CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM HISTOLOGY
HEART ARTERIESVEINSCAPILLARIES100,000 - 150,000 Km
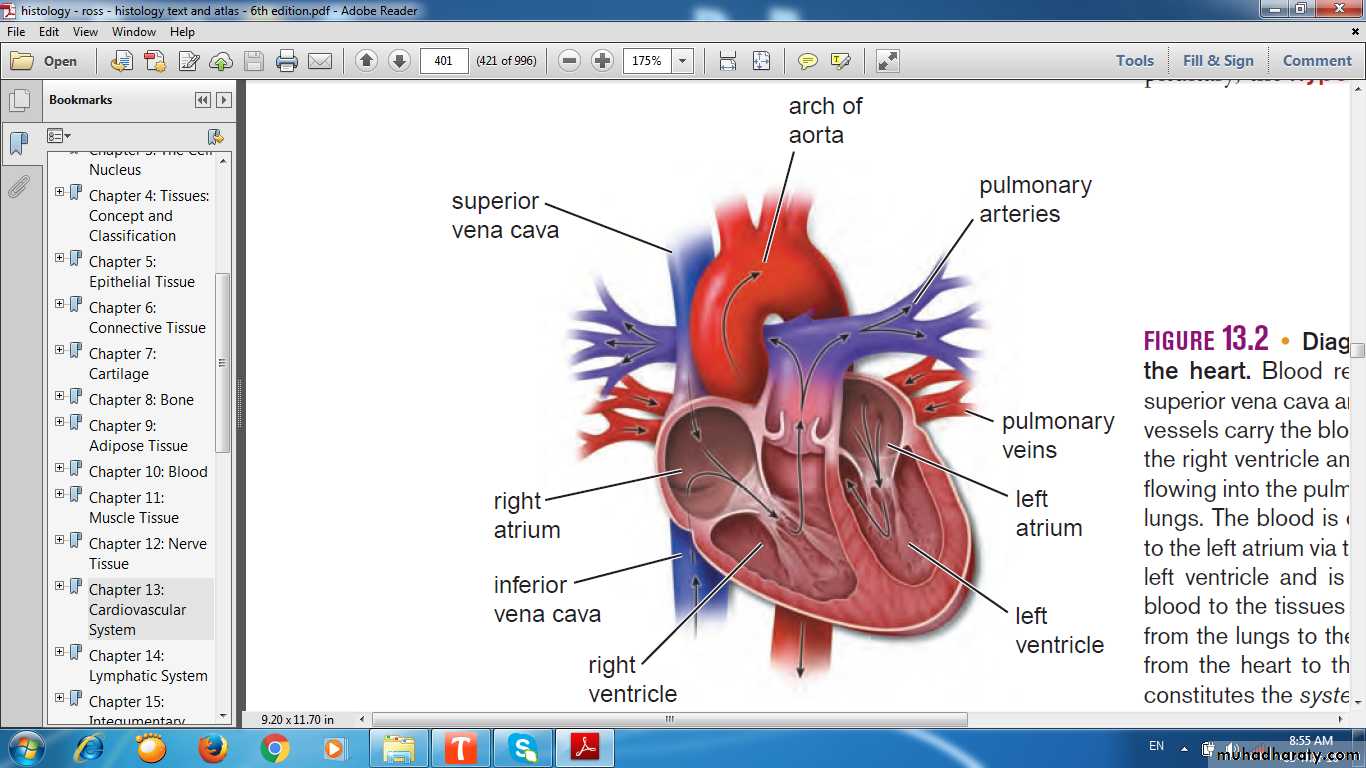
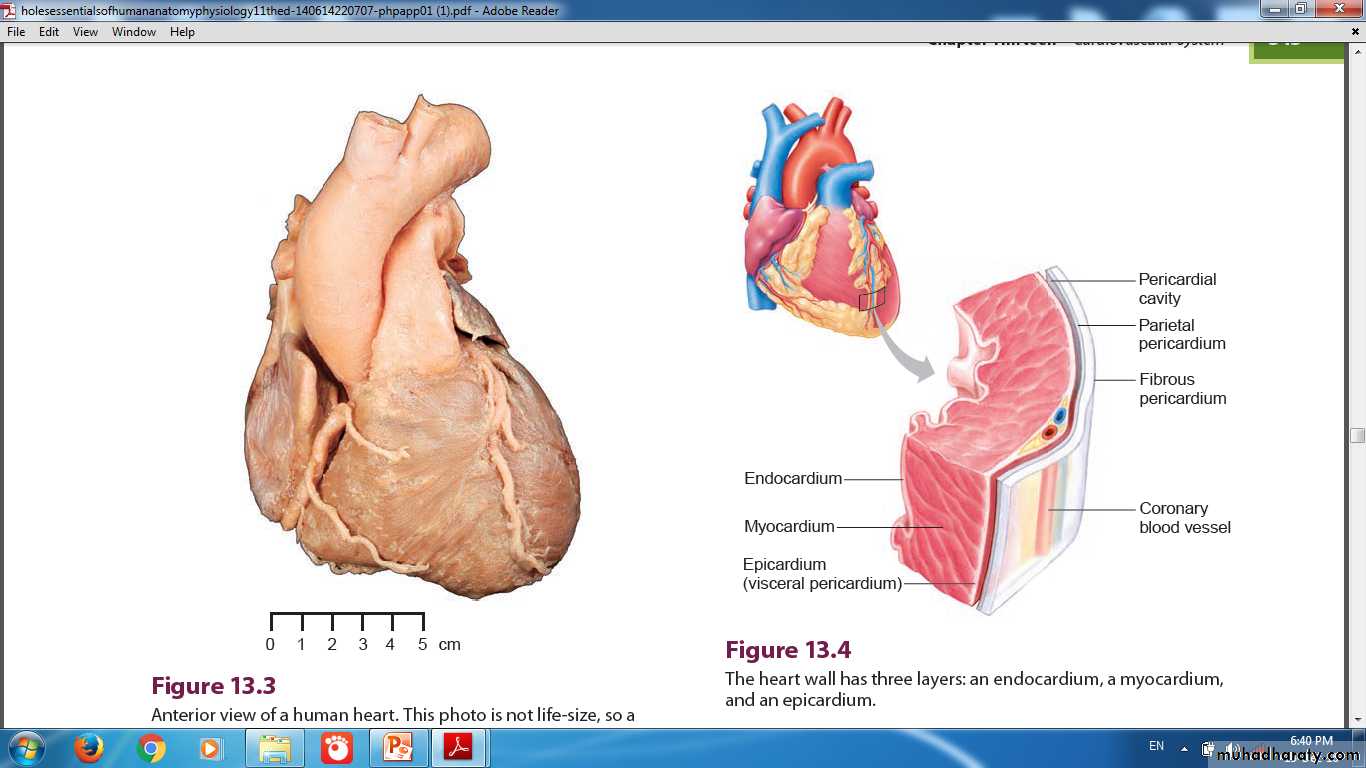
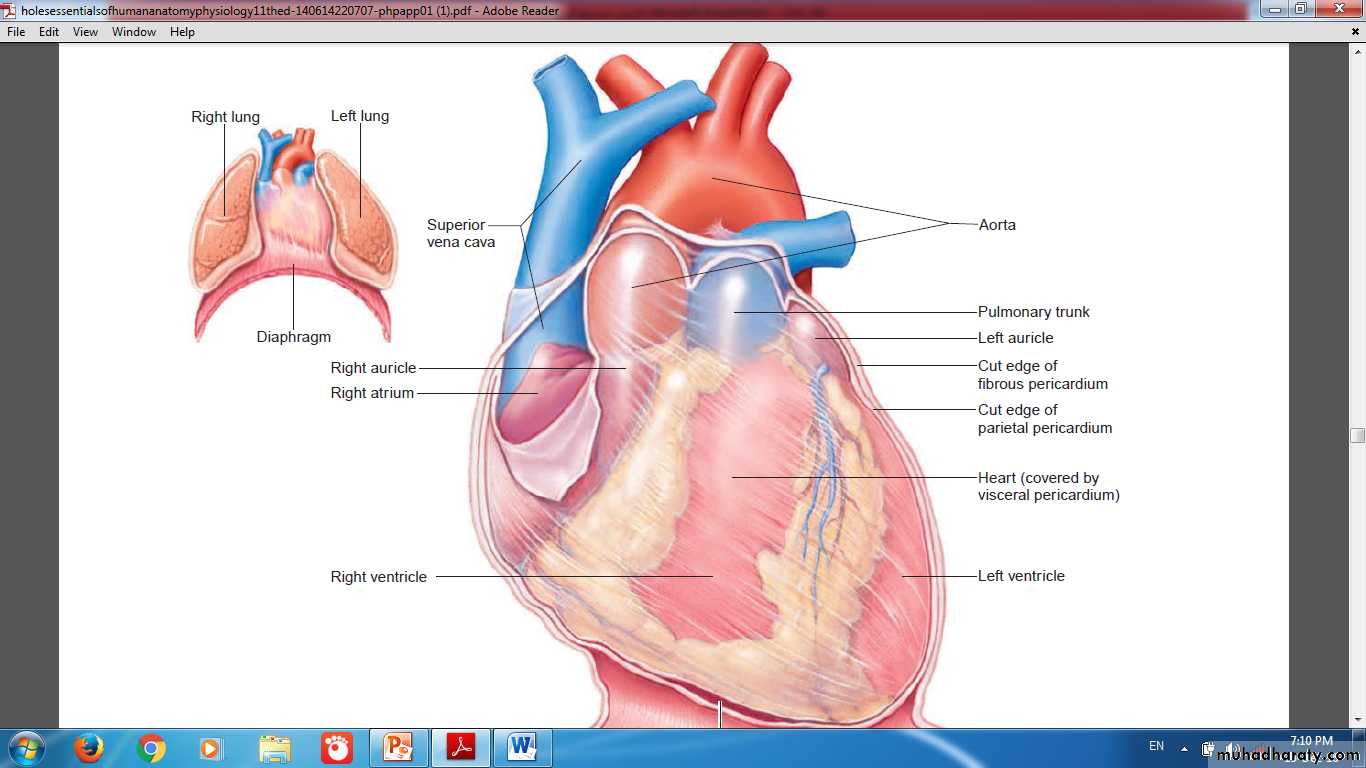
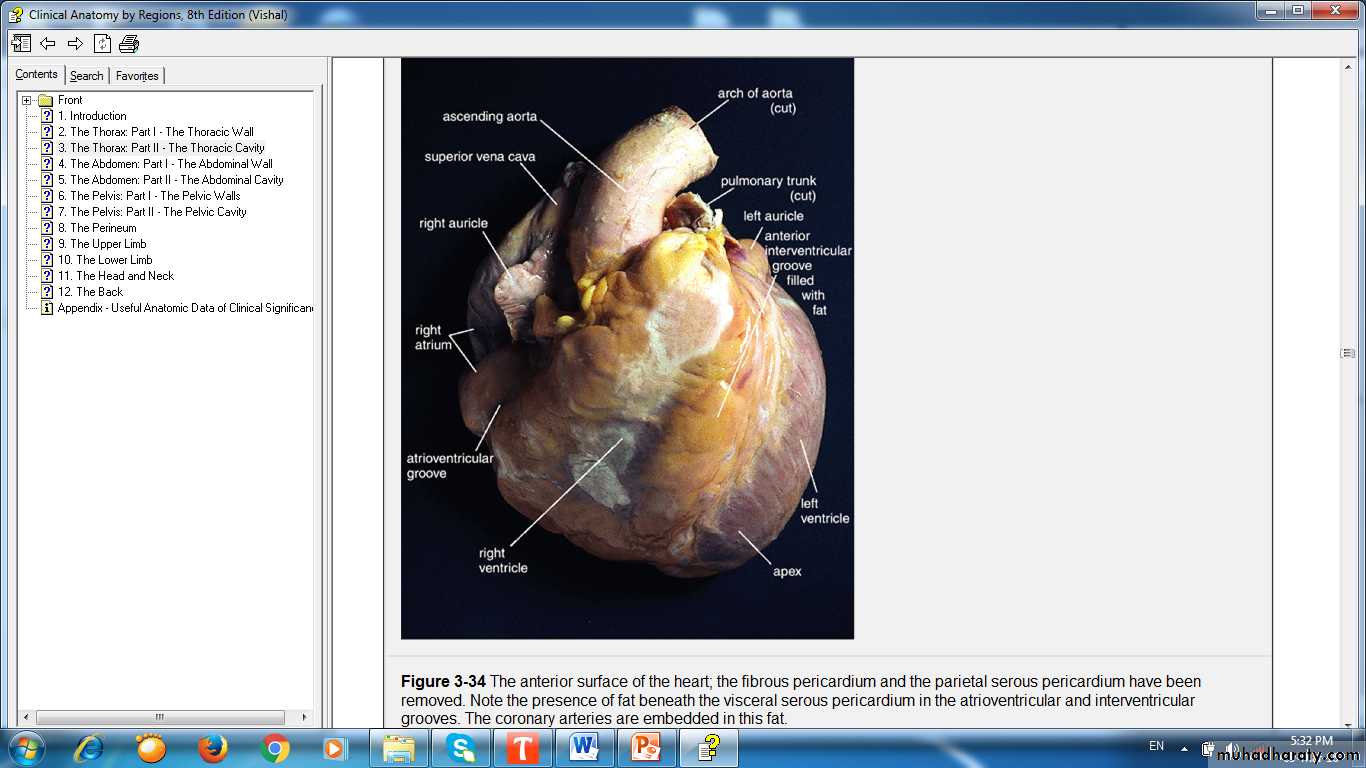
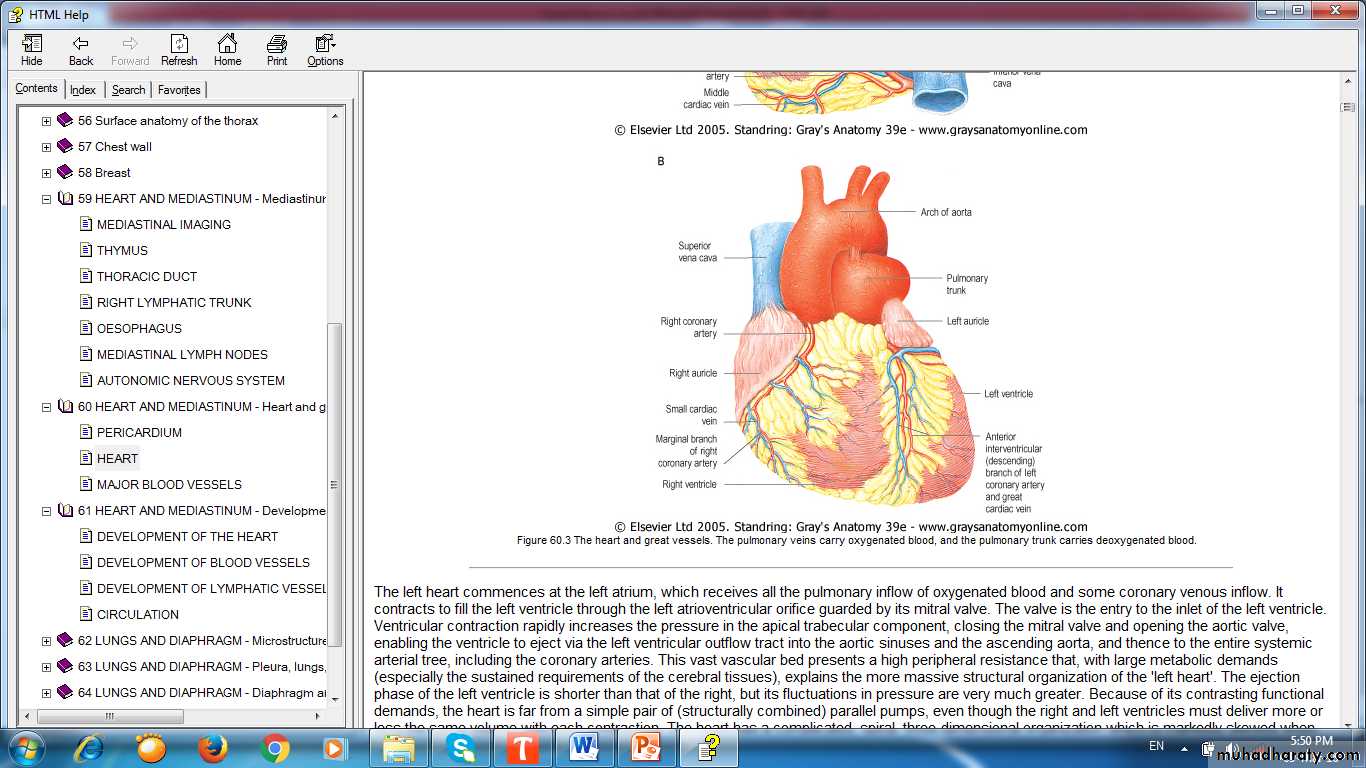
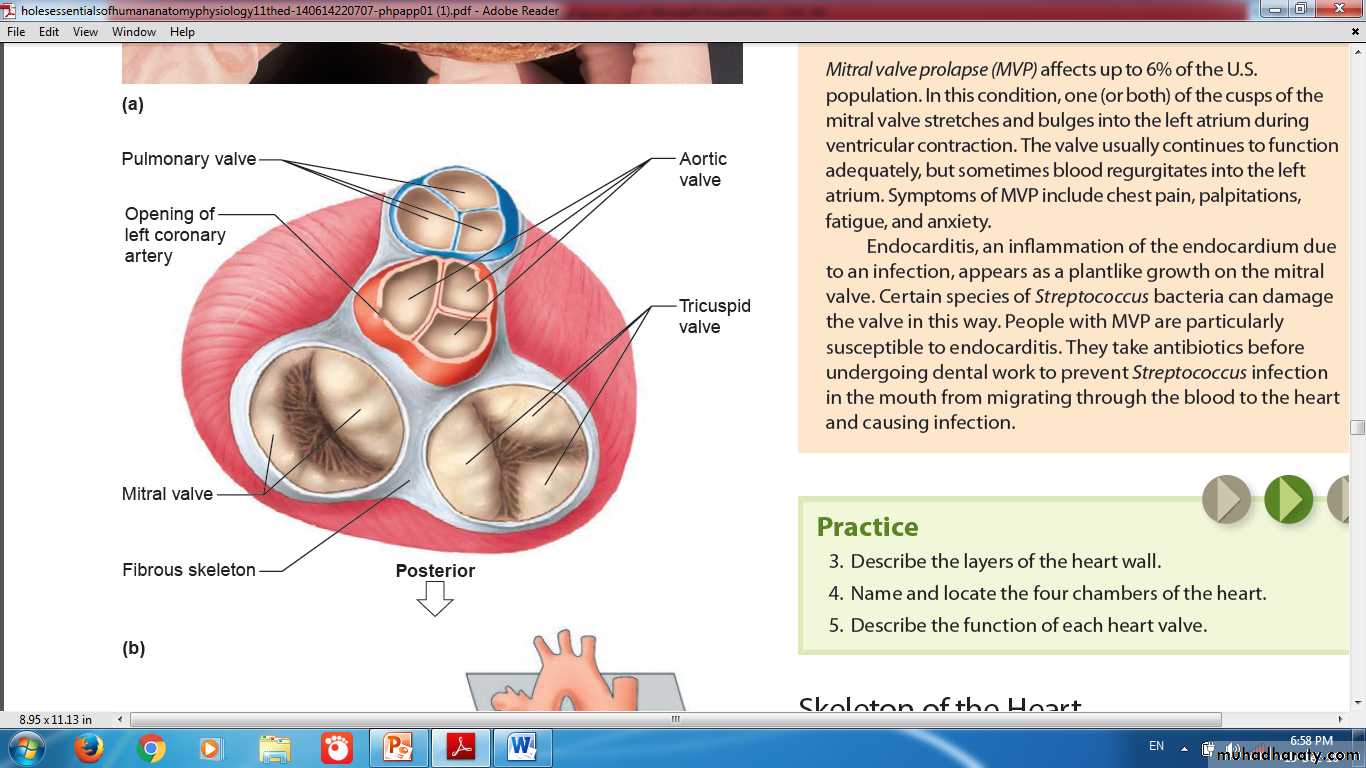
HEARTIs a modified blood vessel, consist of the following layers:
EpicardiumMyocardium
Endocardium
walls of heart chambers consist of three layers:
External EpicardiumMiddle Myocardium
Internal Endocardium
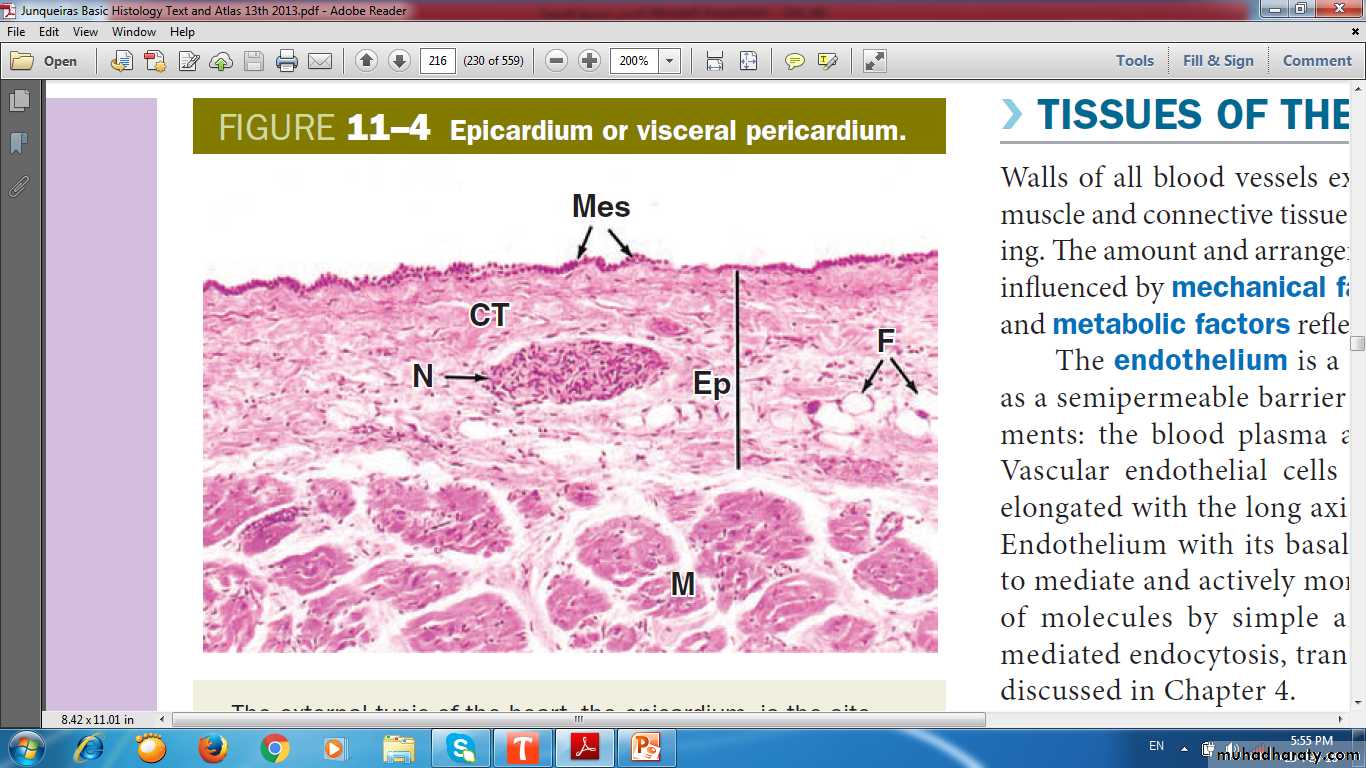
Epicardium (visceral pericardium)
Adipose tissue in Epicardium
Blood vessels in Epicardium
EPICARDIUM
FATCONNECTIVE TISSUE
NERVE
MYOCARDIUM
MESOTHELIUM
Epicardium
Myocardium
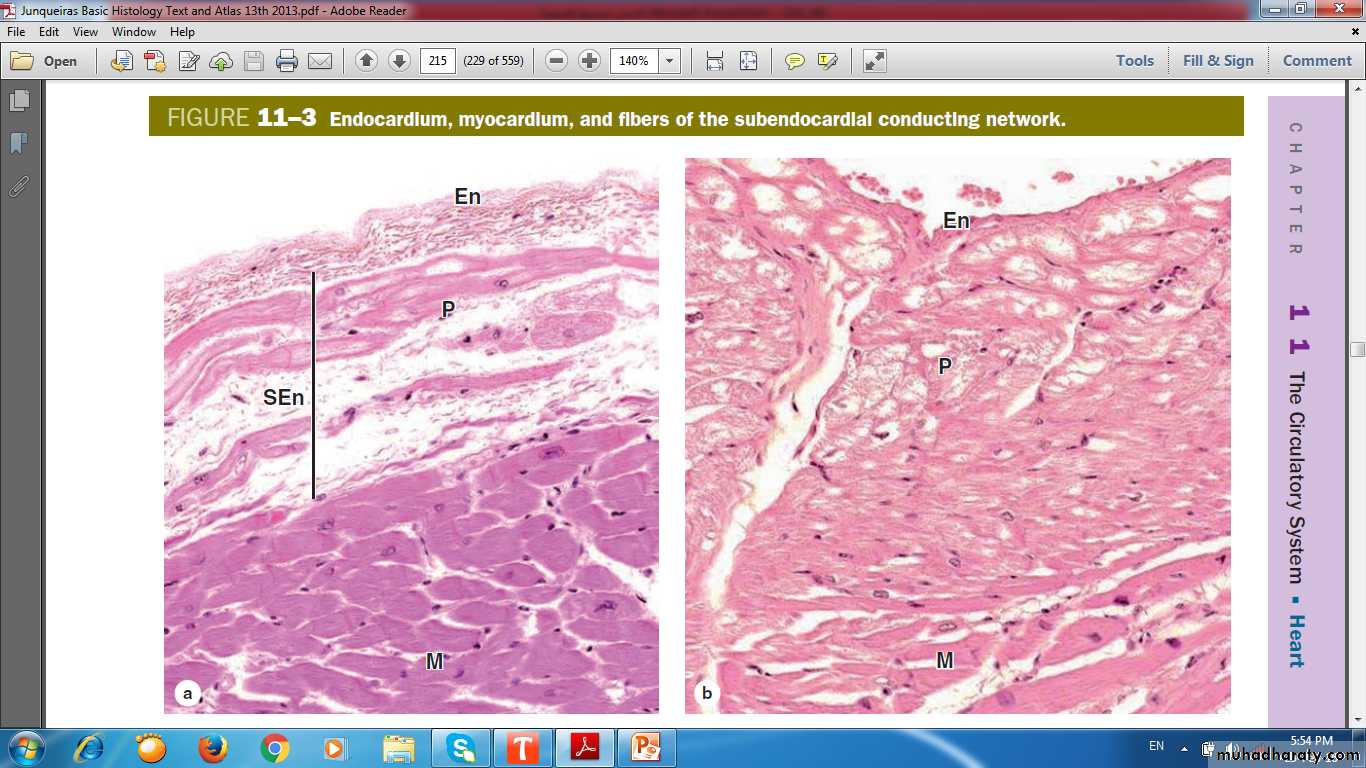
EndocardiumEndothelium & supporting connective tissue
Middle myoelastic layer
Deep layer called the subendocardial layer
ENDOCARDIUM
PURKINJEMYOCARDIUM
Ventricle
Atrium
ENDOCARDIUM
PURKINJE
MYOCARDIUM
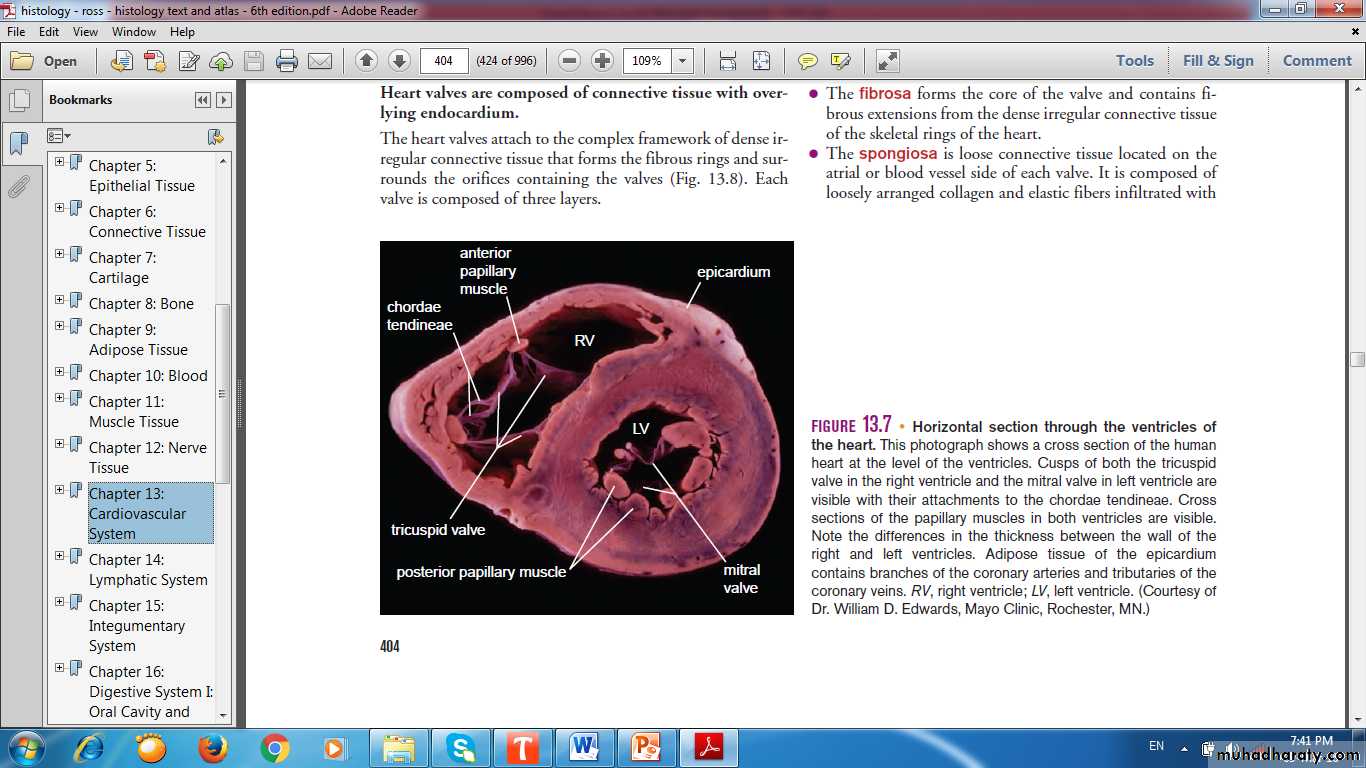
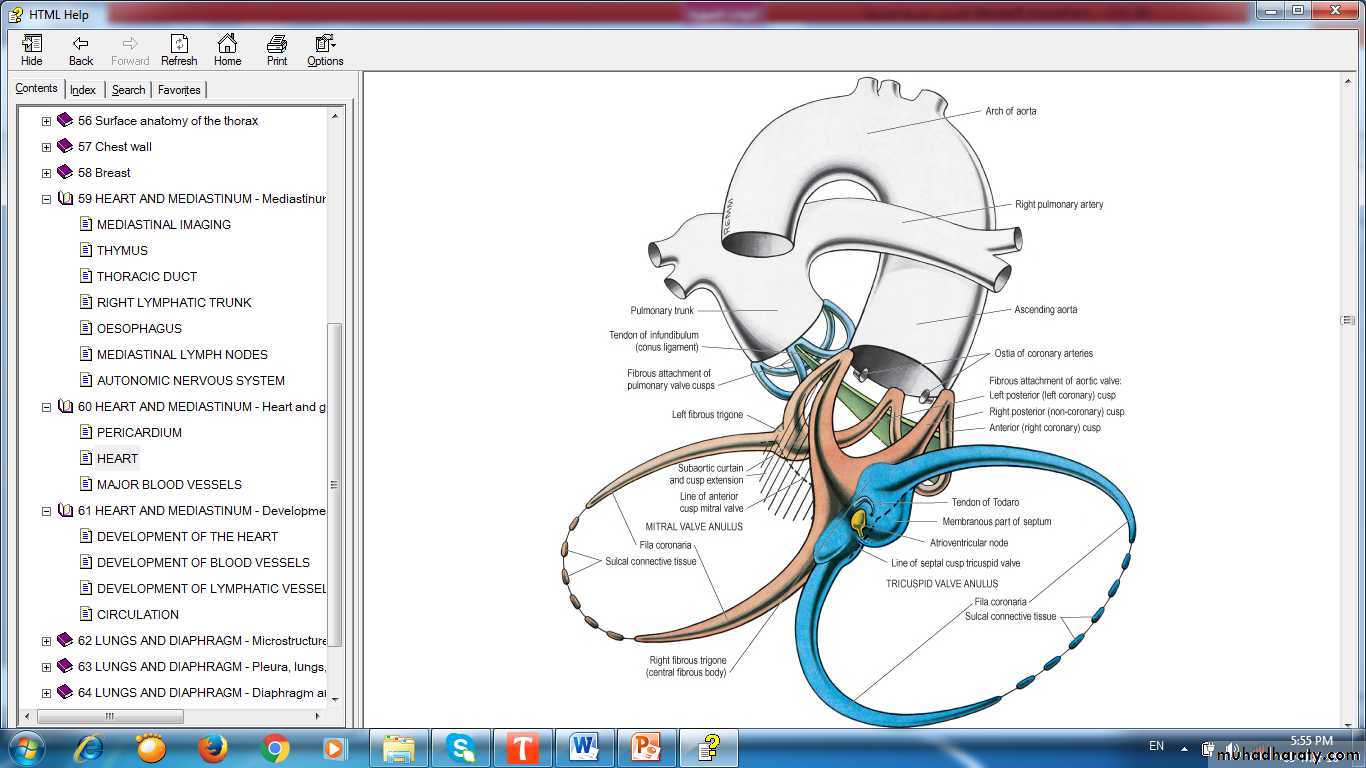
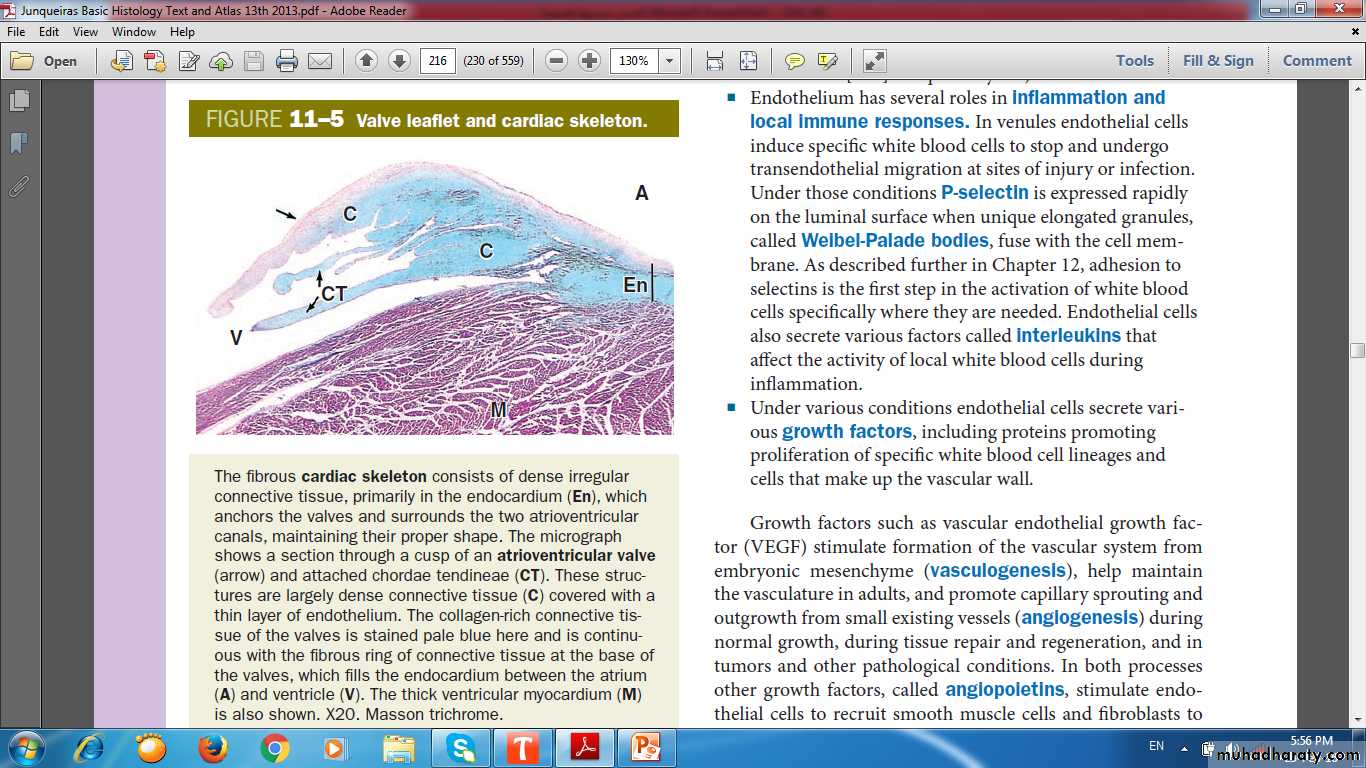
Fibrous skeleton of the heart(Dense fibrous connective tissue)
Endothelium
Connective tissueEndocardium
Atrium
Ventricle
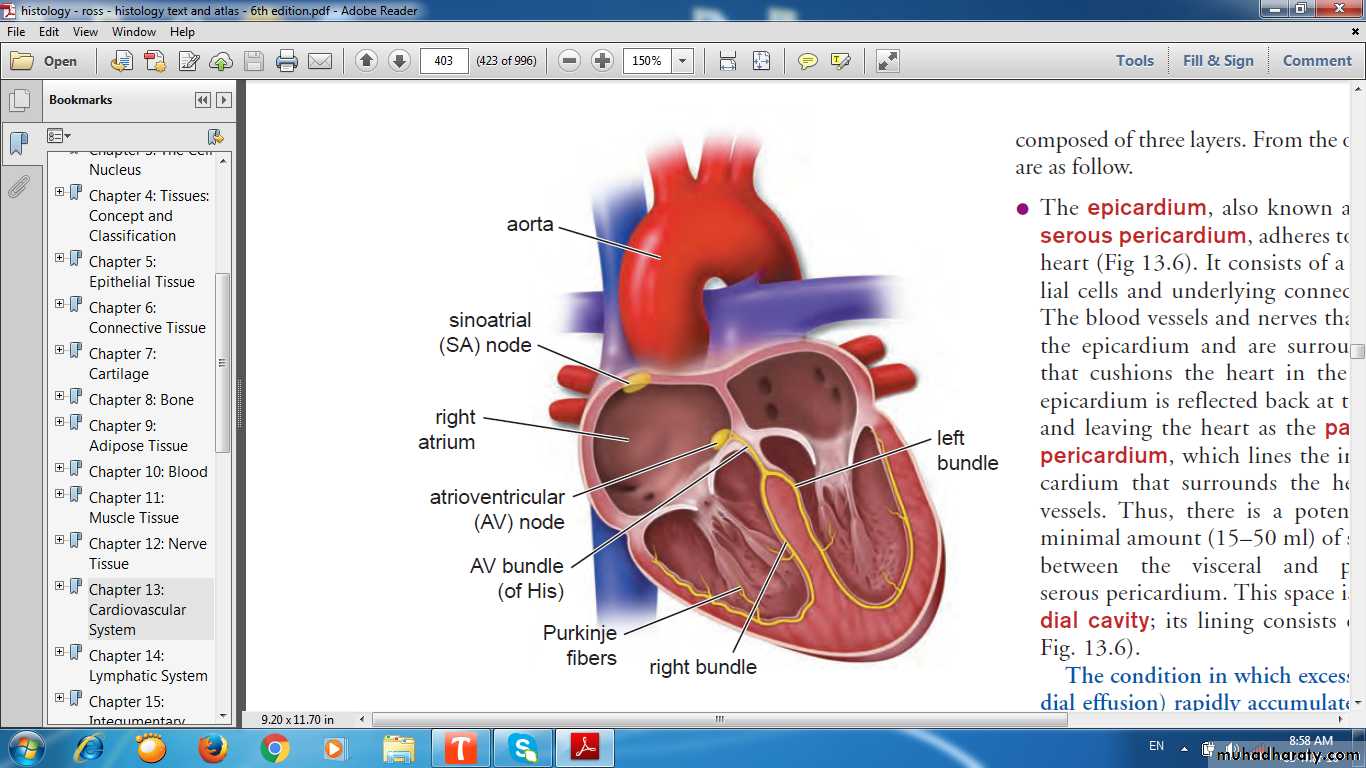
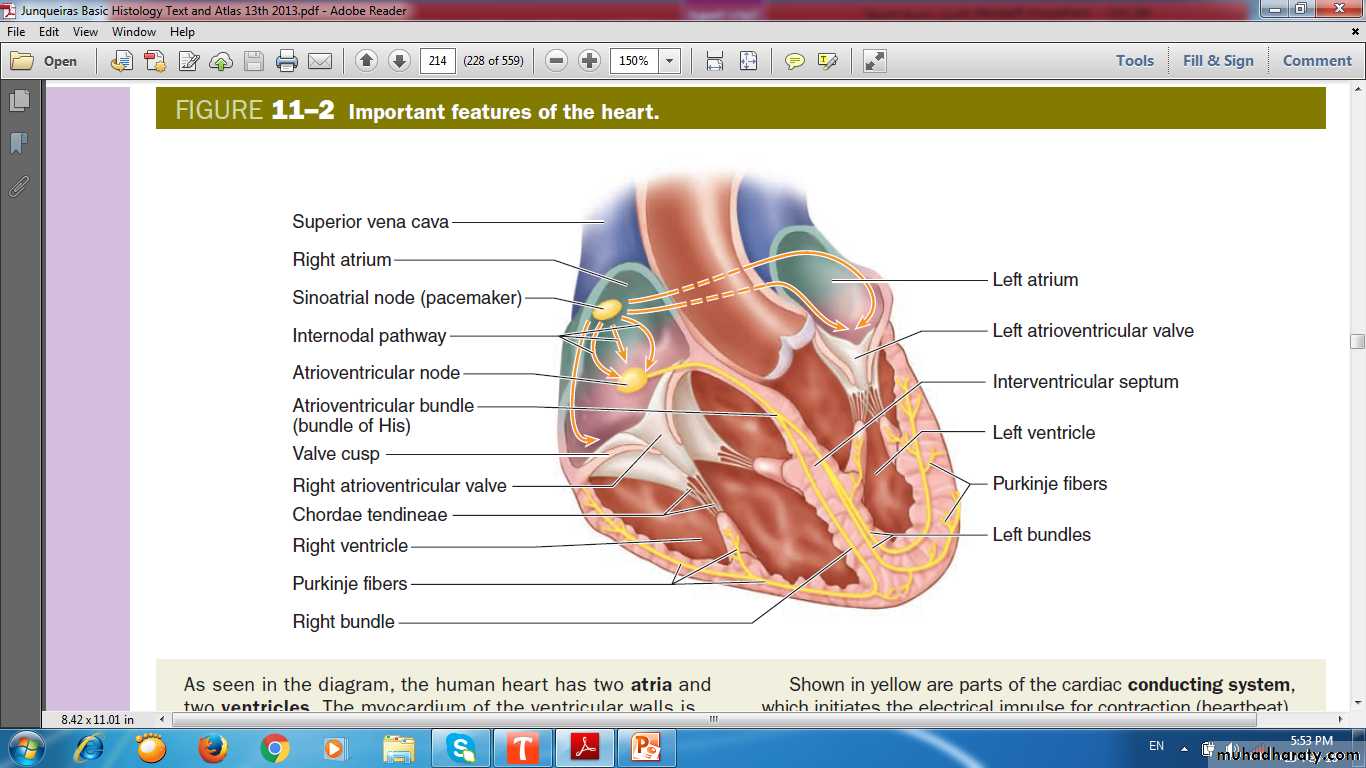
Conductive system of the heart
Sinoatrial (SA) node (pacemaker)Located in the right atrial wall near the S.V.C
6- to 7-mm3
Cardiac muscle cells with smaller size, fewer myofibrils and intercalated disks.
Purkinje fibers
Pale-staining fibersLarger than the adjacent muscle fibers
Sparse, peripheral myofibrils & much glycogen
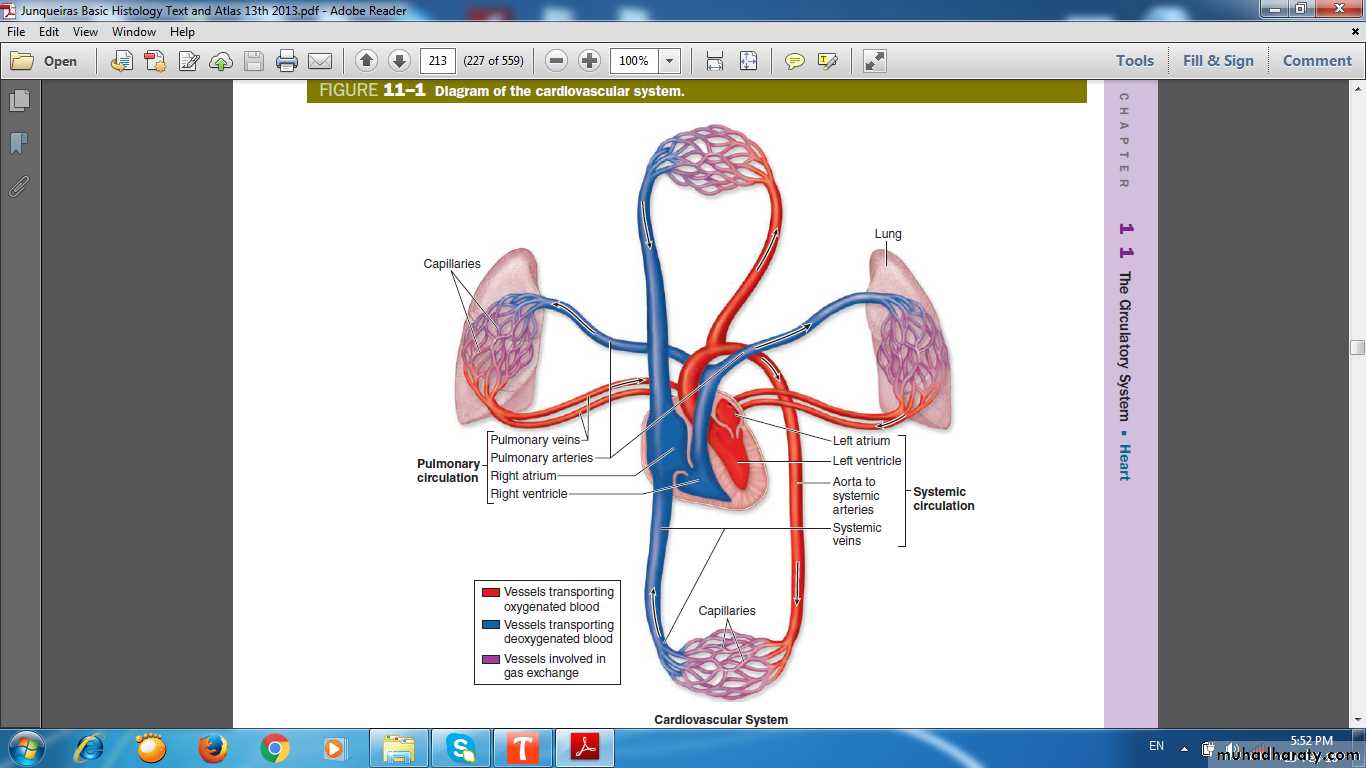
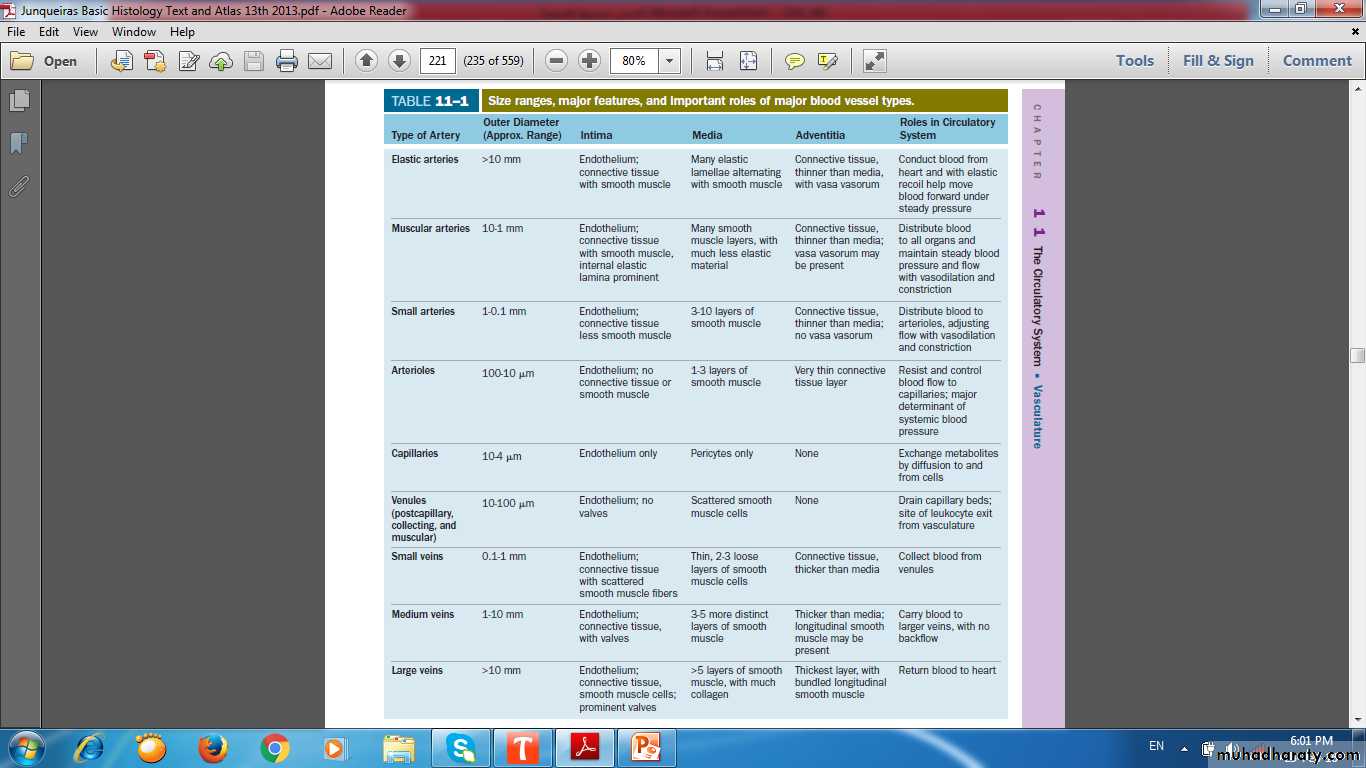
Vascular system
• Elastic Artery• Muscular Artery
• Small Artery
• Arteriole
• Capillary
• Venule
• Small vein
• Medium size vein
• Large vein
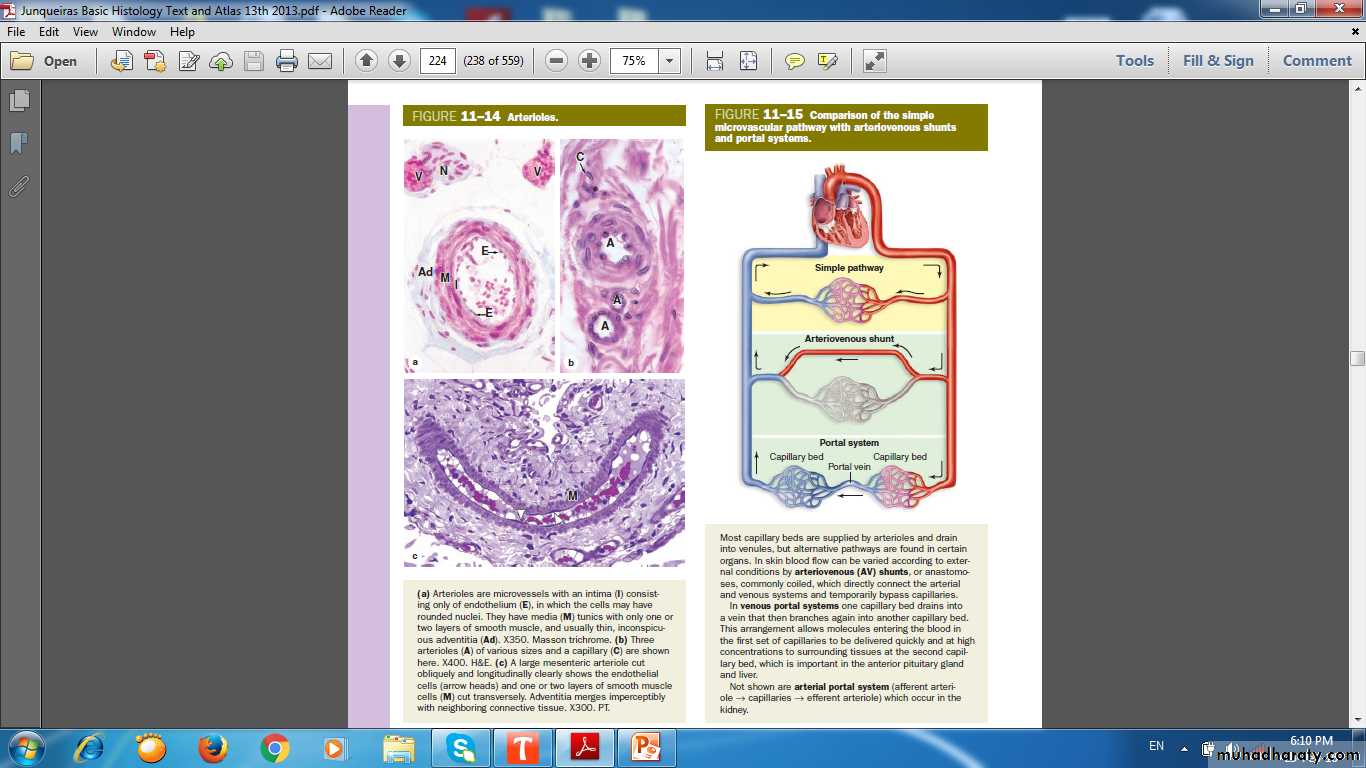
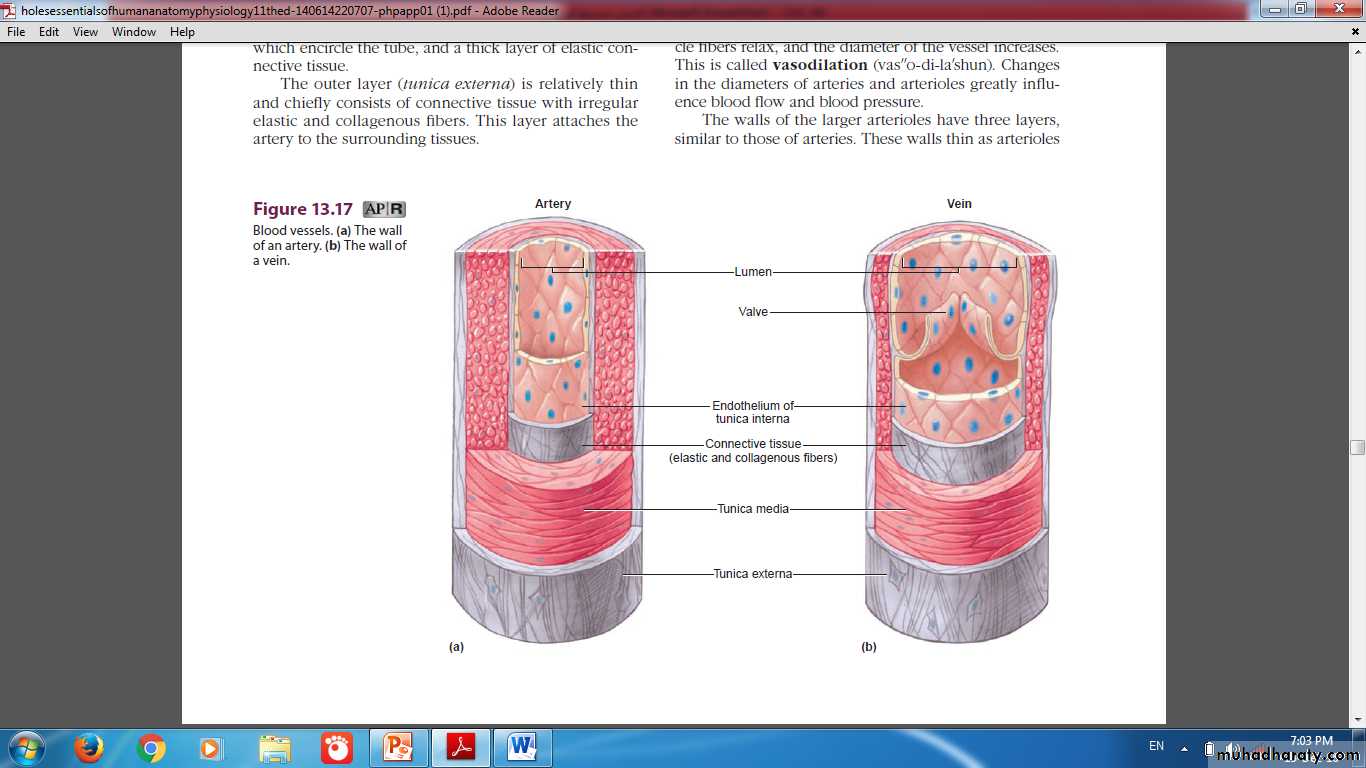
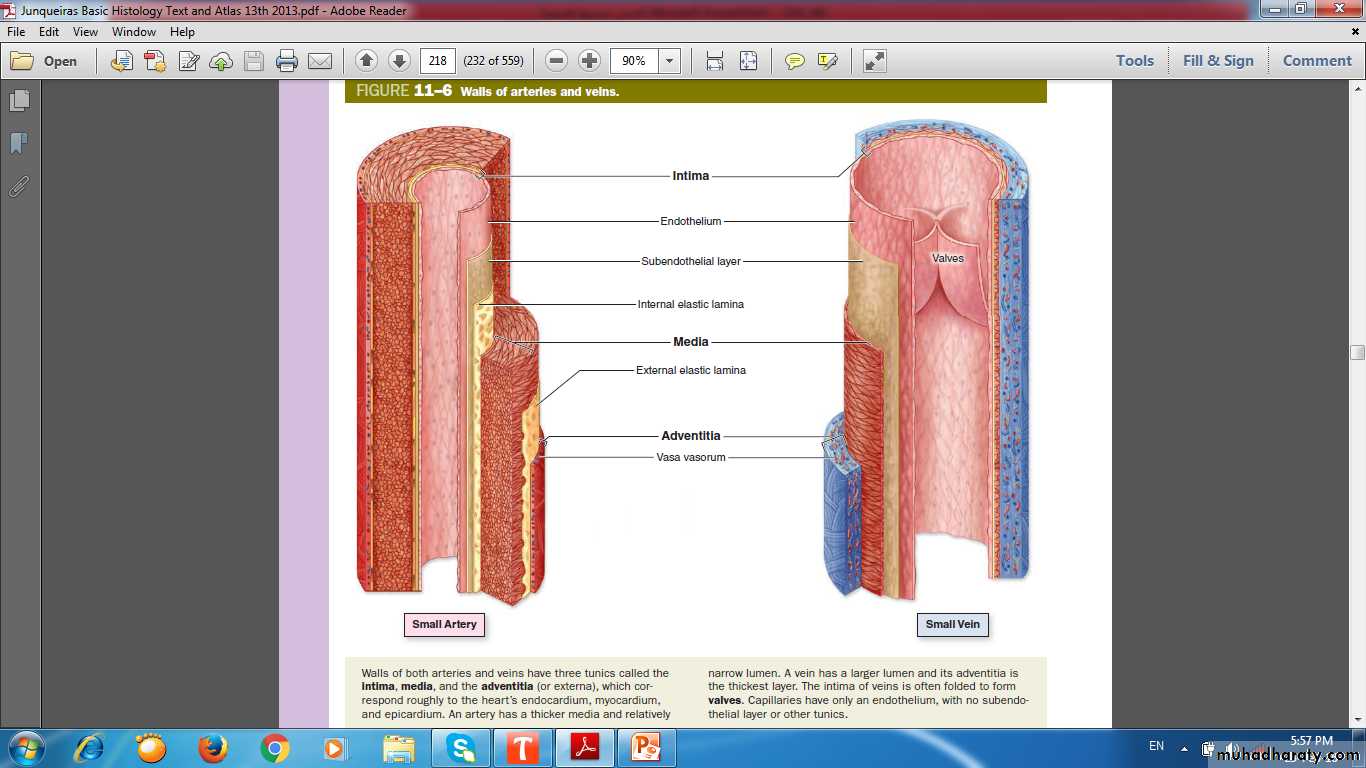
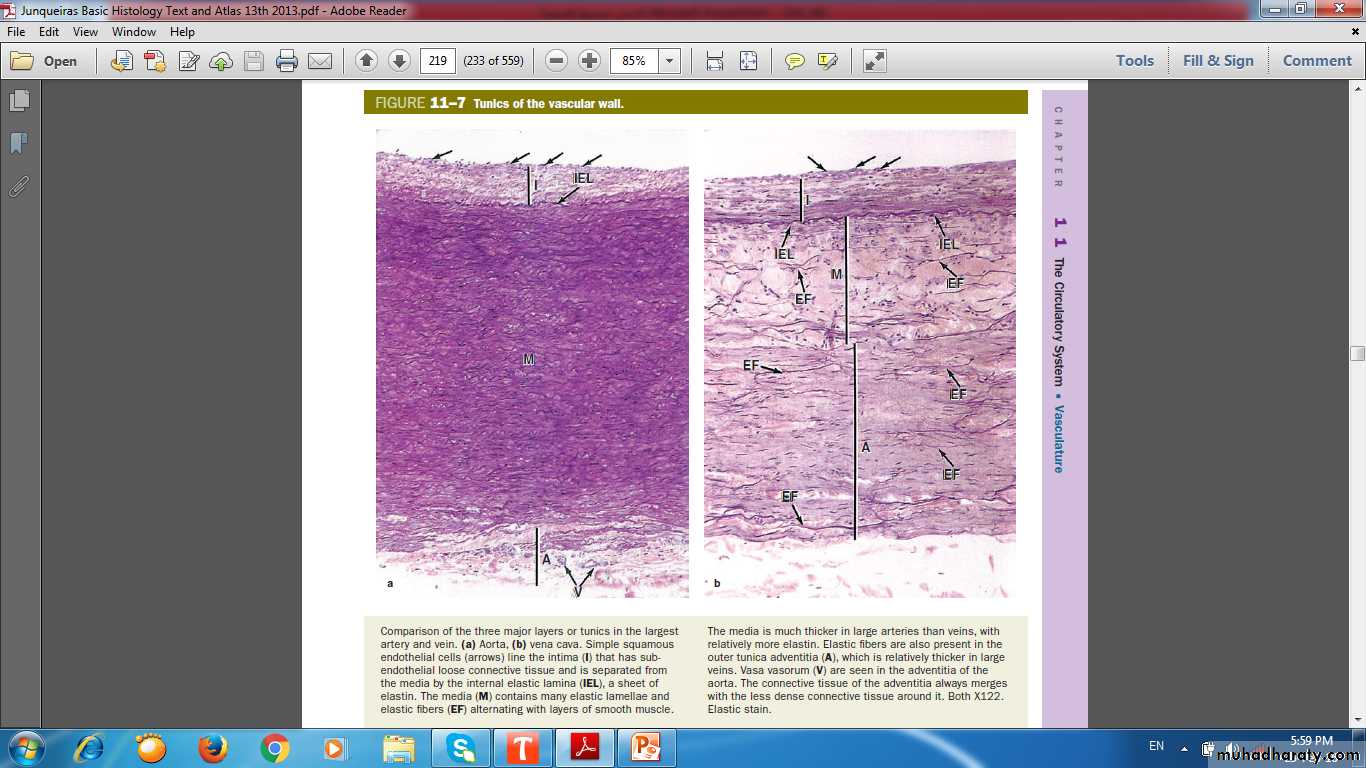
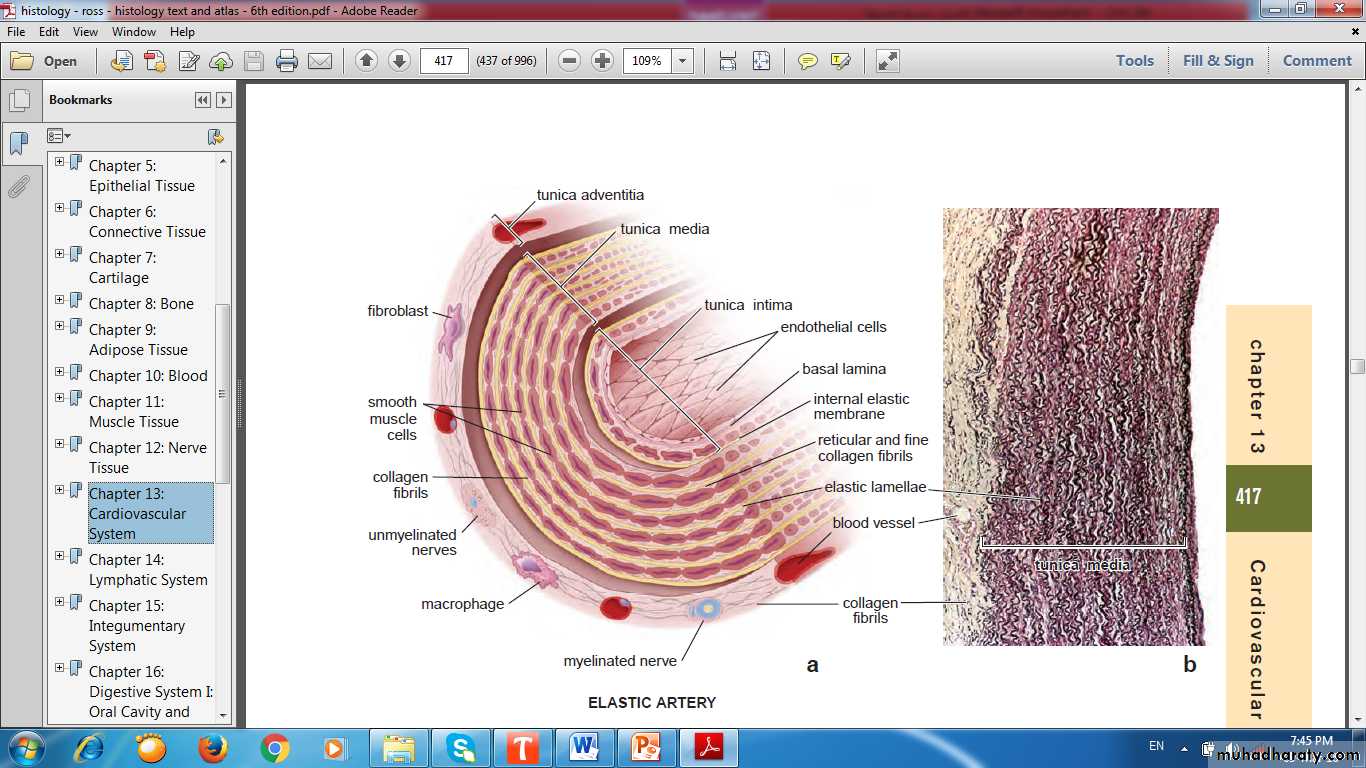
Tunics(Layers) of the vascular wall
ComparisonLumen
Media
Adventitia
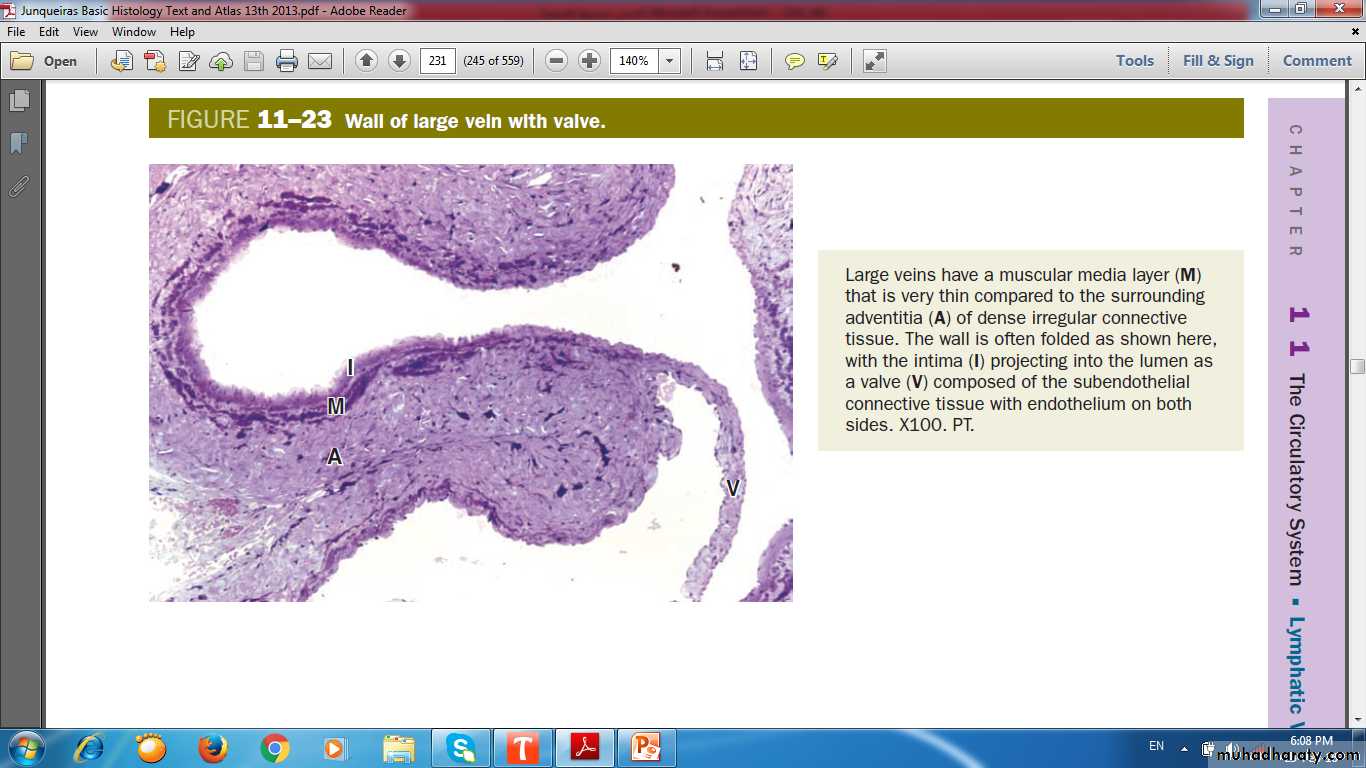
Valves
Tissues of vascular wall
Endothelium:• Metabolite exchange
• Nonthrombogenic surface
• Control of Vascular tone and blood flow
• Role in Inflammation
• Growth factors
Smooth muscle
Occur in the walls of all vessels larger than capillariesArranged helically in layers
Connected by gap junctions
Permit vasoconstriction & vasodilation
Connective tissue
Variable amounts and proportionsCollagen fibers
Elastic fibers
AORTA
VENA CAVAINTIMA
MEDIA
ADVETITIA
INTIMA
MEDIA
ADVETITIA
INTIMA
MEDIAADVENTITIA
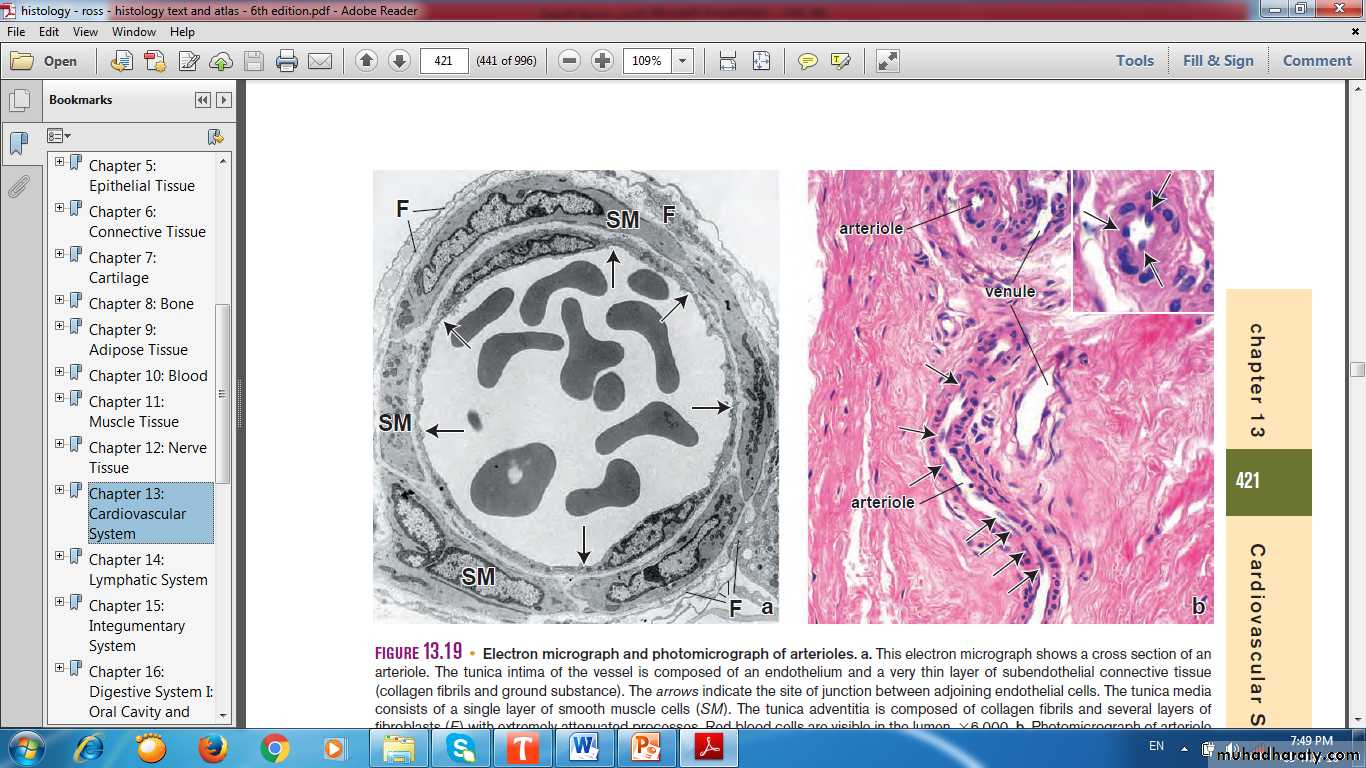
ARTERIOLE
NERVE
VENULE
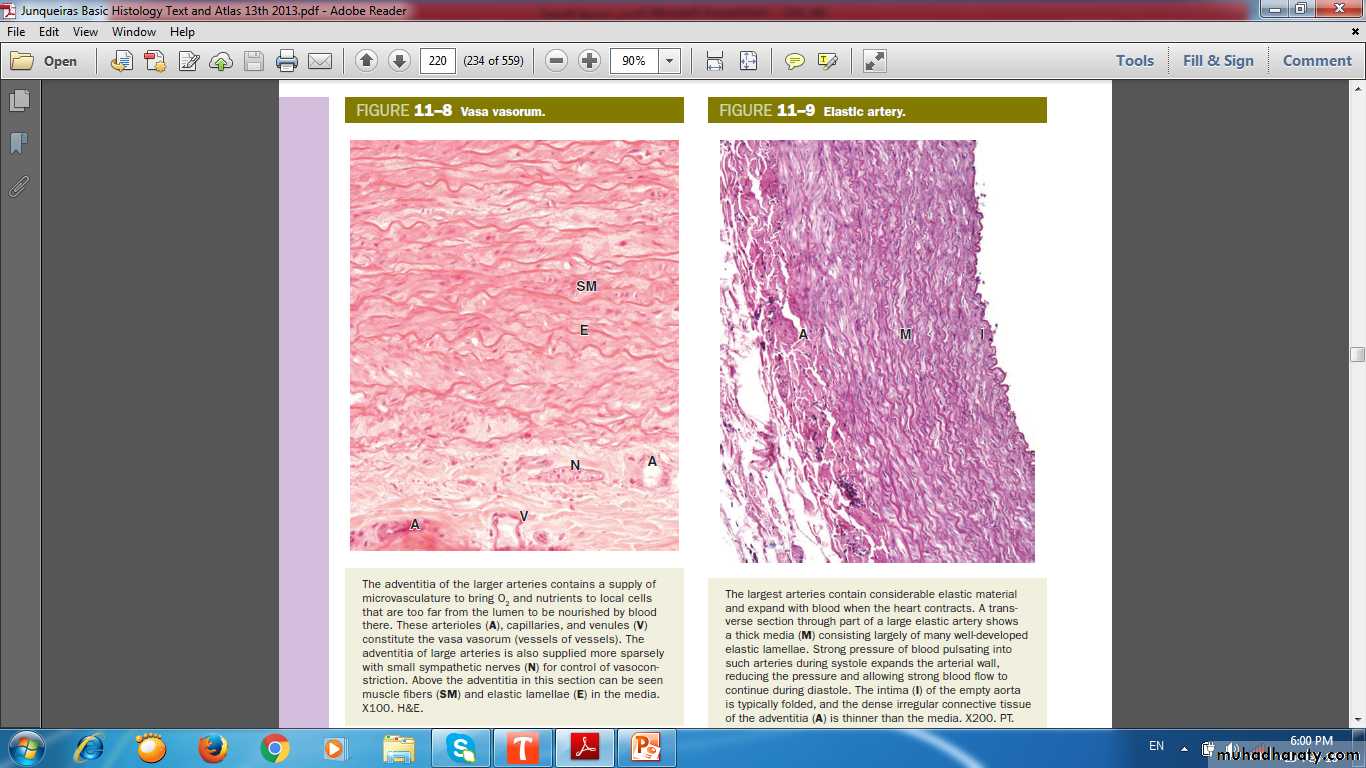
Vasa vasorum
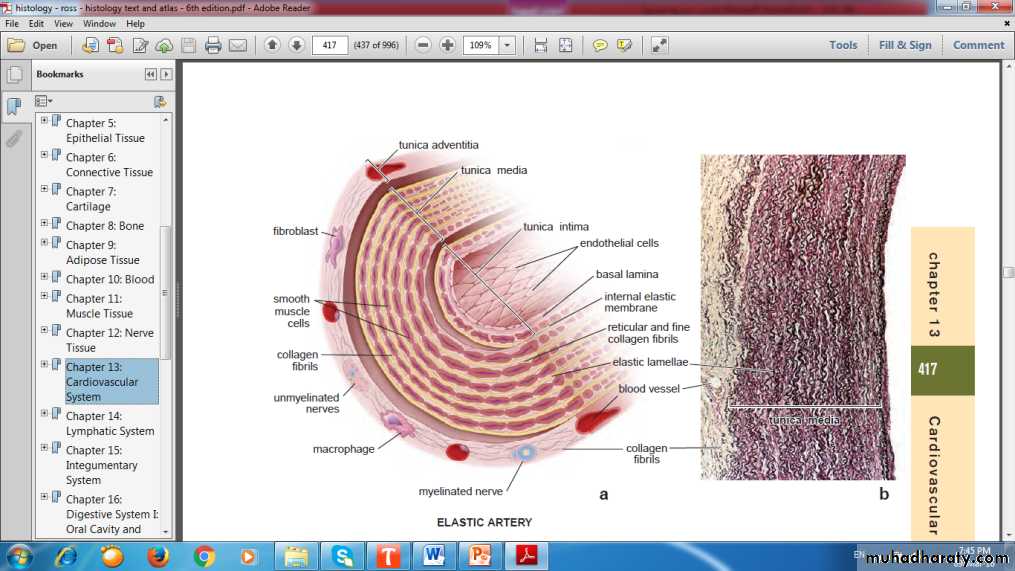
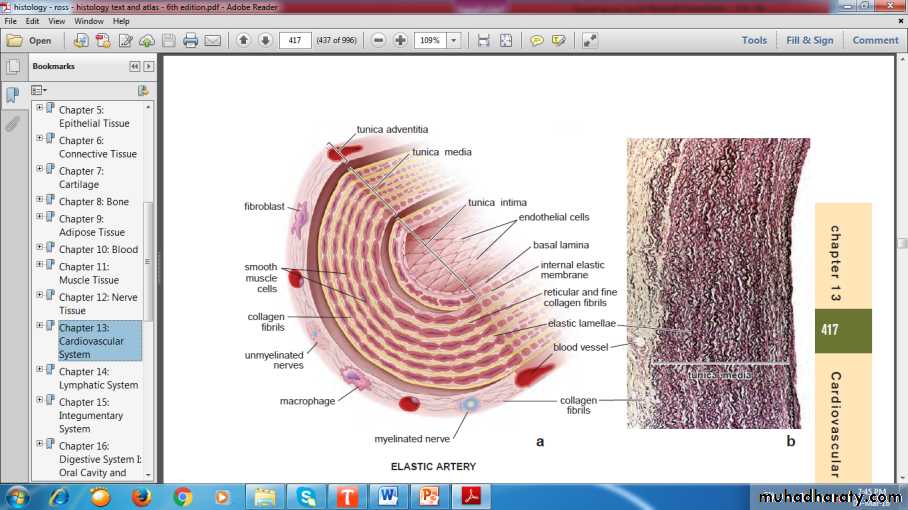
Elastic Artery
Endothelium
Internal Elastic LaminaSmooth Muscle
Vasa Vasorum
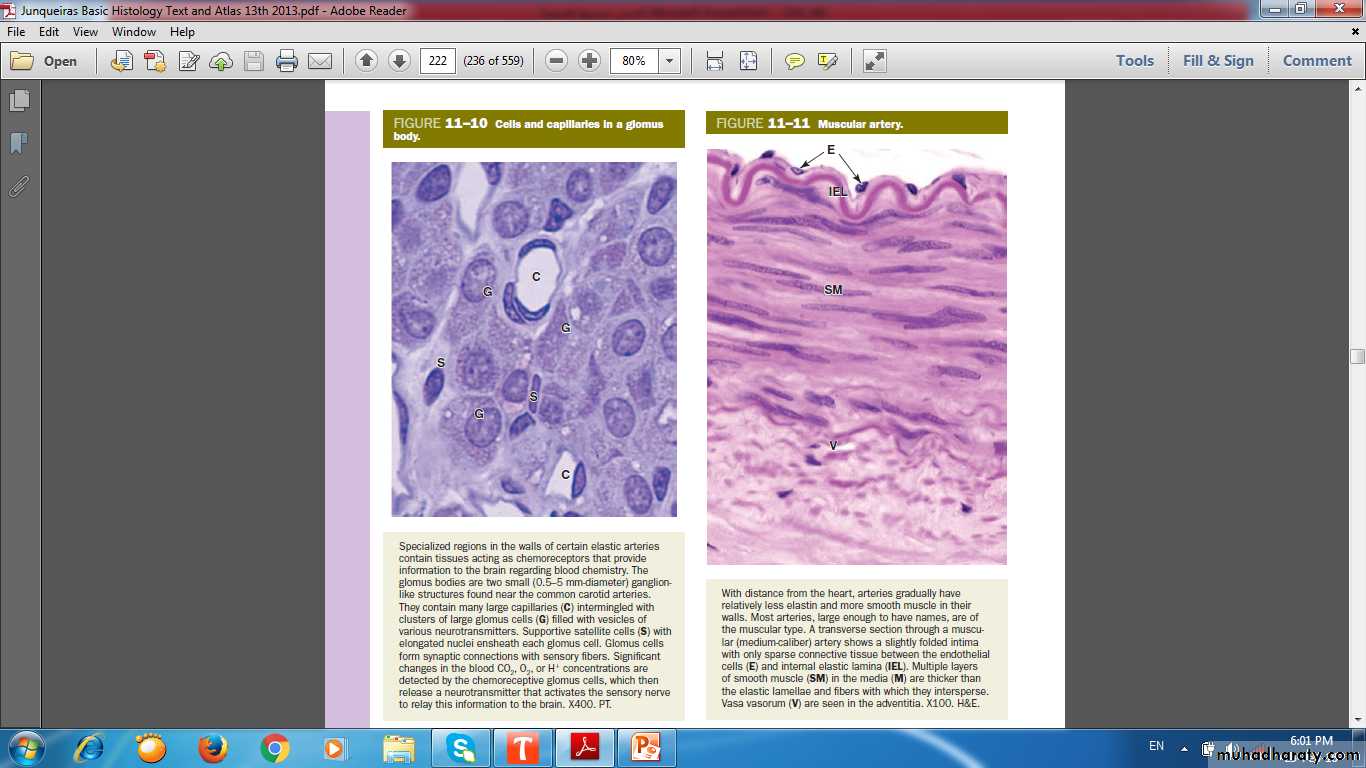
Muscular artery
VENULE
ARTEIOLECAPILLARY
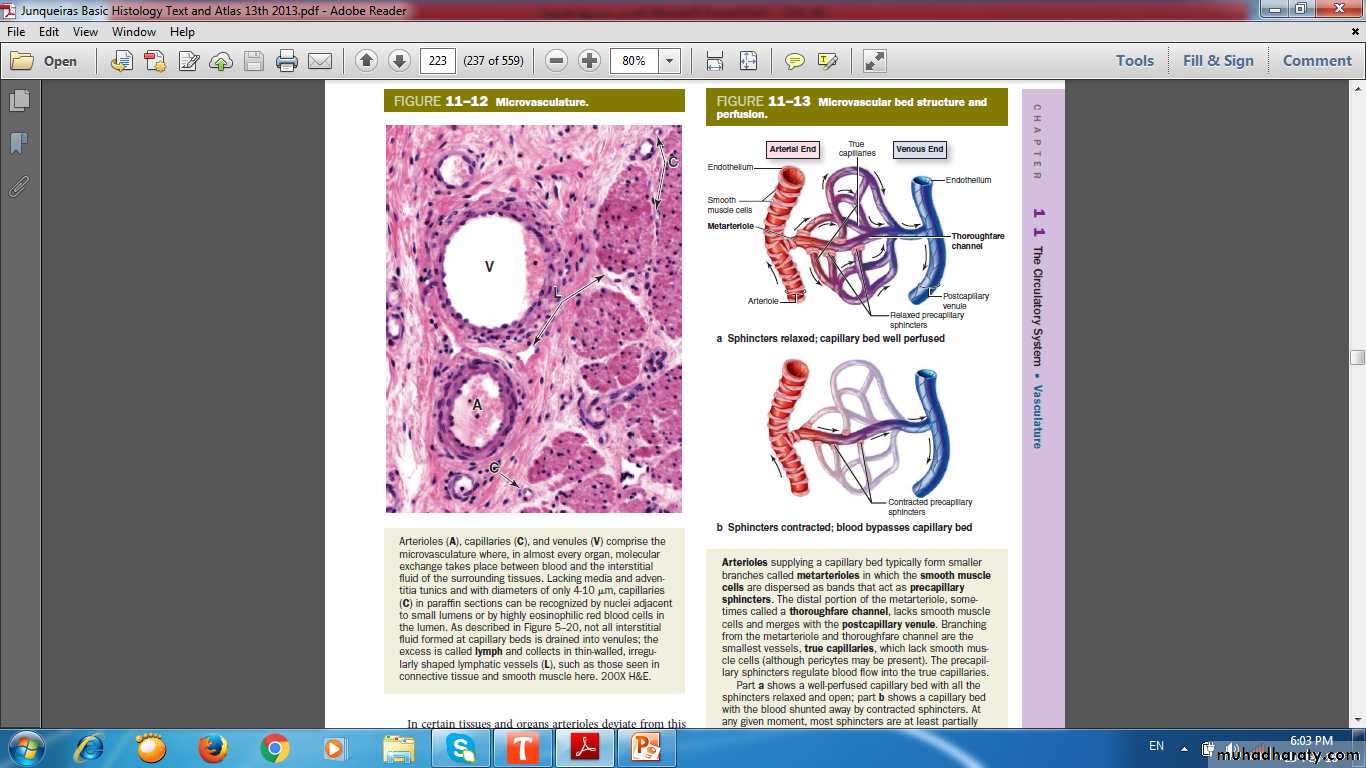
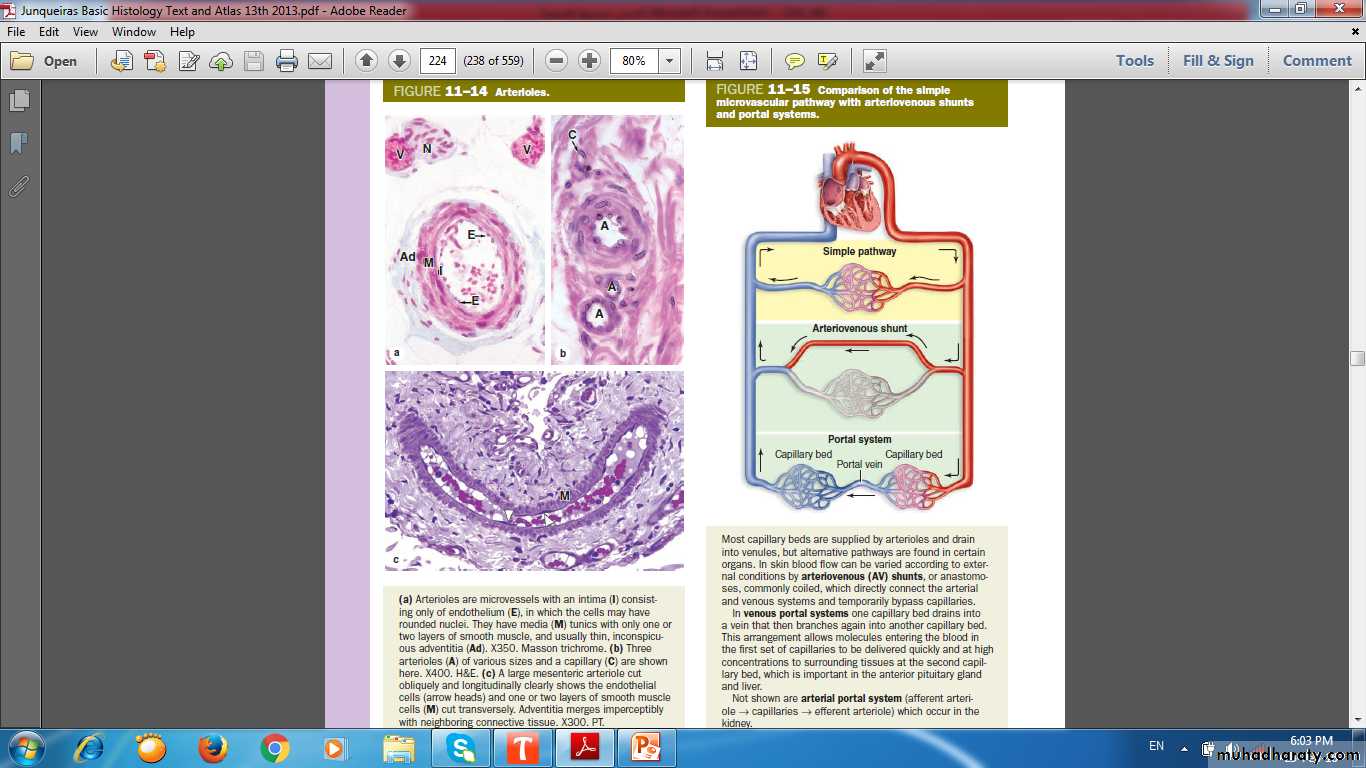
Thoroughfare channel (short circuit bypass channel)
Arteriole
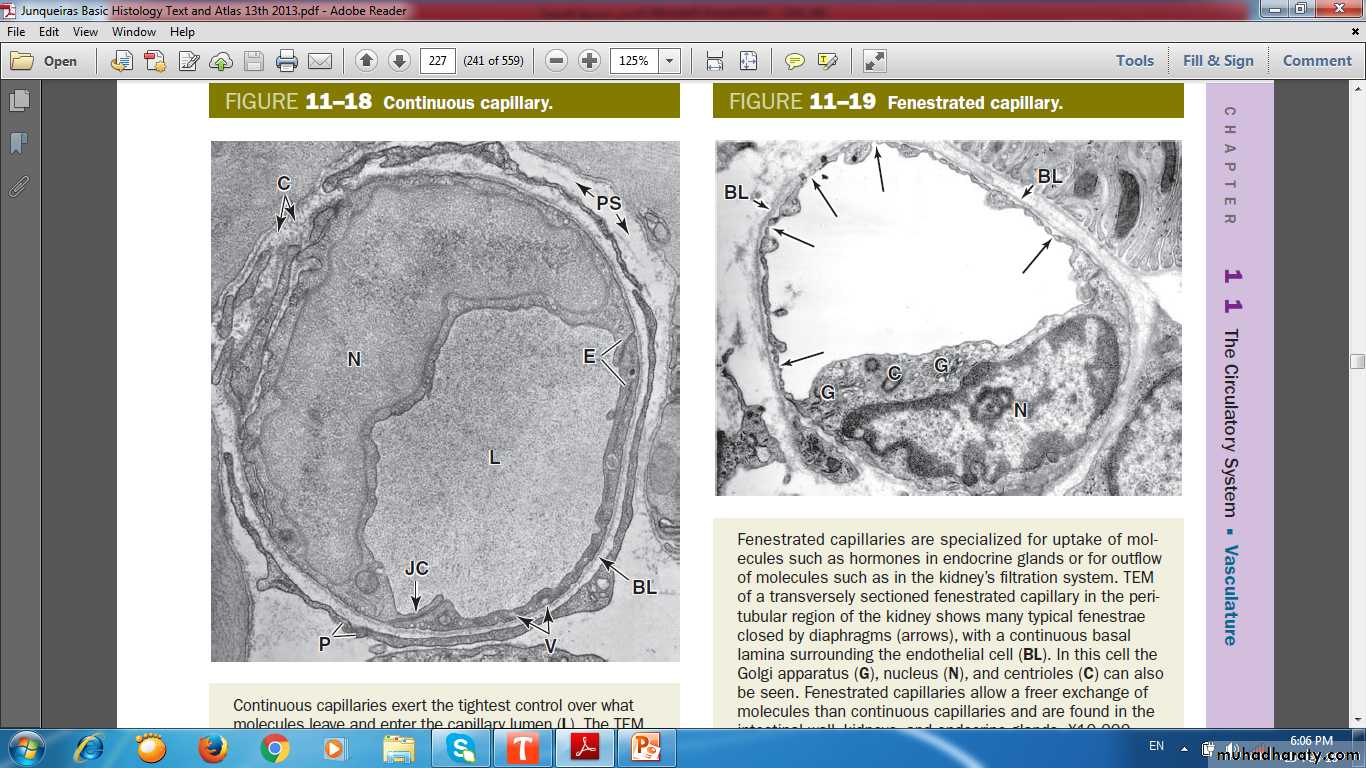
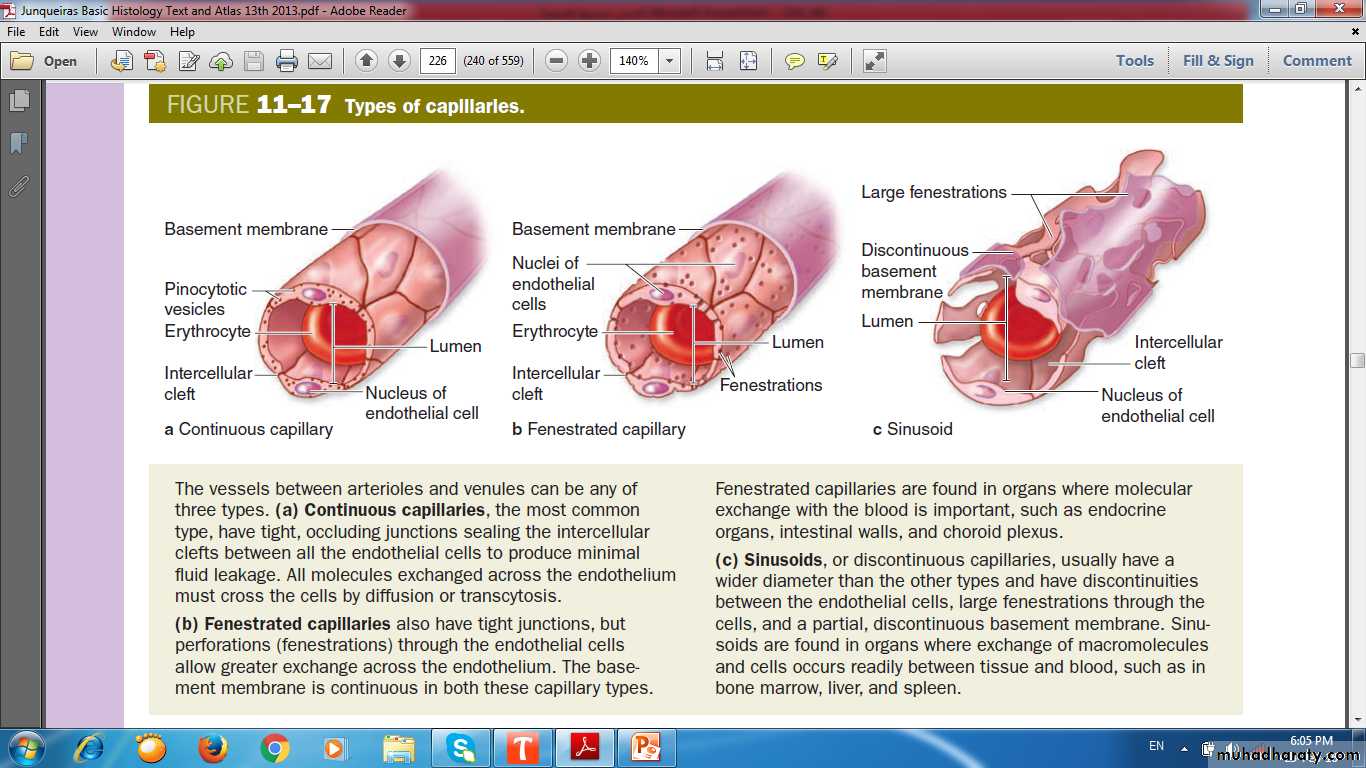
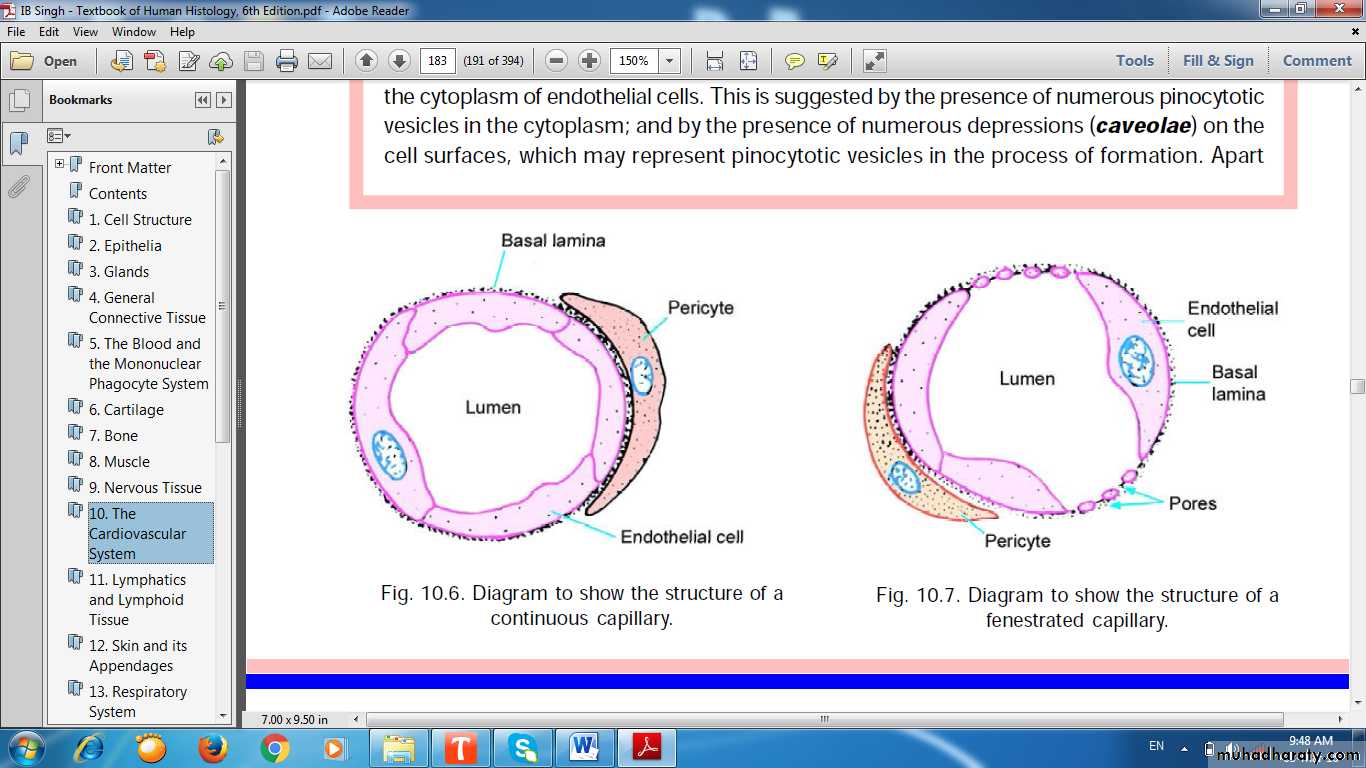
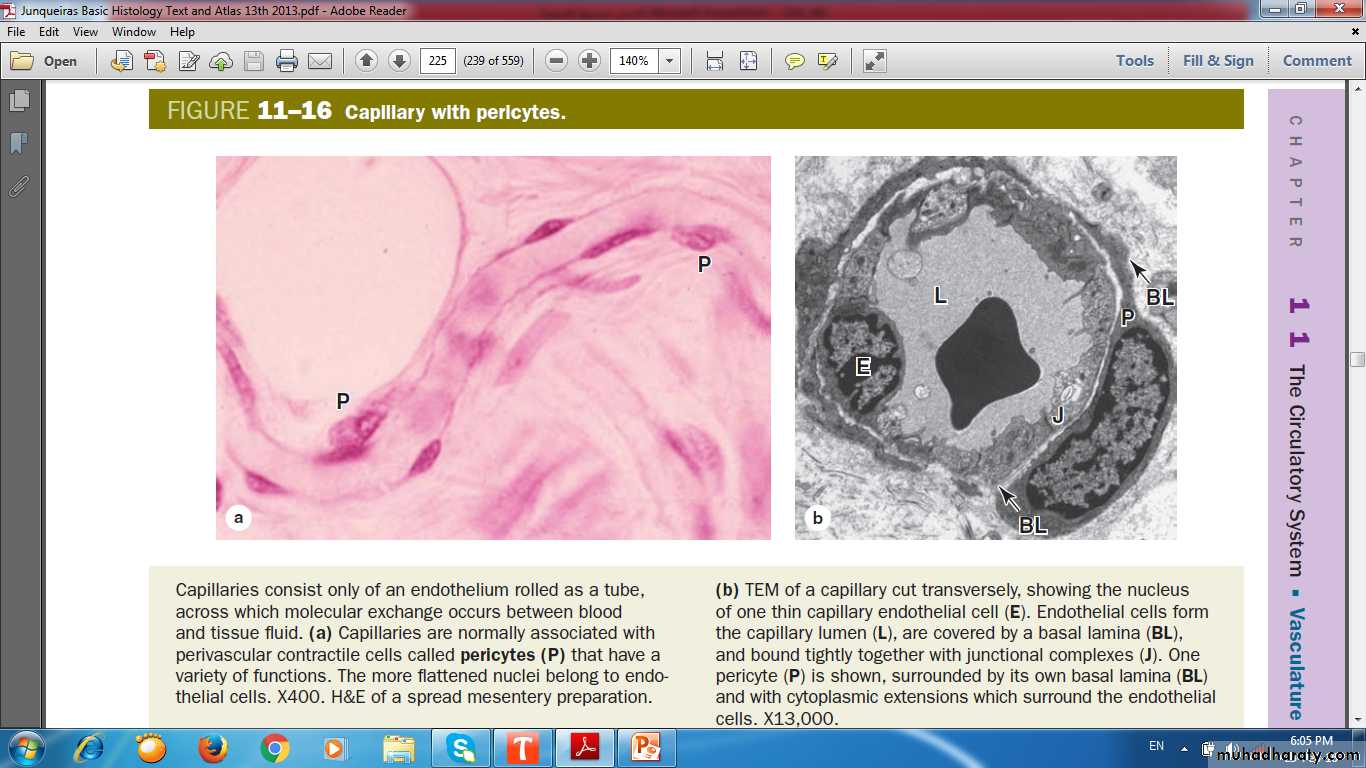
CapillariesSingle layer of endothelial cells rolled up as a tube
Diameter of capillaries varies from 4 to 10 μm
Length not more than 50 μm
90% of the body’s vasculature
Total length of more than 100,000 km
Total surface area of approximately 5000 m2
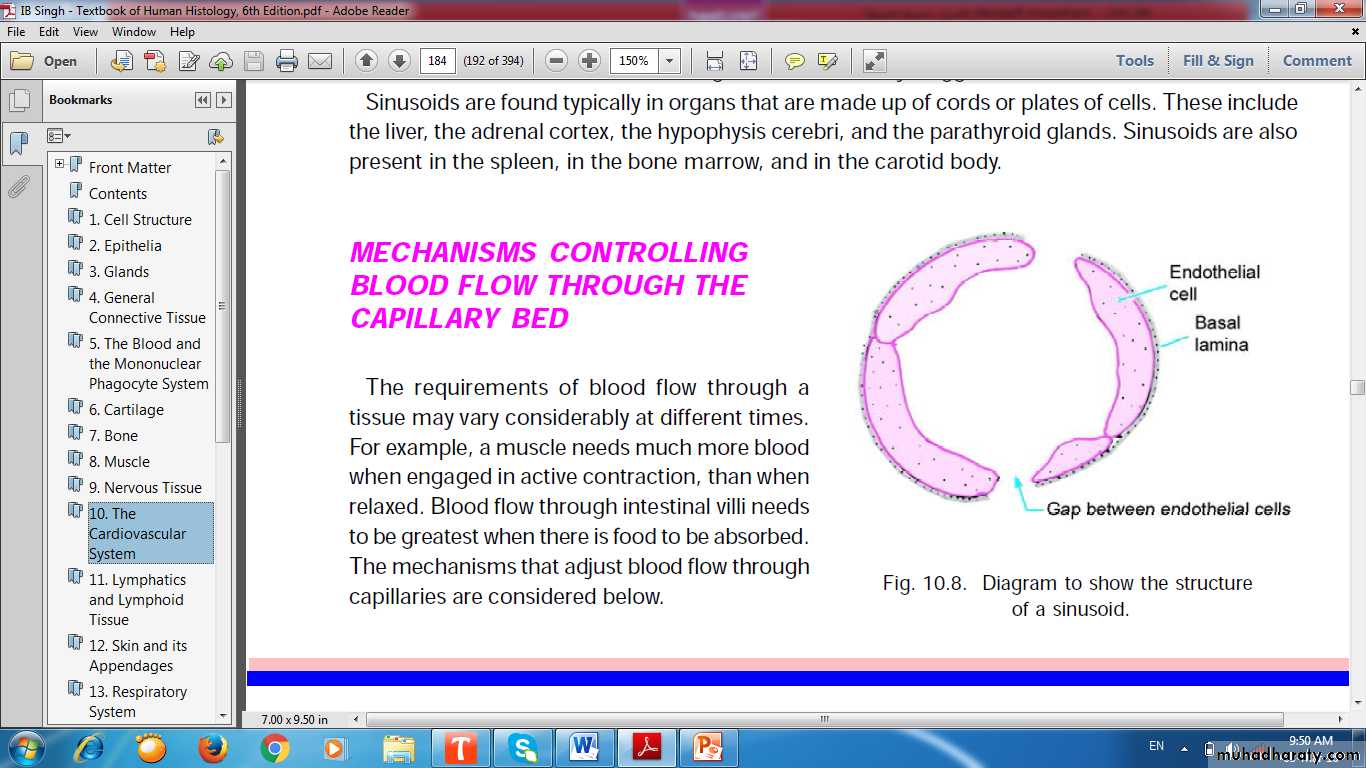
Cyclical opening and closing of the sphincters
Have thin walls, extensive surface area, and slow pulsatile blood flow
Types of capillaries
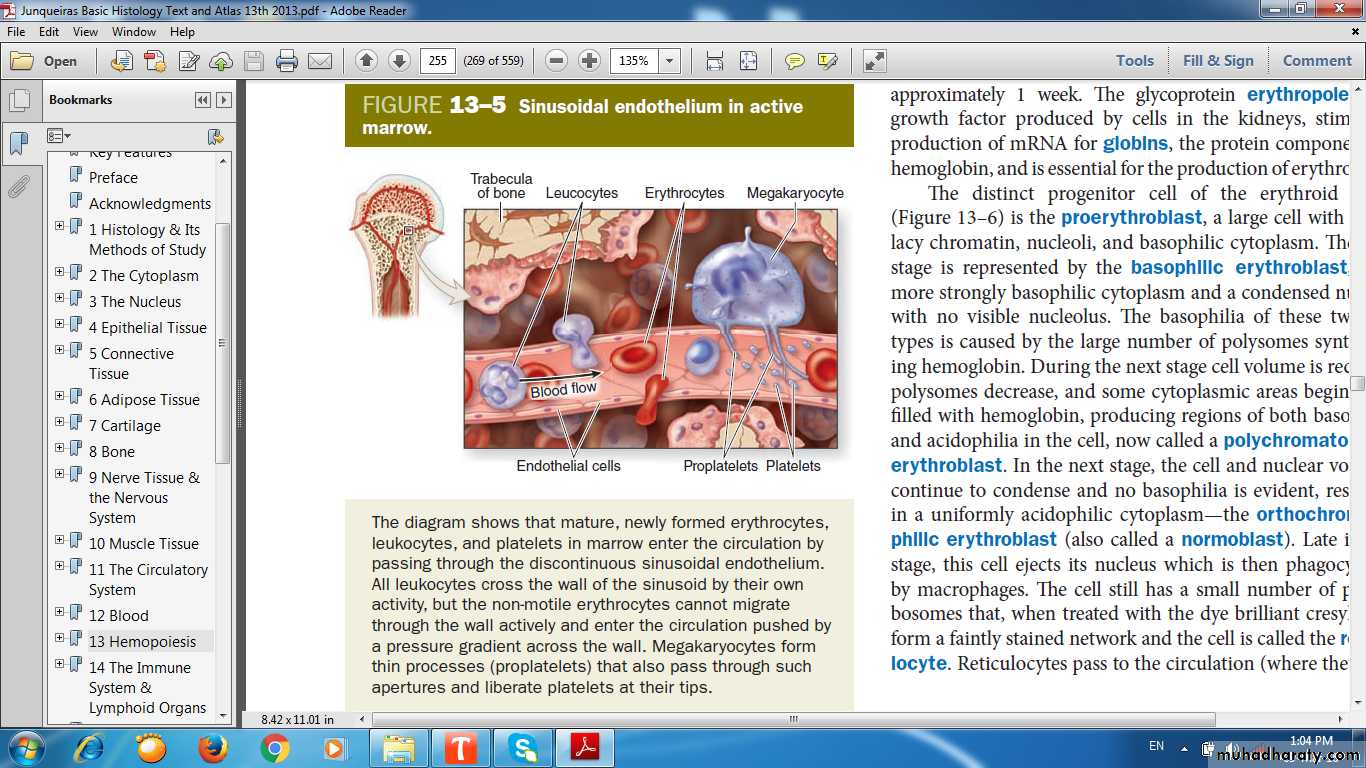
Sinusoid in bone marrow
Pericytes (perivascular contractile cells)
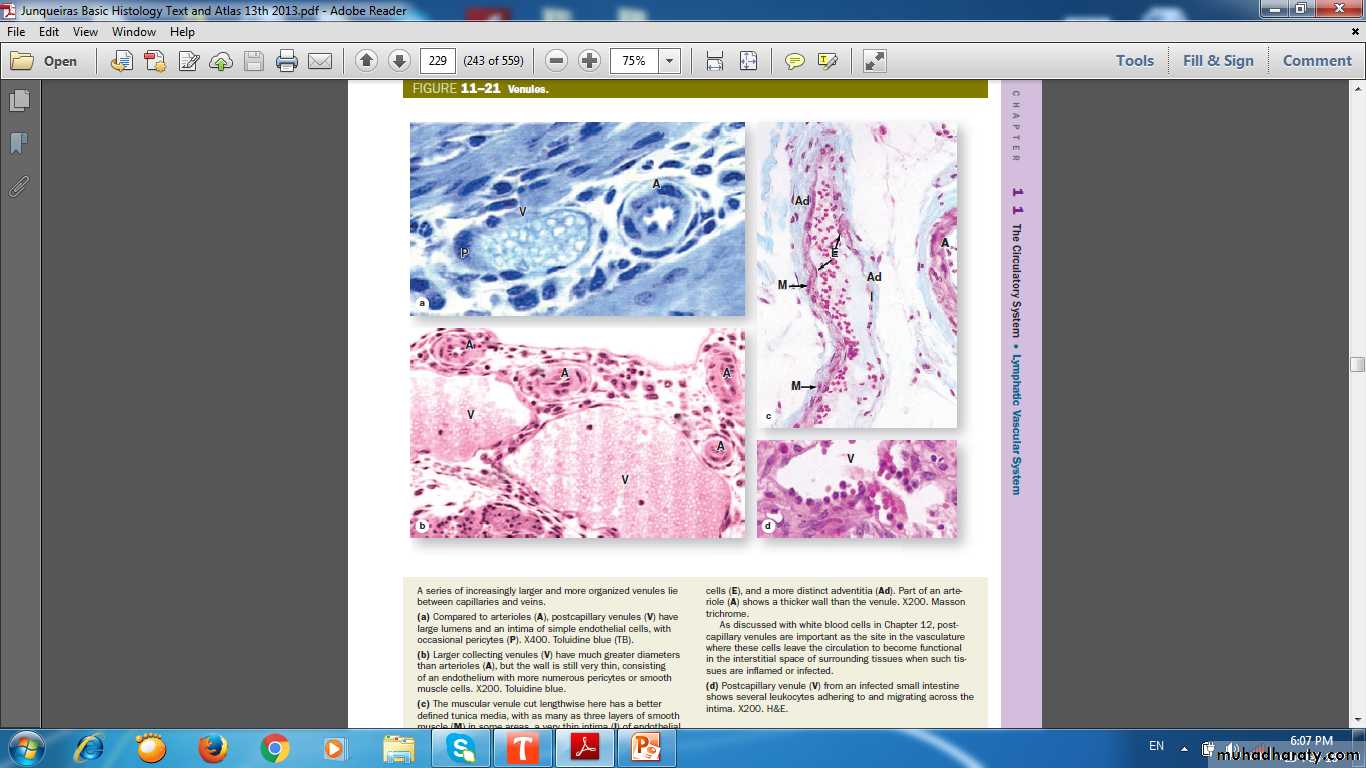
Postcapillary venule with pericyte
Collecting venuleMuscular venule
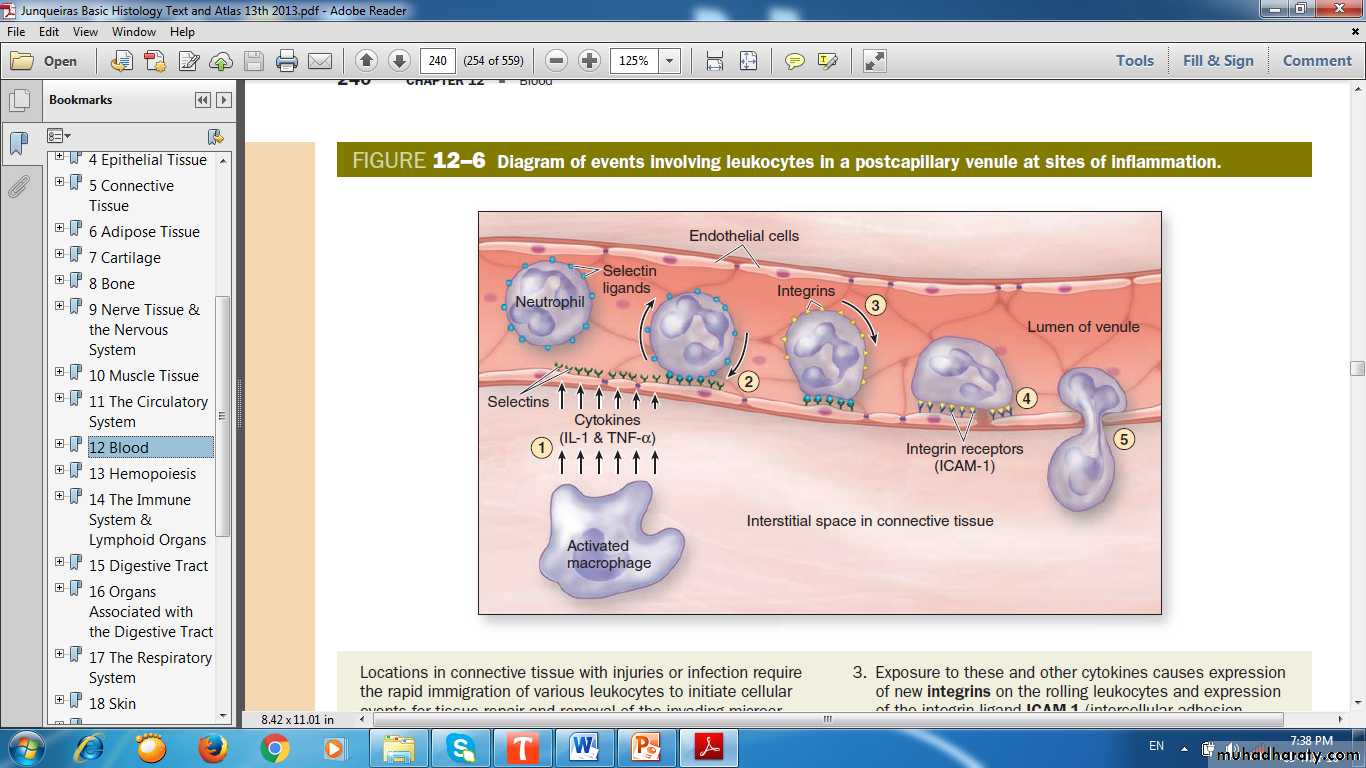
Postcapillary venule with migrating WBC
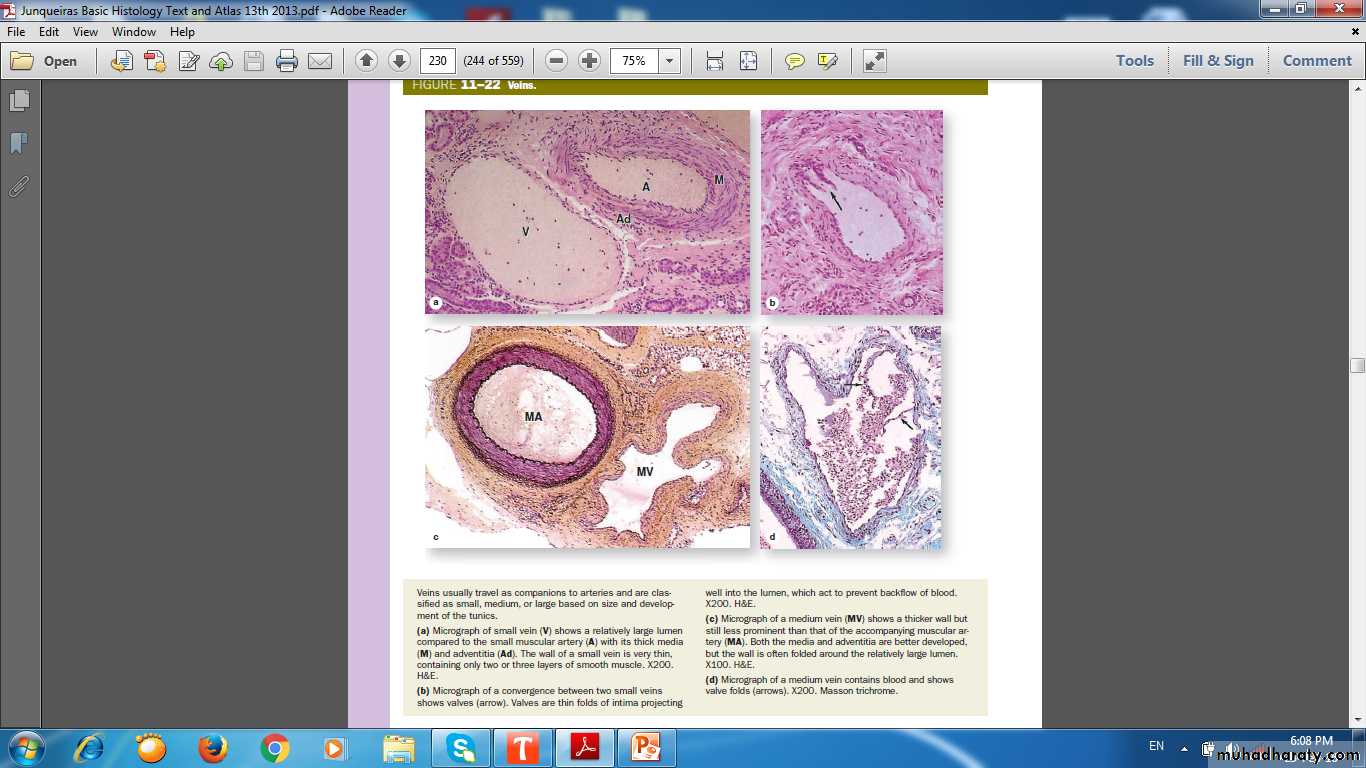
Small vein
Small vein with valveMedium vein
Medium vein with valve fold