Oral HistologyPractical
Edited by Firas1
2
Edited by Firas
3
Edited by Firas
4
Edited by Firas
5
Edited by Firas
6
Edited by Firas
7
Edited by Firas
8
Edited by Firas
9
Edited by Firas
10
Edited by Firas
11
Edited by Firas
12
Edited by Firas
13
Edited by Firas
14
Edited by Firas
15
Edited by Firas
16
Edited by Firas
17
Edited by Firas
18
Edited by Firas
19
Edited by Firas
Cemental Repair
Protective function of cementoblasts afterresorption of root dentin or cementum
Resorption of dentin and cementum due
to trauma (traumatic occlusion, toothmovement, hypereruption)
Loss of cementum accompanied by loss
of attachmentFollowing reparative cementum
deposition attachment is restored20
Edited by Firas
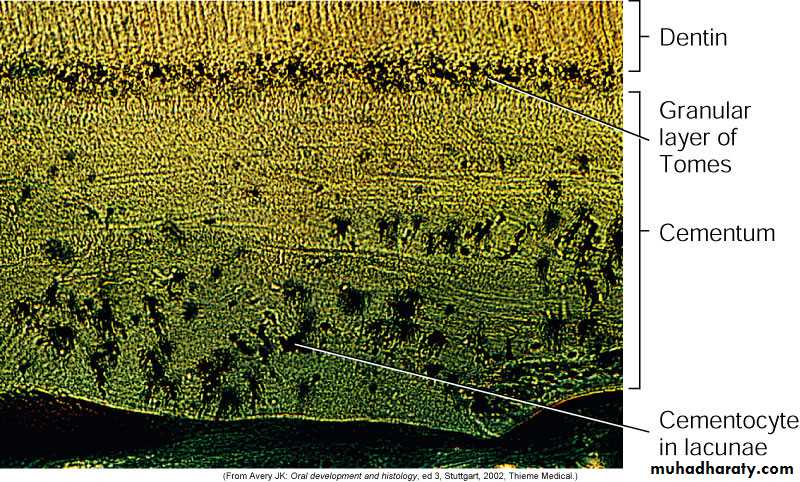
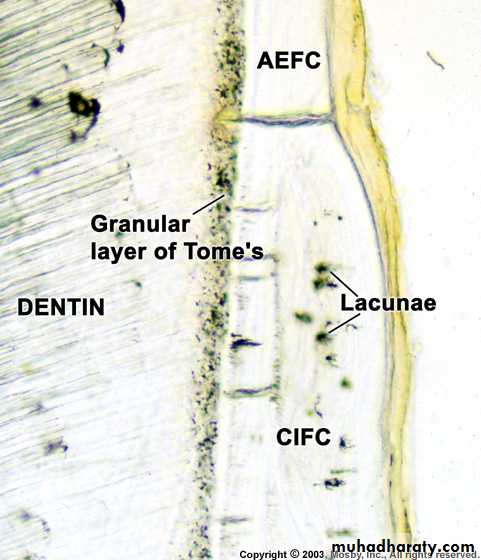
A: Acellular cementum
B: Hyaline layer of Hopwell-SmithC: Granular layer of Tomes
D: Root dentin
Cellular: Has cells
Acellular: No cells and has no structureCellular cementum usually overlies acellular cementum
21Edited by Firas
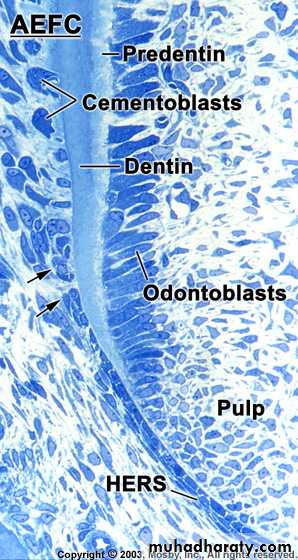
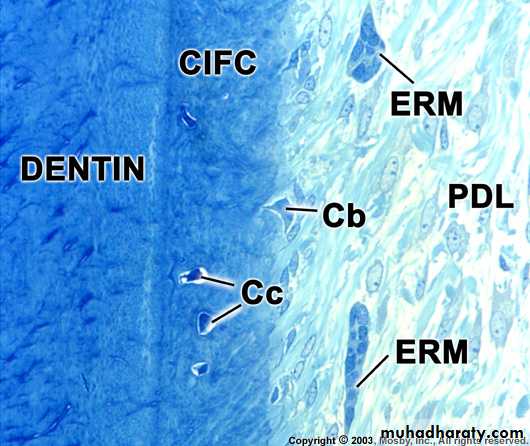
Development of Cementum
Cementum formation occurs along the
entire toothHertwig’s epithelial root sheath (HERS) –
Extension of the inner and outer dental
epithelium
HERS sends inductive signal to ectomesen-
chymal pulp cells to secrete predentin bydifferentiating into odontoblasts
HERS becomes interrupted
Ectomesenchymal cells from the inner portionof the dental follicle come in with predentin by
differentiating into cementoblasts
Cementoblasts lay down cementum
22Edited by Firas
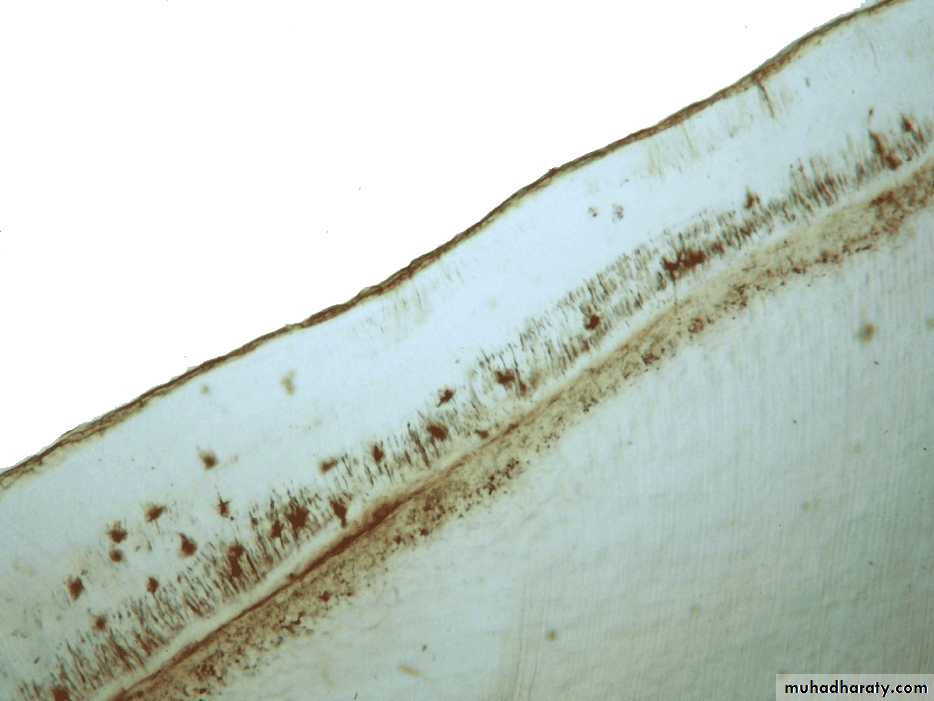
Acellular
Cellular
Variations also noted where acellular and cellular reverse in positionand also alternate
23
Edited by Firas
24
Edited by Firas
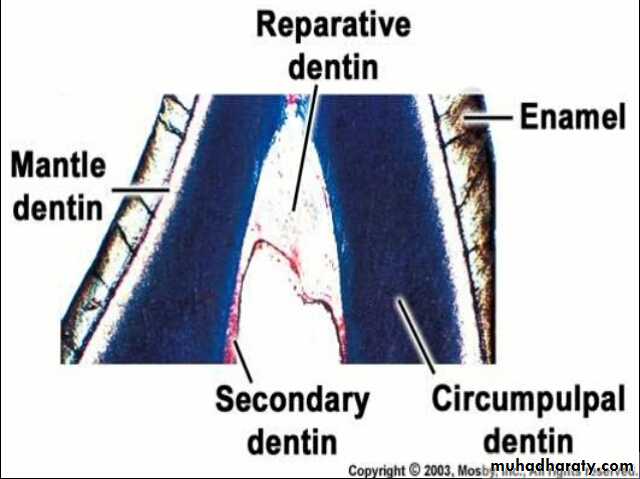
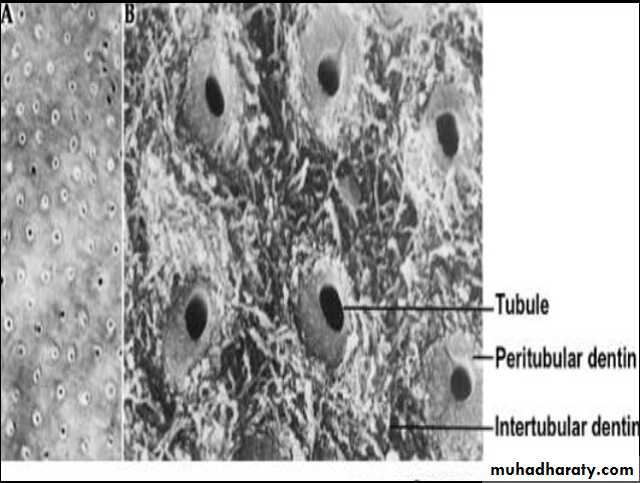
Dentin
GTLacuna of cementocyte
Canaliculus
CEMENTUM
Acellular cementum
Cellular cementum
Hyaline layer
(of Hopewell Smith)
Granular layer of tomes
Dentin with tubules
25
Edited by Firas
26
Edited by Firas
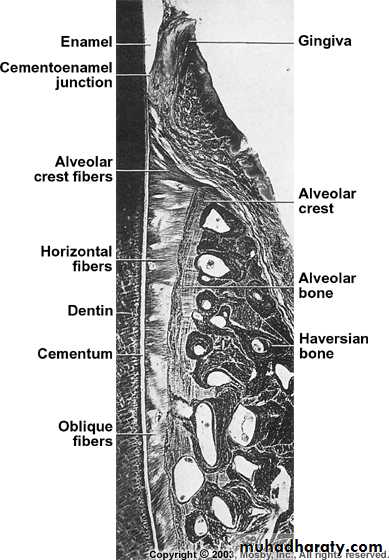
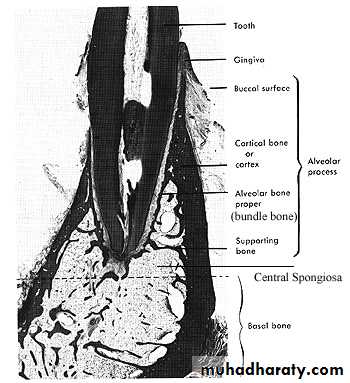
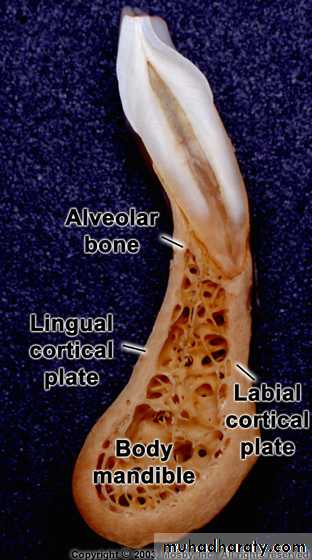
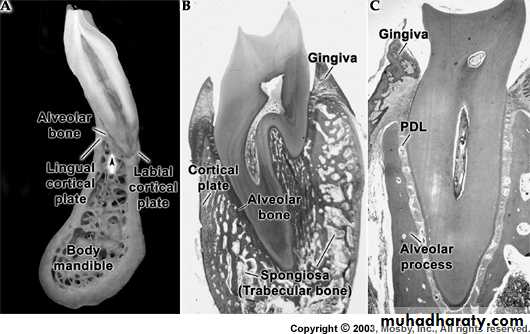
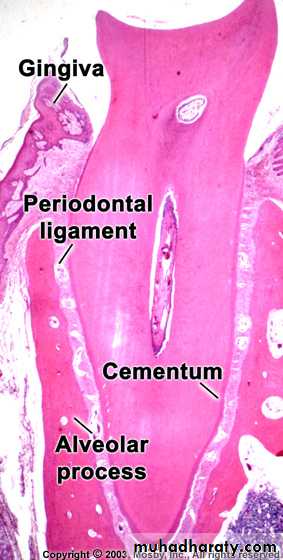
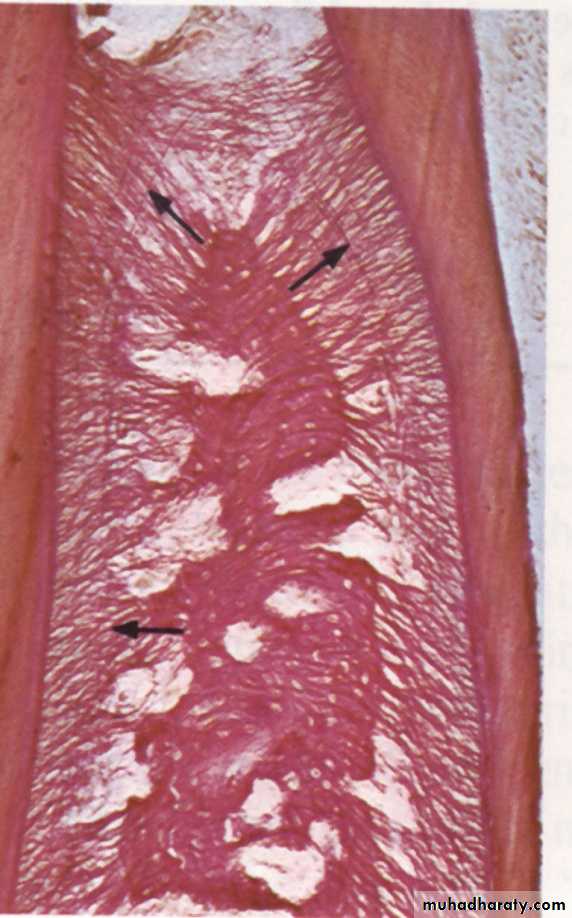
a) outer cortical platesb) a central spongiosa c) bone lining the alveolus (bundle bone)
27
Edited by Firas
28
Edited by Firas
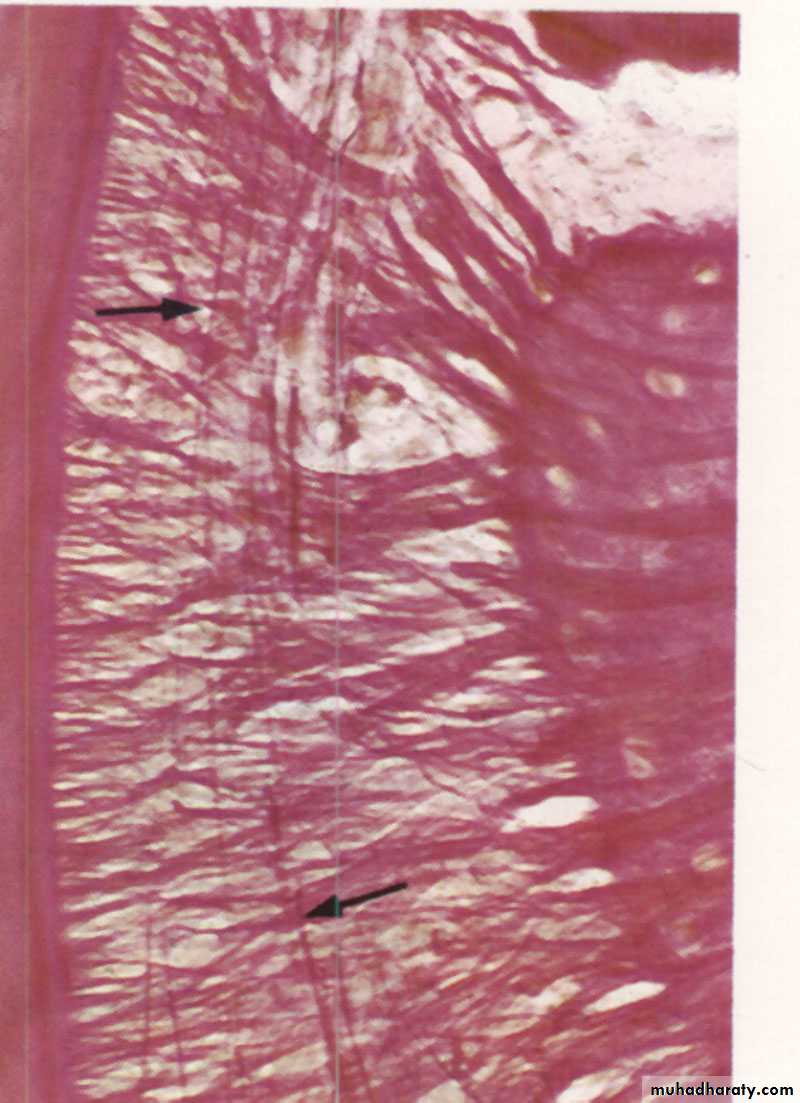
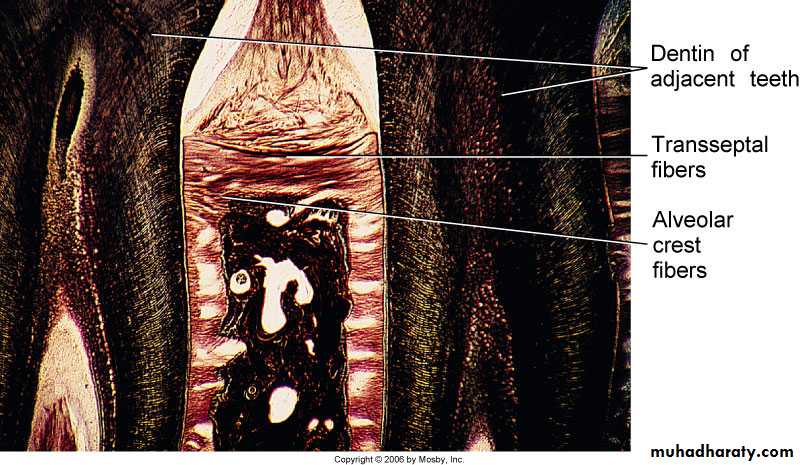
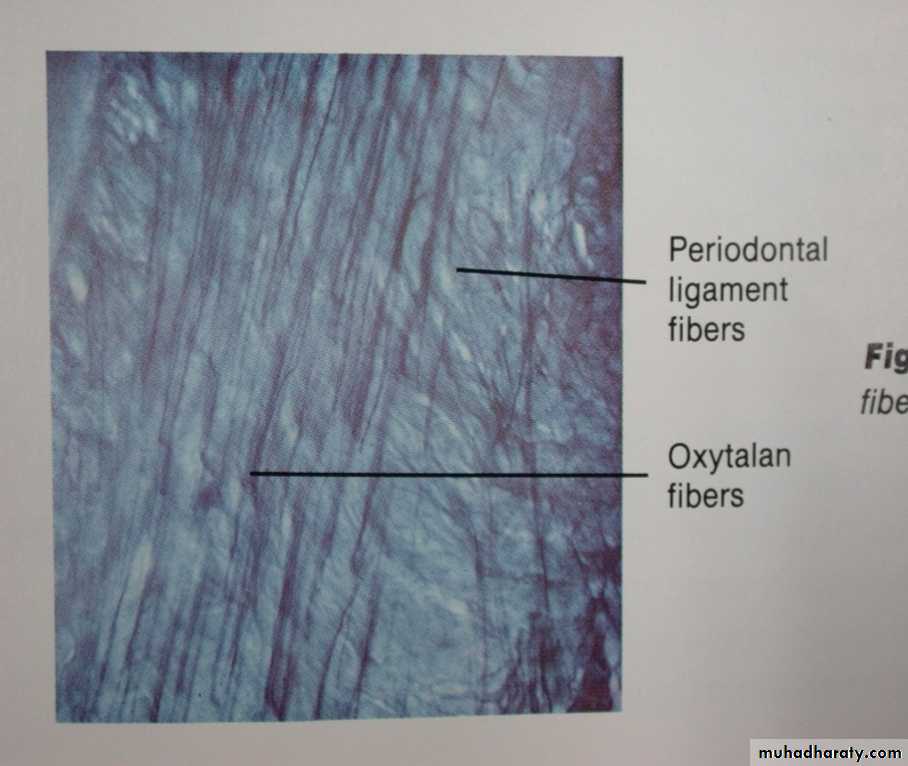
Oxytalan
Berkovitz BK , Holland GR, Moxham BJ.: Color atlas & textbook of oral anatomy. 1978, p115 Fig. 294
Avery JK. Essentials of oral histology and embryology A clinical
approach. 1992, p133 Fig. 11-3
29
Edited by Firas
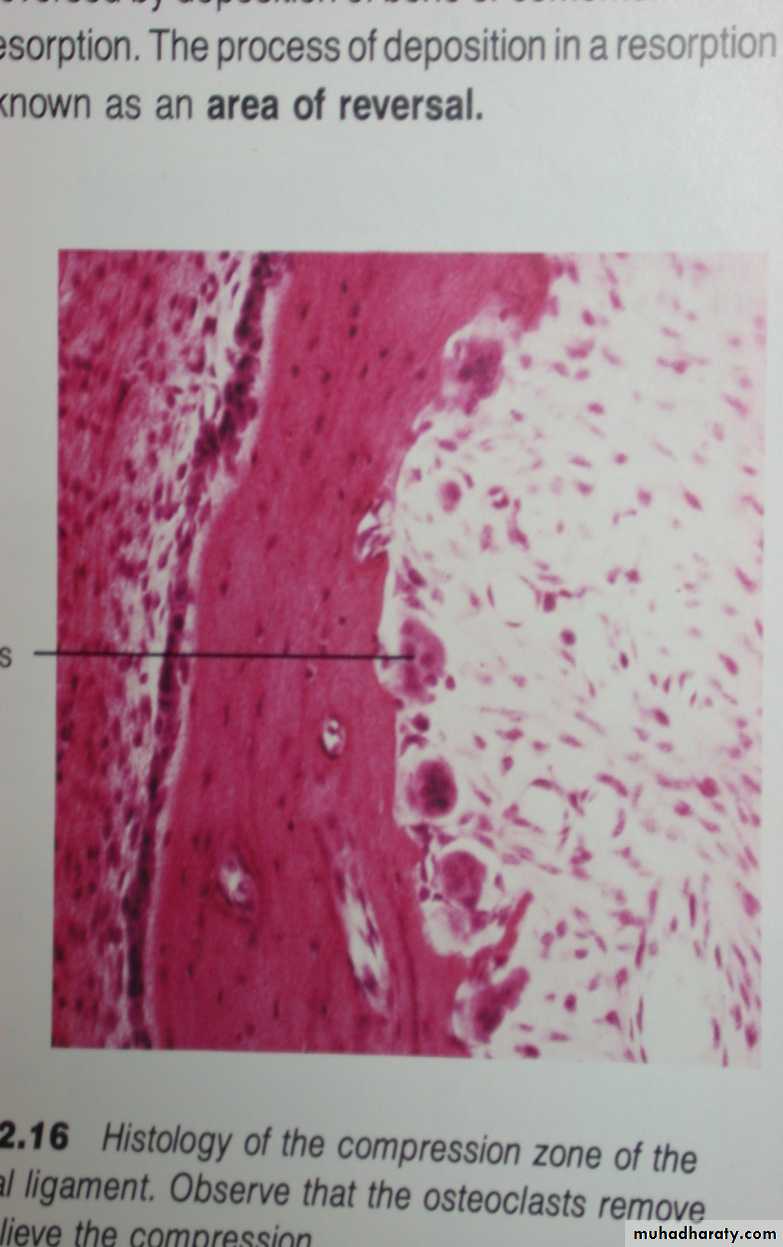
Osteoclasts
* Large and multinucleated, or small
and mononuclear
* The characteristic multinucleated giant
cells exhibit eosinophilic cytoplasm.
* It occupy in Howship’s lacunae,
or surround the end of a bone spicule
in light microscope.
Avery JK. Essentials of oral histology and embryology A clinical
approach. 1992, p149 Fig.12.1630
Edited by Firas
31
Edited by Firas
Cell freezonecell rich zone
32Edited by Firas
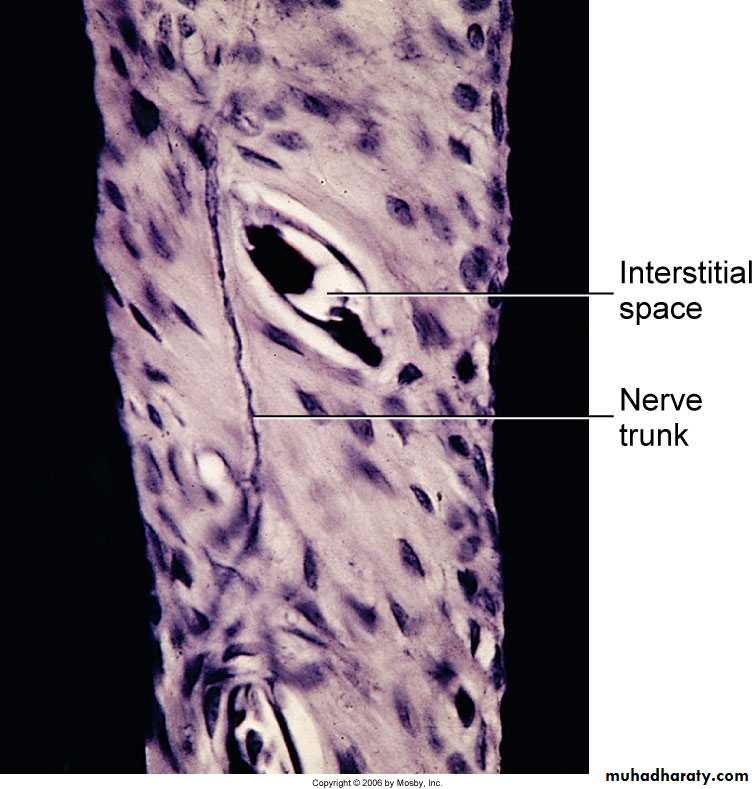
Mylinated axon
33Edited by Firas
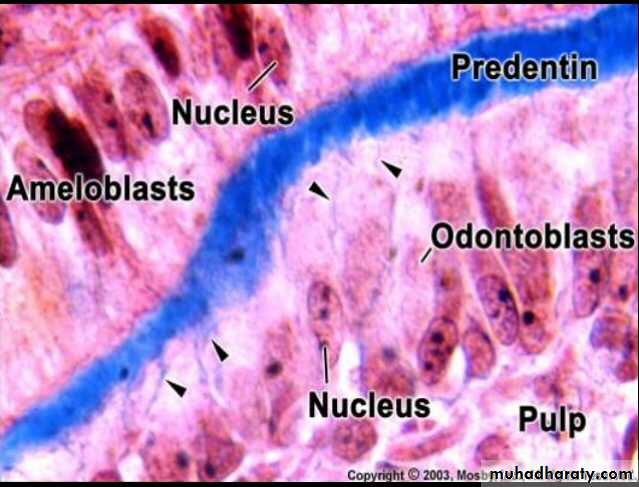
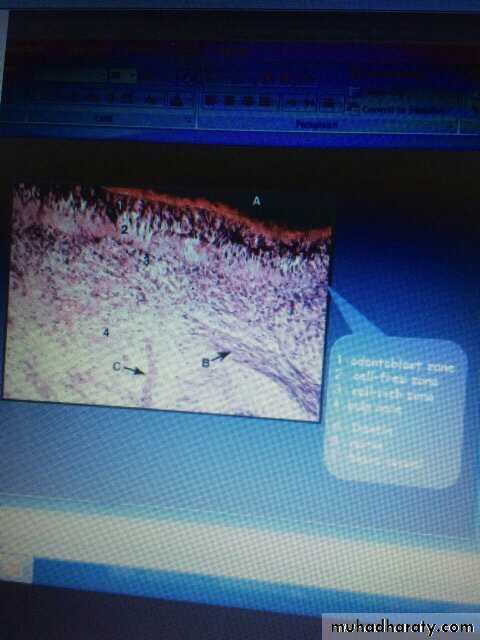
1-odontoblast2-cell free3-cell rich zone
34Edited by Firas
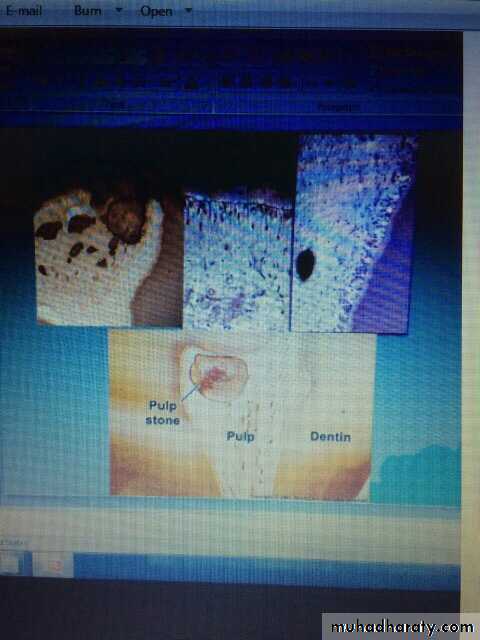
Pulp stone
35Edited by Firas
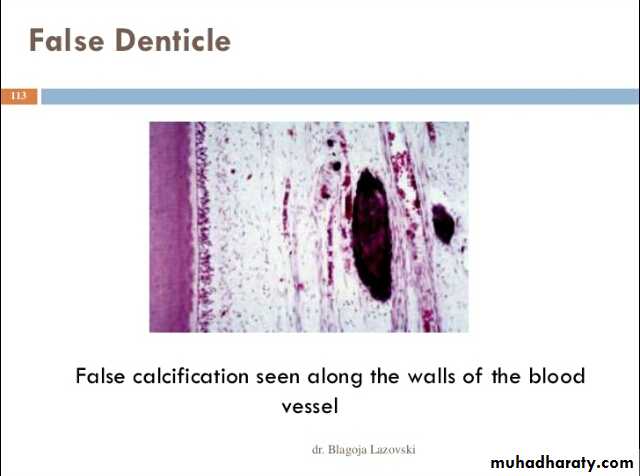
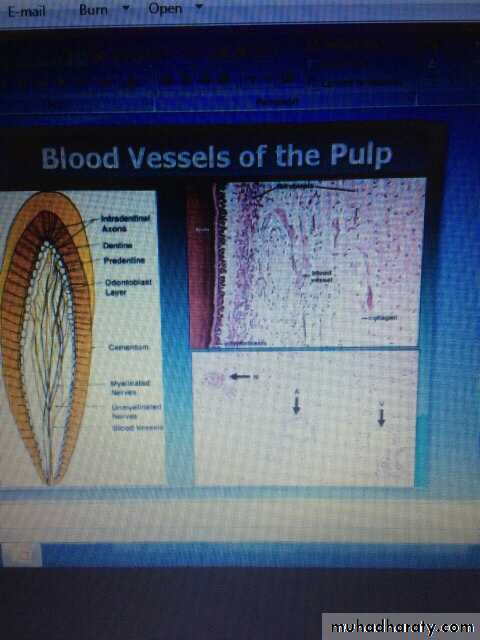
Blood vesselvein vaetery anreve n
36
Edited by Firas