Medically important Cestodes (Tapeworms) of human beings
د.إكرام الحسوLec:1
9-3-2017
Parasitology
1
Class Cestoidea
Order Cyclophyllidea Order PseudophyllideaEchinococcus Spp.
Taenia saginataTaenia solium
Hymenolepis nana
Hymenolepis Diminuta
Diphyllobothrium caninum
Diphyllobothrium latum
2
Echinococcus Spp.
Genus Echinococcus include three different species:
Echinococcus granulosus
E. multilocularisE. vogeli
3Species of
Echinococcus Definitive host Intermediate hostE. granulosus Dogs and other canidae Sheep, goats, swine and
other herbivoresE. Multilocularis Foxes, dogs and wolves Small rodents
E. Vogeli dogs Small rodents4
E.granulosis
5
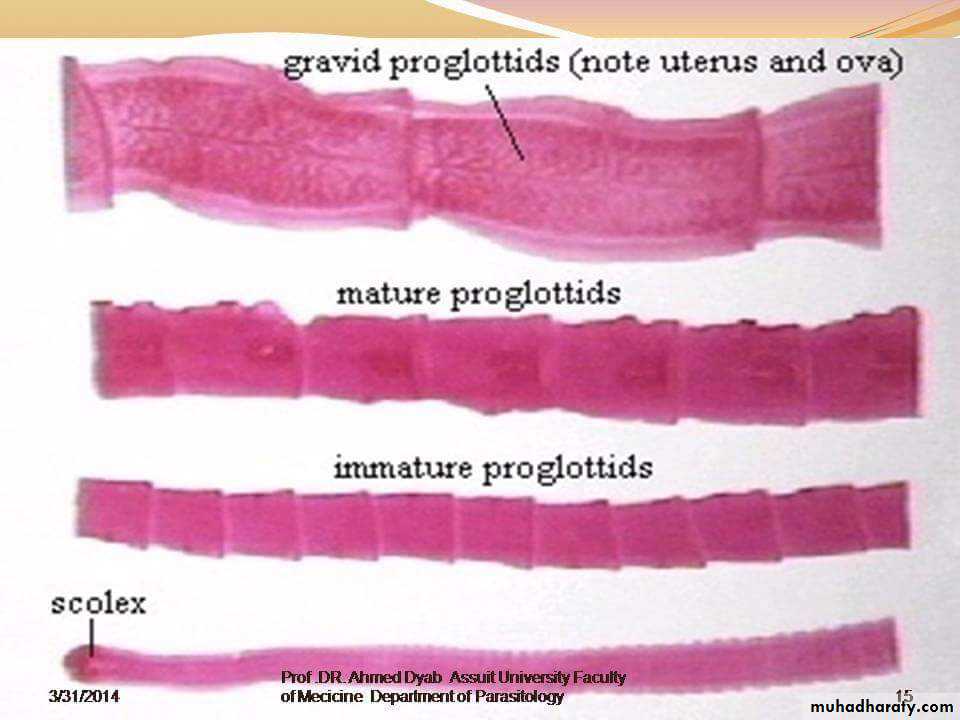
Morphology of adult worm
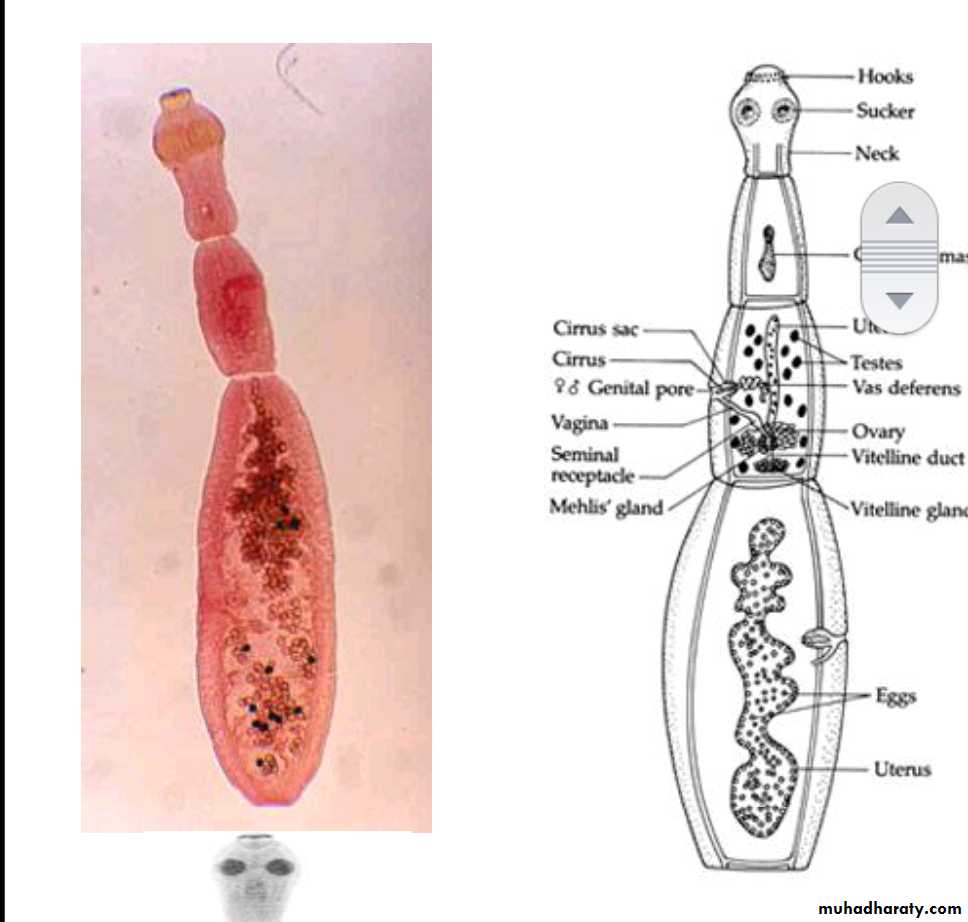
2-6 mm long. hermaphroditeThe body consist of:
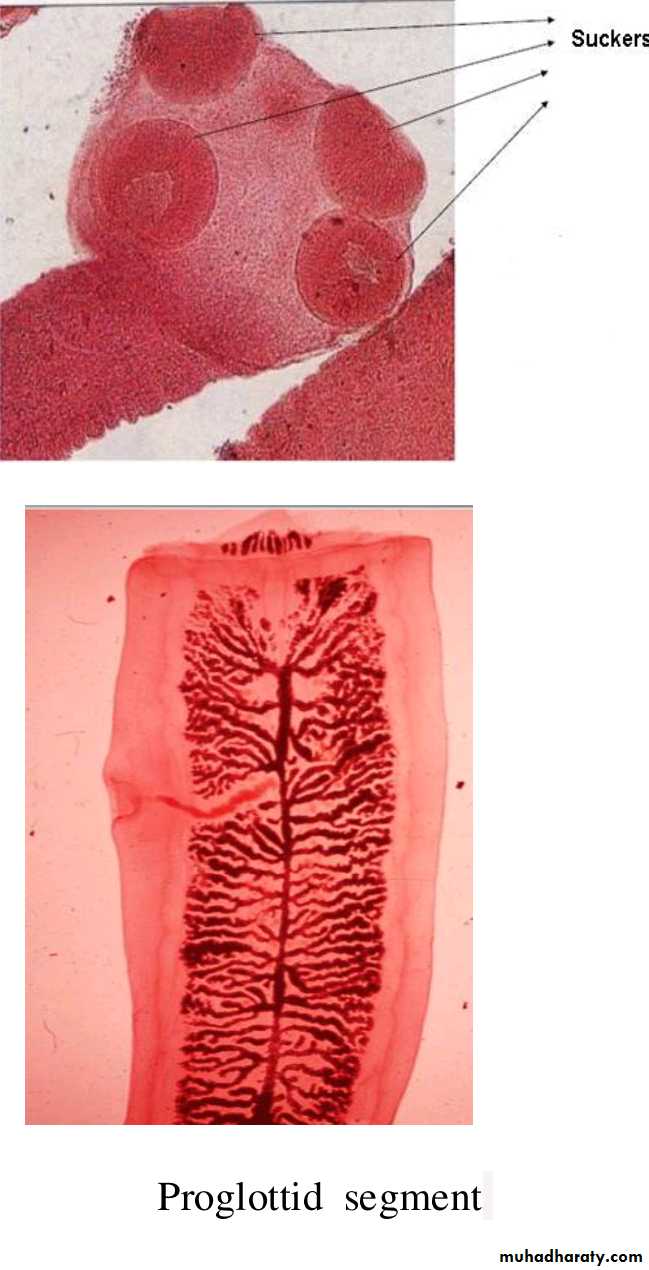
head (scolex) with 4 suckers and rostellum with two rows of hooks.
three segments (proglottids):Immature, mature and gravid.
6
7
The mature segment: contain fully developed male and female sexual organs .
The gravid segment: contain only uterus full with eggs.
8
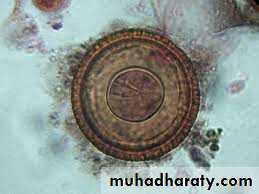
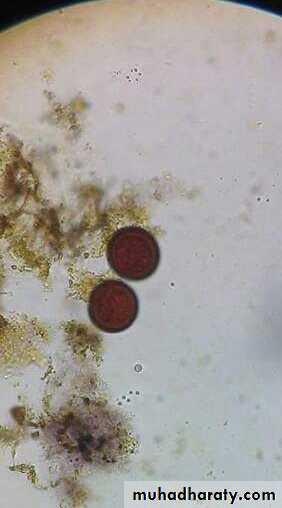
Morphology of the eggs (Taenia spp. Eggs).
Spherical, 35-45um in diameter .Hexacanth Embryo centrally located .
Radially staited shell .
Infective stage to human, sheep & cattle .
The same egg of Echinococcus Spp., Taenia saginata & T. solium
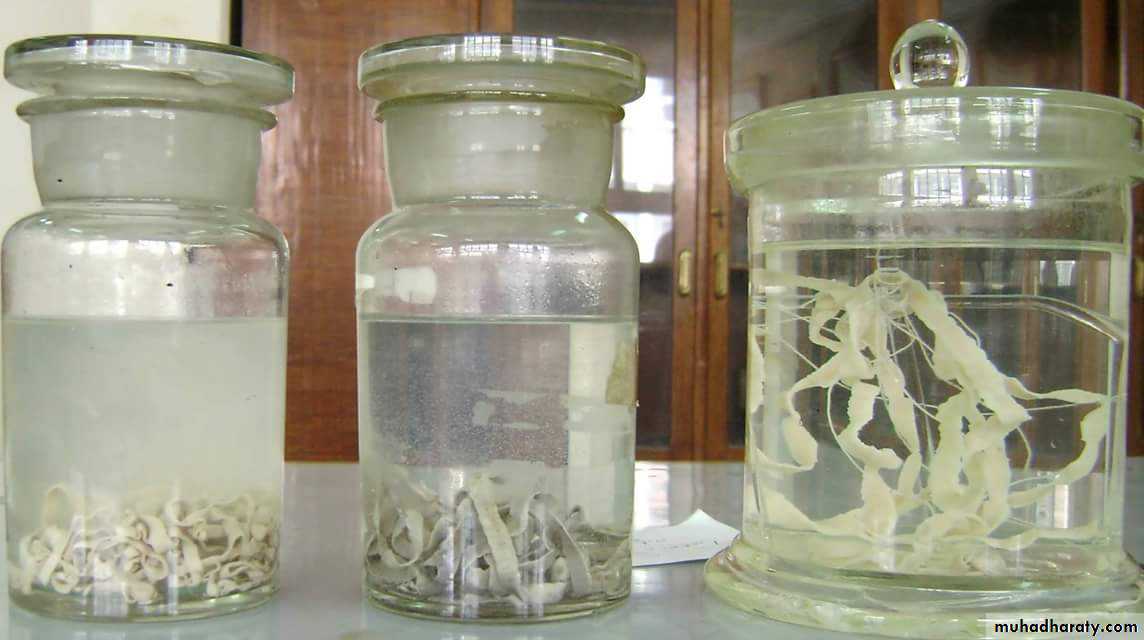
Taenia spp. Eggs
9
10
Life cycle
11
The adult E. granulosus inhabit the upper part of small intestine of the definitive(final) hosts, dogs or other canids( cats, foxes and wolves).
Gravid proglottids release eggs that are passed in the feces .
These eggs are infective stage to a suitable intermediate host (sheep, goat, cattle and man).
12
After ingestion, the eggs hatches in small intestine and releases an oncospher (emberyo) that penetrates the intestinal wall and migrates through the circulatory system to various organs, especially the liver and lungs.
In these organs, the oncosphere develops into a hydatid cyst that enlarges gradually, producing protoscolicis inside the cyst.
13
The dogs ( definitive host ) and other canids becomes infected by ingesting the H. cyst-containing organs of the infected intermediate host. After ingestion, the scolex evaginate, attach to the intestinal mucosa , and develop into adult stages in 30 to 80 days.
14
Hydatid disease (hydatidosis)
Is caused by the larval stages (hydatid cyst) of tapeworm called Echinococcus granulosus.
15
Types of hydatid cysts
Unilocular Osseous
Multilocular or alveolar16
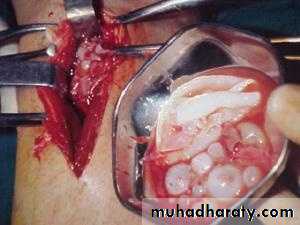
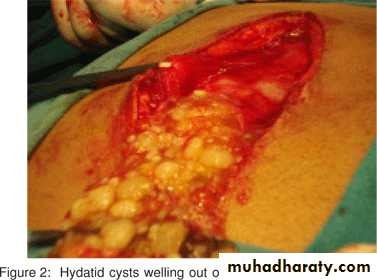
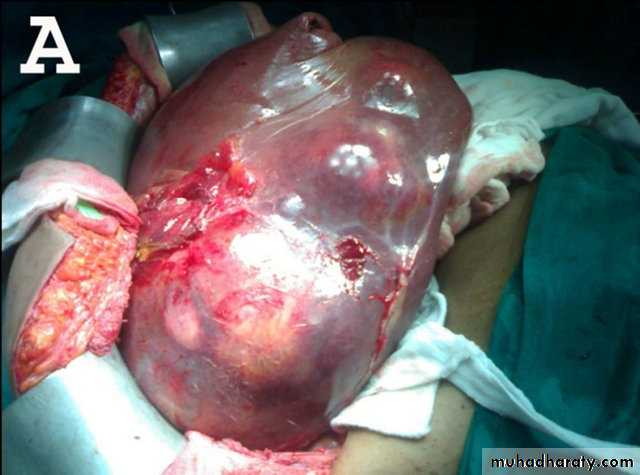
Unilocular type:
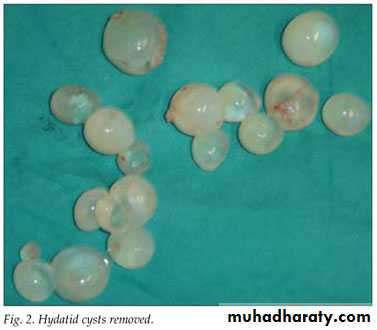
It is the larval stage of E. granulosus composed of single cavityThe majority of human H. cysts are unilocular type .
It may reach 15 cm or more in diameter after 10 to 20 Years.17
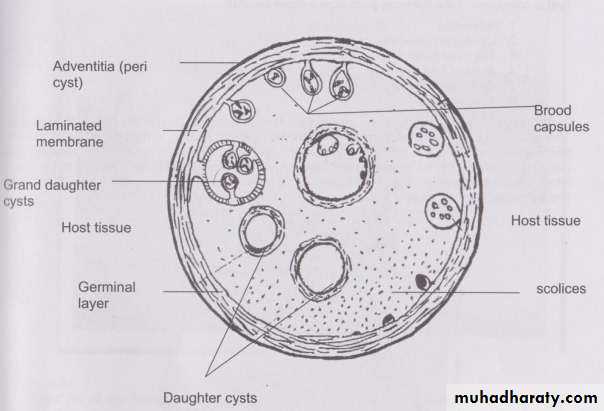
Morphology:
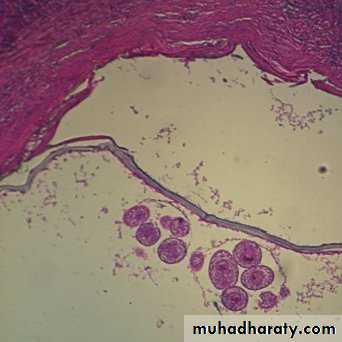
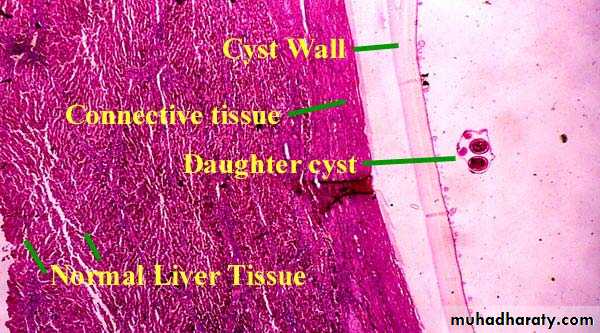
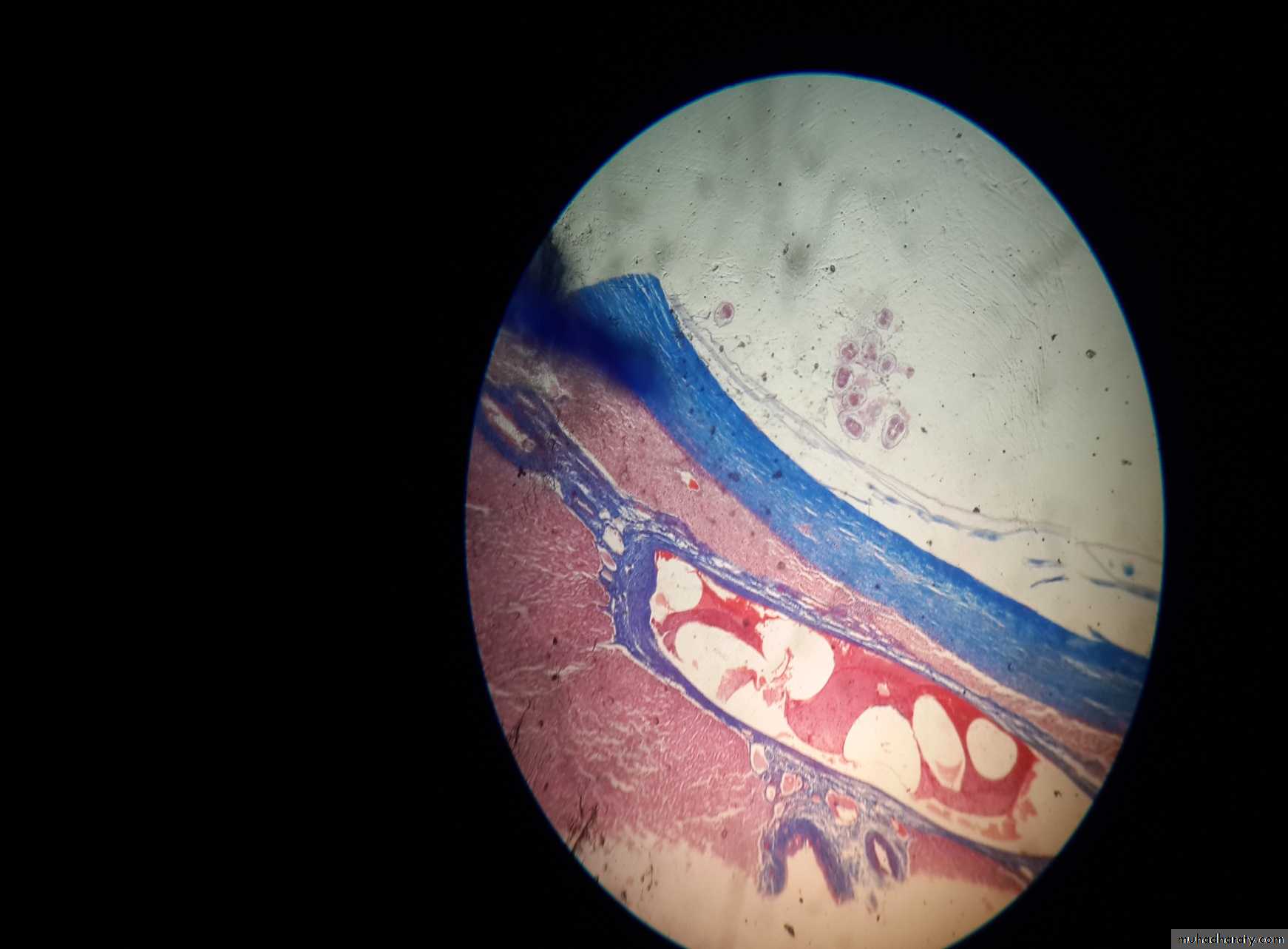
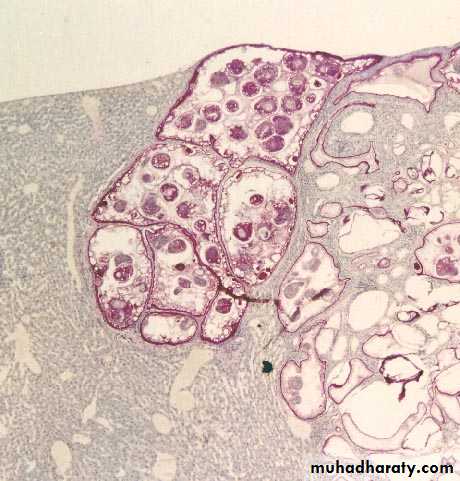
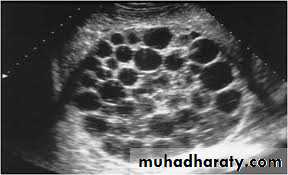
Unilocular hydatid cyst consist of three layers with central fluid contain protoscolicesThe three layers are :
1- Inner germinal layer2- non-nucleated laminated layer
3- Outer (fibrous layer)
18
1- Inner germinal layer :thin, delicate, one cell layer and nucleated.
19From inner germinal layer the following structures arise:
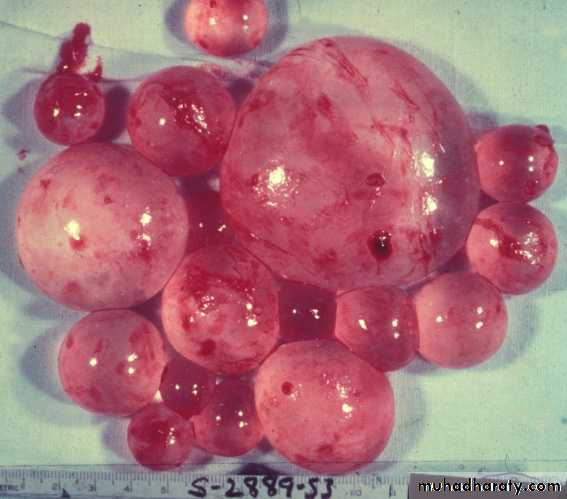
A- Brood Capsule: Develop from germinal layer and hold by short pedicle to the germinal layer. In the brood capsule multiple protoscolices develops.Hydatid cyst with protoscolices and brood capsule is known as fertile hydatid cyst. Sometimes hydatid cyst will not contain protoscolices, so it is known as sterile or acephalocyst.
Fertile hydatid cyst is more dangerous because:
• each protoscolex will develop to adult worm when ingested by definitive host
• if fertile hydatid cyst rupture it will lead to dissemination of the disease.
20
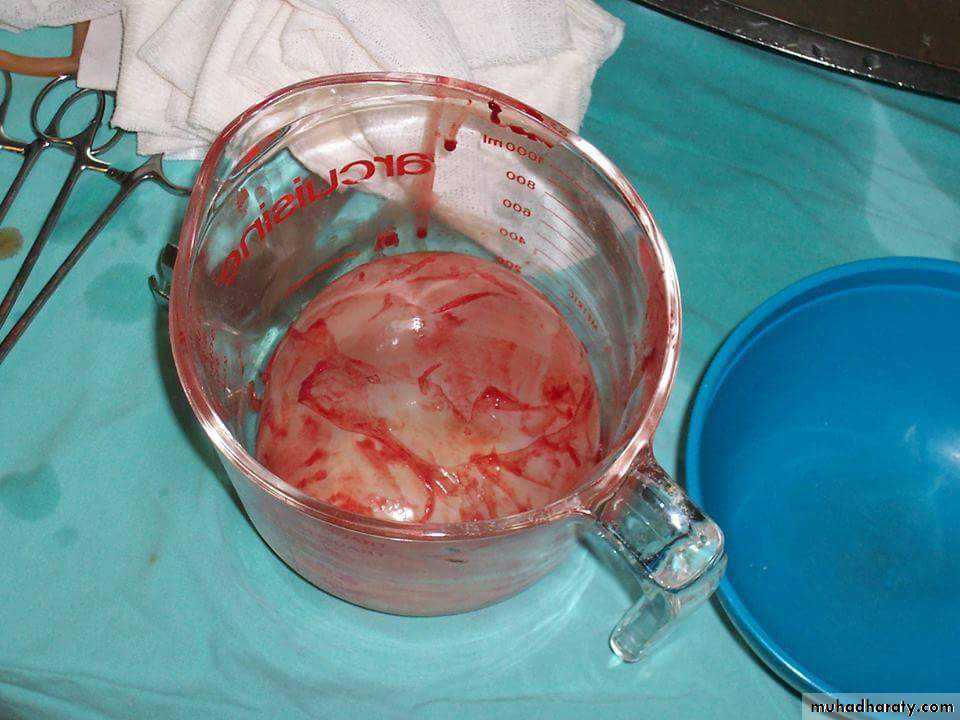
B- Hydatid Fluid: The cavity of unilocular hydatid cyst is filled with hydatid fluid, which is highly antigenic, bacteriologically sterile and
colorless.
21
C- Hydatid Sand: If the brood capsule detached from germinal layer, the brood capsule and protoscolices become free in hydatid fluid and they are called hydatid sand.
D- Endogenous Daughter Cyst: morphologically resemble mother cyst but it is smaller in size and free in hydatid fluid.
22
2- non-nucleated laminated layer.
3- Outer (fibrous layer):This layer formed as a result of defense mechanism of the host against the parasite.23
24
25
26
27
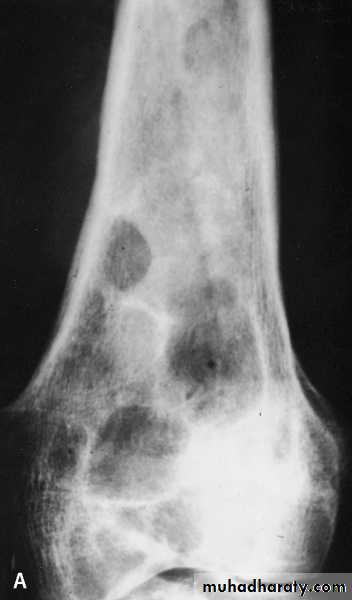
osseous H. cyst :
When the embryo of E. granulosus reaches bony tissues it will develop to osseous hydatid cyst.The larva grows as a protoplasmic stream that erodes the cancellous tissues and lead to multiple bone fractures.
It is occur in the ends of long bones and pelvic arch
sterile never produces brood capsule and protoscolices with little or no fluid and no fibrous capsule.
28
Multilocular or Alveolar Hydatid Cyst
It is the larval stage of E. multilocularis, it is composed of numerous small spaces or cavities, separated from each other by connective tissue. Each space filled with jelly-like matrix, mostly it is sterile but occasionally it may contain protoscolices. The germinal and laminated layers are poorly developed, it has no fibrous capsule.It is occurs usually in the liver and rarely in lung. Because of its fast growth, it is usually fatal.
29
Rupture of Hydatid Cyst:
Rupture of hydatid cyst may occur naturally, due to coughing, muscle strain or surgical procedures. Such patients may suffer from anaphylactic shock, eosinophilia and allergic reactions or even death.The escape cyst fluid with protoscolices has the capacity of spreading to other sites and forming a new cyst (secondary hydatidosis).
Rupture of the cyst are most important than the mass effect of the cyst, except in the brain where the mass effect has severe consequences.
30
Epidemiology
Worldwide in its distribution .
Rural infection more than urban aeas because it is a sheep raising areas .
31Transmission
• Ingestion of uncooked vegetables and fruits(lettuce &parsley) & drinking water contaminated with eggs.• handling soil or animal hair that containing eggs.
32
Pathogenesis and Symptomatology
• 1. Disease called Hydatid Cyst, Hydatid disease, Hydatosis.2. No symptoms until the cyst gets large or ruptures.
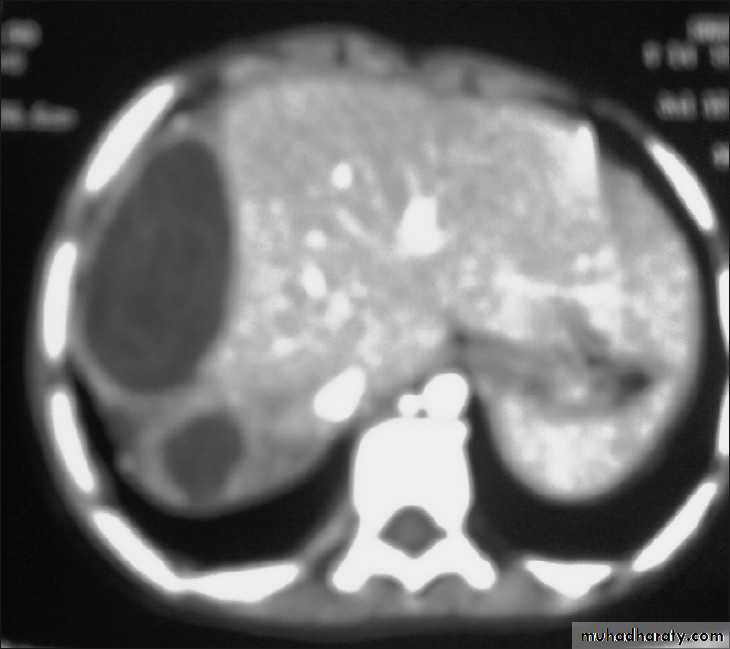
333. Hepatic Hydatid cyst
• Liver affected in about 65 % of patients• Approximately 70% right lobe is affected.
• Usually no symptoms until the cyst reach 10 cm in diameter : hepatomegaly, nausea, vomiting
34
35
4. Pulmonary H.cyst
Lung affected in about 23% .Rupture of pulmonary H.cyst into bronchules results in :coughing, shortness of breath, secondary bacterial infection.
36
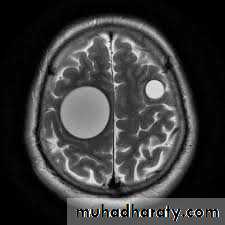
5. Hydatid cyst of brain
Brain occasionally affected, produce mass effect.Other organs, Bones, muscle, Kidney, heart and pancrease.
37
Diagnosis
• Clinical manifestations.• 2. Imaging techniques:
• X-ray picture: useful to detect the calcified cyst.
• Ultrasound scan.
• MRI & CT scan.
•
38
• 3. Serology tests :
Indirect immunofluescence.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
39
Treatment
1. Surgical operation to remove the cyst is the only
option for the treatment.
2. Mebendazol or albendazol
given to reduce the risk of secondary hydatidosis,
it also given for 60 days duration on 200 mg dose
to reduce the size of the cyst. Before the surgical
interference.
40
Prevention &control
1. Avoiding close contact with dogs.
2. Careful washing of the vegetable with running water.
3. Preventing home-slaughter of sheep will prevent dogs from consuming infected viscera.
41
Taenia saginata & Taenia solium
Lec:2د.إكرام الحسو
42
Taenia saginata Beef tapeworm
Taenia solium Pork tapewormDisease : Taeniasis.
43
Morphology of adult
1. They are flat , hermaphroditic worms ,
live in small intestine of man.
2. Adult worms consist of a head , neck and
segmented body (proglottids) may reach
thousands.
44
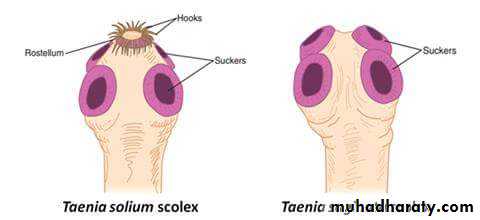
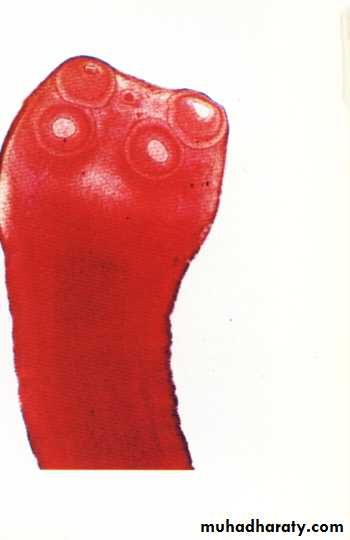
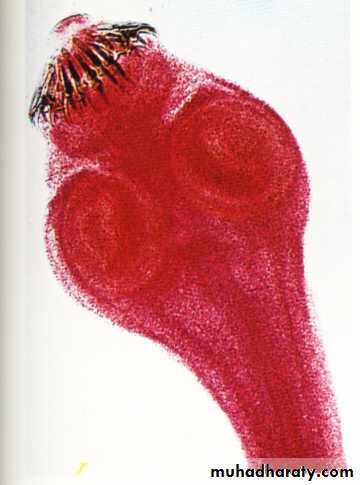
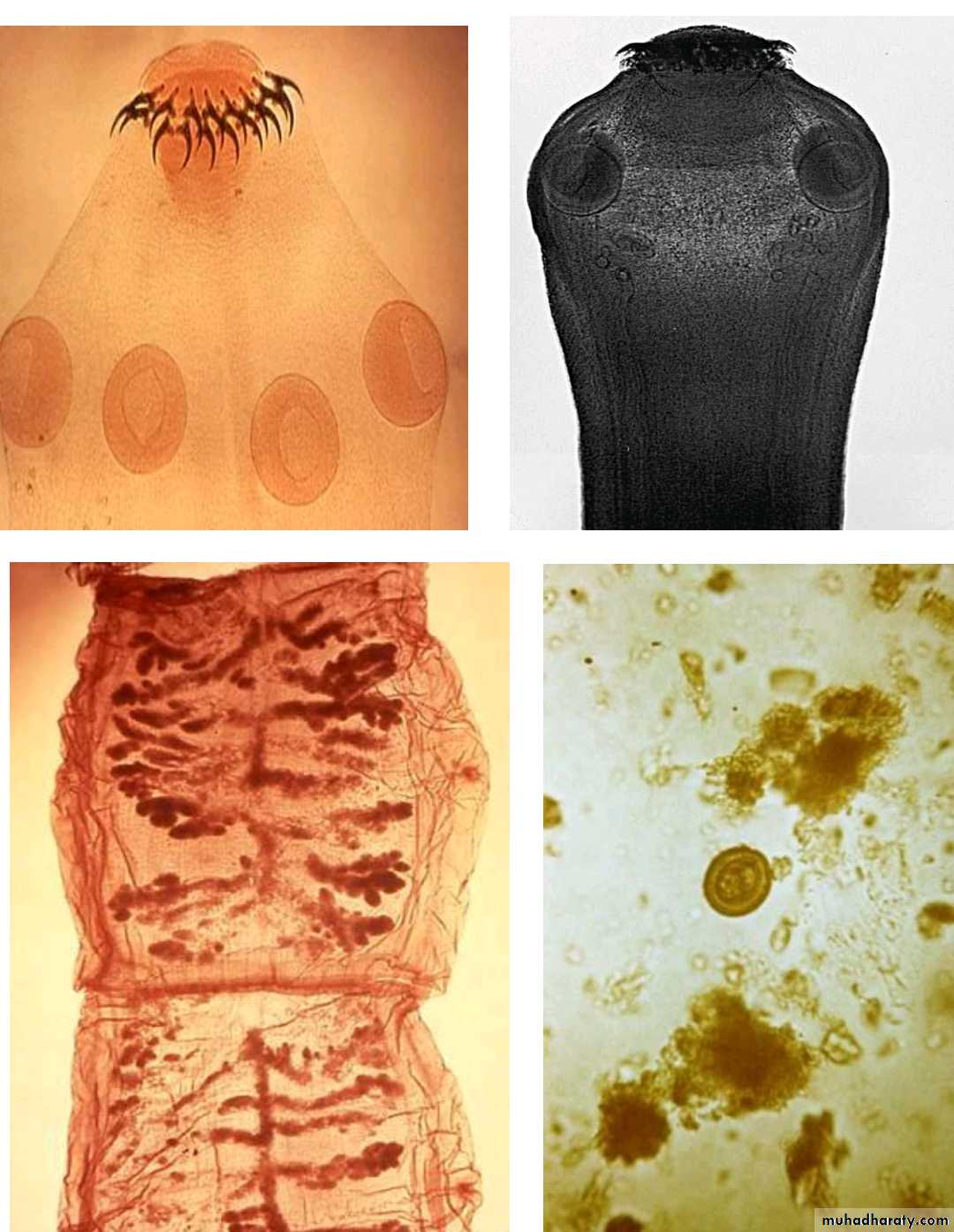
3. The head (scolex) contain suckers (T. saginata), or suckers & hooks (T. solium).
45
Scolex of T. saginata
Scolex of T. Solium46
4. Mature segment contain both male & female
sexual organs.5. Gravid segment contain only uterus full with
eggs which usually passed with eggs out withfeces as diagnostic stages.
47
48
6. The length of adult worms is usually 4-10 m for T. saginata and 2-7 meter for T. solium.
7 . T. saginata usually have 1,000 to 2,000 segments,
while T. solium have an average of 1,000 segments.49
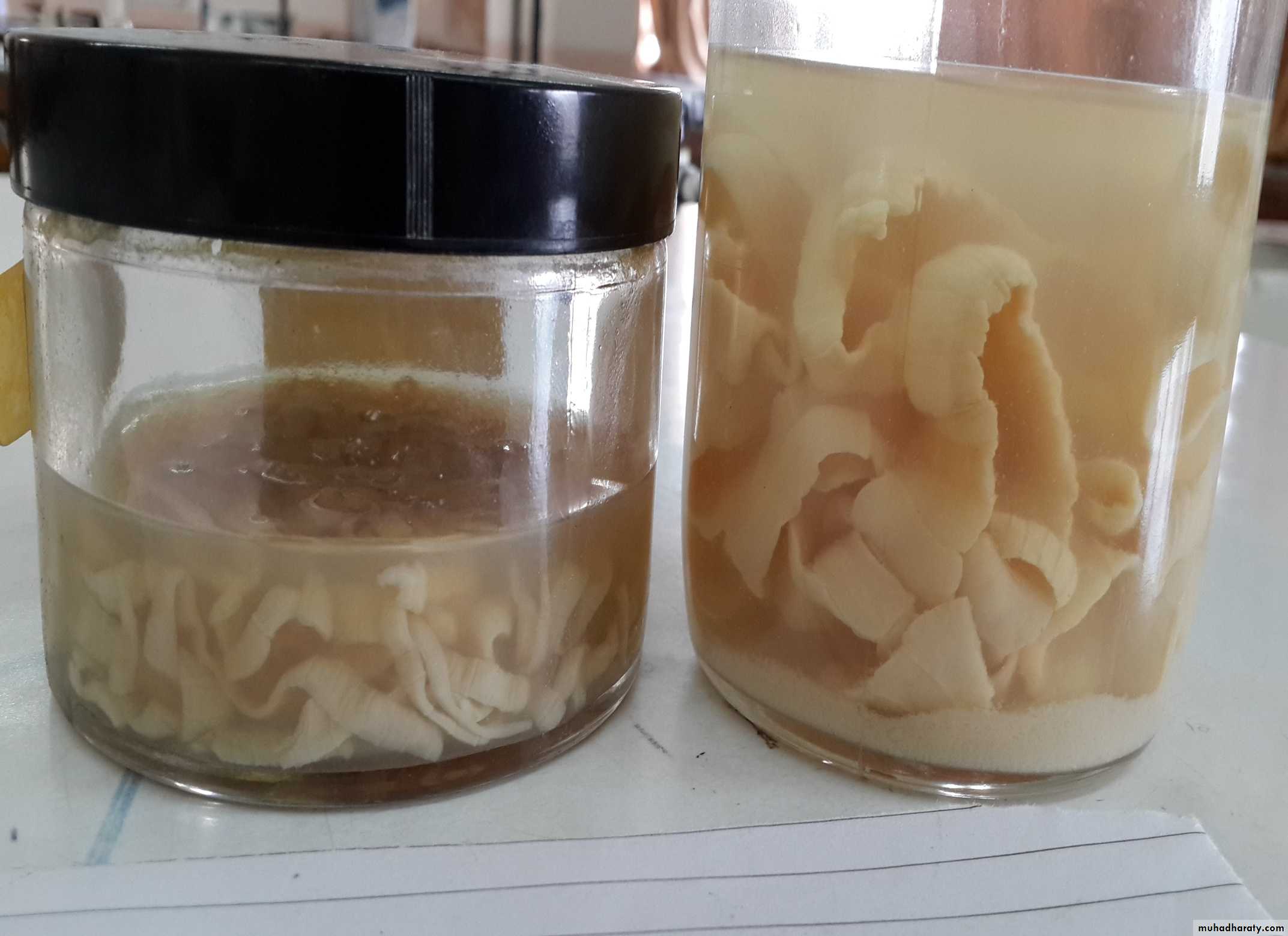
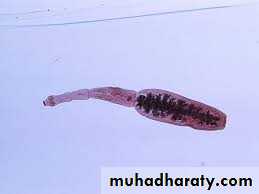
Adult worm of Taenia saginata
50Adult worm of Taenia solium
51
52
53
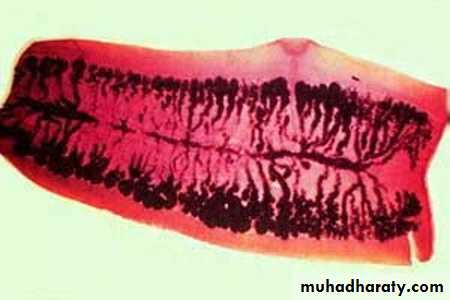
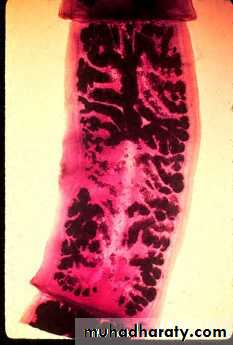
Gravid segment of T.Saginata
longer than wide consist of median uterus with 15-30 lateral uterine branches with unilateral genital pore .Gravid segment of T.Solium
7 – 13 lateral uterine branches.54
Gravid segment of T.Saginata
Gravid segment ofT.Solium
55
56
57
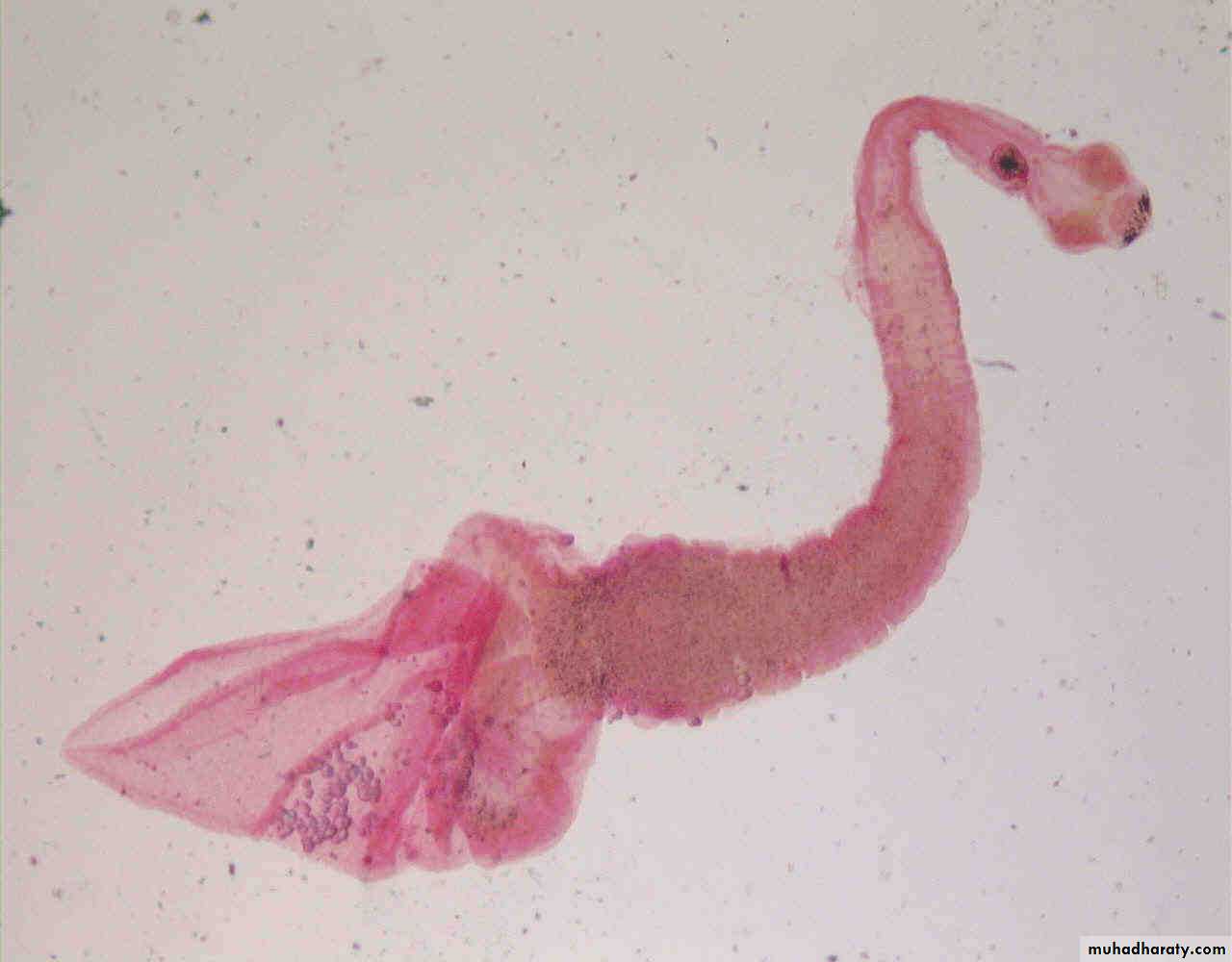
Cysticercoids larva
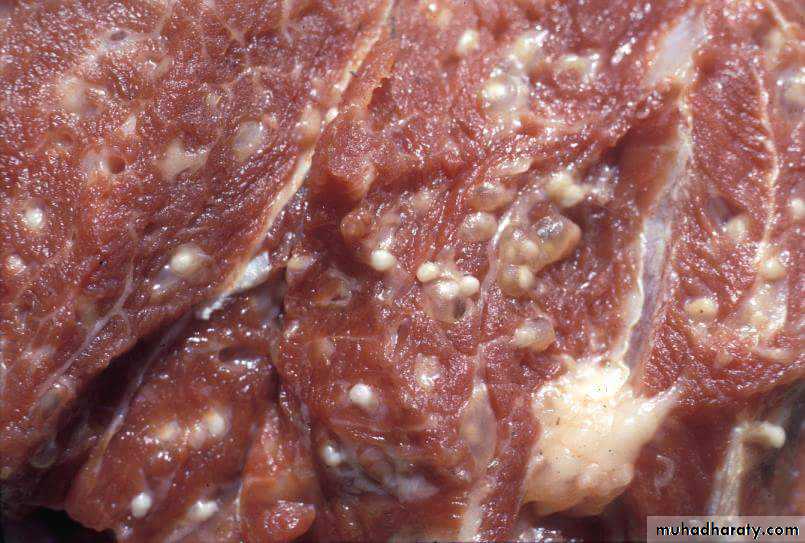
It is bladder like cyst called bladder worm with invagenated or evagenated scolex .They are infective stages to human and they are two type :• C. Bovis: scolex without hooks in the muscles of cattles (T.saginata).
• C.cellulosae : scolex with hooks in muscles of pigs (T.solium).58
Cysticercus bovis
Cysticercus cellulosae59
Life cycle of T. saginata and Taenia solium
601.Humans are the only definitive hosts for T.saginata
and T. solium. Eggs or gravid proglottids are passedwith feces .
2.The intermediate host ( Cattle for T. saginata and
pigs for T. solium) .3.The intermediate hosts become infected by ingesting vegetation contaminated with eggs or gravid proglottids
61
4. In the animal's intestine, the oncospheres hatch,
invade the intestinal wall, and migrate to thestriated muscles, where they develop into
cysticercus larva.
5. Humans become infected by ingesting raw or
undercooked infected meat with cysticercus larva.62
.
6. In the human intestine, the cysticercus develops over 2 months into an adult tapeworm, which can survive for years.
7. The adult tapeworms attach to the small intestine by their scolex .
63
Transmission
Human infection with Taenia spp occur byeating under-cooked beef or pork containing
cysticercoids larva.
64
Epidemiology
T. saginata: Cosmopolitan in beef eating
countries, found in Europe, Asia & America.
T. solium: Cosmopolitan in pork eating countries,
found in Latin America, Africa& central Asia.65
Clinical Features:
1. mild abdominal symptoms.
2.because of the large size of the worm, it may be responsible for acute intestinal obstruction and anemia
3.Occsionally appendicitis can result from individual segment which may be lodged in the appendicial lumen
Taeniasis caused by T. solium : there is risk of development of cysticercosis.
66
Laboratory Diagnosis
Microscopic identification of scolex and segments in feces are diagnostic for taeniasis.The gravid segments can differtiate between T.saginata and T. solium but the eggs are morphologically identical, and indistinguishable between taenia species.
67
Treatment
Niclosamide is the drug of choice four tablets (2 mg) in a single dose after a light meal .In case of infection with T.Solium antivomiting drugs should be given one hour before treatment to prevent autoinfection with eggs, and 2 hours after treatment, saline purgative should be given to flush out of the worm to prevent cysticercosis .
68
Prevention
1. Treatment of infected patients .
2. Personal hygiene and enviromental sanitation are
important .
3. Inspection of pork & beef meat for cysticercus larva .
4. Cooking very well the meat before eating. 45-50 C for at least half hour is enough to kill the larvae.
5. Freezing at minus 2-10 C for 4 days enough to kill the larvae .
69
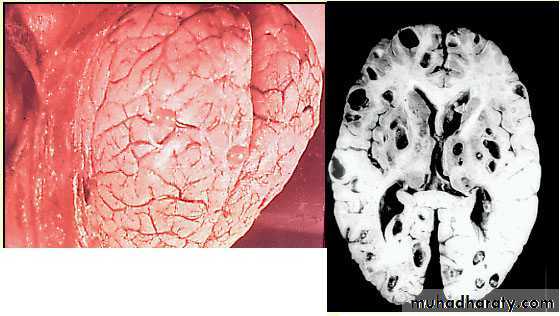
Cysticercosis
The most frequent and sever disease caused by accidental ingestion of eggs or by autoinfection may occurs in T. solium by regurgitation of gravid proglottid into the stomach & releas the eggs which pass to small intestine where embryo become free after hatching process , then penetrate the wall of the small intestine & carried via blood to different tissue of the body .
70
The most frequent locations are subcutaneous and intramuscular tissues , then eye and brain . they also may occur in the liver , lung , heart and abdominal cavity .
71
72
The most serious type of cysticercosis is neurocysticercosis which can lead to epilepsy , lesion in the brain , blindness and tumor like growths and be can be fatal.
73
74
Diagnosis of human cysticercosis :
1-Biopsy.:confirming the presence of hooks in the scolex of C. cellulosae by histopathological examination ofbiopsy materials
2-Serology(ELISA, IFAT).
3-MRI or CT scan of the brain.
75
Treatment of cysticercosis
Usually asymptometicmanagement for patients with neurocysticercosis depend on the number and location of cysts, in this case surgical treatment indicated.
Praziquantil(5–10 mg/kg, single-administration) .
76