
1
Lec 7
RUBELLA AND OTHER CONGENITAL VIRAL
INFECTIONS
RNA enveloped viruses
RUBELLA VIRUS
Rubella virus is a member of Togaviridae family (but it is not
transmitted by arthropods.
Disease: German measles(3-day measles), and congenital rubella syndrome.
Important properties:
One piece of single-stranded RNA.
Icosahedral nucleocaspid.
Lipoprotein envelope.
It has positive-strand RNA and therefore has no virion polymerase.
Surface spikes contain hemagglutinin.
Transmission & Epidemiology:
The virus is transmitted via droplets andfrom mother to fetus transplacentally
The disease occurs worldwide, and throughout the year with a peak incidence
in spring.
Infection during the first trimester of pregnancy results in abnormalities in the
infant in about 85% of cases, whereas detectable defects are found in about
16% of infants who acquired infection during the second trimester
Pathogenesis & Immunity:
Initial replication of the virus occurs in the nasopharynx and local lymph
nodes. From there it spreads via blood to the internal organs and skin.
The origin of the rash is unclear; it may be due to Ag-Ab-mediated vasculitis.
Infection leads to lifelong immunity. Second cases of rubella do not occur;
similar rashes are caused by other viruses, such as coxsackievirus and
echovirus. Ab cross the placenta and protects the newborn.

2
Clinical Findings:
A- RUBELLA: It is a milder, shorter disease than measles. After an incubation
period of 14-21 days, a brief prodromal period with fever and malaise is
followed by a maculopapular rash, which starts on the face and progresses
downward to involve extremities. Posterior auricular lymphadenopathy is
characteristic. The rash typically lasts 3 days.
B- CONGENITAL RUBELLA SYNDROME: the significance of rubella virus
is not as a cause of mild childhood disease but as a teratogen. When a
nonimmune pregnant woman is infected during the 1
st
trimester, especially the
1
st
month, significant congenital malformations can occur as a result of
maternal viremia and fetal infection. The increased rate of abnormalities during
the early weeks of pregnancy is attributed to the very sensitive organ
development that occurs at that time. The malformations are widespread and
involve primarily the heart (e.g., patent ductus arteriosus), the eyes (e.g.,
cataracts), and the brain (e.g., deafness and mental retardation). Congenitally
infected infants have significant IgM titers and persistent IgG titers long after
maternal Ab has disappeared.
Progressive rubella panencephalitis, a rare complication that develops in the
second decade of life in children with congenital rubella, is a severe neurologic
deterioration that inevitably progresses to death
Lab Diagnosis:
Virus can be grown in cell culture, but it produces little CPE, it is usually
identified by its ability to interfere with echovirus CPE. If rubella virus is
present in patient's specimen and has grown in the cell culture, no CPE will
appear when the culture is super-infected with an echovirus.
Rising Ab titer 4-fold or greater between acute-phase and convalescent-phase
sera in the hemagglutination inhibition test or ELISA.
Observing the presence of IgM Ab in single acute-phase serum sample may
help in diagnosis.
Pregnant woman exposed to rubella virus, the presence of IgM Ab indicates
recent infection, whereas a 1:8 or greater titer of IgG Ab indicates immunity
and protection of the fetus.
If recent infection has occurred, an amniocentesis can reveal whether there is
rubella virus in amniotic fluid, which indicates definite fetal infection.
Treatment: No antiviral therapy.
Prevention:
Immunization with live attenuated vaccine with measles and mumps (MMR)
subcutaneously at age of 15 months, and to unimmunized young adult woman
3
if they are not pregnant and will use contraception for the next 3 months.
Vaccine is a live one it should not be given to immunocompromized patients or
to pregnant woman.
Vaccine has caused significant reduction in the incidence of rubella and
congenital rubella syndrome. It induces respiratory IgA interrupting the spread
of the virus by nasal carriage. The vaccine induces lifelong immunity in 95%
of recipients.
Immune serum globulins IG can be given to pregnant woman in 1
st
trimester,
but it may fail to prevent fetal infection.
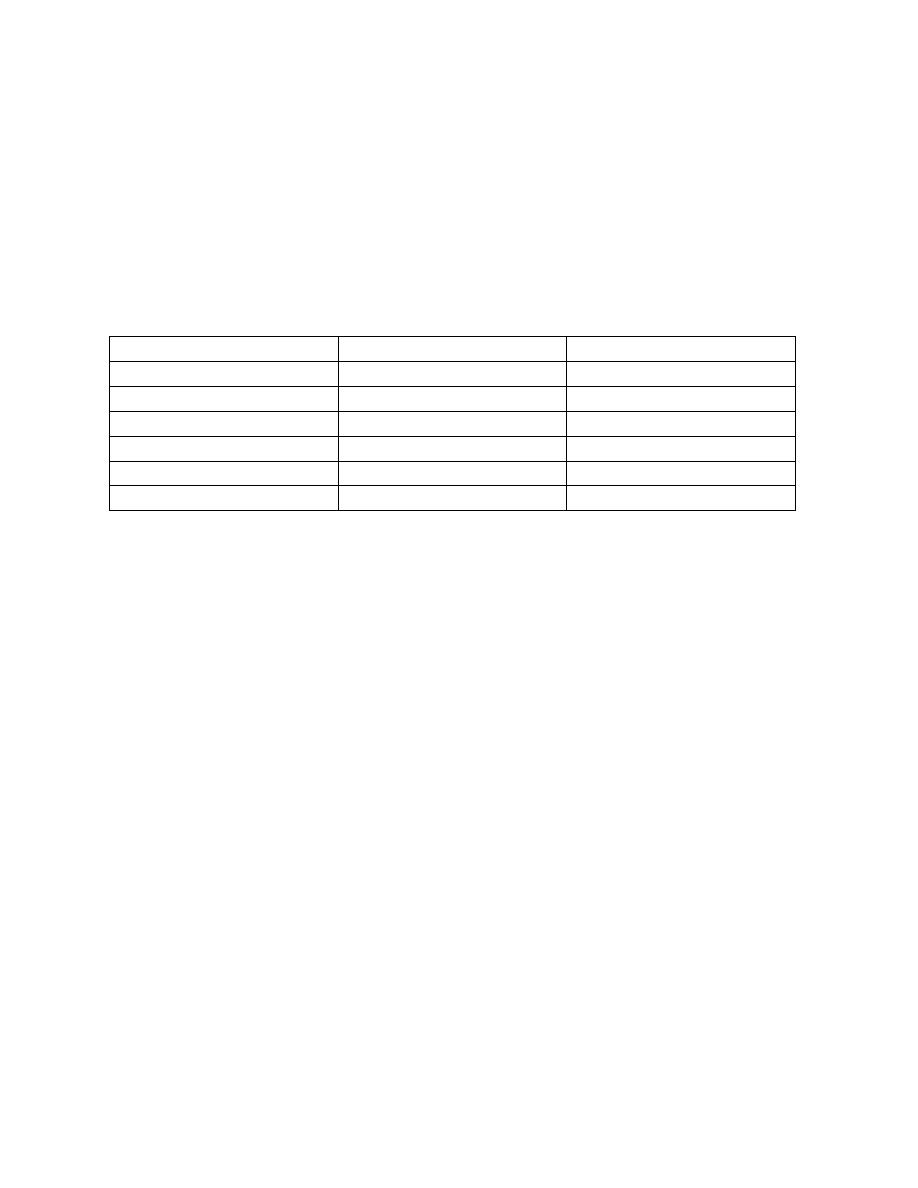
Overview of congenital viral infections
Viruses
Prenatal (in utero)
Natal (during delivery)
Rubella
+
-
CMV
+
++
HSV
-
++
HBV
+
++
HIV
+
++
Parvovirus B19
+
-
Other rare viruses (enterovirus, VZV, HPV, measles and mumps)
*In utero infection results in Five main consequences:
1.Intrauterine death
2.Intrauterine growth retardation
3.Prematurity
4.Congenital defects
5.persistent infection after delivery
*Why some viruses cause congenital defects and others not?
This depends on:
1.the ability of the virus to be transmitted to the fetus
2.the ability of the virus to cause damage to the fetus (Teratogenicity)
3.the stage of gestation (in the first trimester because of the process of
organogenesis)
Diagnosis of Congenital viral infections
Prenatal: detection of IgM in the mother, or IgG raising titer.
Postnatal: most importantly is detection of IgM in the neonate, because IgG
crosses the placenta, while IgM doesn’t.
Prenatally nowadays using amniocentesis and detect the virus directly mainly
using molecular methods
