HISTOLOGY OF SKIN (Derma)(Integument)(Cutaneous layer)
Skin
Largest Single Organ( 15% to 20% of body weight)Surface Area of (1.5 to 2 m²)
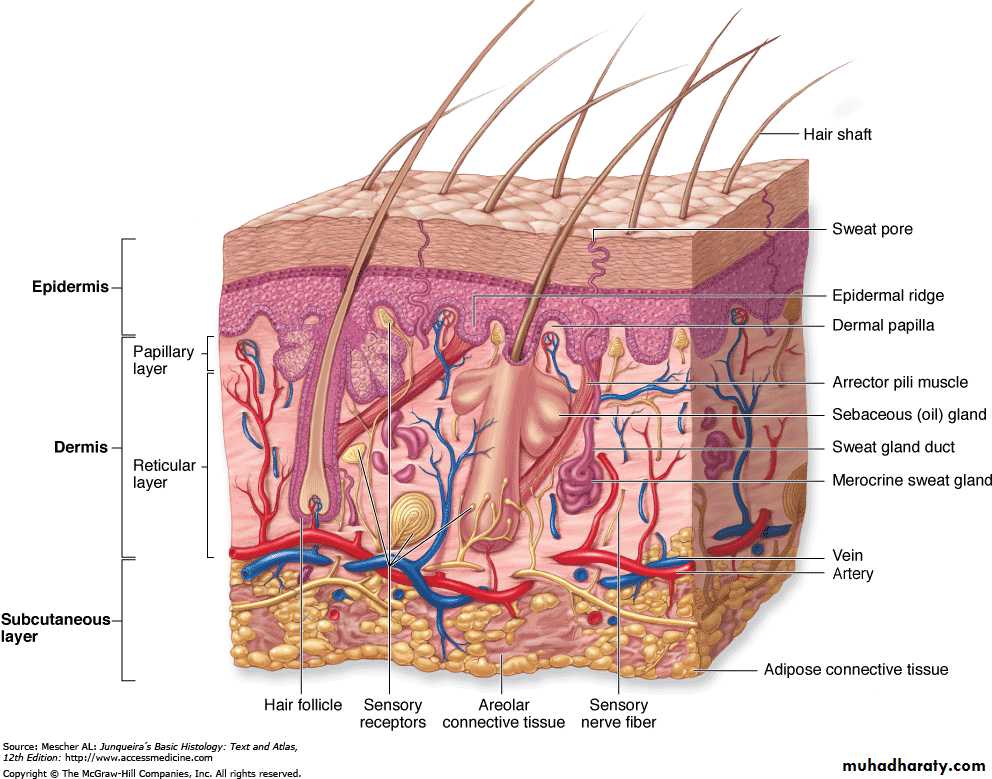
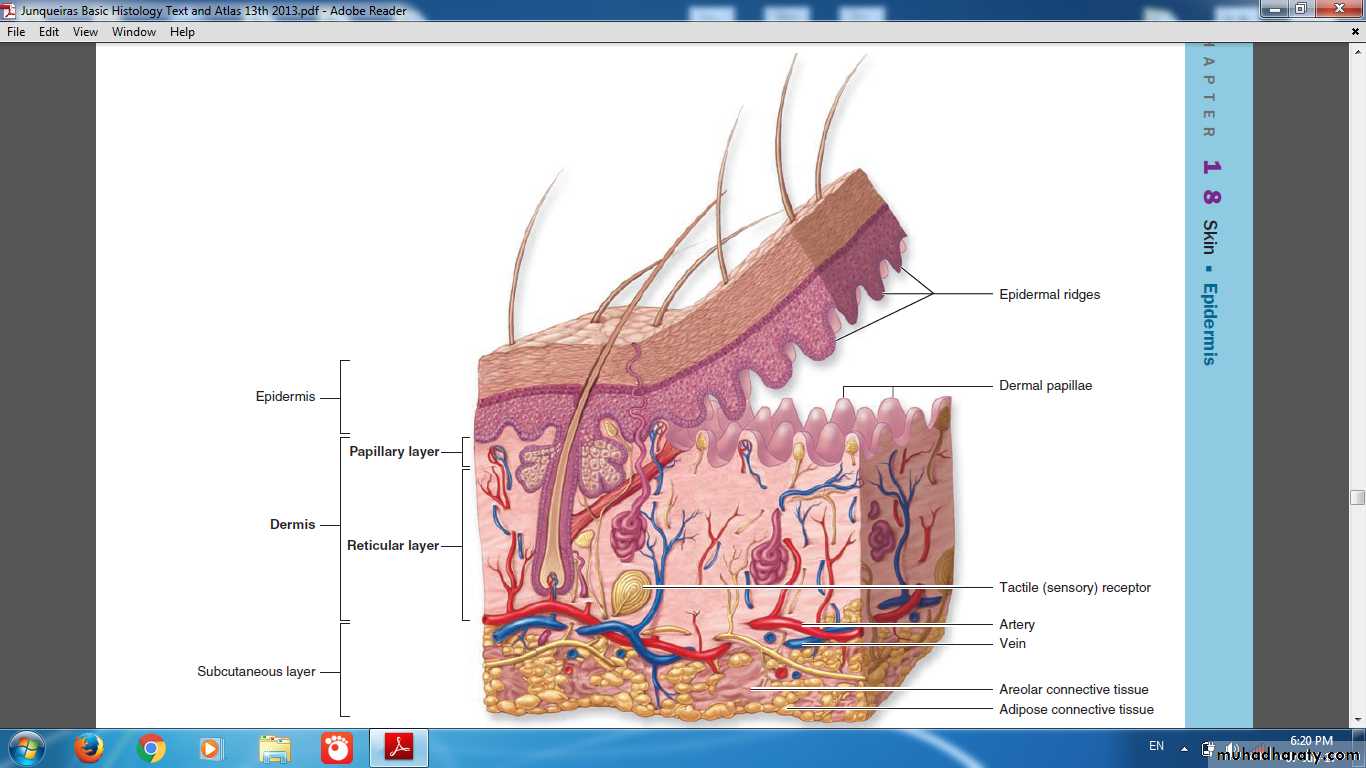
Composed of (Epidermis & Dermis)
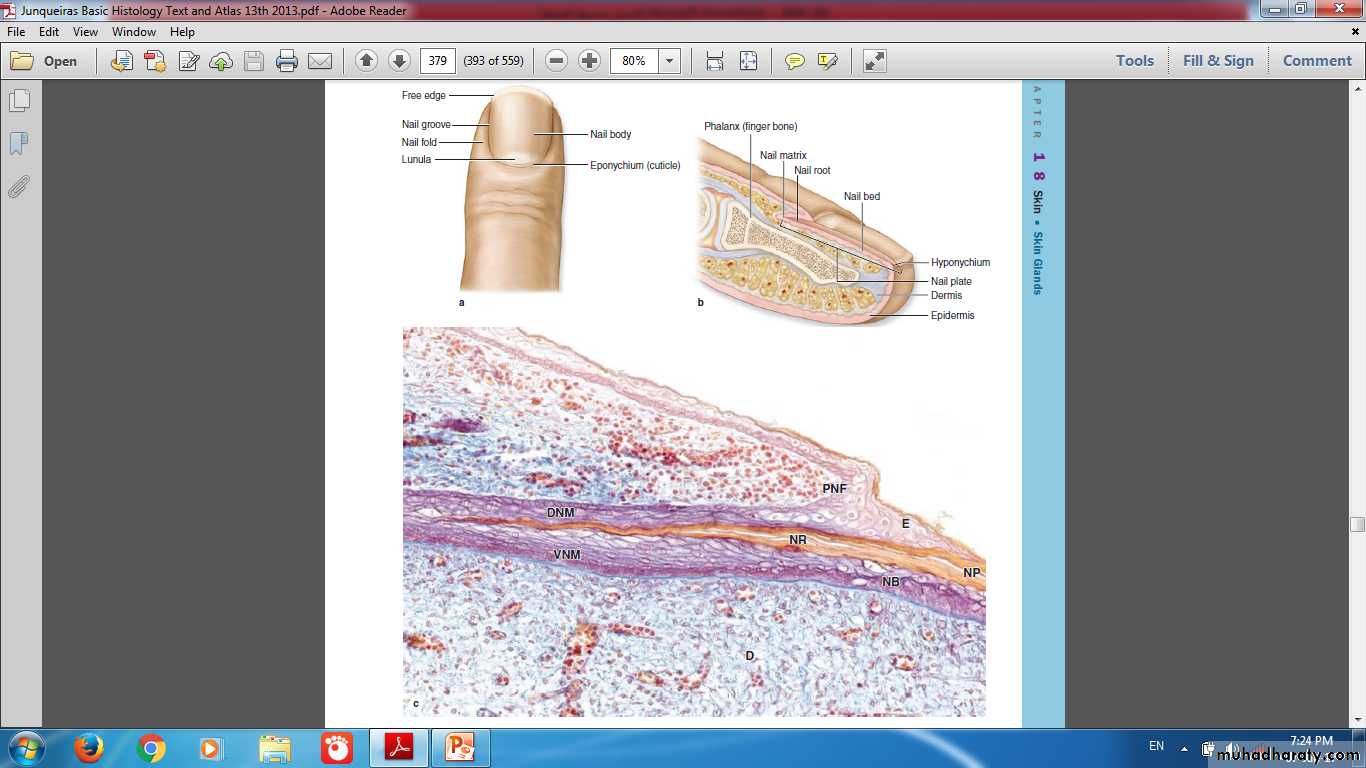
Skin Appendages
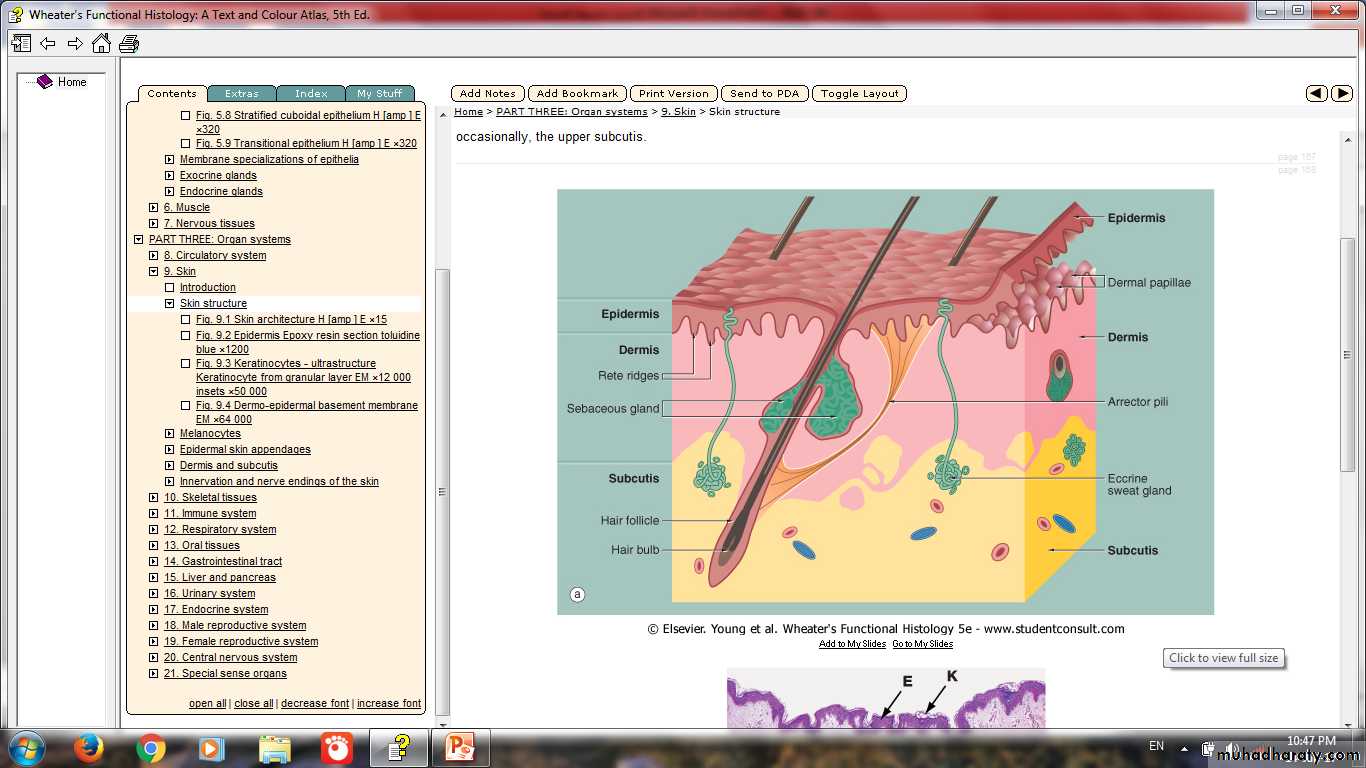
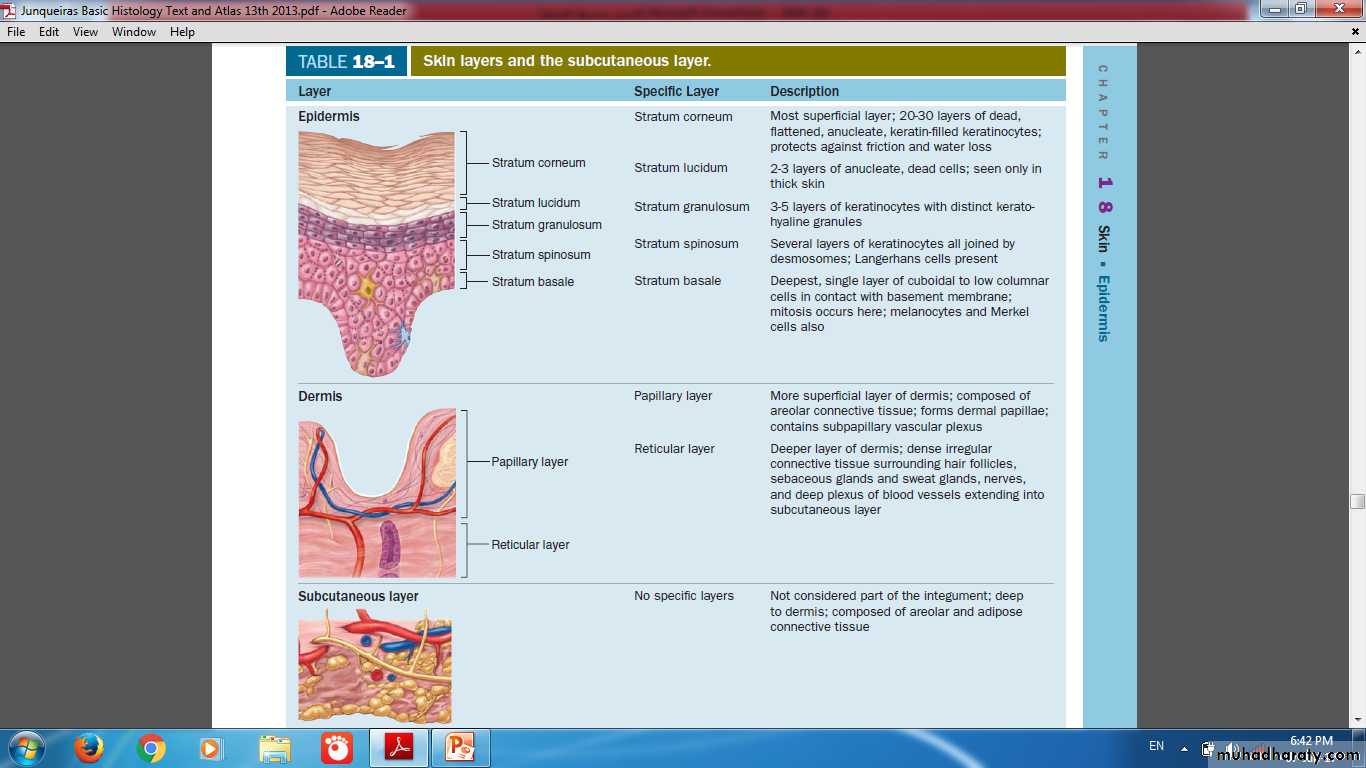
Layers of Skin
Appendages of SkinHairNail Sweat glandsSebaceous glands
Functions of skin
ProtectionSensation
Thermoregulation
Metabolic
Cosmetic
Skin is a permeability barrier against excessive loss or uptake of water
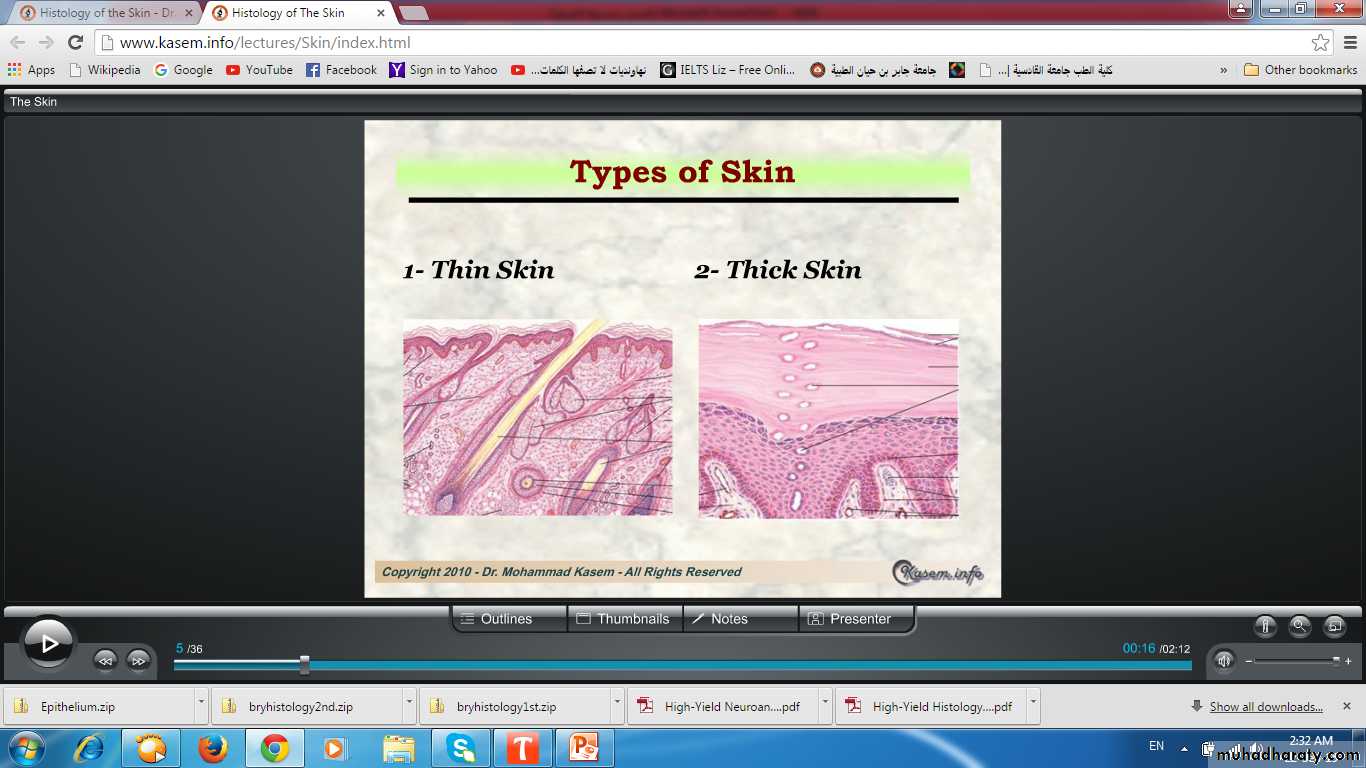
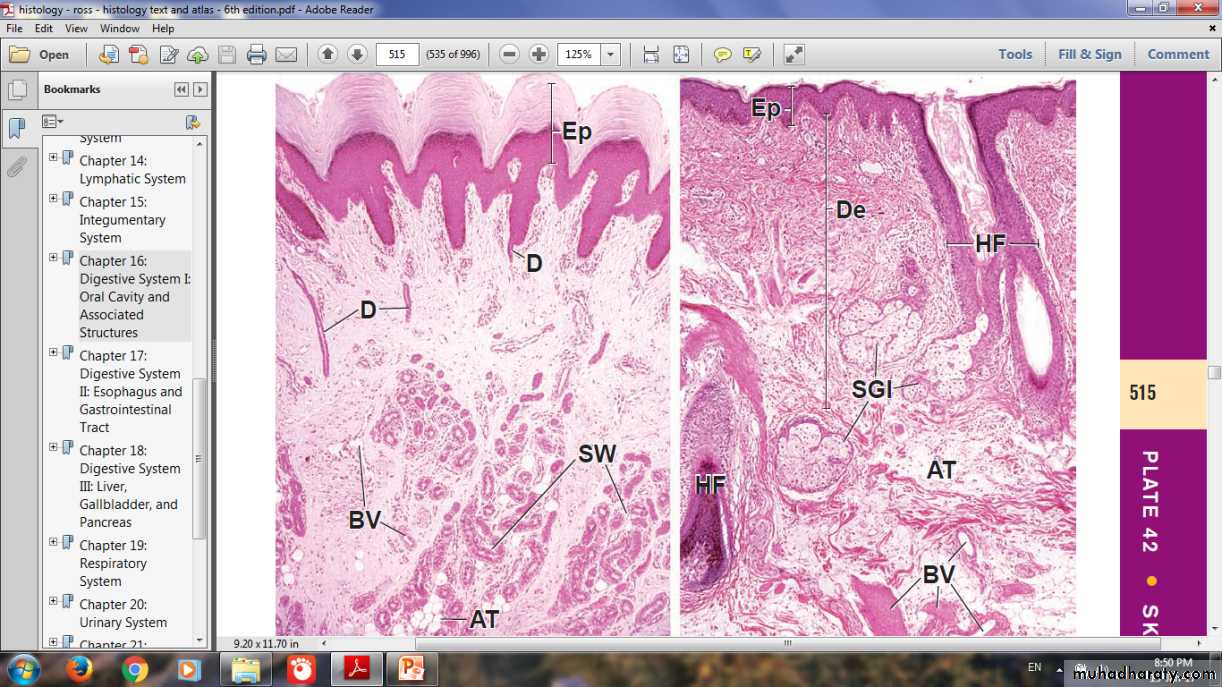
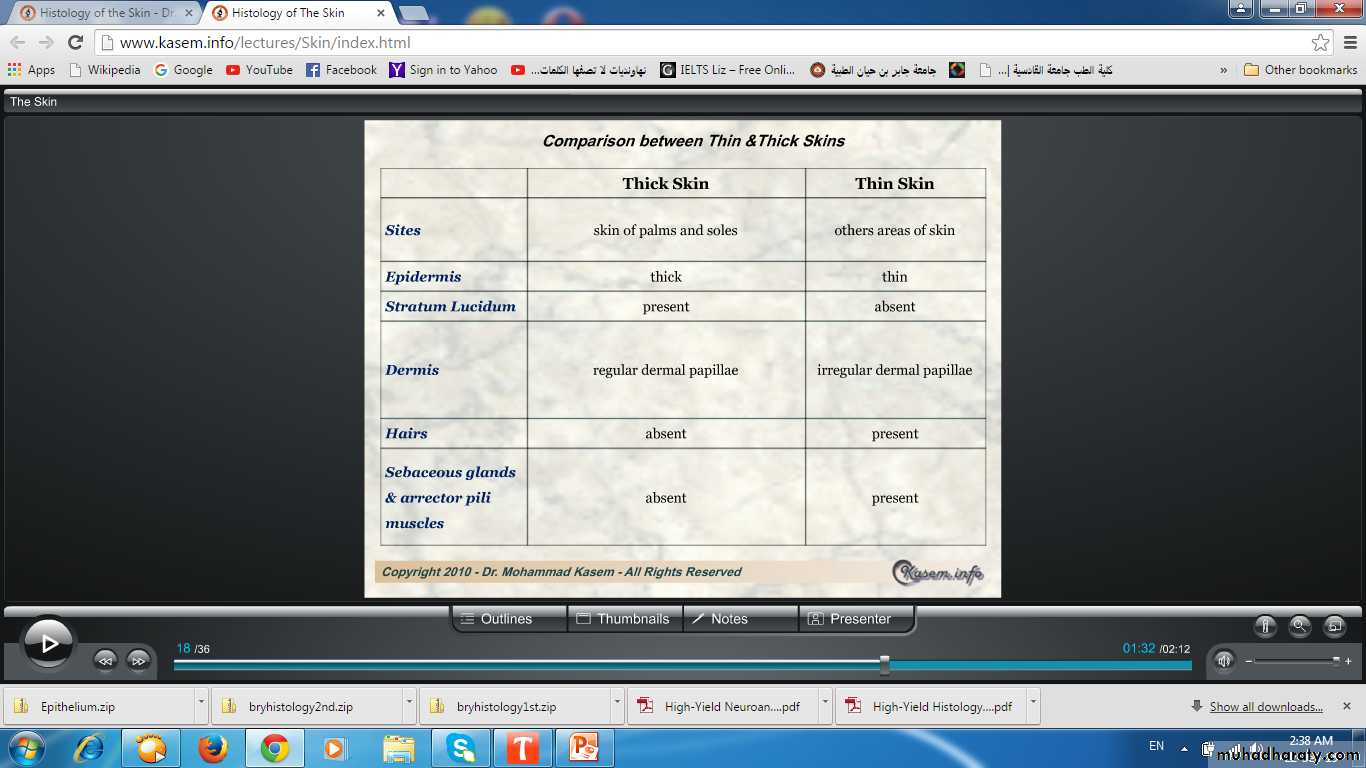
Types of skinAccording to thickness of epidermis
Thick & Thin Skin
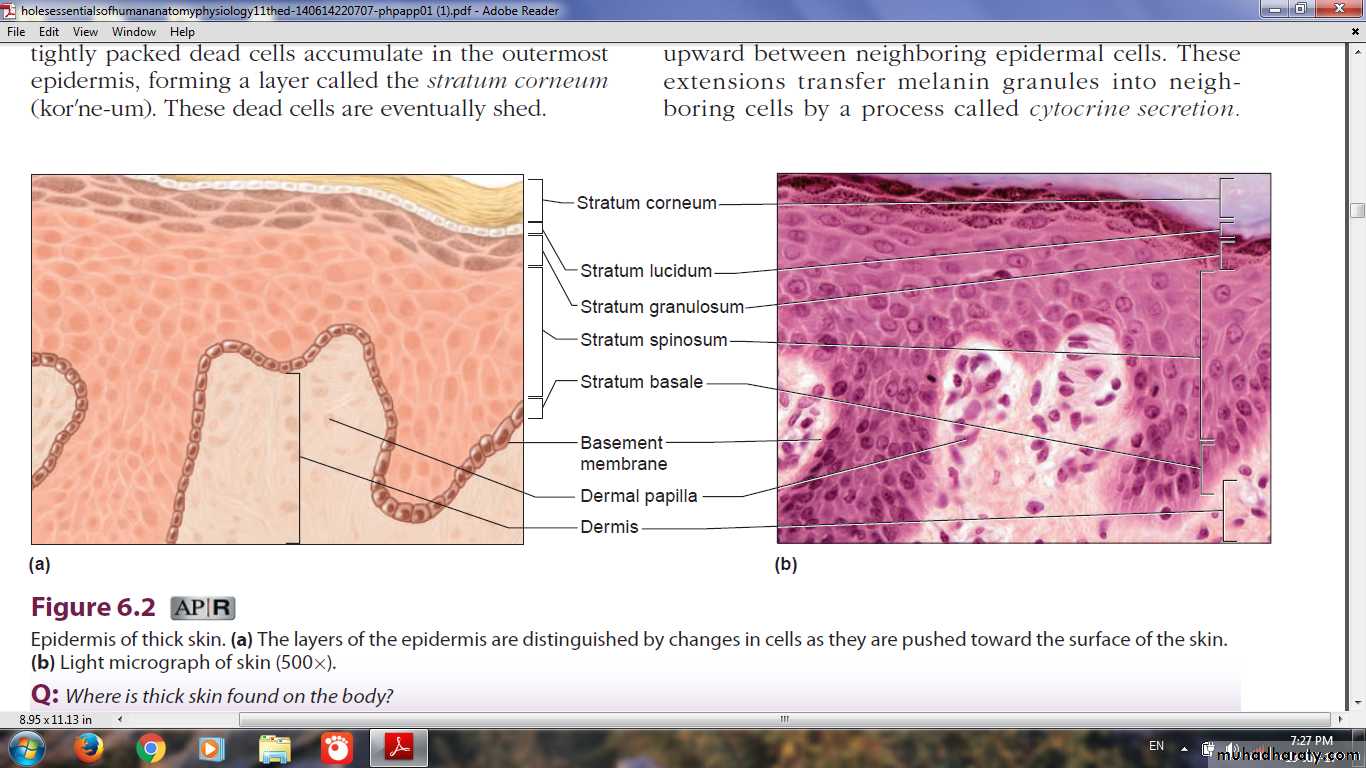
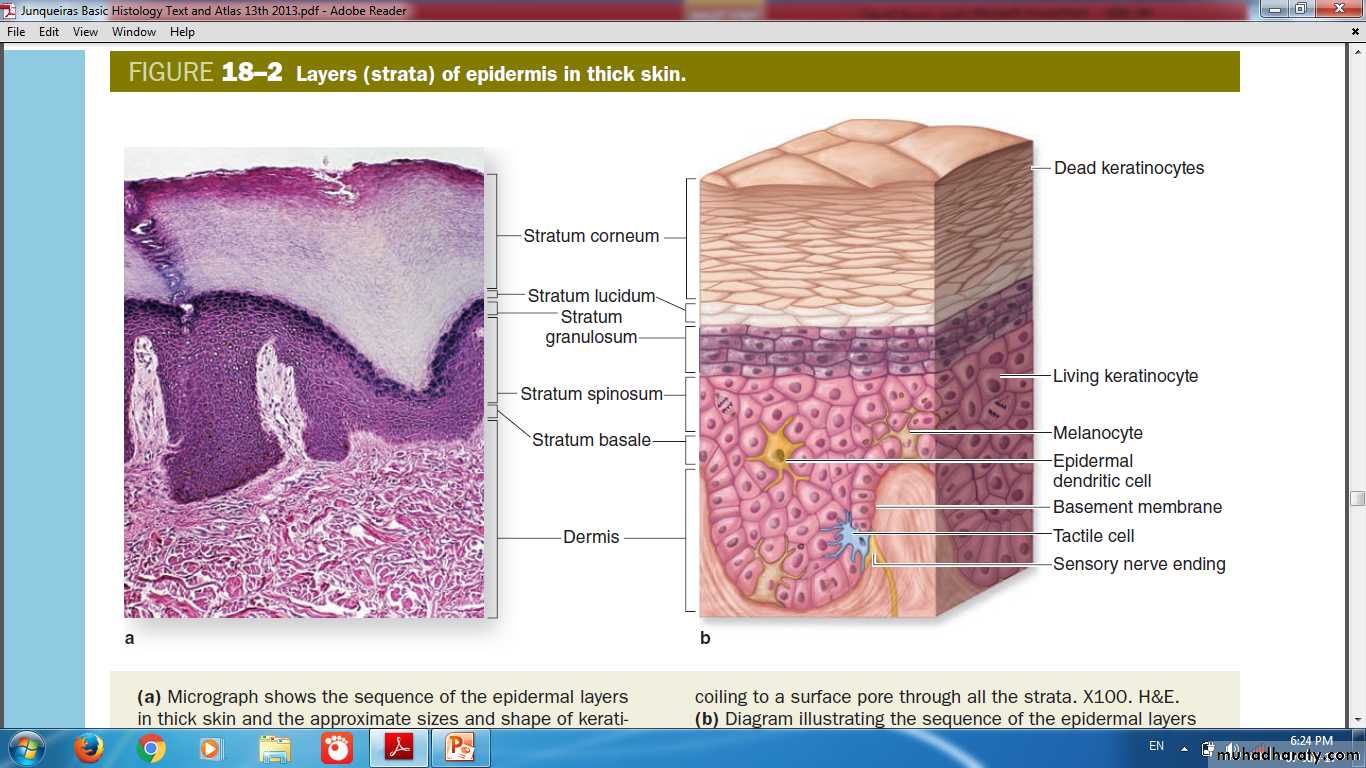
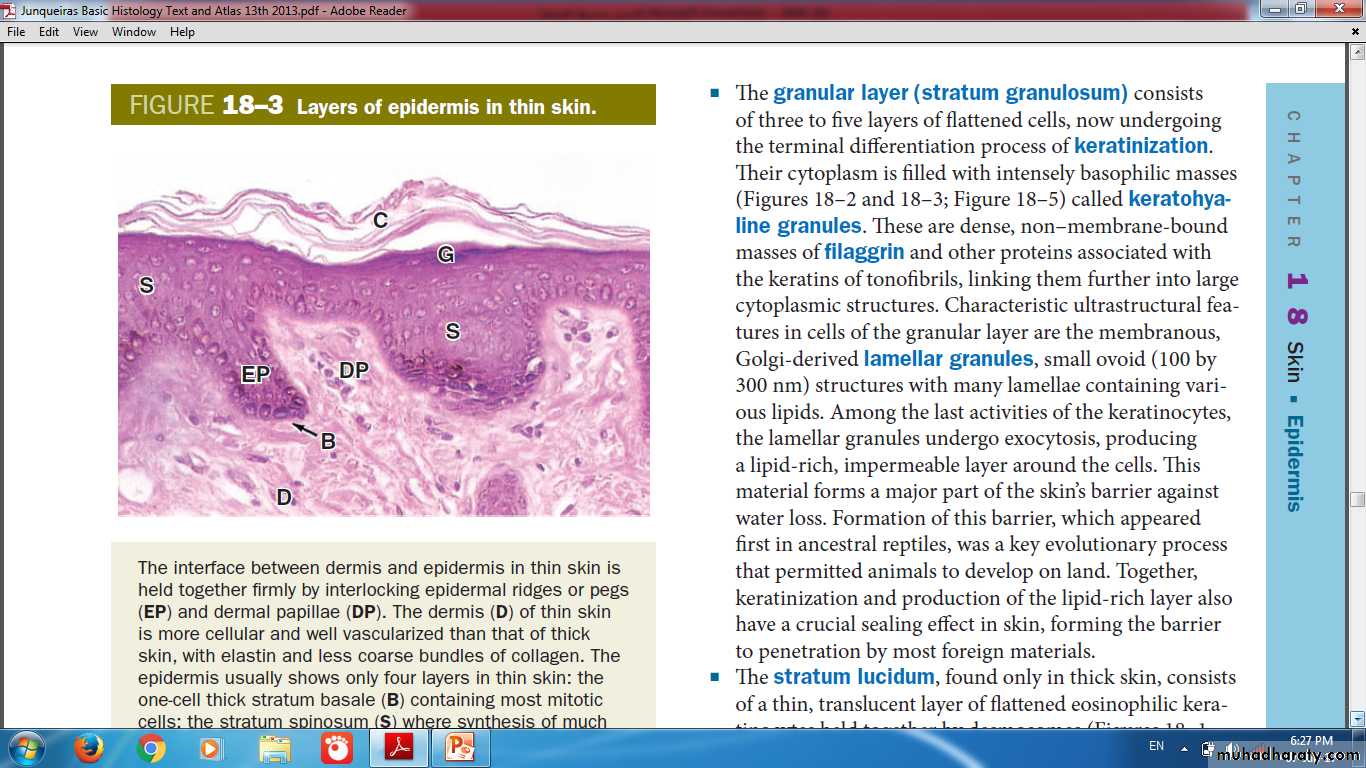
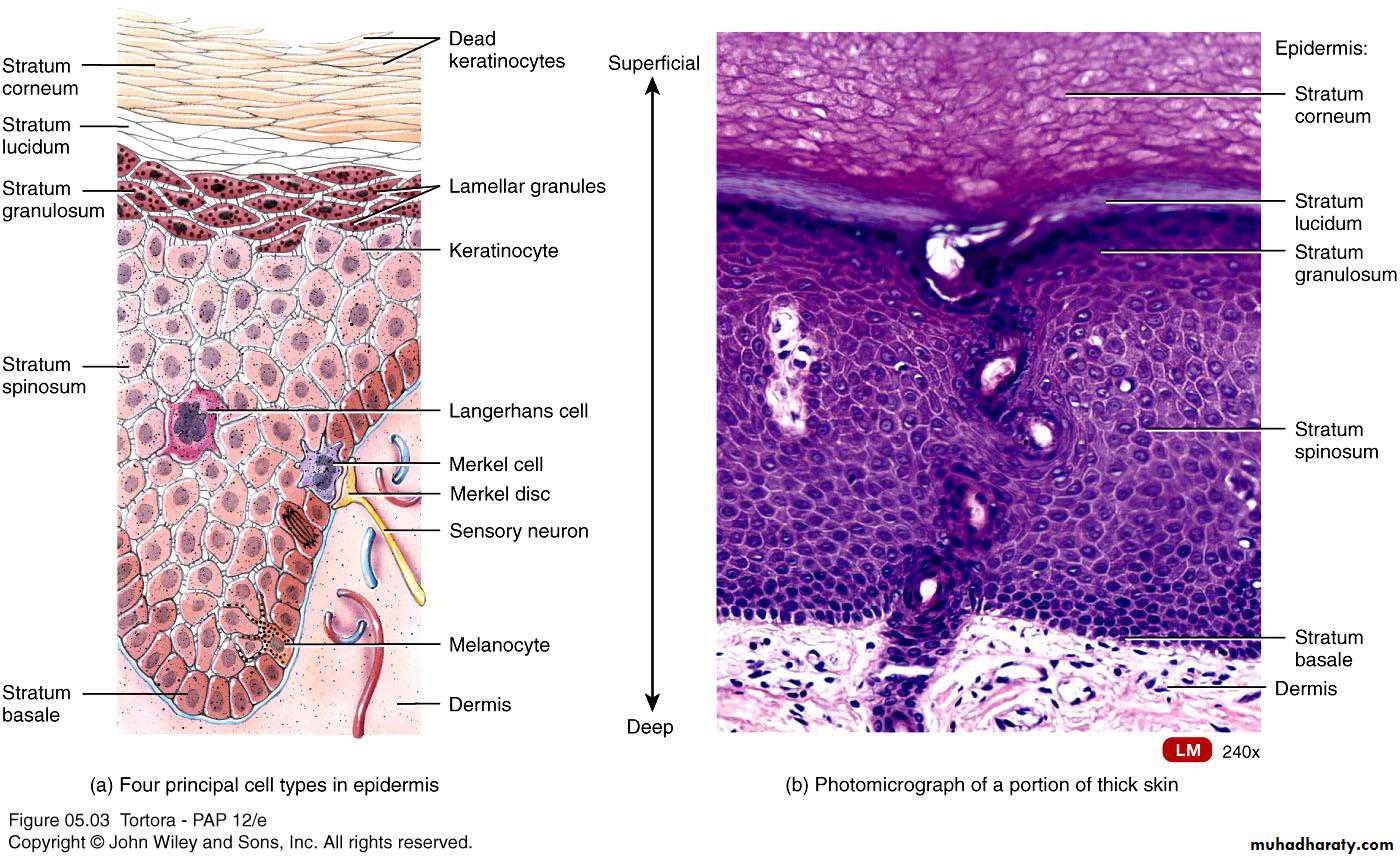
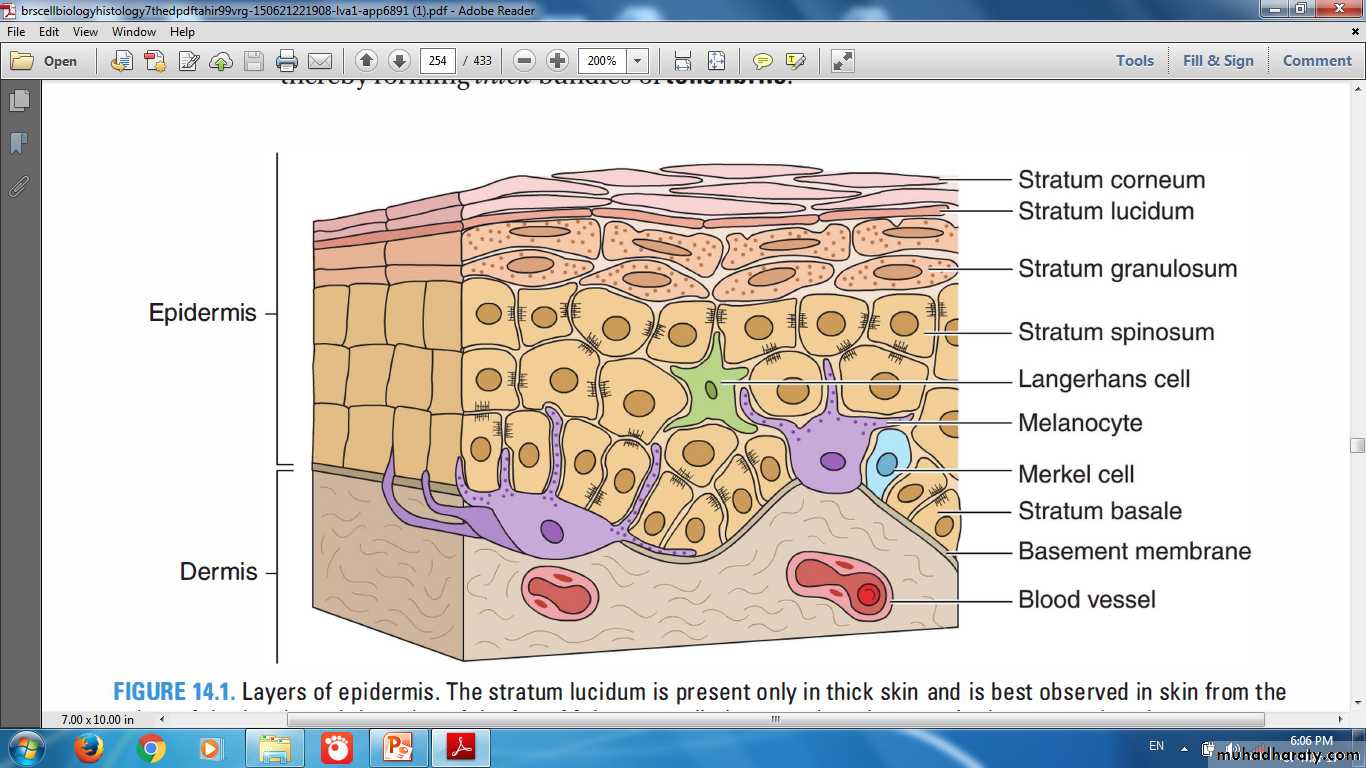
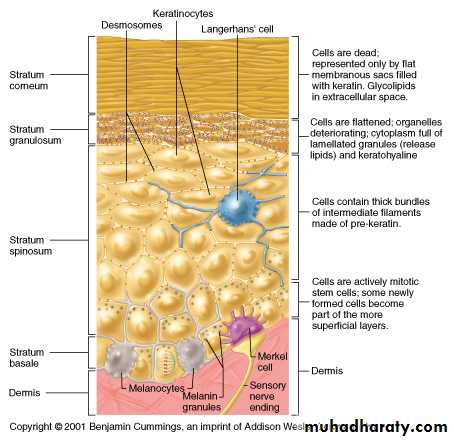
Layers of Epidermis
Stratum BasaleStratum Spinosum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Corneum
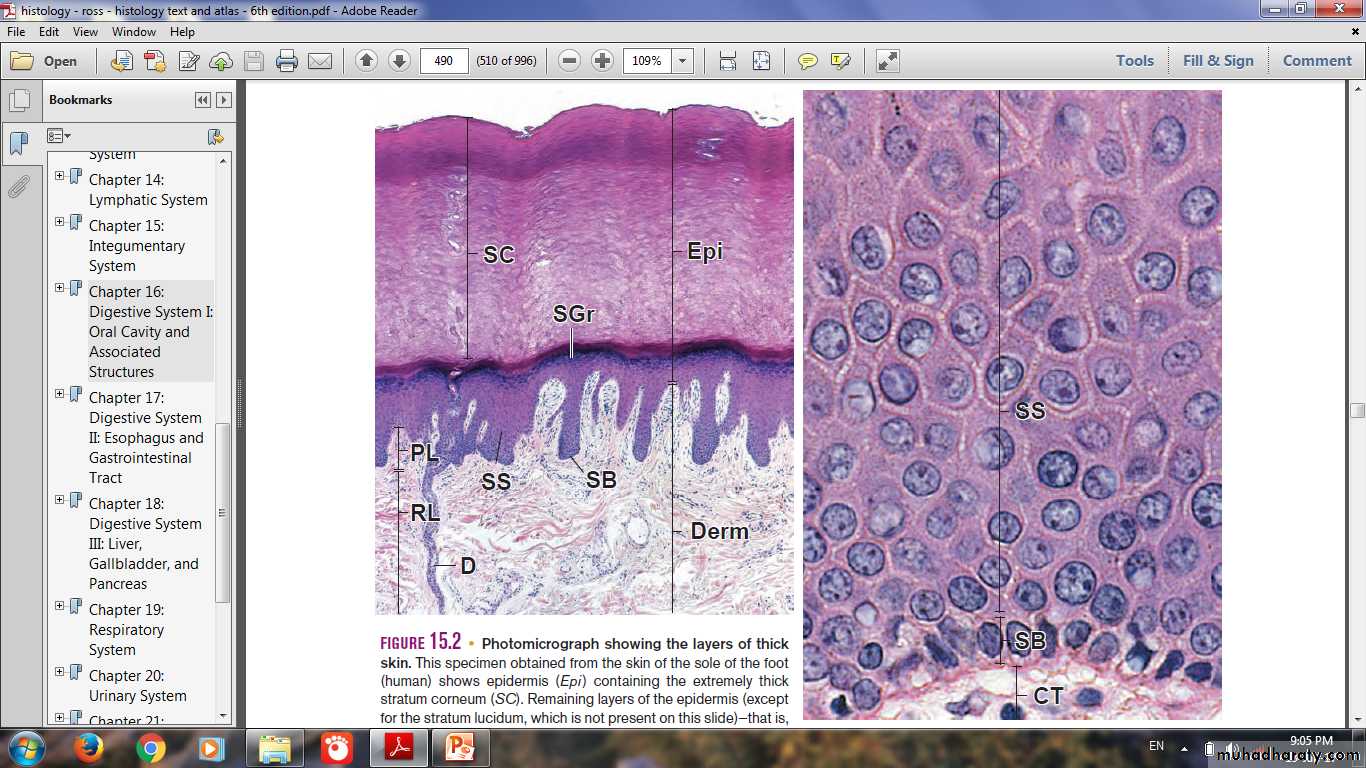
Layers (strata) of Epidermis in (Thick Skin)
Layers of Epidermis in (Thin Skin)
Basale
SpinosummGranulosum
Corneum
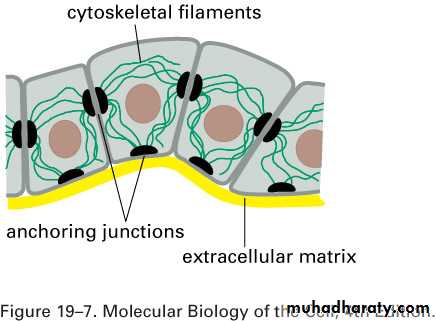
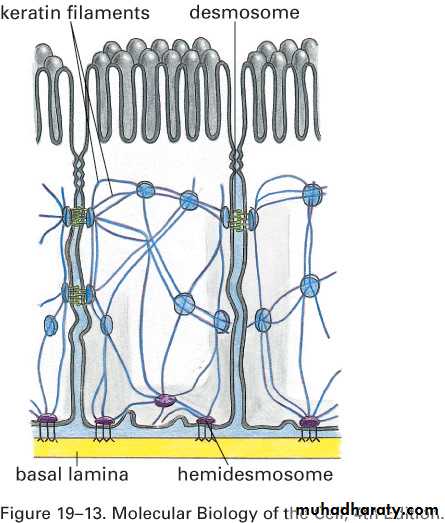
Cytoskeleton in Stratum basale
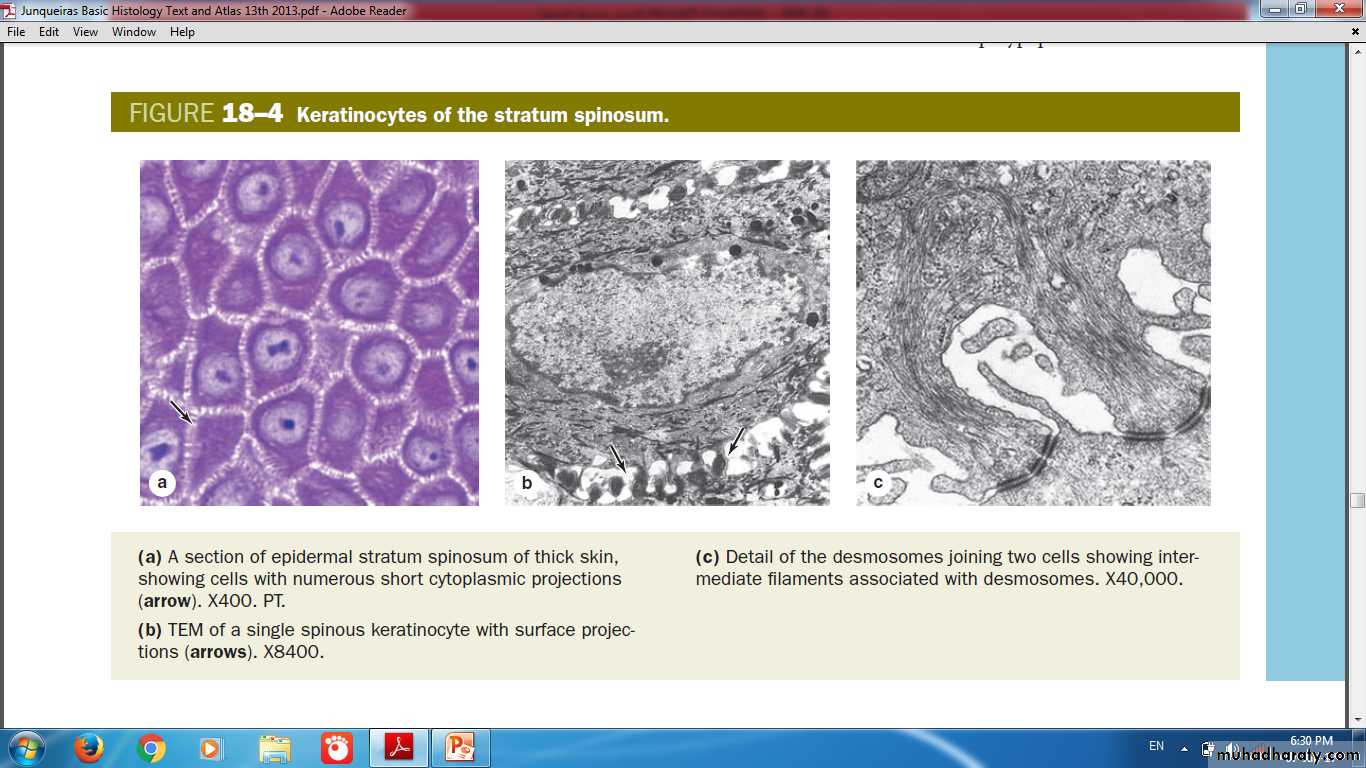
• keratins, cytoskeletal intermediate filaments• Desmosomes
• Hemidesmosomes
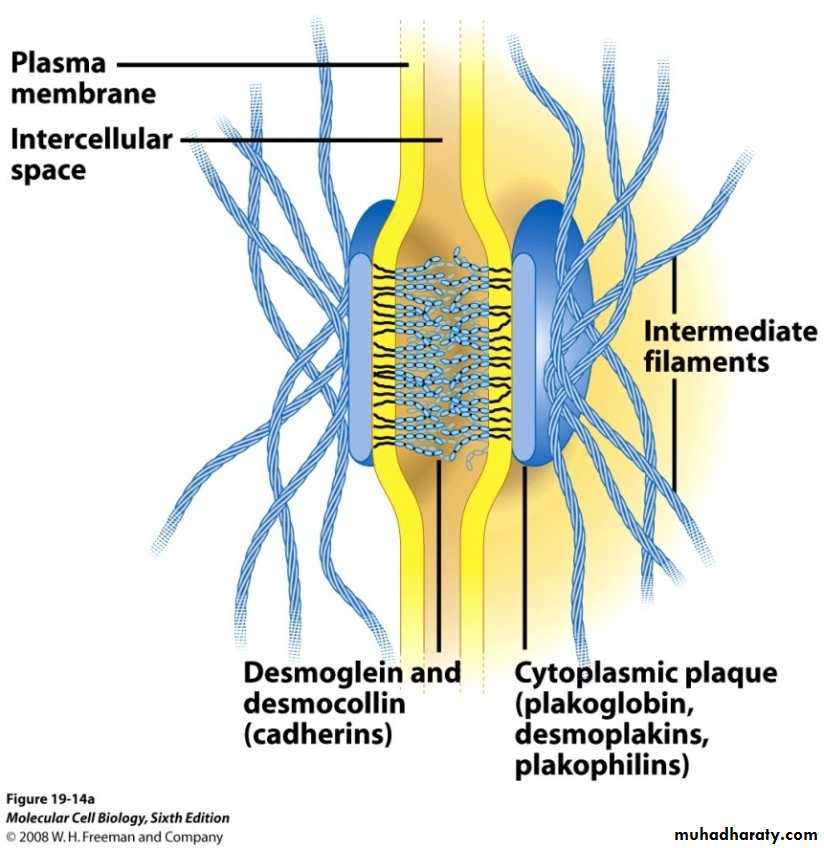
Desmosomes
Stratum Germinativum Combined zone of basal layer & cells Just above it that may still divide
Stratum Basale
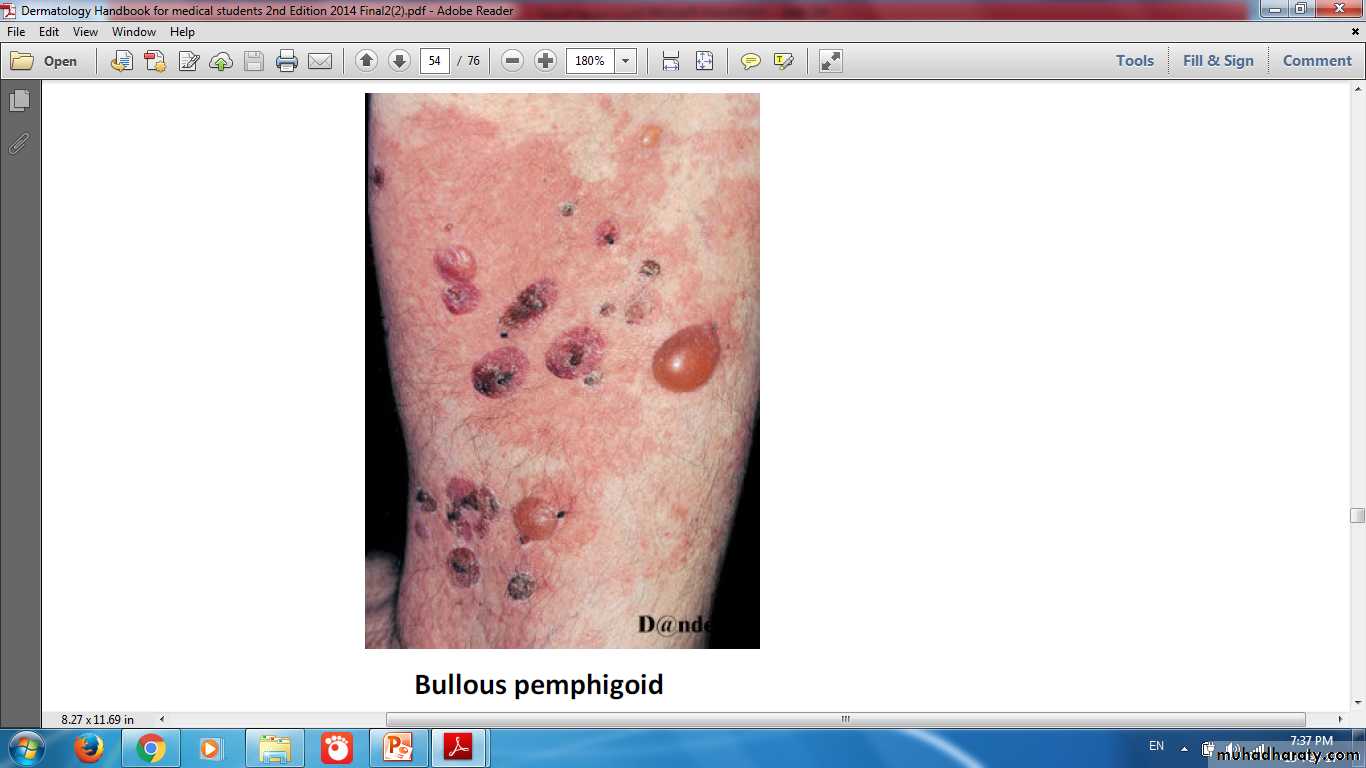
Stratum SpinosumLoss of intercellular junctions lead to blistering disorder (Pemphigus)
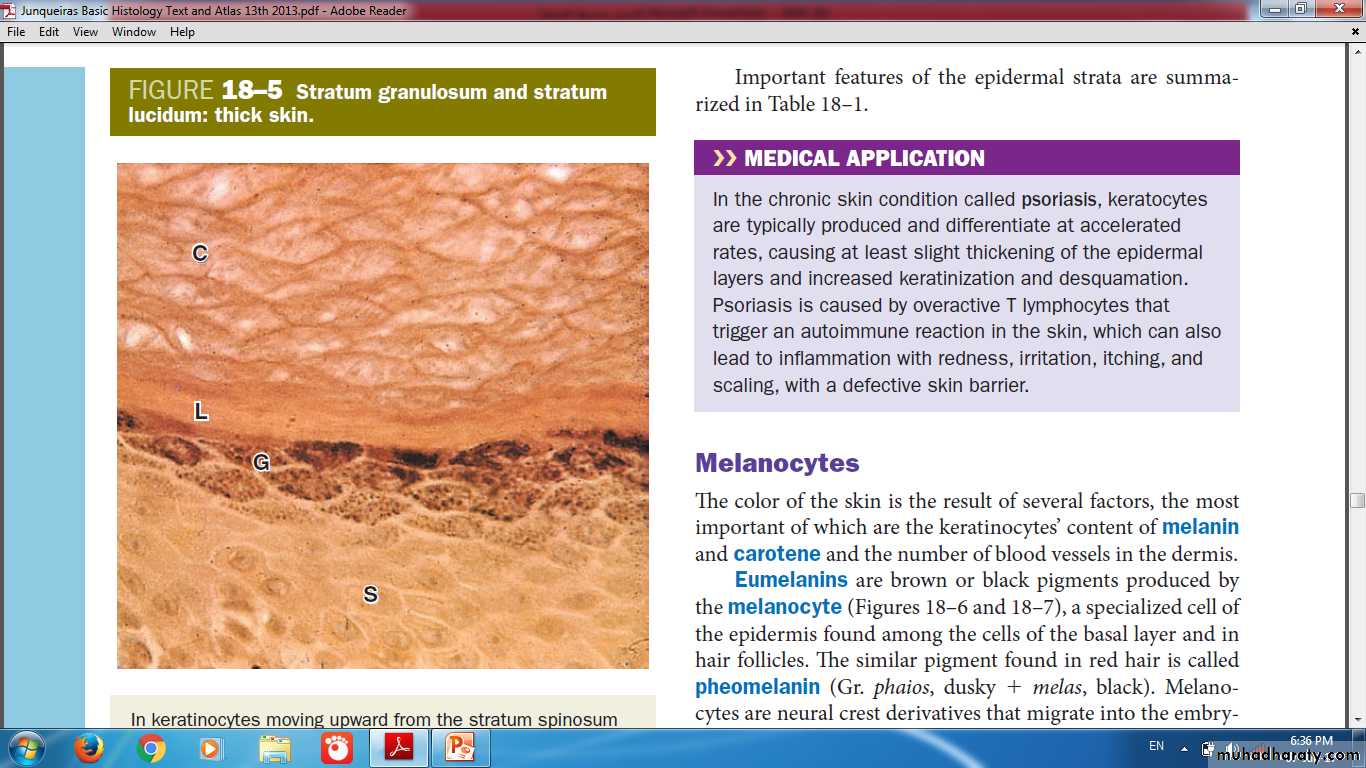
Stratum Granulosum& Stratum Lucidum (Thick skin)
corneum
lucidumGranulosum
Spinosum
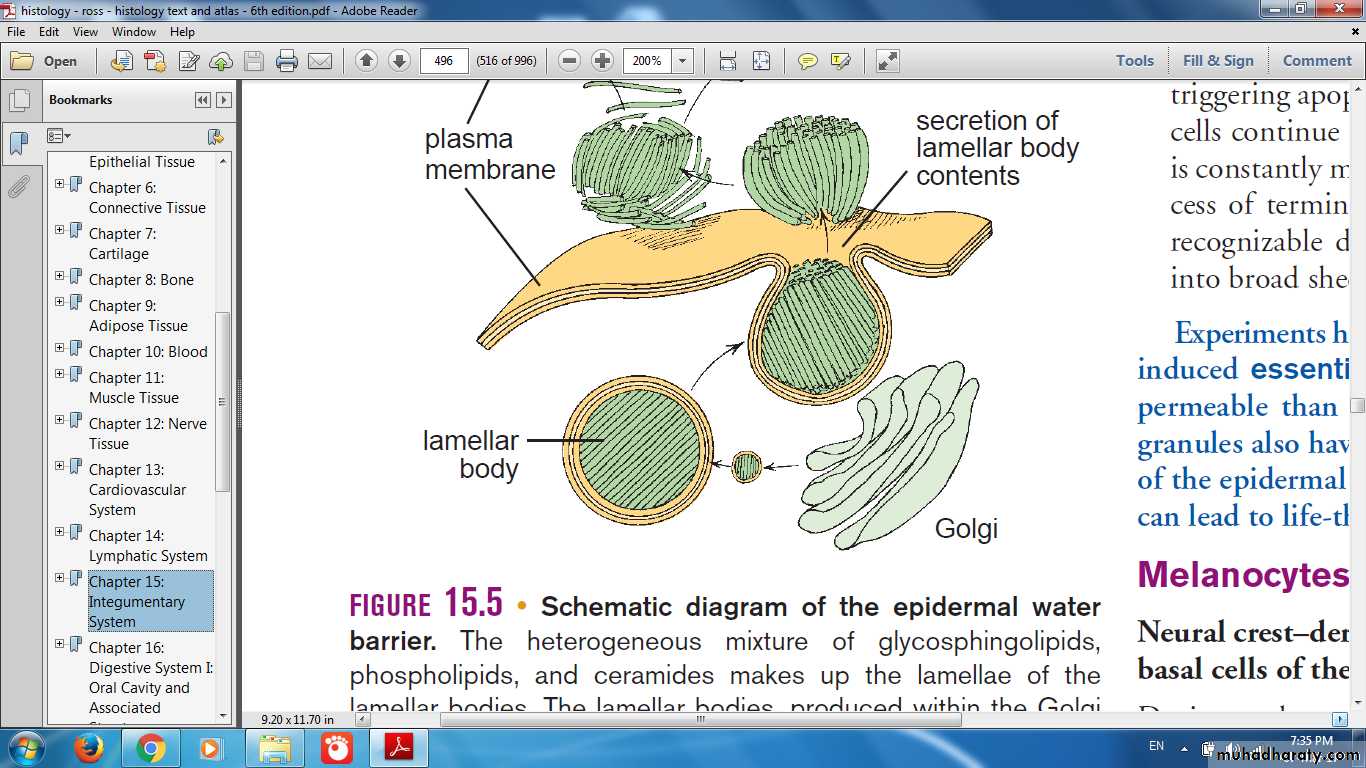
Keratohyaline Granules
Ultrastructural lamellar granulesexocytosis
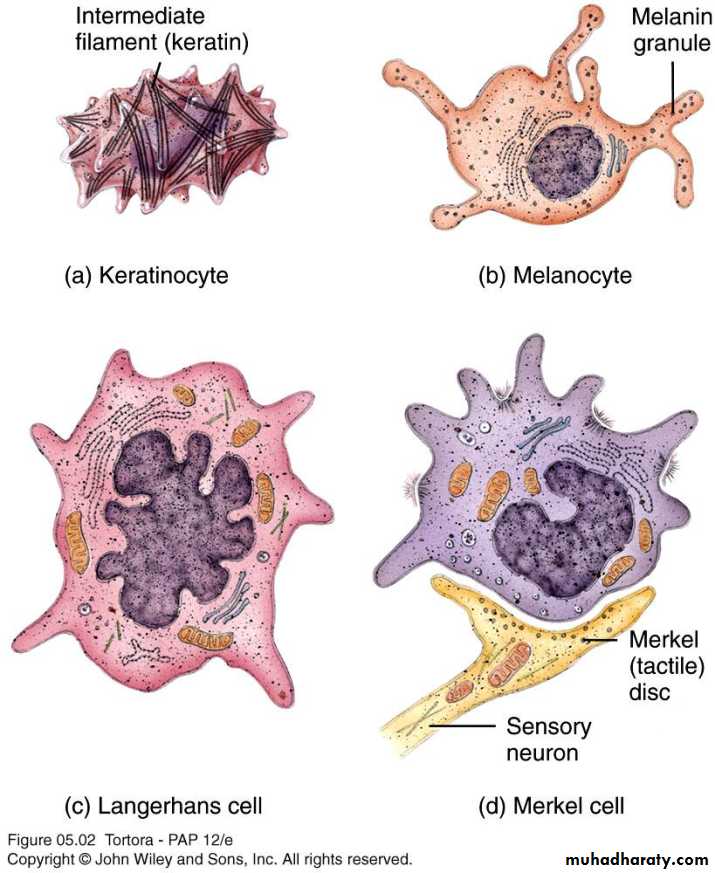
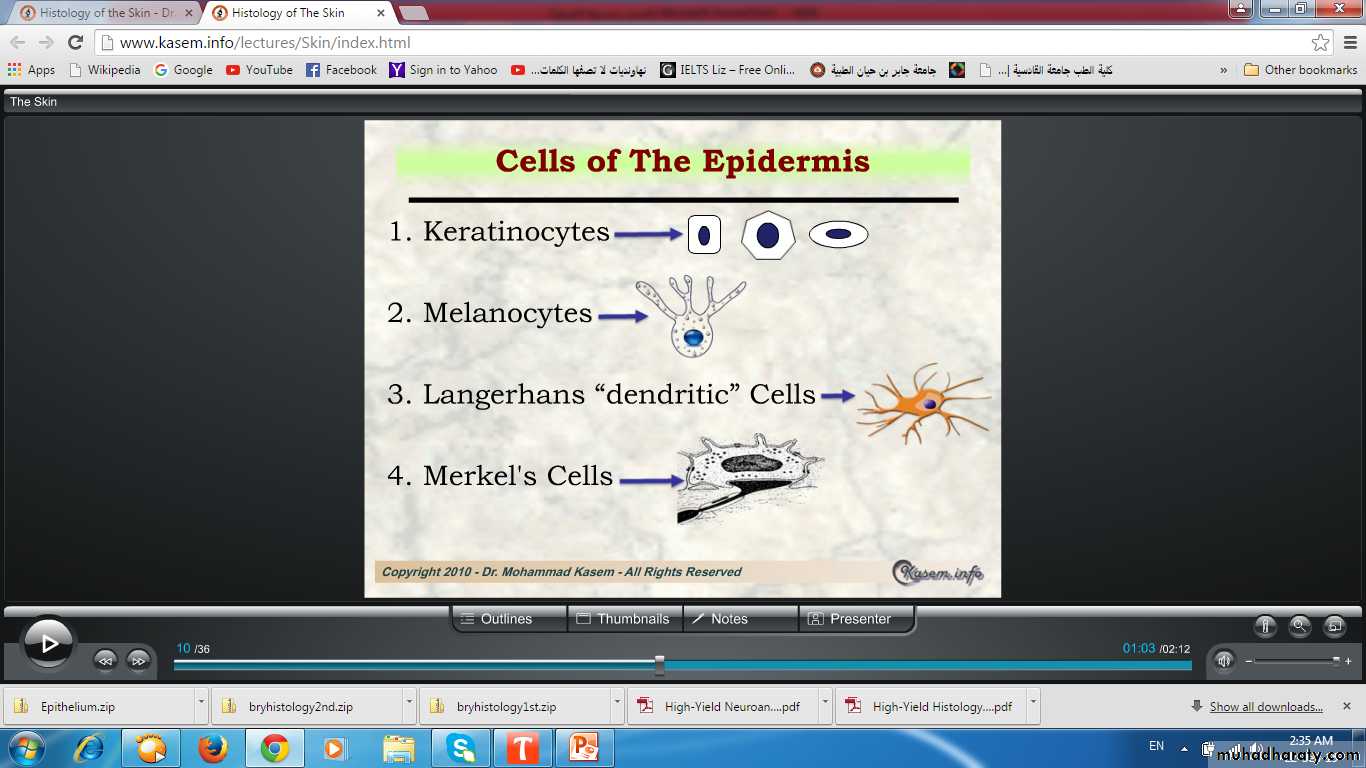
Cells of skin
• Keratinocytes• Melanocytes
• Langerhans cells (dendritic cells)
• Merkel cells(tactile cells)
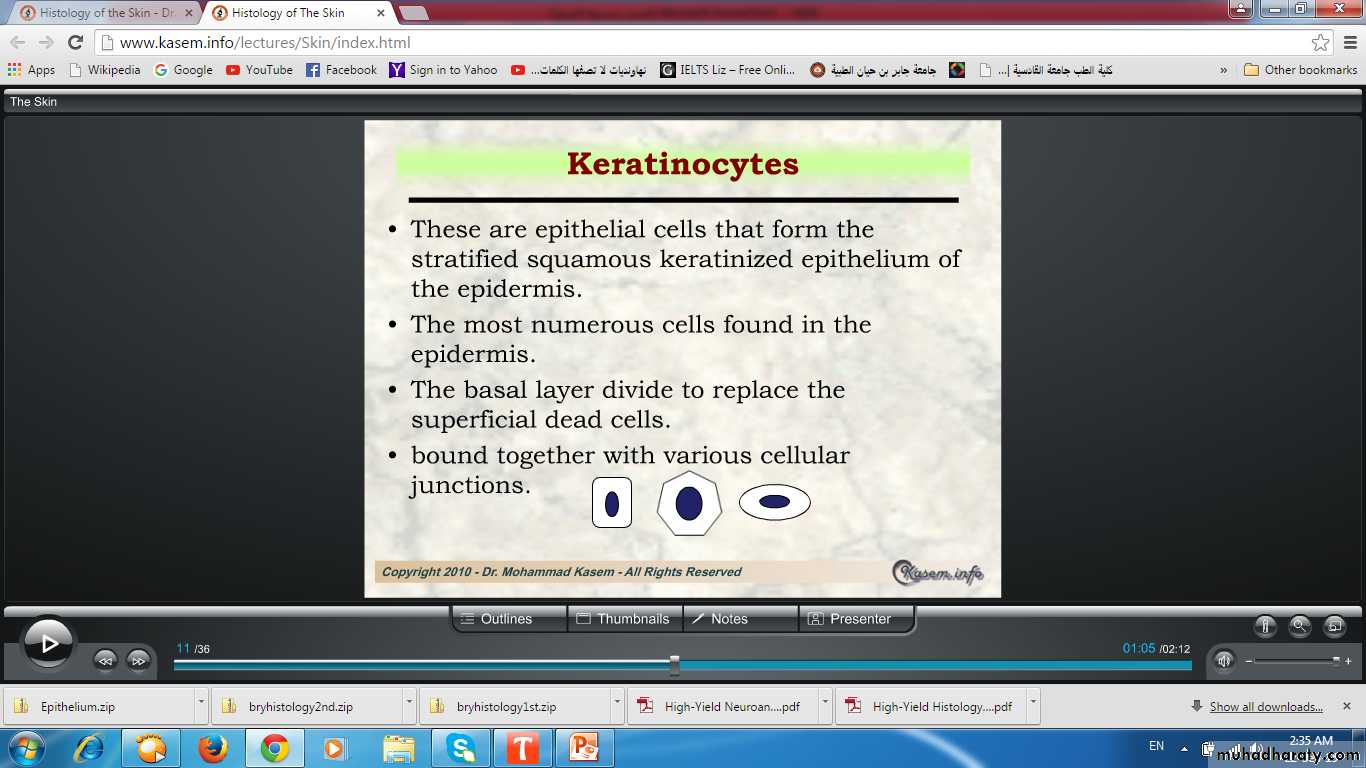
Keratinocytes & other cells
Keratinocytes of stratum spinosum(Thickest layer with tonofibrils)
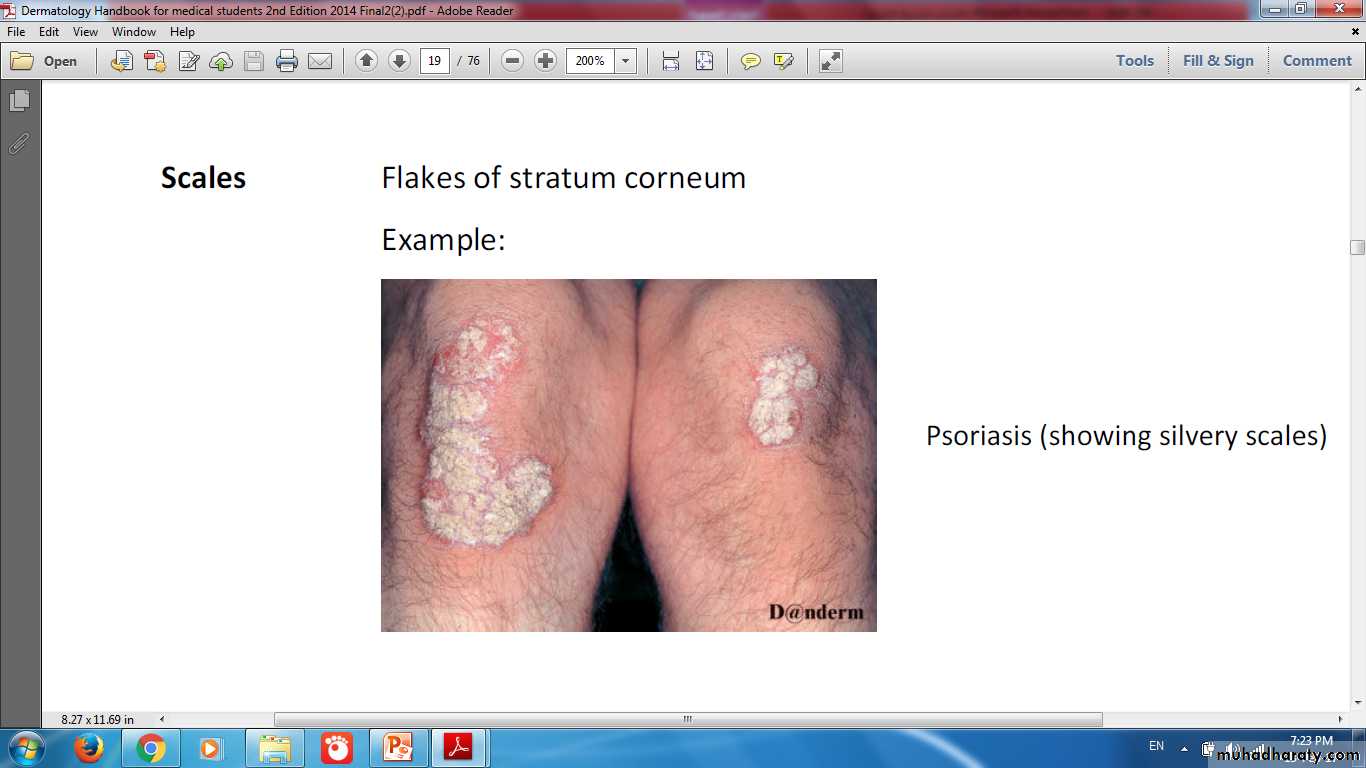
Psoriasis Changes in Epidermal turnover time
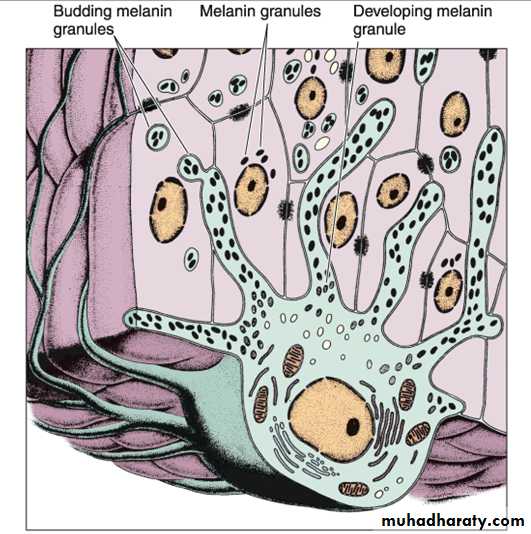
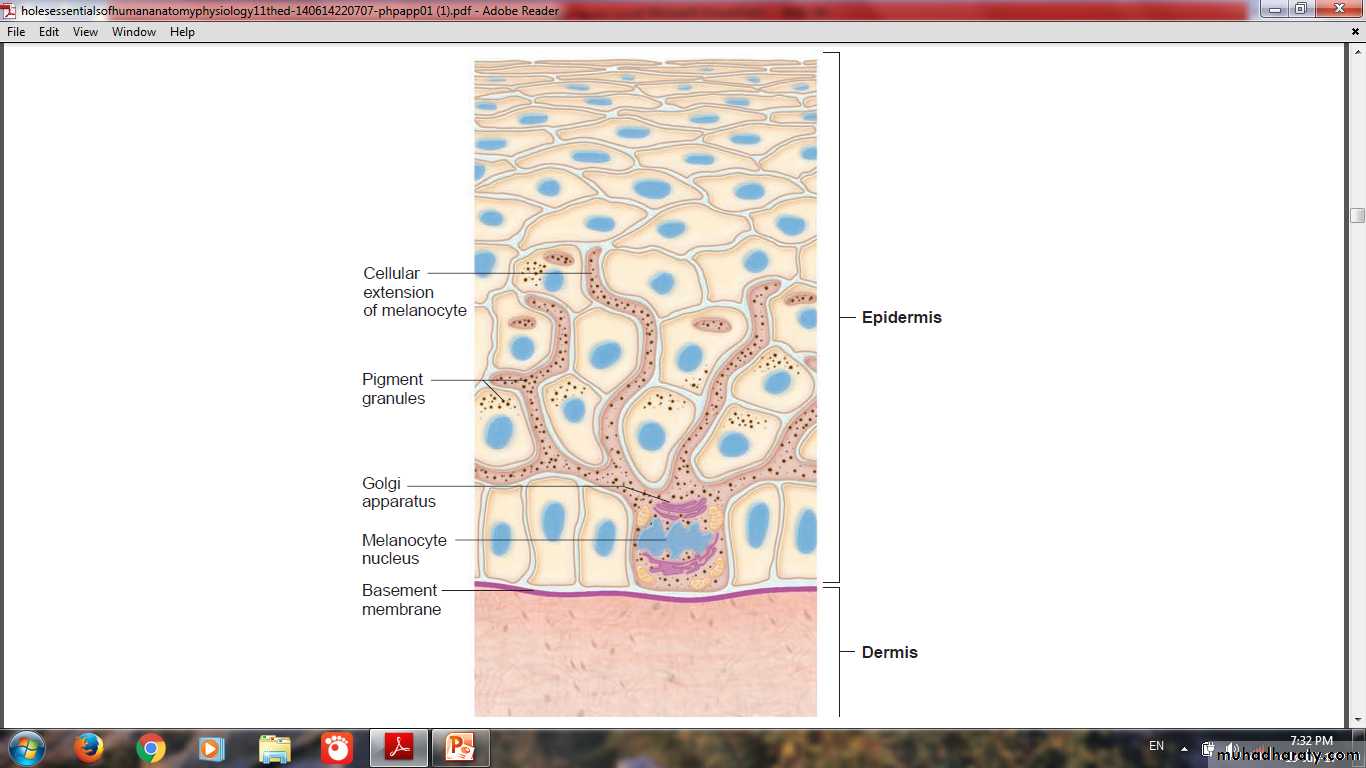
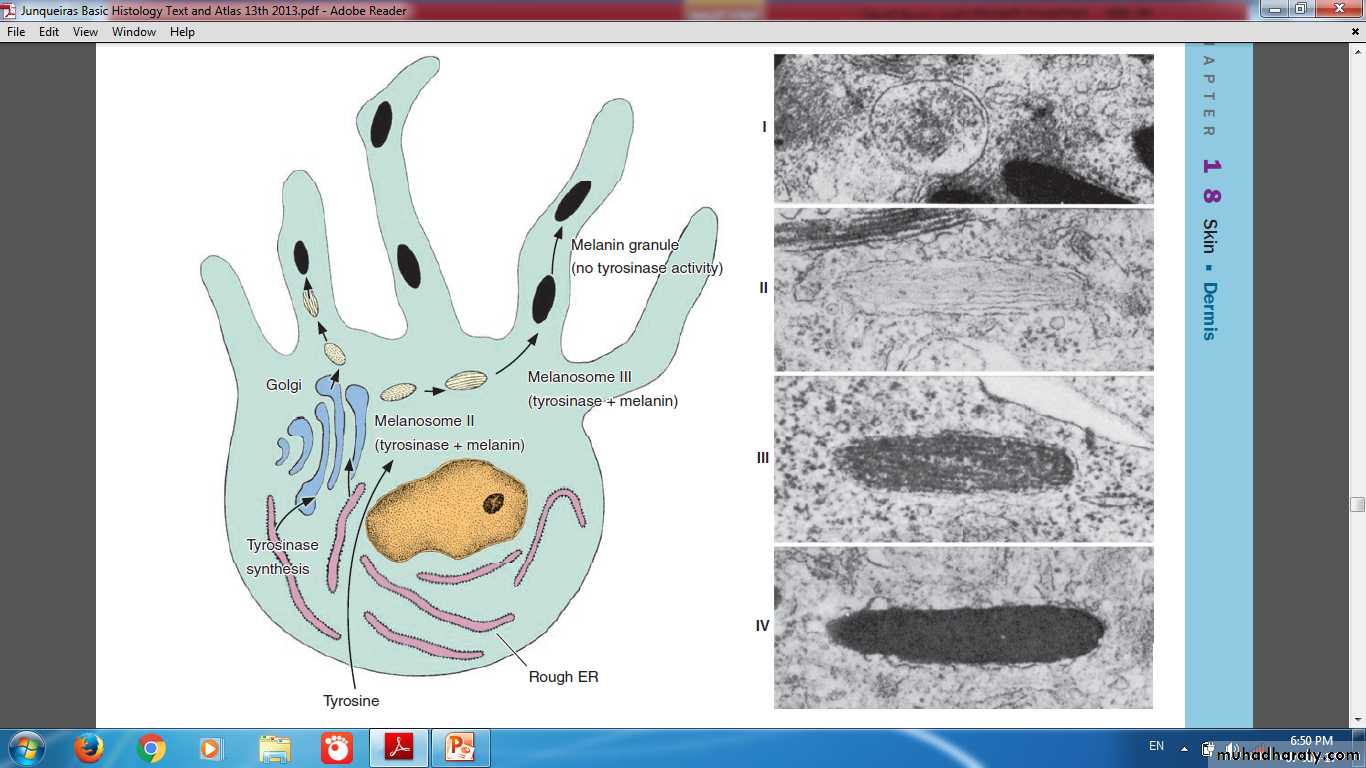
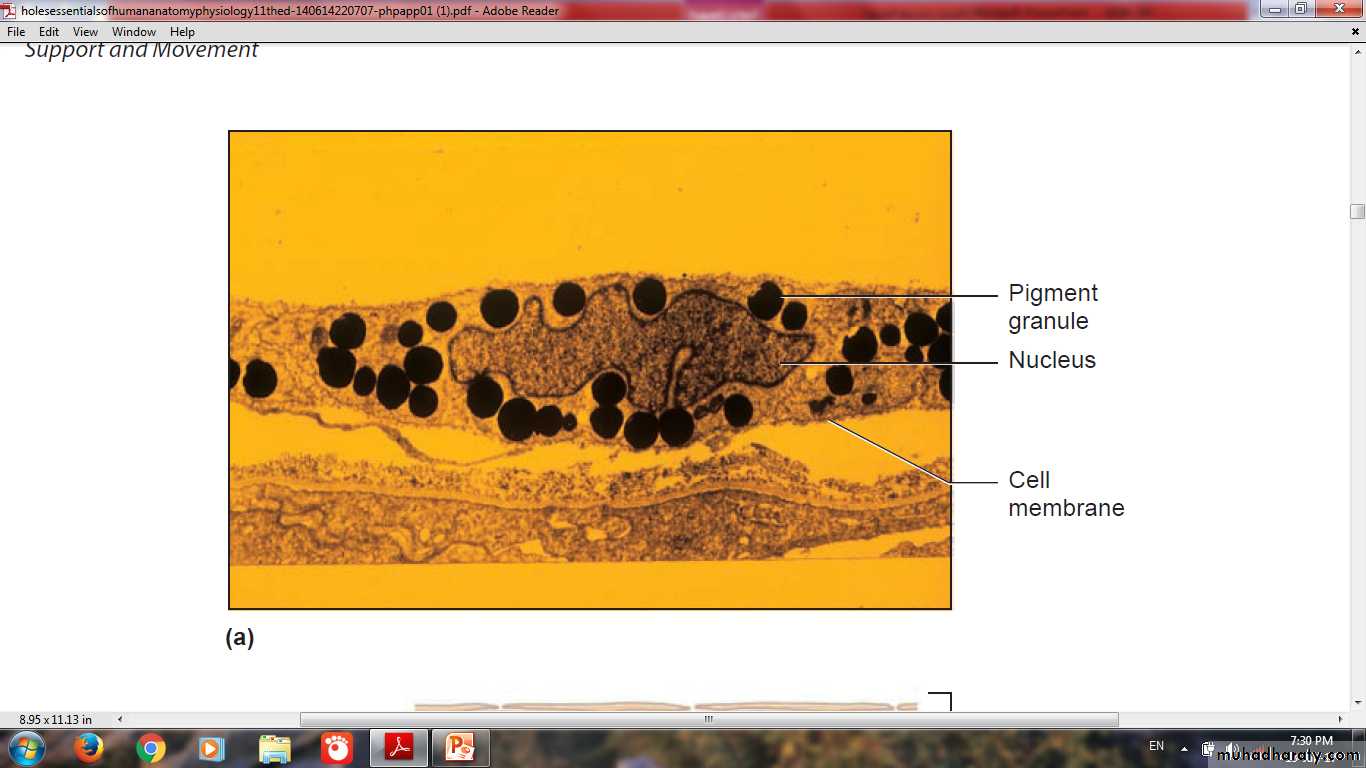
MelanocyteOriginate from neural crest
Give the skin it’s color
Present in stratum basale
Melanin granules migrate through the cytoplasmic extensions to enter keratinocytes
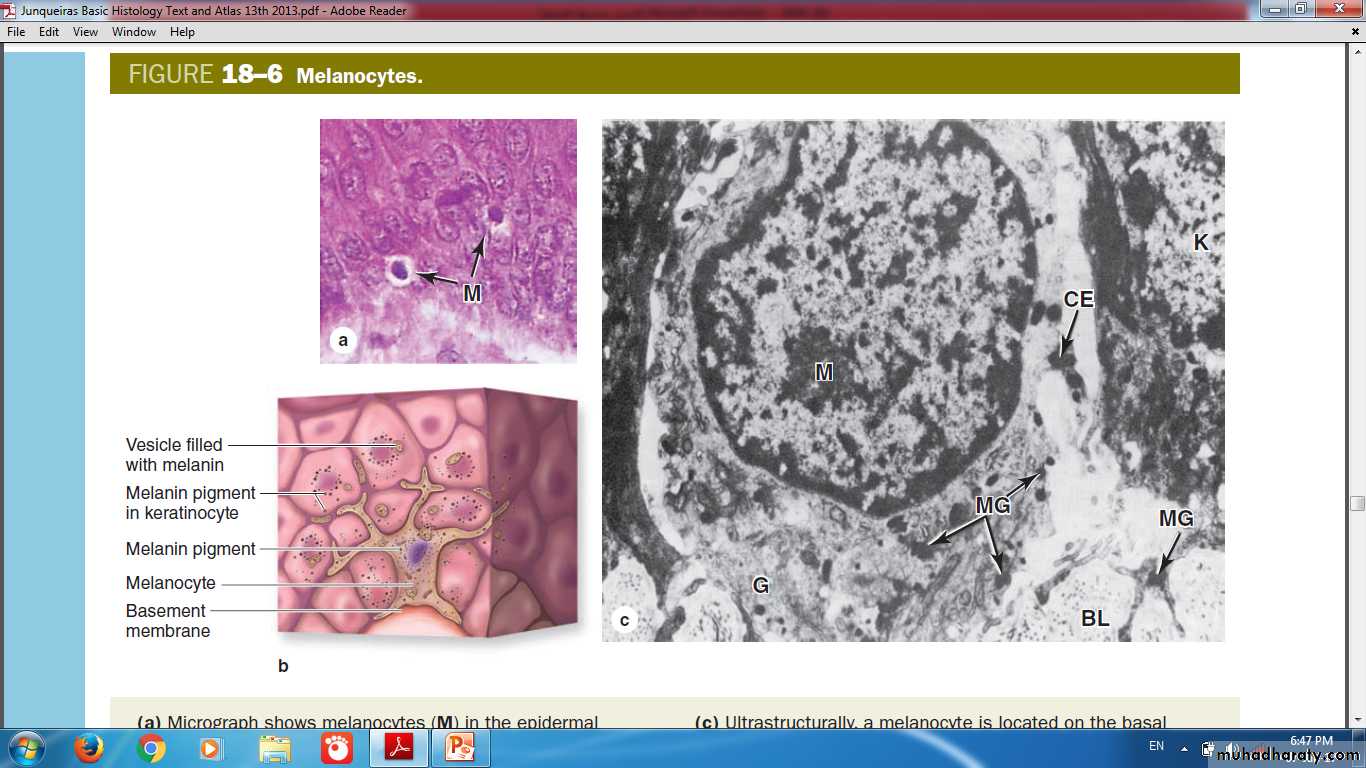
Melanocyte
Contain pigment (Eumelanin or Pheomelanin)They have pale-staining, rounded cell bodies
Attached by hemidesmosomes to the basal lamina
lacking attachments to the neighboring keratinocytes
Keratinocytes are the main depots of melanin
Melanocytes are pale staining cells
Melanocyte Extensions
Melanosome FormationDarkening of the skin (tanning) after exposure to solar radiation is a two-step process
Physicochemical reaction darkens preexisting melaninParacrine factors secreted by keratinocytes experiencing increased UV radiation
Main Factors Affecting Skin Color:
MELANINCAROTENE
SKIN THICKNESSHEMOGLOBIN
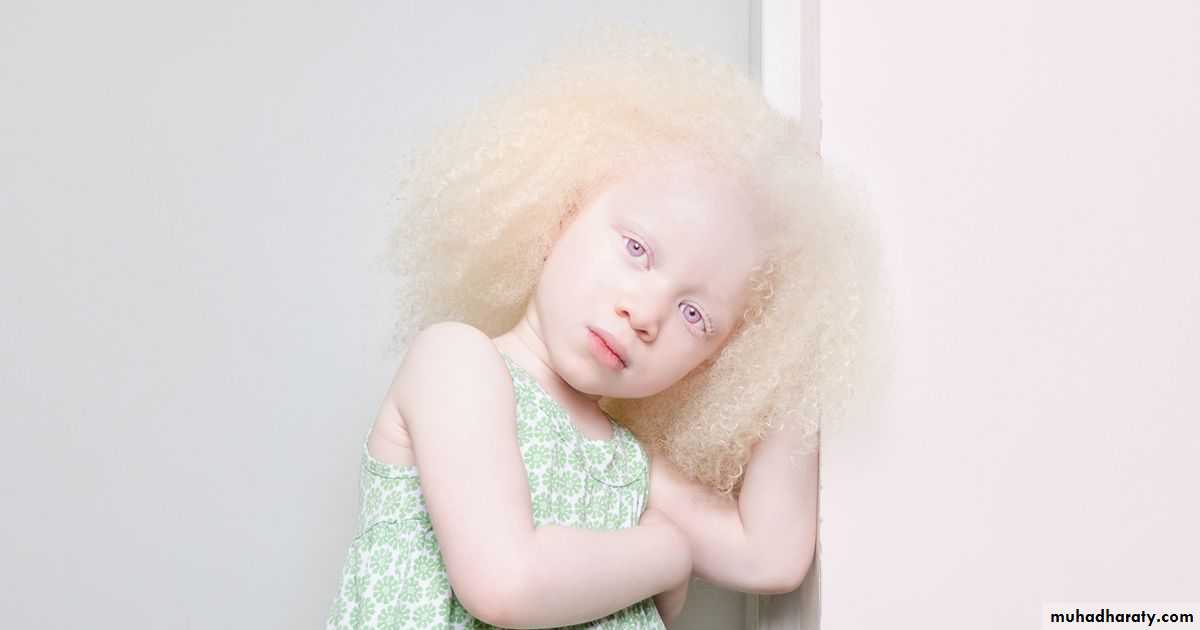
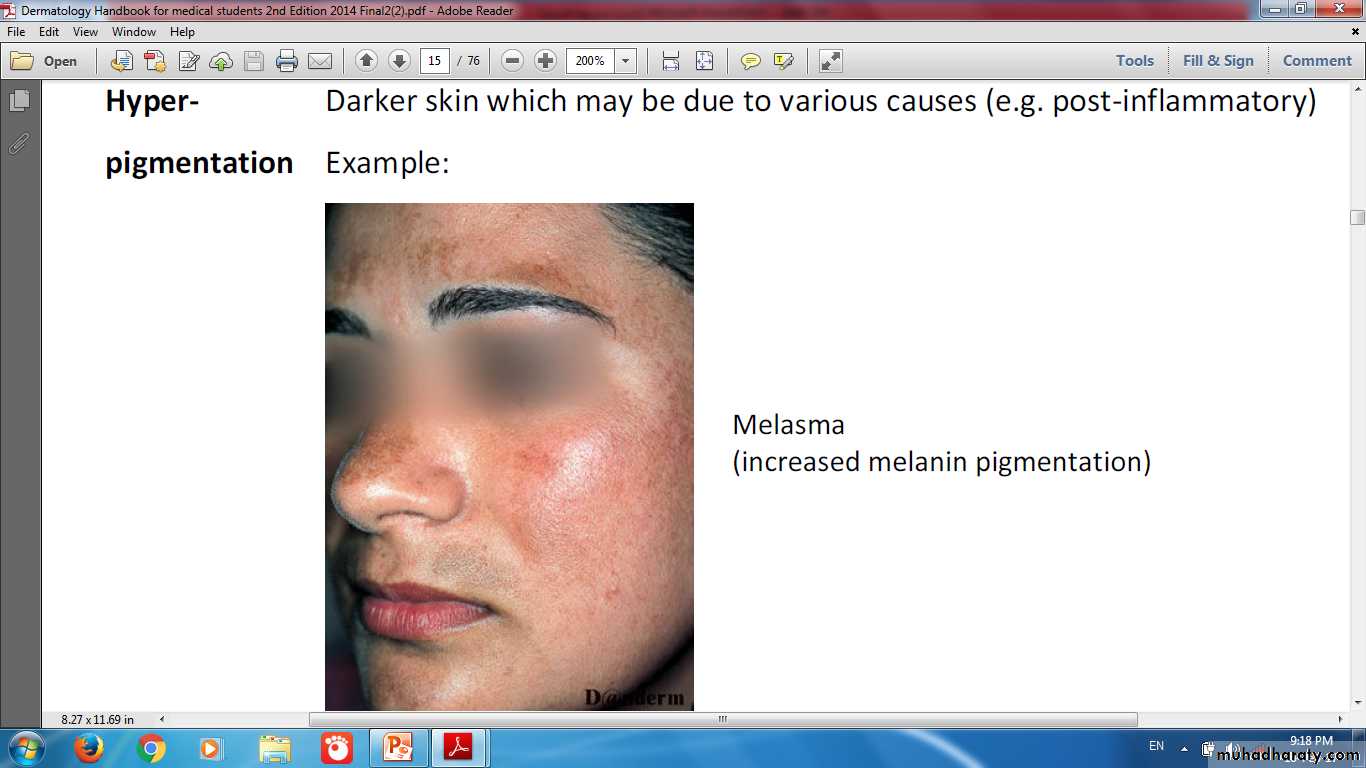
Changes in pigmentation of the skin (Hypo- or Hyper-pigmented skin)AlbinismDeficiency of tyrosinase enzyme lead to Hypopigmentation
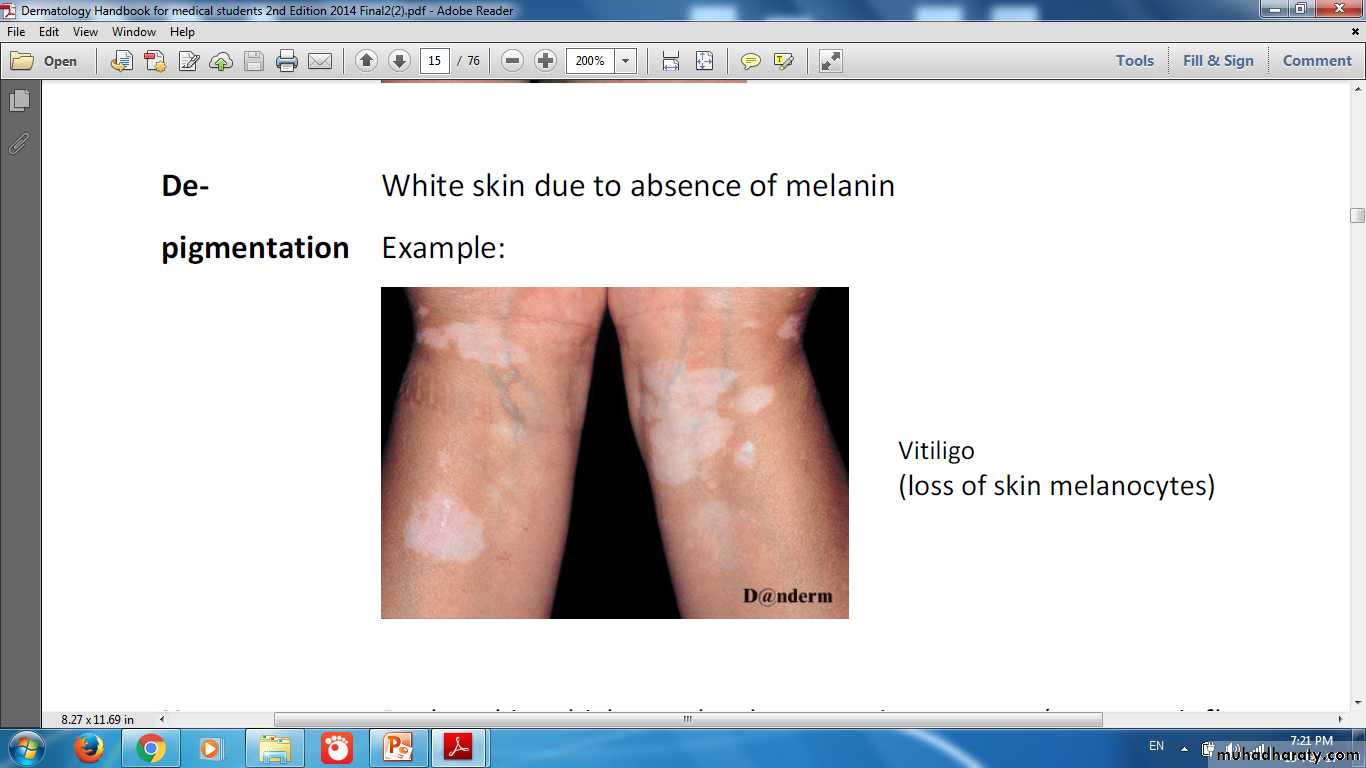
Vitiligo Loss of skin melanocytes lead to Depigmentation
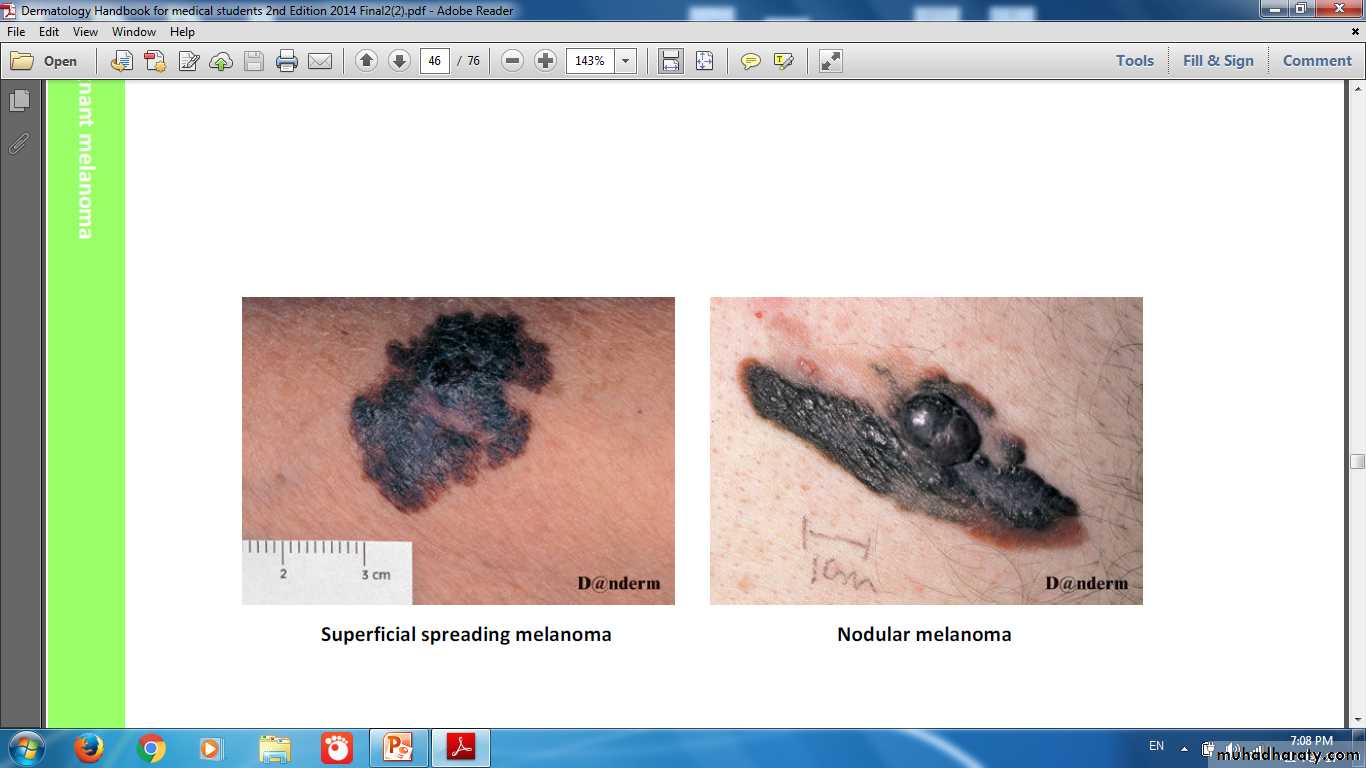
Mole Normal proliferation of melanocyteMelanoma Dividing rapidly & malignantly transformed melanocytes
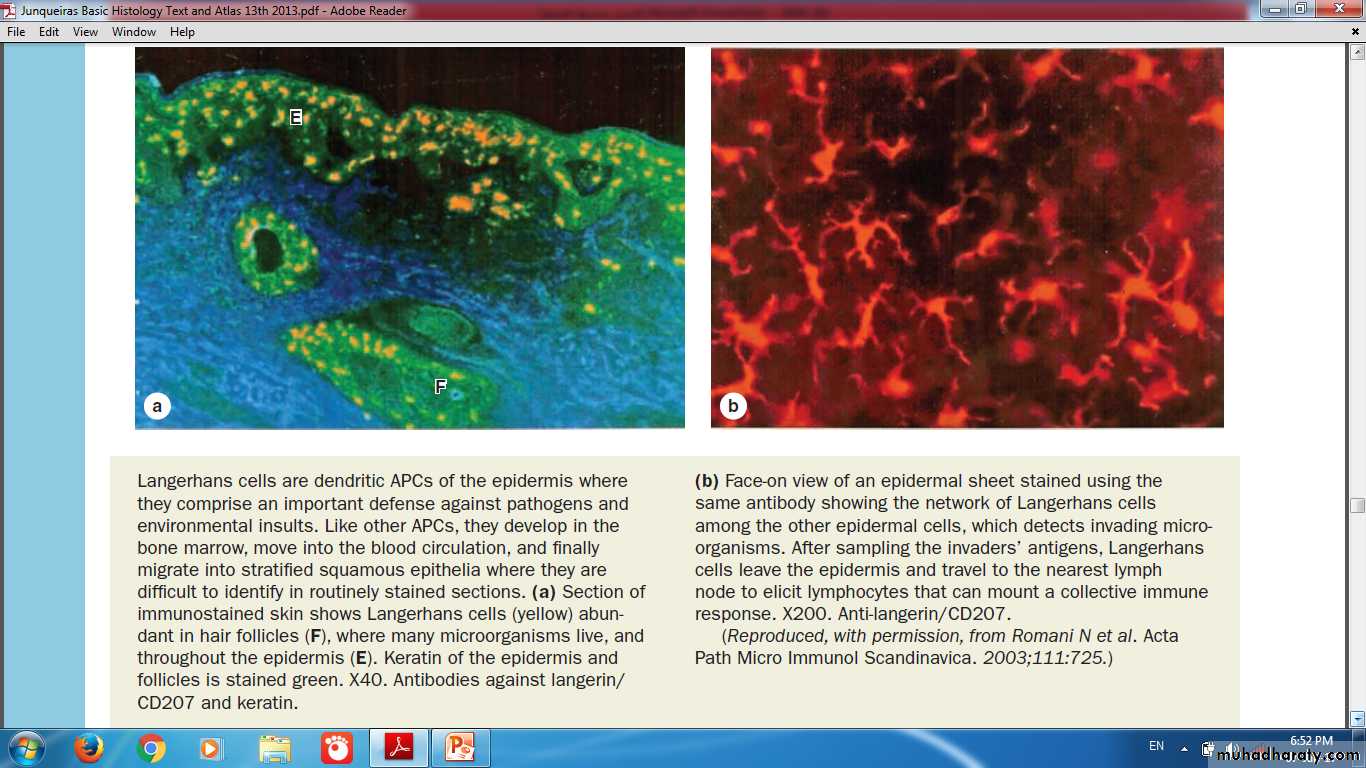
Langerhans Cells
Network of Langerhans Cells (APCs)
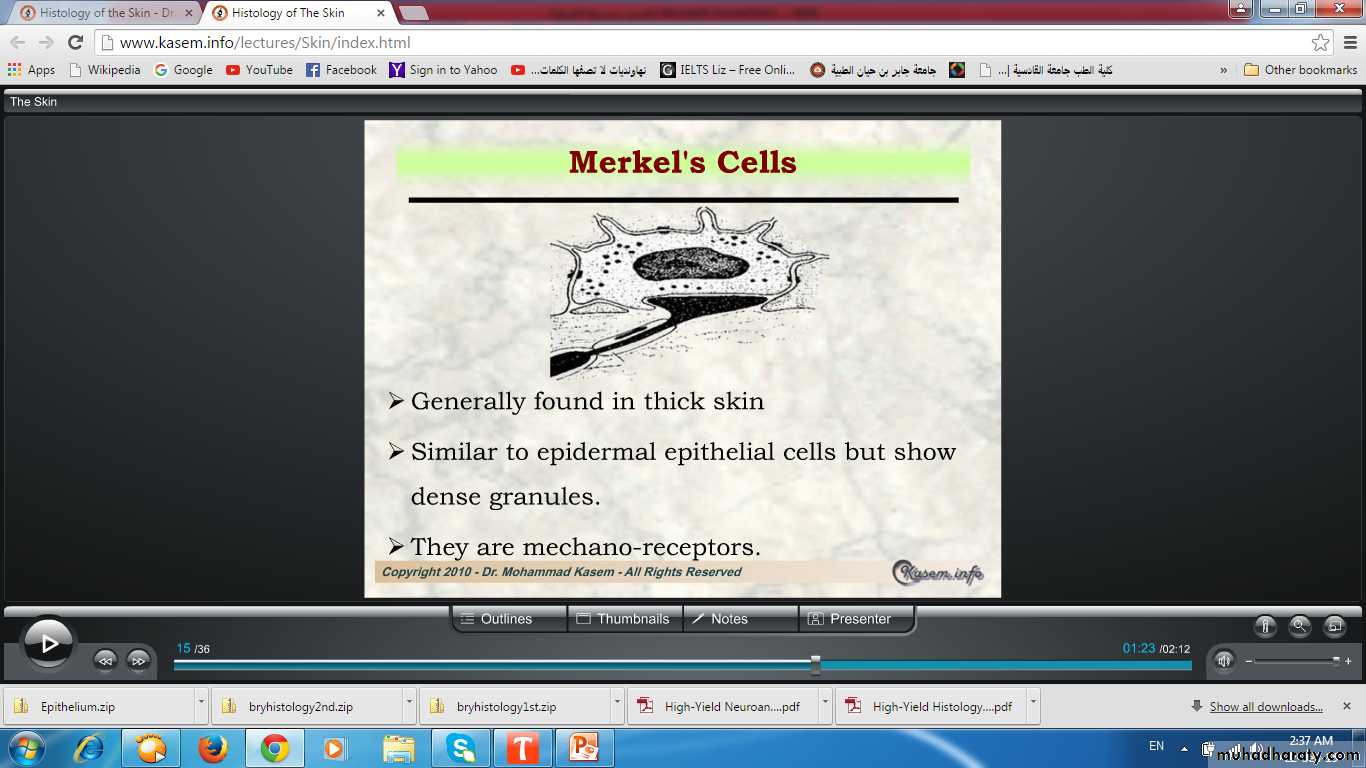
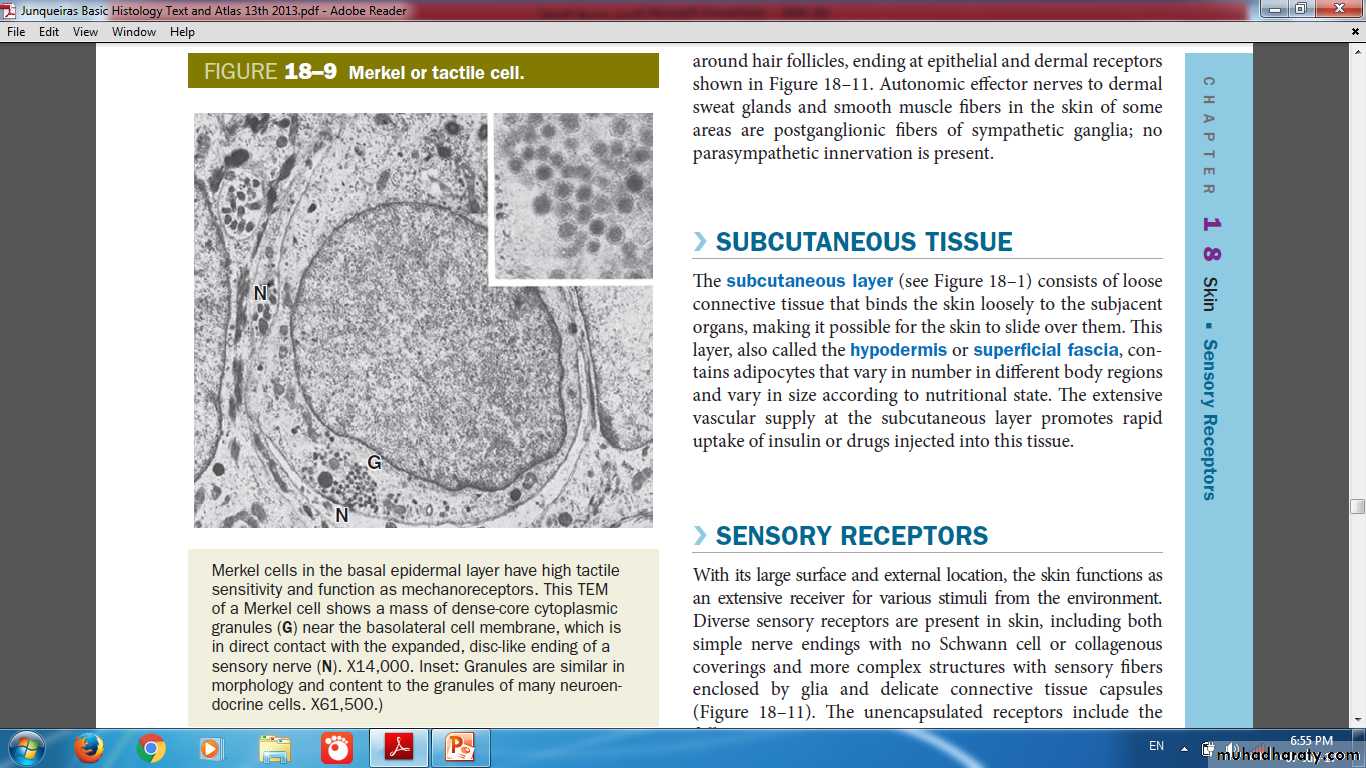
Merkel (Tactile cells)
Merkel (Tactile cells)
Granules
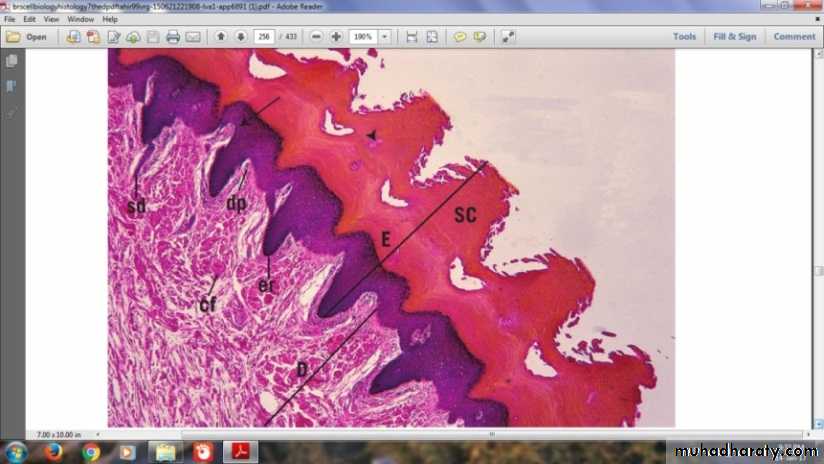
Nerve endDermal-Epidermal InterdigitationsPeg & socketRidges & grooves
Dermal-Epidermal Interdigitations
Irregular junction between the dermis and epidermisProjections called (dermal papillae) interdigitate with invaginating (epidermal ridges)
To increase surface of contact & strengthen adhesion of the two layers
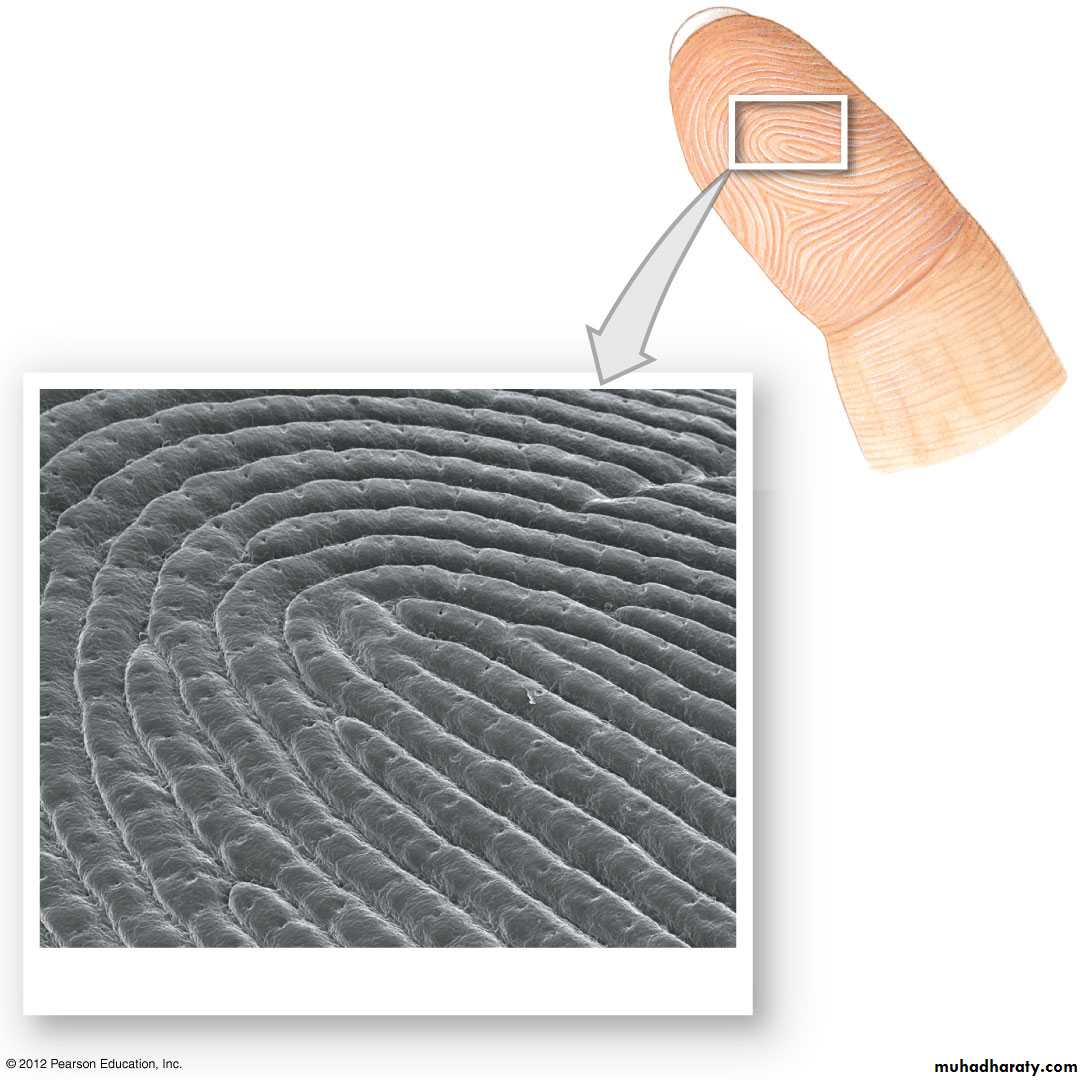
SEM 25
Finger& Foot prints (Dermatoglyphs)loops, arches& whorls
Desmosomes &Hemidesmosomes
Dermo- Epidermal Junction Abnormality
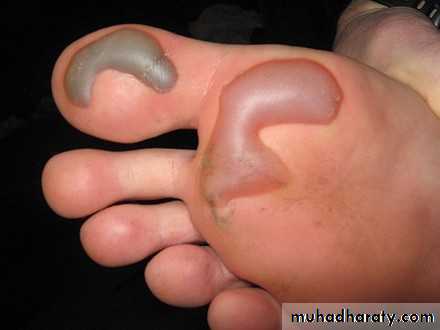
Friction Blisters
Dermis
layer of connective tissueThickness varies with the region of the body
The surface of the dermis is very irregular
Papillary layer
Includes the dermal papillaeConsists of thin layer of loose connective tissue
Types I and III collagen fibers
Fibroblasts and scattered mast cells, macrophages & other leukocytes
From this layer, anchoring fibrils of type VII collagen insert into the basal lamina
Reticular layer
Much thicker than papillary layer
Dense irregular connective tissue (mainly bundles of type I collagen)
More fibers & fewer cells than the papillary layer
A network of elastic fibers is also present, providing elasticity to the skin
Between the collagen and elastic fibers are abundant proteoglycans rich in dermatan sulfate