
Connective tissue
Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer
Department of Anatomy/ Histology section

Learning objectives
At the end of this Lecture, the 1
st
medical student will be able to:
•
Define the components of connective tissue
•
List the cells found in connective tissue and state their origin
•
Describe the light and electron microscopic features of connective
tissue cells
•
Correlate the histological features of connective tissue cells with
their functions
•
State the types of collagen fibers and mention their location
•
State the histological characteristics of reticular fibers
•
Compare between collagen and reticular fibers
•
State the histological characteristics of elastic fibers
•
Define the types of ground substances and state their functions
•
Compare between the different types of ground substances
•
State few related disorders
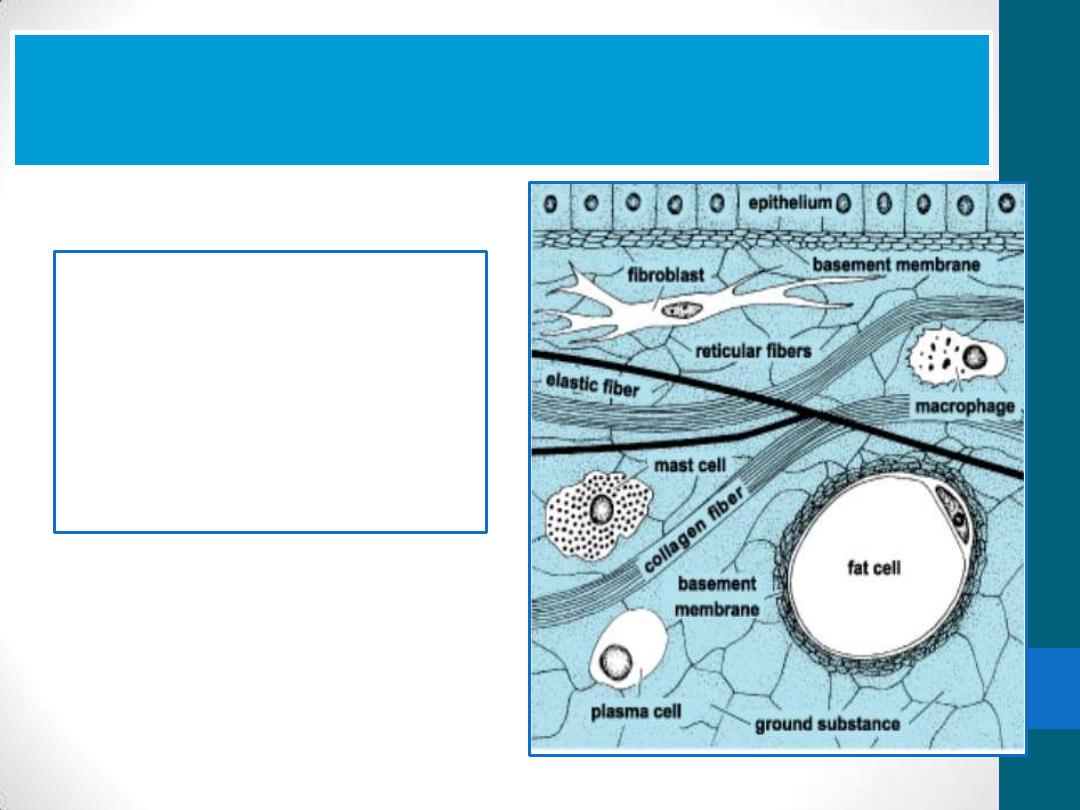
Connective tissue is formed by three
classes of components:
•
Cells
•
Fibers
•
ground substance
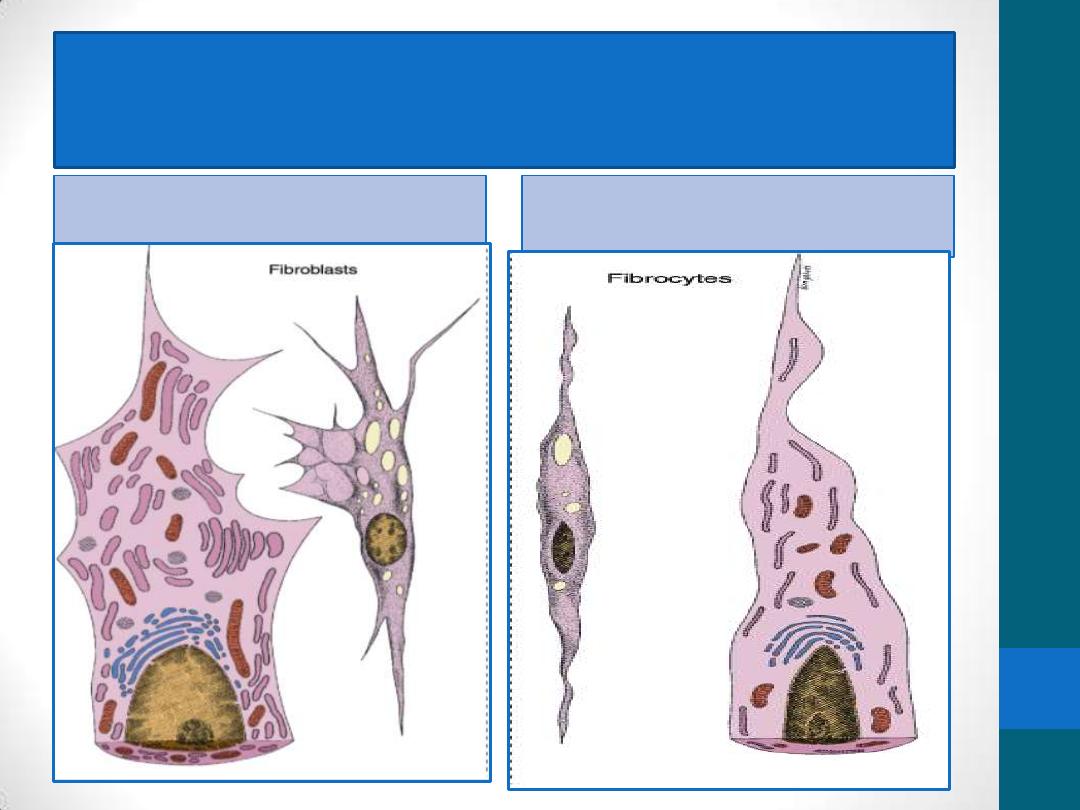
Fibroblasts :
Two stages of activity
Active
Quiescent
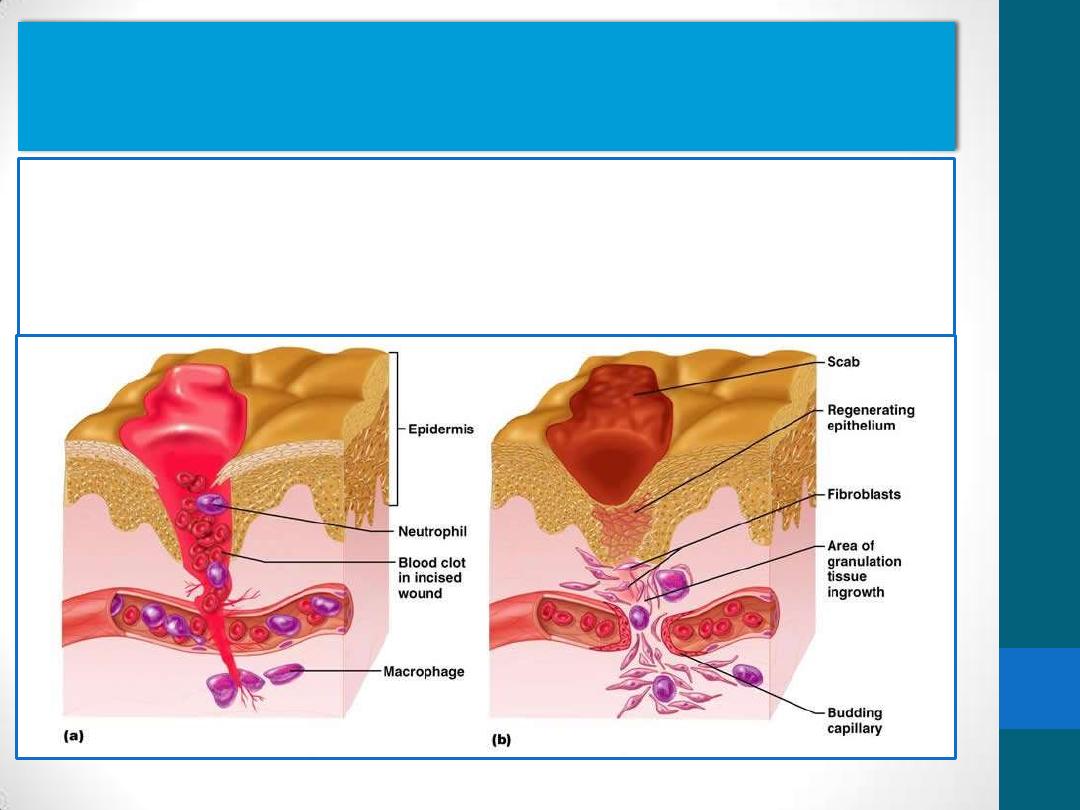
The regenerative capacity of the connective tissue is
clearly observed when tissues
•
are destroyed by inflammation or traumatic injury e.g. the
healing of surgical incisions
•
The main cell type involved in repair is the fibroblast.
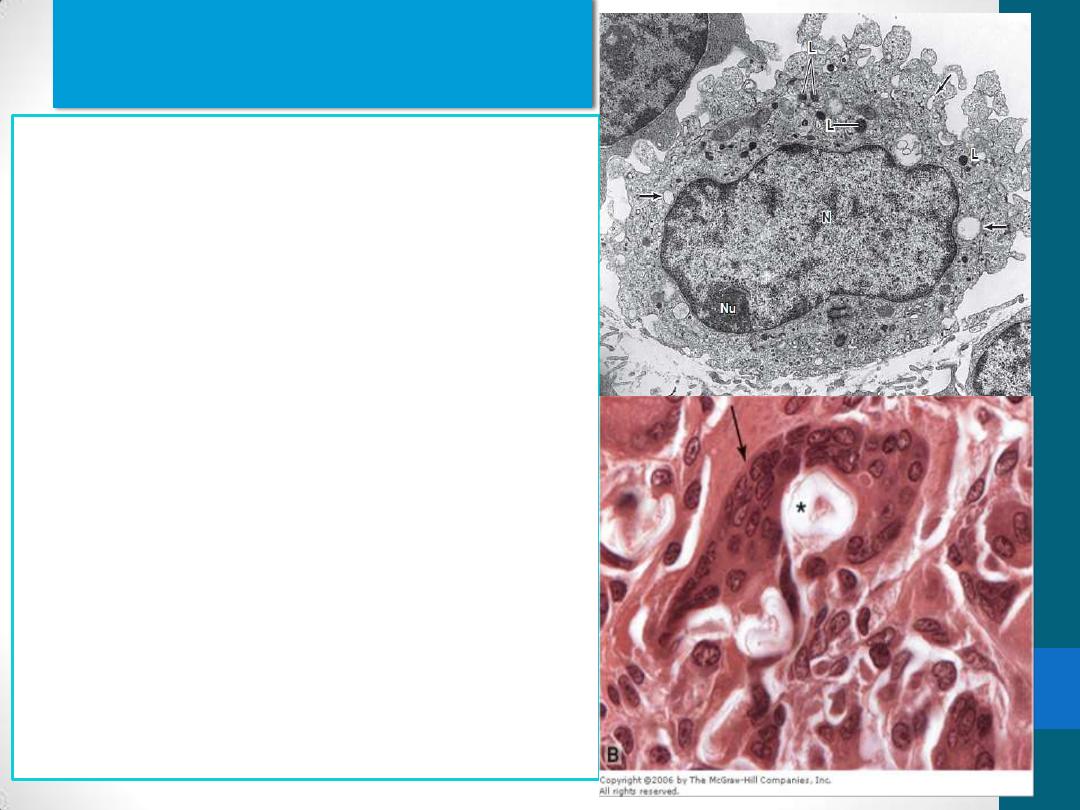
Macrophages
long-living cells and may survive for
months in the tissues.
Monocytes and macrophages are
the same cell at different stages of
maturation.
IN TEM, they shown to have:
Irregular surface with pleats,
protrusions, and indentations
well-developed Golgi complex,
Many lysosomes
When adequately stimulated,
macrophages may increase in size
and fuse to form multinuclear
giant cells, usually found only in
pathologic conditions.
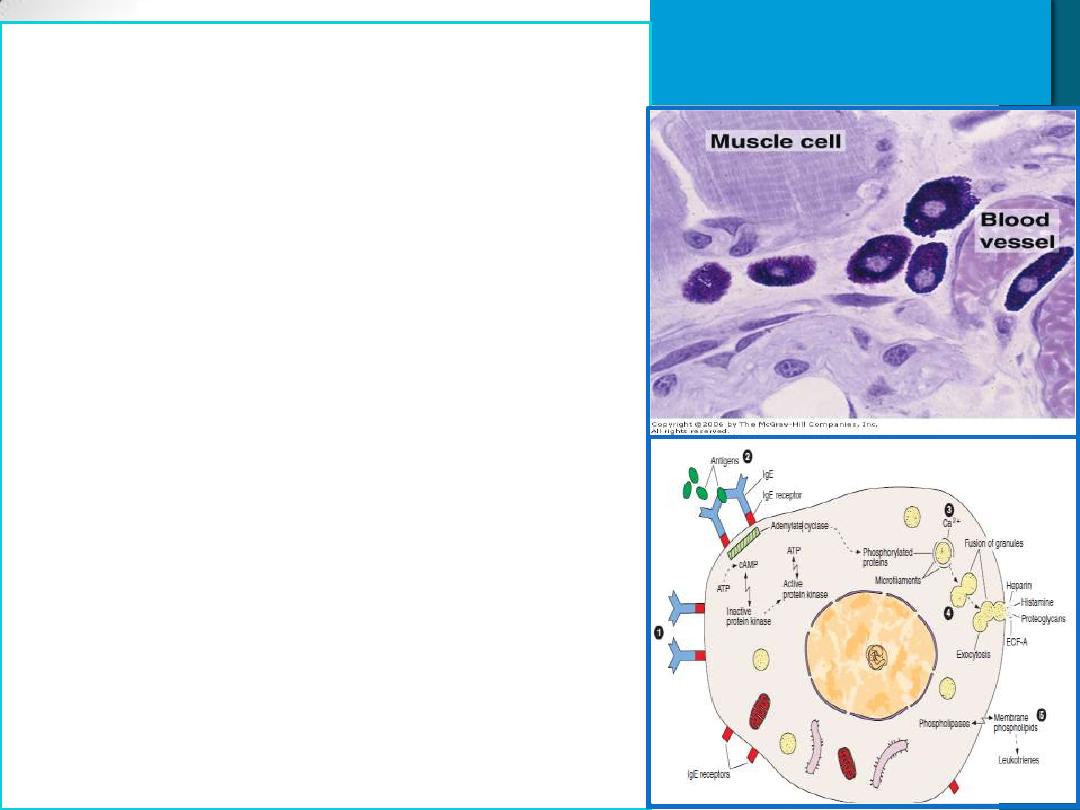
Mast Cells
Cytoplasm is filled with Basophilic
secretory granules(Heparin,
Histamine,..)
similar to basophilic leukocytes
Two populations of mast cells in
connective tissues
1. Perivascular mast cells numerous near
small blood vessels
in skin & Mesenteries
2. Mucosal mast cell numerous in tissues
lining
digestive & respiratory tracts
These major locations suggest that
mast cells place themselves strategically
to function as sentinels detecting
invasion by microorganisms.
promotes the allergic reactions also
known as immediate hypersensitivity
reactions (anaphylactic shock)
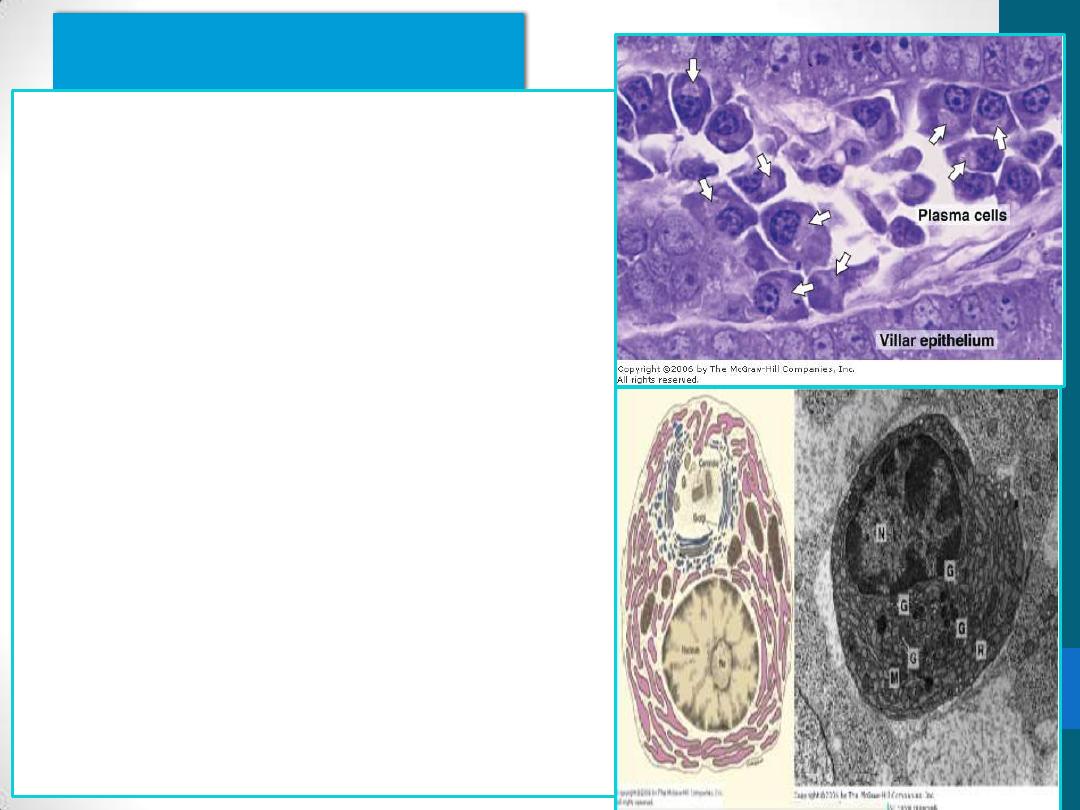
Plasma Cells
B lymphocytes –derived
synthesis of antibodies(IgE)
basophilic cytoplasm due to
their richness in RER
Arrows - pale area -
juxtanuclear Golgi complex &
centrioles
The nucleus
spherical but eccentrically
placed
Clock-face appearance
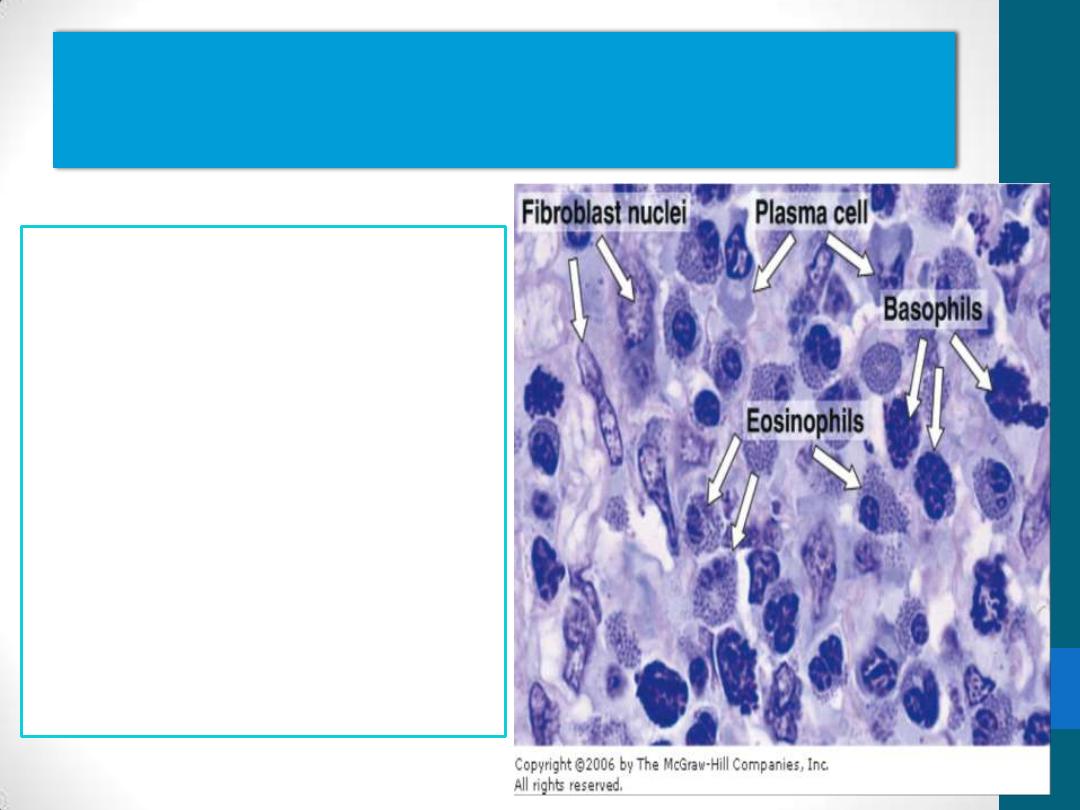
Leukocytes (white blood cells)
•
a population of
wandering cells in
connective tissue
•
They leave blood to
enter connective tissue
by a process called
diapedesis
•
Diapedesis increases
greatly during
inflammation.
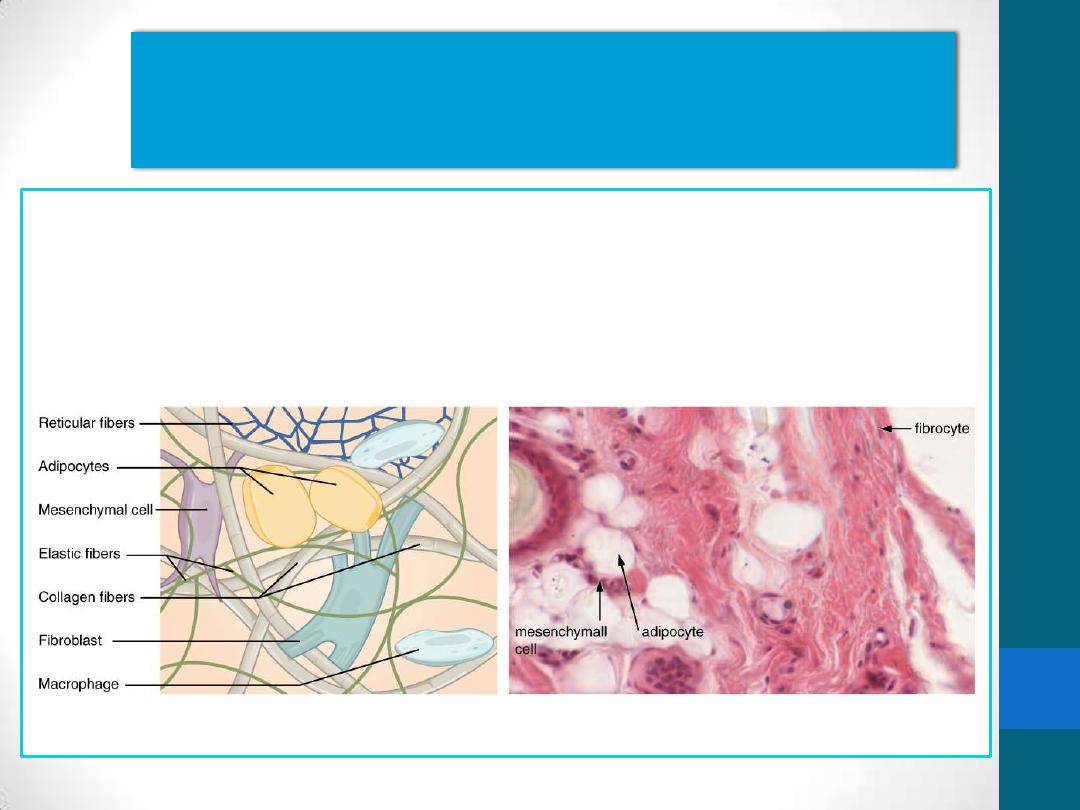
Adipocytes( fat cells)
•
connective tissue cells that have become specialized for storage of
neutral fats or for the production of heat.
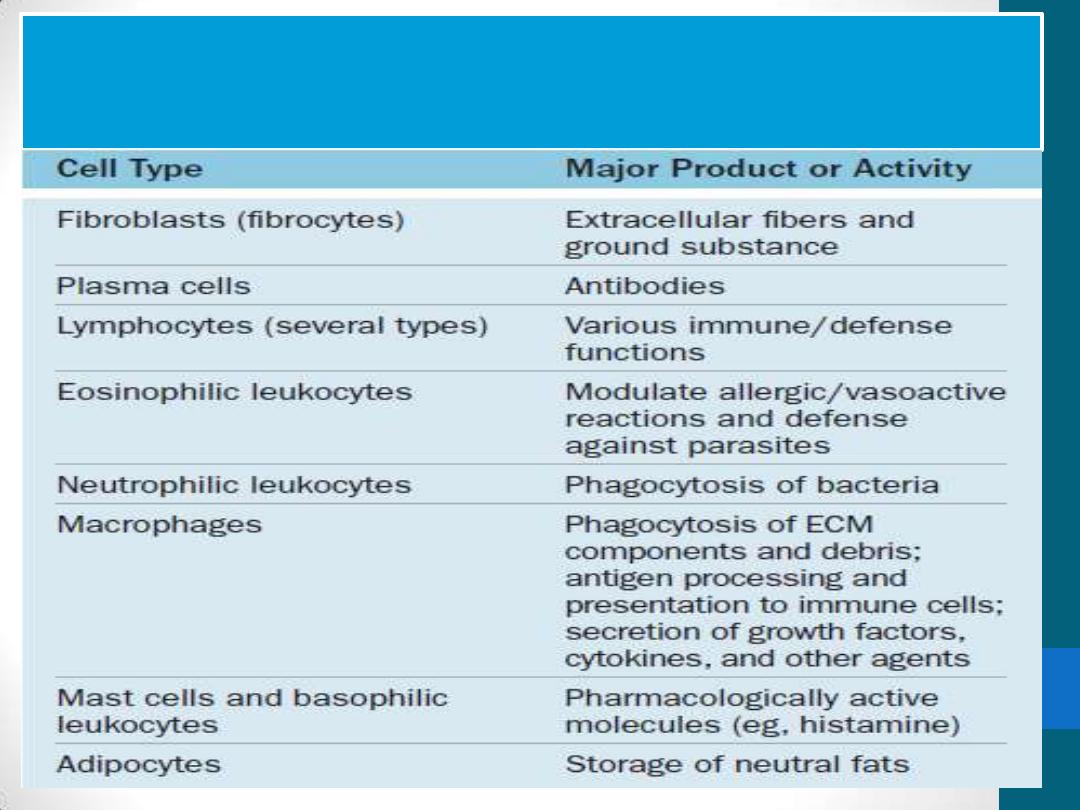
Functions of cells in connective
tissue proper
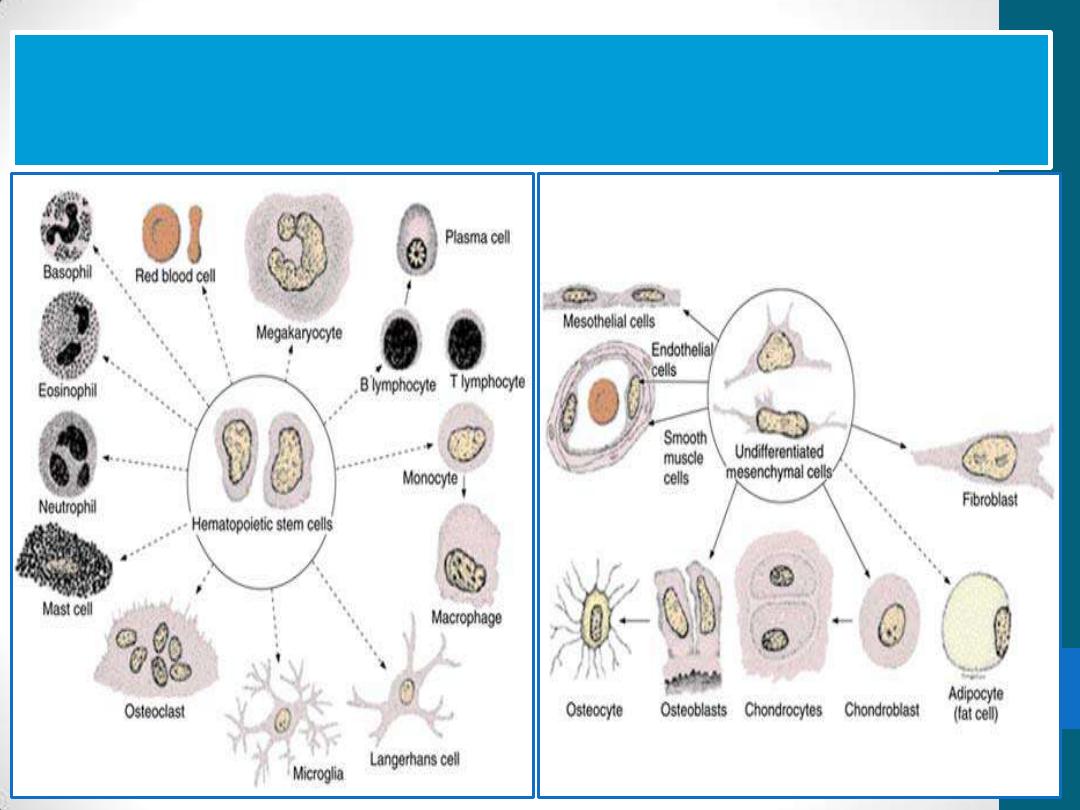
All connective tissue cells are derived from
two types of stem cells

Quiz (1)

The Connective tissue cell that is responsible
for synthesis of Antibodies is
1. Fibroblast
2. Macrophage
3. Mast cell
4. Plasma cell
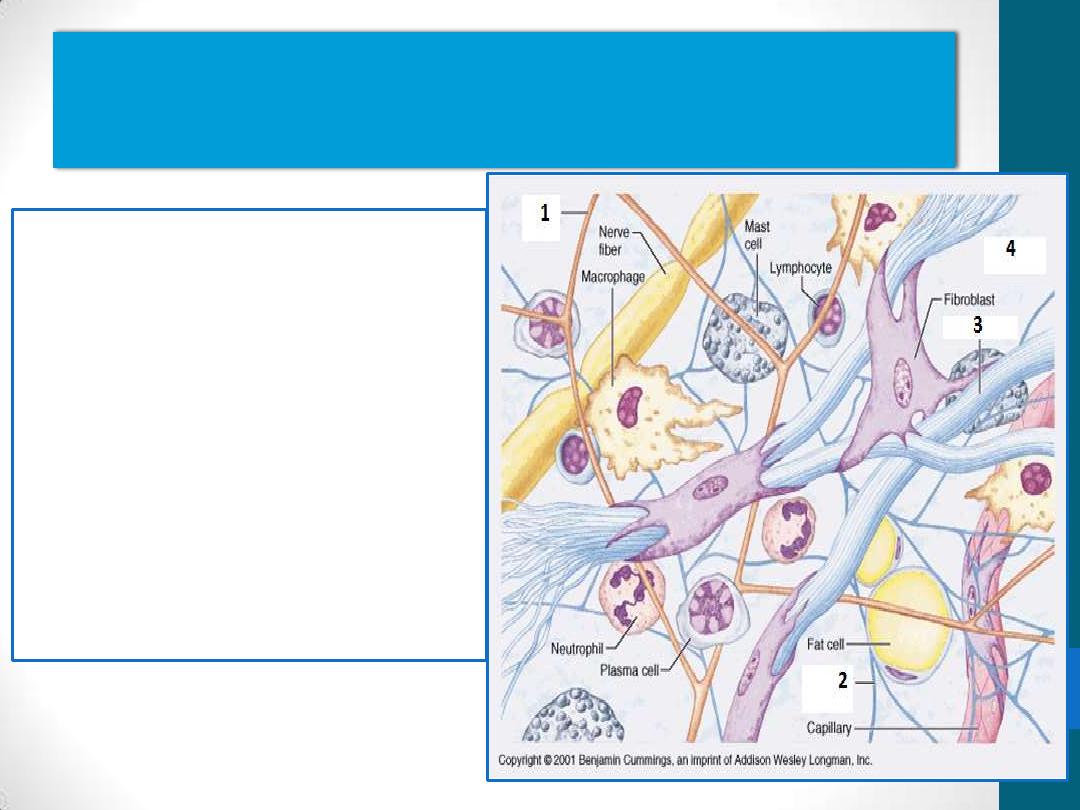
The connective tissue fibers
•
There are three types
of fibers:
1.
Collagen
2.
Reticular
3.
Elastic
•
are formed by proteins
(collagen & elastin)
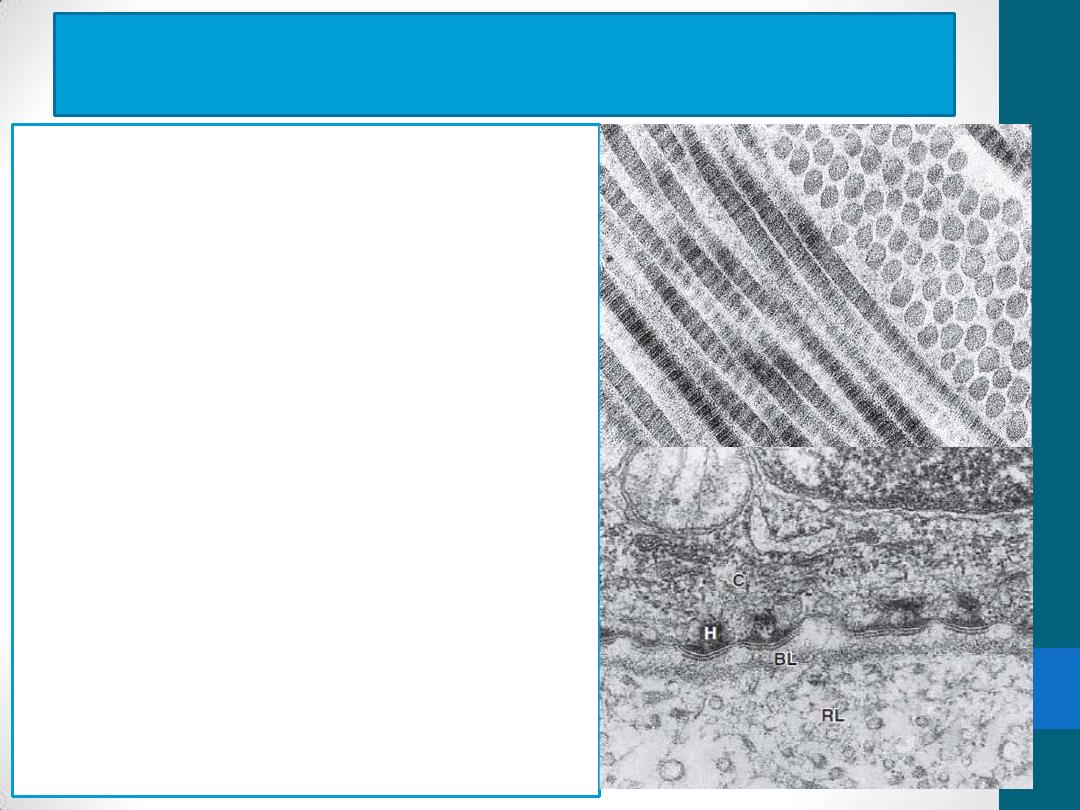
Classification of Collagen Fibers
1.
Fibrillar collagens:
collagen
types I, II, and III
Collagen type I
, the most abundant
and widely distributed collagen
(tendons, organ capsules, and
dermis)
2. Sheet-forming collagens:
collagen
type IV
(external laminae and the
basal lamina in all epithelia)
3. Linking/anchoring collagens:
Type
VII collagen
binds type IV & anchors
the basal lamina to the underlying
reticular lamina in basement
membranes.

Collagen renewal
Very slow process in general
tendons and ligaments(collagen is very
Stable)
periodontal ligament(the collagen turnover rate is
high)
To be renewed, the collagen must first be degraded.
Degradation is initiated by specific enzymes called
collagenases
Many pathologic conditions are directly attributable to
insufficient or abnormal collagen synthesis
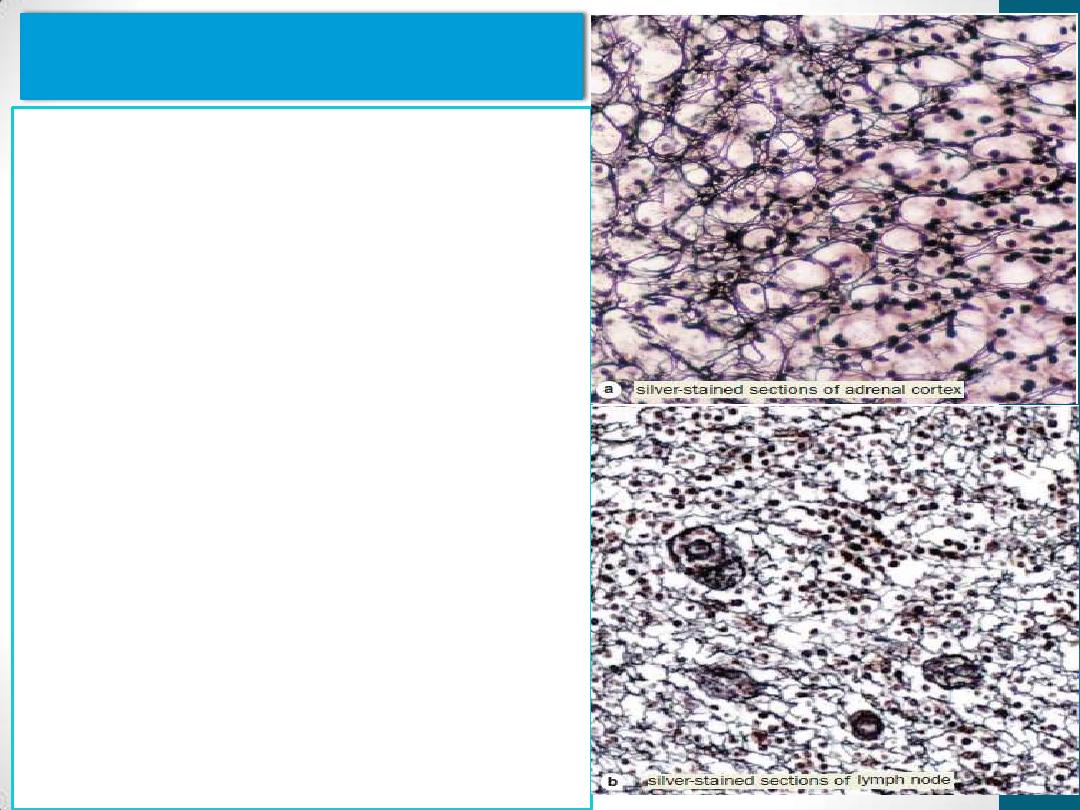
Reticular fibers
consist mainly of collagen type III
form an extensive network in
hematopoietic organs & some
lymphoid organs (e.g., spleen and
lymph nodes)
Surround smooth muscle and
nerve fibers, and small blood
vessels.
stroma of Liver & endocrine
glands
are seldom visible in hematoxylin
and eosin (H&E) preparations but
are characteristically stained black
by impregnation with silver salts
are also periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
positive . Reticular fibers contain
up to 10% carbohydrate as
opposed to 1% in most other
collagen fibers.
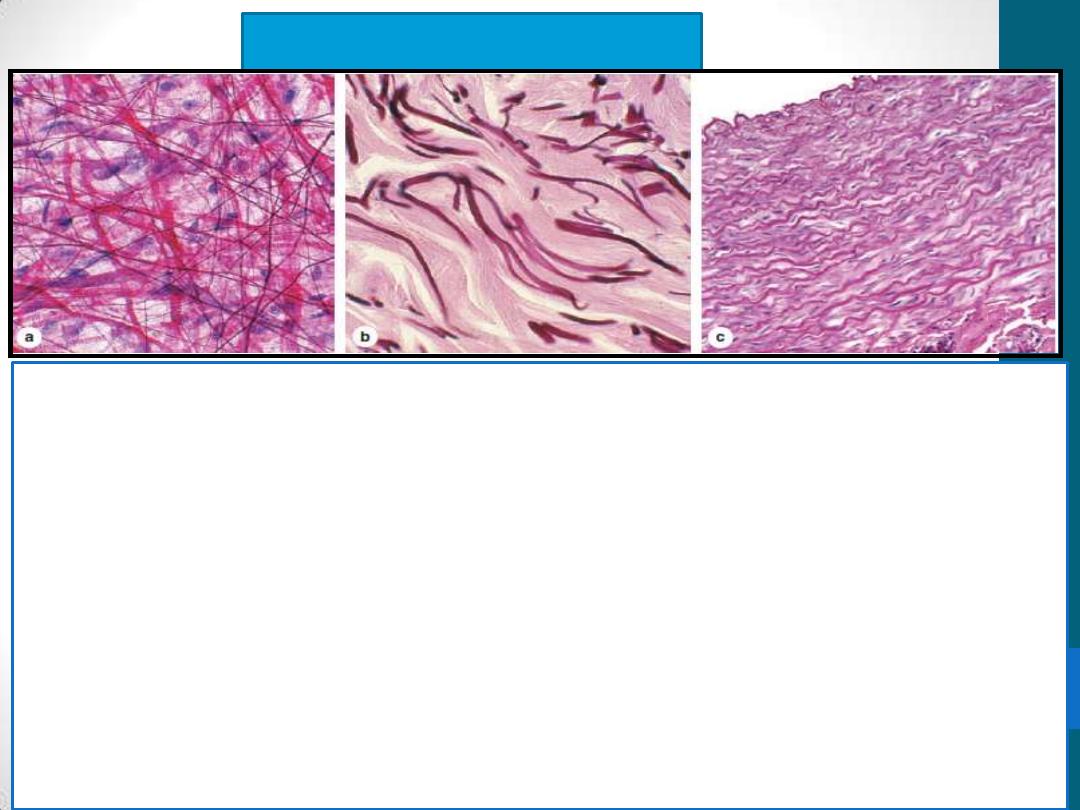
Elastic Fibers
•
are also thinner than the type I collagen fibers and form sparse
networks interspersed with collagen bundles
•
have physical properties similar to those of rubber, allowing tissues
to be stretched and return to their original shape.
•
In the wall of large blood vessels, especially arteries, elastin also
occurs as fenestrated sheets called elastic lamellae.
•
Elastic fibers and lamellae stain poorly with H&E; they are stained
more darkly than collagen in other stains such as orcein and
aldehyde fuchsin

Ground Substance
1. Glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides)
•
linear polysaccharides formed by repeating disaccharide units
•
5 glycosaminoglycan types
1.
Keratan sulfate
2.
Chondroitin sulfate
3.
Dermatan sulfate
4.
Heparan sulfate
5.
Hyaluronic acid
GAGs are intensely hydrophilic, contributing to the viscosity of
ground substance, and are polyanions, binding a great number of
cations (usually sodium)
Ground Substance
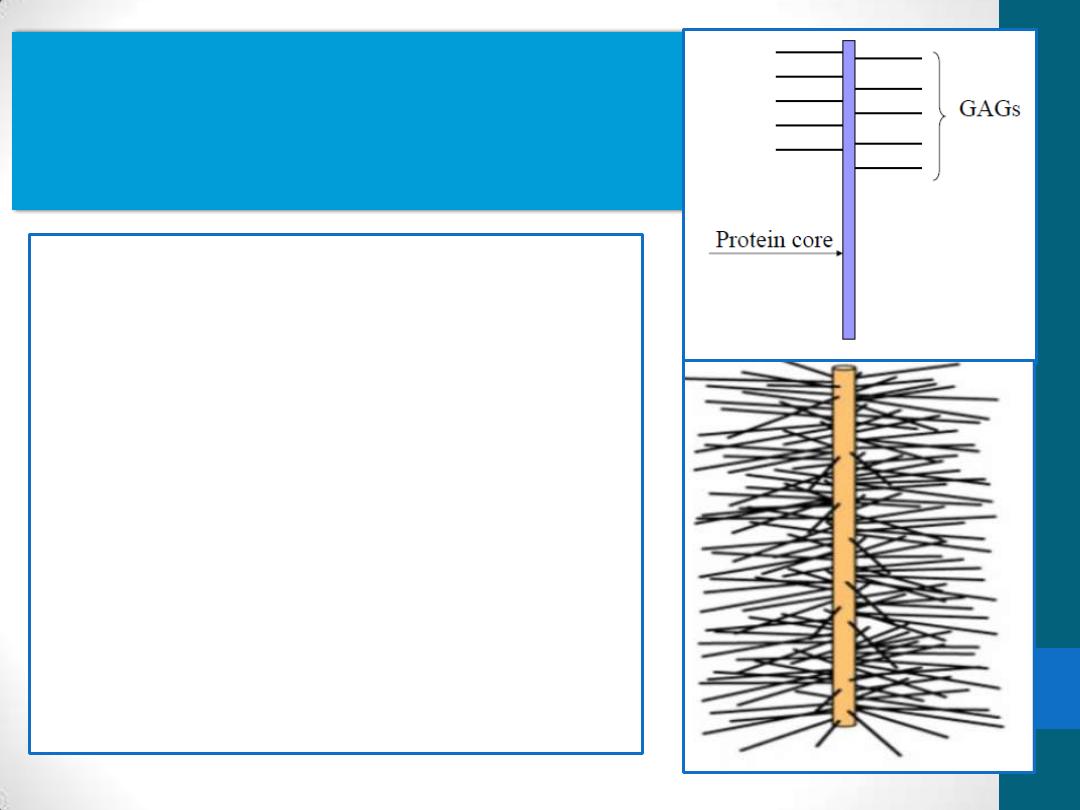
2. Proteoglycans
•
linear chains of
Glycosaminoglycans are bound
covalently to a protein core
•
generally having more
carbohydrate than do
glycoproteins
anchoring cells to the matrix
bind many protein growth
factors
Ground Substance
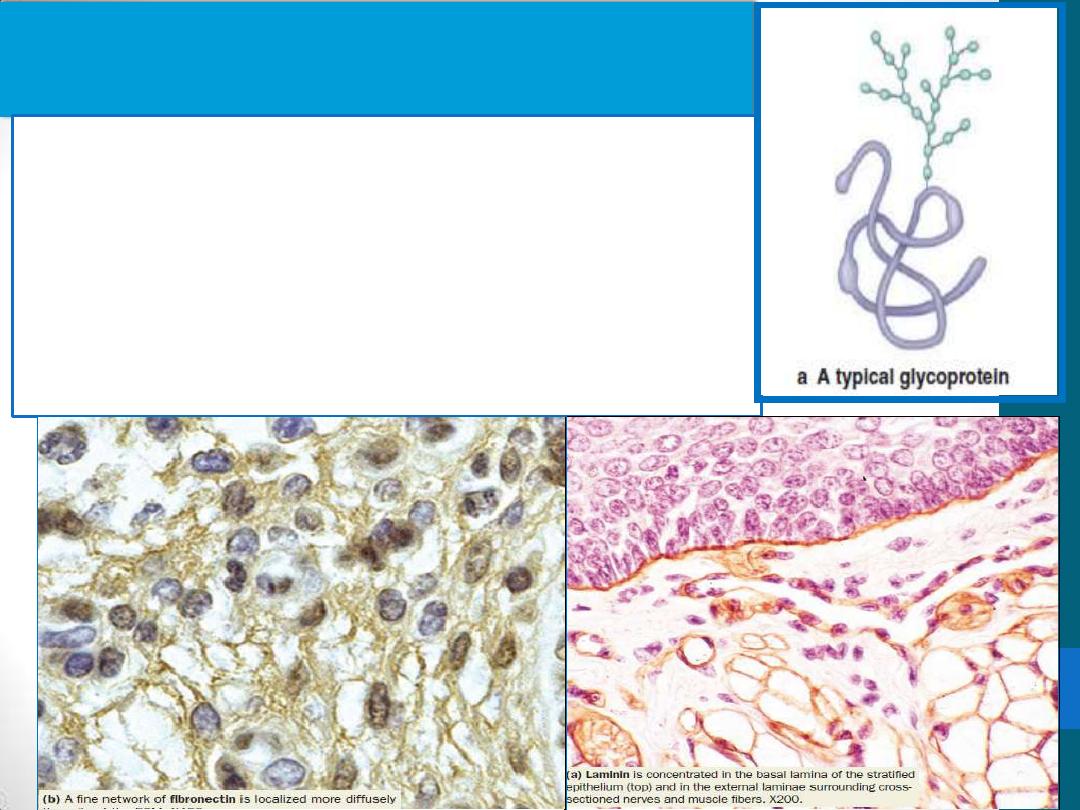
3. Multiadhesive glycoproteins
are usually globular proteins with branched
oligosaccharide side-chains. Their polypeptide
content is generally greater than their polysaccharide
content
Laminin provides adhesion for epithelial and other
cells (all basal and external laminae are rich in
laminin)
Fibronectin is important both for cell adhesion and
cellular migration through the ECM.
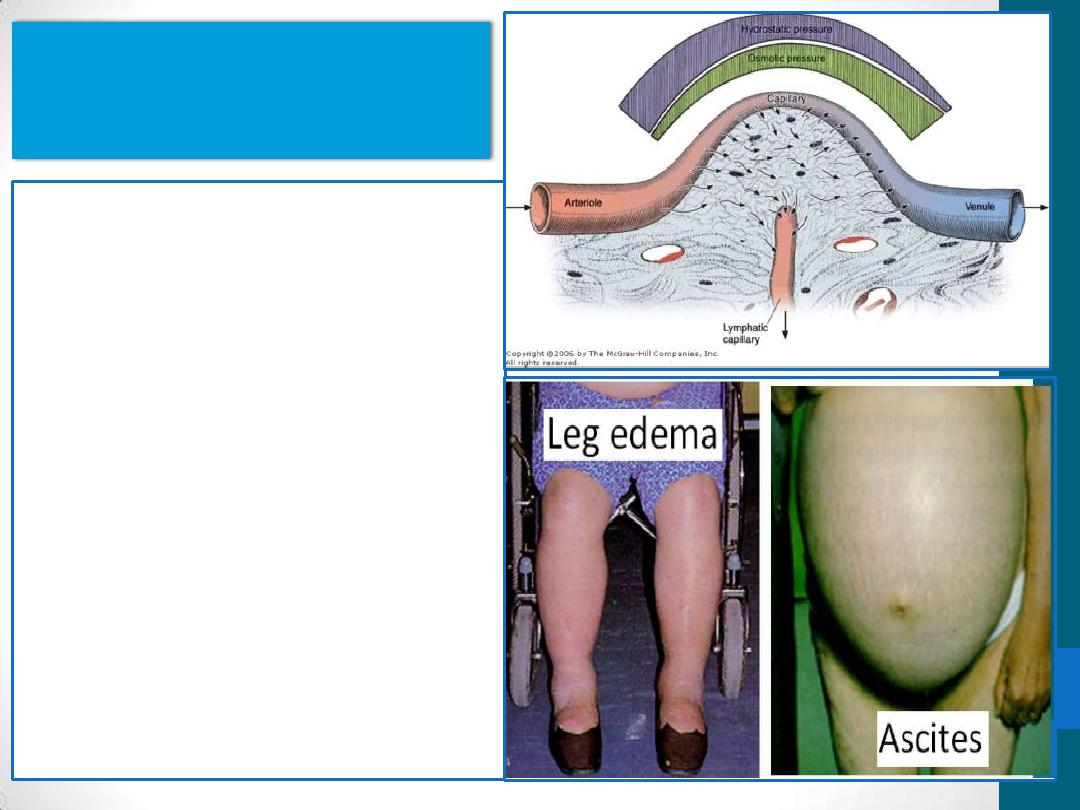
Interstitial fluid
•
is similar to blood
plasma in its content of
ions and diffusible
substances.
•
contains plasma
proteins of low
molecular weight
•
Edema: accumulation of
water in the extracellular
spaces of connective
tissue

Quiz (2)

Laminin & fibronrctin are
1. Glycosaminogiycans
2. proteoglycan
3. glycoproten
4. None of the above

Summary
•
Connective tissue consists of cells, fibers and ground
substances
•
Connective tissue cells are fibroblasts, macrophages,
mast cells, plasma cells, adipocytes and leukocytes
•
Connective tissue fibers consist of collagen , reticular
and elastic fibers
•
Ground substances are of three types:
glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans and glycoprotein
•
Connective tissue contains a small amount of tissue
fluid
