
Practical Physical pharmacy
Definitions:
- True solution: is a mixture of two or more components that form a
homogenous molecular dispersion. The components are referred to the solute &
the solvent .
- Solute: is the dissolved agent (less abundant part of the solution).
- Solvent: is the component in which the solute is dissolved (more abundant part
of the solution).
-A saturated solution: is one in which an equilibrium is established between
dissolved and undissolved solute at a definite temperature.
-An unsaturated solution: or subsaturated solution is one containing the
dissolved solute in a conc. below that necessary for complete saturation at a
definite temperature.
Solubility: in a quantitative way: it is the concentration of the solute in a
saturated solution at a certain temperature.
in a qualitative way: it is the spontaneous interaction of two or more substances
(solute & solvent) to form a homogeneous molecular dispersion.
The solubility of a compound depends upon the physical and chemical
properties of the solute and the solvent, as well as upon such factors as
temperature, pressure, the pH of the solution ……
The solubility of a drug can be expressed in terms of:
- Molarity
- Normality
- Molality
- Mole fraction
- percentage (% w/w, % w/v, % v/v).
Solvents can be divided to:
1- Polar solvents
2- Non polar solvents
Polar solvents such as water act as solvents according to the following
mechanisms:
1- Owing to their high dielectrical constant, they can reduce the force of
attraction between oppositely charging ions in crystals such as NaCl.
2- Polar solvents break the covalent bonds of potentially strong electrolytes by
acid-base reactions, for e.g. water bring about the ionization of an acid.
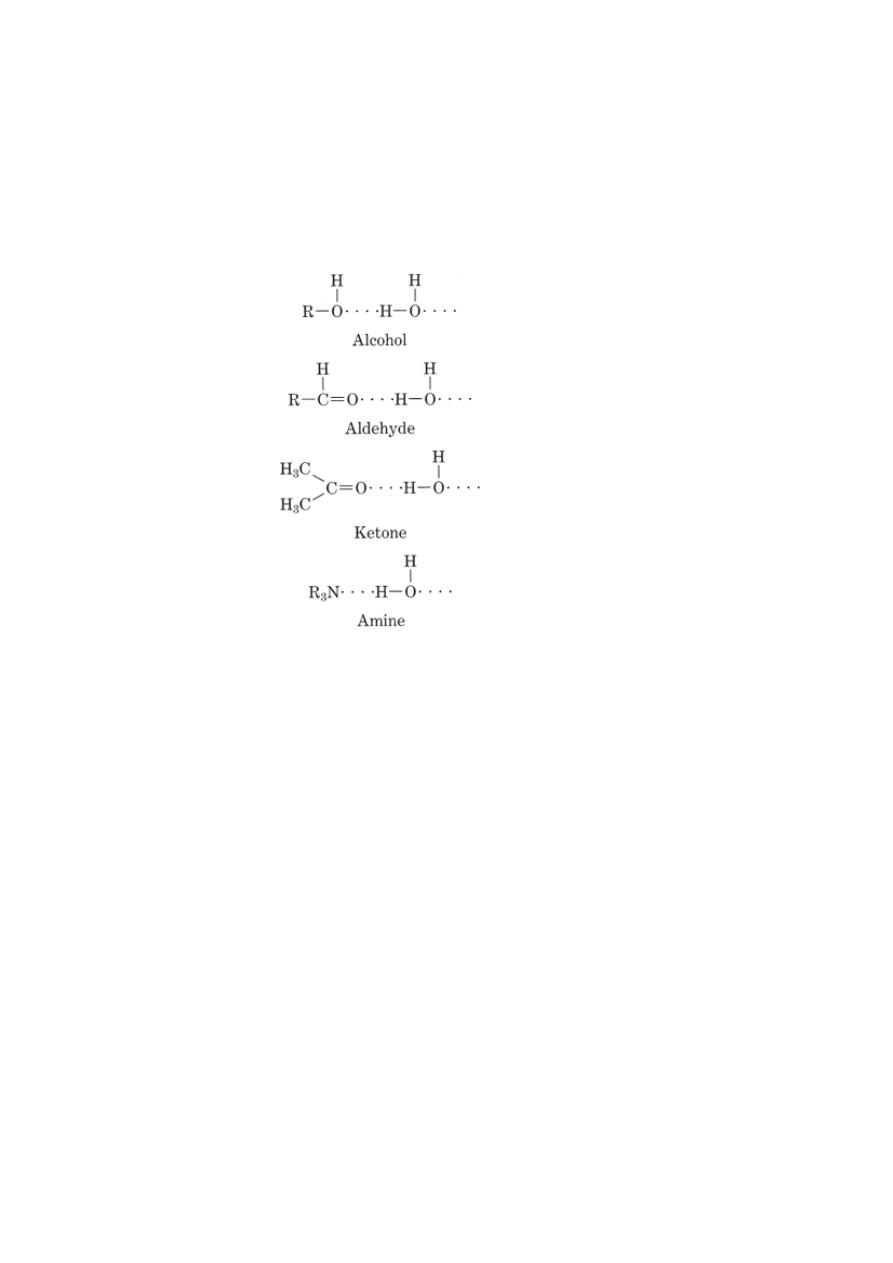
3- Polar solvents are capable of solvating molecules and ions through H-bond
formation.
Methods of increasing solubility
1- solvent combinations (use of co-solvent):
The solute is more soluble in a mixture of solvents than in one solvent e.g.
S.A. dissolve in water-alcohol mixture more than it's solubility in water alone
according to the role Like-dissolve-Like (S.A. is an organic solute dissolve more
easily in an organic solvent) in addition to the ability of alcohol to form H-bond
with S.A.
The aim of the experiment:
is to increase the solubility of S.A. (weak organic acid, slightly soluble in
water) by solvent combination.
Procedure:
1- put 0.1 gm of S.A. in a conical flask.
2- Add 10 mls of D.W and shake the flask and observe the solubility.
3- Add from burett drop by drop absolute alcohol with continuous (hard)
shaking until all the crystals of salicylic acid dissolve.

4- Measure the amount of alcohol used.
5- Calculate the percent (v/v%) of alcohol used in the final mixture.
2- Salt formation(effect of PH on the solubility)
Most weak electrolytes can be retained in the solution by adjusting PH so as
to keep ionized solute in ionized form.
When a weak acid dissolve in water it will be ionized, so if the PH decrease
the solubility will decrease and if the PH increase the solubility will increase.
Vice versa in the solution of weak base.
The aim of experiment:
Is to observe the effect of acid and base on the solubility of S.A.
Procedure:
1- Put 0.1 gm of S.A. in a conical flask.
2- Add 10 mls of D.W. and shake the flask and observe the solubility.
3- Add NaOH to the flask with continuous shaking and observe the result.
4- Add few drops of concentrated HCl to the clear layer of the solution and
observe the result.
3- complexation
It has been found that insoluble drugs can form soluble complex with some
compounds. Complexation relies on relatively weak forces such as londen
forces, hydrophobic interaction, dipole-dipole interaction,… That change
physical but not chemical properties like solubility, stability ,melting
point,….etc
Complexation occur by using complexing agent (chelating agent).
It has been found that inorganic and organic materials which do not themselves
ionized may be rendered soluble in polar solvents by complexation with
electrolytes.
Complexes can be used to increase the solubility of some insoluble drugs e.g.
indomethacin+ β-cyclodextrin, aspirine+ TSC.

In the same time they can decrease the solubility of some drugs e.g. tetracycline
+ Ca
+2
because they form insoluble complex.
Aim of the experiment:
the aim of this experiment is to solubilize I
2
in water with KI.
Procedure:
put 0.1 gm I
2
in conical flask.
add 10 ml water, shake and observe.
add 0.2 gm potassium iodide.
Observe the result and write the equation for it .

