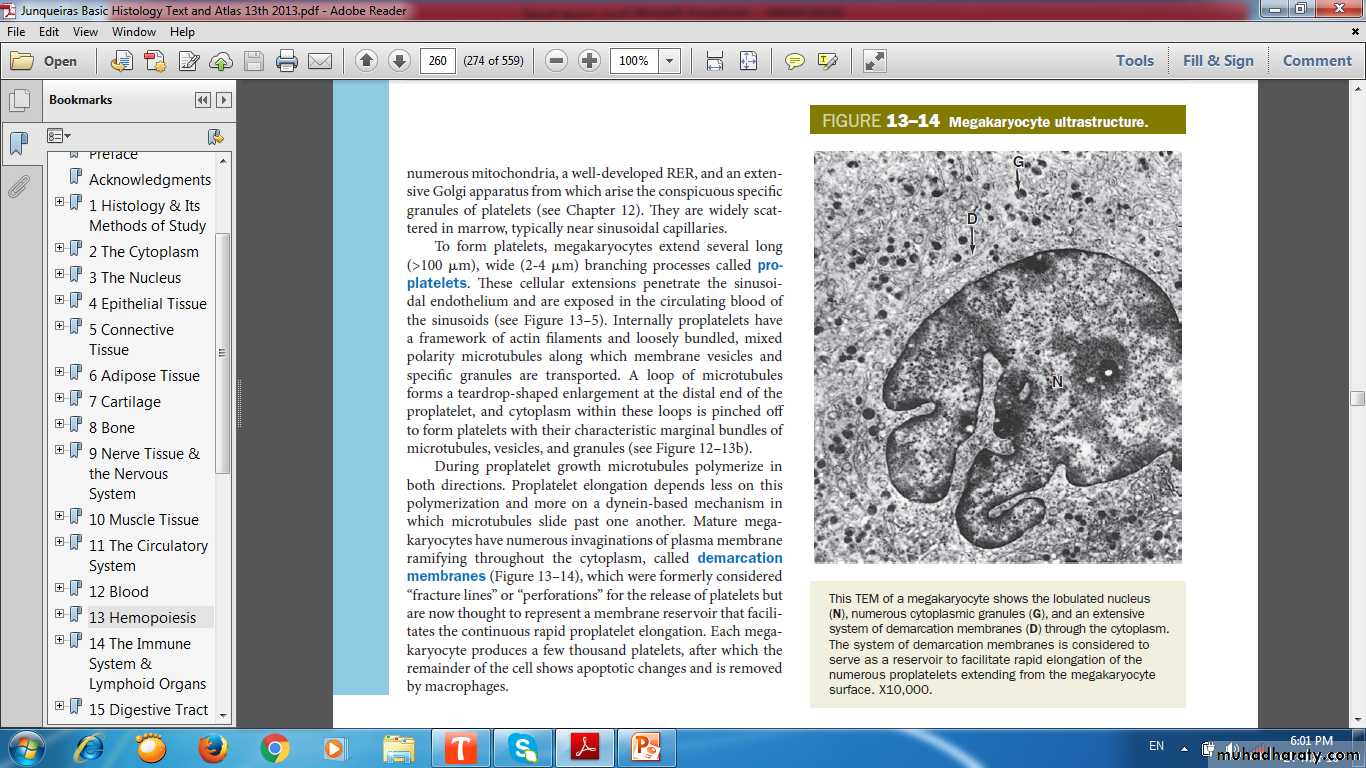
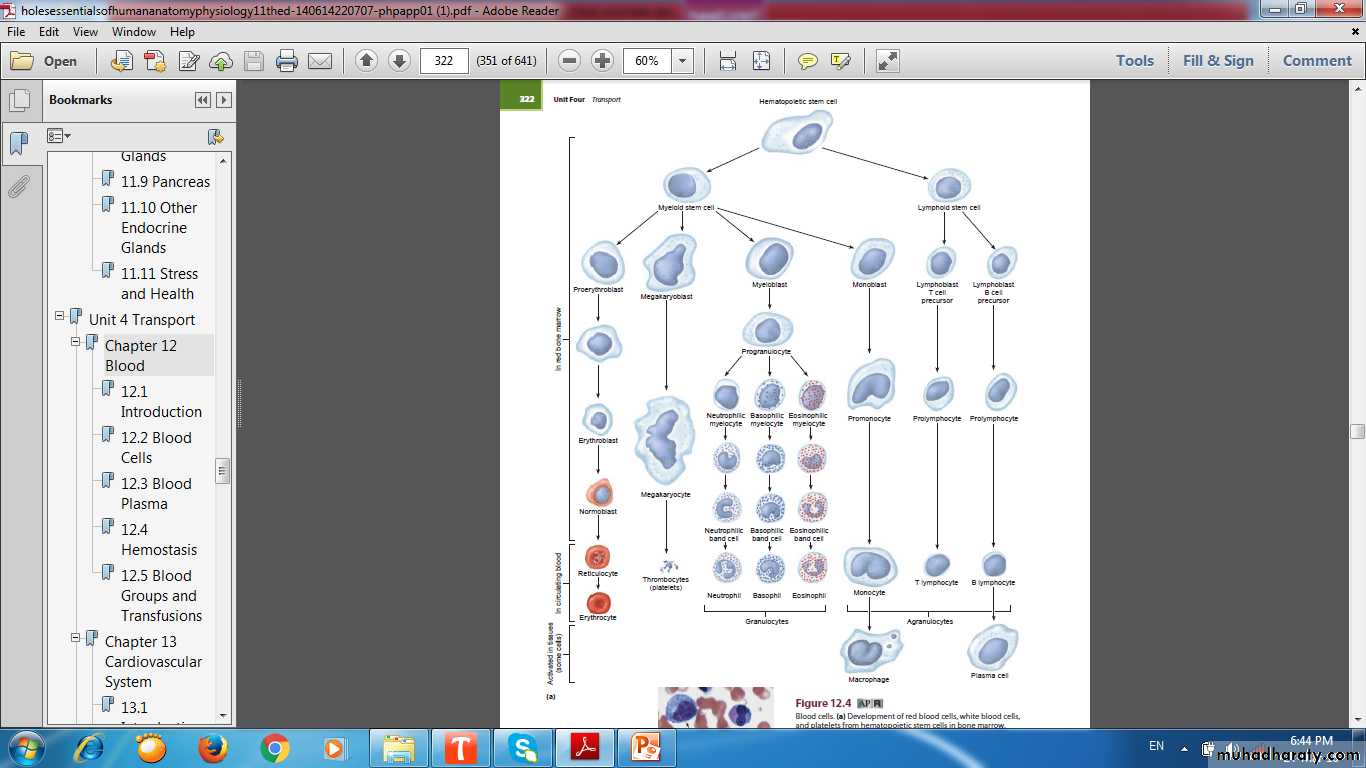
Hemopoiesis (Hematopoiesis)(Blood Formation)
Hemopoiesis (Gr. haima , blood + poiesis , a making) include:
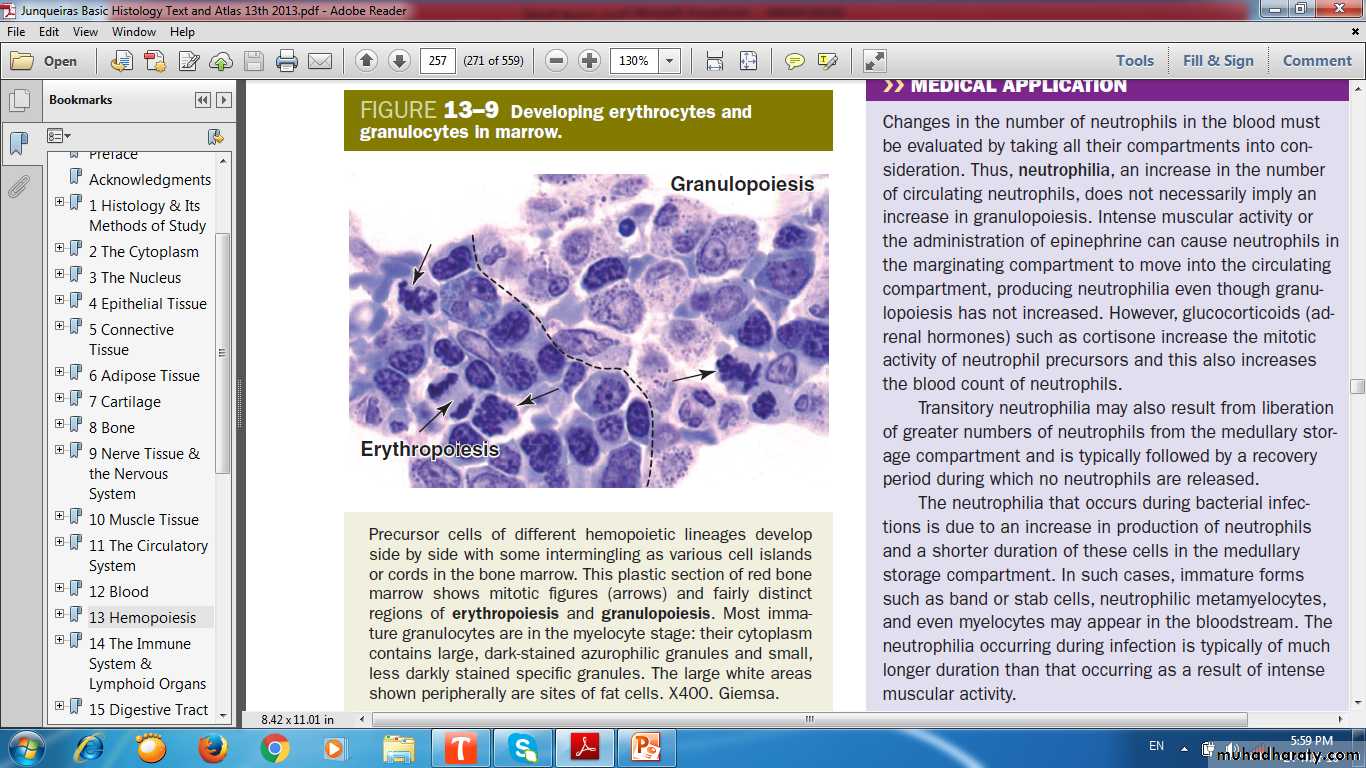
ErythropoiesisLeukopoiesis
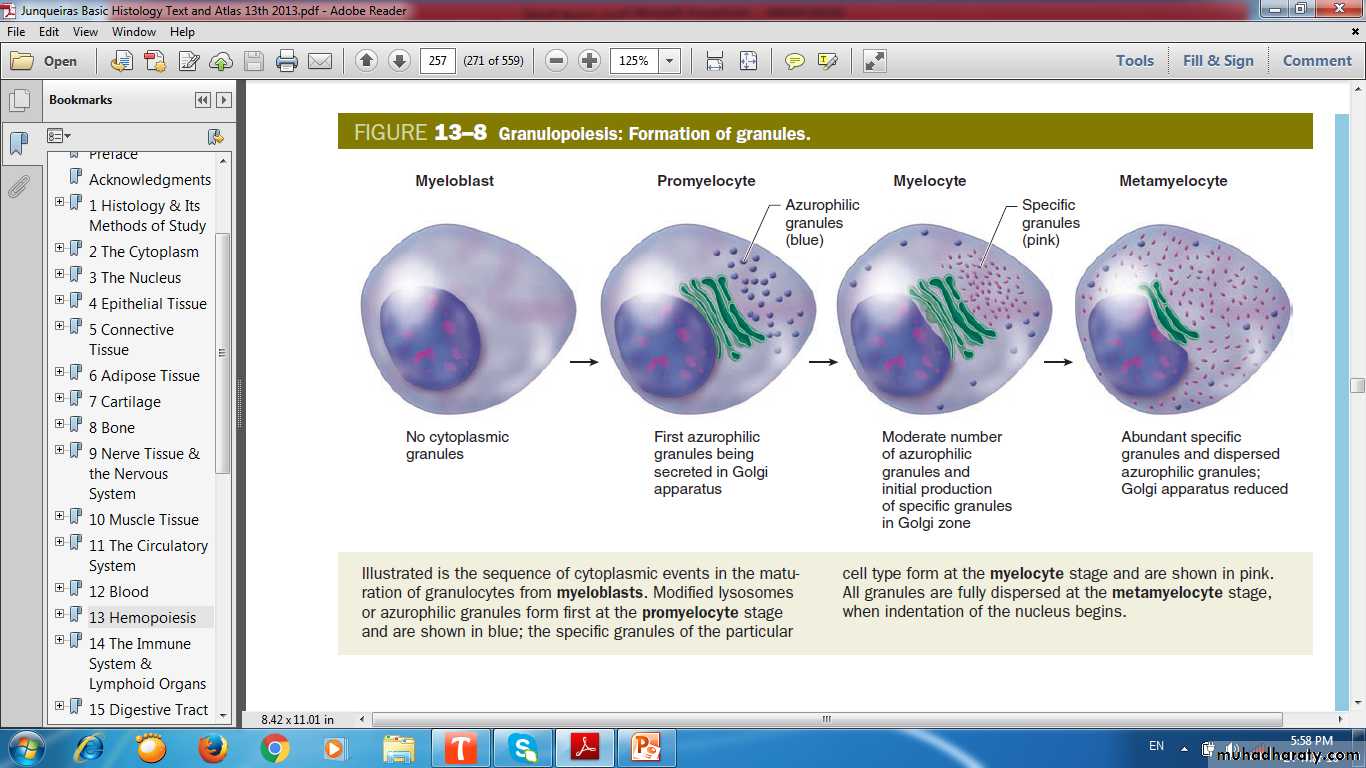
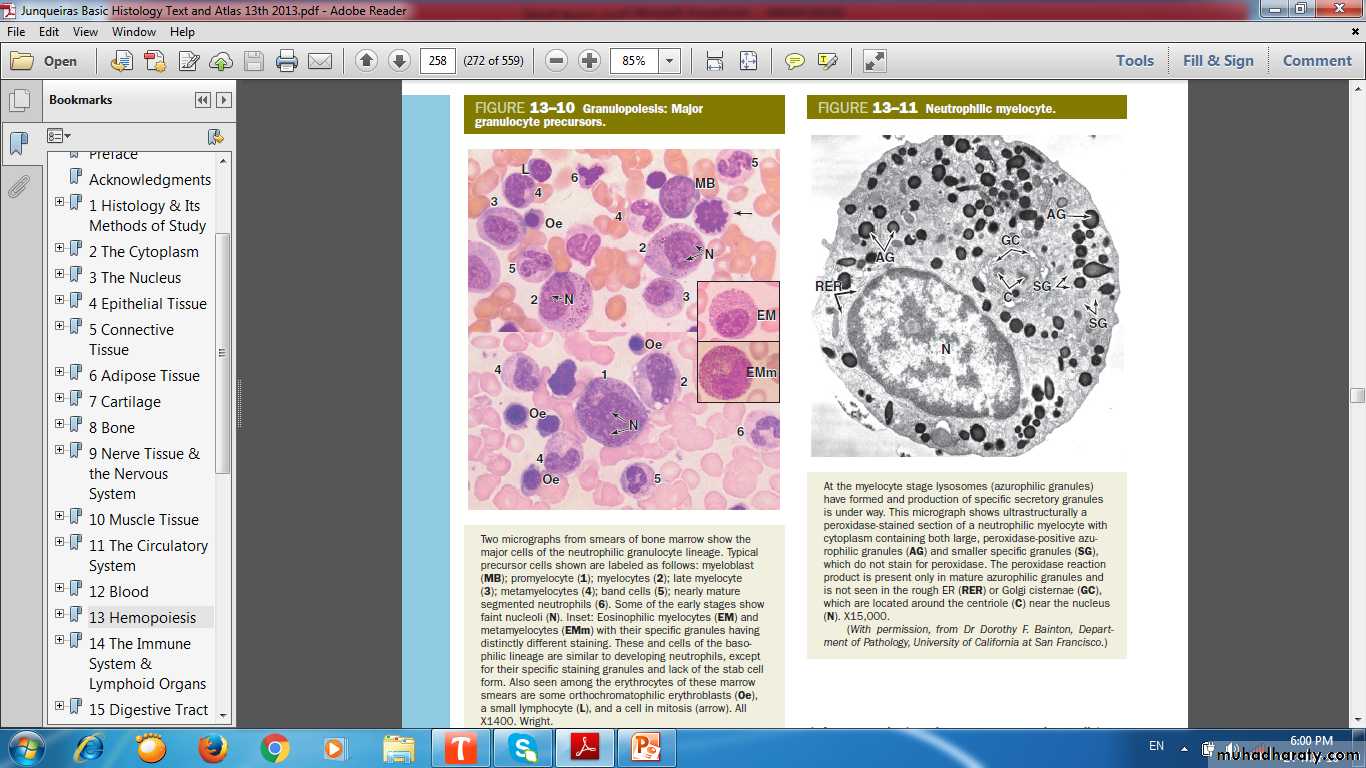
Granulopoiesis
Monocytopoiesis
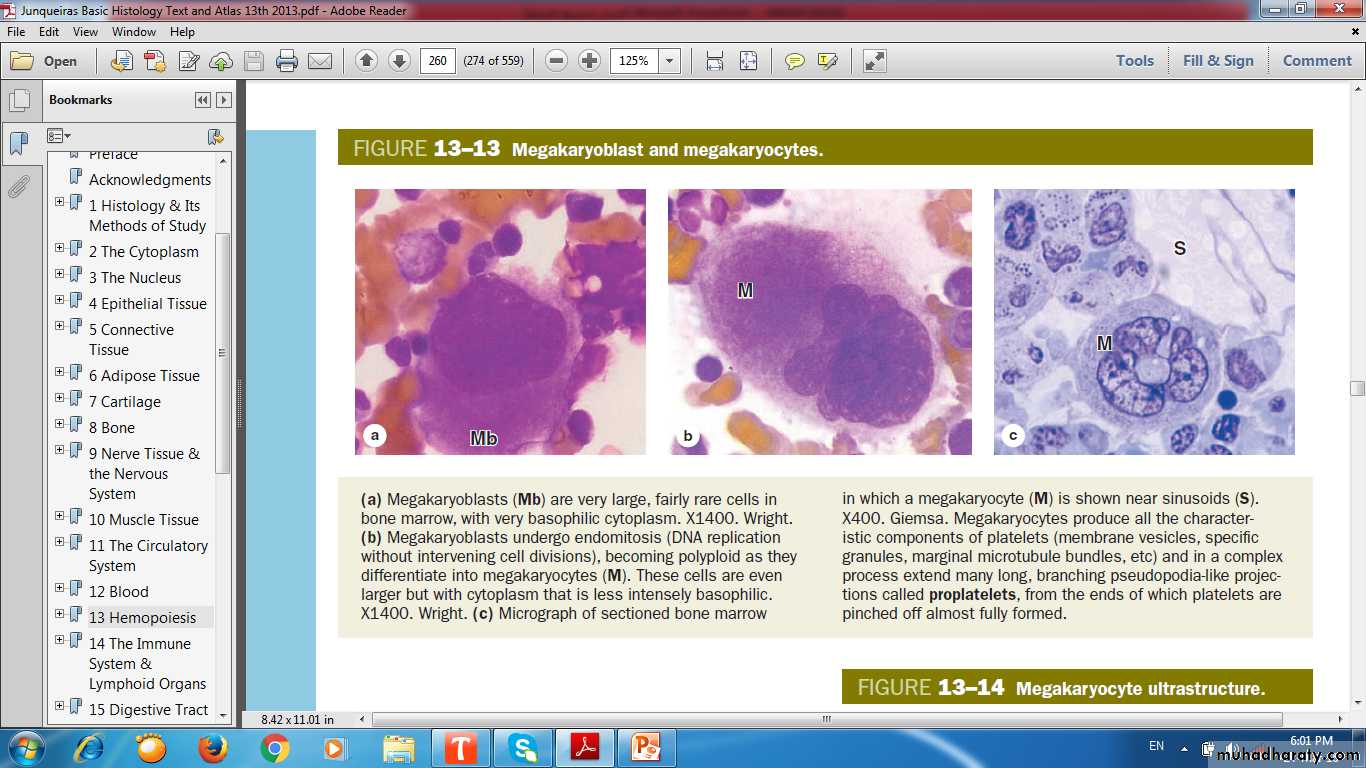
Thrombopoiesis
Lymphopoiesis
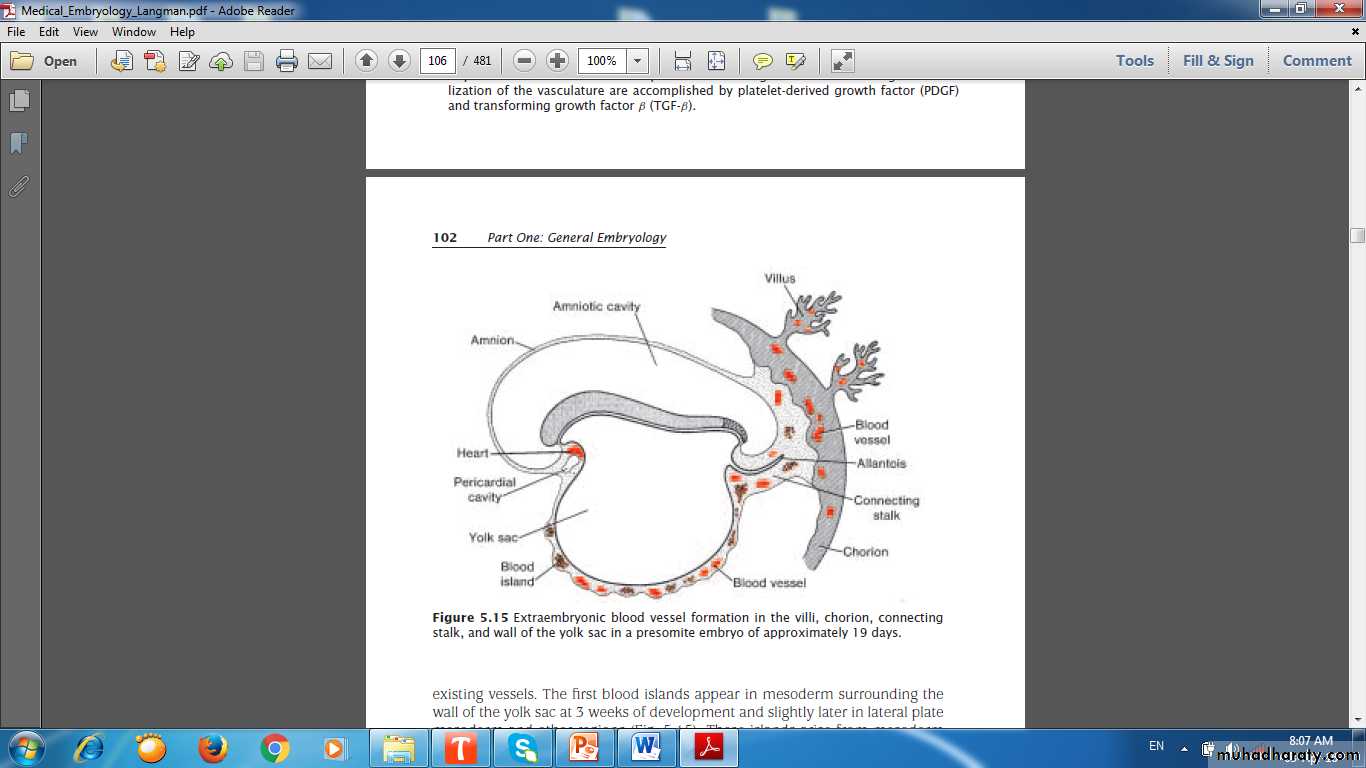
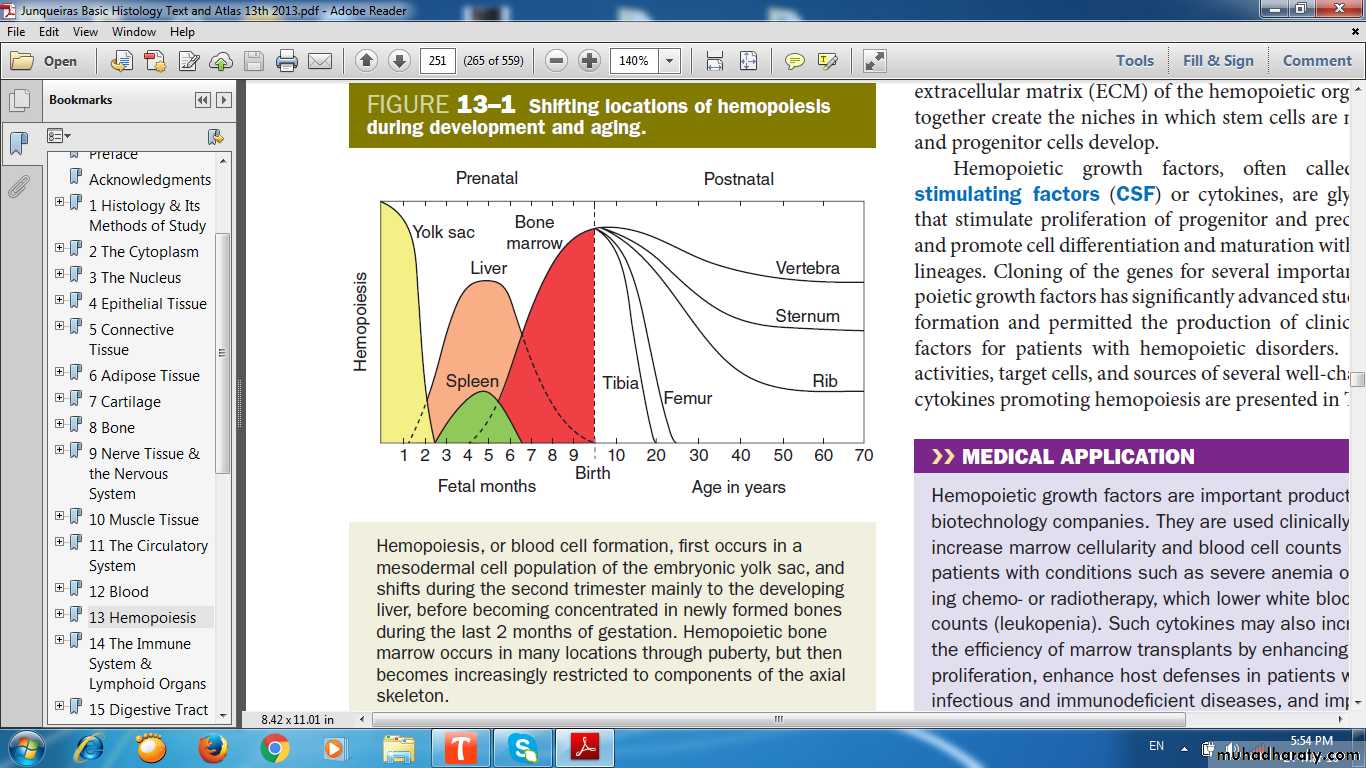
Hemopoiesis Initiated in Early Embryonic Development & Continue.
• Yolk-sac phase.• Hepatic phase.
• Bone marrow phase.
1
2
3
1
2
3
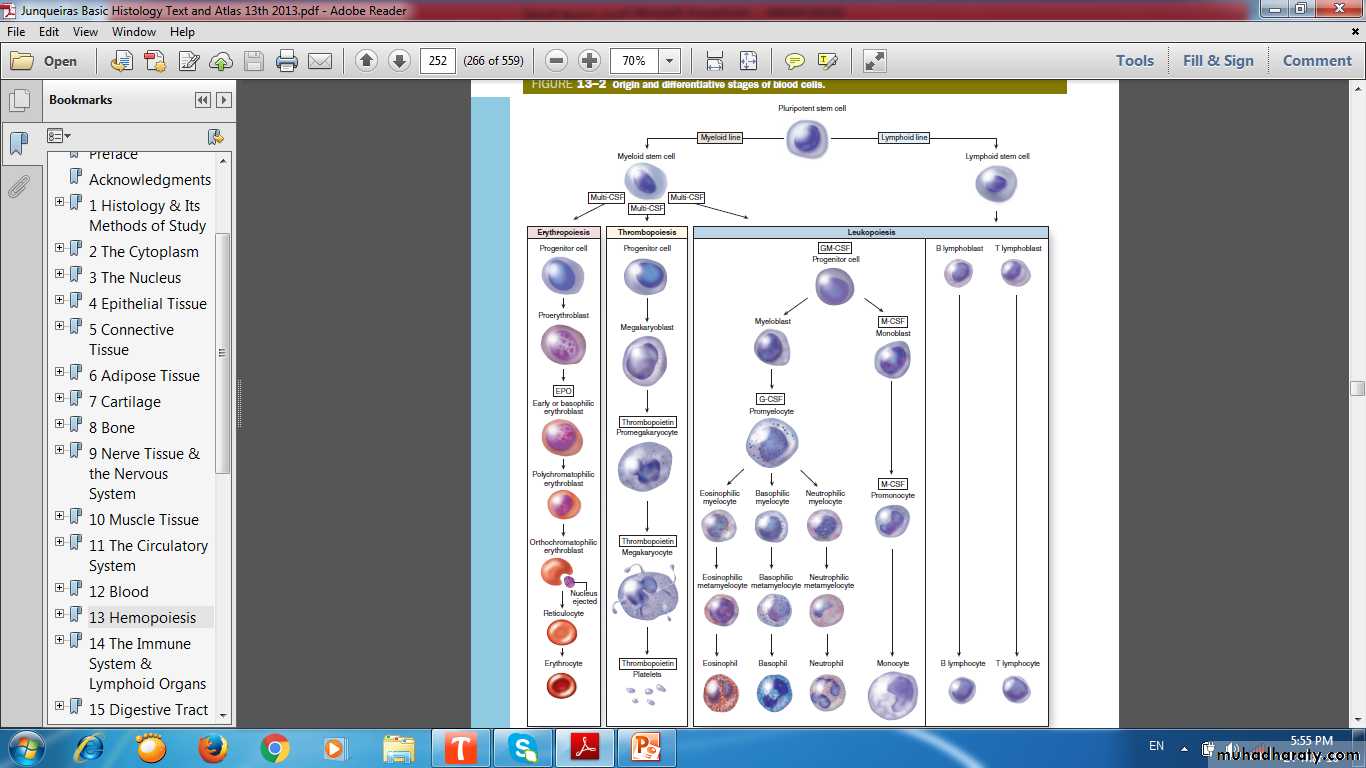
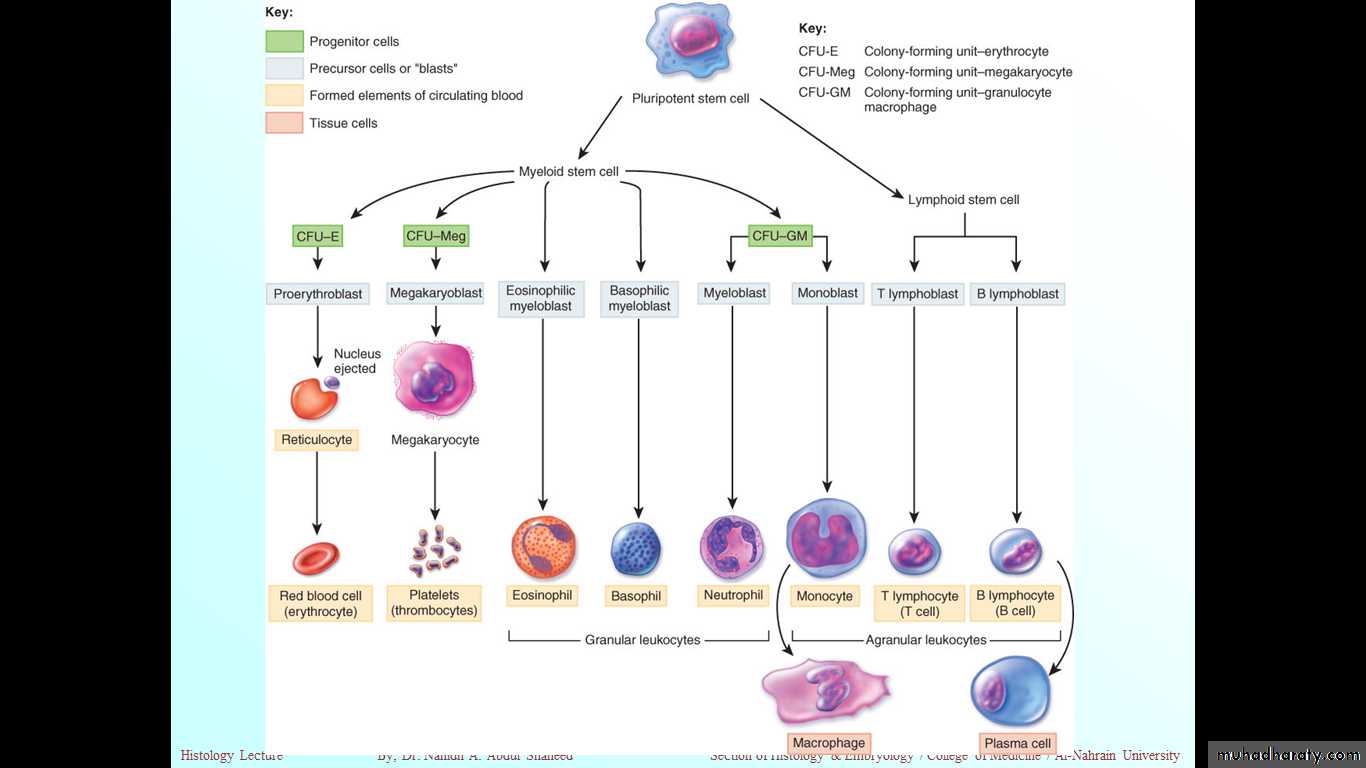
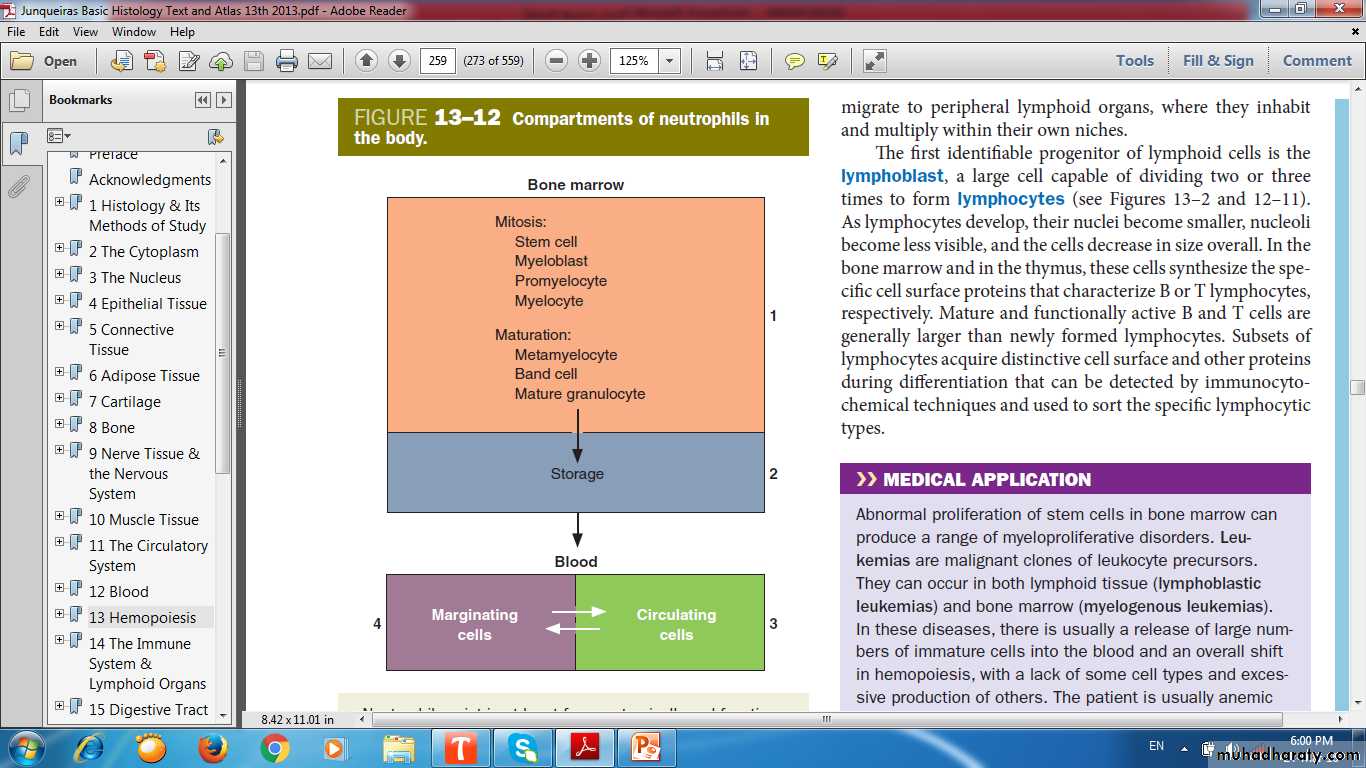
Hemopoietic Stem Cells
pluripotent stem cell single major type of stem cells in the bone marrow that can give rise to all the blood cell types .pluripotent stem cell potentials (committed to produce specific blood cells):
Lymphoid cells (Progenitor & Precursor)CFU
Myeloid cells (Progenitor & Precursor)CFU
Colony-Forming Units (CFUs), The progenitor cells for blood cells
Erythroid lineage of CFU-erythrocytes (CFU-E).
Thrombocytic lineage of CFU-megakaryocytes (CFU-Meg).
Granulocyte-monocyte lineage of CFU-granulocytes monocytes (CFU-GM)
Lymphoid lineage of CFU-lymphocytes of all types (CFU-L).
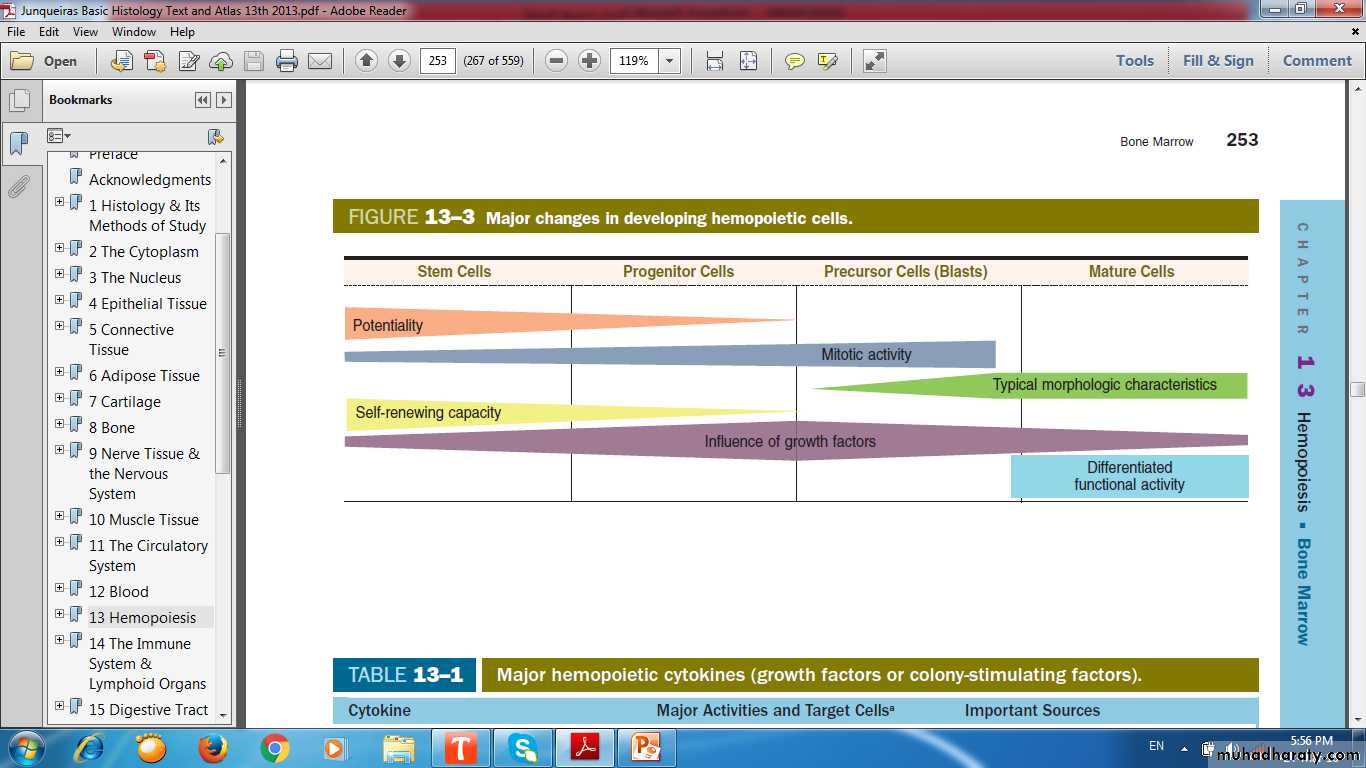
Hemopoietic cells
POTENTIALITY.SELF RENEWING.
MITOTIC ACTIVITY.
INFLUENCE BY GROWTH FACTORS.
TYPICAL DIFFERENTIATION.
TYPICAL FUNCTION.
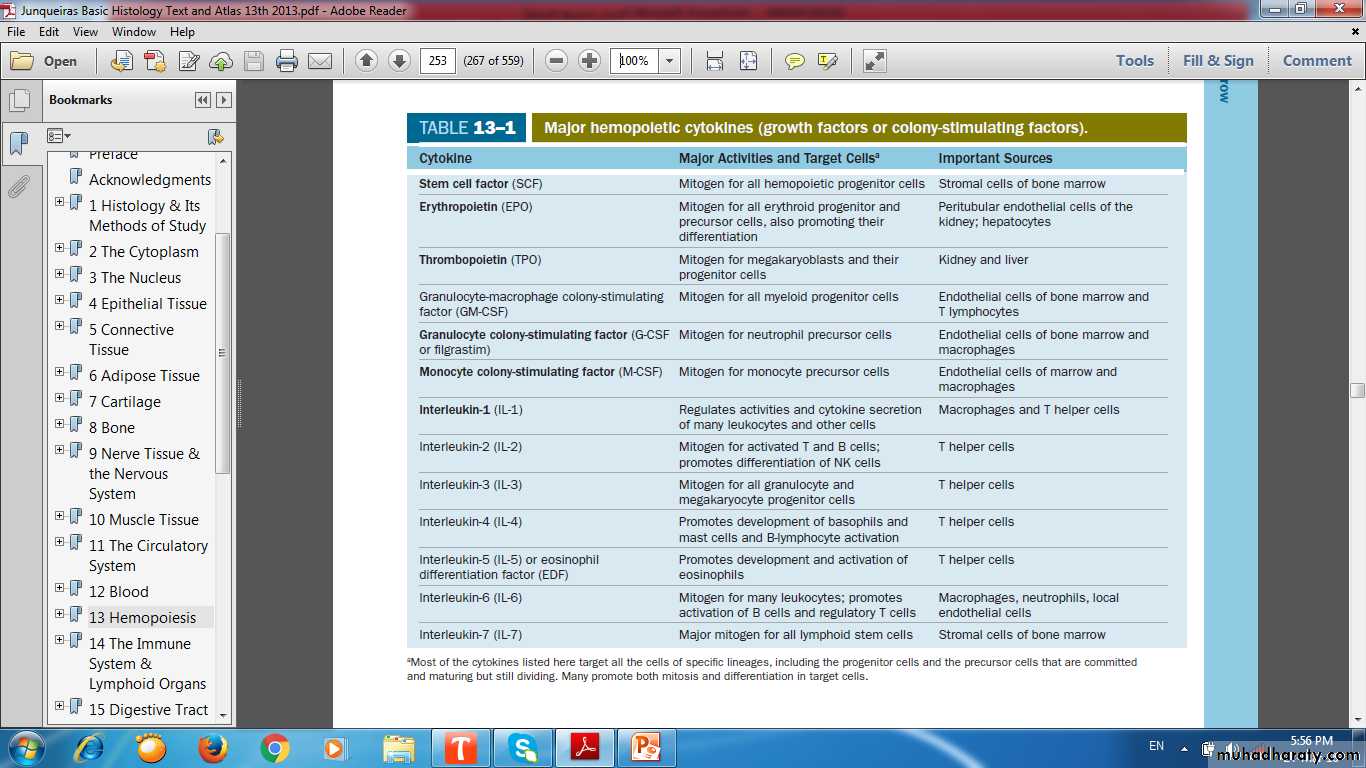
Colony Stimulating Factors CFU orGrowth factors
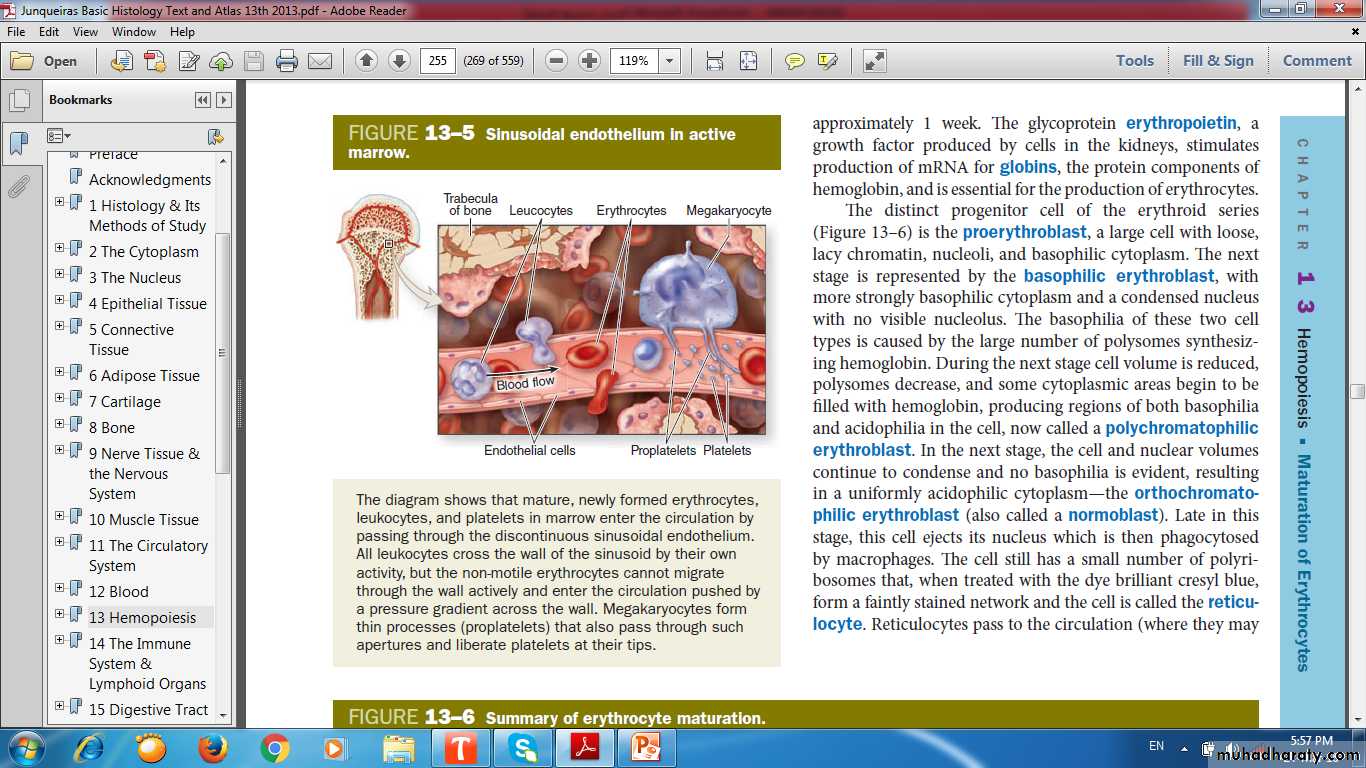
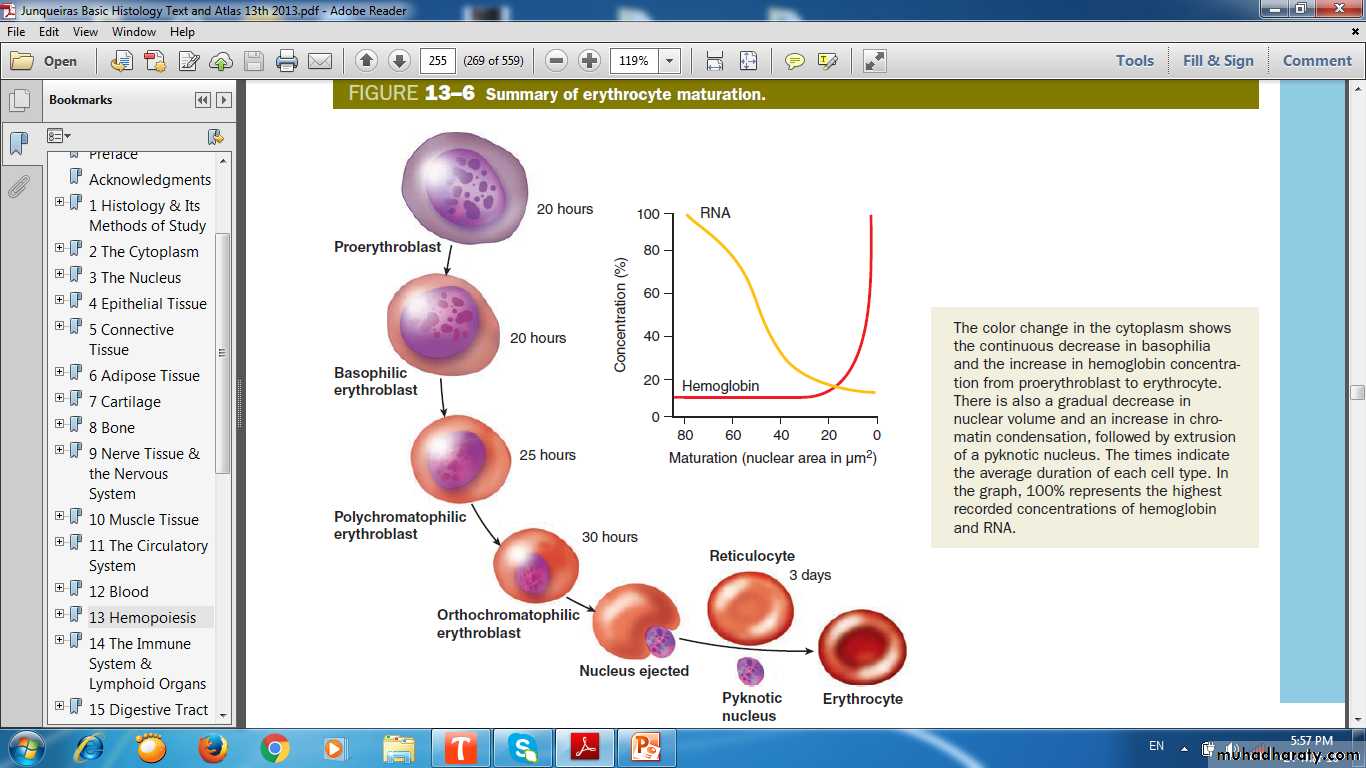
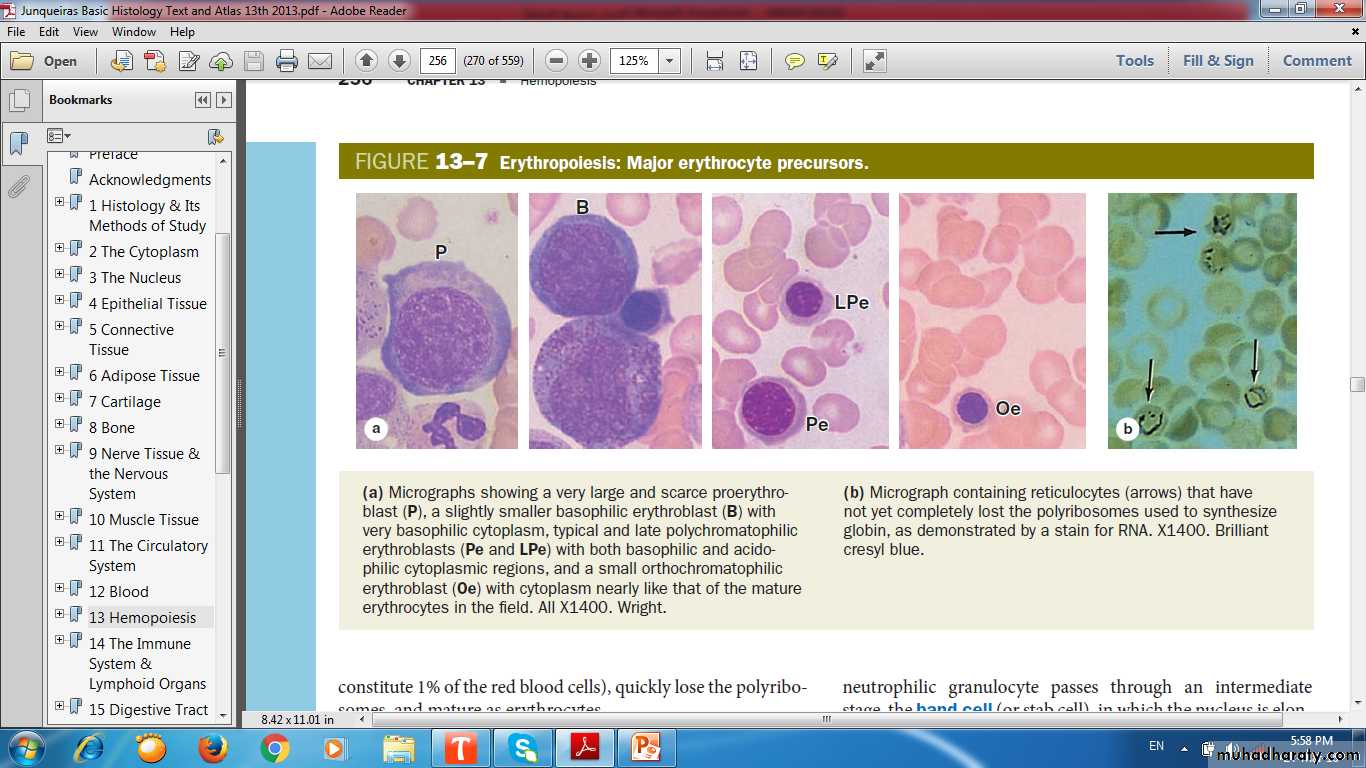
Cytoplasmic transition from RNA- rich to hemoglobin-filled.
Proerythroblasts
Erythroblasts
Basophilic
Polychromatophilic
Orthochromatophilic