemia.-growth phase
Its characterized by
1-Rapid increase in the swelling of haemangiom.2-Tens and shining of overlying skin.
3-Surrounding area of ecchymosis and pitichia.
4-Bleeding tendency.
Laboratory finding :
1-Dicreas platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
2-Dissimination intravascular coagulation
3-Decrease plasma fibrinogen
4-Prolong blooding time
5-Atteration in factor V,VIII,prothrombin time and thrombin time
5-Larg visceral lesion or multiple lesion can cause congestive heart failure secondary to shunting of blood.
6- functional impairment.
TreatmentIn general most lesions treated non surgically .
Factors affects the mode of intervention :
1-Site : eyelid or medial cantus treated by local injection of steroid2- Size : big perineal haemangioma can be treated by diverting colostomy
3-Multiplicity : multiple lesion need systemic steroid
4-Presence of complications
Emergency treatment confind for life threatinig haemangioma
Example:1- Massive liver enlargement
2-Conjestive heart failure high out put
3-Hearing or vision loss
4-Airway obstruction
Treatment options
1- Active are intervention with close monitoring
2- Waiting involution of tumor3- Laser therapy which may cause edema and later scaring
4- Intra lesion cortico steroid
5- Interferon
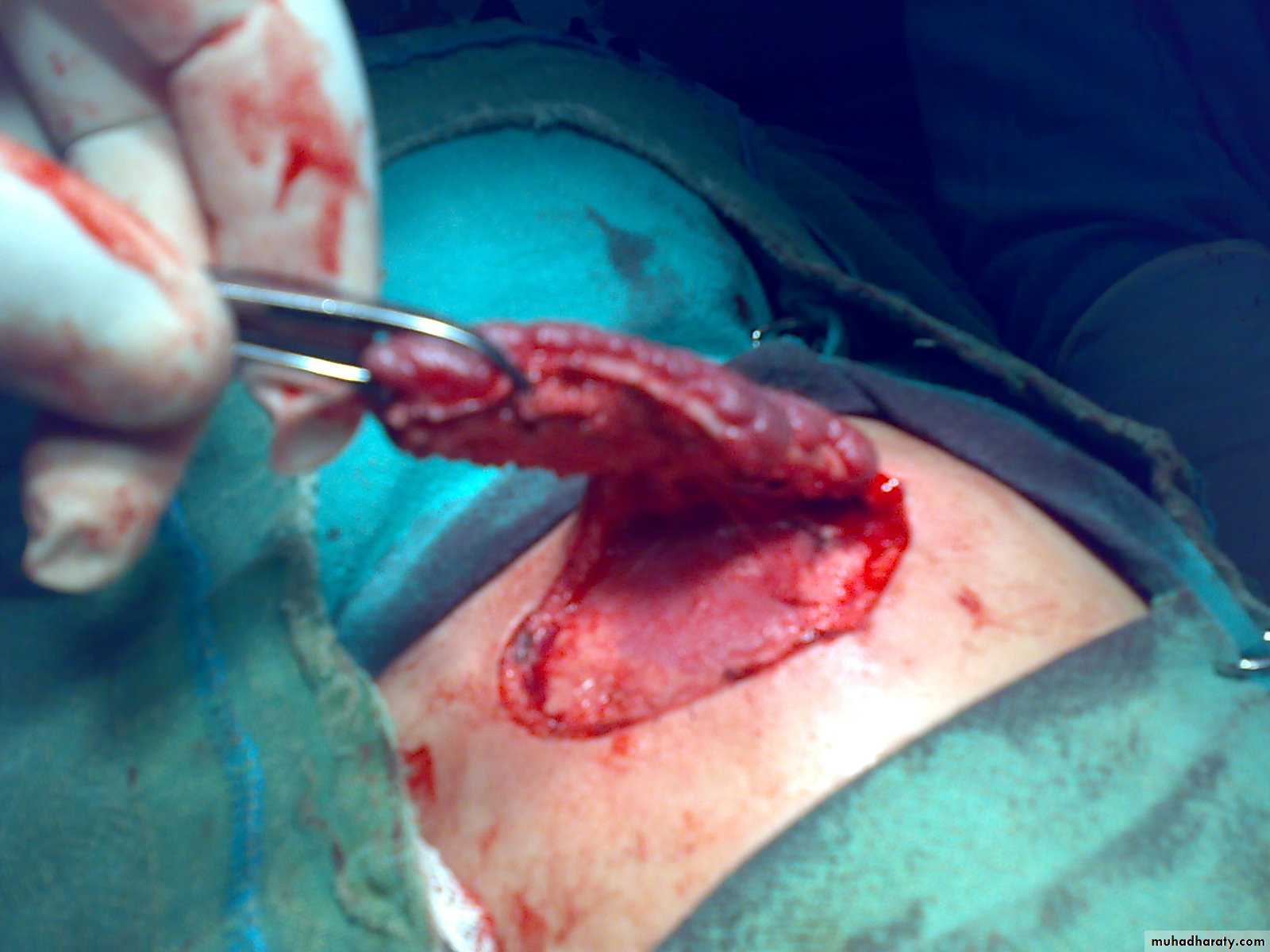
6- Excisional surgery
7- Systemic cortico steroid
8- Other drugs like bleomycin, cyclophosphamide.
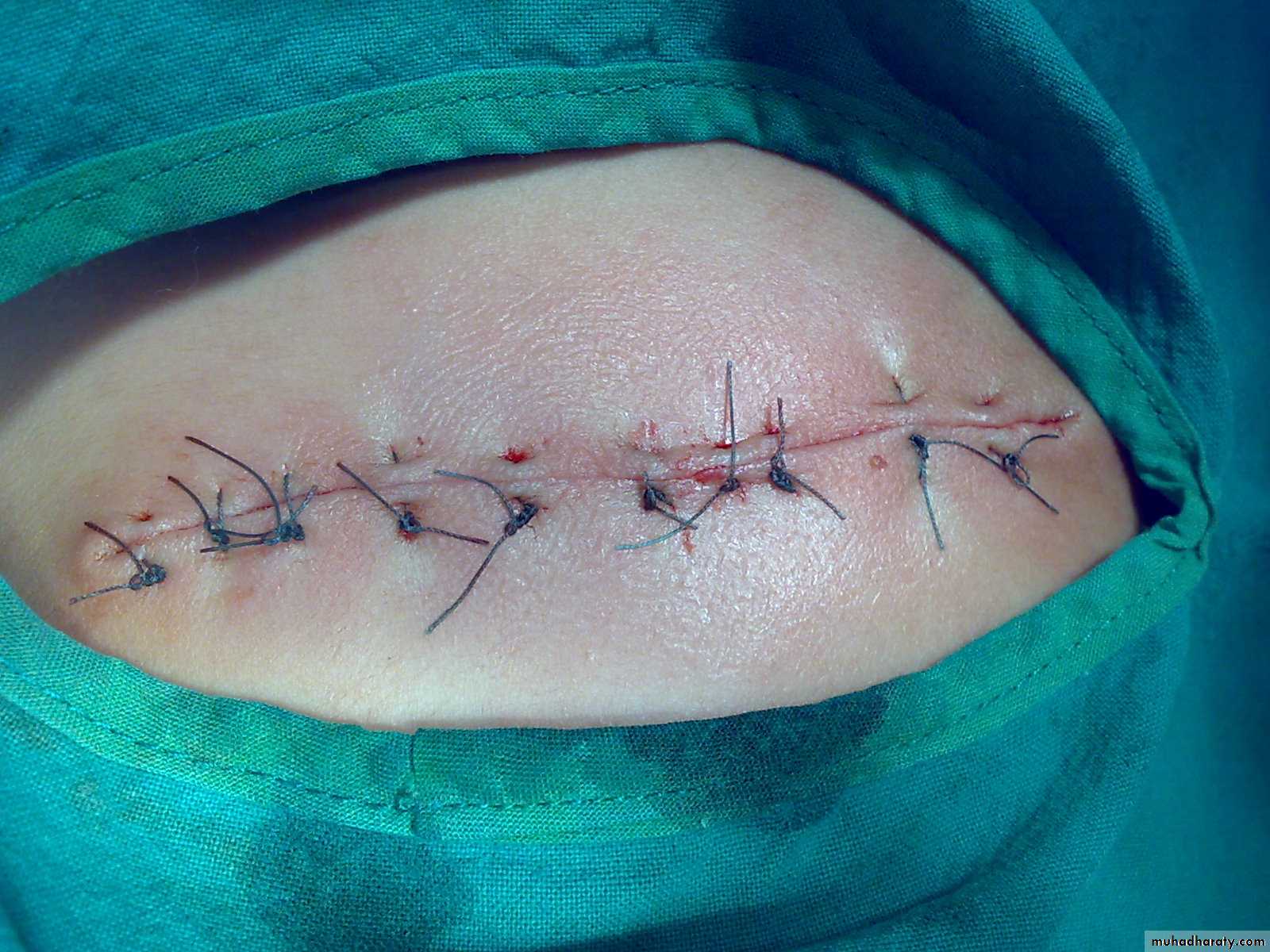
Surgery
indication in proliferative phase in infancy1-Visual or subglottic obstruction
2-Compression of eye globe
3-Bleeding
4-Ulceration
5-Lesion with high risk of searing
Indication in involution phase
1-befer school age2-Post ulcerative searing or residual skin
3-For cosmetic purposes