Introduction to the excitable
tissue
Lecture 1
Dr. Hanan Luay

Objectives:
Upon completion of this lecture ,the
student will be able to:
1-Define excitable tissues .
2-Identify the ionic basis of the
resting membrane potential.
3-Describe the importance of Na
⁺-K ⁺
pump.


What is irritability
?
An ability of all living tissues to
respond to stimuli (either external
or internal environment)
What is excitability?
An ability of specialized cells
to respond to certain stimuli
by producing electrical signals
known as action potential at
its membrane

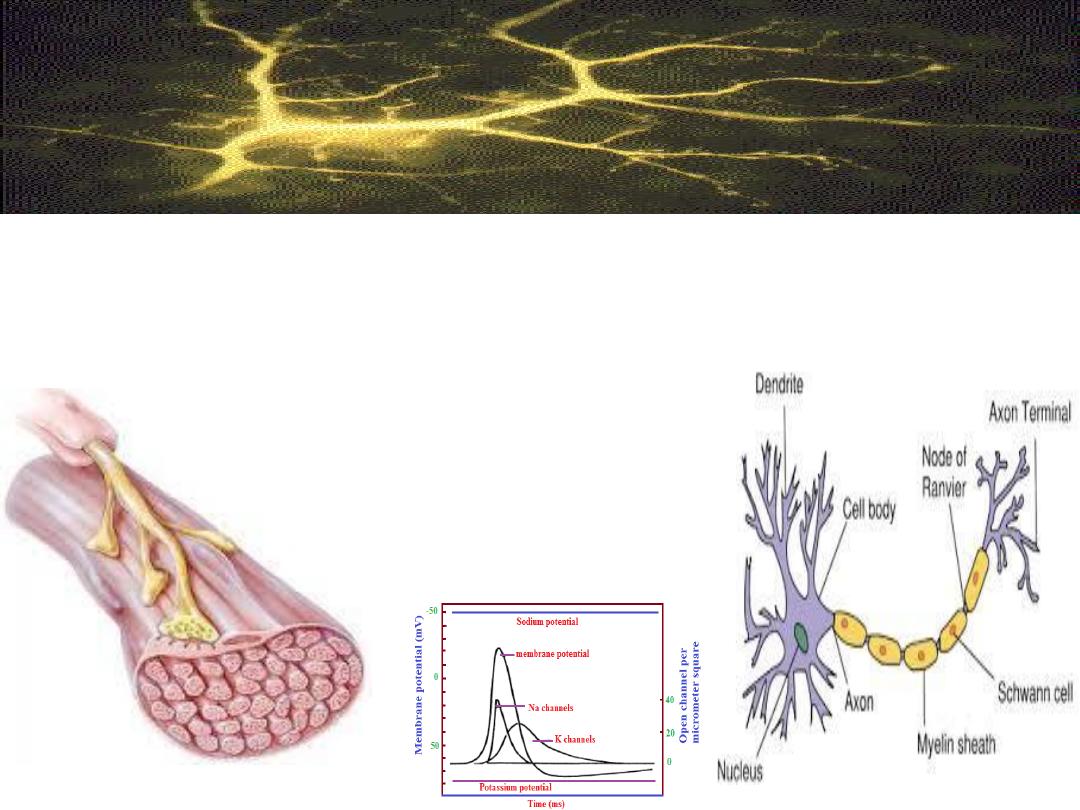
Muscle and nerve are excitable tissues.
They are excitable because they have
electrical phenomenon i.e. they are
polarized.
The neurons are excitable cells
specialized for reception,
integration and transmission of
nerve impulses.
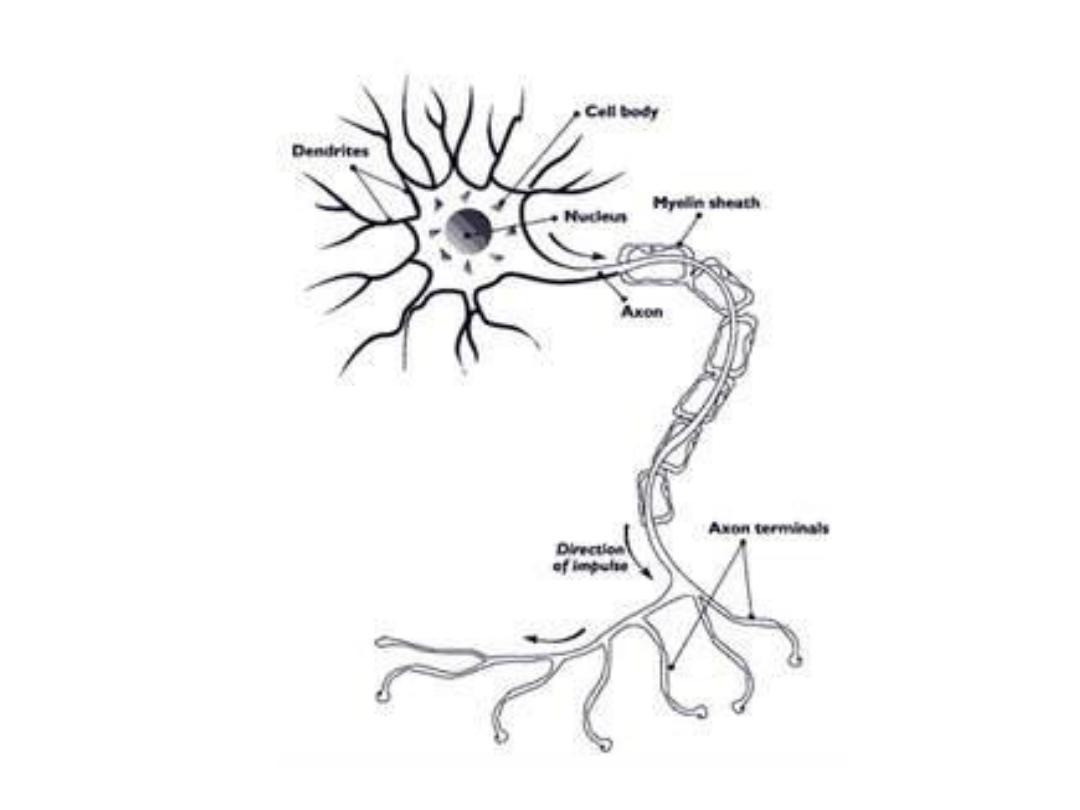

What are 2 basic properties of excitable
cell
membranes?
1. The membranes have an electrical
excitability across it, and may transmit an
impulse
along
the
membrane
2. The membranes contain a variety of ion
channels (pores) that may be opened or
closed, allowing specific ions to flow across.
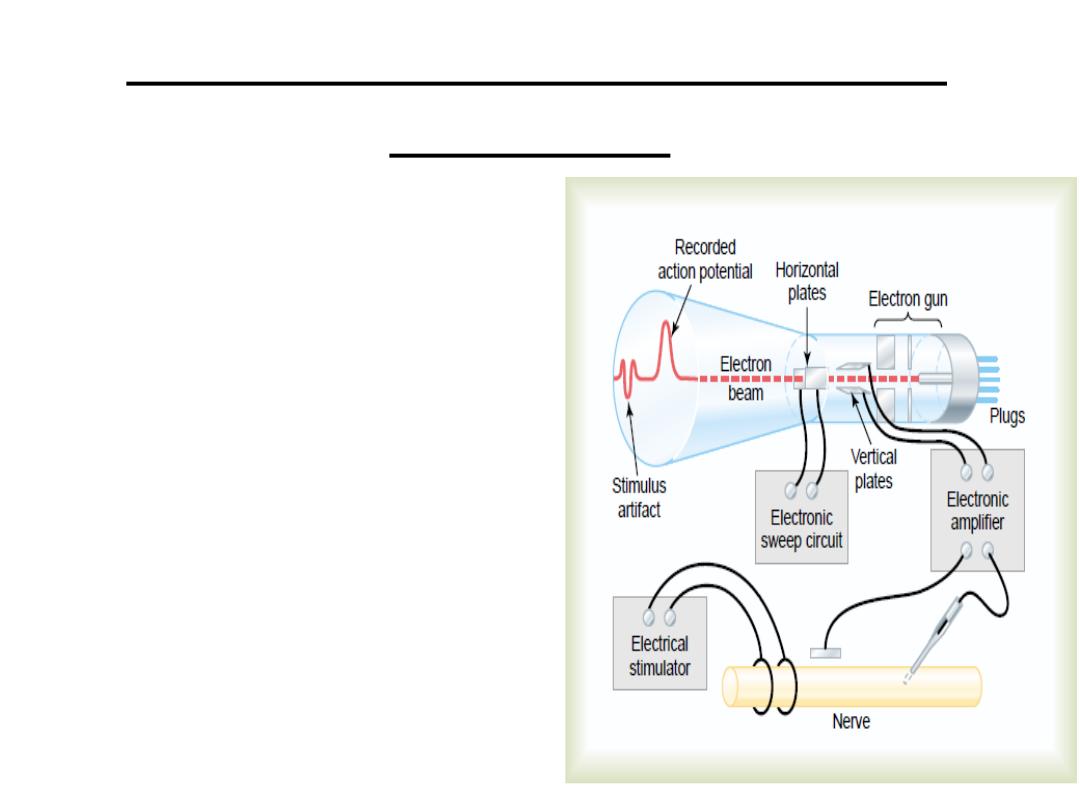
The electrical phenomena of the
nerve cells:
The cathode ray oscilloscope
can be calibrated in such a way
that an
upward
deflection of
the line indicates that the inside
of the membrane has become
less negative (or more positive)
compared to the outside of the
membrane. A
downward
deflection of the line,
conversely, indicates that the
inside of the cell has become
more negative.
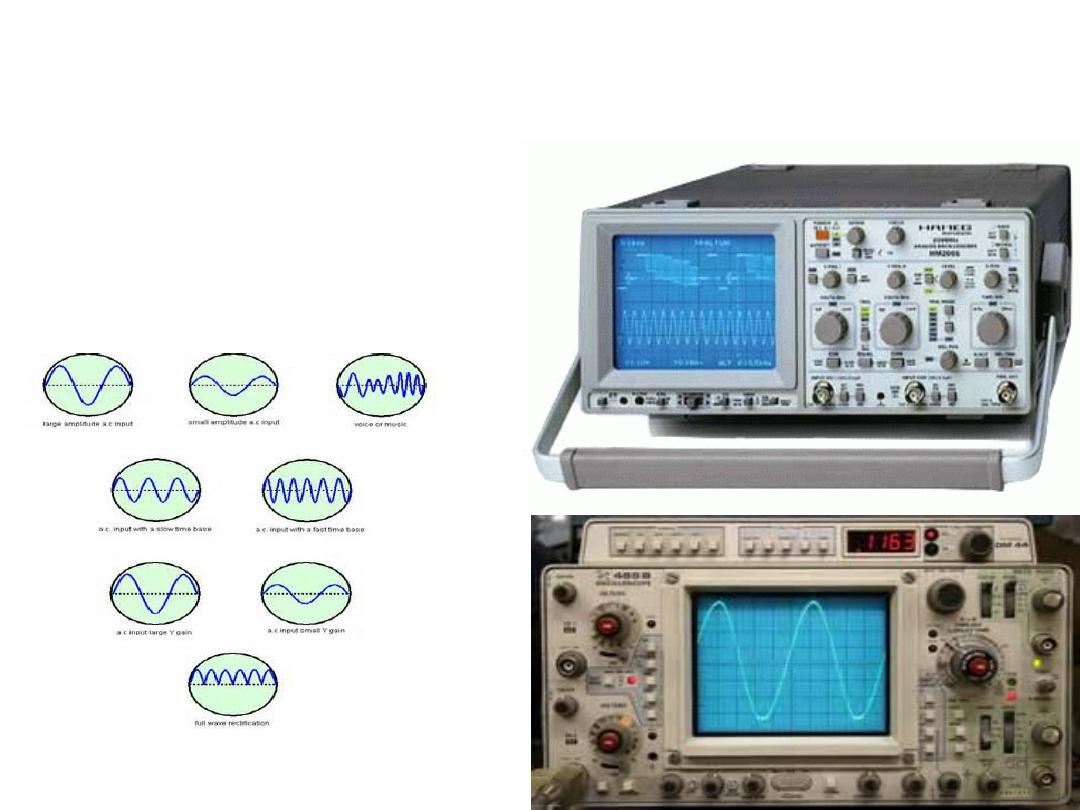
As long as the electrodes are outside the
membrane, the recorded potential is
zero, which is the potential of the
extracellular fluid as the electrode
passes inside, the voltage decreases ,
and a membrane potential is recorded.
Which is called the
resting membrane
potential
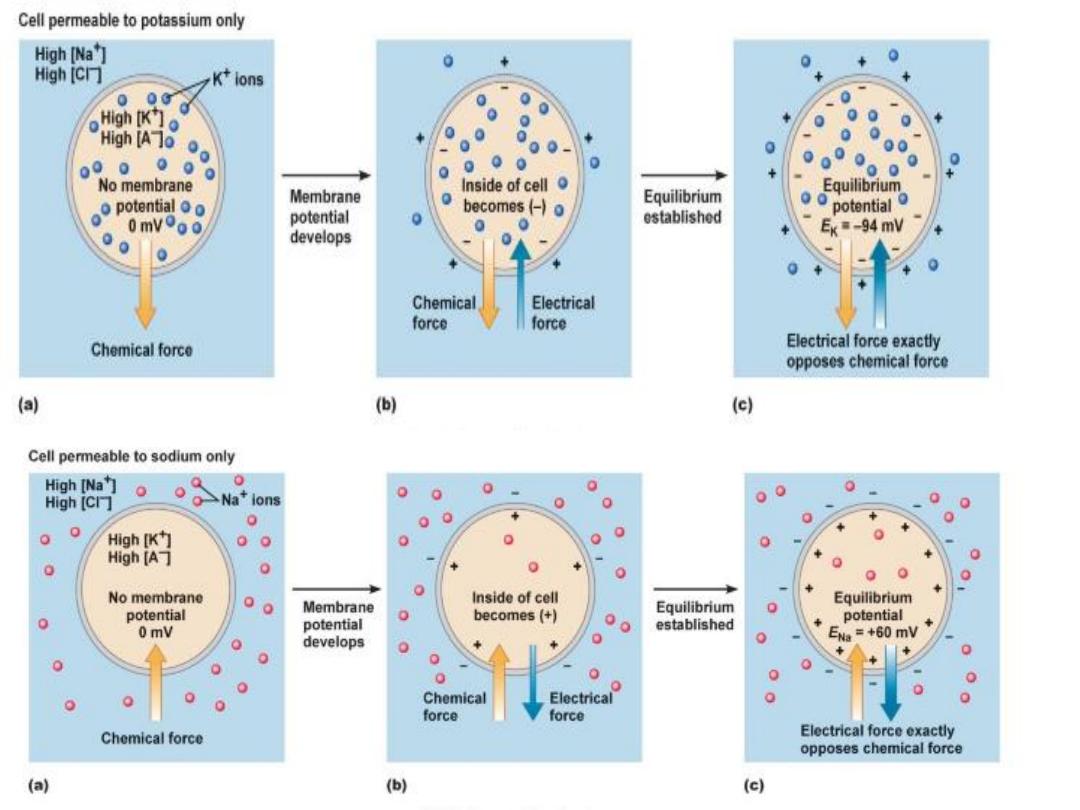
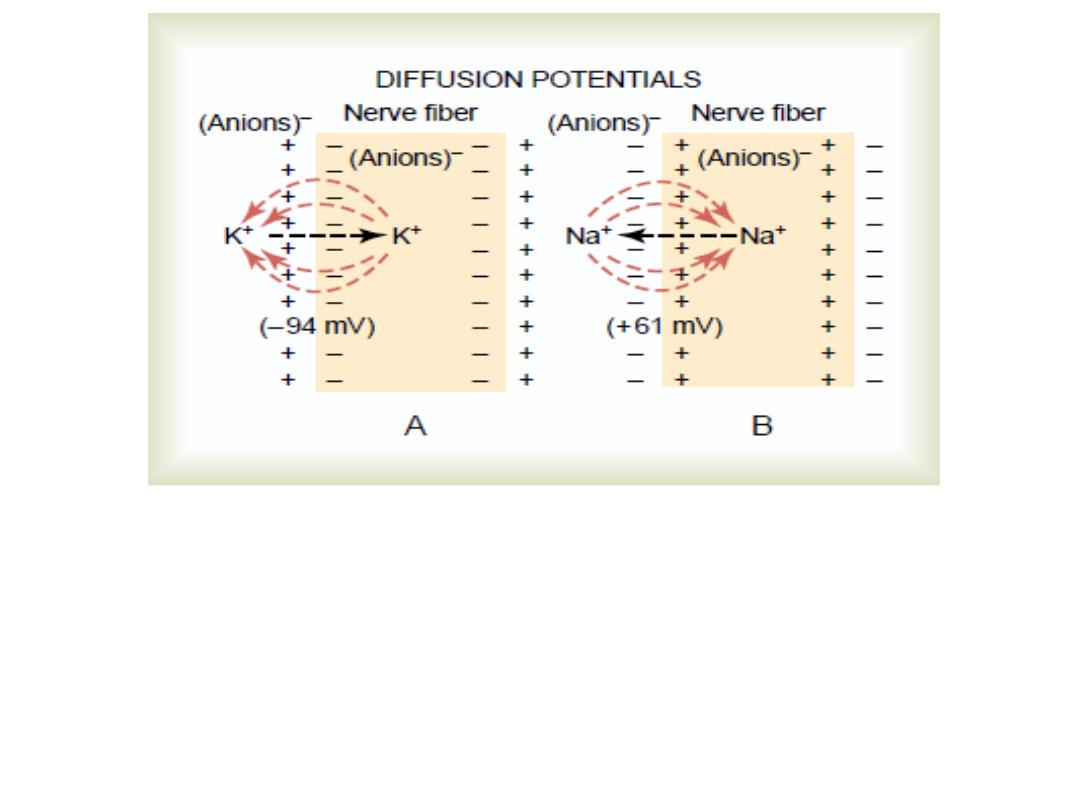
Nernest
equation
The equilibrium potential for K
+
is around -90 mv.
While for Na
+
is around +60 mv (i.e no net
movement of ion across the membrane
)
- It is measured by Nernest equation
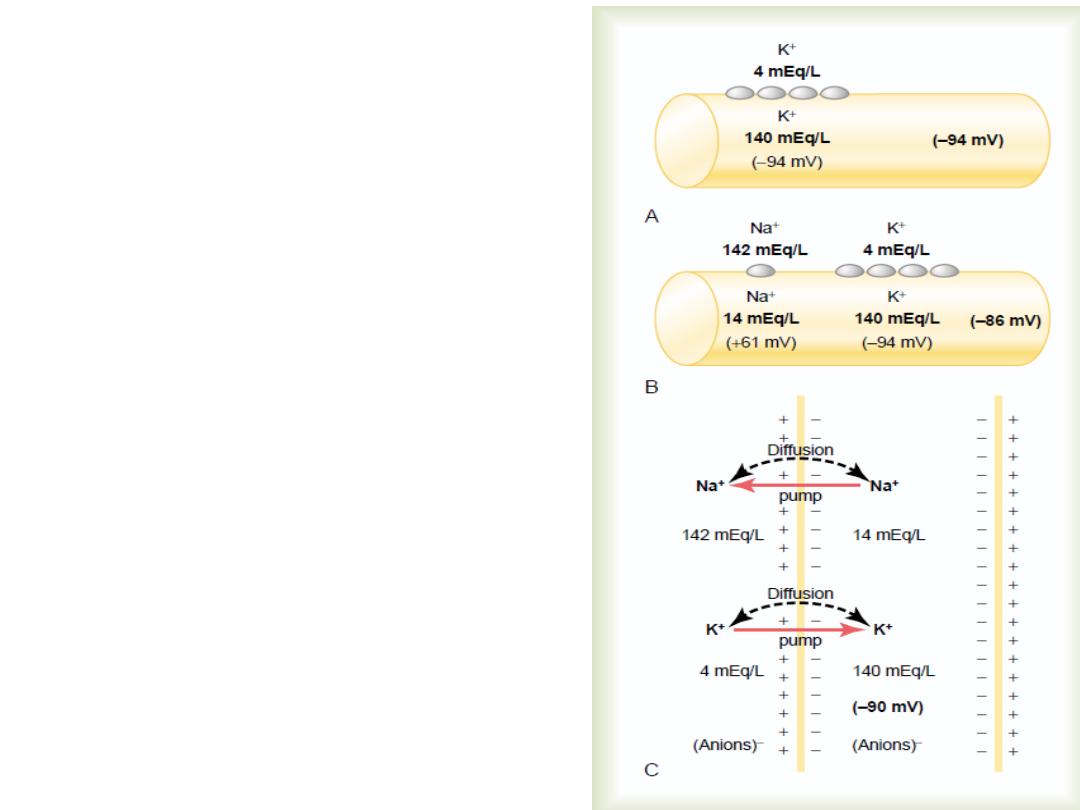
The leakage of K and Na ions through the nerve membrane
It is because of the concentration gradient across the cell
membrane, Na ions try to pass inside the cell down their
concentration gradient .K ions try to pass outside the cell
down the concentration gradient, but the channels in the
cell
membrane
are
more
permeable
to
K
ions
than
to
Na
ions
about
100
times
.

Membrane potential
:
It means separation of electric charges
across the membrane, or to a difference in
the relative number of cations and anions in
the intracellular fluid and
extracellular fluid
.

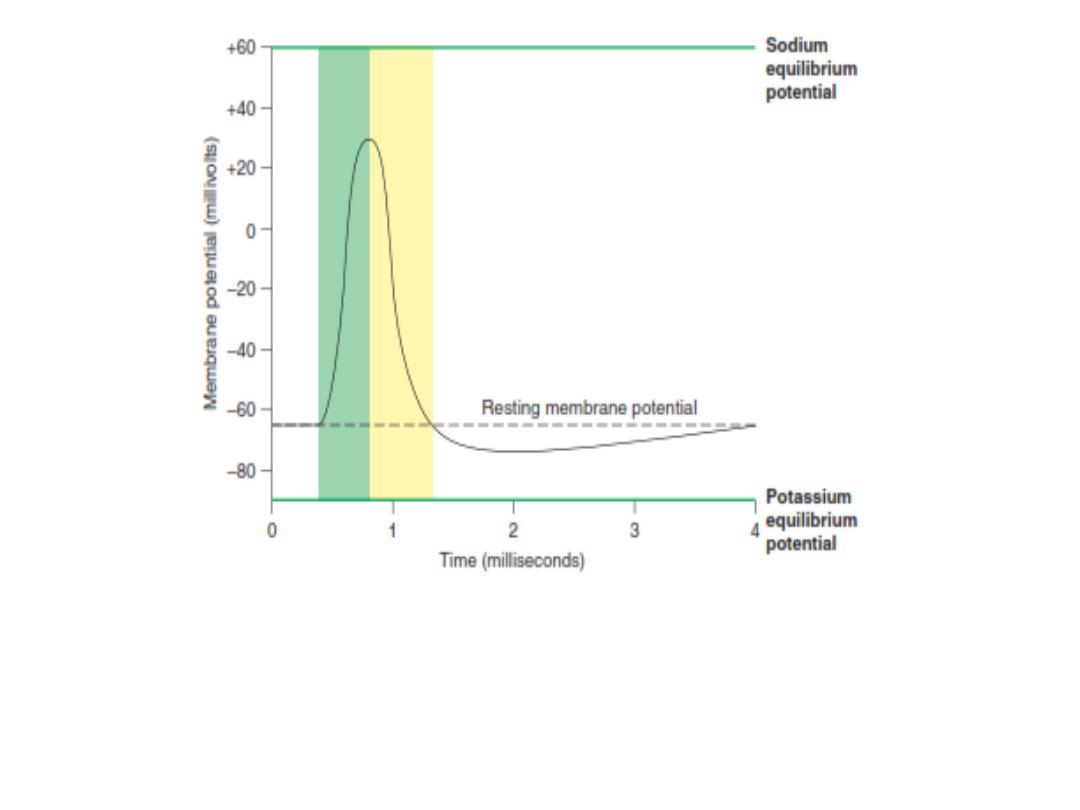
Resting membrane potential
Membrane potential difference
(transmembrane voltage) that exists
when cell membranes of excitable
tissues are not producing an action
potential (at rest
).
The resting membrane potential of a large nerve fiber
when not transmitting nerve signal is about -90 mv i.e.
the potential inside the fiber is 90 mv (actually it is -70
mv in small nerve fibers, but -90 mv in large nerves).

The ionic basis of the resting
membrane potential:
1-The contribution of the K
⁺ion diffusion
potential.
2-The contribution of the Na
⁺ion diffusion
potential through the nerve membrane.
3-The contribution of the Na
⁺_K⁺ion
pump. (contribute to 20% of the membrane
potential)
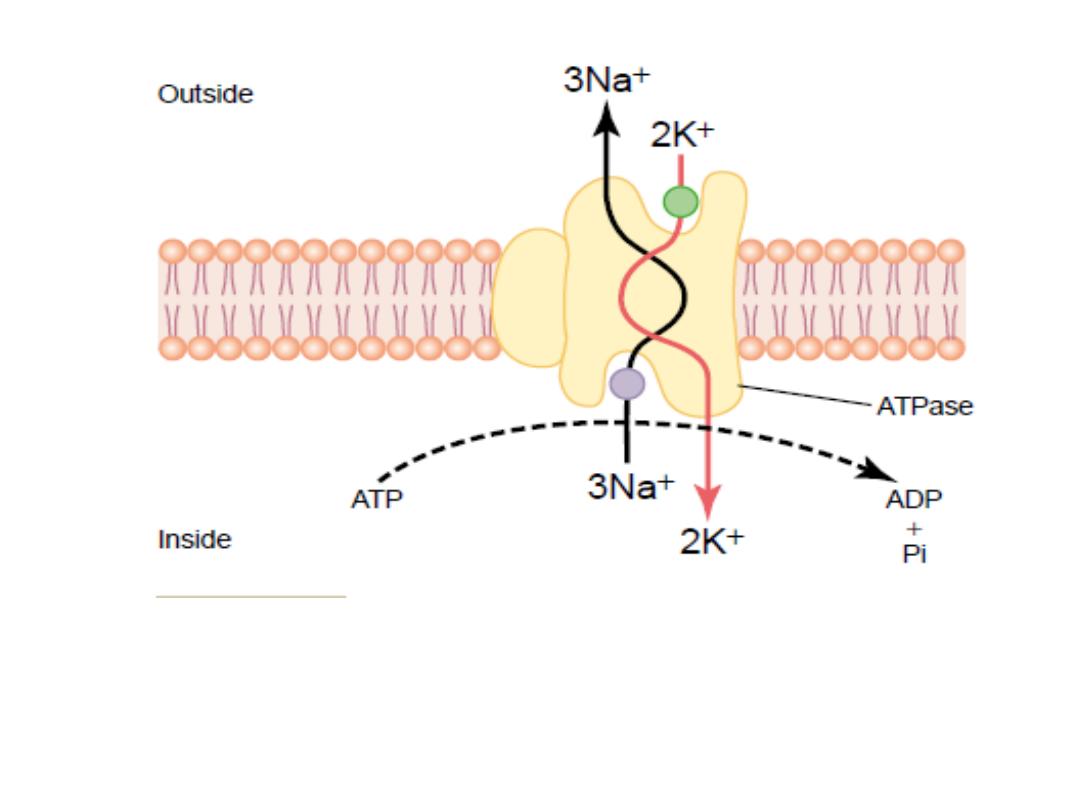
Na- K pump
(
(Guyton,2012
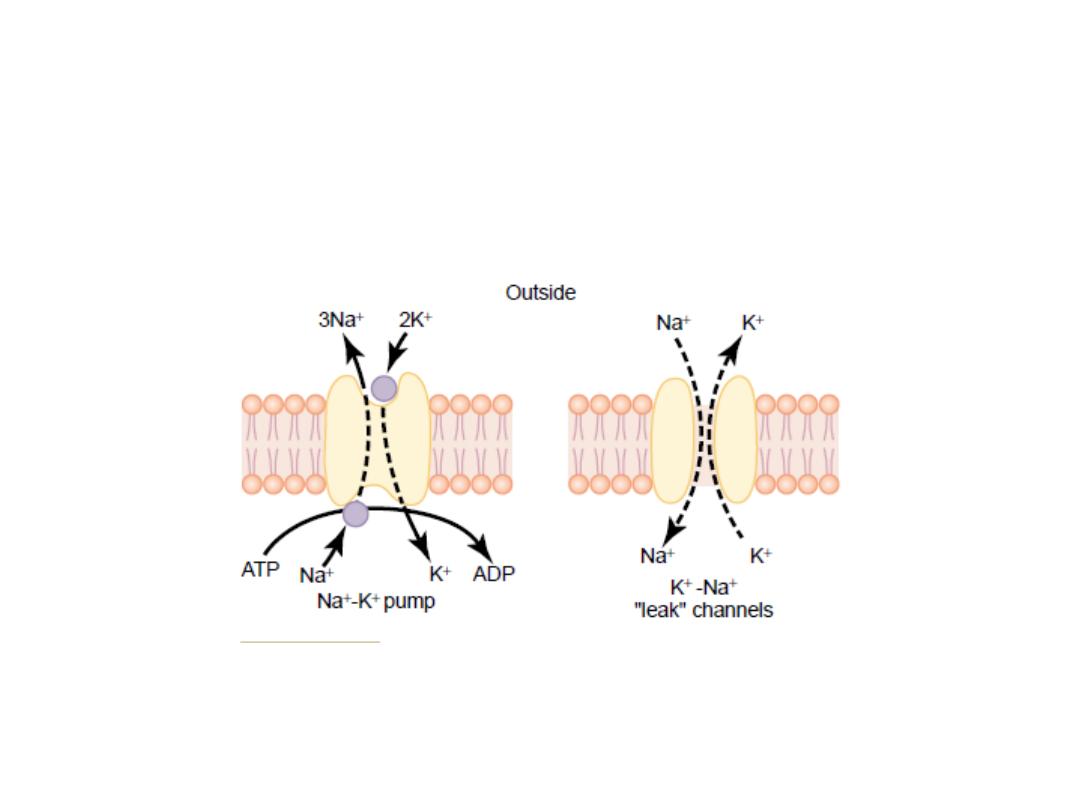

K ion pump:
-
The Na
It pumps Na ions to the outside of the cell and K
ions to the inside, this pump requires energy.
Because more positive charges are pumped to the
outside than inside (3 Na ions to the outside for
each 2 K ions to the inside) i.e. Na ions accumulate
outside the cell while K accumulates inside the
cell, ………………………………………
leaving
a net deficit of positive ions inside leading
to a negative potential across the membrane.

The final resting membrane potential
reflects a balance between the electrochemical
forces
associated
with
each
ion
.
The more permeable the membrane is for
an ion, the more the equilibrium potential
of that ion will influence the membrane
potential.

In summary,
-
Muscle and nerve are excitable tissues and they are
polarized
.
-
They have resting membrane potential when there is no
stimulus applied.
-
The 3 factors that contribute to the negative charges
inside the membrane are:
1-The diffusion of k ions to the outside of the membrane is
more than the diffusion of Na ions to the inside.
2-The Na-K pump.
3-The presence of negatively charged proteins inside the
membrane.

So what is the difference
between excitable and
non excitable tissues?
In non-excitable cells, such as epithelial cells and
adipose cells (and others), the resting membrane
potential does not change over time. In excitable cells,
upon stimulation of the cell, the membrane potential
can change dramatically for short periods of time
(milliseconds).Therefore, in excitable cells the
membrane potential is not always at the resting
membrane potential.

Reference:
Guyton A.C. and Hall J.E (2006).Textbook of
Medical Physiology.
