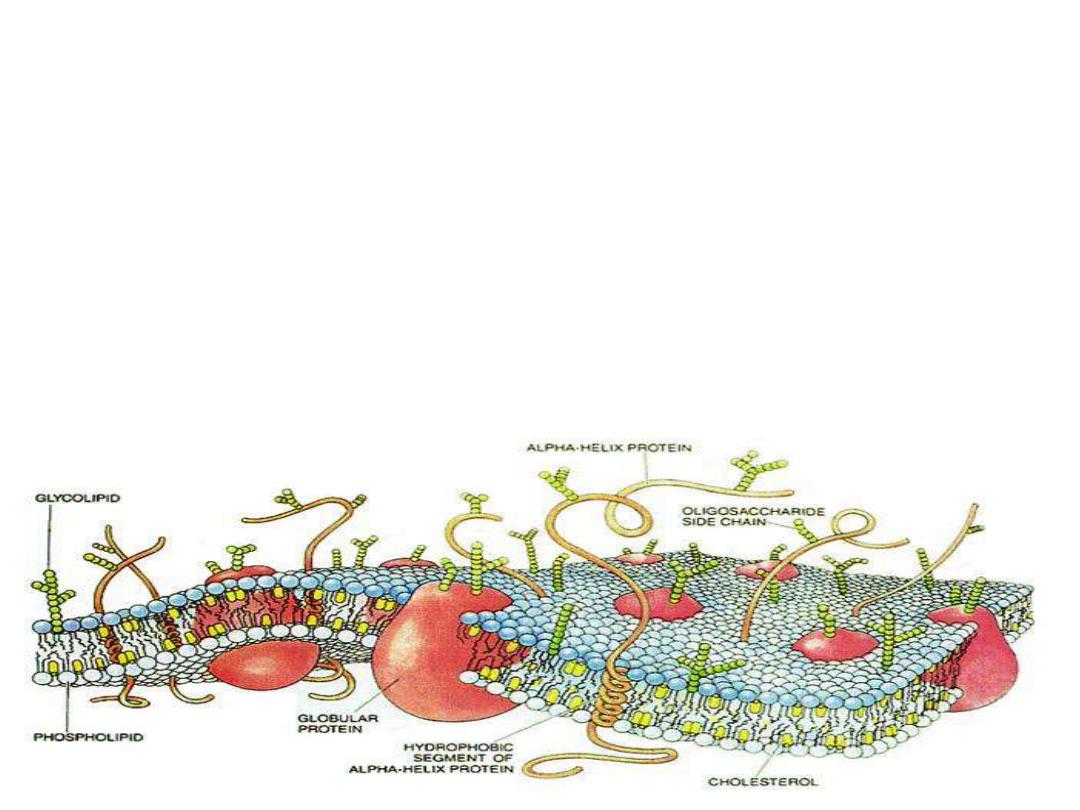
Cell Membrane II
Dr.Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
Prof. Genetic Engineering
& Biotechnology
.
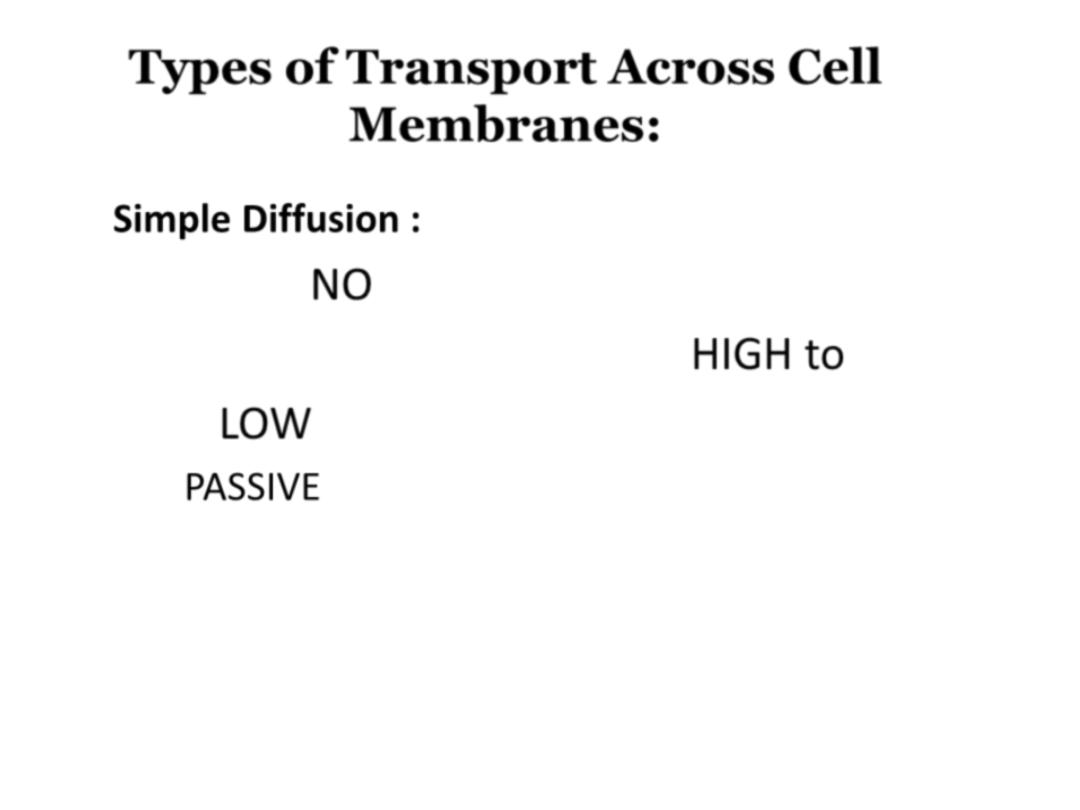
1-Simple Diffusion :
•
Requires:
NO energy
• Molecules move from area of
HIGH to
LOW concentration
•
is a PASSIVE process which means no energy is
used to make the molecules move, they have a
natural
KINETIC ENERGY.
Types of Transport Across Cell
Membranes:
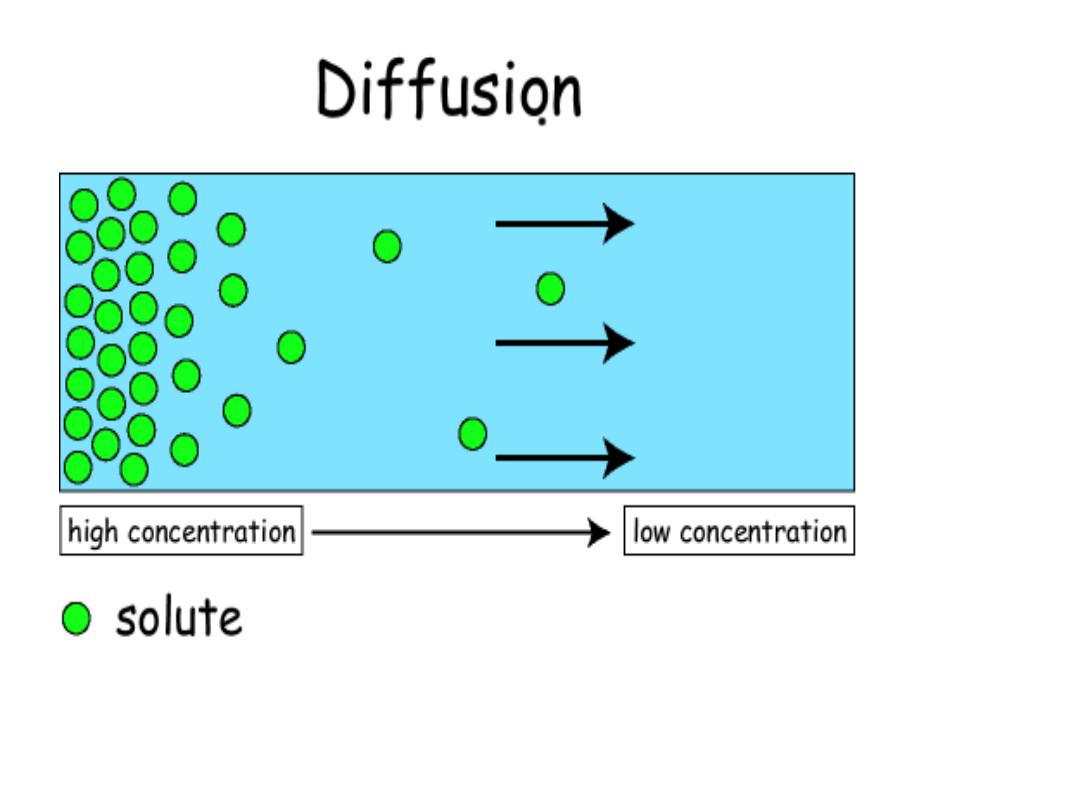
.
Solute moves
DOWN
concentration gradient
(HIGH to LOW)
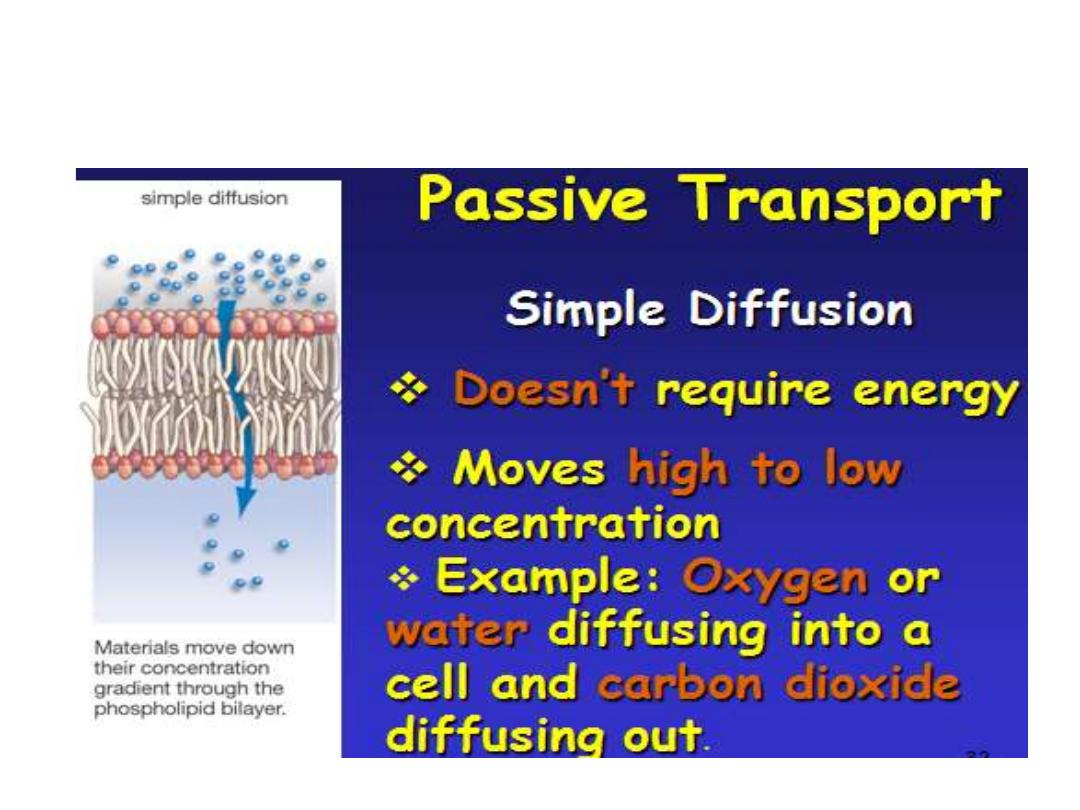
2-passive Transport:
.
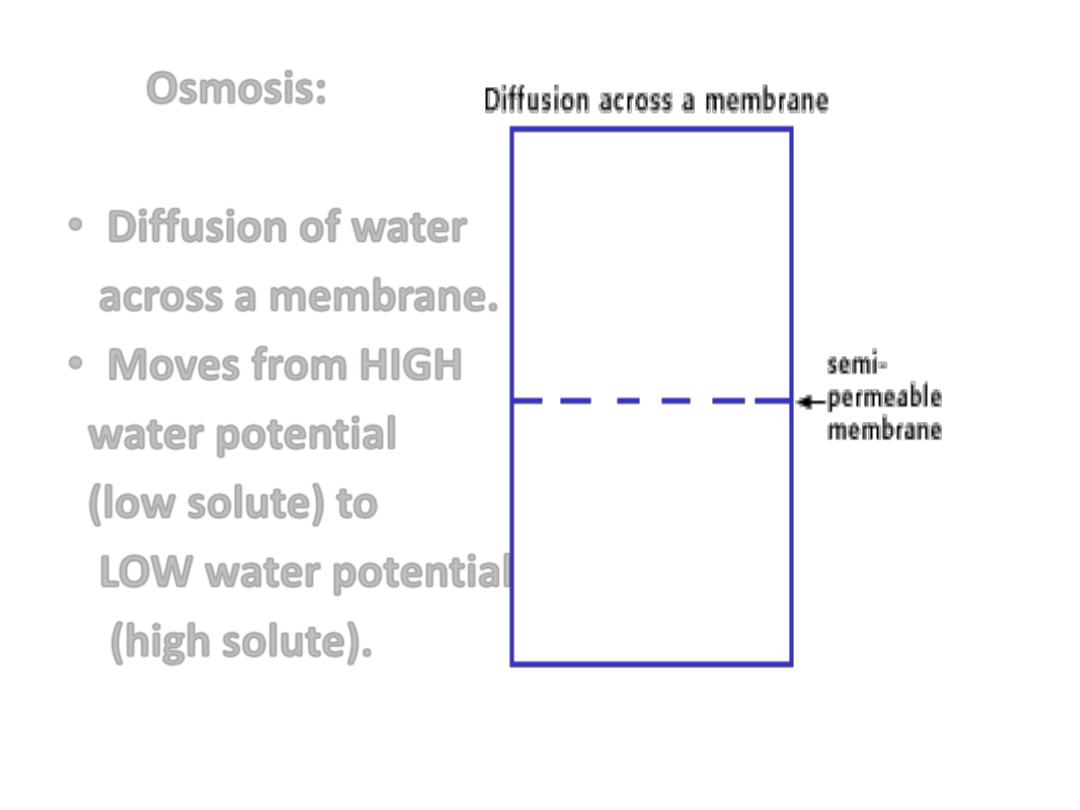
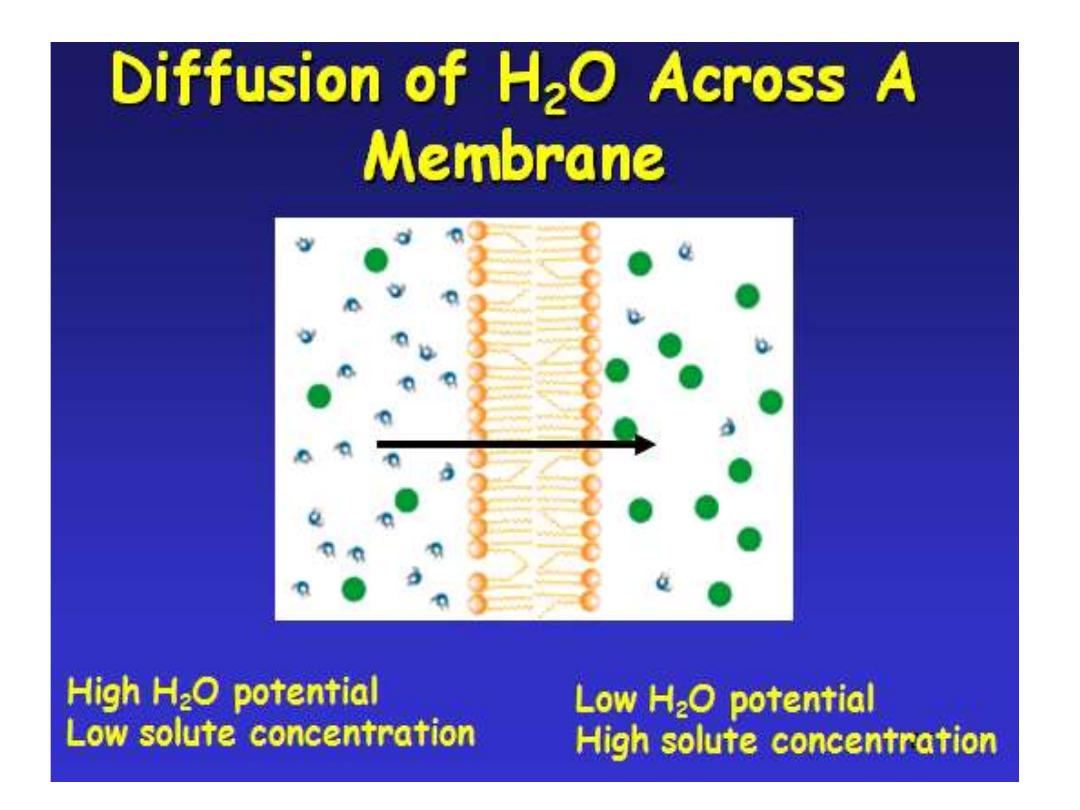
• 3-Osmosis:
• Diffusion of water
across a membrane.
• Moves from
HIGH
water potential
(low solute) to
LOW water potential
(high solute).
.

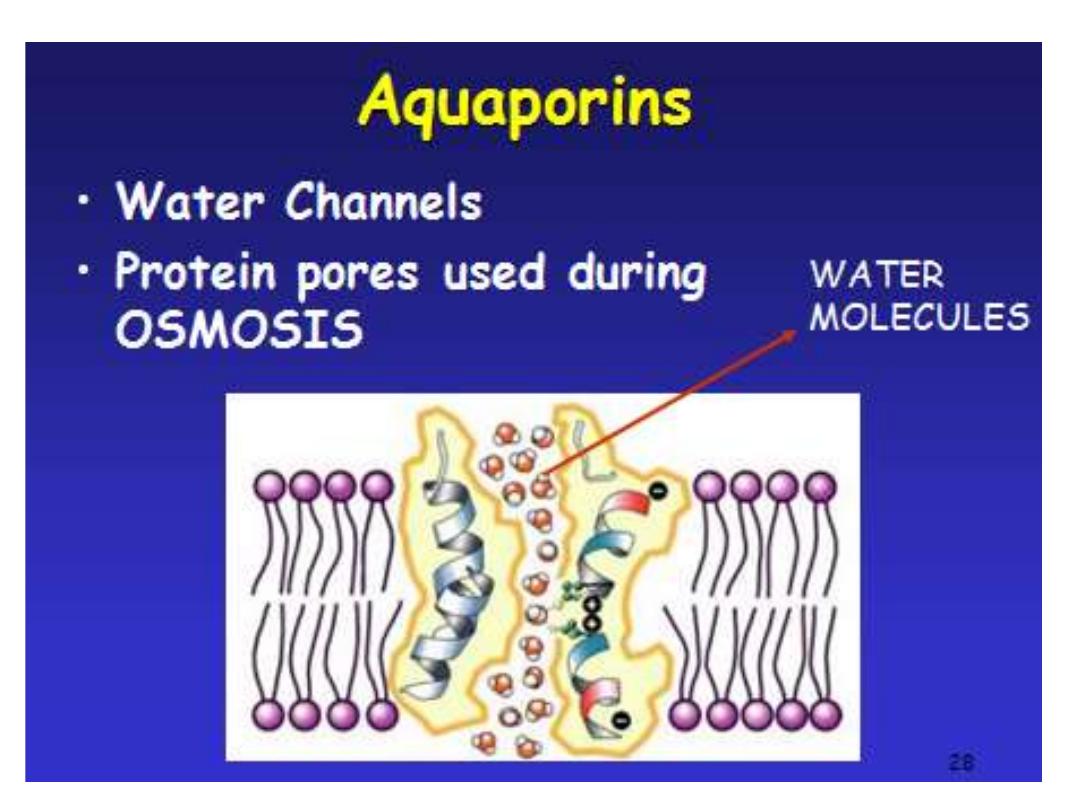
• Channel proteins
are embedded in the cell
membrane & have a pore for materials to
cross.
• Carrier proteins
can change shape to move
material from one side of the membrane to
the other
Types of Transport Proteins:
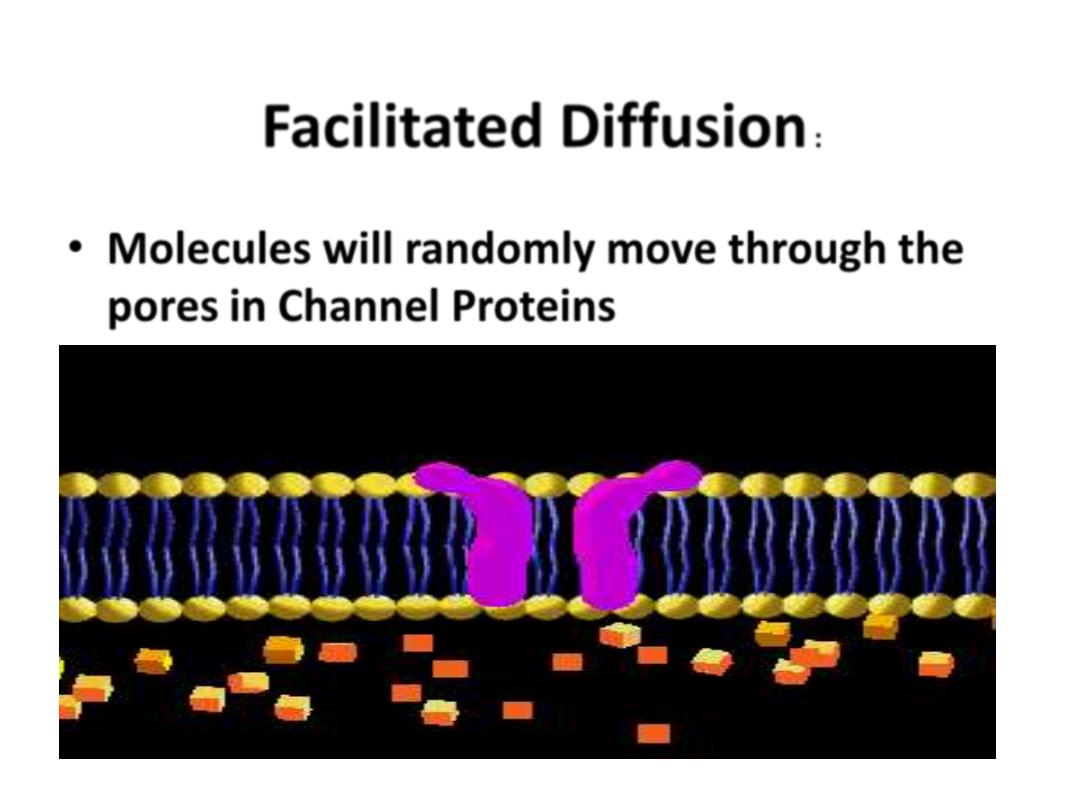
• Molecules will randomly move through the
pores
in
Channel Proteins
Facilitated Diffusion
:
.
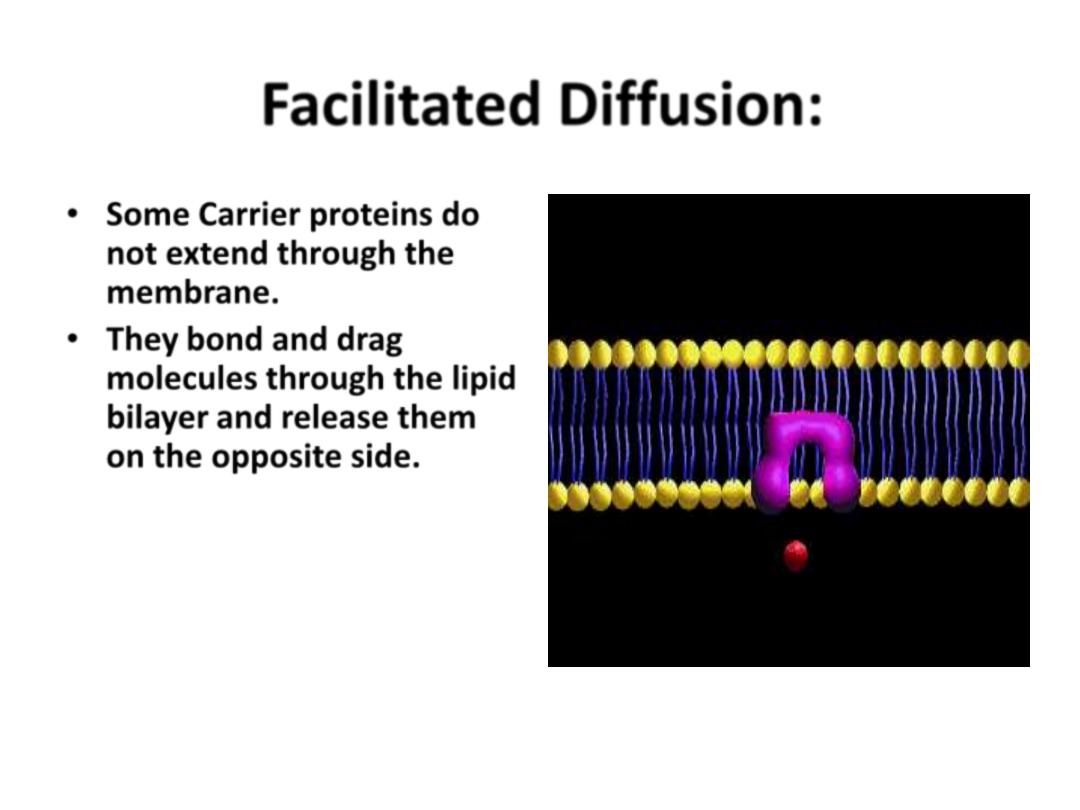
• Some Carrier proteins do
not extend through the
membrane.
• They
bond and drag
molecules through the lipid
bilayer and release them
on the opposite side.
Facilitated Diffusion:
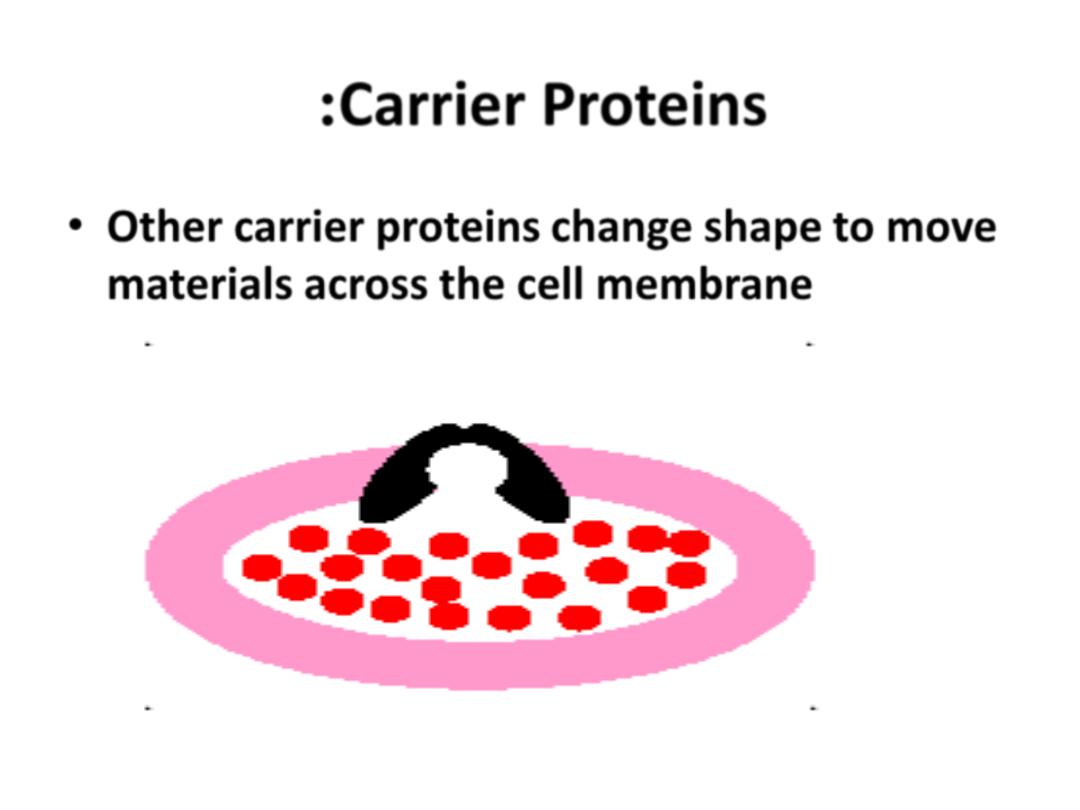
• Other carrier proteins
change shape
to move
materials across the cell membrane
:Carrier Proteins
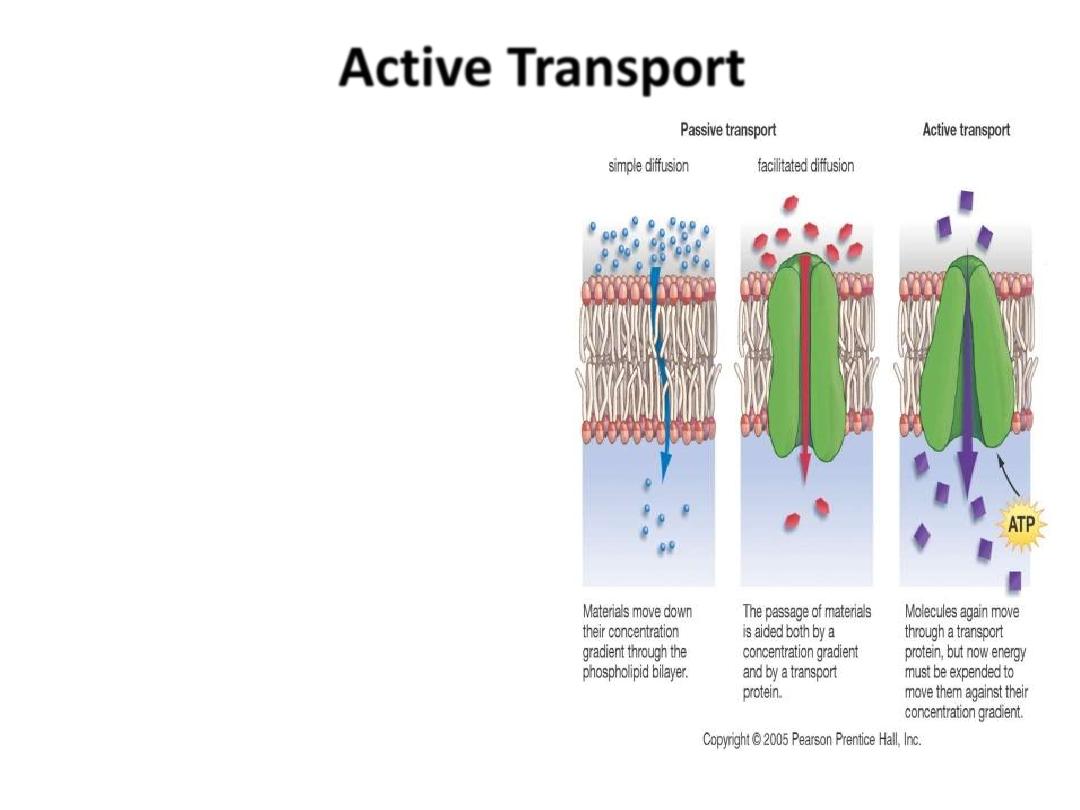
Requires energy or
ATP
Moves materials from
LOW to HIGH
concentration
AGAINST
concentration
gradient
- Examples:
Pumping Na
+
(sodium ions) out and
K
+
(potassium ions) in against
strong concentration
gradients
.
Called Na+-K+ Pump
Active Transport
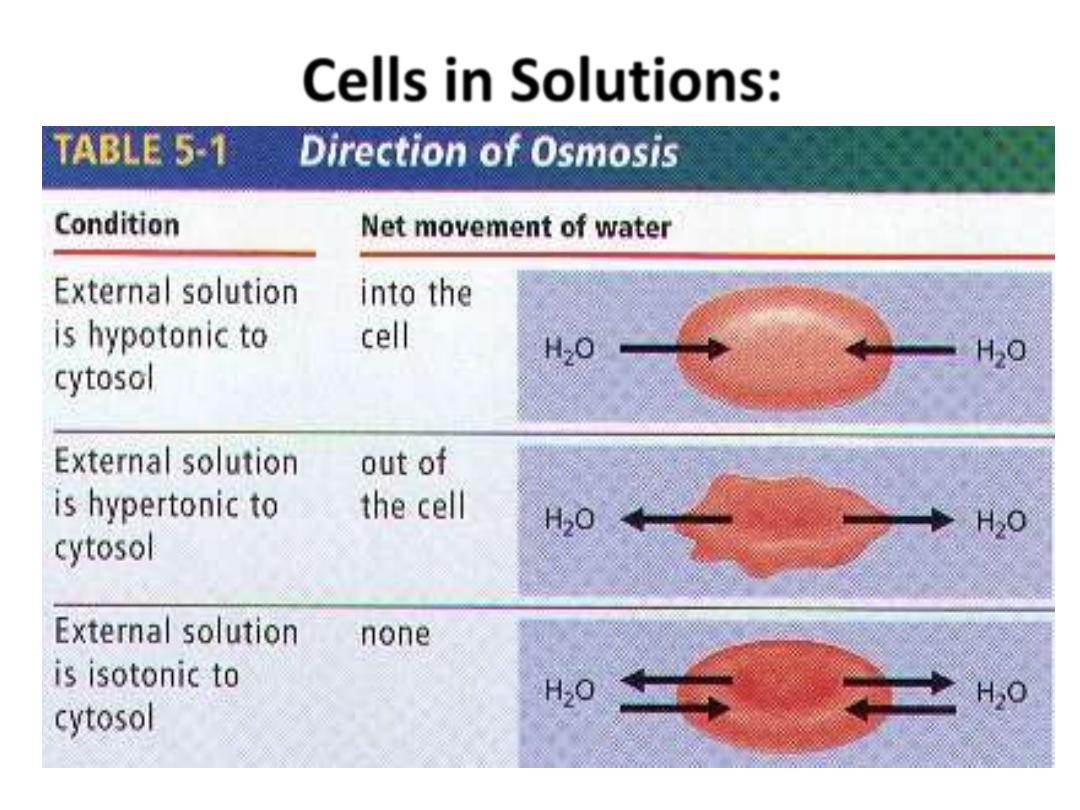
Cells in Solutions:
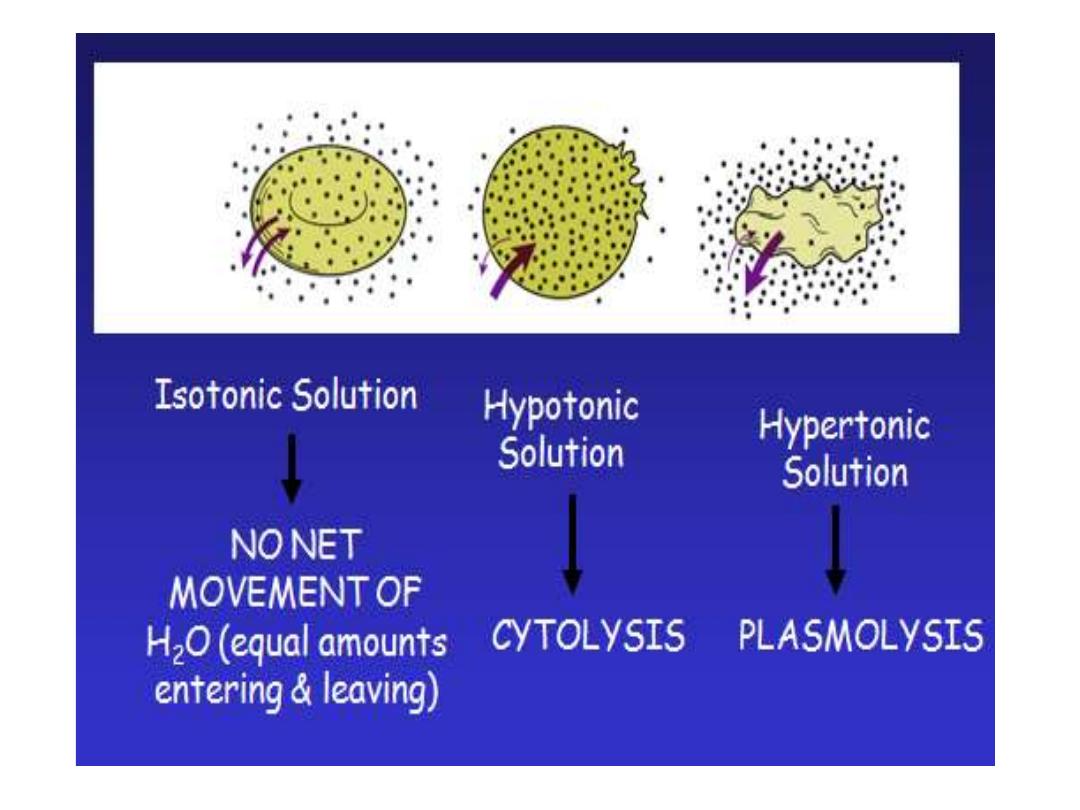
.
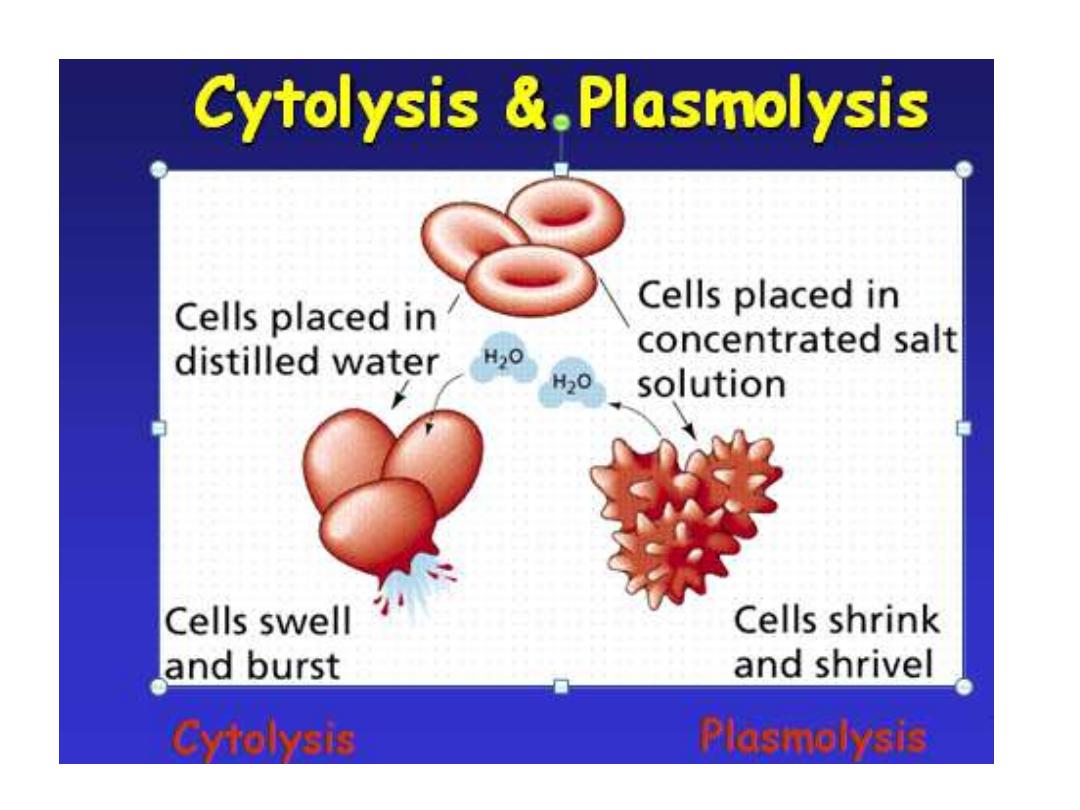
.

Just as material can be brought into the cell by
invagin and formation of a vesicle, the membrane of a
vesicle can be fused with the plasma membrane,
extruding its contents to the surrounding medium. This
is the process of
exocytosis.
• Exocytosis occurs in:
- various cells to remove undigested residues of
substances brought in by endocytosis.
- to secrete substances such as hormones and enzymes.
-to transport a substance completely across a cellular
barrier.
Exocytosis:
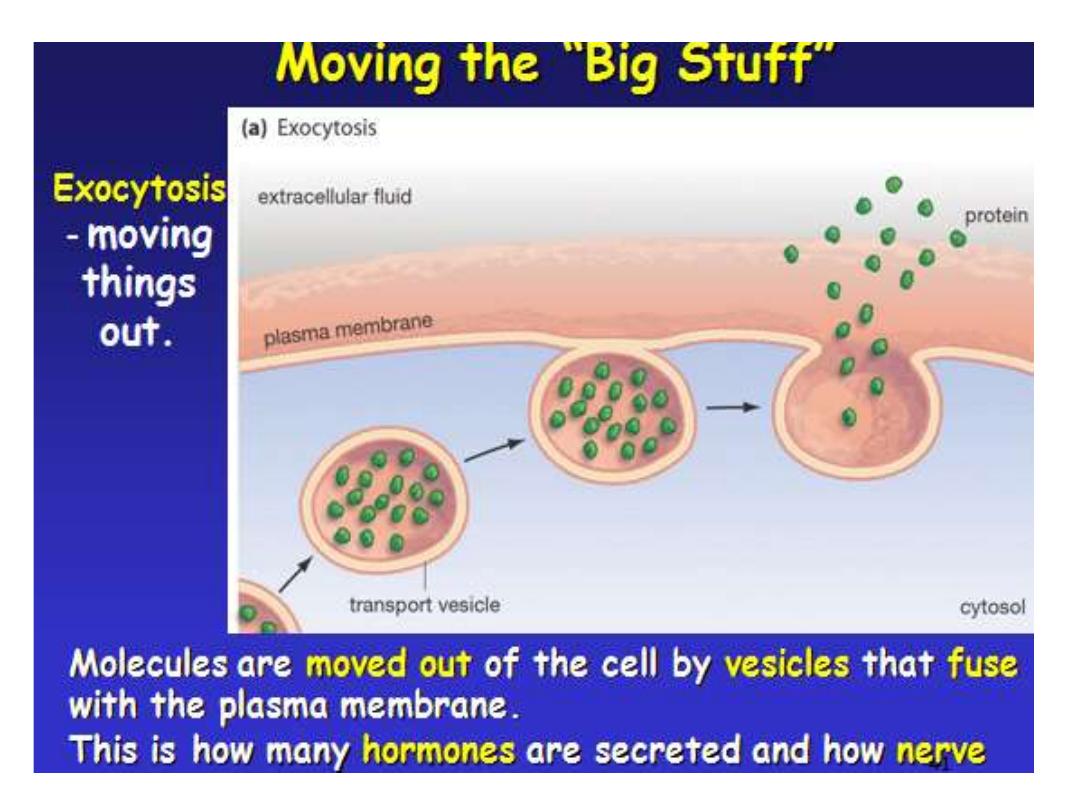
.
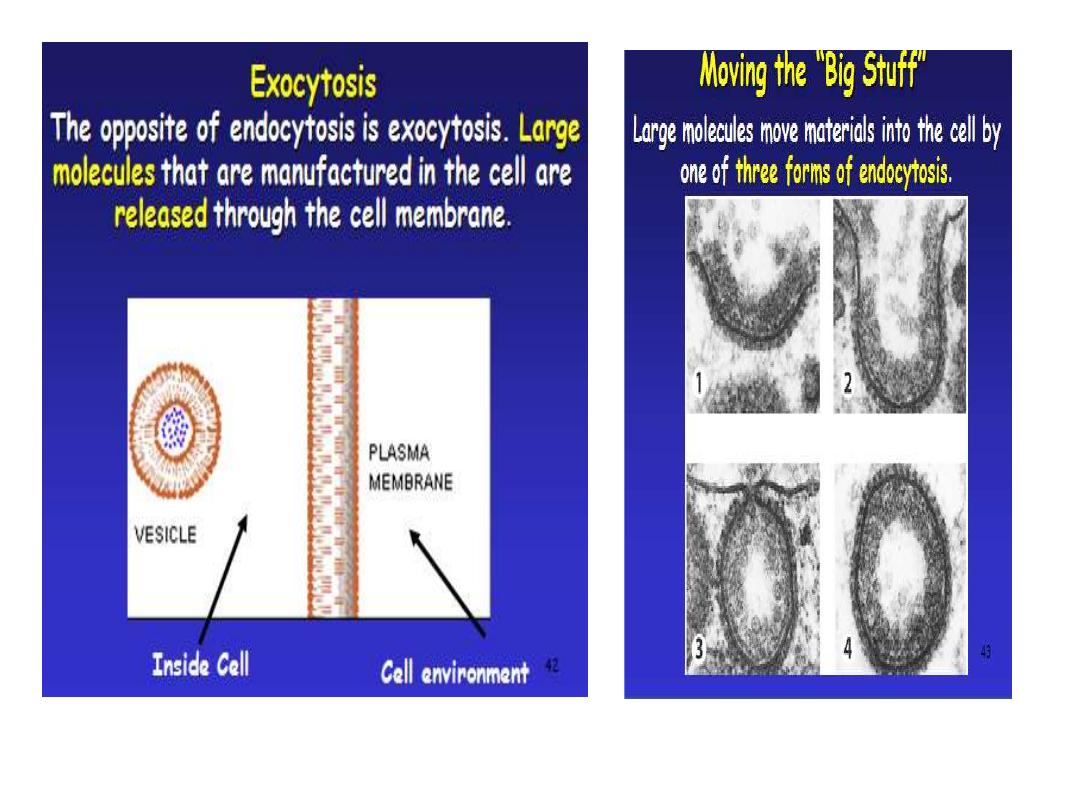
.

• In the process of exocytosis, the undigested
waste-containing food vacuole or the secretory
vesicle budded from Golgi apparatus, is first
moved by cytoskeleton from the interior of the
cell to the surface. The vesicle membrane comes
in contact with the plasma membrane.
• The lipid molecules of the two bilayers
rearrange themselves and the two membranes
are, thus, fused. A passage is formed in the
fused membrane and the vesicles discharges its
contents outside the cell.
.

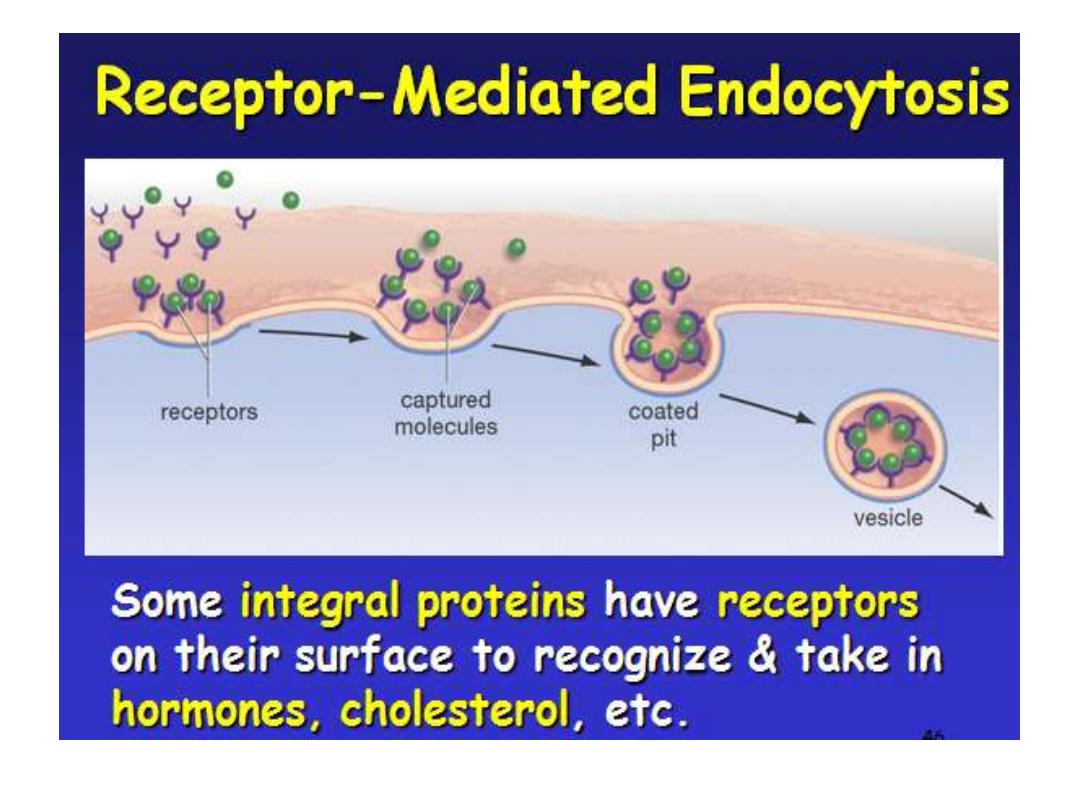
is the process in which cells absorb molecules
by engulfing them. The plasma membrane creates
a small deformation inward, called an invagin, in
which the substance to be transported is
captured.
The deformation then pinches off from the
membrane on the inside of the cell, creating a
vesicle containing the captured substance.
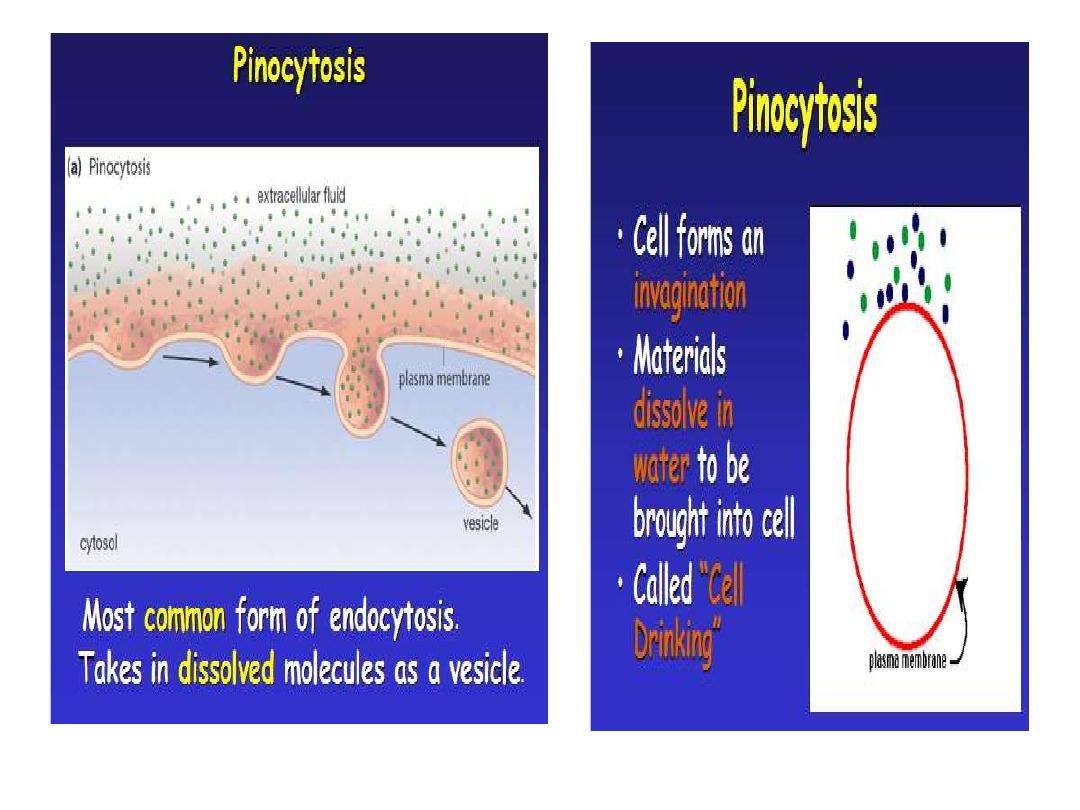
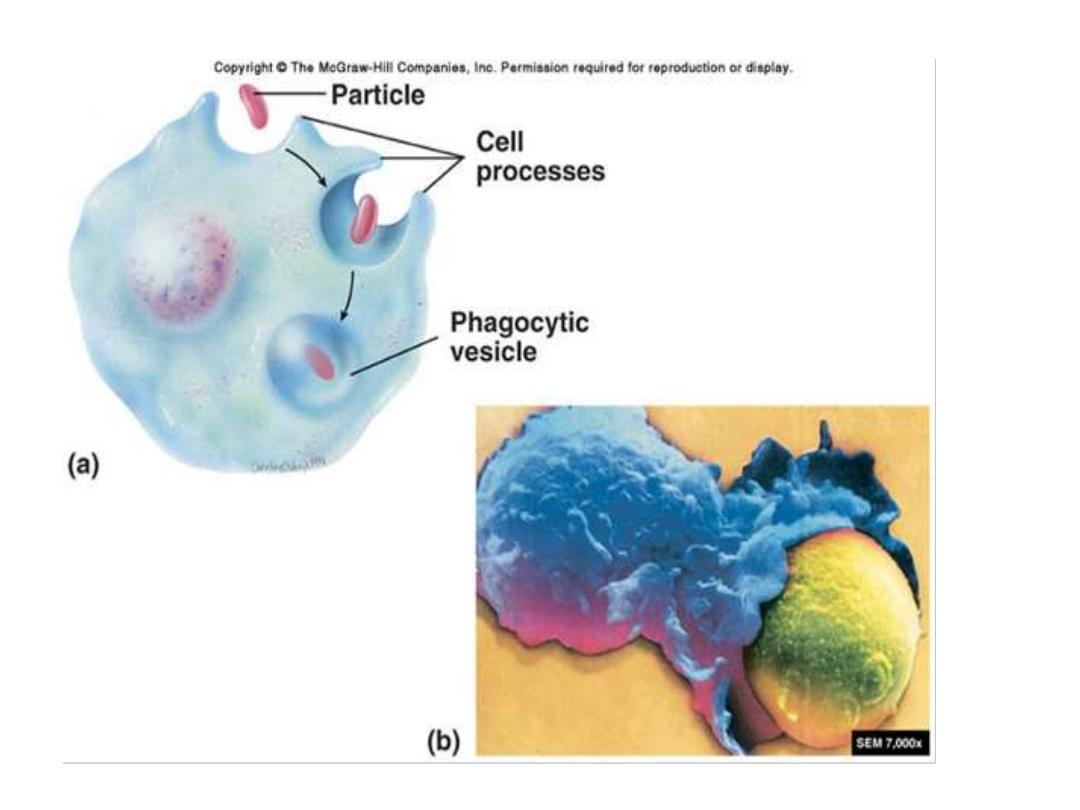
Endocytosis is a pathway for internalizing solid
particles (cell eating or phagocytosis), small
molecules and ions (cell drinking or pinocytosis),
and macromolecules.
Endocytosis requires energy and is thus a form
of active transport.
Endocytosis:
.
.
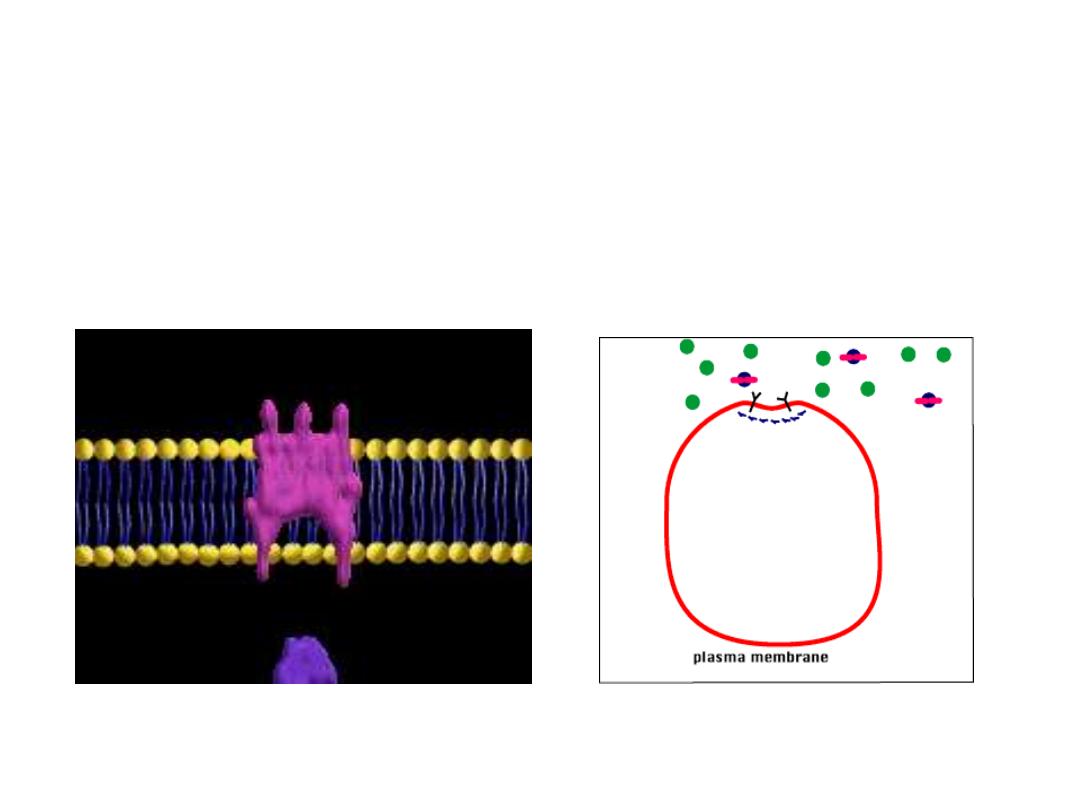
Receptor Proteins:
These proteins are used in intercellular communication. In this figure you
can see the a hormone binding to the receptor. This causes the receptor
protein release a signal to perform some action
.
.

.

Thank You
