Root Canal Irrigation
Dr. Ahmed JawadIntroduction
Irrigation is an important part of root canal treatment, it represent the chemical phase of canal preparation.microorganisms are removed mechanically during canal preparation and eradicated chemically using irrigants.
They are present in the lumen of the root canal as a biofilm adhering to the canal walls.
The smear layer is a layer of microcrystalline and organic particle debris that is found spread on root canal walls after root canal instrumentation.
Its removal may aid in better adaptation of the obturating material to the walls.
It consist of
Organic layer removed by irrigants
Inorganic layer removed by chealating agent
Functions of Irrigants
Rinsing of debrisLubrication of the canal system which facilitates instrumentation
Dissolution of remaining organic material
Antibacterial properties
Softening and removing the smear layer
Penetrating into areas inaccessible to instruments, thereby extending the cleaning process.
Ideal Properties of an Ideal Irrigation Solution
• Have broadspectrum antimicrobial properties.
• Aid in the debridement of the canal system.
• Have the ability to dissolve necrotic tissue or derbis.
• Have low toxicity level.
• Be a good lubricant.
• Have low surface tension so that it can easily flow into inaccessible areas.
• Be able to effectively sterilize the root canals (disinfect them)
• Be able to prevent formation of smear layer during instrumentation or disolve the latter once it is formed.
Factors modifying the activity of irrigating solutions
• Concetration : tissue disolving capability of NaOCL is higher at 5.2%• Contact: Irrigant must come in contact with the substrate.
• Presence of organic tissue: Organic tissues must be removed for effective irrigantion
• Quantity of irrigant used ; increase in quantity increase the effectiveness.
• Gauge of irrigating needle: 27 or 28 is preferred for better penetration in the canal.
• 6.Surface tension of irrigant: lower the surface tension, better is wettiability.
• 7.Temperature of irrrigant: Warming the NaOCL increase its efficacy.• 8. Frequency of irrigation: More is ferquency, better are the result.
• 9.Canal diameter : Wider the canal,better is action of irrigant
• 10.Age of irrigant: Freshly prepared solutions are more efficient than older ones.
Classification of Irrigation solutins
Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl)
It is the most commonly used irrigant due to its potent antibacterial effect, it has pH value (12-13.1)It is provided in bottles of 5.2% concentration, but it could be diluted up to 0.05%.
Warming of NaOCl increases its dissolution effect
It is extremely irritant to the vital tissues so it should be used carefully by:
Gentile injection
The use of small needles
Avoid locking the syringe in the canals
Advantages of NaOCl
Gross debridementDissolution of tissue
Lubricant
Antibacterial
Cheep and commercially available
Chlorhexidine Gluconate (0.2-2%)
It has a prolonged antibacterial effect due to its ability to bind to hydroxyapatite crystalsIt has low toxicity compared to NaOCl
It does not have tissue solvent action
EDTA
Ethylene Diamine Tetra acetic Acid, it is a chelating agent that react with calcium ions present in dentin.It is used to enlarge narrow, curved and calcified canals
It also aids in the removal of smear layer (inorganic part)
It is available in the form of gel that is applied in the canals to facilitate instrumentation or in the form of Liquid to be used as a final irrigation for smear layer removal before obturation.
Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2 ) 3 %
It is odorless, clear liquidIts effervescence action is capable for removing loose debris from inside the canal
Also the release of ozone (O3) has antibacterial activity against anaerobic bacteria
if this irrigant passes to the periapical tissue the patient will have a post
operative pain or even tissue
emphysema could happen
MTAD
M Mixture ofT Tetracycline
A Acid (citric acid)
D Detergent
It has the advantages of being antibacterial, chelating and detergent agent
The effectiveness of MTAD to completely remove the smear layer is enhanced when low concentrations of NaOCl (1.3%) are used as an intracanal irrigant before the use of MTAD.
Irrigation Techniques
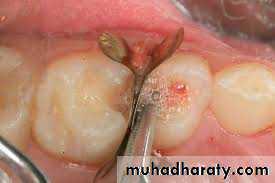
SyringeThe technique involves dispensing of an irrigant into a canal through needles/cannulas of variable gauges, either passively or with agitation. The latter is achieved by moving the needle up and down the canal space.
Closed end, side-port delivery improve the hydrodynamic activation of an irrigant and reduce the chance of apical extrusion
Brushes
They are adjuncts that have been designed for debridement of the canal walls or agitation of root canal irrigant.Manual-Dynamic Irrigation
It is often difficult for the irrigant to reach the apical portion of the canal because of the so-called vapor lock effectResearches has shown that gently moving a small instrument up and down in short 2- to 3-mm strokes within an instrumented canal can produce a hydrodynamic effect eliminating the vapor lock because the space previously occupied by air is replaced by the instrument, carrying with it a film of irrigant to the working length.
Machine assisted1.Rotary brushes
This highly flexible microbrush is molded entirely from polypropylene and might be used manually with a rotary action. However, it is more effective when attached to a contra-angle handpiece running at 600 rpm2.Continuous Irrigation During Rotary Instrumentation
The Quantec-E irrigation system is a self-contained fluid delivery unit that is attached to the Quantec-E Endo System. It uses a pump console, 2 irrigation reservoirs, and tubing to provide continuous irrigation during rotary instrumentation .3.Sonic
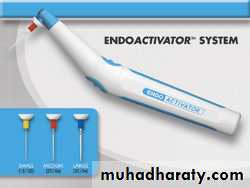
• The EndoActivator System is a more recently introduced sonically driven canal irrigation system, It consists of a portable handpiece and 3 types of disposable polymer tips of different sizes. These tips are claimed to be strong and flexible and do not break easily.Because they are smooth, they do not cut dentin.
4.Ultrasonic
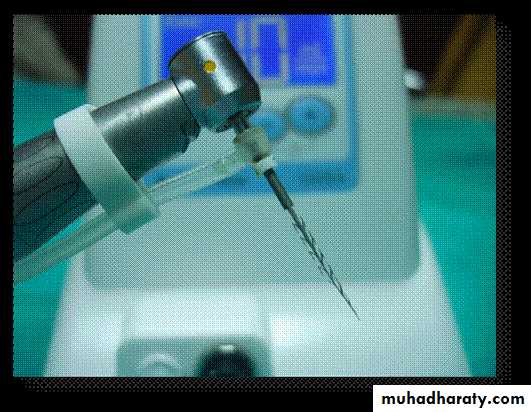
Eg; Irrisafe fileManufactured from stainless steel, it is small, parallel-shaped, and noncutting, making the instruments easy to use during passive ultrasonic irrigation with sodium hypochlorite.
It is more effective than syringe irrigation due to the much higher velocity and volume of irrigant flow that created in the canal during ultrasonic irrigation
5.Pressure Alternation Devices
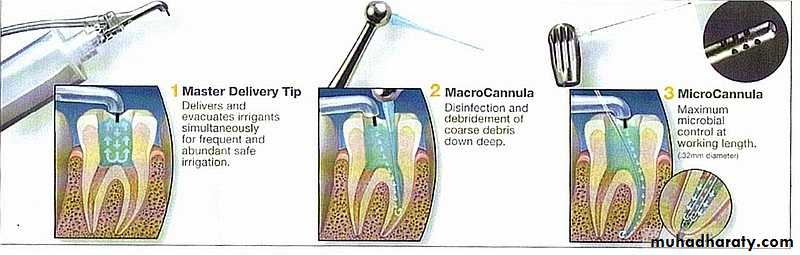
EndoVac SystemThis system is comprised of three parts for 3 steps:
1.Gross Debris Evacuation with the Master Delivery Tip2.Coarse Debris Evacuation with the MacroCannula
3.MicroCannula Microscopic Debris Evacuation
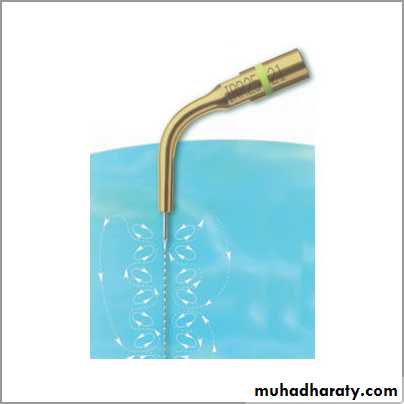
6.Laser-activated irrigation (LAI)
Erbium laser has been introduced as a method for activating the irrigant.
In water ,activation of the laser may result in the formation of
large elongated vapor bubbles, which expand and
collapse resulting in development of negative
pressure. Therefore LASER works as fluid pump in
the canal increasing the efficiency of irrigation