
2
Objectives
•
State the levels of body organization
•
Name the body system
•
Define the anatomical position and the
directional terms used in relation to the body
•
Describe the planes of the body
•
Identify the body cavities
•
Analyze, define, and pronounce the combining
forms that relate elements and systems of the
body
Nov-16
Nov-16
3

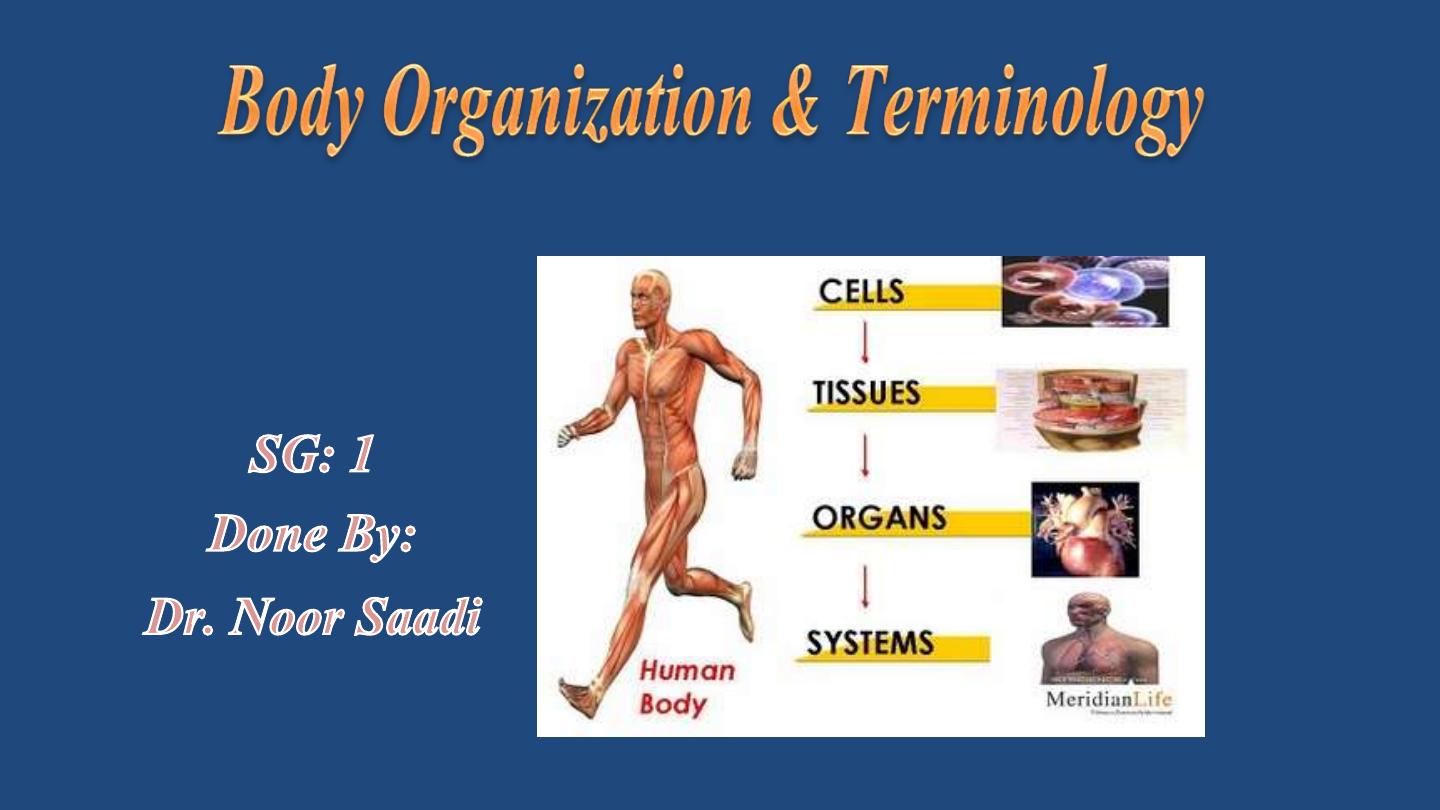
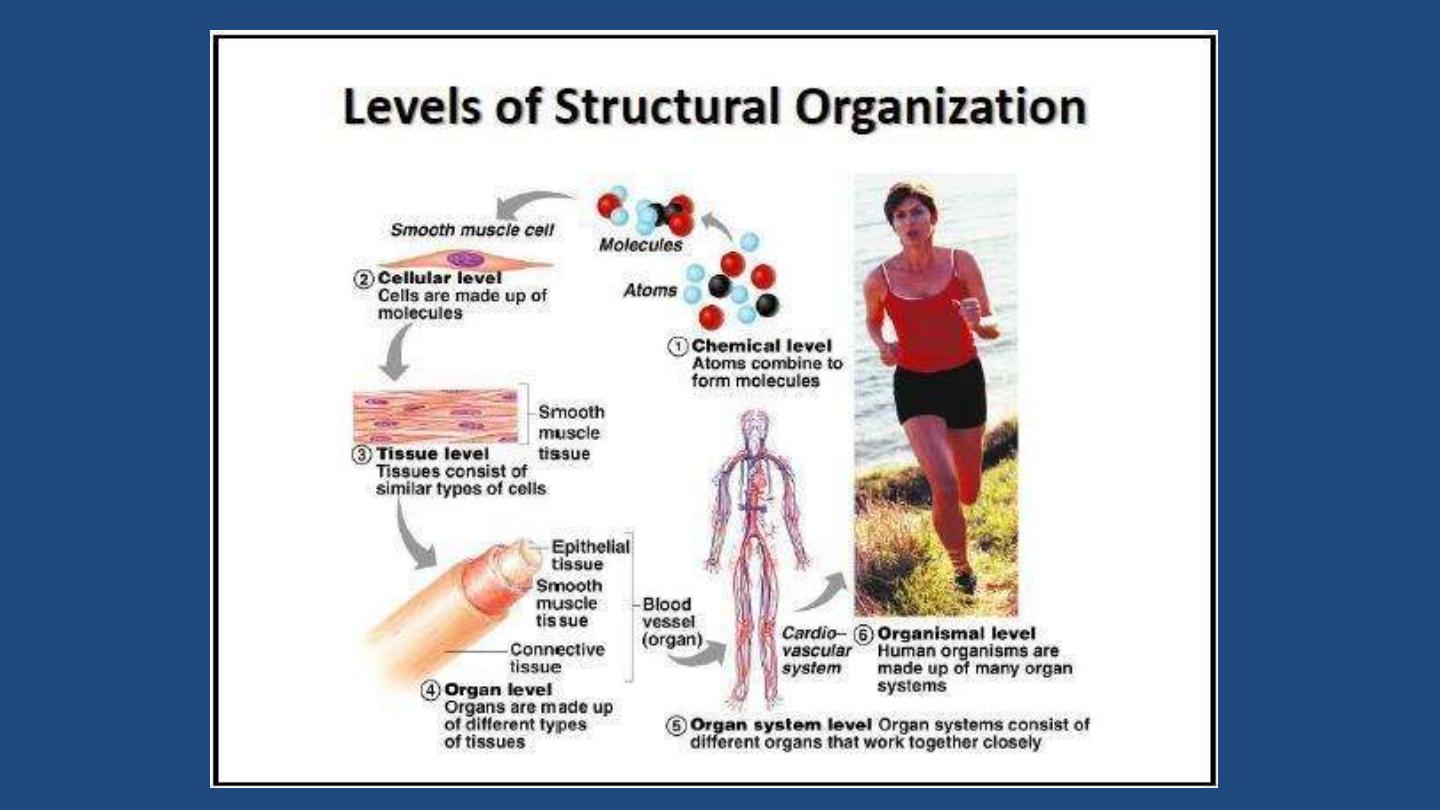
Levels of body Organization
• Chemical
– atoms combined to form molecules
• Cellular
– cells are made of molecules
• Tissue
– consists of similar types of cells
• Organ
– made up of different types of tissues
• Organ system
– consists of different organs
that work closely together
• Organismal
– made up of the organ systems
Nov-16
4
5
Body Structure and Organization
The body is organized from its smallest element,
the cell, to the collection of systems.
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Systems
Entire Body
Nov-16
6
Cells
Cells
•Vary in size, shape, and function.
•Need food, water, and oxygen to live
and function.
•Contain three basic structures:
-
Cell Membrane
- outer covering of the cell.
-
Nucleus
- central portion of each cell
responsible for directing cell activities.
-
Cytoplasm
- substance surrounding the nucleus
and is responsible for reproduction and
movement.
Nov-16
7
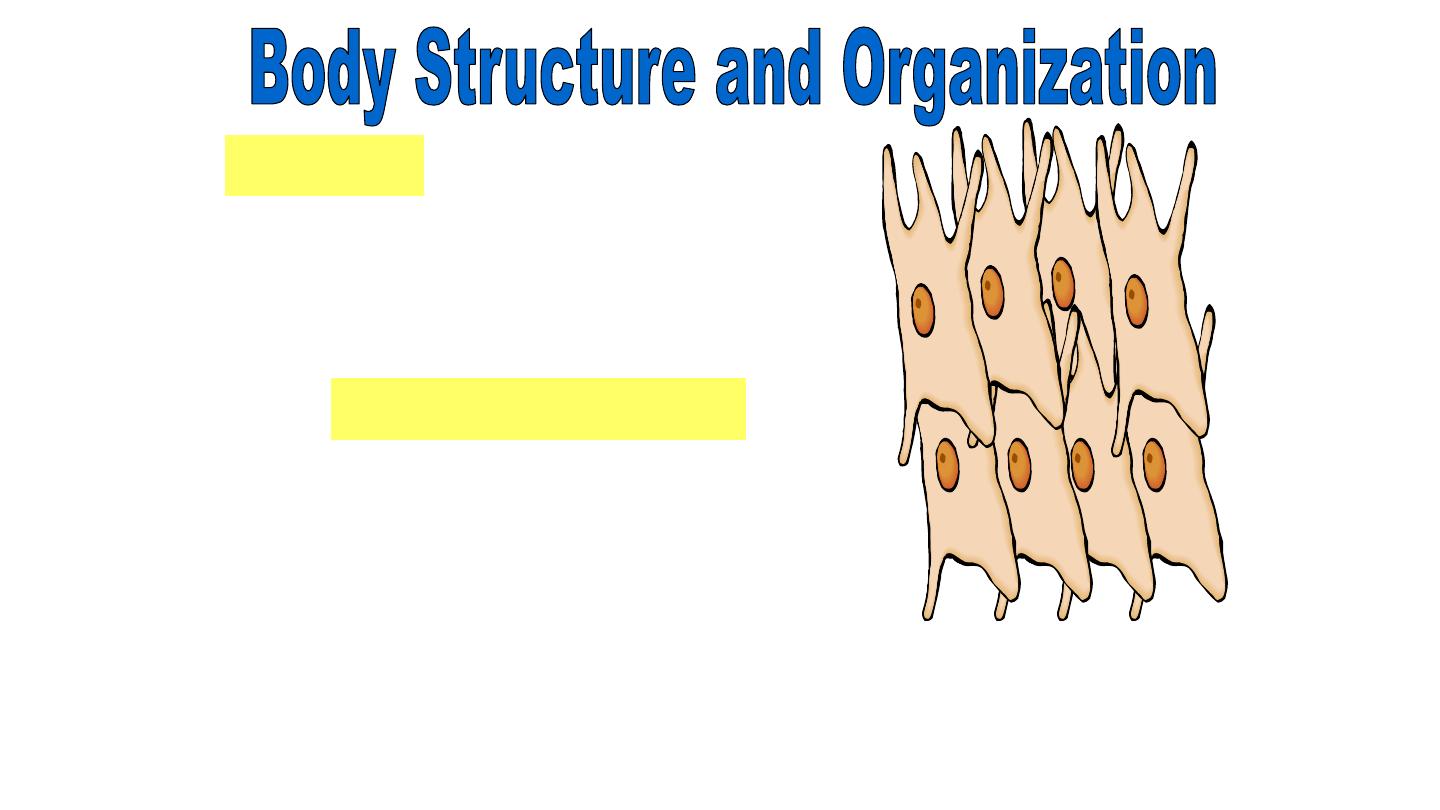
Tissues
Tissues
Groups of cells that work together
to perform the same task are
called
tissues
.
Types of Tissues
•Connective tissue
•Epithelial tissue
•Muscle tissue
•Nervous Tissue
Connective Tissue
Nov-16
8
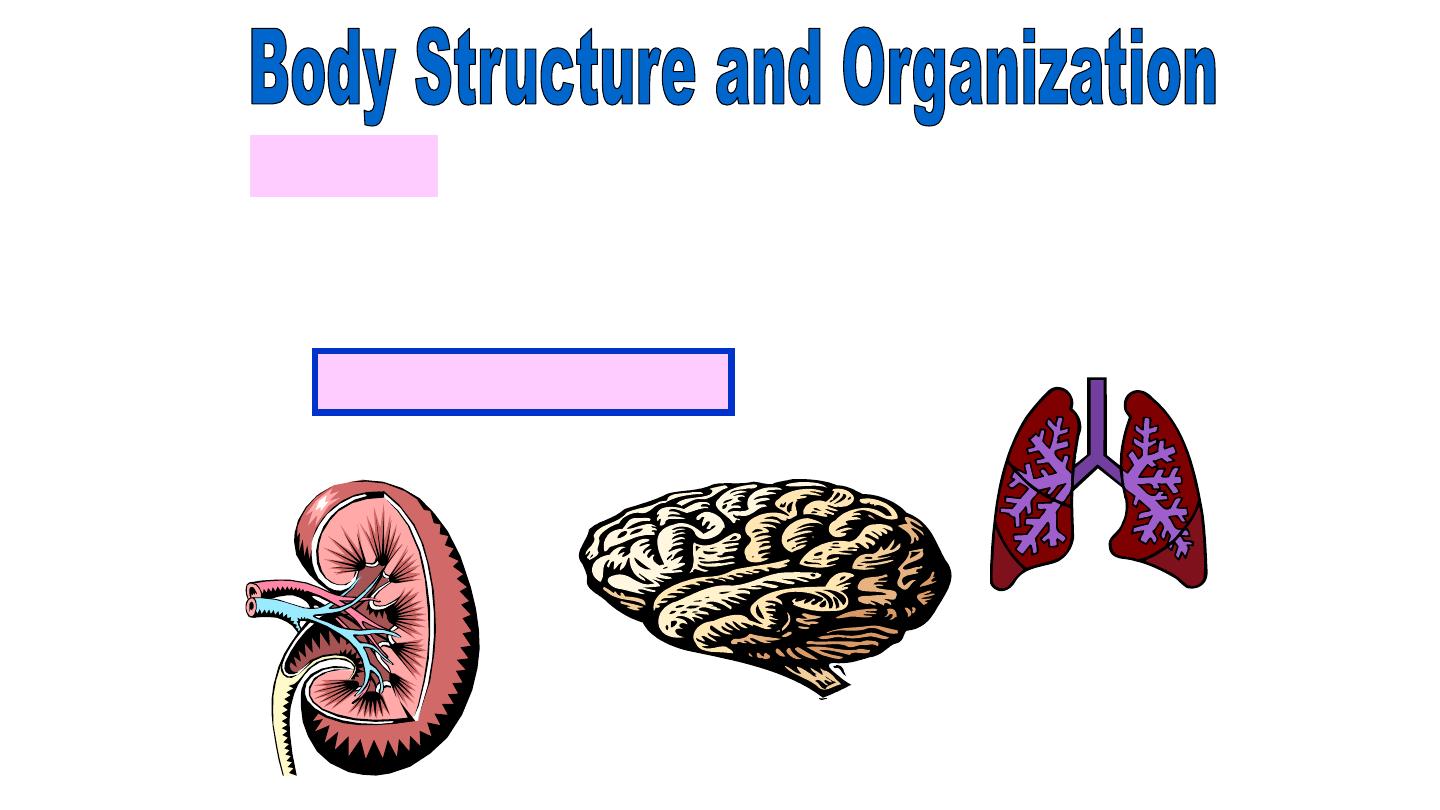
Organs
Organs
Groups of tissues that work together to
perform a specific function are called
organs
.
Organ Examples:
kidney
lungs
brain
Nov-16
9
Systems
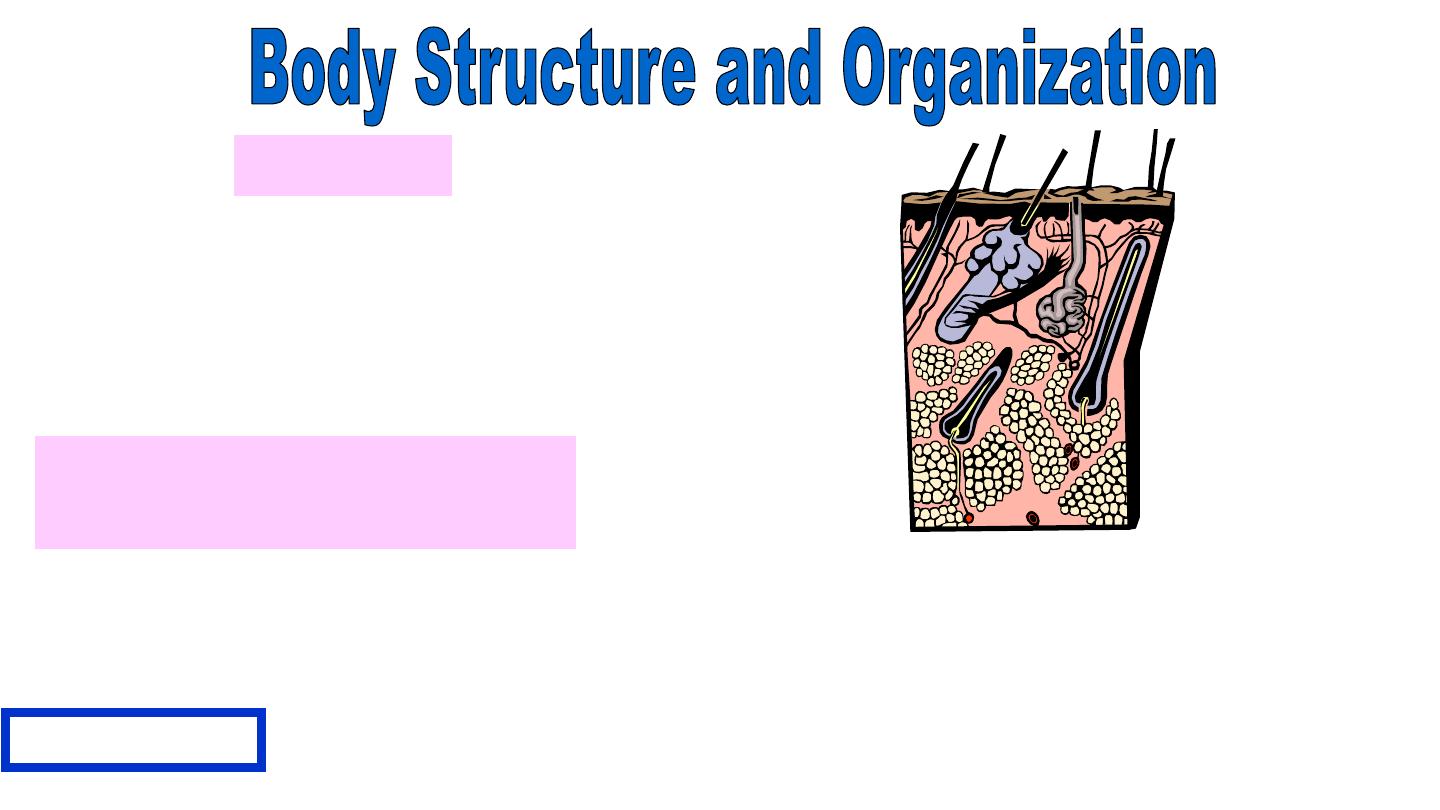
Systems
Groups of organs that
work together to perform
one of the body’s major
functions are called
systems
.
Integumentary
System
Consists of:
Skin
Hair
Nails
Sweat glands
Oil glands
protects the body against invasion by bacteria: regulate body
temperature and water content.
Nov-16
10
Musculoskeletal System
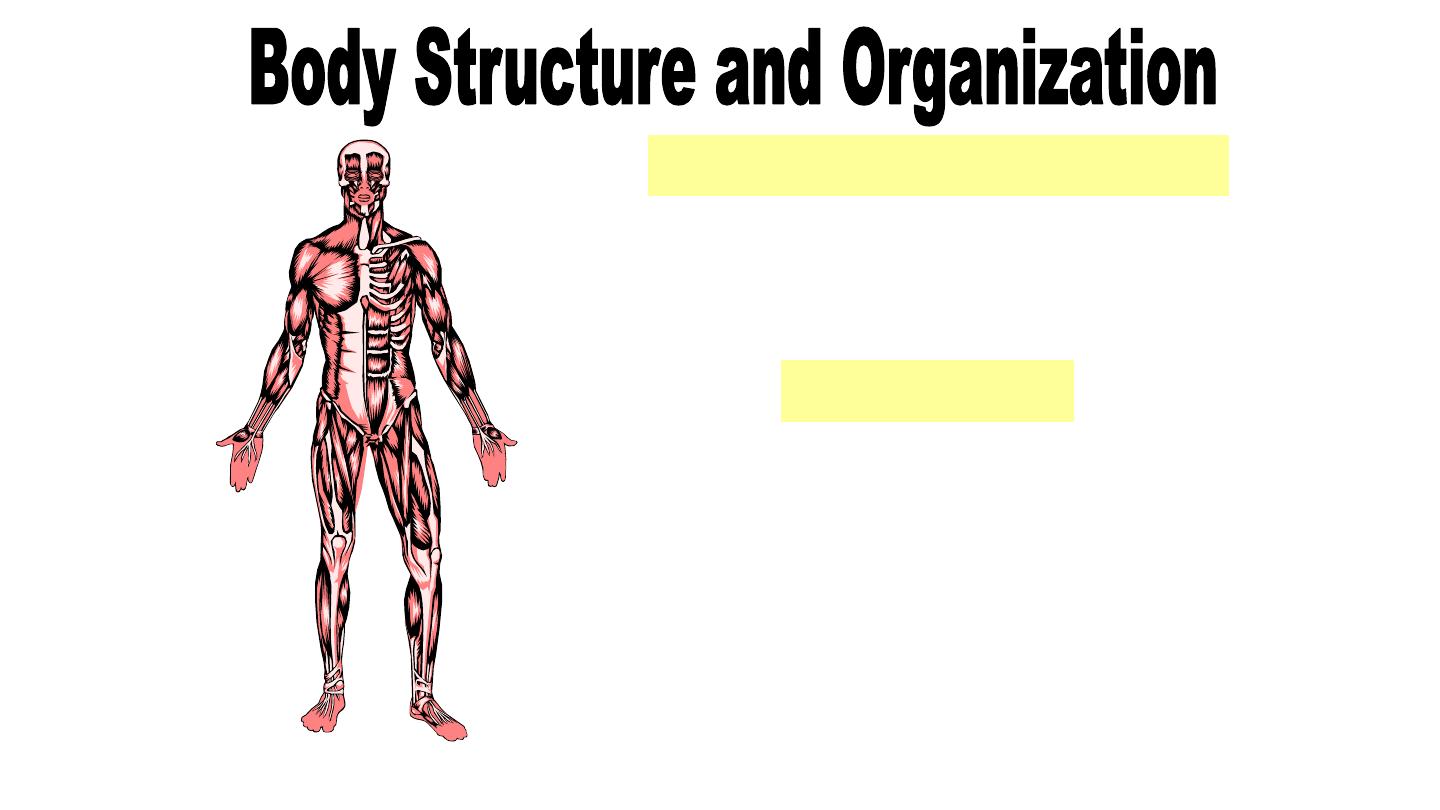
Musculoskeletal System
Supports the body, protects
organs and provides body
movement.
Consists of:
•Muscles
•Bones
•Cartilage
Nov-16

11
Cardiovascular System
Circulatory System
Pumps and transports blood throughout the
body. Blood carries nutrients and removes
waste from the tissues.
Consists of:
•Heart
•Blood Vessels
Nov-16
12
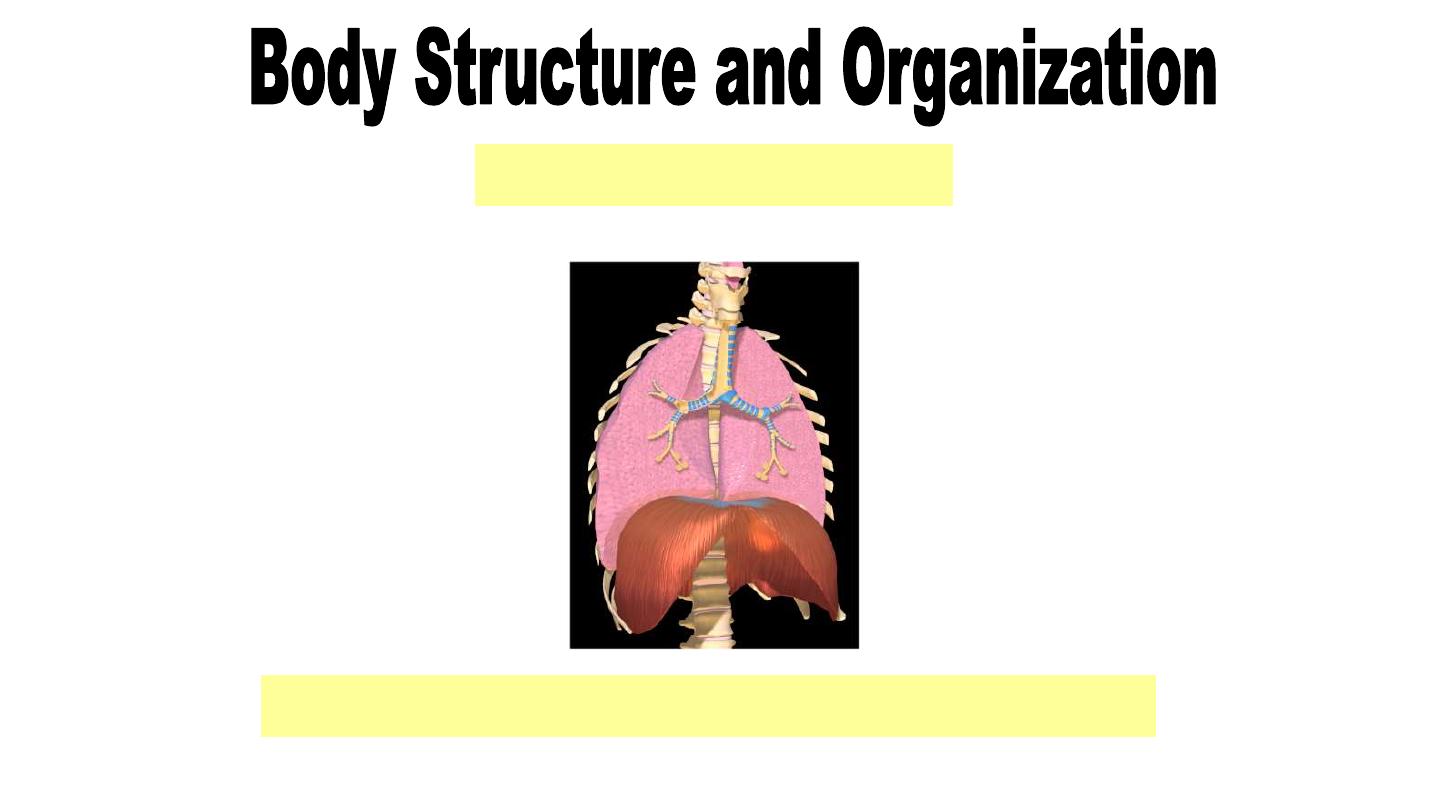
Respiratory System
Respiratory System
Consists of the lungs and the airways
•Performs respiration
Nov-16
13
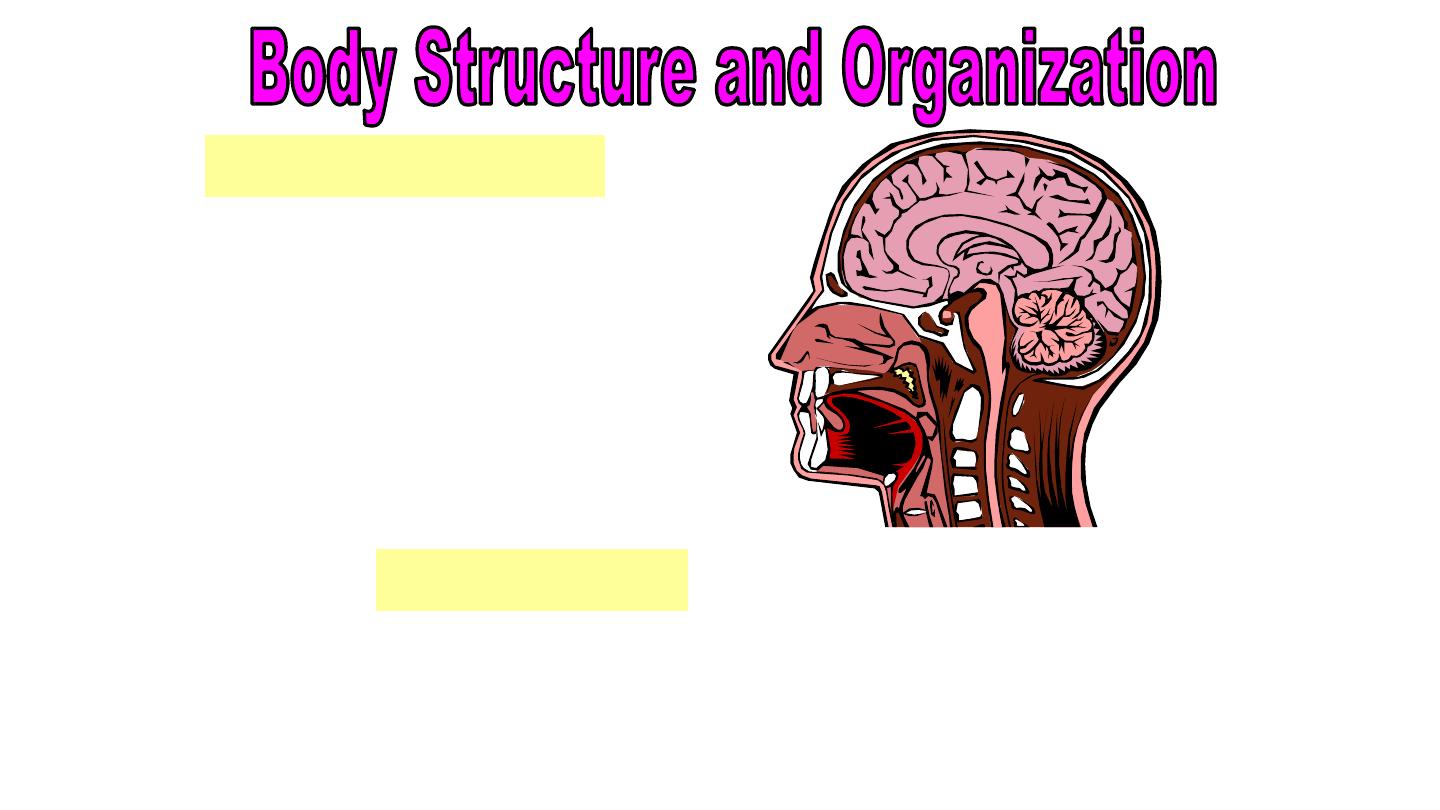
Nervous System
Nervous System
Regulates most of the
body’s activities and
sends and receives
messages from
sensory organs.
Consists of :
Brain
Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nerves
Nov-16
14
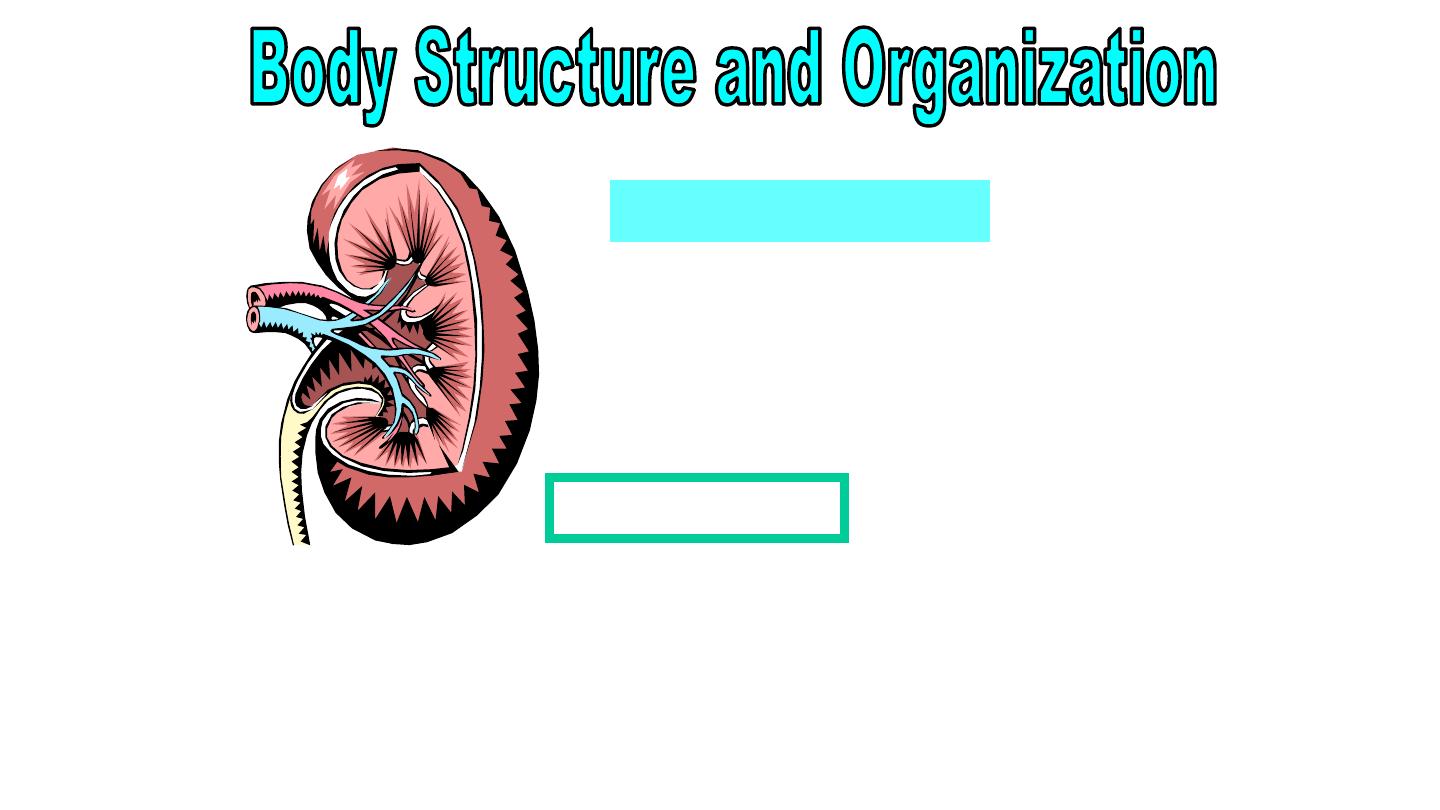
Urinary System
Urinary System
•Eliminates metabolic waste
•Helps to maintain acid-base
and water-salt balance
•Helps regulate blood pressure
Consists of:
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
Nov-16
15
Lymphatic and Immune System
Immune System
Consists of:
•Lymph
•Lymphatic Vessels
•Lymphatic Glands
•Nonspecific Defenses of the
Immune System
Reproductive System
Permits the creation of new life
Nov-16
16
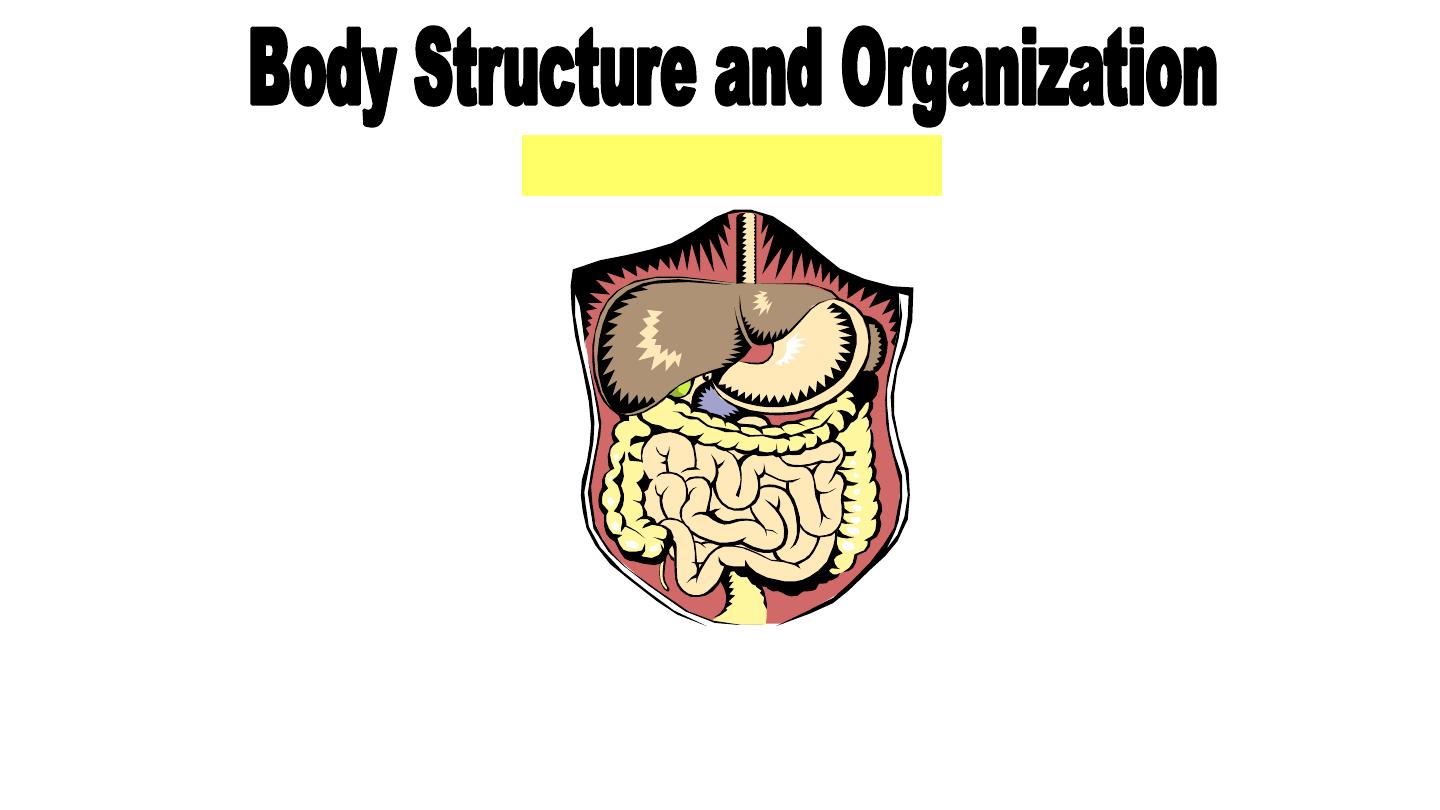
Digestive System
Digestive System
Includes all organs of digestion and
excretion of waste.
Nov-16
17
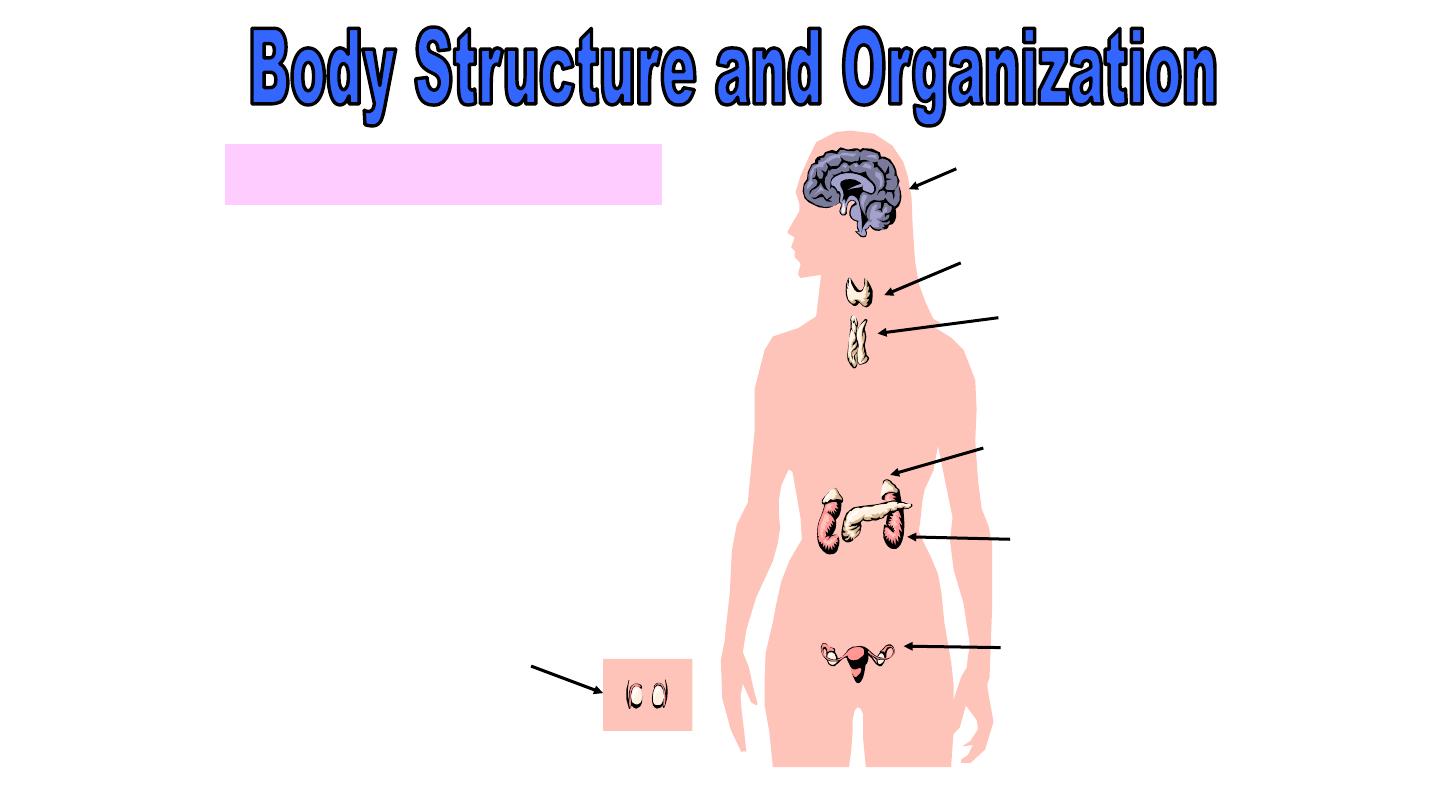
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Includes the glands that
secrete
hormones
for the
regulation of several body
activities.
pancreas
testes
ovaries
adrenal
thyroid
pituitary
parathyroid
Nov-16
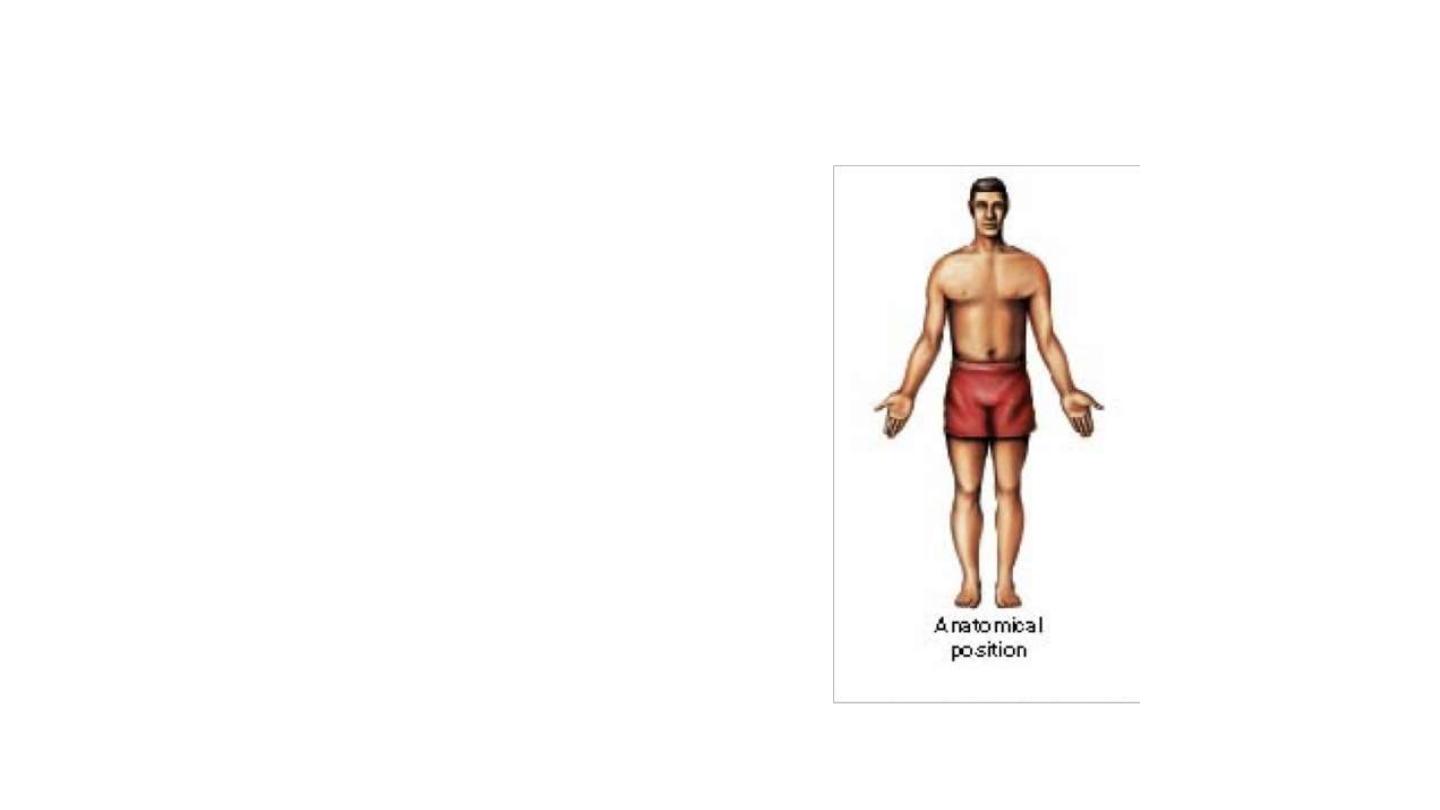
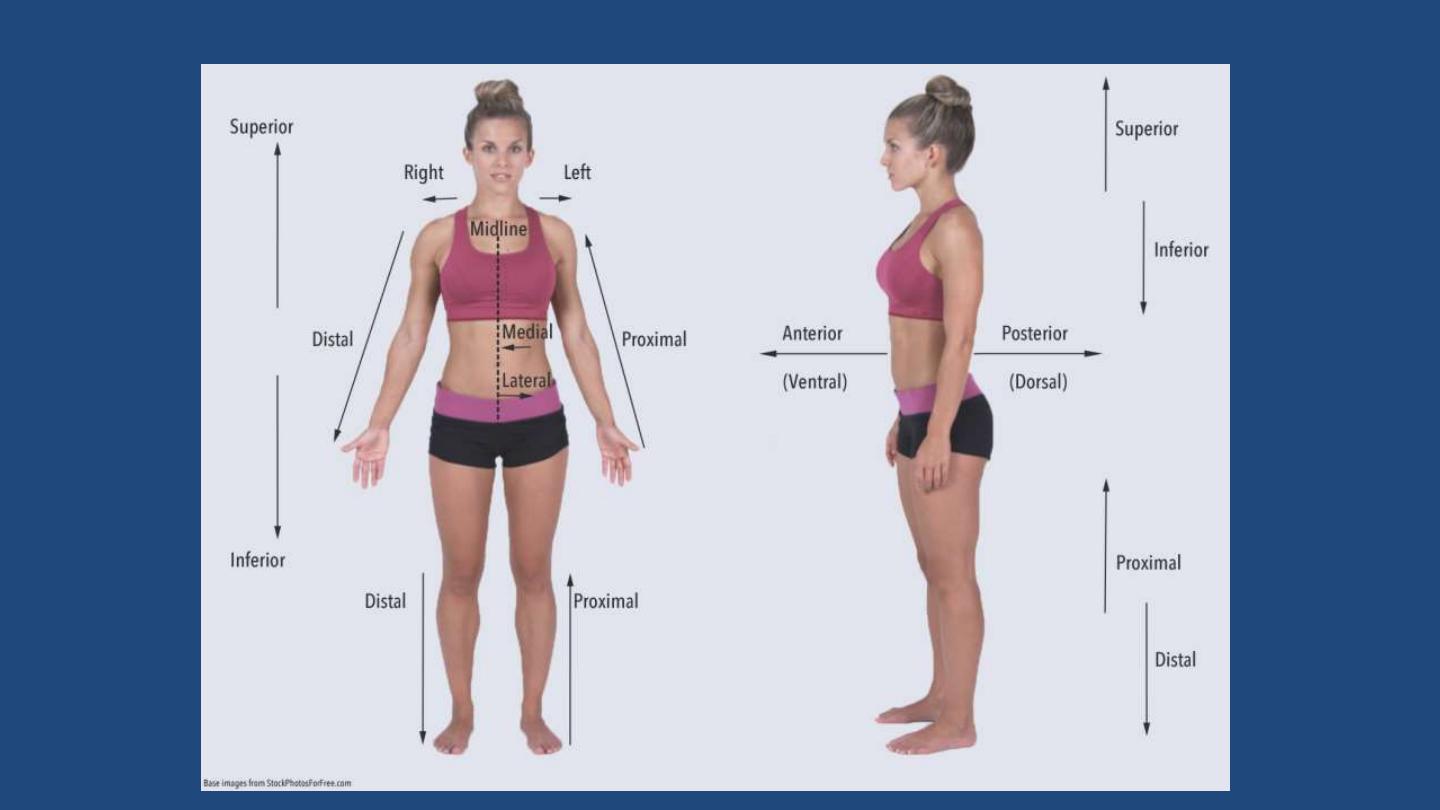
Anatomical Position
• B
ody erect
• F
eet slightly apart
• P
alms facing forward
• T
humbs point away
from body
Figure 1.7a
Nov-16
18
Body Position & Directional terms
TERM
DIERECTION
EXAMPLE
Anterior or Ventral
Toward the Front, away from the
back of the Body
The nose is on the Anterior side of the
face.
Posterior or Dorsal
Near the back; toward the back of
the body
The spine is on the posterior side of the
body
Superior or cephalic
Above; toward the head
The neck is superior to the chest
Inferior or Caudal
Below; toward the soles of the feet The Knee is inferior to the hip; the stomach
is inferior to the chest.
Proximal
Near the point of attachment to the
trunk
The elbow is proximal to the wrist .
Distal
Farther from the point of the
attachment to the trunk
The fingers are Distal to the wrist.
Nov-16
19
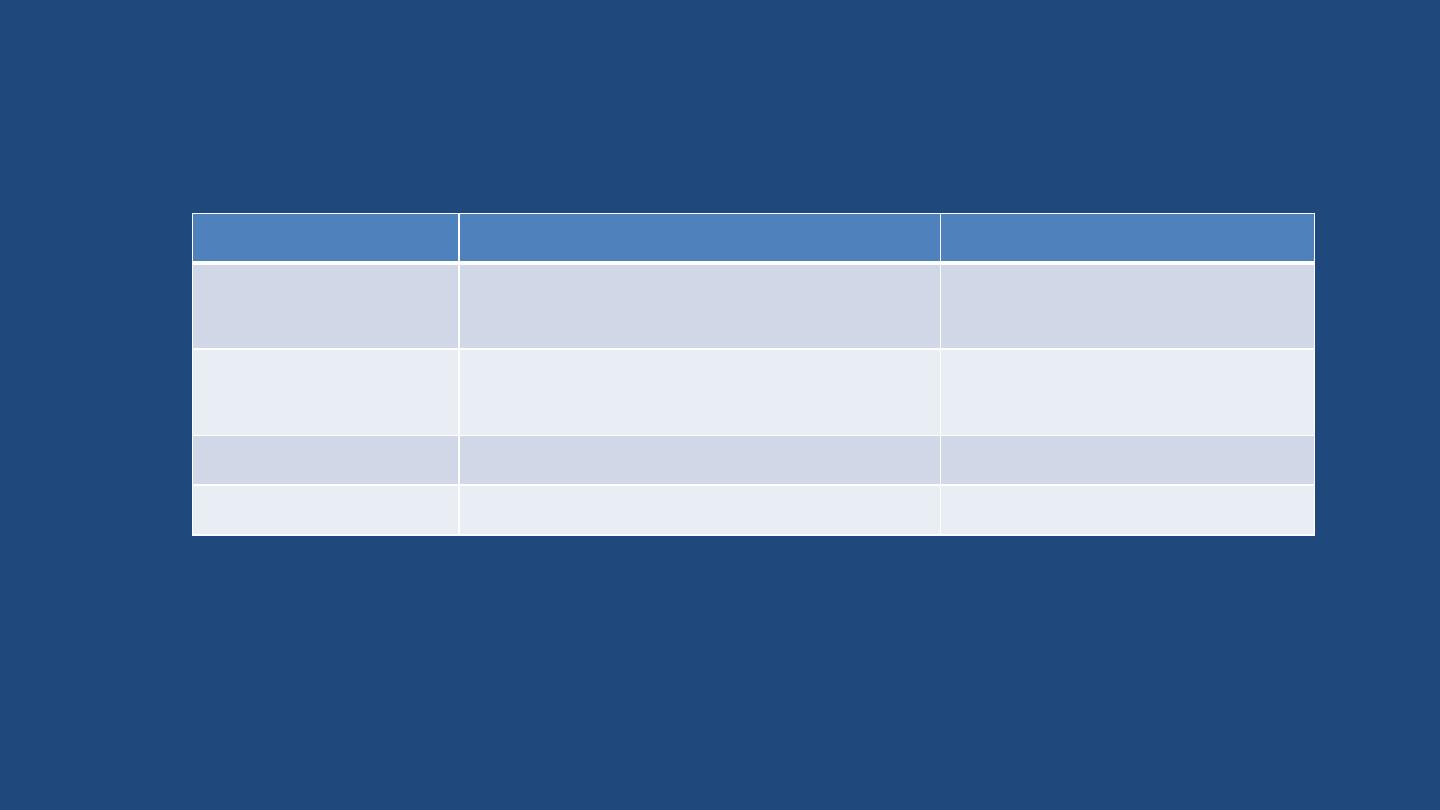

Continuation
TERM
Direction
Example
Lateral
Pertaining to the side; away from the
middle
The eyes are lateral to the nose
Medial
Towards the middle of the body
The nose is medial to the eyes
Prone
Lying Horizontal and Face down
Supine
Lying Horizontal and Face up
Nov-16
20
Nov-16
21
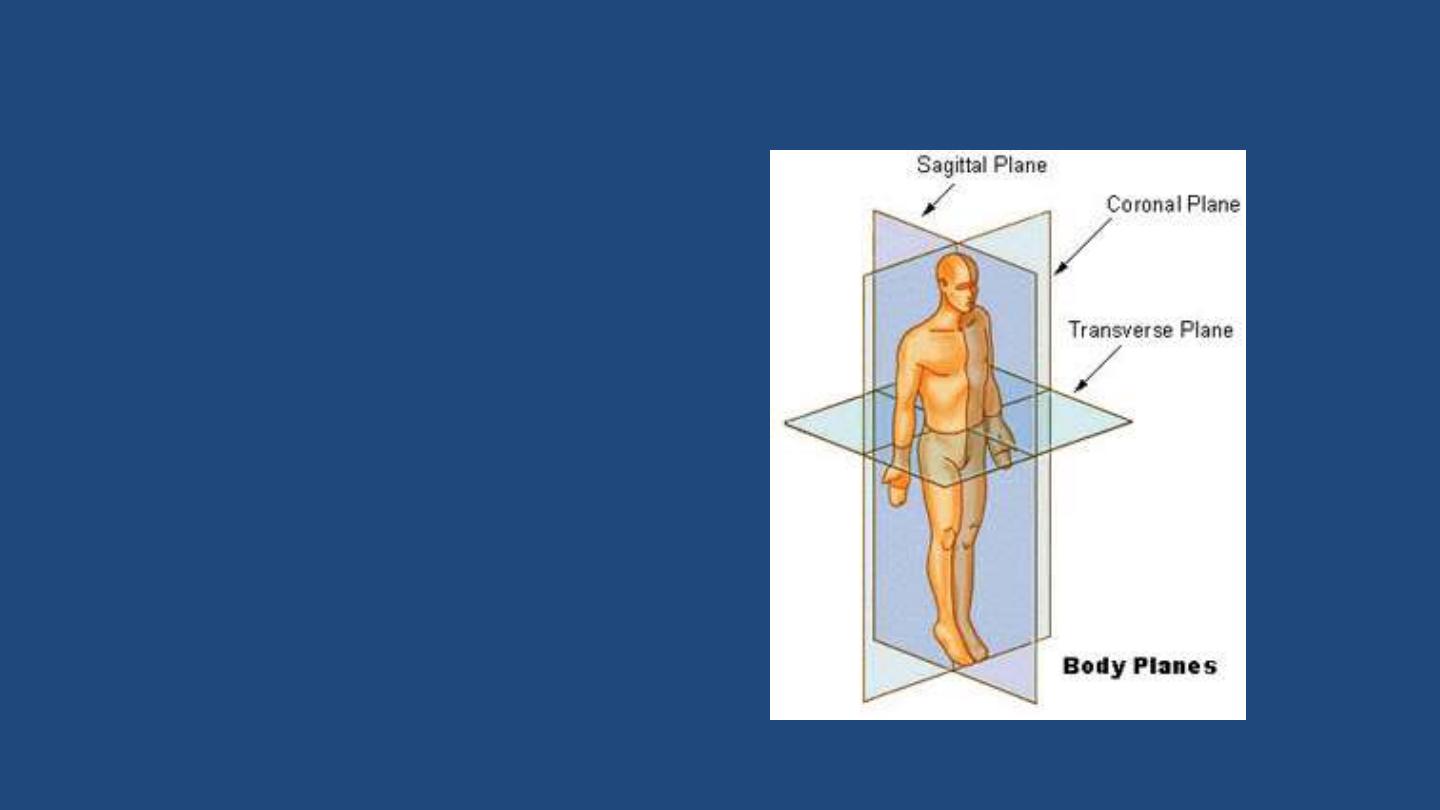
Body planes
1- frontal plane
; this plane separate
the body
into front
and back
portion (also called anterior and
posterior portion).
2- sagittal plane
: this vertical plane
divides the body or organ into
unequal left and right sides .
The
midsagittal plane
divides the body
or organ into equal left and right
sides.
3- transverse or horizontal plane:
this plan seperates the body into
supperior and inferior portions.
Nov-16
22
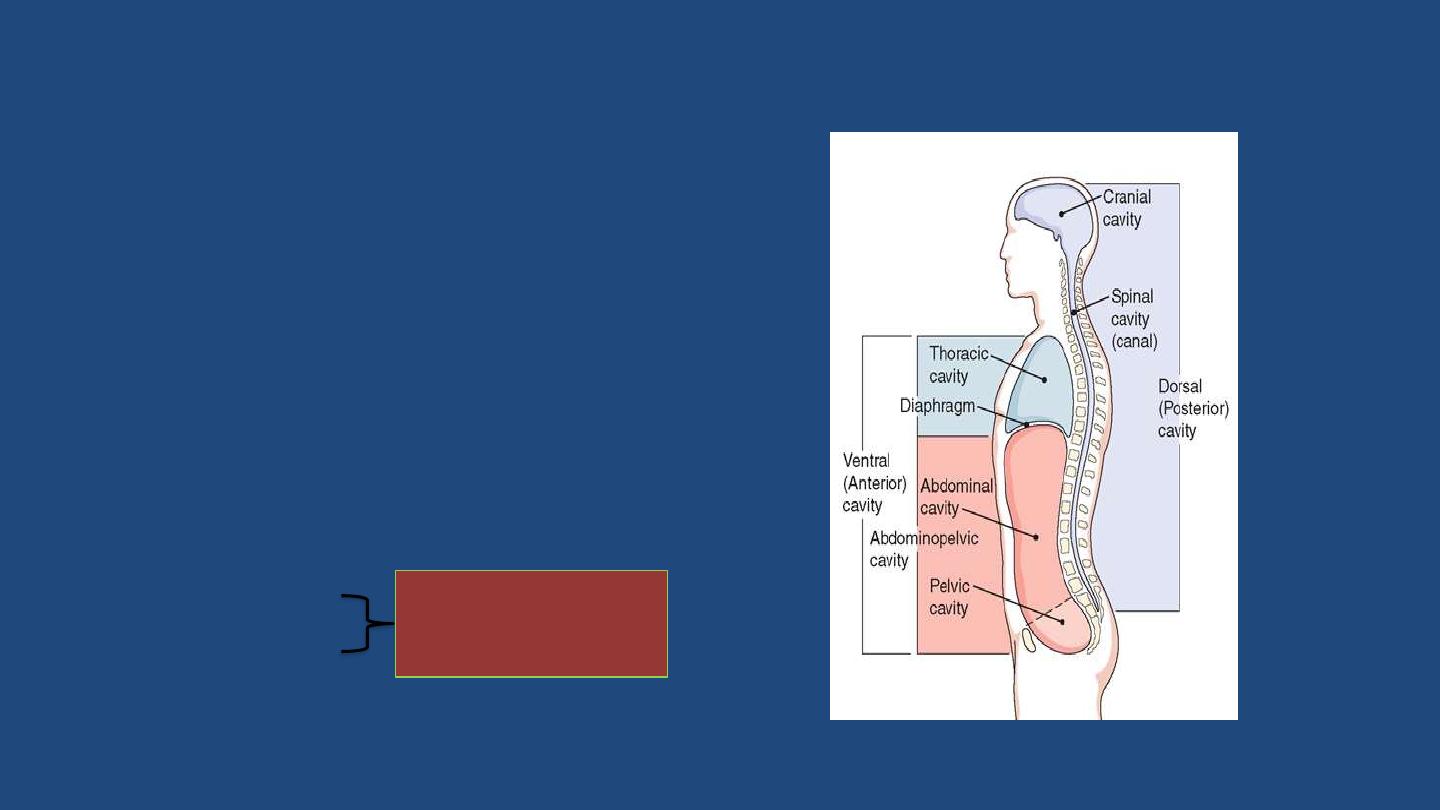
Body cavity and divisions
Body cavity:
a hallow space that contain
body organs, has two major cavities
1-
The cavity in the back of the body called
(dorsal cavity) subdivided
into
- Cranial cavity
- Spinal cavity
2-
The frontal body cavity called
(ventral cavity)
extend from the neck to the pelvis
and is
subdivided into
- Abdominal cavity
- Pelvic cavity .
- Thoracic cavity
Abdominopelvic
cavity
Nov-16
23

Body Cavities
• Thoracic cavity
is subdivided into pleural cavities, the
mediastinum, and the pericardial cavity
– Pleural cavities
– each houses a lung
– Mediastinum
– contains the pericardial cavity, and
surrounds the remaining thoracic organs
– Pericardial cavity
– encloses the heart
Nov-16
24
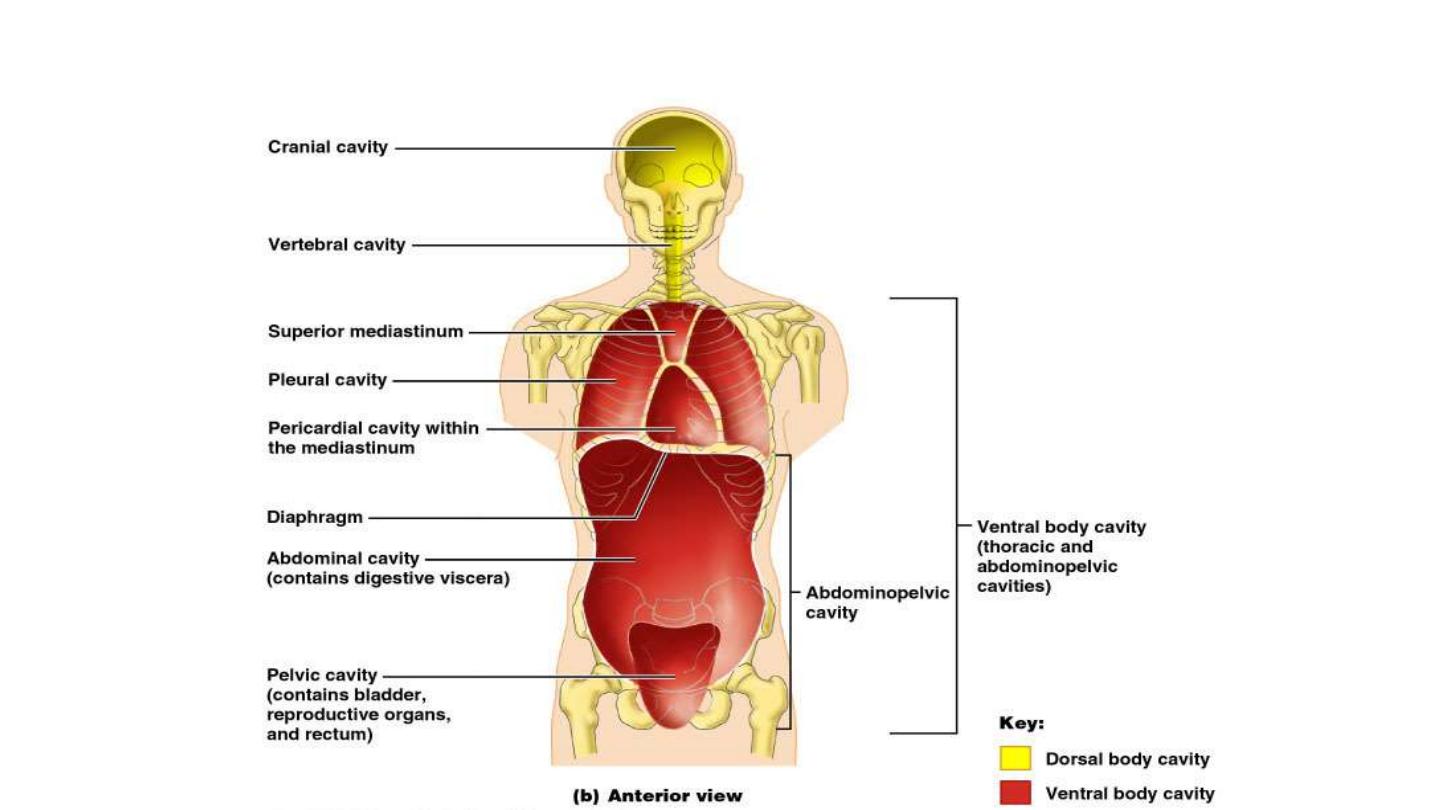
Body Cavities
Figure 1.9b
Nov-16
25
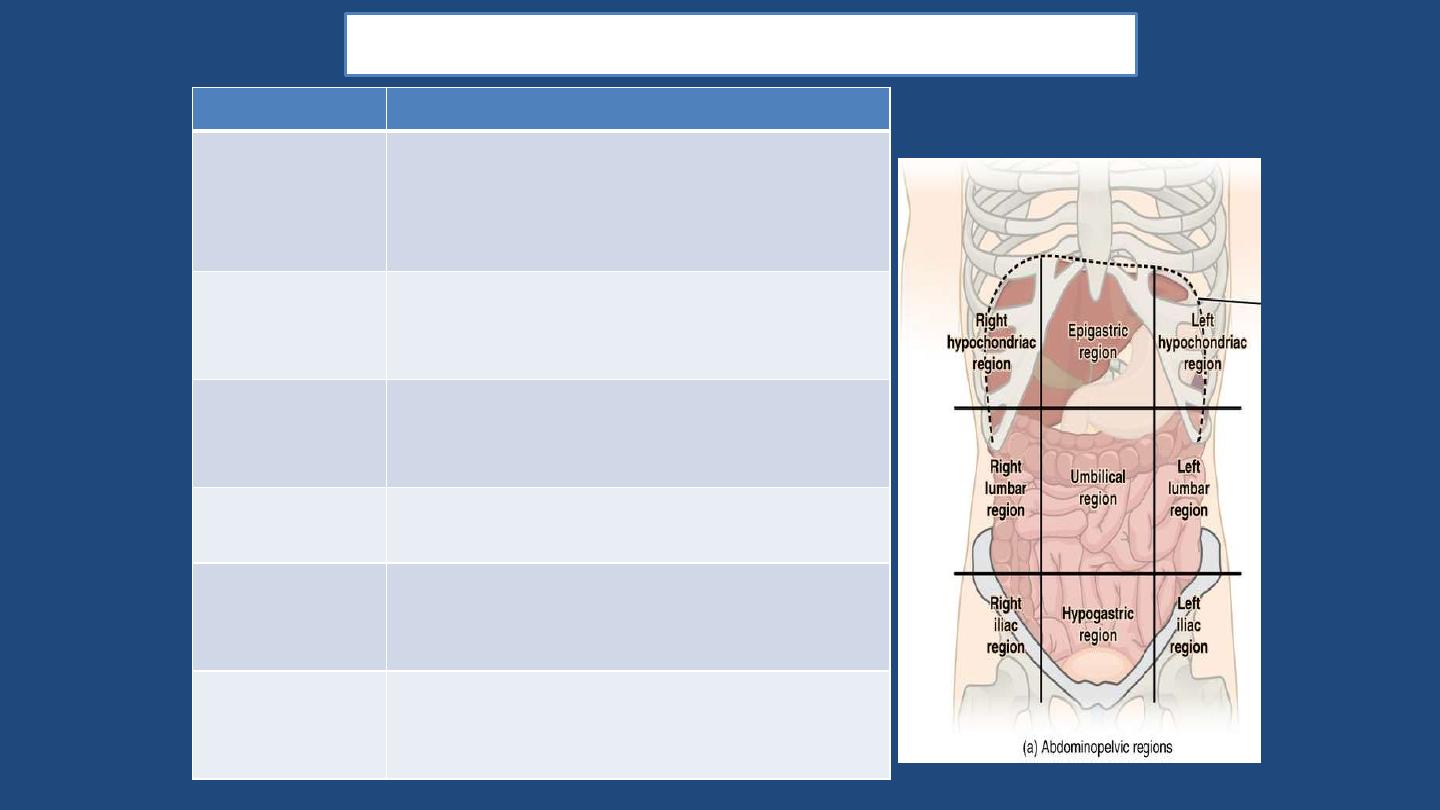
Division of abdominal cavity (nine regions)
TERM
MEANING
Hypochondriac
(2)
they are right & left region located Below
the ribs; also used as a noun to refer to a
person who has imaginary illness
Hypo- (below), -chondriac (ribs).
Epigastric
Above the Stomach situated between right
& left Hypochondriac region . Epi (Above);
gastric (stomach).
Lumbar (2)
they are right & left region located at the
waist level on either side of the navel (
umbilicus)
Umbilical
Is the middle section it contain belly button
or umbilicus.
Hypogastric
Below the Stomach , located in the middle
section below the Umbilical region . Hypo-
(Below); -gastric (stomach).
Inguinal (2)
they are right & left inguinal region they are
located on either side of the Hypogastric
section . Inguinal is also refers to Groin
Nov-16
26
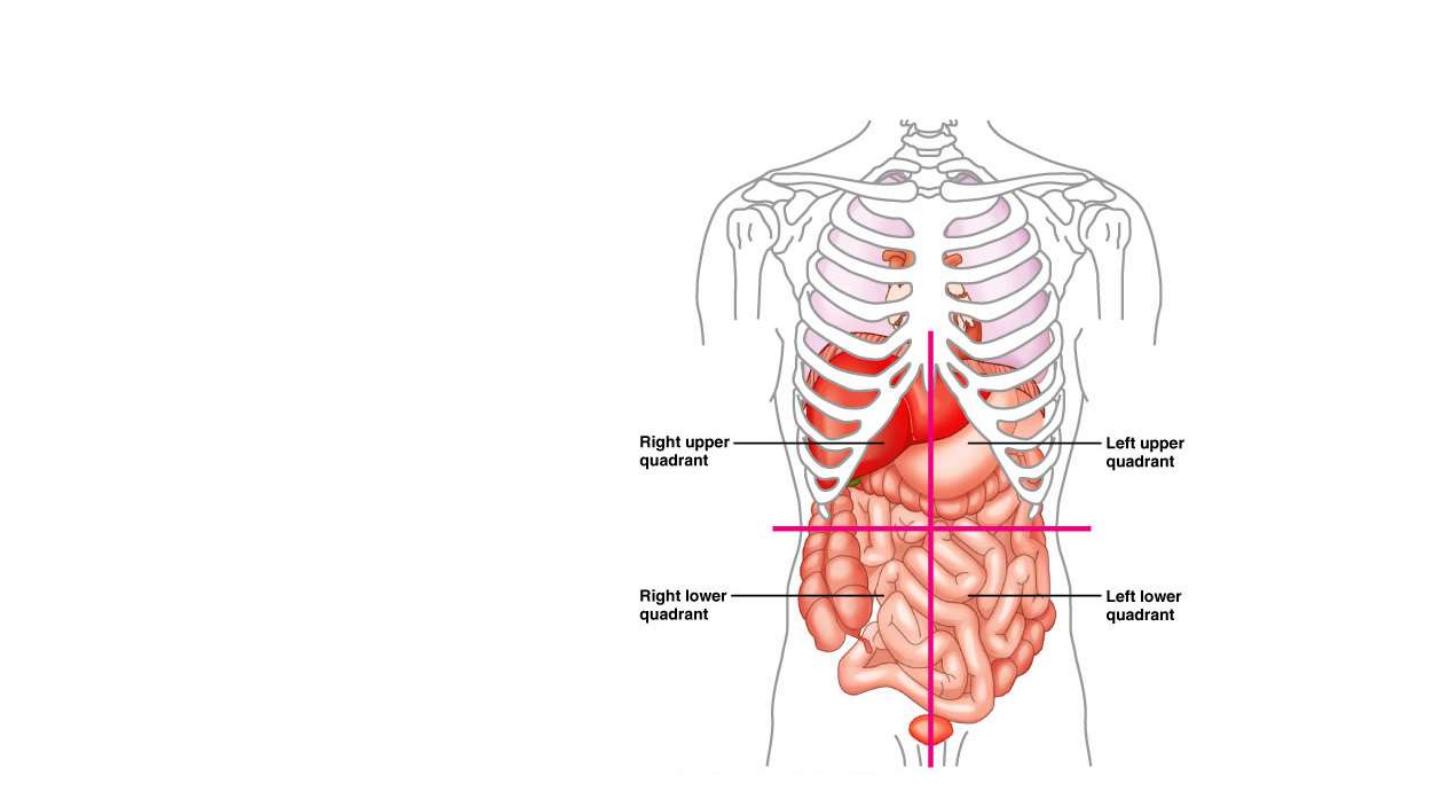
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
• Right upper
(RUQ)
• Left upper
(LUQ)
• Right lower
(RLQ)
• Left lower
(LLQ)
Figure 1.12
Nov-16
27
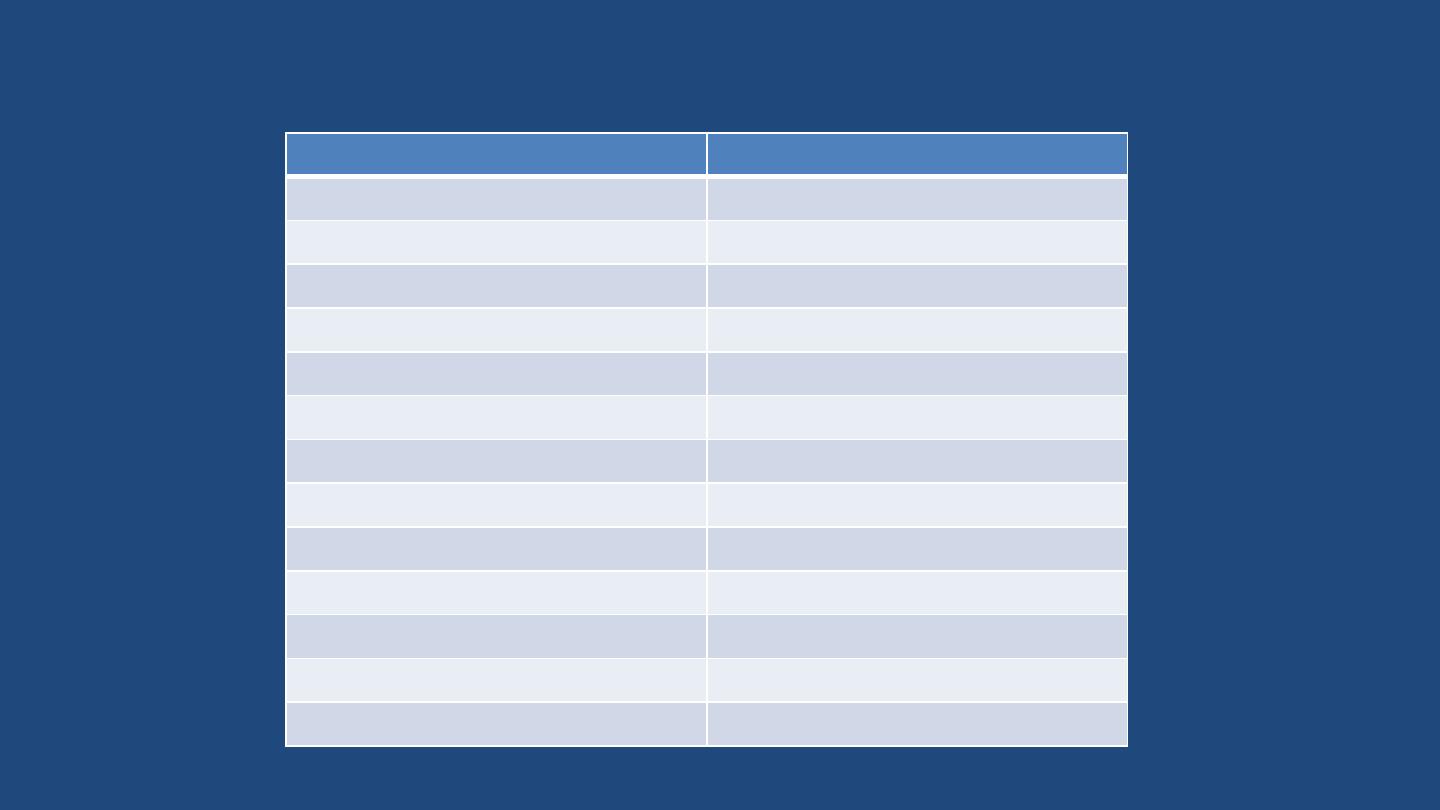
Word elements/Body Organization
ROOT
MEANING
Anter/o
Front, anterior
Cerv/o
Neck
Chondr/o
Cartilage
Cyt/o, cyte
Cell
Dors/o
Back
Inguin/o
Groin
My/o
Muscle
Myel/o
Spinal cord
Neur/o
Nerve, neuron
Poster/o
Posterior/Back
Proxim/o
Near
Super/o
Superior
Trans/o
Across
Nov-16
28
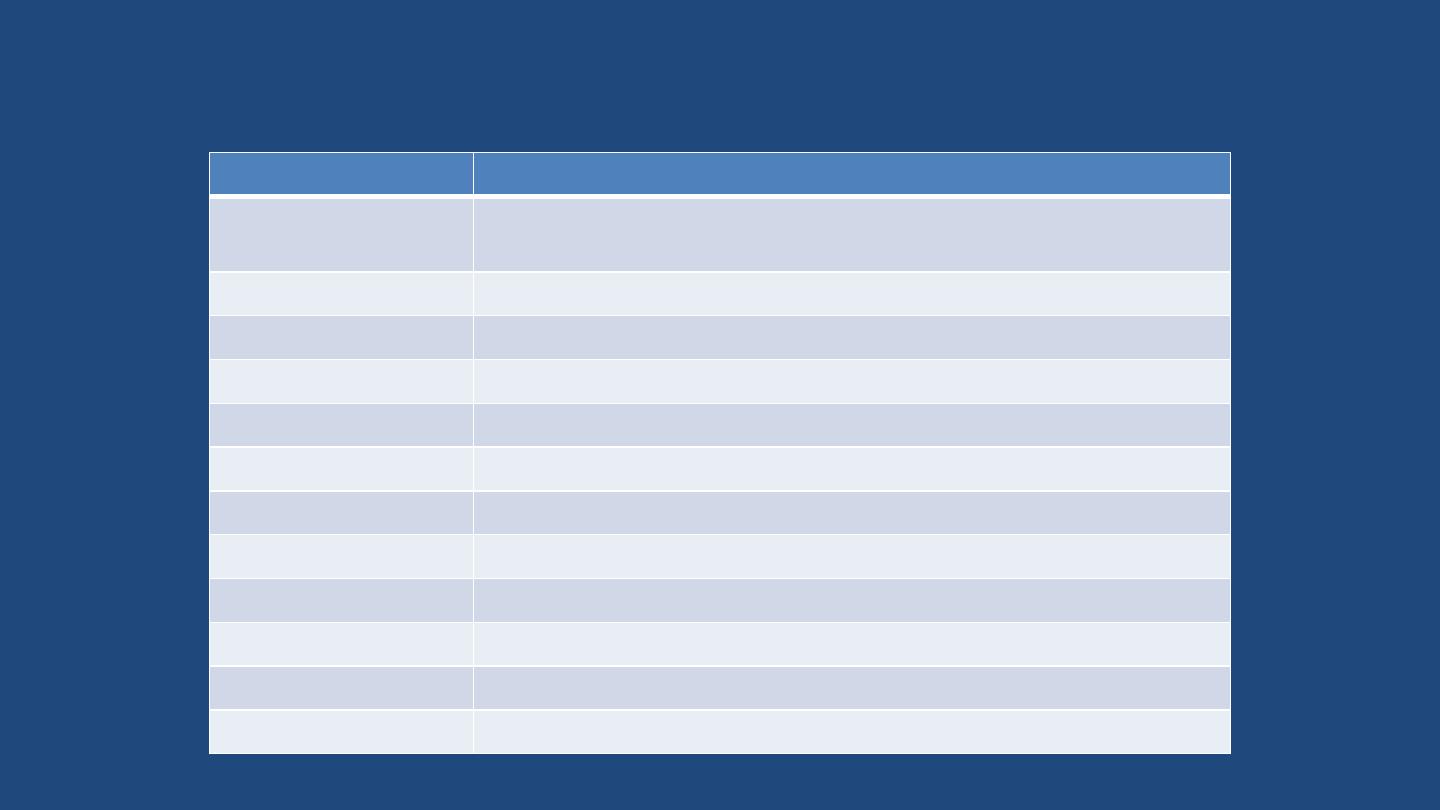
Study Table. Body Organization
TERM
MEANING
Abdominopelvic
Adjective meaning abdomen & pelvis; used to describe the body
subcavities contained in the ventral cavity
Cervical
Pertaining to the neck
Chromosome
Component of the cell nucleus that contains genes
Coccyx
Tailbone
Diaphragm
Muscles that separate the thoracic & the abdominopelvic cavities
Myalgia
My- (Muscle ); -algia (pain). Muscle pain
Sacrum
5 Fused bones of the Lower limb
Superior
Above; toward the cranium
inferior
Below; in a direction away from cranium
Thoracic
Adjective for the chest
Thorax
Chest
Viscera
Internal Organs
Nov-16
29

Nov-16
30
